m6A Regulator Information
General Information of the m6A Regulator (ID: REG00001)
| Regulator Name | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO; U6 small nuclear RNA (2'-O-methyladenosine-N(6)-)-demethylase FTO; U6 small nuclear RNA N(6)-methyladenosine-demethylase FTO; mRNA (2'-O-methyladenosine-N(6)-)-demethylase FTO; m6A(m)-demethylase FTO; mRNA N(6)-methyladenosine demethylase FTO; tRNA N1-methyl adenine demethylase FTO; KIAA1752
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | FTO | ||||
| Sequence |
MKRTPTAEEREREAKKLRLLEELEDTWLPYLTPKDDEFYQQWQLKYPKLILREASSVSEE
LHKEVQEAFLTLHKHGCLFRDLVRIQGKDLLTPVSRILIGNPGCTYKYLNTRLFTVPWPV KGSNIKHTEAEIAAACETFLKLNDYLQIETIQALEELAAKEKANEDAVPLCMSADFPRVG MGSSYNGQDEVDIKSRAAYNVTLLNFMDPQKMPYLKEEPYFGMGKMAVSWHHDENLVDRS AVAVYSYSCEGPEEESEDDSHLEGRDPDIWHVGFKISWDIETPGLAIPLHQGDCYFMLDD LNATHQHCVLAGSQPRFSSTHRVAECSTGTLDYILQRCQLALQNVCDDVDNDDVSLKSFE PAVLKQGEEIHNEVEFEWLRQFWFQGNRYRKCTDWWCQPMAQLEALWKKMEGVTNAVLHE VKREGLPVEQRNEILTAILASLTARQNLRREWHARCQSRIARTLPADQKPECRPYWEKDD ASMPLPFDLTDIVSELRGQLLEAKP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | fto family | ||||
| Function |
RNA demethylase that mediates oxidative demethylation of different RNA species, such as mRNAs, tRNAs and snRNAs, and acts as a regulator of fat mass, adipogenesis and energy homeostasis . Specifically demethylates N(6)-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA, the most prevalent internal modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) in higher eukaryotes . M6A demethylation by FTO affects mRNA expression and stability . Also able to demethylate m6A in U6 small nuclear RNA (snRNA). Mediates demethylation of N(6),2'-O-dimethyladenosine cap (m6A(m)), by demethylating the N(6)-methyladenosine at the second transcribed position of mRNAs and U6 snRNA . Demethylation of m6A(m) in the 5'-cap by FTO affects mRNA stability by promoting susceptibility to decapping . Also acts as a tRNA demethylase by removing N(1)-methyladenine from various tRNAs . Has no activity towards 1-methylguanine . Has no detectable activity towards double-stranded DNA . Also able to repair alkylated DNA and RNA by oxidative demethylation: demethylates single-stranded RNA containing 3-methyluracil, single-stranded DNA containing 3-methylthymine and has low demethylase activity towards single-stranded DNA containing 1-methyladenine or 3-methylcytosine . Ability to repair alkylated DNA and RNA is however unsure in vivo. Involved in the regulation of fat mass, adipogenesis and body weight, thereby contributing to the regulation of body size and body fat accumulation . Involved in the regulation of thermogenesis and the control of adipocyte differentiation into brown or white fat cells. Regulates activity of the dopaminergic midbrain circuitry via its ability to demethylate m6A in mRNAs (By similarity). Plays an oncogenic role in a number of acute myeloid leukemias by enhancing leukemic oncogene-mediated cell transformation: acts by mediating m6A demethylation of target transcripts such as MYC, CEBPA, ASB2 and RARA, leading to promote their expression.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 79068 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Regulator Type | WRITER ERASER READER | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||

|
|||||
| Target Genes | Click to View Potential Target Genes of This Regulator | ||||
Full List of Target Gene(s) of This m6A Regulator and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
FTO can regulate the m6A methylation of following target genes, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulted from the regulation of certain target gene.
Browse Target Gene related Disease
Browse Target Gene related Drug
ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 5B (ARL5B)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 7.32E-01 p-value: 5.39E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion and migration | |||
In-vitro Model |
T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 |
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| Response Summary | FTO up-regulated ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 5B (ARL5B) by inhibiting miR-181b-3p. The carcinogenic activity of FTO in promoting the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via the FTO/miR-181b-3p/ARL5B signaling pathway. | |||
Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 2 (ASB2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.19E-01 p-value: 3.80E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tretinoin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| RNA degradation (hsa03018) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| Mono-Mac-6 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1426 | |
| Response Summary | FTO enhances leukemic oncogene-mediated cell transformation and leukemogenesis, and inhibits all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced AML cell differentiation, through regulating expression of targets such as Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 2 (ASB2) and RARA by reducing m6A levels in these mRNA transcripts. | |||
Apolipoprotein E (APOE)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
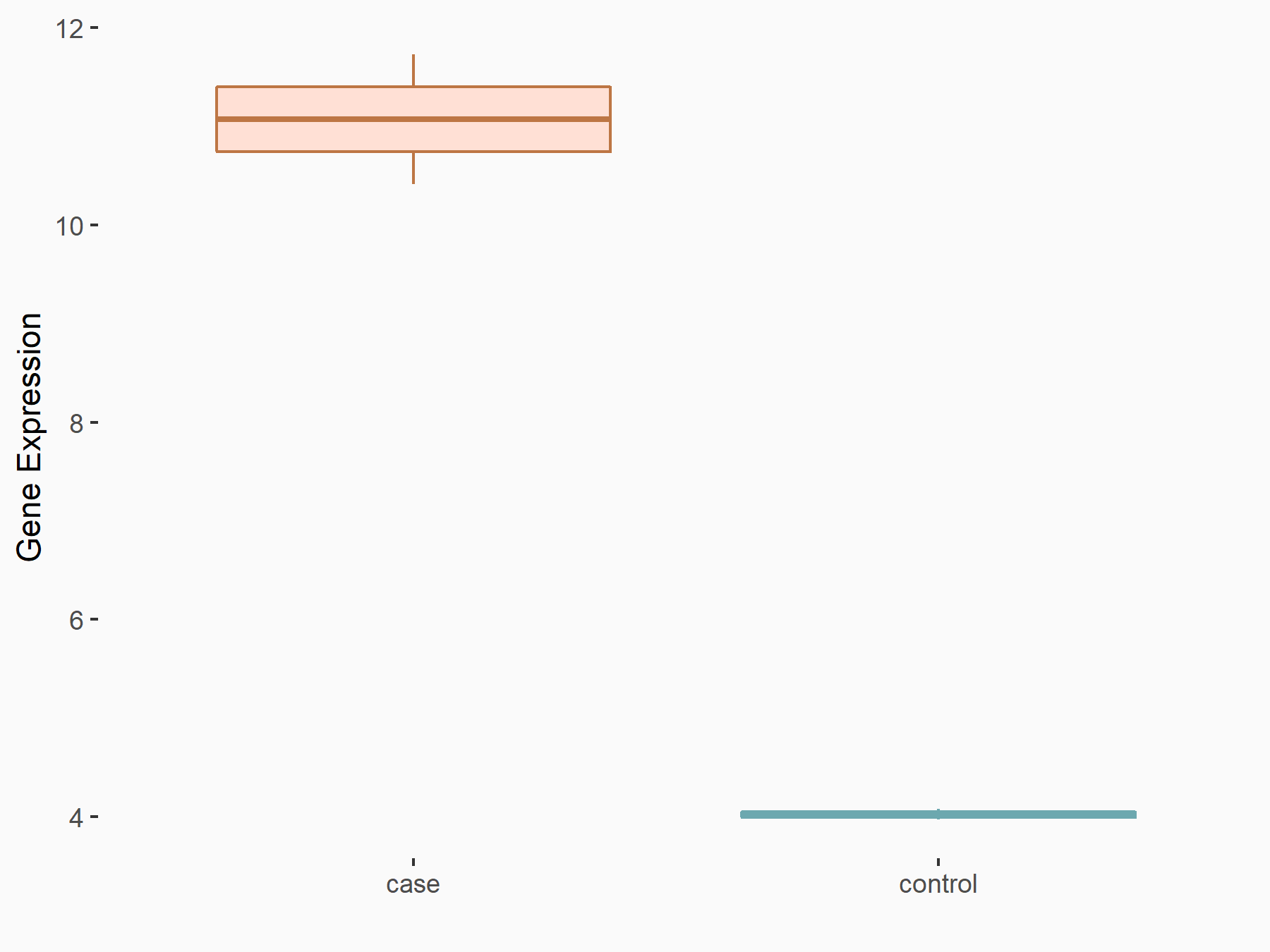  |
logFC: 1.26E+00 p-value: 1.34E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
In-vitro Model |
TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| K1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2537 | |
| IHH-4 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2960 | |
| B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 | |
| Response Summary | FTO acts as a tumor suppressor to inhibit tumor glycolysis in Papillary thyroid cancer(PTC). FTO/Apolipoprotein E (APOE) axis inhibits PTC glycolysis by modulating IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. | |||
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.55E-01 p-value: 1.57E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators in breast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such as Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators in breast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such as Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators in breast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such as Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. | |||
ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 10 (ABCC10)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse hippocampus | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mice hippocampus
Control: Wild type hippocampus
|
GSE94098 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.58E-01 p-value: 2.09E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gefitinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | ABC transporters | hsa02010 | ||
In-vitro Model |
PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were randomized into three groups (n = 7/group), 1 × 107 PC9 cells absorbed exosomes were subcutaneously injected into the Bilateral groin of mice. Treatment began 1 week following injection, the mice were intraperitoneally injected with gefitinib (30 mg/kg/day). | |||
| Response Summary | Not only FTO knockdown enhanced the gefitinib sensitivity of GR cells but also FTO reduction in donor exosomes alleviated the acquired resistance of recipient non-small cell lung cancer PC9 cells. FTO/YTHDF2/ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 10 (ABCC10) axis played a role in intercellular transmission of GR cell-derived exosome-mediated gefitinib resistance. | |||
BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 3.13E+00 p-value: 6.97E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell colony formation | ||||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
4 T1 (Mouse breast cancer cells) | |||
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 5 4-week-old female Balb/c mice were randomly grouped and injected with 1 × 106 shCtrl, shFTO or shFTO/shBNIP3 KD 4 T1 cells. For tumor metastasis mouse model, 5 4-week-old female Balb/c mice were randomly grouped and injected with 1 × 106 shCtrl, shFTO or shFTO/shBNIP3 KD 4 T1 cells via tail vein. For orthotopic xenograft mouse model, 5 4-week-old female NOD/SCID mice were randomly grouped. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO mediated m6A demethylation in the 3'UTR of BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) mRNA and induced its degradation via an YTHDF2 independent mechanism. FTO serves as a novel potential therapeutic target for breast cancer. | |||
Sepsis [ICD-11: 1G40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [69] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Sepsis [ICD-11: 1G40] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | To assess mortality rates, mice were intraperitoneally administered LPS (30 mg/kg), with mdivi (3 mg/kg) given intraperitoneally 1 h before LPS challenge and then continued for 3 consecutive days. The 72-h mortality was subsequently recorded. For evaluating heart injury, mice received an injection of LPS (10 mg/kg), with songorine (10 or 50 mg/kg) administered 1 h before and 12 h after LPS treatment. Mice were euthanized 24 h later for heart collection. | |||
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [68] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
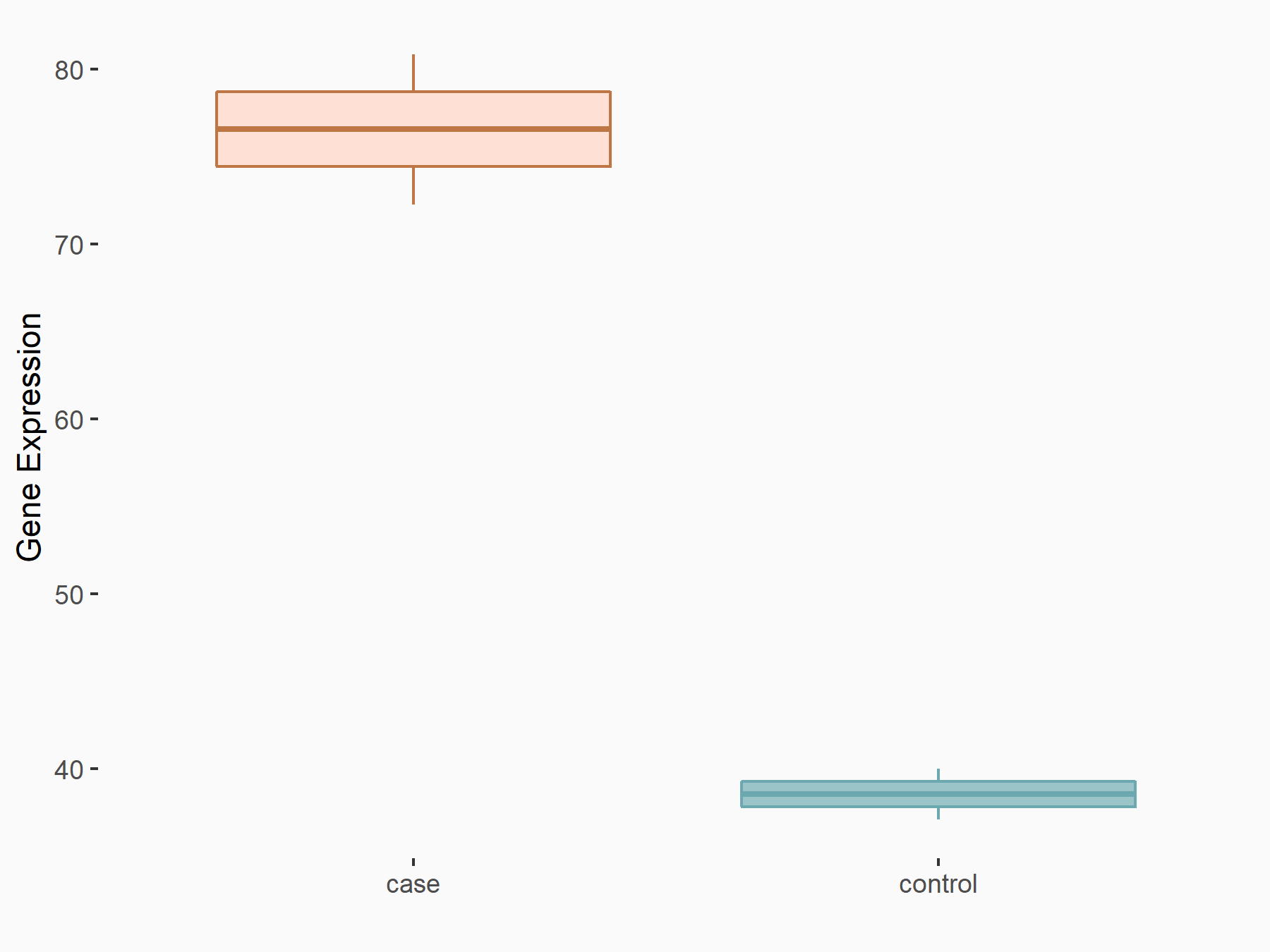  |
logFC: 9.72E-01 p-value: 3.86E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
In-vitro Model |
B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
Caveolin-1 (CAV1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 3.45E+00 p-value: 8.00E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the tumor growth analysis, AGS cells were subcutaneously injected into nude mice, and then the tumor volumes were monitored every 5 days. Tumor volumes were estimated based on the length and width and calculated using the following formula: tumor volume = (length × width2)/2. About 1 month later, the nude mice were sacrificed, and then tumors were excised, pictured, and weighed. For the tumor metastasis analysis, AGS cells were injected into nude mice by Tail Vein. About 1 month later, the nude mice were sacrificed, and then lung with metastasis lesions were excised, pictured, and counted. | |||
| Response Summary | This study demonstrated that the key demethylase of m6A FTO promoted the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via regulating the mitochondrial fission/fusion and metabolism. In terms of mechanism, FTO improved the degradation of Caveolin-1 (CAV1) mRNA via its demethylation. | |||
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
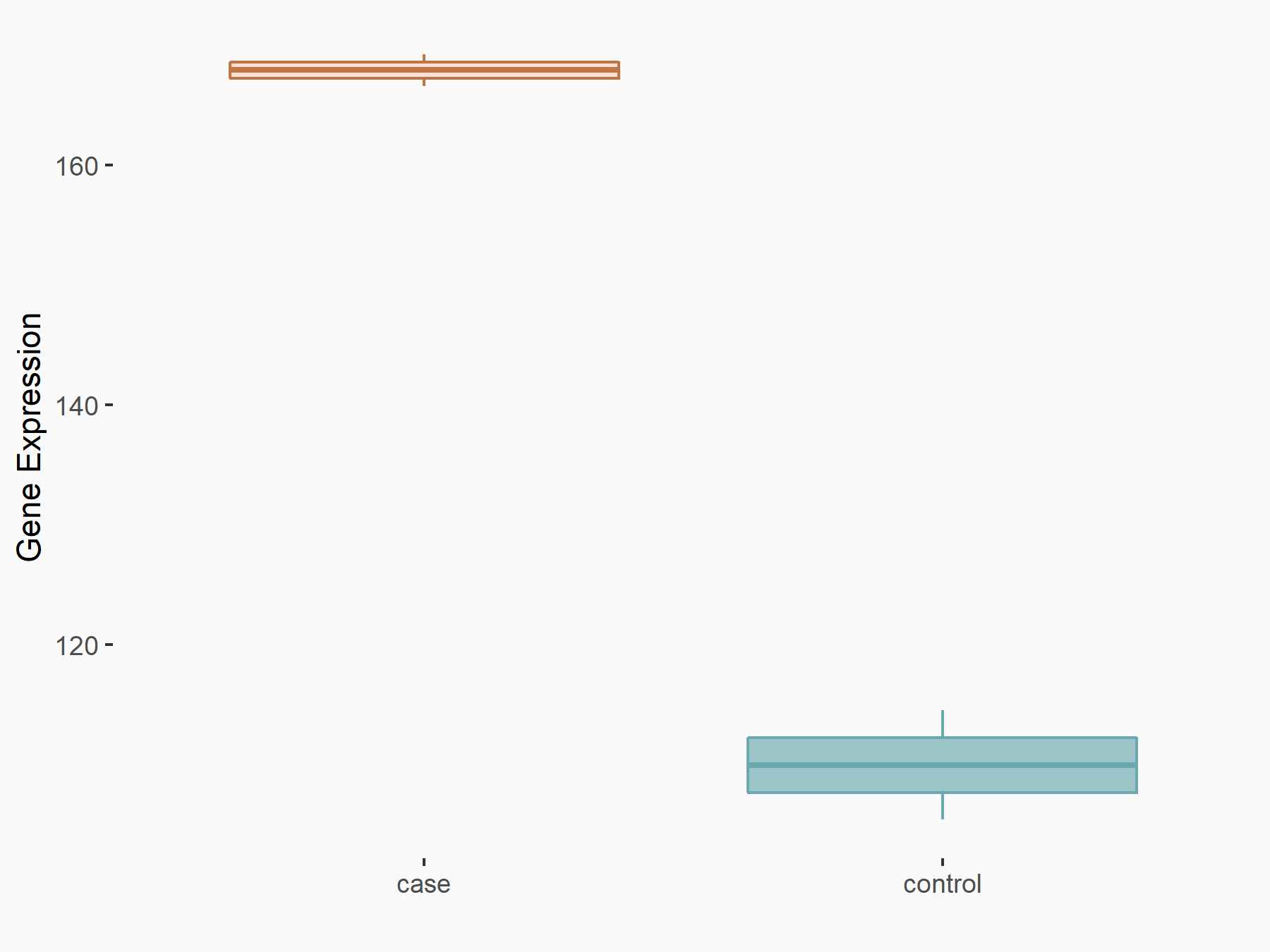 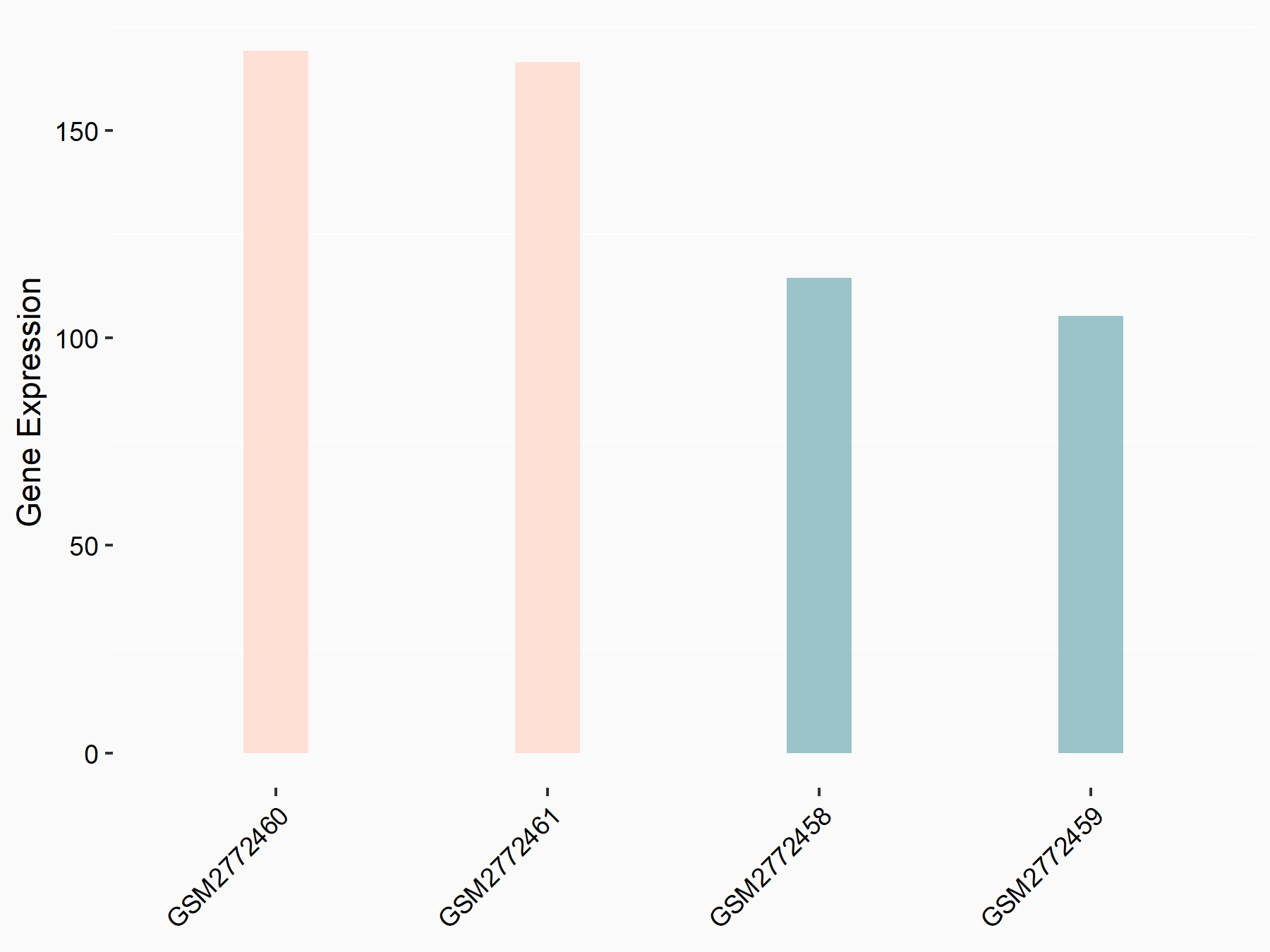 |
logFC: 6.07E-01 p-value: 3.92E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.4] | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
Cell death activator CIDE-3 (CIDEC)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse liver | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mouse liver tissue
Control: Wild type mouse liver tissue
|
GSE125785 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -2.15E+00 p-value: 6.18E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Lipogenesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | After being fed with high-fat diet for 4 weeks, mice were given twice vena caudalis injection of control siRNA or Cidec siRNA (50 ug/mouse) mixed with liposome. Liposomes were prepared as described elsewhere. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO increased the lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by increasing nuclear translocation of SREBP1c and SREBP1c maturation, thus improving the transcriptional activity of LD-associated protein Cell death activator CIDE-3 (CIDEC).The studies provide new mechanistic insight into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) mediated by FTO. | |||
Collagenase 3 (MMP13)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 2.41E+00 p-value: 4.00E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell growth and migration | |||
In-vitro Model |
Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| In-vivo Model | Stable down-regulated FTO cells were prepared in Eca-109 and KYSE150 and subcutaneously injected into the flank of nude mouse with 2 × 106 cells per mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | Up-regulation of FTO is frequently observed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues, and FTO facilitates cell proliferation and migration in ESCC by up-regulating Collagenase 3 (MMP13). | |||
Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
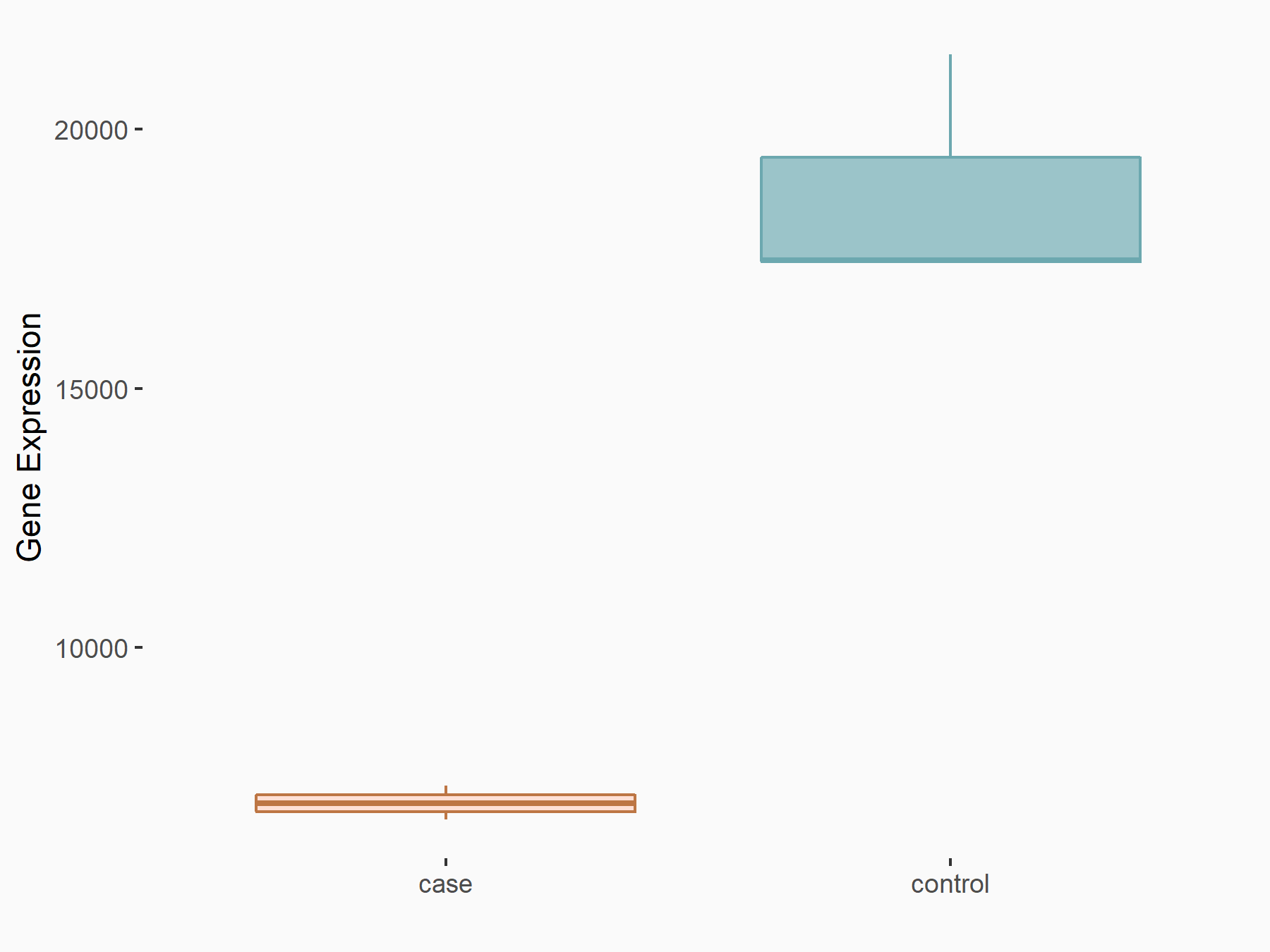 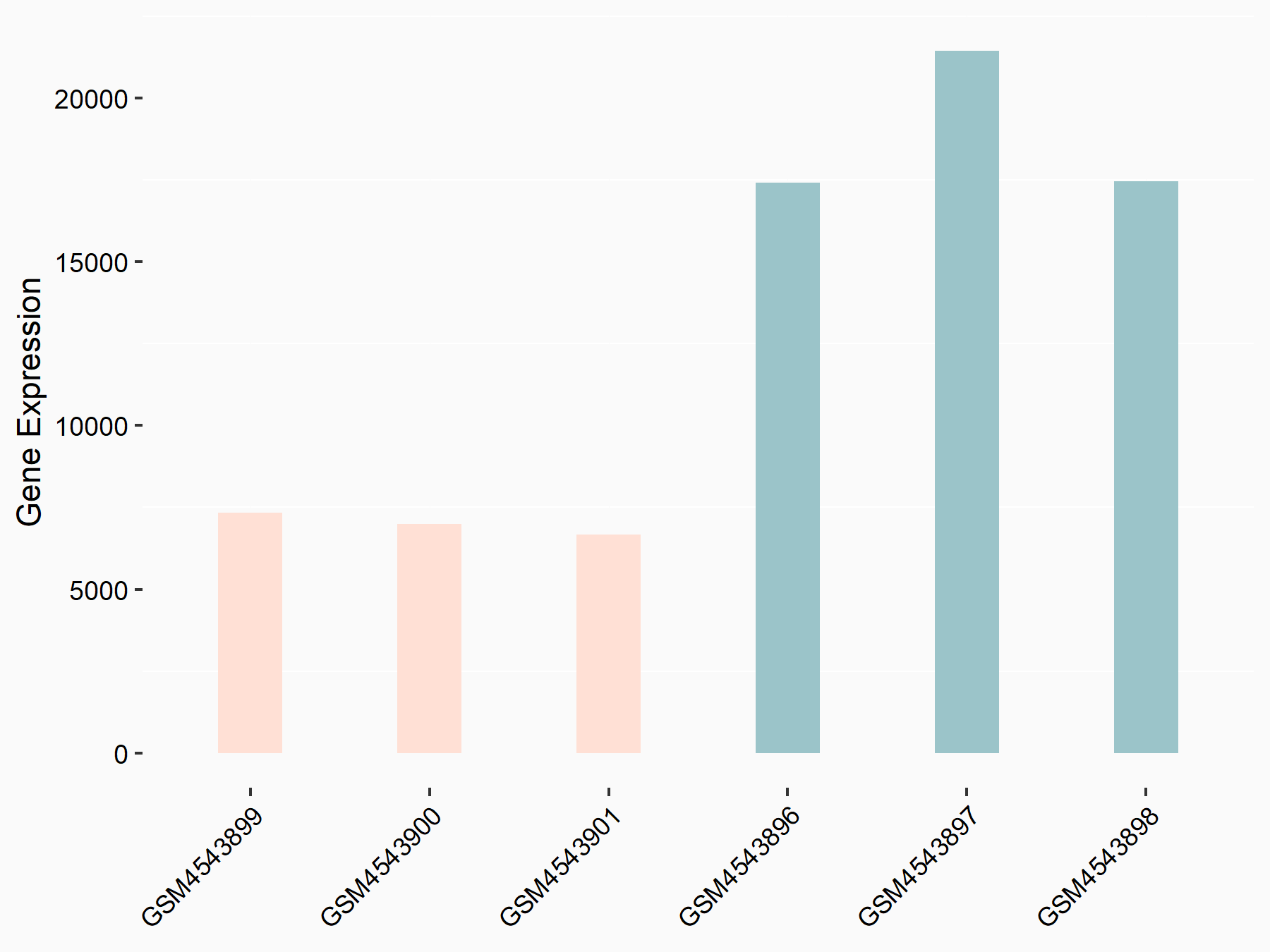 |
logFC: -1.42E+00 p-value: 2.68E-47 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 6 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Chloroquine | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 5 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | CB-839 | Phase 2 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 6 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | GLS-IN-968 | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Cyclin-A2 (CCNA2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 7.89E-01 p-value: 6.22E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin gallate | Phase 3 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent Cyclin-A2 (CCNA2) and CDK2 expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [14] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Arrest cell cycle at S phase | ||||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | FTO knockdown markedly decreased the expression of Cyclin-A2 (CCNA2) and CDK2, crucial cell cycle regulators, leading to delayed entry of MDI-induced cells into G2 phase. m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 recognized and decayed methylated mRNAs of CCNA2 and CDK2, leading to decreased protein expression, thereby prolonging cell cycle progression and suppressing adipogenesis. The adipocyte life cycle, including proliferation and adipogenesis, has become a potential target for many bioactive compounds and drugs for the prevention and treatment of obesity. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16-OVA cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shFTO B16-OVA cells
Control: shNC B16-OVA cells
|
GSE154952 | |
| Regulation |
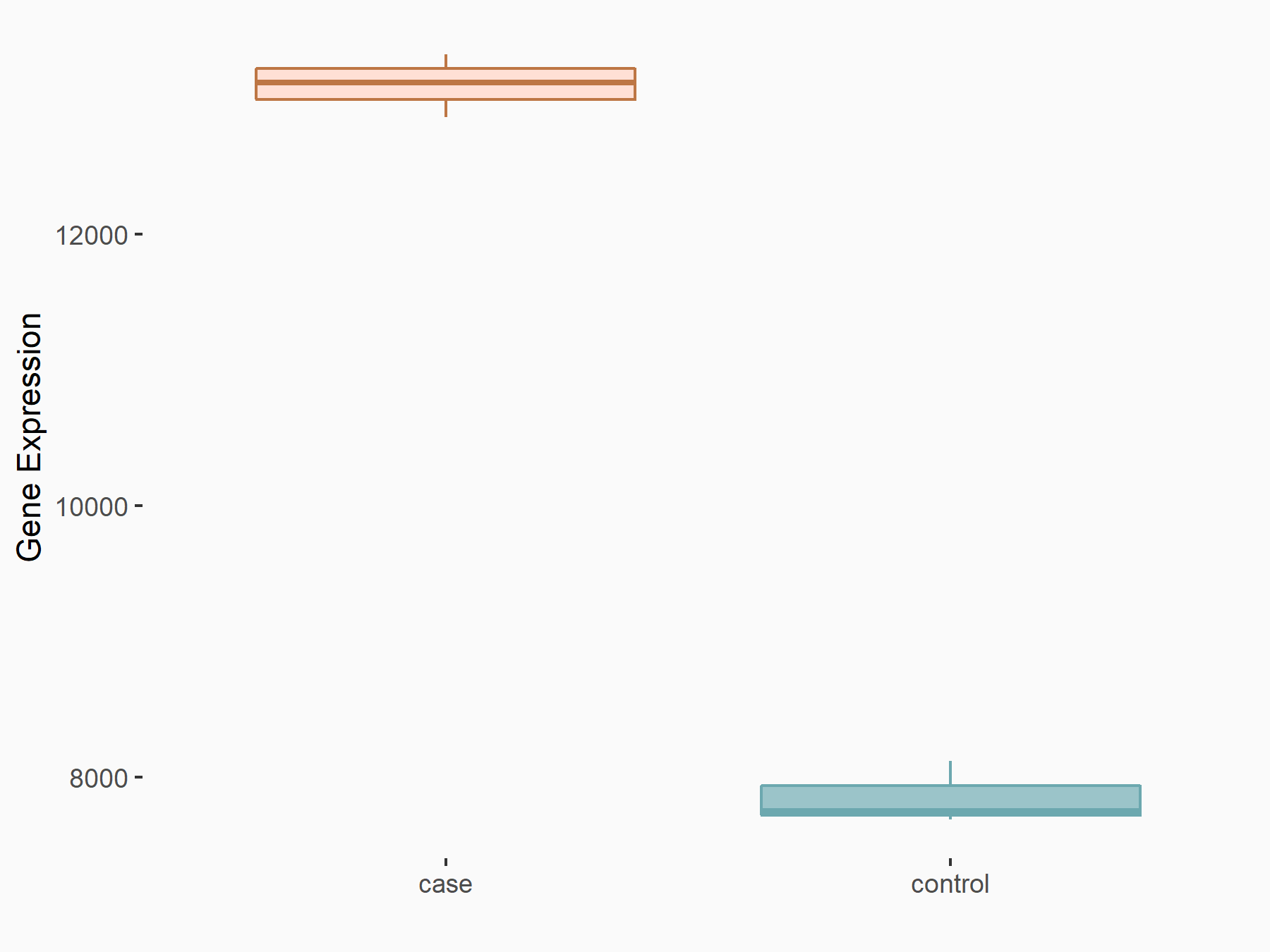 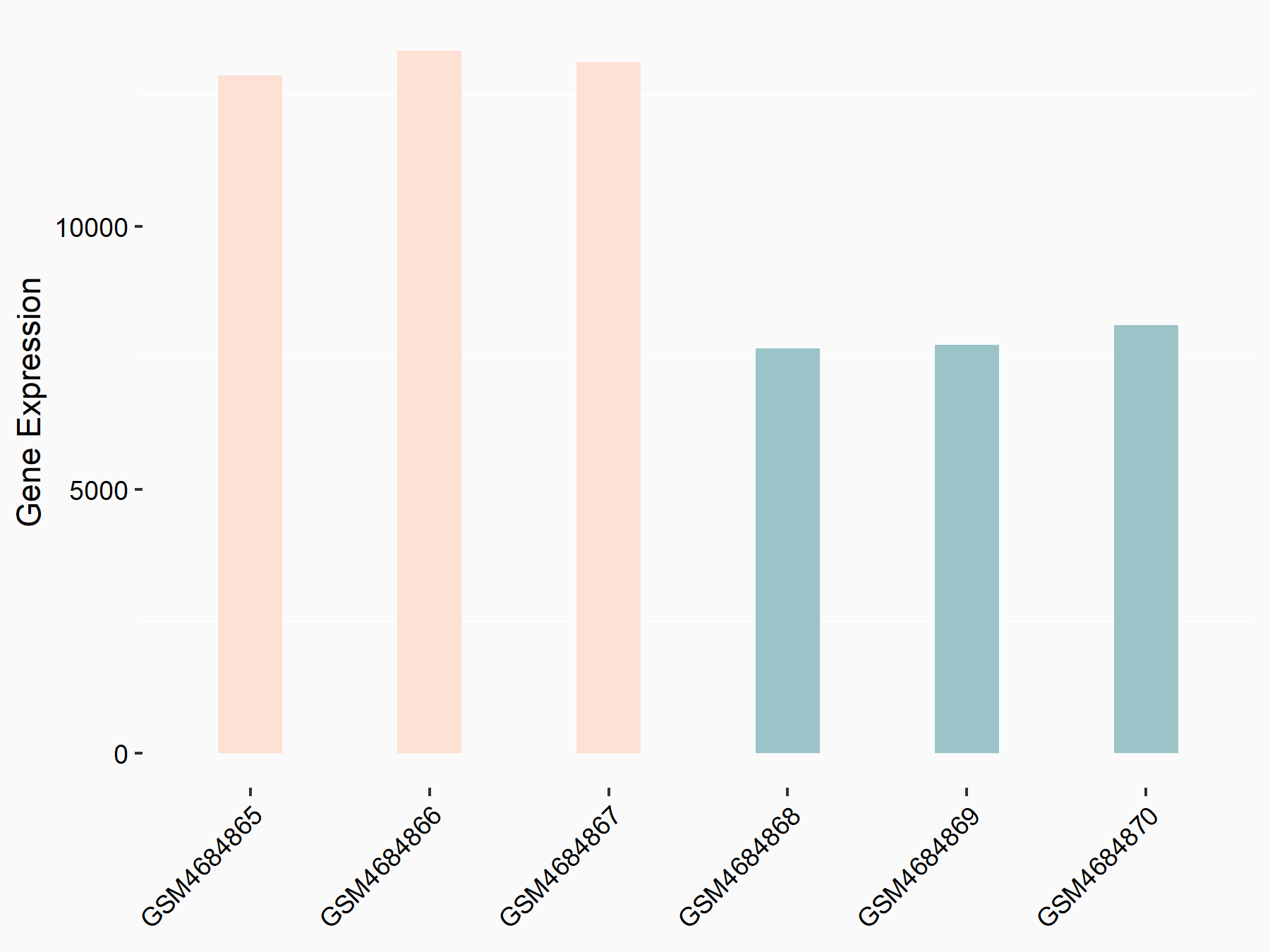 |
logFC: 7.39E-01 p-value: 1.49E-28 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin gallate | Phase 3 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [14] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Arrest cell cycle at S phase | ||||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | FTO knockdown markedly decreased the expression of CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), crucial cell cycle regulators, leading to delayed entry of MDI-induced cells into G2 phase. m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 recognized and decayed methylated mRNAs of CCNA2 and CDK2, leading to decreased protein expression, thereby prolonging cell cycle progression and suppressing adipogenesis. The adipocyte life cycle, including proliferation and adipogenesis, has become a potential target for many bioactive compounds and drugs for the prevention and treatment of obesity. | |||
Retinopathy [ICD-11: 9B71]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [77] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic retinopathy [ICD-11: 9B71.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 9.72E-01 p-value: 1.24E-24 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [16] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Decreased G0/G1 phase | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HET-1A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3702 |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| KYSE-450 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1353 | |
| KYSE-70 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1356 | |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| In-vivo Model | The number of cells inoculated in each mouse was 4 × 106, 1 × 106, 2 × 106 and 1 × 106, respectively. | |||
| Response Summary | The elevated FTO in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma decreased m6A methylation of LINC00022 transcript, leading to the inhibition of LINC00022 decay via the m6A reader YTHDF2. LINC00022 directly binds to Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A) protein and promotes its ubiquitination-mediated degradation, thereby facilitating cell-cycle progression and proliferation. | |||
Dapper homolog 1 (DACT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse liver | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mouse liver tissue
Control: Wild type mouse liver tissue
|
GSE125785 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.21E+00 p-value: 4.60E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Response Summary | FTO could reduce the mRNA stability of Dapper homolog 1 (DACT1) via m6A demethylation, which decreased DACT1 expression and further activated the Wnt signaling pathway. The oncogenic effect of FTO on osteosarcoma was dependent on DACT1. | |||
Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16-OVA cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shFTO B16-OVA cells
Control: shNC B16-OVA cells
|
GSE154952 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.69E-01 p-value: 1.09E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Pathway Response | Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | ||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Response Summary | Glucose Is Involved in the Dynamic Regulation of m6A in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.high-glucose stimulation enhances FTO expression, which leads to decreased m6A, and the lower m6A induces methyltransferase upregulation; FTO then triggers the mRNA expression of FOXO1, FASN, G6PC, and Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2), and these four genes were correlated with glucose and lipid metabolism. | |||
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
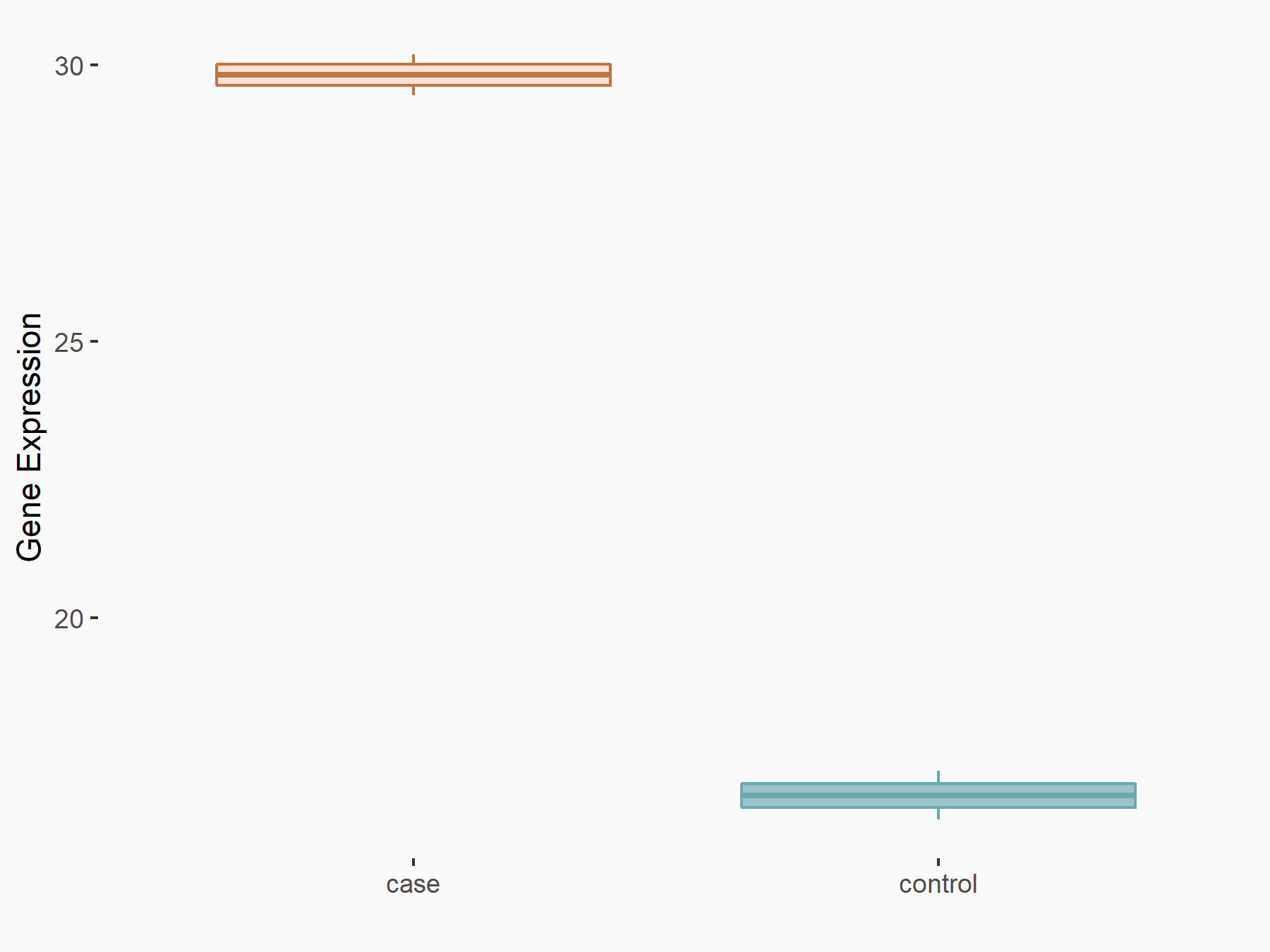 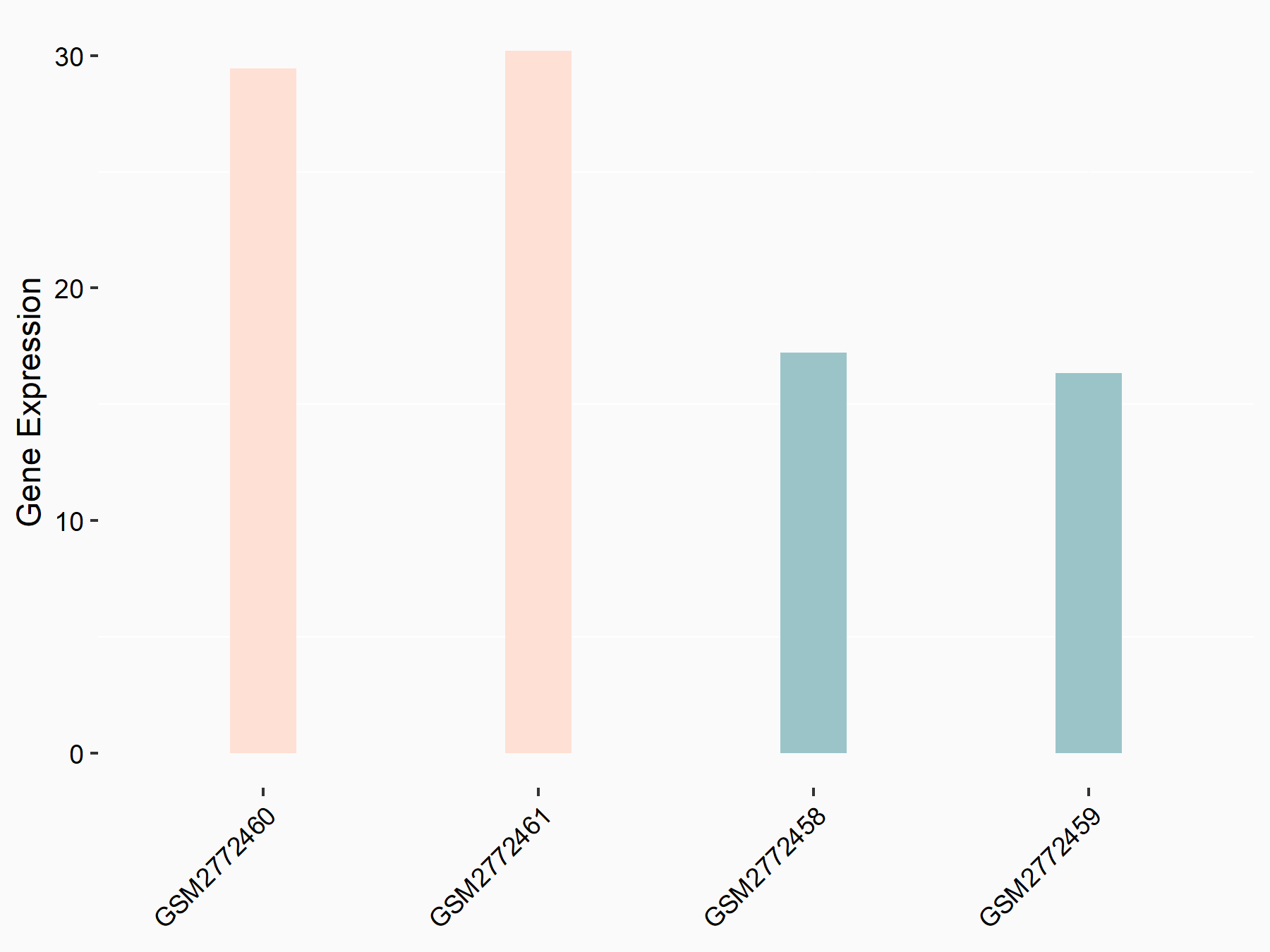 |
logFC: 7.94E-01 p-value: 7.54E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Fluorouracil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Paclitaxel | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Ephrin type-B receptor 2 (ERK/EPHB2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.37E+00 p-value: 3.20E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
OCI-AML-3 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1844 |
| OCI-AML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1619 | |
| Response Summary | FTO depended on its m6A RNA demethylase activity to activate PDGFRB/Ephrin type-B receptor 2 (ERK/EPHB2) signaling axis. FTO-mediated m6A demethylation plays an oncogenic role in NPM1-mutated Acute myeloid leukemia(AML). | |||
Frizzled-10 (FZD10)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse hippocampus | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mice hippocampus
Control: Wild type hippocampus
|
GSE94098 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.03E-01 p-value: 7.74E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | PARPi | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
UWB1.289 | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B079 |
| PEO1 | Ovarian cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2686 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 107 PARP inhibitor resistant PEO1 cells were suspended in 200 uL PBS : Matrigel (1:1) unilaterally injected subcutaneously into the right dorsal flank of 6-8 week-old female immunocompromised non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD/SCID) gamma (NSG) mice. When the average tumor size reached ~100 mm3, the mice were then randomized into four groups and treated with vehicle control, Olaparib (50 mg/kg), XAV939 (5 mg/kg) or a combination daily for 18 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Downregulation of m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 was sufficient to increase Frizzled-10 (FZD10) mRNA m6A modification and reduce PARPi sensitivity, the finding elucidates a novel regulatory mechanism of PARPi resistance in EOC by showing that m6A modification of FZD10 mRNA contributes to PARPi resistance in BRCA-deficient EOC cells via upregulation of Wnt/Bete-catenin pathway. | |||
G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: FTO inhibition NB4 cells
Control: NB4 cells
|
GSE103495 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -7.40E-01 p-value: 1.34E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [15] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Response Summary | Metformin could inhibit adipogenesis and combat obesity, metformin could inhibit protein expression of FTO, leading to increased m6A methylation levels of G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1) and Cdk2(two crucial regulators in cell cycle). Ccnd1 and Cdk2 with increased m6A levels were recognised by YTHDF2, causing an YTHDF2-dependent decay and decreased protein expressions. | |||
Pulmonary hypertension [ICD-11: BB01]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [87] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pulmonary hypertension [ICD-11: BB01] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Twelve adult female SD rats, aged 6-8 weeks and weighing 200 g, were purchased from the experimental animal center of Xuzhou Medical University, China (GRADE II). The animal experience program was approved by the Committee of institutions for Animal Protection and use (IACUC). The rats were randomly divided into control group (n = 6) and hypoxia group (n = 6). They were fed in 60% humidity for 21 days, and the hypoxia group was fed under (3% O2) hypoxia. After the establishment of the rat model, the rats were anesthetized with sevoflurane (4.5%), and their hearts and lungs were taken for follow-up study. | |||
Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 (NMDAR1/GRIN1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | UMRC2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: FTO knockdown UMRC2 cells
Control: Wild type UMRC2 cells
|
GSE139123 | |
| Regulation |
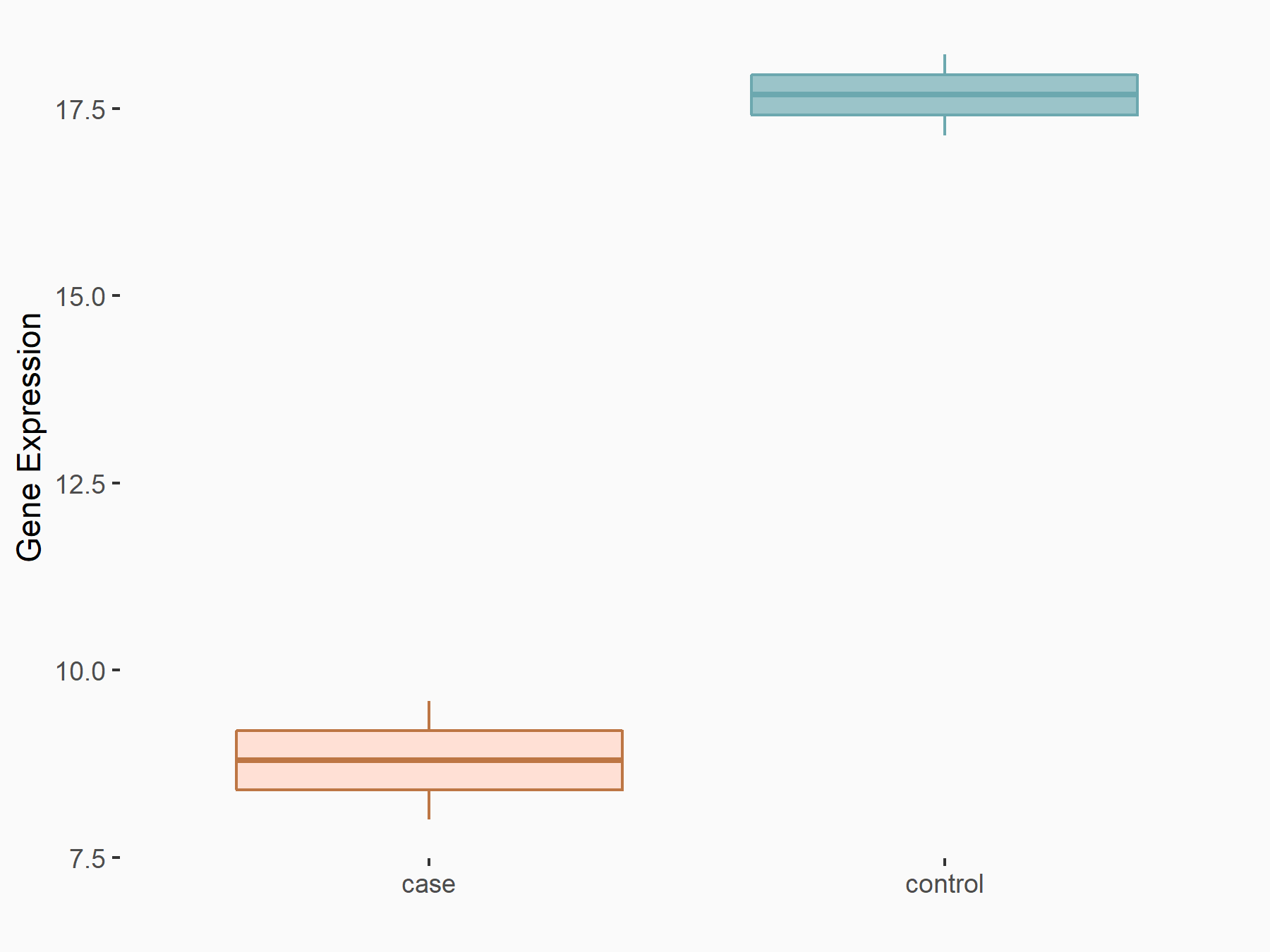 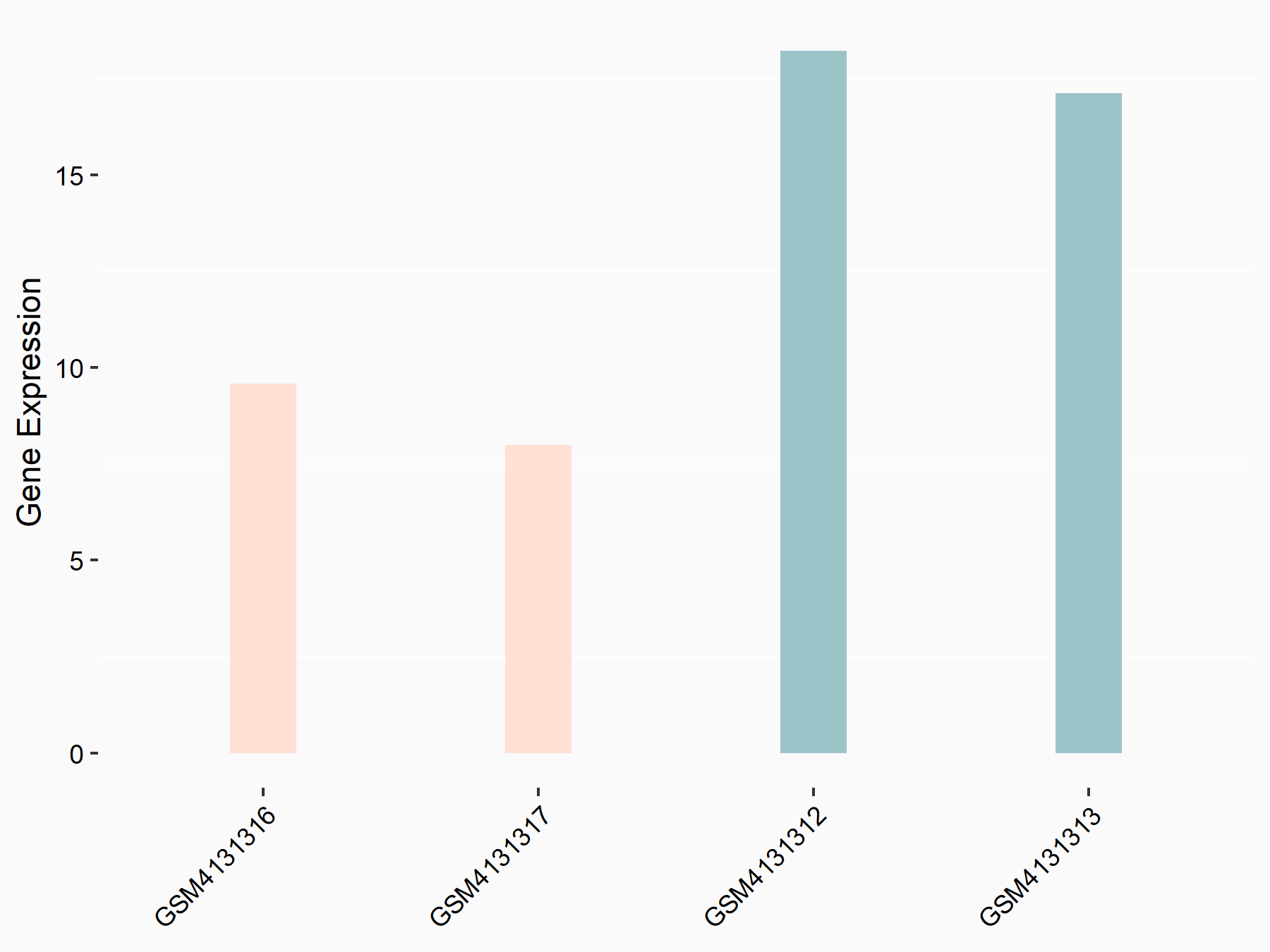 |
logFC: -9.35E-01 p-value: 3.38E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| PC-12 | Lung papillary adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S979 | |
| SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In-vivo Model | Two weeks after the stereotaxic surgery, all the animals were intraperitoneally injected with apomorphine at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg to induce the contralateral rotations. Ten minutes after the injection, a video was used to record the rotations of each rat for 20 min. Only those 6-OHDA induced rats showing robust contralateral turning (>7 turns/min) that were injected with 6-OHDA were used in subsequent experiments. | |||
| Response Summary | Decreased m6A in dopaminergic cells by overexpressing a nucleic acid demethylase, FTO, or by m6A inhibitor. m6A reduction could induce the expression of Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 (NMDAR1/GRIN1), and elevate oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx, resulting in dopaminergic neuron apoptosis. m6A modification plays a vital role in the death of dopaminergic neuron, which provides a novel view of mRNA methylation to understand the epigenetic regulation of Parkinson's disease. | |||
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16-OVA cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shFTO B16-OVA cells
Control: shNC B16-OVA cells
|
GSE154952 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.35E-01 p-value: 1.84E-09 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [23] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair | |||
| Cell proliferation and migration | ||||
In-vitro Model |
VSMC (Human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells) | |||
| Response Summary | FTO expression significantly contributes to the phenotype conversion of VSMCs and the aortic dissecting aneurysm by the demethylation function (m6A), thereby providing a novel therapeutic target. Knockdown of FTO suppresses the Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B) levels and Klf5 expression regardless of AngII treatment. | |||
Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
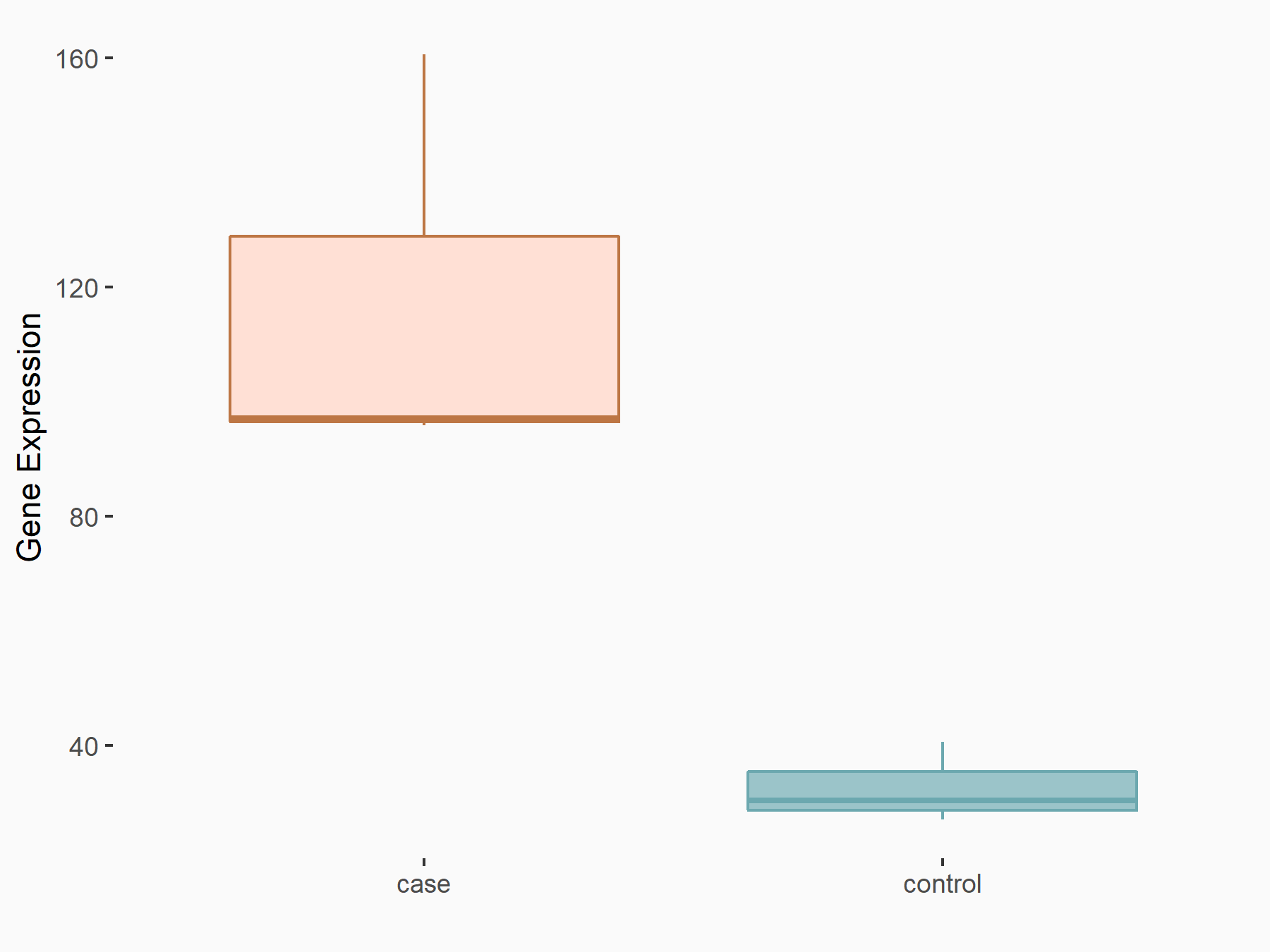 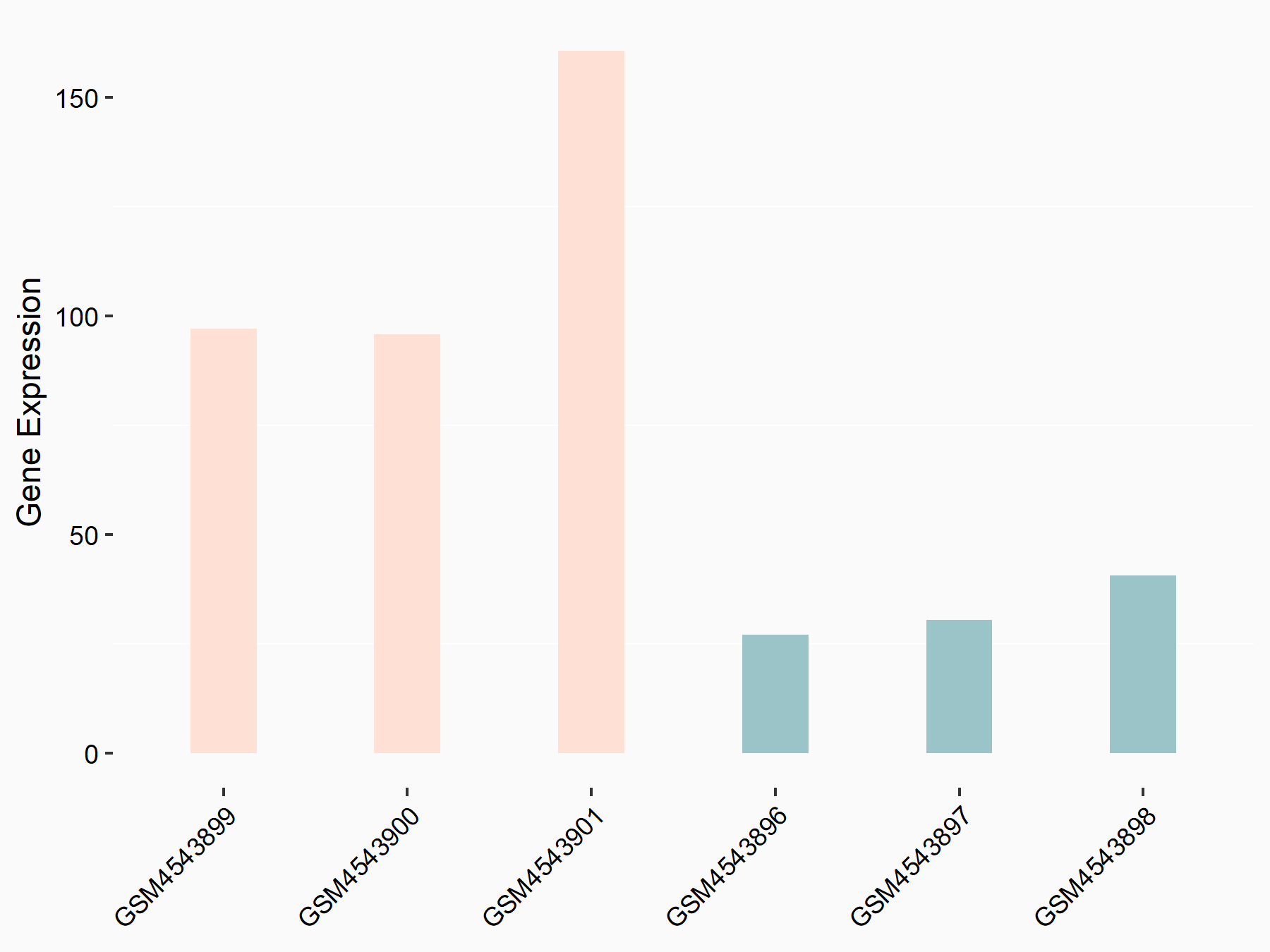 |
logFC: 1.83E+00 p-value: 7.08E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [24] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
1H8 [Mouse hybridoma against human BMSC] | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_A7TU |
| In-vivo Model | FtoKO mice were backcrossed to WT C57BL/6 mice to remove Cre and bred to homozygosity. Results are reported for male mice on the same genetic background (C57BL6/J). For the diet-induced bone loss studies, mice were fed a 60% high-fat diet (D12492, Research Diets) from 6 wk of age to 24 wk. Genotyping strategies are available upon request. NBD (KKKKKKKKGGTALDWSWLQTE) with the Trp to Ala substitutions designed to render the peptide inactive underlined, was a gift from D.C.G. and dissolved in water before use. Next, 10 mg/kg NBD was intraperitoneally injected in 29-wk old FtoOc KO mice every other day for 9 d. One day after the last injection, bone was harvested for analysis of DNA damage. | |||
| Response Summary | Loss of Fto also increased susceptibility of osteoblasts to genotoxic damage from metabolic stress induced by exposure to HF is also consistent with this model for FTO action. FTO functions intrinsically in osteoblasts through Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A)-NF-Kappa-B signaling to enhance the stability of mRNA of proteins that function to protect cells from genotoxic damage. | |||
Heat shock factor protein 1 (HSF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -7.09E-01 p-value: 1.48E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.1] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Bortezomib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
RPMI-8226 | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0014 |
| MM1.R | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8794 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 3×106 RPMI8226/MM1R-Luc cells were intravenously injected into NCG mice to establish a disseminated human MM xenograft model. The in vivo antitumor effect of the FTO inhibitor MA2 combined with or without the first-line chemotherapeutic agent BTZ was evaluated as follows: 3 days post xenotransplantation, MA2 (20 mg/kg), or vehicle control was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) daily for 10 days, and BTZ was injected intraperitoneally on days 1, 4, 8, and 11. Mouse serum was collected at specified time points during the treatment, and the tumor burden was monitored by detecting myeloma cell-secreted Lambda light chains via a Human Lambda ELISA Kit (Bethyl Laboratories, No. E88-116). Tumor development was monitored weekly after treatment with an in vivo imaging system (IVIS, SI Imaging, Lago, and LagoX). Luciferin (150 mg/kg, YEASEN, Shanghai, China) was injected intraperitoneally into the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO significantly promotes MM cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting Heat shock factor protein 1 (HSF1)/HSPs in a YTHDF2-dependent manner. FTO inhibition, especially when combined with bortezomib (BTZ) treatment, synergistically inhibited myeloma bone tumor formation and extramedullary spread in NCG mice. | |||
Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha (HSP90/HSP90AA1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 7.64E-01 p-value: 2.38E-12 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [26] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell migration and proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | |||
| Response Summary | m6A regulated cell proliferation by influencing apoptosis of U251 cells through regulating Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha (HSP90/HSP90AA1) expression.m6A level was decreased in glioma tissue, which was caused by decreased METTL3 and increased FTO levels. | |||
Integrin alpha-6 (ITGA6)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 5.89E-01 p-value: 3.48E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HT-1197 | Recurrent bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1291 |
| HT-1376 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1292 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/cnu/nu mice (4-5 weeks old) were used for the xenograft experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 6 for each group) and injected with 5 × 106 HT-1197 cells in control group or FTO plasmid group, respectively. | |||
| Response Summary | In bladder cancer, the changes in m6A methylation level mainly appeared at 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) of MALAT1 and NOTCH1 transcripts, and at 3' UTR of CSNK2A2 and Integrin alpha-6 (ITGA6) transcripts, responding to the overexpression of FTO. SFPQ could influence the FTO-mediated m6A RNA demethylation, eventually affecting the gene expression. | |||
Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.90E-01 p-value: 1.74E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [28] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SNU-216 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3946 |
| MKN7 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1417 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| Response Summary | FTO was an independent risk factor for overall survival (OS) of GC patients and FTO could promote GC metastasis by upregulating the expression of Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1) via decreasing its m6A level. | |||
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.83E+00 p-value: 2.17E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Atorvastatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1), downregulated those of KLF2 and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Krueppel-like factor 2 (KLF2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16F10 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout B16F10 cells
Control: B16F10 cells
|
GSE134388 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.68E+00 p-value: 3.25E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Atorvastatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, downregulated those of Krueppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Krueppel-like factor 5 (KLF5)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.34E+00 p-value: 1.46E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [23] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair | |||
| Cell proliferation and migration | ||||
In-vitro Model |
VSMC (Human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells) | |||
| Response Summary | FTO expression significantly contributes to the phenotype conversion of VSMCs and the aortic dissecting aneurysm by the demethylation function (m6A), thereby providing a novel therapeutic target. Knockdown of FTO suppresses the p-GSK3-beta levels and Krueppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) expression regardless of AngII treatment. | |||
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse liver | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mouse liver tissue
Control: Wild type mouse liver tissue
|
GSE125785 | |
| Regulation |
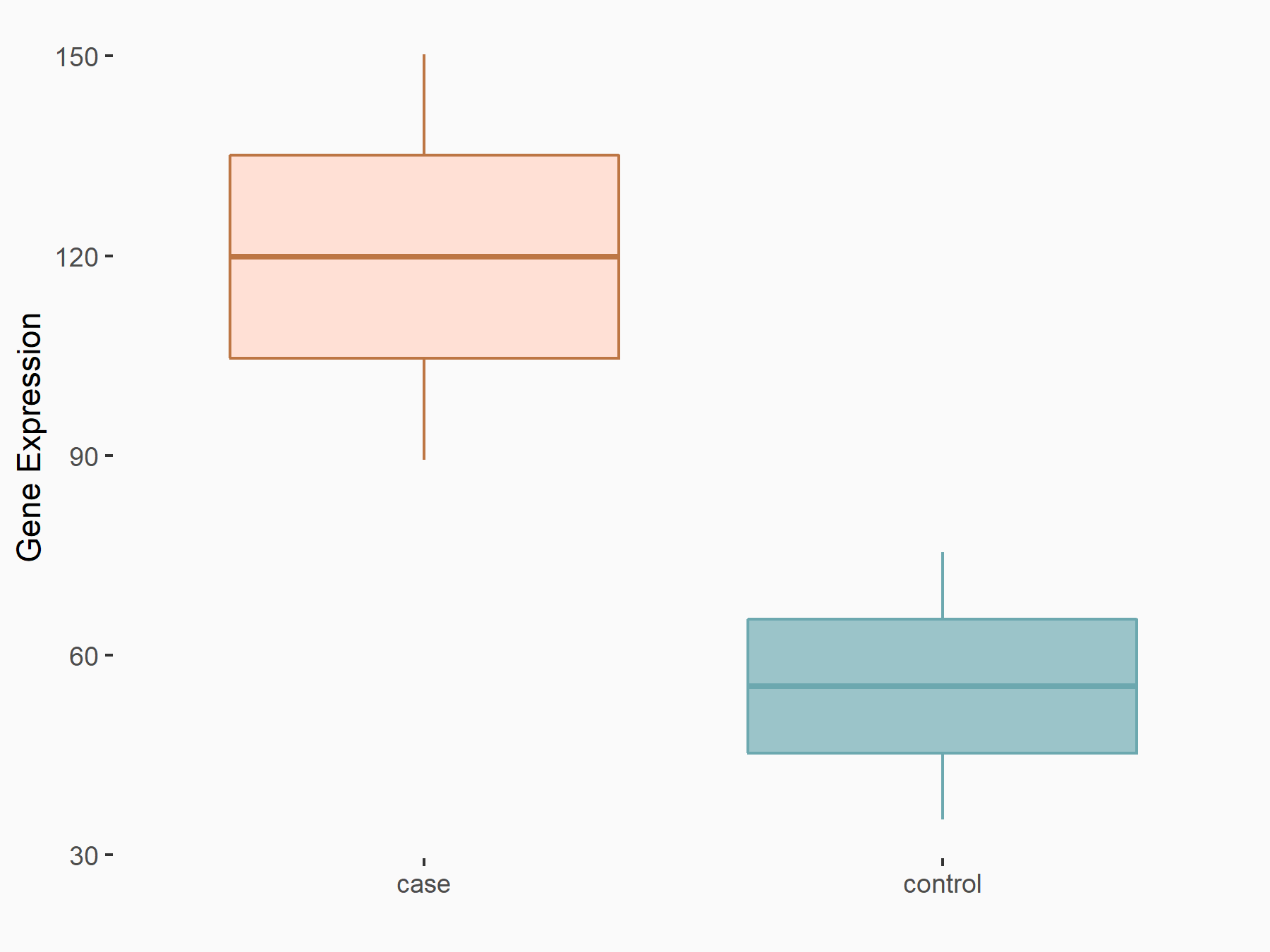 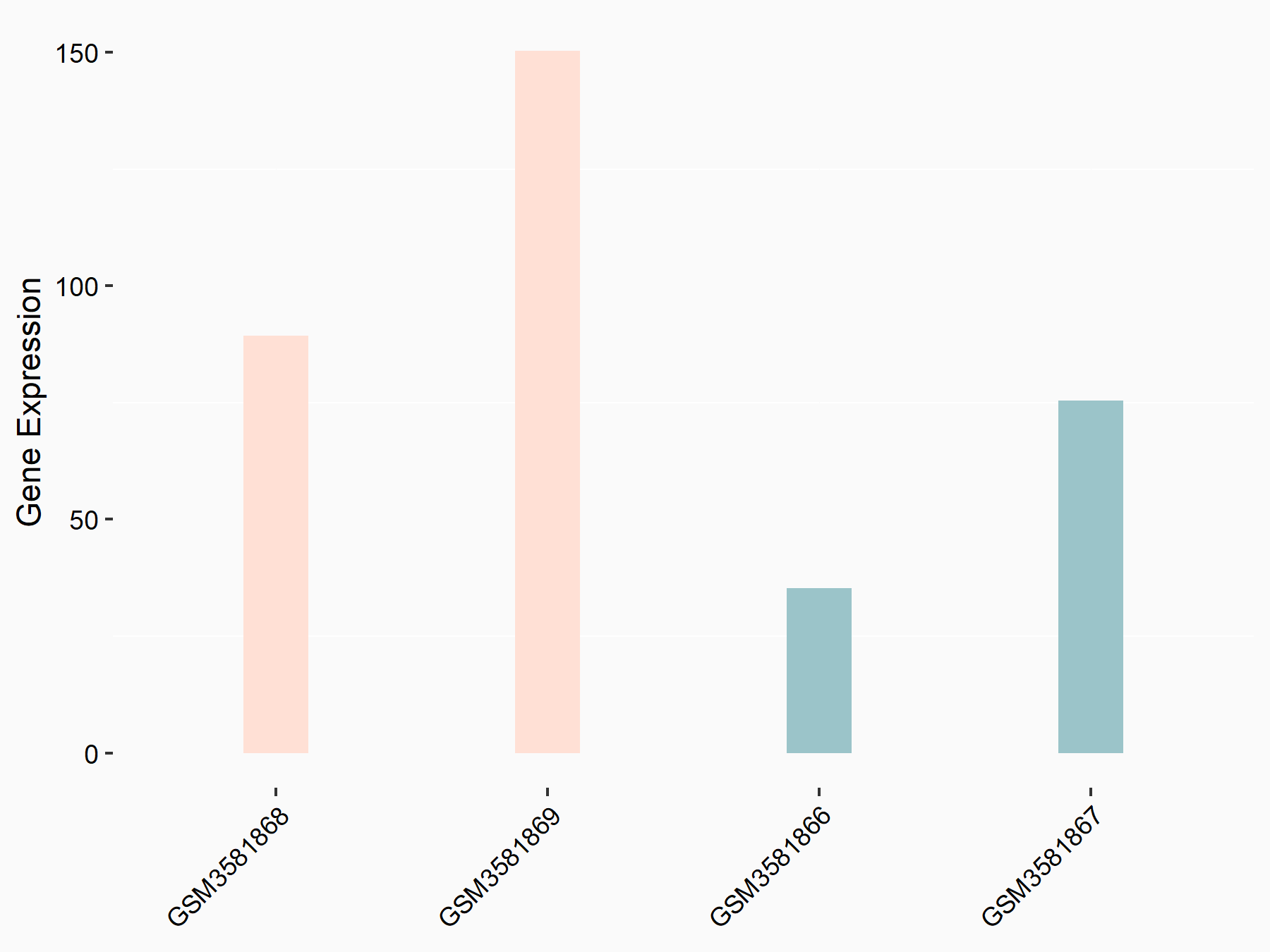 |
logFC: 1.12E+00 p-value: 2.09E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [30] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
In-vitro Model |
MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [30] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
In-vitro Model |
MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [30] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
In-vitro Model |
MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
Matrix metalloproteinase-24 (MMP24)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | HEK293 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: FTO knockdown HEK293T cells
Control: HEK293T cells
|
GSE78040 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.43E-01 p-value: 7.94E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pain disorders [ICD-11: 8E43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [31] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuropathic Pain [ICD-11: 8E43.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mice were anesthetized with Nembutal. The lower back was dissected until the transverse lumbar process was exposed. After the process was removed, the underneath L4 spinal nerve was ligated with a silk 6-0 thread. A slight distal location was chosen for transection around the ligation site. Subsequent layers of muscle and skin were closed. The sham groups undertook identical procedures, but without the transection or ligature of the corresponding nerve. The intraspinal injection was performed as described previously. In short, after anesthetized with Nembutal, mice underwent hemilaminectomy at the L1-L2 vertebral segments. The intraspinal injection was carried out ipsilaterally on the left side. By using a glass micropipette, each animal received two injections (5 × 105 TU per injection, 0.8 mm from the midline, 0.5 mm apart in rostrocaudal axis, 0.5 mm deep) of lentivirus following the L3-L4 dorsal root entry zone after exposure of spinal cord. The tip of glass micropipette should reach a depth of lamina II-IV of the spinal cord. Finally, the dorsal muscle and skin were sutured layer by layer. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO was colocalized with Matrix metalloproteinase-24 (MMP24) in spinal neurons and shown increased binding to the Mmp24 mRNA in the spinal cord after SNL. SNL promoted the m6A eraser FTO binding to the Mmp24 mRNA, which subsequently facilitated the translation of MMP24 in the spinal cord, and ultimately contributed to neuropathic pain genesis. | |||
Melanocortin receptor 4 (MC4R)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 7.52E-01 p-value: 2.88E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [32] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
WPMY-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3814 |
| PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 | |
| LNCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0395 | |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| 22Rv1 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1045 | |
| In-vivo Model | PCa cells carrying the transfected plasmid were subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient mice at a rate of 1 × 106 cells per mouse according to a previous study. Tumor formation in the two groups of mice was observed and recorded by a designated personnel every day, and the volume of the tumors was measured. The nude mice were sacrificed 21 days after tumor formation, and the tumors were removed to measure their volume and weight. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO was downregulated in PCa and its expression level showed a relevance to the prognosis of PCa patients. Additionally, FTO could regulate the proliferation, migration and invasion of PCa via regulating the expression level of Melanocortin receptor 4 (MC4R). | |||
Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.81E-01 p-value: 3.45E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)/CEBPA signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [33] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
In-vitro Model |
NCI-H322 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1556 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were randomized into several groups. For the subcutaneous implantation model, 1 × 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank regions of female BALB/c nude mice (4-5 weeks). For lung colonization assays, 1 × 106 cells were injected into the tail vein of female NOD/SCID mice (6-7 weeks), and 6 weeks later the lung was removed and fixed with 10% formalin. | |||
| Response Summary | Wnt/Beta-catenin-mediated FTO downregulation and underscored the role of m6A modifications of Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC) mRNA in regulating tumor cell glycolysis and growth. | |||
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.4] | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)/CEBPA signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [34] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | RC cells SW480 at logarithmic growth phase were prepared into cell suspension with a concentration of about 1 × 107/100 L, which was then injected into the left axilla of nude mice with a 1 ml syringe to establish a subcutaneous mouse xenograft model. Once the tumor volume reached about 50 mm3, the nude mice were injected with miR-96 antagomir or NC antagomir (10 nmol once every 5 days for 5 weeks). After 5 weeks, the mice were euthanized, after which the subcutaneous transplanted tumor was removed, and weighed. | |||
| Response Summary | MiR-96 antagomir could potentially retard the cancerogenesis in colorectal cancer via AMPK-alpha-2-dependent inhibition of FTO and blocking FTO-mediated m6A modification of Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC). | |||
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [36] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| HPDE | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4376 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| Response Summary | FTO has been indicated to interact with Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC) proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor and to enhance its stability by decreasing its m6A level.the aforementioned observations indicate a novel mechanism for the regulation of pancreatic cancer cells by FTO. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [37] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [38] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and migration | |||
In-vitro Model |
HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| Response Summary | FTO interacts with transcripts of E2F1 and Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC), inhibition of FTO significantly impairs the translation efficiency of E2F1 and Myc.FTO plays important oncogenic role in regulating cervical cancer cells' proliferation. | |||
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [100] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [101] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 |
| Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 | |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| TE-10 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1760 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were acclimatized and fed for one week. Then, they were randomly divided into two groups: sh-NC group and sh-SHMT2 group. Cells transfected with sh-NC or sh-SHMT2 were subsequently cultured routinely. Next, cells with logarithmic growth phase (1 ×106) were taken and injected to the right axilla of nude mice. After subcutaneous inoculation, the mice were observed for their mental status, activity, and tumor formation. The tumor volume was monitored every 4 days, and the mice were euthanized after 28 days. Tumor tissues were separated and weighed from nude mice. A portion of the dissected tumor tissue was fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin blocks and sectioned. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [88] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Male BALB/c nude mice (aged 4-6 weeks; n = 5/group) were obtained from Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). MHCC97H or Huh7 cells (2 × 106 cells/mouse) stably transfected with lentivirus containing different plasmids in 100 μL DMEM were subcutaneously or orthotopically implanted into the nude mice. | |||
Myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16-OVA cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shFTO B16-OVA cells
Control: shNC B16-OVA cells
|
GSE154952 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.18E-01 p-value: 2.06E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [35] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| In-vivo Model | Twenty-four specific pathogen free female BALB/c nude mice (age: 6 weeks, weight: 15 ~ 18 g) were purchased from Slac Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd., and subcutaneously injected with SW620 cells stably transfected with oe-NC, oe-GSK3-Beta + oe-NC, or oe-GSK3-Beta + oe-c-Myc to establish a subcutaneous xenograft tumour model in nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | GSK3beta inhibited Myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF1) expression by mediating FTO-regulated m6A modification of MZF1 and then decreased the proto-oncogene c-Myc expression, thus hampering CRC cell proliferation. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [39] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.2] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | mRNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
16HBE14o- | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0112 |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| CHLH-1 (The human squamous lung cancer cell line) | ||||
| NCI-H226 | Pleural epithelioid mesothelioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1544 | |
| CHLH-1 (The human squamous lung cancer cell line) | ||||
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| Response Summary | FTO enhanced Myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF1) expression by reducing m6A levels and mRNA stability in MZF1 mRNA transcript, leading to oncogenic functions. The functional importance of FTO in the tumor progression of LUSC and provides a potential therapeutic target for LUSC treatment. | |||
Negative growth regulatory protein MyD118 (GADD45B)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | HEK293 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout HEK293 cells
Control: Wild type HEK293 cells
|
GSE79577 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.04E-01 p-value: 5.27E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [40] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | |||
| Cell Process | DNA repair | |||
In-vitro Model |
GPM (Goat primary myoblasts) | |||
| In-vivo Model | Sixteen female goats in good body condition and suitable for pregnancy were selected. All selected goats underwent estrus synchronization treatment and were naturally mated. After 75 days of gestation, four male fetuses were removed from five pregnant goats during abortion operations, and their longissimus muscle samples were collected. | |||
| Response Summary | Negative growth regulatory protein MyD118 (GADD45B)-mediated m6A modification in Negative growth regulatory protein MyD118 (GADD45B) mRNA drives skeletal muscle differentiation by activating the p38 MAPK pathway, which provides a molecular mechanism for the regulation of myogenesis via RNA methylation. | |||
Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
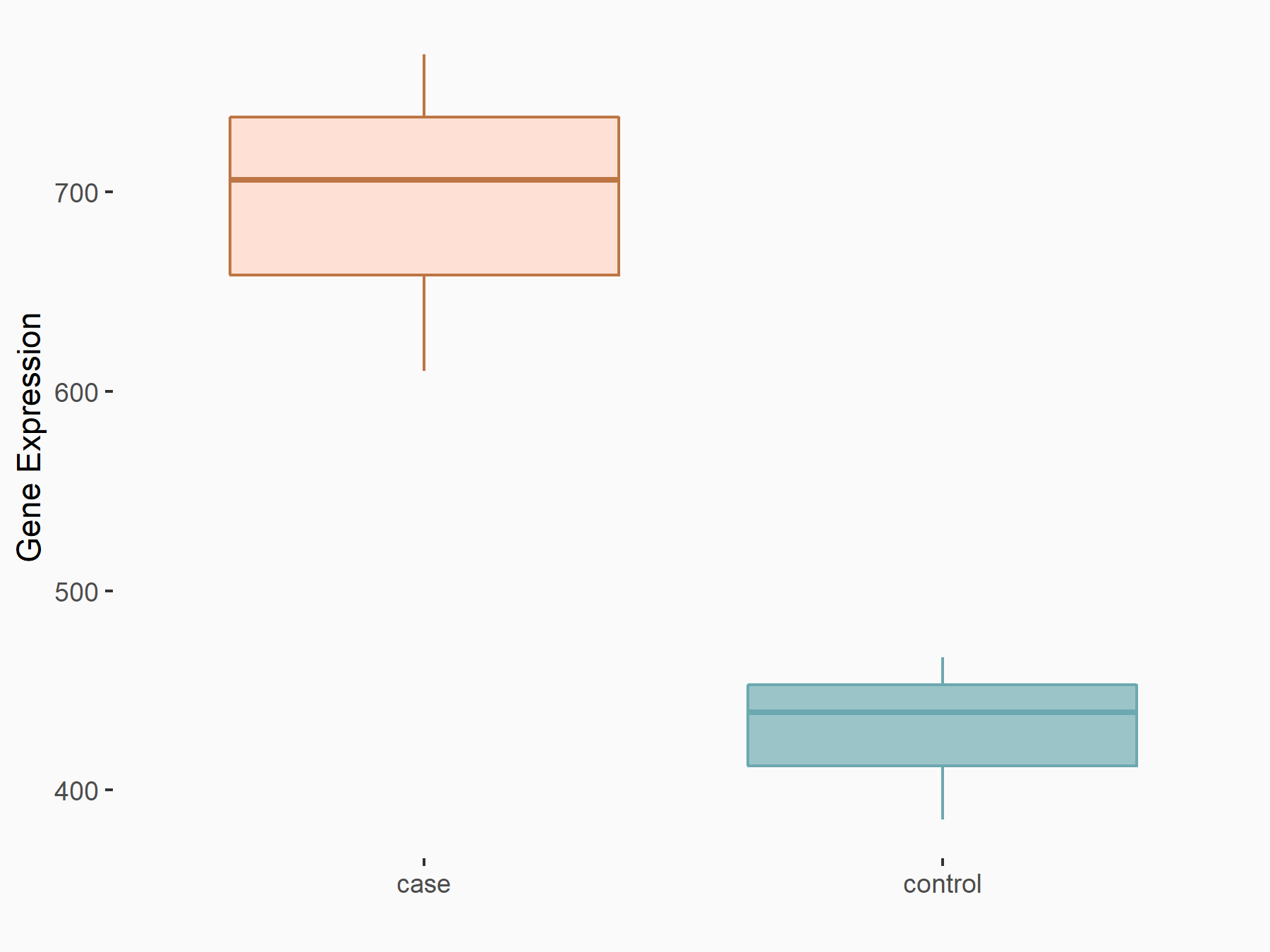 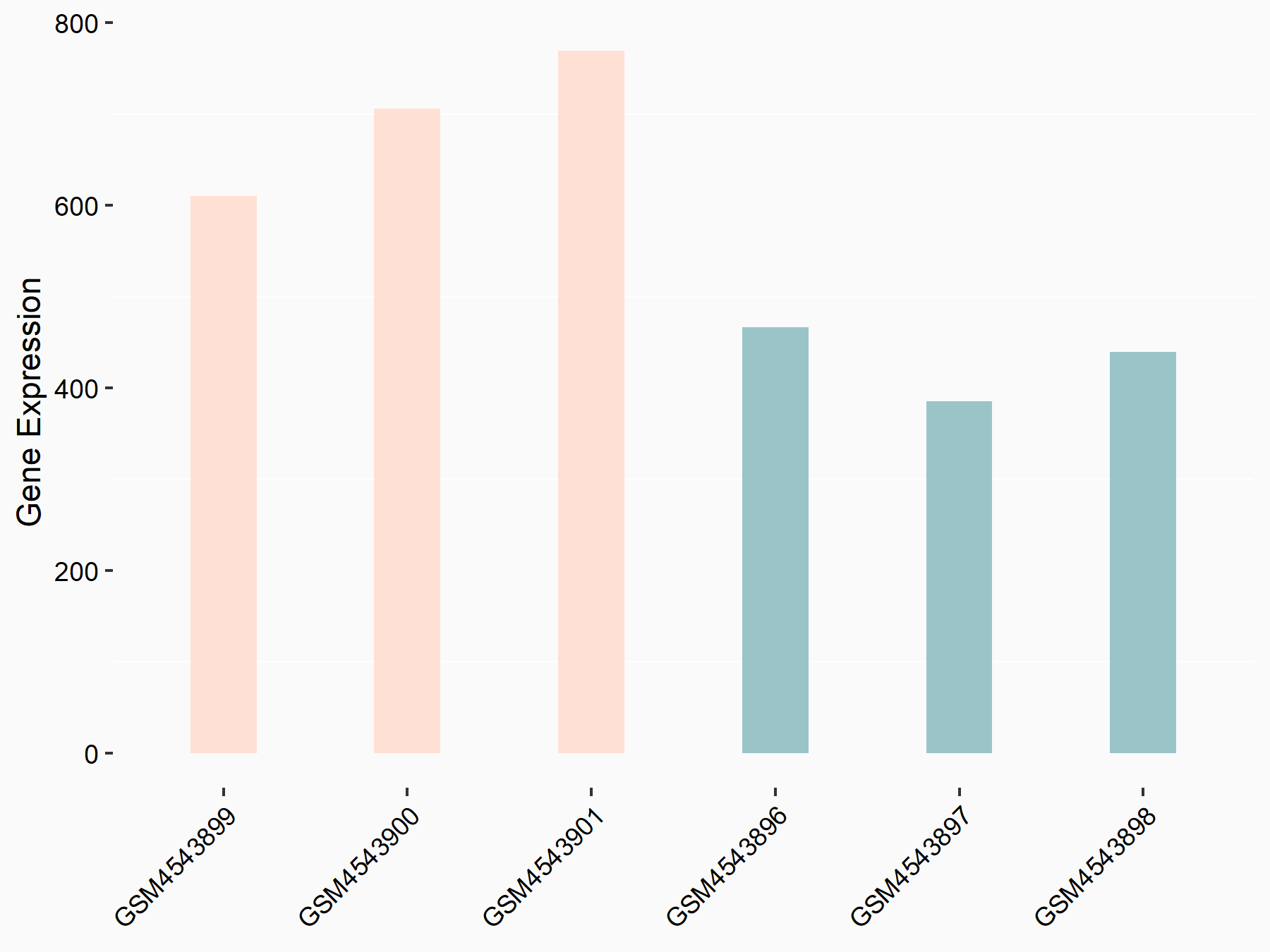 |
logFC: 6.94E-01 p-value: 5.11E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HT-1197 | Recurrent bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1291 |
| HT-1376 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1292 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/cnu/nu mice (4-5 weeks old) were used for the xenograft experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 6 for each group) and injected with 5 × 106 HT-1197 cells in control group or FTO plasmid group, respectively. | |||
| Response Summary | In bladder cancer, the changes in m6A methylation level mainly appeared at 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) of MALAT1 and Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) transcripts, and at 3' UTR of CSNK2A2 and ITGA6 transcripts, responding to the overexpression of FTO. SFPQ could influence the FTO-mediated m6A RNA demethylation, eventually affecting the gene expression. | |||
Neutral amino acid transporter B(0) (SLC1A5)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.02E+00 p-value: 5.80E-30 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [41] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Responsed Drug | GLS-IN-968 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | |||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | |||
In-vitro Model |
UMRC2-vec (CCRCC isogenic cell lines that are VHL-deficient) | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic inactivation of FTO using multiple orthogonal approaches revealed that FTO inhibition selectively reduces the growth and survival of VHL-deficient cells in vitro and in vivo. Integrated analysis of transcriptome-wide m6A-seq and mRNA-seq analysis identified the glutamine transporter Neutral amino acid transporter B(0) (SLC1A5) as an FTO target that promotes metabolic reprogramming and survival of VHL-deficient ccRCC cells. GLS1 inhibitors that target mitochondrial glutaminase and the conversion of glutamine to glutamate are currently being evaluated in early-phase clinical trials in ccRCC. These findings identify FTO as a potential HIF-independent therapeutic target for the treatment of VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma. | |||
Nucleophosmin (NPM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -7.88E-01 p-value: 1.66E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
OCI-AML-3 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1844 |
| OCI-AML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1619 | |
| Response Summary | FTO depended on its m6A RNA demethylase activity to activate PDGFRB/ERK signaling axis. FTO-mediated m6A demethylation plays an oncogenic role in Nucleophosmin (NPM1)-mutated Acute myeloid leukemia(AML). | |||
P5C reductase 1 (PYCR1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -8.46E-01 p-value: 2.98E-19 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [42] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mRNA surveillance pathway | hsa03015 | ||
| RNA degradation | hsa03018 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| RT-4 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0036 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| EJ (Human bladder cancer cells) | ||||
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
| In-vivo Model | T24 cells were subcutaneously injected into the mice (1 x 106 cells / injecting site). | |||
| Response Summary | FTO decreased N6-methyladenosine methylation level in P5C reductase 1 (PYCR1) through its demethylase enzymatic activity and stabilized PYCR1 transcript to promote bladder cancer initiation and progression. | |||
PDH kinase 1 (PDK1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -7.19E-01 p-value: 8.18E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [43] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Temozolomide | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Citrate cycle | hsa00020 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| Cell Process | Aerobic glycolysis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| SHG-44 | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6728 | |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| Response Summary | Long noncoding RNA just proximal to X-inactive specific transcript facilitates aerobic glycolysis and temozolomide chemoresistance by promoting stability of PDH kinase 1 (PDK1) mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner in glioblastoma multiforme cells. JPX interacted with N6-methyladenosine (m6A) demethylase FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) and enhanced FTO-mediated PDK1 mRNA demethylation. | |||
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 2.20E+00 p-value: 2.69E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [44] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | ||
In-vitro Model |
hMSCs (Human osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells (HUXMA-01001, Cyagen Biosciences, Suzhou, China)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | Conditional knockout of Fto in bone in mice was generated as previously described. Throughout the study, mice were maintained on a 12 h: 12 h light:dark cycle in a specific pathogen-free facility. | |||
| Response Summary | Both depletion of FTO and application of the FTO inhibitor FB23 or FB23-2 impaired osteogenic differentiation of human MSCs. Knockdown of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) promoted FTO-induced expression of the osteoblast biomarkers ALPL and OPN during osteogenic differentiation. This study demonstrates the functional significance of the FTO-PPARG axis in promoting the osteogenesis of human MSCs and sheds light on the role of m6A modification in mediating osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. | |||
Platelet-derived growth factor C (PDGFC)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.37E+00 p-value: 3.21E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [45] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
In-vitro Model |
SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| HPDE | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4376 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| Capan-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0237 | |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | The right flanks of mice were injected subcutaneously with 2 × 106 MiaPaCa-2 cells stably expressing shFTO and a scrambled shRNA in 100 uL PBS. Tumors were measured using an external caliper once per week, and tumor volume was calculated with the formula: (length × width2)/2. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO downregulation leads to increased m6A modifications in the 3' UTR of Platelet-derived growth factor C (PDGFC) and then modulates the degradation of its transcriptional level in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner, highlighting a potential therapeutic target for PDAC treatment and prognostic prediction. | |||
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRB)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.89E-01 p-value: 9.80E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
OCI-AML-3 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1844 |
| OCI-AML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1619 | |
| Response Summary | FTO depended on its m6A RNA demethylase activity to activate Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRB)/ERK signaling axis. FTO-mediated m6A demethylation plays an oncogenic role in NPM1-mutated Acute myeloid leukemia(AML). | |||
PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1a/PPARGC1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 4.58E+00 p-value: 7.10E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [46] | |||
| Responsed Disease | clear cell renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Oxidative stress | |||
| ROS production | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| 769-P | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1050 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five- to 6-week-old male athymic nude mice purchased by Charles River were used for the xenograft model. 769-P cells stably expressing Ctrl, FTO and FTO-mut were trypsinized and washed twice to thrice with standardized PBS, and then, 5 × 106 cells in 100 uL of PBS was subcutaneously injected into the flanks of the mice (five mice per group). Mice were monitored twice every week for tumour growth, and tumour diameters were measured using a caliper. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO plays a critical anti-tumorigenic role in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Restored expression of FTO, through reducing m6A levels in mRNA transcripts of its critical target gene PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1a/PPARGC1A), increases mitochondrial content, ROS production and oxidative damage, with the most important effect of repressed tumour growth. | |||
Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [47] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Myogenic differentiation | |||
| mTOR signaling pathway (hsa04150) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
MPM (Mouse primary myoblasts from about 10-day-old C57BL/6J were isolated) | |||
| C2C12 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0188 | |
| HEK293-FT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6911 | |
| In-vivo Model | To generate doxycycline-inducible skeletal muscle-specific FTO deletion mice, FTOflox/flox mice were crossed with HSA-Cre mice to generate FTOflox/+ HSA-Cre mice, which were then crossed to FTOflox/flox mice to generate FTOflox/flox and FTOflox/flox HSA-Cre mice. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO downregulation suppressed mitochondria biogenesis and energy production, showing as the decreased mitochondria mass and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) content, the downregulated expression of mtDNA-encoding genes and PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1a/PPARGC1A) gene, together with declined ATP level. These findings provide the first evidence for the contribution of FTO for skeletal muscle differentiation. | |||
Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
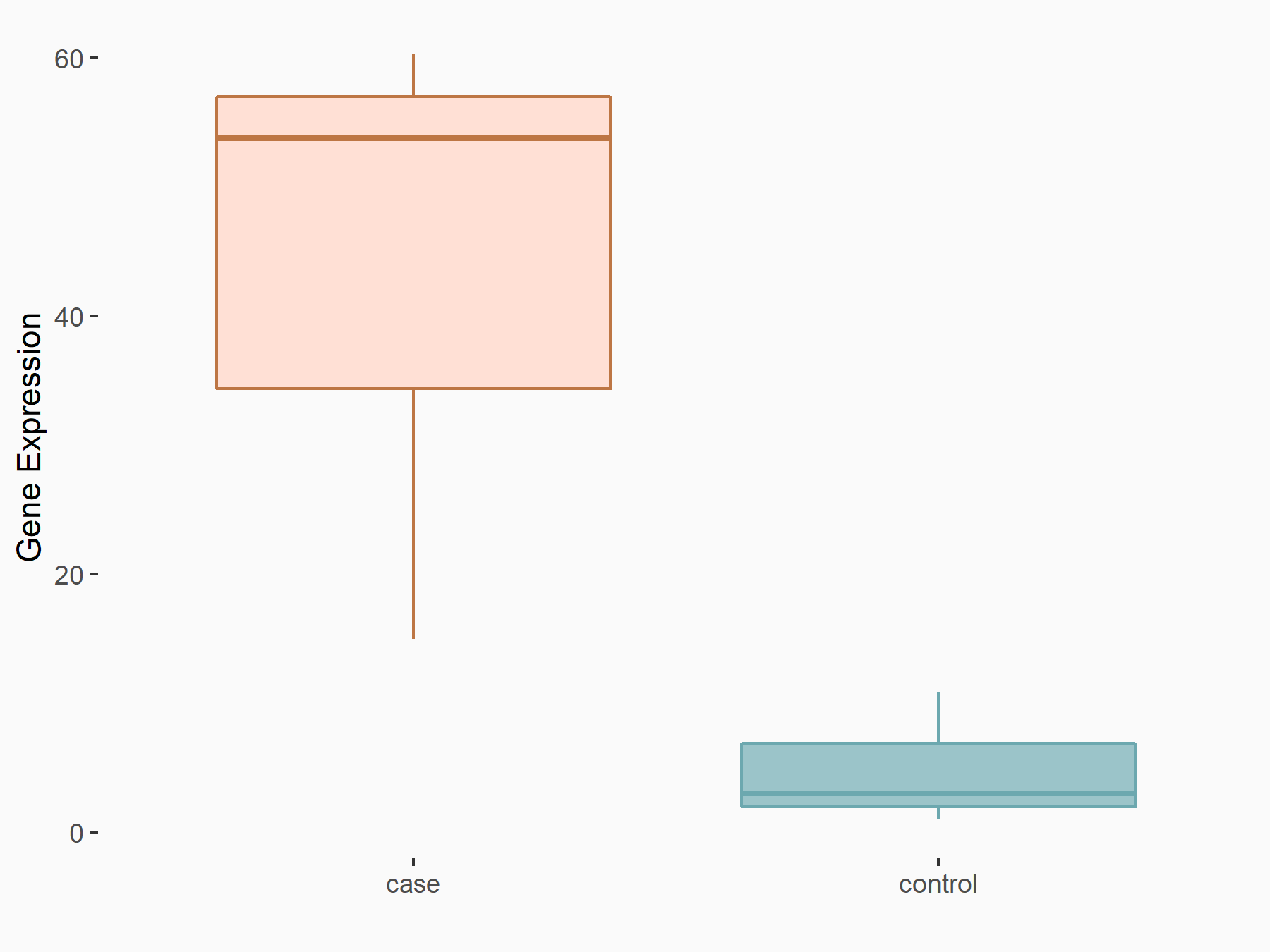 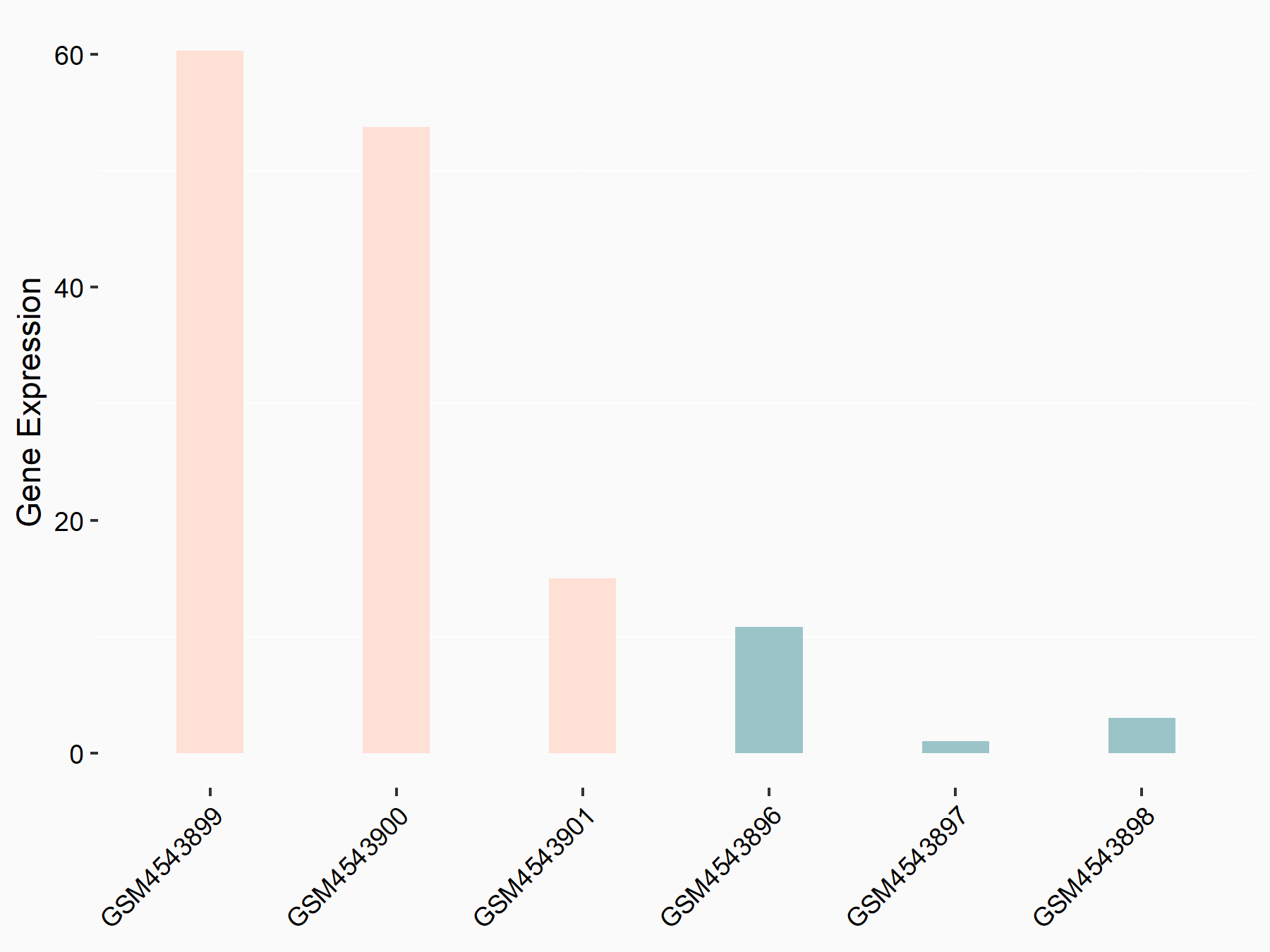 |
logFC: 3.22E+00 p-value: 3.45E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [48] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Response Summary | Arecoline-induced FTO promotes the stability and expression levels of Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) transcripts through mediating m6A modification and MYC activity, respectively. PD-L1 upregulation confers superior cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to T-cell killing to OSCC cells. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [37] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.52E+00 p-value: 5.79E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [49] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | ||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| In-vivo Model | The transfected cells (2×106) were directly subcutaneously injected in to flank of mice. The width and length were measured every six days. After three weeks, the mice were killed and the necropsies were weighted. | |||
| Response Summary | The overexpression of demethylase FTO in the HCC tissue and cells. FTO could regulate the demethylation of Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM) in the hepatocellular carcinoma. | |||
Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 (IQGAP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.41E-01 p-value: 2.42E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [50] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasome pathway degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous xenotransplanted tumor models, cells were injected subcutaneously (5 × 106 for MHCC97H or 1×106 for PLC cells per mouse). | |||
| Response Summary | AMD1 could stabilize the interaction of Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 (IQGAP1) with FTO, which then promotes FTO expression and increases HCC stemness. | |||
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.60E+00 p-value: 6.61E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BMSCs (BMSCs were obtained from the femurs and tibias of 2-3-week-old Sprague-Dawley male rats (Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | Female C57BL/6J mice (14 weeks old) were treated with bilateral ovariectomy under general anesthesia. Eight weeks after surgery, tibial plateau was harvested and the structure were evaluated with a SCANCO Medical uCT 40 scanner. | |||
| Response Summary | RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes osteoporosis through demethylating Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) mRNA and inhibiting osteogenic differentiation. | |||
Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 (SERCA2a/ATP2A2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 5.91E-01 p-value: 1.58E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Energy metabolism disorder [ICD-11: 5C53]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [52] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Energy metabolism disorder [ICD-11: 5C53] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Energy metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
AC16 [Human hybrid cardiomyocyte] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4U18 |
| Response Summary | FTO modification of N6 -methyladenosine is associated with myocardial cell energy metabolism disorder. FTO reduced the m6A level of Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 (SERCA2a/ATP2A2) mRNA through demethylation, thus promoting SERCA2a expression, maintaining calcium homeostasis, and improving energy metabolism of H/R cardiomyocytes. | |||
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [116] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.53E-01 p-value: 1.38E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Transport and catabolism | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | As cells (5 million) in Matrigel or As-T (1 million) cells in PBS with or without gene manipulations were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of female mice (6-8 weeks of age). For treatment with CS1 or CS2, As-T cells (1 million) in PBS were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of 6-week-old female nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO deletion inhibited arsenic-induced tumorigenesis. Epidermis-specific FTO deletion prevented skin tumorigenesis induced by arsenic and UVB irradiation. NEDD4L was identified as the m6A-modified gene target of FTO. Arsenic stabilizes FTO protein through inhibiting Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)-mediated selective autophagy. FTO-mediated dysregulation of mRNA m6A methylation as an epitranscriptomic mechanism to promote arsenic tumorigenicity. Arsenic suppresses p62 expression by downregulating the NF-kappaB pathway to upregulate FTO. | |||
Human skin lesions [ICD-11: ME60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Human skin lesions [ICD-11: ME60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Transport and catabolism | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | As cells (5 million) in Matrigel or As-T (1 million) cells in PBS with or without gene manipulations were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of female mice (6-8 weeks of age). For treatment with CS1 or CS2, As-T cells (1 million) in PBS were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of 6-week-old female nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO deletion inhibited arsenic-induced tumorigenesis. Epidermis-specific FTO deletion prevented skin tumorigenesis induced by arsenic and UVB irradiation. NEDD4L was identified as the m6A-modified gene target of FTO. Arsenic stabilizes FTO protein through inhibiting Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)-mediated selective autophagy. FTO-mediated dysregulation of mRNA m6A methylation as an epitranscriptomic mechanism to promote arsenic tumorigenicity. Arsenic suppresses p62 expression by downregulating the NF-kappaB pathway to upregulate FTO. | |||
Macroscopic changes of size of the kidney [ICD-11: MF54]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [117] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Macroscopic changes of size of the kidney [ICD-11: MF54.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Canagliflozin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase ULK1 (ULK1/ATG1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.13E-01 p-value: 1.25E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [55] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 |
| SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 5 × 106 cells in 200 ul PBS were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of nude mice. After injection, cisplatin treatment was initiated on day 5. Mice were injected with 5 mg/kg cisplatin or PBS solution in the abdominal cavity once a week for 3 weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of FTO reversed cisplatin resistance of SGC-7901/DDP cells both in vitro and in vivo, which was attributed to the inhibition of Serine/threonine-protein kinase ULK1 (ULK1)-mediated autophagy. These findings indicate that the FTO/ULK1 axis exerts crucial roles in cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. | |||
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
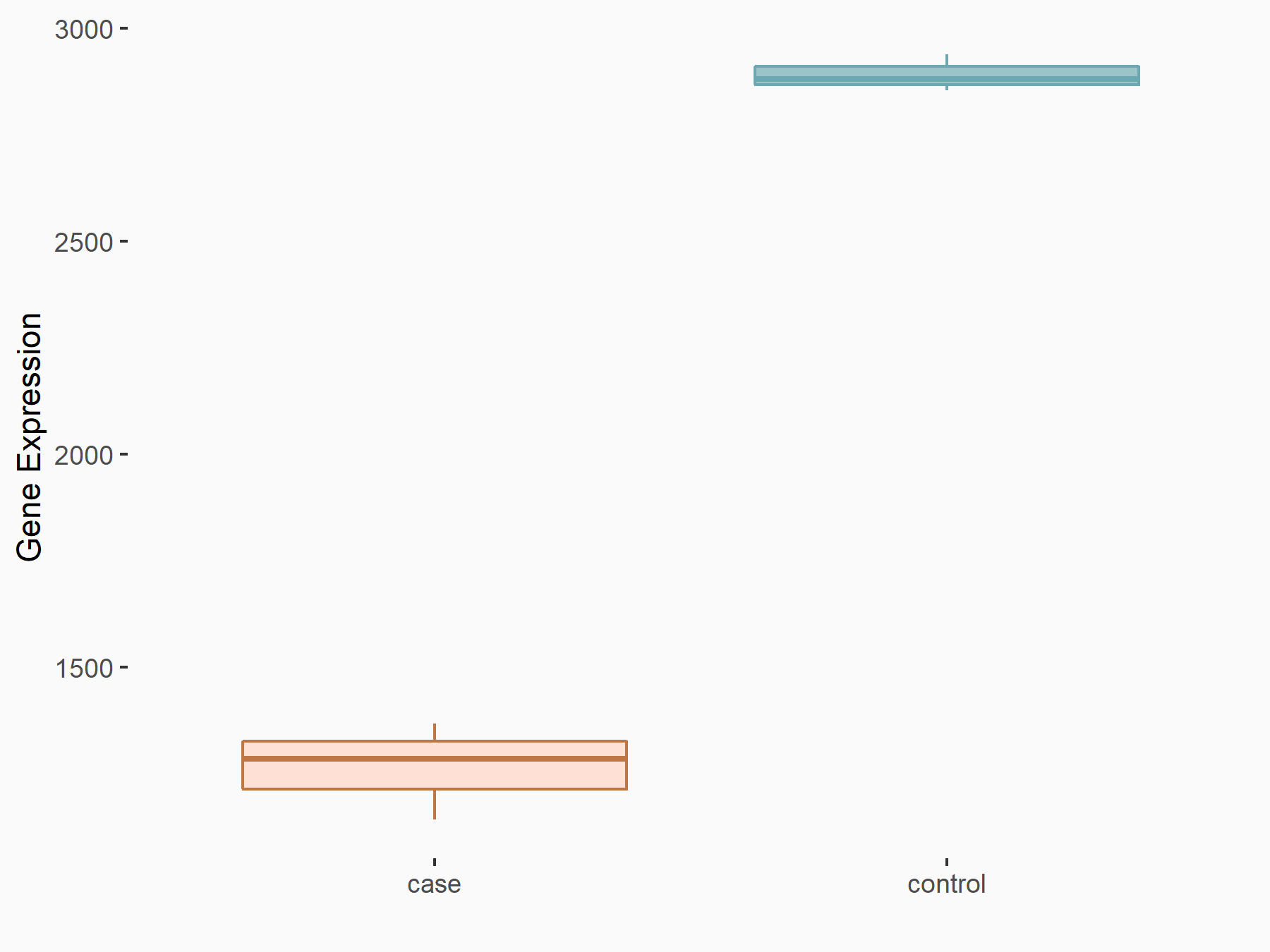 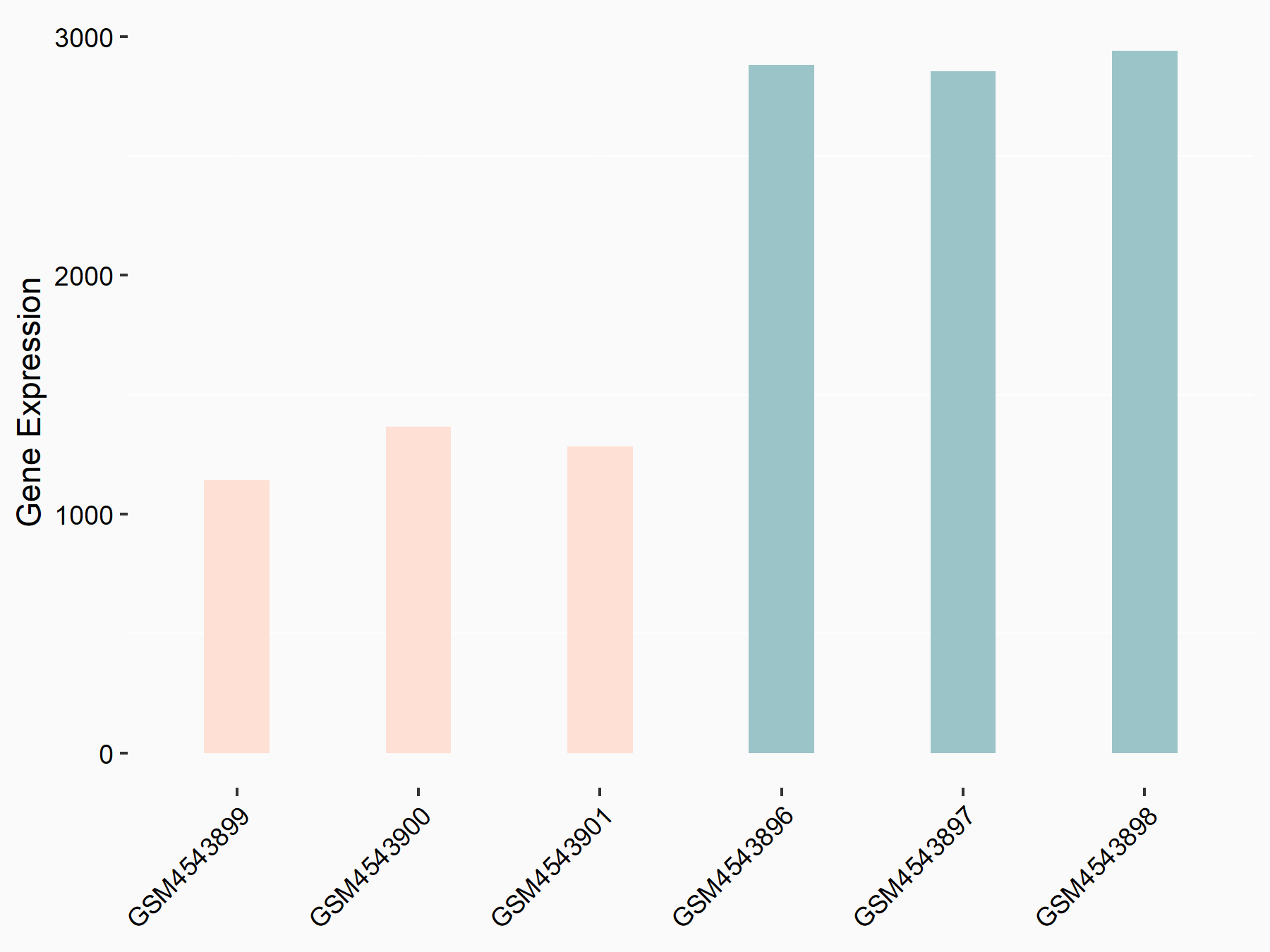 |
logFC: -1.19E+00 p-value: 4.36E-38 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Lipogenesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | After being fed with high-fat diet for 4 weeks, mice were given twice vena caudalis injection of control siRNA or Cidec siRNA (50 ug/mouse) mixed with liposome. Liposomes were prepared as described elsewhere. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO increased the lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by increasing nuclear translocation of Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1) and SREBP1c maturation, thus improving the transcriptional activity of LD-associated protein CIDEC.The studies provide new mechanistic insight into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) mediated by FTO. | |||
Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial (SOD2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.09E-01 p-value: 6.85E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [56] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.1] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Bortezomib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Response Summary | FTO promotes Bortezomib resistance via m6A-dependent destabilization of Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial (SOD2) expression in multiple myeloma. | |||
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TFPI-2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.23E+01 p-value: 1.69E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [57] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| cell migration | ||||
| cell invasion | ||||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation of Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TFPI-2) mRNA in PC cells, thereby increasing mRNA stability via the m6A reader YTHDF1. | |||
Transcription factor PU.1 (SPI1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | TPC_1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: FTO overexpression TPC_1 cells
Control: TPC_1 cells
|
GSE199206 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -7.40E+00 p-value: 4.06E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [58] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U-118MG | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0633 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c male nude mice were 4 weeks old. GBM cells with stable overexpression or knockdown of FTO and ovNC or shNC were transduced with lentivirus expressing luciferase. The cells were intracranially injected at a density of 5 × 105/10 uL into every mouse to form an orthotopic xenograft model. Coordinates of injection were 1 mm anterior and 2.5 mm right to the bregma, at a depth of 3.5 mm (the right frontal lobes of the mouse). Every 6 days, bioluminescence imaging (IVIS Lumina Series III; PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA) was used to image the mouse. At 8 days, we randomly chose 5 mice from each group to euthanize them, and their brain tissues were fixed with paraformaldehyde for further study. Another 5 mice were used for survival time analysis. For DB2313 (563801; MedKoo) anti-tumor research, male nude mice were subcutaneously injected with 5 × 106 U87MG cells suspended in 0.1 mL PBS. After 7 days, mice were intraperitoneally injected with DB2313 at density of 10 mg/kg/day dissolved in PBS solvent containing 10% DMSO for 7 days. The other group treated with vehicle only was set as the control group. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO inhibited growth, migration and invasion of GBM cells in vitro and in vivo.decreased FTO expression could induce the downregulation of MTMR3 expression by modulating the processing of pri-miR-10a in an m6A/HNRNPA2B1-dependent manner in GBM cells. Furthermore, the transcriptional activity of FTO was inhibited by the transcription factor Transcription factor PU.1 (SPI1). | |||
Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
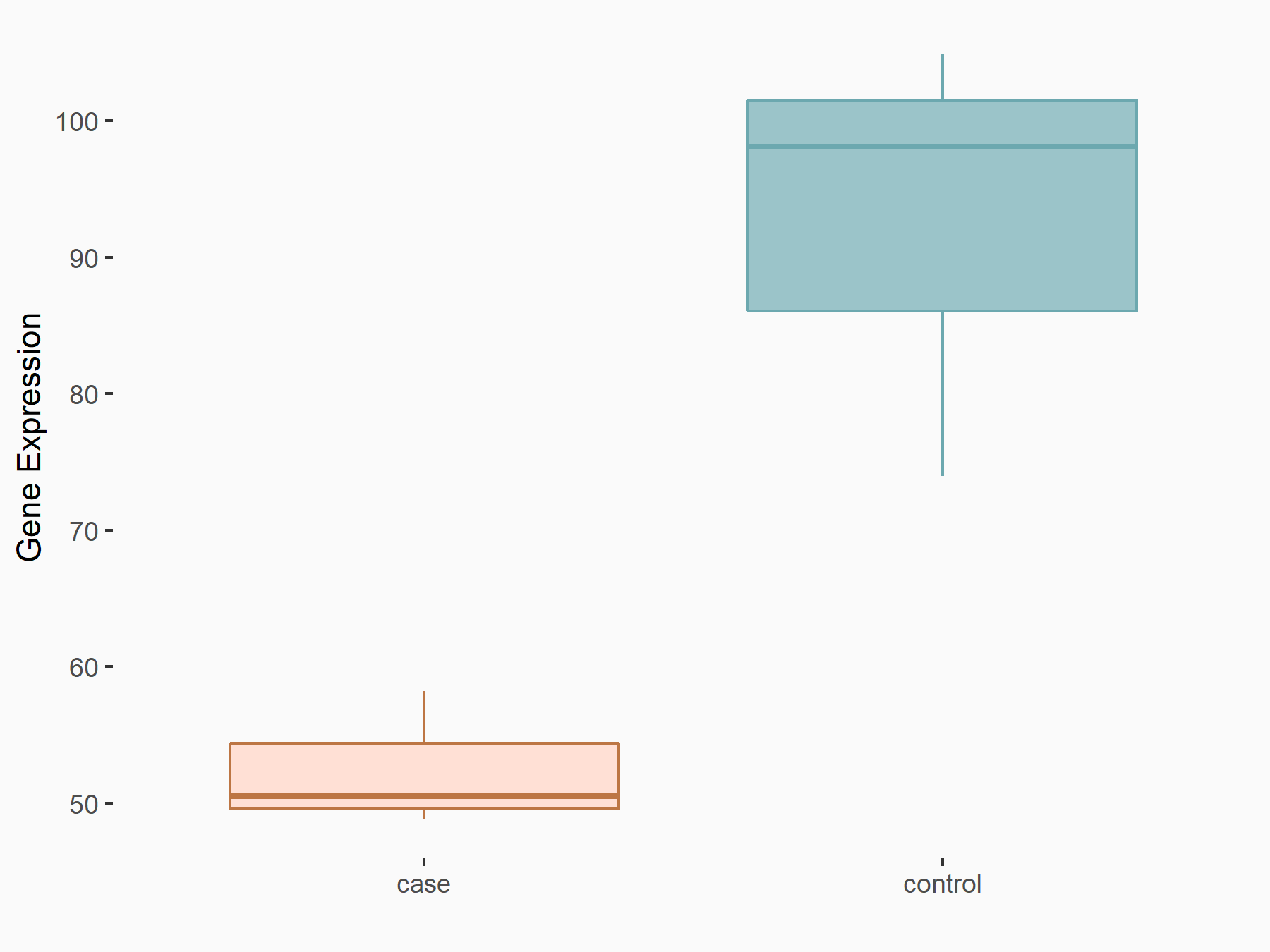 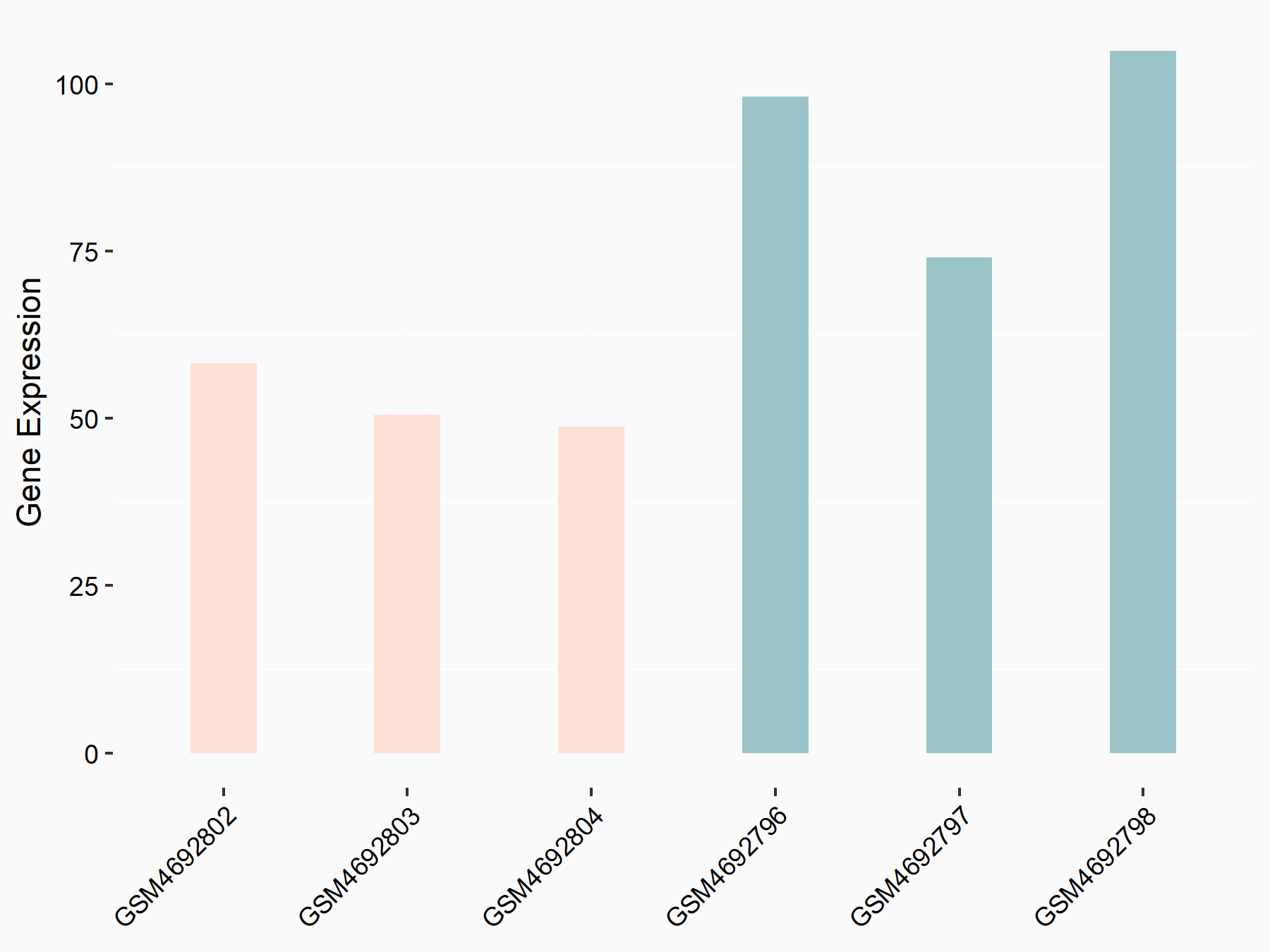 |
logFC: -8.13E-01 p-value: 2.61E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
In-vitro Model |
B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.87E-01 p-value: 5.76E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [59] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Response Summary | Stable knockdown of FTO inhibited OSCC cell viability, colony formation, and tumor growth. Further, FTO depletion increased Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) m6A modification at mRNA 3'-untranslated region, accelerating the degradation of YAP1 mRNA, a well-documented oncogene promoting OSCC progression. | |||
Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [60] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
Neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (Primary myocyte cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | After anesthesia (50 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium, intraperitoneal injection), the left thorax was cut to expose the heart, and the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery was ligated by 7/0 sterile suture. Myocardial ischemia was induced by 30 min of LAD coronary artery ligation and following 2 h of reperfusion. Sham group mice underwent the same surgical procedure without LAD coronary artery ligation. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO down-expressed in myocardial IRI mice and hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced cardiomyocytes. Moreover, FTO uninstalled the methylation of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) mRNA, and enforced the stability of Yap1 mRNA.The study reveals the role of FTO in H/R-induced myocardial cell injury via m6A-dependent manner, which provided a new approach to improve myocardial IRI. | |||
Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-4 (TEAD2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.75E-01 p-value: 4.59E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [61] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCCC-9810 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6908 |
| HIBEPIC (Human intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells) | ||||
| HuCC-T1 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0324 | |
| RBE | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4896 | |
| TFK-1 | Cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2214 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1.5 × 106 TFK1 cells with or without FTO overexpression were injected subcutaneously into the left and right flanks of 6-week-old female athymic nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | RNA decay assay showed that oncogene Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-4 (TEAD2) mRNA stability was impaired by FTO. The overexpression of FTO suppressed tumor growth in vivo. In conclusion, our study demonstrated the critical roles of FTO in Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. | |||
Transgelin (SM22alpha)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | TPC_1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: FTO overexpression TPC_1 cells
Control: TPC_1 cells
|
GSE199206 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.14E-01 p-value: 1.66E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [62] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
VSMC (Human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells) | |||
| Response Summary | FTO knockdown elevated Transgelin (SM22alpha) expression and m6A-binding protein IGF2BP2 enhanced SM22alpha mRNA stability by recognizing and binding to m6A methylation modified mRNA. m6A methylation-mediated elevation of SM22alpha restrained VSMC proliferation and migration and ameliorated intimal hyperplasia in T2DM. | |||
Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme ATG7 (ATG7)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.18E+00 p-value: 1.81E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line was transfected with LV2-1 or LV2-NC. Thereafter, BALB/c nude mice (6-week old) were intraperitoneally injected with SKOV3 cells. The mice were killed after 5 weeks, and the number of ascites was determined. | |||
| Response Summary | CircRAB11FIP1 promoted autophagy flux of ovarian cancer through DSC1 and miR-129. CircRAB11FIP1 can serve as the possible marker for EOC diagnosis and treatment. CircRAB11FIP1 regulated the mechanism of autophagy through m6A modification and direct binding to mRNA. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to the mRNA of FTO and promoted its expression. CircRAB11FIP1 directly bound to miR-129 and regulated its targets Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme ATG7 (ATG7) and ATG14. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to desmocollin 1to facilitate its interaction with ATG101. CircRAB11FIP1 mediated mRNA expression levels of ATG5 and ATG7 depending on m6A. | |||
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [64] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Autophagy | |||
| Adipogenesis regulation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Pig primary preadipocytes (Isolated from cervical subcutaneous adipose tissue of piglets) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Mice were maintained at 22 ± 2 ℃ with a humidity of 35 ± 5% under a 12 h light and 12 h dark cycle, with free access to water and food. For the HFD experiment, female control (Ftoflox/flox) and adipose-selective fto knockout (Fabp4-Cre Ftoflox/flox, fto-AKO) mice were fed with high-fat diet (60% fat in calories; Research Diets, D12492) for the desired periods of time, and food intake and body weight were measured every week after weaning (at 3 weeks of age). | |||
| Response Summary | Atg5 and Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme ATG7 (ATG7) were the targets of YTHDF2 (YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2). Upon FTO silencing, Atg5 and Atg7 transcripts with higher m6A levels were captured by YTHDF2, which resulted in mRNA degradation and reduction of protein expression, thus alleviating autophagy and adipogenesis. | |||
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [68] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse hippocampus | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mice hippocampus
Control: Wild type hippocampus
|
GSE94098 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.17E-01 p-value: 3.60E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Atorvastatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM1) and ICAM-1, downregulated those of KLF2 and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.67E-01 p-value: 5.83E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HT-1197 | Recurrent bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1291 |
| HT-1376 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1292 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/cnu/nu mice (4-5 weeks old) were used for the xenograft experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 6 for each group) and injected with 5 × 106 HT-1197 cells in control group or FTO plasmid group, respectively. | |||
| Response Summary | In bladder cancer, the changes in m6A methylation level mainly appeared at 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) of Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) and NOTCH1 transcripts, and at 3' UTR of CSNK2A2 and ITGA6 transcripts, responding to the overexpression of FTO. SFPQ could influence the FTO-mediated m6A RNA demethylation, eventually affecting the gene expression. | |||
Kidney failure [ICD-11: GB6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [66] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kidney failure [ICD-11: GB6Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
NIT-1 | Insulin tumor | Mus musculus | CVCL_3561 |
| Response Summary | m6A modification is co-regulated by METTL3 and FTO in cadmium-treated cells. Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1), LncRNA-PVT1 and m6A modification could be key nodes for cadmium-induced oxidative damage, and highlight their importance as promising preventive and therapeutic targets in cadmium toxicity. | |||
Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line was transfected with LV2-1 or LV2-NC. Thereafter, BALB/c nude mice (6-week old) were intraperitoneally injected with SKOV3 cells. The mice were killed after 5 weeks, and the number of ascites was determined. | |||
| Response Summary | CircRAB11FIP1 promoted autophagy flux of ovarian cancer through DSC1 and miR-129. CircRAB11FIP1 can serve as the possible marker for EOC diagnosis and treatment. CircRAB11FIP1 regulated the mechanism of autophagy through m6A modification and direct binding to mRNA. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to the mRNA of FTO and promoted its expression. CircRAB11FIP1 directly bound to miR-129 and regulated its targets ATG7 and ATG14. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to desmocollin 1to facilitate its interaction with ATG101. CircRAB11FIP1 mediated mRNA expression levels of Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5) and ATG7 depending on m6A. | |||
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Dac51 | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [64] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Autophagy | |||
| Adipogenesis regulation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Pig primary preadipocytes (Isolated from cervical subcutaneous adipose tissue of piglets) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Mice were maintained at 22 ± 2 ℃ with a humidity of 35 ± 5% under a 12 h light and 12 h dark cycle, with free access to water and food. For the HFD experiment, female control (Ftoflox/flox) and adipose-selective fto knockout (Fabp4-Cre Ftoflox/flox, fto-AKO) mice were fed with high-fat diet (60% fat in calories; Research Diets, D12492) for the desired periods of time, and food intake and body weight were measured every week after weaning (at 3 weeks of age). | |||
| Response Summary | Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5) and Atg7 were the targets of YTHDF2 (YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2). Upon FTO silencing, Atg5 and Atg7 transcripts with higher m6A levels were captured by YTHDF2, which resulted in mRNA degradation and reduction of protein expression, thus alleviating autophagy and adipogenesis. | |||
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [68] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
Autophagy-related protein 101 (ATG101)
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line was transfected with LV2-1 or LV2-NC. Thereafter, BALB/c nude mice (6-week old) were intraperitoneally injected with SKOV3 cells. The mice were killed after 5 weeks, and the number of ascites was determined. | |||
| Response Summary | CircRAB11FIP1 promoted autophagy flux of ovarian cancer through DSC1 and miR-129. CircRAB11FIP1 can serve as the possible marker for EOC diagnosis and treatment. CircRAB11FIP1 regulated the mechanism of autophagy through m6A modification and direct binding to mRNA. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to the mRNA of FTO and promoted its expression. CircRAB11FIP1 directly bound to miR-129 and regulated its targets ATG7 and ATG14. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to desmocollin 1to facilitate its interaction with Autophagy-related protein 101 (ATG101). CircRAB11FIP1 mediated mRNA expression levels of ATG5 and ATG7 depending on m6A. | |||
Beclin 1-associated autophagy-related key regulator (ATG14)
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line was transfected with LV2-1 or LV2-NC. Thereafter, BALB/c nude mice (6-week old) were intraperitoneally injected with SKOV3 cells. The mice were killed after 5 weeks, and the number of ascites was determined. | |||
| Response Summary | CircRAB11FIP1 promoted autophagy flux of ovarian cancer through DSC1 and miR-129. CircRAB11FIP1 can serve as the possible marker for EOC diagnosis and treatment. CircRAB11FIP1 regulated the mechanism of autophagy through m6A modification and direct binding to mRNA. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to the mRNA of FTO and promoted its expression. CircRAB11FIP1 directly bound to miR-129 and regulated its targets ATG7 and Beclin 1-associated autophagy-related key regulator (ATG14). CircRAB11FIP1 bound to desmocollin 1to facilitate its interaction with ATG101. CircRAB11FIP1 mediated mRNA expression levels of ATG5 and ATG7 depending on m6A. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [70] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Li-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3840 | |
| SNU-182 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0090 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Li-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3840 | |
| SNU-182 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0090 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| THLE-2 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3803 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous tumor models, 1.5 × 106 HUH7 cells (e.g., negative control, AC115619-overexpressing cells) in 50 μL PBS with 50 μL Matrigel were administered to male BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks of age) by subcutaneous injection and cell line-derived xenografts (CDX) were established.For lung metastasis models, luciferase-tagged lentivirus transfected into HUH7 cells (1 × 106/100 μL PBS) was injected into male BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks of age) via tail vein. | |||
Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HT-1197 | Recurrent bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1291 |
| HT-1376 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1292 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/cnu/nu mice (4-5 weeks old) were used for the xenograft experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 6 for each group) and injected with 5 × 106 HT-1197 cells in control group or FTO plasmid group, respectively. | |||
| Response Summary | In bladder cancer, the changes in m6A methylation level mainly appeared at 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) of MALAT1 and NOTCH1 transcripts, and at 3' UTR of Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2) and ITGA6 transcripts, responding to the overexpression of FTO. SFPQ could influence the FTO-mediated m6A RNA demethylation, eventually affecting the gene expression. | |||
Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [71] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Adherens junction | hsa04520 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and migration | |||
In-vitro Model |
CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 |
| FaDu | Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1218 | |
| Tu 686 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4916 | |
| HN-6 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8129 | |
| HEp-2 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1906 | |
| Response Summary | FTO expression was significantly upregulated in HNSCC datasets and tissues. FTO expression was significantly correlated with Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin) expression. Moreover, it exerted a tumorigenic effect by increasing CTNNB1 expression in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia [ICD-11: 2E66]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [72] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2E66.2] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| In-vivo Model | Either SiHa cells or FTO overexpressed SiHa cells were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of 4- to 6-week-old female athymic nude mice (CAS, Beijing, China). The mice were divided into four groups (N = 6). After transplantation, tumor size was measured by caliper every other day. Tumor volume was calculated using the formula: volume = (length × width2)/2. When the tumor volumes reached 50 mm3, the animals were treated with intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every other day for seven times and local irradiation of 8 Gy one time. | |||
| Response Summary | The mRNA level of FTO is elevated in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) tissues when compared with respective adjacent normal tissues.FTO enhances the chemo-radiotherapy resistance both in vitro and in vivo through regulating expression of Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin) by reducing m6A levels in its mRNA transcripts and in turn increases excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1) activity. | |||
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53)
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [73] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Erianin | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Acute kidney failure [ICD-11: GB60]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure [ICD-11: GB60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
| In-vivo Model | Induced AKI in c57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal cisplatin injection and treated the animal with vehicle or an FTO inhibitor meclofenamic acid (MA) for 3 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Meclofenamic acid increased Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) mRNA and protein levels in AKI both in vitro and in vivo, and FTO overexpression reduced p53 expression and reversed the MA-induced p53 increase in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury Acute kidney injury. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure [ICD-11: GB60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
| In-vivo Model | Induced AKI in c57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal cisplatin injection and treated the animal with vehicle or an FTO inhibitor meclofenamic acid (MA) for 3 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Meclofenamic acid increased Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) mRNA and protein levels in AKI both in vitro and in vivo, and FTO overexpression reduced p53 expression and reversed the MA-induced p53 increase in cisplatin-induced Acute kidney injury. | |||
Chloride intracellular channel protein 4 (CLIC4)
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [75] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
RWPE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3791 |
| PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 | |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| LNCaP C4-2 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4782 | |
| In-vivo Model | Approximately 2×106 PCa cells (DU145 transfected with shFTO and shNC) were injected subcutaneously in mice. The tumor volume (V = (0.5*length*width2)) was measured with Vernier caliper every week. Ten mice were randomly divided into two groups, 2×106 cells transfected with shFTO and shNC were resuspended with 100 uL PBS and injected into the mouse tail vein to create a metastatic model. After 7 weeks, the mice were anesthetized, and D-luciferin (#D-Luciferin, Apexbio) was injected intraperitoneally, then used the IVIS imaging system (Caliper Life Sciences) to visualize the luciferase signal. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO suppresses PCa proliferation and metastasis through reducing the degradation of Chloride intracellular channel protein 4 (CLIC4) mRNA in an m6A dependent manner. | |||
Constitutive NOS (eNOS)
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Atorvastatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, downregulated those of KLF2 and Constitutive NOS (eNOS), and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [78] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | Approximately 1 × 107 stably transfected T24 cells were subcutaneously injected into BALB/c nude mice. The length (L) and width (W) of the tumours were measured weekly using callipers, while their volume was calculated using the equation: V = (L × W2)/2. After 4 weeks of injections, the mice were euthanised, and the tumour tissues were removed and weighed. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO promoted bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via the FTO/miR-576/Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) pathways in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
Cytochrome P450 2C8 (CYP2C8)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [79] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | hsa00982 | ||
| Cell Process | Drug-metabolizing | |||
In-vitro Model |
HepaRG | Hepatitis C infection | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9720 |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| Response Summary | In the Hepatocellular carcinoma cells YTHDC2 promotes CYP2C8 mRNA degradation via recognizing the m6A in CYP2C8 mRNA, which is installed by METTL3/14 and removed by FTO. | |||
Desmocollin-1 (DSC1)
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line was transfected with LV2-1 or LV2-NC. Thereafter, BALB/c nude mice (6-week old) were intraperitoneally injected with SKOV3 cells. The mice were killed after 5 weeks, and the number of ascites was determined. | |||
| Response Summary | CircRAB11FIP1 promoted autophagy flux of ovarian cancer through Desmocollin-1 (DSC1) and miR-129. CircRAB11FIP1 can serve as the possible marker for EOC diagnosis and treatment. CircRAB11FIP1 regulated the mechanism of autophagy through m6A modification and direct binding to mRNA. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to the mRNA of FTO and promoted its expression. CircRAB11FIP1 directly bound to miR-129 and regulated its targets ATG7 and ATG14. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to desmocollin 1to facilitate its interaction with ATG101. CircRAB11FIP1 mediated mRNA expression levels of ATG5 and ATG7 depending on m6A. | |||
DNA excision repair protein ERCC-1 (ERCC1)
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia [ICD-11: 2E66]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [72] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2E66.2] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| In-vivo Model | Either SiHa cells or FTO overexpressed SiHa cells were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of 4- to 6-week-old female athymic nude mice (CAS, Beijing, China). The mice were divided into four groups (N = 6). After transplantation, tumor size was measured by caliper every other day. Tumor volume was calculated using the formula: volume = (length × width2)/2. When the tumor volumes reached 50 mm3, the animals were treated with intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every other day for seven times and local irradiation of 8 Gy one time. | |||
| Response Summary | The mRNA level of FTO is elevated in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) tissues when compared with respective adjacent normal tissues.FTO enhances the chemo-radiotherapy resistance both in vitro and in vivo through regulating expression of beta-catenin by reducing m6A levels in its mRNA transcripts and in turn increases DNA excision repair protein ERCC-1 (ERCC1) activity. | |||
DNA polymerase kappa (Pol Kappa/POLK)
Exposure to radiation [ICD-11: PH73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [80] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Exposure to radiation [ICD-11: PH73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | DNA repair | |||
| Nucleotide excision repair (hsa03420) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
A-375 | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0132 |
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 | |
| Response Summary | Methylation at the 6 position of adenosine (m6A) in RNA is rapidly (within 2 min) and transiently induced at DNA damage sites in response to ultraviolet irradiation. This modification occurs on numerous poly(A)+ transcripts and is regulated by the methyltransferase METTL3 and the demethylase FTO. DNA DNA polymerase kappa (Pol Kappa/POLK), which has been implicated in both nucleotide excision repair and trans-lesion synthesis, required the catalytic activity of METTL3 for immediate localization to ultraviolet-induced DNA damage sites. | |||
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4-like (NEDD4L)
Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Transport and catabolism | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | As cells (5 million) in Matrigel or As-T (1 million) cells in PBS with or without gene manipulations were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of female mice (6-8 weeks of age). For treatment with CS1 or CS2, As-T cells (1 million) in PBS were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of 6-week-old female nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO deletion inhibited arsenic-induced tumorigenesis. Epidermis-specific FTO deletion prevented skin tumorigenesis induced by arsenic and UVB irradiation. E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4-like (NEDD4L) was identified as the m6A-modified gene target of FTO. Arsenic stabilizes FTO protein through inhibiting p62-mediated selective autophagy. FTO-mediated dysregulation of mRNA m6A methylation as an epitranscriptomic mechanism to promote arsenic tumorigenicity. Arsenic suppresses p62 expression by downregulating the NF-kappaB pathway to upregulate FTO. | |||
Human skin lesions [ICD-11: ME60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Human skin lesions [ICD-11: ME60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Transport and catabolism | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | As cells (5 million) in Matrigel or As-T (1 million) cells in PBS with or without gene manipulations were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of female mice (6-8 weeks of age). For treatment with CS1 or CS2, As-T cells (1 million) in PBS were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of 6-week-old female nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO deletion inhibited arsenic-induced tumorigenesis. Epidermis-specific FTO deletion prevented skin tumorigenesis induced by arsenic and UVB irradiation. E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4-like (NEDD4L) was identified as the m6A-modified gene target of FTO. Arsenic stabilizes FTO protein through inhibiting p62-mediated selective autophagy. FTO-mediated dysregulation of mRNA m6A methylation as an epitranscriptomic mechanism to promote arsenic tumorigenicity. Arsenic suppresses p62 expression by downregulating the NF-kappaB pathway to upregulate FTO. | |||
Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 11 (HSD17B11)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [81] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 |
| KYSE-510 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1354 | |
| In-vivo Model | Nude mice were randomly divided into five groups of six mice each, and the mice in each group were received subcutaneous injections of shFTO, scrambled shNC, FTO OE, and vector KYSE510 cells (5×106 tumor cells/mouse), respectively. The tumor size and weight of mice were measured 1 week later, which was recorded as day 0, and then measured once every other day; and the tumor volumes were calculated using the following formula: (length×width2)/2.When the tumor maximum diameter was close to 15 mm, the mice were euthanized and the tumor tissues were collected for immunohistochemistry analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO relys on the reading protein YTHDF1 to affect the translation pathway of the Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 11 (HSD17B11) gene to regulate the formation of lipid droplets in esophageal cancer cells. | |||
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [82] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
Fatty acid synthase (FASN)
Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [83] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Deficiency of lipid accumulation | |||
| Cellular apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Response Summary | FTO regulates hepatic lipogenesis via FTO-dependent m6A demethylation in Fatty acid synthase (FASN) mRNA and indicate the critical role of FTO-mediated lipid metabolism in the survival of HepG2 cells. This study provides novel insights into a unique RNA epigenetic mechanism by which FTO mediates hepatic lipid accumulation through m6 A modification and indicates that FTO could be a potential target for obesity-related diseases and cancer. | |||
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Pathway Response | Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | ||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Response Summary | Glucose Is Involved in the Dynamic Regulation of m6A in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.high-glucose stimulation enhances FTO expression, which leads to decreased m6A, and the lower m6A induces methyltransferase upregulation; FTO then triggers the mRNA expression of FOXO1, Fatty acid synthase (FASN), G6PC, and DGAT2, and these four genes were correlated with glucose and lipid metabolism. | |||
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [83] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Deficiency of lipid accumulation | |||
| Cellular apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Response Summary | FTO regulates hepatic lipogenesis via FTO-dependent m6A demethylation in Fatty acid synthase (FASN) mRNA and indicate the critical role of FTO-mediated lipid metabolism in the survival of HepG2 cells. This study provides novel insights into a unique RNA epigenetic mechanism by which FTO mediates hepatic lipid accumulation through m6 A modification and indicates that FTO could be a potential target for obesity-related diseases and cancer. | |||
Flotillin-2 (FLOT2)
Ovarian dysfunction [ICD-11: 5A80]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [84] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Polycystic ovary syndrome [ICD-11: 5A80.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
KGN | Ovarian granulosa cell tumor | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0375 |
| Response Summary | FTO induced the dysfunctions of GCs by upregulating Flotillin-2 (FLOT2), suggesting that FTO/FLOT2 plays a role in the pathophysiology of polycystic ovarian syndrome. | |||
Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1)
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Response Summary | Glucose Is Involved in the Dynamic Regulation of m6A in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. High-glucose stimulation enhances FTO expression, which leads to decreased m6A, and the lower m6A induces methyltransferase upregulation; FTO then triggers the mRNA expression of Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1), FASN, G6PC, and DGAT2, and these four genes were correlated with glucose and lipid metabolism. | |||
Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [85] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cytarabine | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| In-vivo Model | Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Vst/Vst (NPG) mice (6 weeks old) were divided into three groups and implanted with 4 × 106 cells of control (MV4-11 NC) or FTO-knockdown (MV4-11 KD-1 or KD-2) by tail vein injection, respectively. | |||
Glioblastoma multiforme [ICD-11: XH0MB1]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [86] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma multiforme [ICD-11: XH0MB1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [88] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Male BALB/c nude mice (aged 4-6 weeks; n = 5/group) were obtained from Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). MHCC97H or Huh7 cells (2 × 106 cells/mouse) stably transfected with lentivirus containing different plasmids in 100 μL DMEM were subcutaneously or orthotopically implanted into the nude mice. | |||
Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 1 (G6PC/G6PC1)
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Pathway Response | Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Response Summary | Glucose Is Involved in the Dynamic Regulation of m6A in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.high-glucose stimulation enhances FTO expression, which leads to decreased m6A, and the lower m6A induces methyltransferase upregulation; FTO then triggers the mRNA expression of FOXO1, FASN, Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 1 (G6PC/G6PC1), and DGAT2, and these four genes were correlated with glucose and lipid metabolism. | |||
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||
In-vitro Model |
LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | For CDX model, nude mice (female, 4-6-week-old) were subcutaneously injected with 5 × 106 HCT116 cells on the both flank. For PDX model, the patient tumors were divided into small pieces and then inoculated on both flank of nude mice. For knockdown FTO mice model, FTO mice model, two weeks after inoculation, the shFTO#3 lenti-virus injected into the tumor for three consecutive days. For combined medication mice model, intraperitoneal injection of Rhein and Olaparib was started one week after inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | Targeting FTO significantly suppresses cancer cell growth and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity, which not only mediating the balance of intracellular ROS by regulating Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) expression, but also maintaining genome instability by regulating PARP1 expression. These findings shed light on new molecular mechanisms of CRC development and treatments mediated by m6A modification. | |||
Hexokinase-2 (HK2)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [90] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the mouse xenograft model, 2 × 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank regions of female BALB/c nude mice (4-5 weeks). | |||
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (G9a)
Pain disorders [ICD-11: 8E43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [91] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuropathic Pain [ICD-11: 8E43.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PC12 | Rat adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
| In-vivo Model | After the animal was anesthetized with isoflurane, a midline incision in the lower lumbar back region was made and the lumbar articular process was exposed and then removed. The exposed DRG was injected with viral solution (1-1.5 ul in rats and 0.5-1 ul in mice) through a glass micropipette connected to a Hamilton syringe. The pipette was retained for 10 min after injection. Animals showing signs of paresis or other abnormalities were excluded. The injected DRGs were stained with hematoxylin/eosin to examine the integrity of their structure and whether they contained visible leukocytes. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO contributes to neuropathic pain through stabilizing nerve injury-induced upregulation of Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (G9a), a neuropathic pain initiator, in primary sensory neurons. | |||
Homeobox protein Hox-B13 (HOXB13)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [92] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
SNU-5 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0078 |
| NCI-N87 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1603 | |
| MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male nu/nu mice between 4 and 6 weeks of age received subcutaneous injections of equivalent AGS cells expressing either control or LV-HOXB13 within 30 min of harvesting on the right and left flanks. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO suppresses Homeobox protein Hox-B13 (HOXB13) methytlation; FTO and HOXB13 expression promotes GC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. HOXB13 expression intensifies GC invasion through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling via IGF-1R. | |||
Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [93] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
KLE | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1329 |
| AN3-CA | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0028 | |
| In-vivo Model | Female SCID-Beige mice (6 weeks old) were purchased from Vitalriver. AN3CA cells with FTO overexpression or silencing or the appropriate controls (1 × 106) were injected into the lower abdominal cavity of mice (n = 5 mice/group). After 4 weeks, the mice were sacrificed, and tumours were harvested, weighed and photographed. | |||
| Response Summary | This study found high expression of FTO in metastatic endometrial cancer and that this action promote both metastasis and invasion in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, FTO can catalyse demethylation modification in 3'UTR region of Homeobox protein Hox-B13 (HOXB13) mRNA, thereby abolishing m6A modification recognition with the YTHDF2 protein. | |||
Interleukin enhancer-binding factor 3 (ILF3)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [94] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
GBM1 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG57 |
| GBM2 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG58 | |
| GBM3 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG59 | |
| Response Summary | Loss of m6A RNA methylation and increased translation in human glioblastoma cells as well as a role for miRNAs in the modulation of m6A RNA demethylation in genes that are most efficiently translated during glioma stem cells differentiation. Ectopic expression of the RRACH-binding miR-145 induces loss of m6A, formation of FTO/AGO1/Interleukin enhancer-binding factor 3 (ILF3)/miR-145 complexes on a clinically relevant tumor suppressor gene (CLIP3) and significant increase in its nascent translation. | |||
Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic (IDH/IDH1)
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [95] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Response Summary | 1) Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic (IDH/IDH1) mutant cells, likely via a D2-HG-mediated competitive inhibition of the Alpha-KG-dependent RNA demethylase FTO, display significantly elevated RNA methylation; 2) Deregulated RNA methylation should be considered part of the pathogenesis of IDH-mutant tumors, which alongside with the well-characterized DNA and histone disturbances defines a "hypermethylation triad"; 3) the effects of FTO expression on AML pathogenesis need to be interpreted in the context of IDH1/2 mutation since in this setting FTO activity is probably low, irrespective of its expression level. | |||
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Fluorouracil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Paclitaxel | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Human breast ductal carcinoma in situ [ICD-11: 2E65]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [96] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Human breast ductal carcinoma in situ [ICD-11: 2E65.2] | |||
Metastasis-associated protein MTA1 (MTA1)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [97] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mRNA surveillance pathway | hsa03015 | ||
| RNA degradation | hsa03018 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 | |
| LS174T | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1384 | |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| HCT 15 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0292 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| CW-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1151 | |
| In-vivo Model | FTO-overexpressing and control cells (2 × 106 suspended in 100 ul PBS) were subcutaneously injected into each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO inhibited CRC metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. FTO exerted a tumor suppressive role by inhibiting Metastasis-associated protein MTA1 (MTA1) expression in an m6A-dependent manner. Methylated MTA1 transcripts were recognized by an m6A "reader", insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2), which then stabilized its mRNA. | |||
Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN)
Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage [ICD-11: 8B24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [98] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage [ICD-11: 8B24] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
Epilepsy due to structural or metabolic conditions or diseases [ICD-11: 8A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [105] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Epilepsy due to structural or metabolic conditions or diseases [ICD-11: 8A60.5] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [106] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 |
| In-vivo Model | Cerebral I/R injury was induced by MCAO/R surgery following previous method [10]. Rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 2% sodium pentobarbital. After cutting the cervical skin of the rats with surgical scissors, the internal, external and common carotid arteries were separated. Then the proximal ends of the external and the common carotid arteries were ligated and the distal internal carotid artery was clipped. After cutting an incision 1 cm away from the bifurcation of the internal carotid artery with a surgical scissors, the left common carotid artery was slowly inserted into the internal carotid artery of the rats with sutures coated with silicone (head diameter 0.36±0.02 mm, Beijing Sunbio Biotech Co., Ltd., China) until sutures reached the bifurcation of the middle cerebral artery, and the wound was sutured after the sutures were fixed. After blocking blood flow for 1 h, the plug was removed to restore blood flow and reperfusion was performed. Other rats were selected for the Sham group, and the operation procedure was the same as above except for no ligation and insertion. | |||
DOX-induced cardiotoxicity [ICD-11: BA00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [108] | |||
| Responsed Disease | DOX-induced cardiotoxicity [ICD-11: BA00.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
H9c2(2-1) | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0286 |
Reproductive System disorders [ICD-11: SM9Z-SN0Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [109] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Reproductive System disorders [ICD-11: SM9Z-SN0Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
Male reproductive disorders [ICD-11: VV5Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [110] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male reproductive disorders [ICD-11: VV5Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Oxidative stress | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Exposed Sprague-Dawley rats to 0, 250, and 500 mg DEHP per kg body weight per day at the prepuberty stage from postnatal day 22 (PND 22) to PND 35 by oral gavage. | |||
| Response Summary | DEHP worsened testicular histology, decreased testosterone concentrations, downregulated expression of spermatogenesis inducers, enhanced oxidative stress, inhibited the Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)-mediated antioxidant pathway, and increased apoptosis in testes. DEHP is a common environmental endocrine disrupting chemical that induces male reproductive disorders. Additionally, DEHP increased global levels of m6A RNA modification and altered the expression of two important RNA methylation modulator genes, FTO and YTHDC2. | |||
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha/PPARA)
Urinary/pelvic organs injury [ICD-11: NB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [111] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury [ICD-11: NB92.0Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||
In-vitro Model |
LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | For CDX model, nude mice (female, 4-6-week-old) were subcutaneously injected with 5 × 106 HCT116 cells on the both flank. For PDX model, the patient tumors were divided into small pieces and then inoculated on both flank of nude mice. For knockdown FTO mice model, FTO mice model, two weeks after inoculation, the shFTO#3 lenti-virus injected into the tumor for three consecutive days. For combined medication mice model, intraperitoneal injection of Rhein and Olaparib was started one week after inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | Targeting FTO significantly suppresses cancer cell growth and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity, which not only mediating the balance of intracellular ROS by regulating G6PD expression, but also maintaining genome instability by regulating Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) expression. These findings shed light on new molecular mechanisms of CRC development and treatments mediated by m6A modification. | |||
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)
Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
In-vitro Model |
B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) (PDCD1), CXCR4, and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
Protein argonaute-1 (AGO1)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [94] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
GBM1 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG57 |
| GBM2 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG58 | |
| GBM3 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG59 | |
| Response Summary | Loss of m6A RNA methylation and increased translation in human glioblastoma cells as well as a role for miRNAs in the modulation of m6A RNA demethylation in genes that are most efficiently translated during glioma stem cells differentiation. Ectopic expression of the RRACH-binding miR-145 induces loss of m6A, formation of FTO/Protein argonaute-1 (AGO1)/ILF3/miR-145 complexes on a clinically relevant tumor suppressor gene (CLIP3) and significant increase in its nascent translation. | |||
Protein CBFA2T1 (RUNX1T1)
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [112] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Spliceosome (hsa03040) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | FTO-dependent m6A demethylation functions as a novel regulatory mechanism of RNA processing and plays a critical role in the regulation of adipogenesis and obesity. FTO-dependent regulatory role of m6A and SRSF2 in mRNA splicing and adipocyte differentiation. FTO controls exonic splicing of adipogenic regulatory factor Protein CBFA2T1 (RUNX1T1) by regulating m6A levels around splice sites and thereby modulates differentiation. | |||
Protein kinase C-binding protein NELL2 (NELL2)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [113] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell viability | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 |
| NCI-H23 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1547 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| 16HBE14o- | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0112 | |
| In-vivo Model | The nude mice were maintained under pathogen-free conditions and kept under timed lighting conditions mandated by the committee with food and water provided ad libitum. For xenograft experiments, nude mice were injected subcutaneously with 5 × 106 cells resuspended in 0.1 mL PBS. When a tumor was palpable, it was measured every 3 days. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO upregulated the expression of E2F1 by inhibiting the m6A modification of E2F1. The FTO/E2F1/Protein kinase C-binding protein NELL2 (NELL2) axis modulated NSCLC cell viability, migration, and invasion in vitro as well as affected NSCLC tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. | |||
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [114] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
KYSE-450 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1353 |
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| KYSE-180 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1349 | |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| KYSE-140 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1347 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous transplantation model, sh-control, sh-FTO, NC-OE and ERBB2-OE KYSE150 stable cells (6 × 106 per mouse, n = 3 for each group) were diluted to 100 uL PBS + 100 uL Matrigel (BD) and subcutaneously injected to two points in the middle and upper groin of immunodeficient mice to study tumor growth. When the tumor volume reached ~ 1000 mm3 in each group, the nude mice were killed, and the tumors were excised and weighed for histology and further study. The tumor volume was calculated by the formula V = 1/2 × large diameter × (small diameter)2. For a model of lung metastasis in vivo, nude mice were injected with 100 uL WT (wide type), sh-FTO, ERBB2-OE and sh-FTO+ERBB2-OE KYSE150 stable cells (1 × 106 cells per mouse, n = 3 for each group) through tail vein, respectively. Six weeks after injection, the mice were killed and analyzed for metastatic lung tumors. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of FTO drastically suppressed the proliferation, migration, and invasion of ESCC cells,and Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) is the target of FTO, which acts in concert in ESCC tumorigenesis and metastasis. | |||
Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA)
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tretinoin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| RNA degradation (hsa03018) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| Mono-Mac-6 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1426 | |
| Response Summary | FTO enhances leukemic oncogene-mediated cell transformation and leukemogenesis, and inhibits all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced AML cell differentiation, through regulating expression of targets such as ASB2 and Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) by reducing m6A levels in these mRNA transcripts. | |||
RNA cytosine C(5)-methyltransferase NSUN2 (NSUN2)
Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [115] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||
Serine-protein kinase ATM (ATM)
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [118] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MN9D
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_M067 |
| In-vivo Model | Male C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally injected with MPTP hydrochloride (30 mg/kg/day, Sigma, USA) for 5 consecutive days. Control mice were injected with equal volume of 0.9% saline. 3 days after the last injection of MPTP, behavioral tests were performed. | |||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 6 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Chloroquine | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 5 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | CB-839 | Phase 2 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Experiment 6 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | GLS-IN-968 | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [119] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Doxil | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| Response Summary | Decreased doxorubicin resistance by Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) knockdown was abolished by FTO overexpression and decreased doxorubicin sensitivity by STAT3 overexpression was reversed by FTO knockdown, indicating that FTO was implicated in STAT3-mediated doxorubicin resistance and impairment of doxorubicin sensitivity of BC cells. | |||
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [120] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
Splicing factor, proline- and glutamine-rich (SFPQ)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HT-1197 | Recurrent bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1291 |
| HT-1376 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1292 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/cnu/nu mice (4-5 weeks old) were used for the xenograft experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 6 for each group) and injected with 5 × 106 HT-1197 cells in control group or FTO plasmid group, respectively. | |||
| Response Summary | In bladder cancer, the changes in m6A methylation level mainly appeared at 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) of MALAT1 and NOTCH1 transcripts, and at 3' UTR of CSNK2A2 and ITGA6 transcripts, responding to the overexpression of FTO. Splicing factor, proline- and glutamine-rich (SFPQ) could influence the FTO-mediated m6A RNA demethylation, eventually affecting the gene expression. | |||
SRSF protein kinase 2 (SRPK2)
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [112] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Spliceosome | hsa03040 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | FTO-dependent m6A demethylation functions as a novel regulatory mechanism of RNA processing and plays a critical role in the regulation of adipogenesis and obesity. FTO-dependent regulatory role of m6A and SRSF protein kinase 2 (SRPK2) in mRNA splicing and adipocyte differentiation. FTO controls exonic splicing of adipogenic regulatory factor RUNX1T1 by regulating m6A levels around splice sites and thereby modulates differentiation. | |||
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1)
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [122] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| hMC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9Q61 | |
| HK-2 [Human kidney] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| In-vivo Model | FTO over-expression db/db mice were generated through injecting the tail vein with Fto-overexpression lentivirus at 12 weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | Mechanistically, the FTO/Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1)/JAK-STAT axis promotes diabetic kidney disease(DKD) pathogenesis via promoting inflammation. Moreover, FTO expression is significantly decreased in DKD, and overexpression of FTO can dramatically alleviate kidney inflammation. | |||
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [70] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Li-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3840 | |
| SNU-182 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0090 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Li-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3840 | |
| SNU-182 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0090 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| THLE-2 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3803 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous tumor models, 1.5 × 106 HUH7 cells (e.g., negative control, AC115619-overexpressing cells) in 50 μL PBS with 50 μL Matrigel were administered to male BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks of age) by subcutaneous injection and cell line-derived xenografts (CDX) were established.For lung metastasis models, luciferase-tagged lentivirus transfected into HUH7 cells (1 × 106/100 μL PBS) was injected into male BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks of age) via tail vein. | |||
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3)
Ossification of spinal ligaments [ICD-11: FA83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [123] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ossification of spinal ligaments [ICD-11: FA83] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Transcription factor E2F1 (E2F1)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [37] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, Transcription factor E2F1 (E2F1) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [38] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and migration | |||
In-vitro Model |
HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| Response Summary | FTO interacts with transcripts of Transcription factor E2F1 (E2F1) and Myc, inhibition of FTO significantly impairs the translation efficiency of E2F1 and Myc.FTO plays important oncogenic role in regulating cervical cancer cells' proliferation. | |||
Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC)
Vascular disorders of the liver [ICD-11: DB98]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [124] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular disorders of the liver [ICD-11: DB98.B] | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 (USP7)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [125] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | P22077 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H522 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1567 | |
| HSAEC (Human small airway epithelial cells) | ||||
| RERF-LC-A1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4402 | |
| NCI-H1882 | Lung small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1504 | |
| NCl-H466 (Human lung cancer cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Equal numbers of A549 cells expressing either control or shFTO were injected subcutaneously, within 30 min of harvesting, over the right and left flanks in male nu/nu mice between 4 and 6 weeks of age. | |||
| Response Summary | The m6A demethylase FTO promotes the growth of Non-small cell lung cancer cells by increasing the expression of USP7.Genetic knockdown or pharmacological inhibition (P5091 or P22027) of Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 (USP7) reduced the proliferation rate of lung cancer cells and decreased the capacity of colony formation of lung cancer cells in vitro, whereas lung cancer cells growth inhibition by FTO knockdown is restored by overexertion of USP7. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [125] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | P5091 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H522 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1567 | |
| HSAEC (Human small airway epithelial cells) | ||||
| RERF-LC-A1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4402 | |
| NCI-H1882 | Lung small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1504 | |
| NCl-H466 (Human lung cancer cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Equal numbers of A549 cells expressing either control or shFTO were injected subcutaneously, within 30 min of harvesting, over the right and left flanks in male nu/nu mice between 4 and 6 weeks of age. | |||
| Response Summary | The m6A demethylase FTO promotes the growth of Non-small cell lung cancer cells by increasing the expression of USP7.Genetic knockdown or pharmacological inhibition (P5091 or P22027) of Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 (USP7) reduced the proliferation rate of lung cancer cells and decreased the capacity of colony formation of lung cancer cells in vitro, whereas lung cancer cells growth inhibition by FTO knockdown is restored by overexertion of USP7. | |||
Ubiquitin-like protein ATG12 (ATG12)
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Dac51 | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [126] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 1 × 106 luciferase-labeled tumor cells were injected subcutaneously with SN-exo or Ctr-exo. | |||
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [104] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 | |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| C-4-II | Human papillomavirus-related cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1095 | |
|
HT3
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8FA | |
| In-vivo Model | Four-six-week-old male BALB/c nude mice were supplied by Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Company (Beijing, China) and fed in a specific pathogen-free environment with a temperature of 25°C and a humidity of 60%. 2 × 106 Hela cells stably transfected with pSilencer vector or pSilencer/FTO were inoculated subcutaneously into the flanks of the nude mice. After 7 days, the width and length measurement of tumors was performed every 2 days. Nude mice were killed at 28 days after cell inoculation and then tumor tissues were weighed. | |||
Zinc finger protein SNAI1 (SNAI1)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [127] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| PaTu 8988t | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1847 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| In-vivo Model | Logarithmic phase PDAC cells (4 × 106/100 μl) were infected using lentiviruses possessing constructs. Then, the nude mice (n = 5 per group) were inoculated into the dorsal flank subcutaneously. | |||
Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2/LINC00022)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [16] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Decreased G0/G1 phase | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HET-1A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3702 |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| KYSE-450 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1353 | |
| KYSE-70 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1356 | |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| In-vivo Model | The number of cells inoculated in each mouse was 4 × 106, 1 × 106, 2 × 106 and 1 × 106, respectively. | |||
| Response Summary | The elevated FTO in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma decreased m6A methylation of Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2/LINC00022) transcript, leading to the inhibition of LINC00022 decay via the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [128] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| NCI-H322 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1556 | |
| NCI-H650 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1575 | |
| HCC827 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2063 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H358 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1559 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| NCI-H23 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1547 | |
| In-vivo Model | Animal experiments were approved by the Hainan Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University. Male BALB/c mice (Vital River, Beijing, China) were subcutaneously injected with H322 cells (1 × 106) transfected with ov-NC, ov-FTO, ov-GAS5 or ov-FTO + ov-GAS5 (n = 5/group). Tumor volume was measured every 7 days, and mice were sacrificed and the tumor tissues were removed for weighting and analyzing after 35 days. Also, tumor tissues were prepared into paraffin sections to carry out Ki67 immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining using SP Kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and TUNEL staining using Colorimetric TUNEL Apoptosis Assay Kit (Beyotime) basing on kit instructions. | |||
HOXC13 antisense RNA (HOXC13-AS)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [129] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| C-4-I | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2253 | |
| Ect1/E6E7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3679 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| Response Summary | FTO-stabilized HOXC13 antisense RNA (HOXC13-AS) epigenetically up-regulated FZD6 and activated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling to drive cervical cancer proliferation, invasion, and EMT, suggesting HOXC13-AS as a potential target for cervical cancer treatment. | |||
Maternally expressed 3 (MEG3)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [130] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
Abortion [ICD-11: JA00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [131] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Abortion [ICD-11: JA00.0] | |||
| In-vivo Model | Sexually mature ICR mice, aged at least 10 weeks, were paired as one female and one male per cage to obtain pregnancies. The time of the vaginal plug sighting was denoted as day 0.5 of the pregnancy. The mice were divided into an FTO protein group and control group, with 10 pairs of mice in each group. Starting on day 0.5 of the pregnancy, mice in the FTO protein group were intraperitoneally injected daily with FTO protein (3.5 ng/kg), whereas those in the control group had daily intraperitoneal injections of equal volumes of saline. Female mice were euthanised on day 13.5 of the pregnancy (day 12.5-14.5), and the total numbers of normal and resorbed embryos were determined, along with the rate of embryo resorption. | |||
Myosin heavy chain associated RNA transcript (MHRT)
Congestive heart failure [ICD-11: BD10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [132] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Congestive heart failure [ICD-11: BD10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
Mouse myocardial cell line (Isolated from heart tissue) | |||
| In-vivo Model | The mice were housed under standardized conditions and received normal diet. The mice were randomly divided into 5 groups (n = 6/each group): (1) Control group: normal mice served as control; (2) TAC-HF group: mice were subjected to transverse aortic constriction (TAC) to establish HF mouse model; (3) Sham group: sham-operated mice were subjected the same surgery without the placement of a ligature; (4) Doxorubicin-HF group: mice were intraperitoneally injected with doxorubicin to construct HF mouse model; and (5) PBS: mice were intraperitoneally injected with equal PBS as control. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression inhibits H/R-indcued apoptosis in myocardial cells by regulating m6A modification of Myosin heavy chain associated RNA transcript (MHRT). FTO is a target gene for heart failure treatment. | |||
Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1)
Kidney failure [ICD-11: GB6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [66] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kidney failure [ICD-11: GB6Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
NIT-1 | Insulin tumor | Mus musculus | CVCL_3561 |
| Response Summary | m6A modification is co-regulated by METTL3 and FTO in cadmium-treated cells. LncRNA-MALAT1, Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1) and m6A modification could be key nodes for cadmium-induced oxidative damage, and highlight their importance as promising preventive and therapeutic targets in cadmium toxicity. | |||
microRNA 145 (MIR145)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [94] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
GBM1 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG57 |
| GBM2 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG58 | |
| GBM3 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_DG59 | |
| Response Summary | Loss of m6A RNA methylation and increased translation in human glioblastoma cells as well as a role for miRNAs in the modulation of m6A RNA demethylation in genes that are most efficiently translated during glioma stem cells differentiation. Ectopic expression of the RRACH-binding miR-145 induces loss of m6A, formation of FTO/AGO1/ILF3/microRNA 145 (MIR145) complexes on a clinically relevant tumor suppressor gene (CLIP3) and significant increase in its nascent translation. | |||
microRNA 155 (MIR155)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [133] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Temozolomide | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Previously prepared U87 cells (5 × 106 cells, 60 uL) stably infected with miRNA were injected subcutaneously in the right flank of the mice, whereas control U87 cells infected with empty vector were injected in the left flank. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Temozolomide by Targeting MYC-microRNA 155 (MIR155)/miR-23a Cluster-MXI1 Feedback Circuit in Glioma. | |||
Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury [ICD-11: NA07]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [134] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury [ICD-11: NA07] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
microRNA 23a (MIR23A)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [133] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Temozolomide | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Previously prepared U87 cells (5 × 106 cells, 60 uL) stably infected with miRNA were injected subcutaneously in the right flank of the mice, whereas control U87 cells infected with empty vector were injected in the left flank. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Temozolomide by Targeting MYC-miR-155/microRNA 23a (MIR23A) Cluster-MXI1 Feedback Circuit in Glioma. | |||
microRNA 576 (MIR576)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [78] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | Approximately 1 × 107 stably transfected T24 cells were subcutaneously injected into BALB/c nude mice. The length (L) and width (W) of the tumours were measured weekly using callipers, while their volume was calculated using the equation: V = (L × W2)/2. After 4 weeks of injections, the mice were euthanised, and the tumour tissues were removed and weighed. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO promoted bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via the FTO/microRNA 576 (MIR576)/CDK6 pathways in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
hsa-miR-129-5p
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line was transfected with LV2-1 or LV2-NC. Thereafter, BALB/c nude mice (6-week old) were intraperitoneally injected with SKOV3 cells. The mice were killed after 5 weeks, and the number of ascites was determined. | |||
| Response Summary | CircRAB11FIP1 promoted autophagy flux of ovarian cancer through DSC1 and hsa-miR-129-5p. CircRAB11FIP1 can serve as the possible marker for EOC diagnosis and treatment. CircRAB11FIP1 regulated the mechanism of autophagy through m6A modification and direct binding to mRNA. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to the mRNA of FTO and promoted its expression. CircRAB11FIP1 directly bound to miR-129 and regulated its targets ATG7 and ATG14. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to desmocollin 1to facilitate its interaction with ATG101. CircRAB11FIP1 mediated mRNA expression levels of ATG5 and ATG7 depending on m6A. | |||
hsa-miR-181b-3p
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion and migration | |||
In-vitro Model |
T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 |
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| Response Summary | FTO up-regulated ARL5B by inhibiting hsa-miR-181b-3p. The carcinogenic activity of FTO in promoting the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via the FTO/miR-181b-3p/ARL5B signaling pathway. | |||
hsa-miR-5581-3p
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [135] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell migration | |||
| cell proliferation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Four-week-old male BALB/c nude mice were used for animal experiments. UM-UC3 cells (2×106 cells per mouse) stably overexpressing miR-5581-3p and NC were injected into the mice to establish the subcutaneous implantation model. Tumor size was measured by a caliper every week, and tumor volume was calculated by the formula: V = (width2×length×0.52). As for the tumor metastasis model, UM-UC3 cells (1×106 cells per mouse) were injected into each mouse via the tail vein. The subcutaneous implantation model used 8 nude mice, whereas the tumor metastasis model used 10 nude mice. Assessment of tumor size and observation of metastasis tumors were done via intraperitoneal inoculation with 15mg/mL, XenoLight D-luciferin Potassium Salt (100 uL; PerkinElmer) with the IVIS Spectrum animal imaging Platform (PerkinElmer) in every mouse. Eventually, mice were sacrificed for tumors and metastases. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO proved as an N6-methyladenosine (m6A) demethylase in decreasing m6A modification was confirmed to regulate the migration and proliferation in Bca, overexpressing hsa-miR-5581-3p partially rescued the effects of the overexpressing SMAD3 and FTO in BCa cells. | |||
hsa_circ_0005630 (circ_RAB11FIP1)
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line was transfected with LV2-1 or LV2-NC. Thereafter, BALB/c nude mice (6-week old) were intraperitoneally injected with SKOV3 cells. The mice were killed after 5 weeks, and the number of ascites was determined. | |||
| Response Summary | hsa_circ_0005630 (circRAB11FIP1) promoted autophagy flux of ovarian cancer through DSC1 and miR-129. CircRAB11FIP1 can serve as the possible marker for EOC diagnosis and treatment. CircRAB11FIP1 regulated the mechanism of autophagy through m6A modification and direct binding to mRNA. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to the mRNA of FTO and promoted its expression. CircRAB11FIP1 directly bound to miR-129 and regulated its targets ATG7 and ATG14. CircRAB11FIP1 bound to desmocollin 1to facilitate its interaction with ATG101. CircRAB11FIP1 mediated mRNA expression levels of ATG5 and ATG7 depending on m6A. | |||
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 15 (ADAMTS15)
Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [136] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||
| In-vivo Model | Male Wistar rats were injected at approximately 1.5 cm distal to the base of the tail with emulsion consisting of collagen (2 mg/ml, Chondrex, USA) and complete Freund's adjuvant(CFA) (5 mg/ml, Chondrex, USA) (at the ratio of 1:1) in a volume of 200 μl per rat. 7 days later, a booster immunization was performed by injecting the same concentration of emulsion as the first immunization in a volume of 100 μl per rat. Subsequently, twice intra-articular injection of adenovirus (Control vector or shFTO, 2 × 108 PFU, 50 μl) (Genechem, Shanghai, China) were prescribed to rats at 8 and 15 days after the primary immunization. Arthritis progression was monitored every three days according to the previously described scoring system ranging from 0 to 4 (0, normal; 1, swelling or redness of paw or a single digit; 2, 2 joints involved; 3, 3 joints involved; 4, severe arthritis of the entire paw and digits). The arthritic score was independently calculated in a blinded manner and defined as the average score of hind paws. | |||
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 2 (ADAMTS2)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [137] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
AC008440.5 (AC008)
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [138] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Chondrocytes (Chondrocytes were isolated from human cartilage and cultured) | |||
| Response Summary | FTO-mediated N6-methyladenosine demethylation downregulated AC008440.5 (AC008) transcription, while lower FTO expression led to upregulation of AC008 transcription in OA. | |||
Apoptosis regulatory protein Siva (SIVA1)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [139] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Fluorouracil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| MC-38 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_B288 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the tumor metastasis mouse model, 5-week-old C57BL/6 mice were randomly grouped and injected with 5 × 105 Control or shFTO stable MC38 cells via tail vein. Drug administration was adopted after 48 h. Drug administration (intraperitoneally): DMSO, 5-FU (50 mg/kg every 2 days) or Rhein (10 mg/kg every 2 days). To detect lung metastasis, mice were killed 2 weeks after tumor cell injection. Lung tissues were harvested and fixed with 4% PFA for paraffin-embedded section and lung metastases were detected with Nikon microscopy. For tumor intraperitoneal mouse model, 2 × 106 Dox-shCtrl, Dox-shFTO stable HCT8/5-FU cells were injected into 5-week-old male BALB/C nude mice. Drug administration was adopted after 48 h. Drug administration (intraperitoneally): DMSO, 5-FU (50 mg/kg every 2 days) or FB23-2 (10 mg/kg every 2 days). For tumor intraperitoneal mouse model, 5 × 105 shCtrl, shFTO-1, shFTO-2 stable MC38 cells were injected into 5-week-old C57BL/6 mice. Drug administration was adopted after 48 h. Drug administration (intraperitoneally): DMSO, 5-FU (50 mg/kg every 2 days) or Rhein (10 mg/kg every 2 days). | |||
Autophagy-related protein 9A (ATG9A)
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Dac51 | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor (NTRK2)
Single episode depressive disorder, severe, without psychotic symptoms [ICD-11: 6A70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [140] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Major depressive disorder [ICD-11: 6A70.3] | |||
In-vitro Model |
SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 |
| In-vivo Model | Rats were housed at 23°C and 55% humidity and were given ad libitum food and water. During acclimatization (1 week), rats were placed randomly (3/cage); however, after initial behavioral testing, they were grouped according to their behavioral phenotypes. All experiments were performed under a light cycle (8:00 AM and 10:00 AM). The protocol to induce LH behavior was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Alabama at Birmingham. The animal study also adhered to the international guidelines for the use and care of laboratory animals. | |||
Beta-1 adrenergic receptor (ADRB1)
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [141] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit gamma (PRKACG)
Macular disorders [ICD-11: 9B75]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [142] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Macular disorders [ICD-11: 9B75.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
CAP-Gly domain-containing linker protein 3 (CLIP3)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [94] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell differentiation | |||
Carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (MLXIPL)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [121] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hepa 1-6 | Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse | Mus musculus | CVCL_0327 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | Overexpression of FTO in the liver of 8-week-old mice was achieved by tail vein injection of adenoviral FTO (Ad-FTO) or control adenovirus (Ad-Ctrl) (5 × 107 pfu/g). Two weeks after injection, mice were sacrificed and tissues were collected. HFD-fed mice were also injected with Ad-FTO or Ad-Ctrl (5 × 107 pfu/g). After 3 weeks, mice were sacrificed and tissue samples were collected. | |||
CD40 ligand (CD40L)
Immune-related diseases [ICD-11: 4B4Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [143] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Immune-related diseases [ICD-11: 4B4Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Circ_GPR137B
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [144] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| HuH-6 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4381 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were subcutaneously inoculated with 6 × 107 HepG2 cells stably transfected with pLV-circGPR137B and empty vectors or Sk-hep-1 cells stably transfected with pLV-sh-circGPR137B/sh-NC. HepG2 cells stably transfected with circGPR137B or pcDNA3.1 were cultured in complete medium. When the cells were 70% confluent, the medium was replaced with fresh medium to remove dead and detached cells. Subsequently, 6 × 107 cells were used to inject into mice via the tail vein. Each mouse was injected with 100ul (6× 106 cells). | |||
Circ_SETD2
Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [145] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Pregnant rats were randomly assigned to 5 groups: normal pregnancy (normal) group, PE group, circSETD2 overexpression (PE + oe-circSETD2) group, METTL3 overexpression (PE + oe-METTL3) group, overexpression control (PE + oe-NC) group, joint treatment (PE + oe-METTL3 + si-circSETD2) group, and joint treatment control (PE + oe-METTL3 + si-NC) group, with 6 rats in each group. After continuous injection of L-NAME for 4 days, the rats in the overexpression and overexpression control groups were further injected with 30 μl lentivirus vector oe-circSETD2, oe-METTL3 or oe-NC solution (GenePharma, Shanghai, China) through the tail vein; after continuous injection of L-NAME for 4 days, the rats in the PE + oe-METTL3 + si-circSETD2 group were further injected with 30 μl lentiviral vector oe-circSETD2 and si-circSETD2 (GenePharma) at the virus titer of 5 × 107 PFU/mL. The rats were euthanized on the 16th day of pregnancy. Then, the chorionic trophoblast tissues were isolated from the placenta of pregnant rats and divided into 2 parts, with 1 part for extraction and detection of tissue RNA, and the other part fixed in the buffer containing 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin, and made into 5 μm sections. | |||
Collagen alpha-1 (COL12A1)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [137] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
Collagen alpha-1 (COL1A1)
Keloid [ICD-11: EE60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [146] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Keloid [ICD-11: EE60.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 (CREB1)
Single episode depressive disorder, severe, without psychotic symptoms [ICD-11: 6A70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [140] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Major depressive disorder [ICD-11: 6A70.3] | |||
In-vitro Model |
SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 |
| In-vivo Model | Rats were housed at 23°C and 55% humidity and were given ad libitum food and water. During acclimatization (1 week), rats were placed randomly (3/cage); however, after initial behavioral testing, they were grouped according to their behavioral phenotypes. All experiments were performed under a light cycle (8:00 AM and 10:00 AM). The protocol to induce LH behavior was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Alabama at Birmingham. The animal study also adhered to the international guidelines for the use and care of laboratory animals. | |||
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (CGAS)
Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury [ICD-11: NA07]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [147] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury [ICD-11: NA07] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vivo Model | Briefly, mice were anesthetized, and the right common carotid artery (CCA) and external and internal carotid arteries were surgically exposed through a neck incision. Then, a filament was introduced into the CCA and advanced into the internal carotid artery until the tip reached the origin of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). Occlusion of the right MCA was induced either transiently for 60 min followed by a reperfusion period of different hours. Sham-operated mice received the same experimental surgery without a filament being inserted into the MCA. For experiments, mice were randomly divided into Sham groups (n = 6), MCAO/R-1 day (n = 6), MCAO/R-3 day (n = 6), and MCAO/R-5 day (n = 6). To investigate the effect of m6A modification on the MCAO/R injury in vivo, thirty-six mice were divided into four groups, including Sham group (n = 12), DMSO group (n = 12), Cycloleucine (Cyc) group (n = 6), and S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) group (n = 6). Cyc, a specific inhibitor of S-adenosyl-methionine mediated methylation (50 mM/kg, MedChemExpress), and SAH (50 mg/kg, Selleck), another m6A specific inhibitor which specifically inhibits the METTL3-METTL14 heterodimer complex, or DMSO (as control) were intraperitoneally injected into the mice for consecutive 3 days before MCAO injury. Three days after MCAO/R injury, the mice brains were collected for the following experiments. | |||
Dickkopf-related protein 2 (DKK2)
Cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [148] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Myocardial Fibrosis [ICD-11: BC43.20] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | He AMI model was induced by permanent ligation of the left coronary artery anterior descending with a 7-0 surgical suture as previously described , and then miR-636 antagomir (10 mg/kg; RiboBio) was injected through the tail vein of mice or the nanoparticles with DKK2 plasmids were administered intraperitoneally in a volume of 200 μL into AMI mice. | |||
Dynamin-1-like protein (DRP1)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [149] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Neuro-2a | Mouse neuroblastoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0470 |
| Neuro-2a | Mouse neuroblastoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0470 | |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 (NEDD4)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [150] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gemcitabine | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
Human Pancreatic Nestin-Expressing cells (Human Pancreatic Nestin-Expressing cells) | |||
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| COLO 357 | Pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0221 | |
| In-vivo Model | Female athymic BALB/C nude mice received a subcutaneous injection of 5 × 106 cells into the axilla (4 weeks old, 18-20 g). The tumor volume (V) was calculated each week using the formula V = (W2 L)/2 after measuring the tumor width (W) and length (L). After the injection of cancer cells, for the gemcitabine treatment cohort, mice were injected with gemcitabine (120 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich) intraperitoneally and weekly according to previous studies . | |||
Estrogen receptor (ESR1)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [151] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
F-box only protein 32 (FBXO32)
Certain specified disorders of muscle [ICD-11: FB32]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [152] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Certain specified disorders of muscle [ICD-11: FB32.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | 3-deazidenosine | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [152] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Certain specified disorders of muscle [ICD-11: FB32.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1)
Macular disorders [ICD-11: 9B75]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [153] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Macular disorders [ICD-11: 9B75.04] | |||
Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [154] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Forkhead box protein O6 (FOXO6)
Chronic glomerulonephritis [ICD-11: GB40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [155] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic glomerulonephritis [ICD-11: GB40] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1)
Single episode depressive disorder, severe, without psychotic symptoms [ICD-11: 6A70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [140] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Major depressive disorder [ICD-11: 6A70.3] | |||
In-vitro Model |
SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 |
| In-vivo Model | Rats were housed at 23°C and 55% humidity and were given ad libitum food and water. During acclimatization (1 week), rats were placed randomly (3/cage); however, after initial behavioral testing, they were grouped according to their behavioral phenotypes. All experiments were performed under a light cycle (8:00 AM and 10:00 AM). The protocol to induce LH behavior was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Alabama at Birmingham. The animal study also adhered to the international guidelines for the use and care of laboratory animals. | |||
Glypican-4 (GPC4)
Uveitis [ICD-11: 9A96]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [156] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Uveitis [ICD-11: 9A96] | |||
| Responsed Drug | FB23-2 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HMC3
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_II76 |
GTPase HRas (HRAS)
Soft tissue sarcoma [ICD-11: XH4UM7]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [157] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Soft tissue sarcoma [ICD-11: XH4UM7] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| 769-P | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1050 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| HCC827 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 5637 cells with ectopic expression of dm6ACRISPR systems were injected subcutaneously (1 × 107 cells/inoculum) into the flanks of 5-wk-old nude mice (Shanghai Model Organisms Center). Tumor formation/growth was assessed until the experimental endpoint, and tumor volume was calculated by the formula: (width)2 × length/2. For tail vein injection, 5637 cells with ectopic expression of dm6ACRISPR systems (5 × 106 cells/0.1 mL PBS) were injected into the lateral tail vein of 5-wk-old nude mice. | |||
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1)
Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [158] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Homeobox protein Hox-D1 (HOXD1)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [159] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
FaDu | Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1218 |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| HOK | Normal | Hexagrammos otakii | CVCL_YE19 | |
hsa-miR-383-5p
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [160] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 |
| Capan-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0237 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
hsa-miR-515-5p
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [161] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [162] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8)
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [163] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.3] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Intraflagellar transport protein 80 homolog (IFT80)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [164] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HN4 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_IS30 |
| HN-6 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8129 | |
| WSU-HN30 | Pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5525 | |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| SCC-9 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1685 | |
| SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 | |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| In-vivo Model | To determine whether lnc-H2AFV-1 overexpression could enhance tumorigenicity in vivo, 1 × 106 HN6 cells stably transduced with LV-lnc-H2AFV-1 or LV-NC were subcutaneously injected into the right and left flanks of six mice. | |||
Kremen protein 2 (KREMEN2)
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [165] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 |
| Caov-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0201 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1 × 105 treated cells were subcutaneously injected into mice with normal drinking water. When the volume of subcutaneous tumors was about 150 mm3, the mice were kept with drinking water containing 1 mg/mL of Dox. After 3 weeks, the xenograft tumors were collected and used for follow-up experiments. | |||
Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane protein FLRT3 (FLRT3)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gefitinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1139 (LINC01139)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [167] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HET-1A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3702 | |
Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 (ACSL4)
Vascular disorders of the liver [ICD-11: DB98]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [124] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular disorders of the liver [ICD-11: DB98.B] | |||
Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [168] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF)
Cushing syndrome [ICD-11: 5A70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [169] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cushing syndrome [ICD-11: 5A70.Y] | |||
NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2)
DOX-induced cardiotoxicity [ICD-11: BA00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [170] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Blood Pressure [ICD-11: BA00] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Nicotine | Approved | ||
| In-vivo Model | SCLC cells were collected, and cell suspensions were prepared at a concentration of 1 × 106 cells per 100 μL PBS and injected subcutaneously into nude mice. When the tumour volume reached 60 mm3, mice were randomly divided into control and treatment groups with five mice in each group. The mice in the treatment group were treated regularly, and chemotherapy drugs (CDDP 3 mg/kg and VP16 2 mg/kg) were administered via intraperitoneal injection. | |||
Neurotrophic factor BDNF precursor form (BDNF)
Single episode depressive disorder, severe, without psychotic symptoms [ICD-11: 6A70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [140] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Major depressive disorder [ICD-11: 6A70.3] | |||
In-vitro Model |
SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 |
| In-vivo Model | Rats were housed at 23°C and 55% humidity and were given ad libitum food and water. During acclimatization (1 week), rats were placed randomly (3/cage); however, after initial behavioral testing, they were grouped according to their behavioral phenotypes. All experiments were performed under a light cycle (8:00 AM and 10:00 AM). The protocol to induce LH behavior was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Alabama at Birmingham. The animal study also adhered to the international guidelines for the use and care of laboratory animals. | |||
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT)
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [171] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATC1)
Spinal deformities [ICD-11: FA70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [172] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Spinal deformities [ICD-11: FA70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C2C12 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0188 |
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit gamma (PIK3R3)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [174] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| In-vivo Model | Eight 4-week-old female nude mice were purchased from Gempharmatech Co. Ltd. and were randomly divided into two groups. In order to establish the in vivo lymph node metastasis model, 3 × 106 SiHa-lv-shFTO or SiHa-lv-shcon cells were slowly injected into the foot pads that containing abundant lymph nodes. After feeding for 20 weeks, we euthanized the nude mice. Lymph nodes in the groin area are dissected and embedded in paraffin for hematoxylin-eosin staining. Our animal experiment research was carried out strictly in accordance with the "Guidelines for the Welfare of Experimental Tumor Animals". | |||
Phospholipid phosphatase 3 (PLPP3)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [175] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Polyunsaturated fatty acid lipoxygenase ALOX12 (ALOX12)
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [73] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Erianin | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
pri-miR-10a
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [58] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U-118MG | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0633 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c male nude mice were 4 weeks old. GBM cells with stable overexpression or knockdown of FTO and ovNC or shNC were transduced with lentivirus expressing luciferase. The cells were intracranially injected at a density of 5 × 105/10 uL into every mouse to form an orthotopic xenograft model. Coordinates of injection were 1 mm anterior and 2.5 mm right to the bregma, at a depth of 3.5 mm (the right frontal lobes of the mouse). Every 6 days, bioluminescence imaging (IVIS Lumina Series III; PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA) was used to image the mouse. At 8 days, we randomly chose 5 mice from each group to euthanize them, and their brain tissues were fixed with paraformaldehyde for further study. Another 5 mice were used for survival time analysis. For DB2313 (563801; MedKoo) anti-tumor research, male nude mice were subcutaneously injected with 5 × 106 U87MG cells suspended in 0.1 mL PBS. After 7 days, mice were intraperitoneally injected with DB2313 at density of 10 mg/kg/day dissolved in PBS solvent containing 10% DMSO for 7 days. The other group treated with vehicle only was set as the control group. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO inhibited growth, migration and invasion of GBM cells in vitro and in vivo.decreased FTO expression could induce the downregulation of MTMR3 expression by modulating the processing of pri-miR-10a in an m6A/HNRNPA2B1-dependent manner in GBM cells. Furthermore, the transcriptional activity of FTO was inhibited by the transcription factor SPI1. | |||
pri-miR-3591
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [176] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Prolyl endopeptidase FAP (FAP)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [177] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | VS-6063 | Phase 2 | ||
In-vitro Model |
NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| HCC827 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2063 | |
| PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | |
| SK-MES-1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0630 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| In-vivo Model | The Laboratory Animal Center of Soochow University provided female BALB/c nude mice (5 weeks old). Mice were kept under specific pathogen-free conditions. They were injected intravenously (i.v.) with FTO-overexpressing and control A549 cells (1.8 × 106 cells/mouse) to establish the in vivo model of NSCLC metastasis, and were then gavaged with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (25 mg/kg, daily) or the FAK inhibitor defactinib (VS6063) (Cat#S7654, Selleck, USA) (25 mg/kg, daily) beginning in the fifth week after injection. The mice were euthanized eight weeks after being inoculated, and their lungs were taken out and preserved in Bouin's solution for macroscopic investigation of metastatic nodules. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung tissues was used to look for micrometastatic foci. | |||
Prostacyclin synthase (PTGIS)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gefitinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Protein Atg16l2 (ATG16L2)
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Dac51 | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
Protein c-Fos (FOS)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [178] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Akata | EBV-related Burkitt lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0148 |
| In-vivo Model | To evaluate the tumorigenic effect of FTO, FTO knockdown or control AGS B95.8 cells (1 × 107 suspended in 150 μL of PBS) were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of B-NDG mice. The diameter and width of the tumours were measured every 4 days and used to estimate the tumour volumes by the standard formula: 0.5 × length × width2. At the end stage, the tumours were removed, imaged and weighed. To investigate the peritoneal dissemination ability of EBVaGC cells, intraperitoneal injection was performed. Briefly, 1 × 107 FTO silencing or control EBVaGC cells suspended in 0.4 mL of PBS were injected into the peritoneal cavity of each mouse. Eight weeks later, all the mice were sacrificed, and the abdominal and intestinal metastatic nodules were excised, counted, photographed and paraffin embedded. For the lung metastasis model, 200 μL of 1 × 106 luciferase-labelled EBVaGC cells from different groups were directly injected into the tail vein of B-NDG mice, and distant and lung metastasis were evaluated using bioluminescent imaging. After 6 or 8 weeks, the mice were euthanized, and the lungs were embedded in paraffin and subjected to haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining to record the micrometastatic nodules using a microscope. All animal experiments were approved by our Institutional Animal Care. | |||
Protein wntless homolog (WLS)
Pain disorders [ICD-11: 8E43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [179] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuropathic pain [ICD-11: 8E43.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PC-12 | Lung papillary adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S979 |
| In-vivo Model | Rats were anesthetized with isoflurane (1.5%-2.5%), and a lateral thigh incision was made. The left sciatic nerve and its three peripheral branches were isolated after sciatic nerve resection. A 5-0 suture was used to ligate the common peroneal and tibial nerves. Then, distal transverse incisions were made at the ligation. All surgical procedures were completed within 20 min, with special care taken to avoid damaging the sural nerve. The rats in the sham group underwent the same sciatic nerve exposure operation as the SNI group except for nerve ligation. | |||
Sclerostin (SOST)
Diabetic [ICD-11: 5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [180] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic [ICD-11: 5A14] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
BMSCs (BMSCs were obtained from the femurs and tibias of 2-3-week-old Sprague-Dawley male rats (Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University)) | |||
|
MC3T3
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_0D74 | |
Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP)
Picornavirus infections presenting in the skin or mucous membranes [ICD-11: 1F05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [181] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Picornavirus infections presenting in the skin or mucous membranes [ICD-11: 1F05.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
RD | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
|
Vero 76
|
N.A. | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0603 | |
| In-vivo Model | In this study, we introduced an animal model of EV71 infection (C4-ZZ1350) based on 3-day-old BALB/c mice inoculated with a lethal dose of EV71 strain (2 × 106 PFU/mouse) by the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route (n = 11 per group). | |||
Threonylcarbamoyladenosine tRNA methylthiotransferase (CDKAL1)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [182] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Fluorouracil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
Thrombospondin-2 (THBS2)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [137] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
TNFAIP3-interacting protein 1 (TNIP1)
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [183] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Briefly, the 8-week-old C57BL/6 male mice were fed with high-fat diet for 4 weeks and then intraperitoneally injected STZ (Sigma-Aldrich, 50 mg/kg STZ after fasting for 6 hours). The STZ injection was conducted for 5 days while the mice drank 10% glucose solution during the treatment. The control mice were injected citrate buffer and fed normal chow. All mice were maintained on their respective diets till sacrifice. Fasting blood glucose was tested 1 week after the last STZ injection, and values of more than 16.7 mmol/L were considered diabetic. | |||
Transducin-like enhancer protein 1 (TLE1)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [184] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Phenethyl isothiocyanate | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 |
| NCI-H226 | Pleural epithelioid mesothelioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1544 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were purchased from the Cancer Institute of the Chinese Academy of Medical Science (Beijing, China). Mice were randomly divided into two groups (eight mice per group), and 3×106 H1299 or H1299-LV-FTO-KD cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank of each mouse. For each group, four mice were treated with PEITC (100 mg/kg) intraperitoneally every two days for 14 days beginning the fifth week after cell injection, while the other four mice were treated with PBS as a control. At the end of the experiment, mice were euthanized, and tumor tissues were dissected for further analysis. Tumor weights were measured, and volumes were calculated (V = D/2 × d2, V: volume; D: longitudinal diameter; d: latitudinal diameter). | |||
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1 (SIRPA)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gefitinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Ubiquitin thioesterase OTUB1 (OTUB1)
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [185] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Erastin | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C666-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7949 |
| HONE-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8706 | |
| In-vivo Model | Three- to four-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were obtained from Guangxi Medical University Laboratory Animal Center and maintained under SPF housing. NPC cells were resuspended in 100 μl of PBS and injected subcutaneously into the flanks of the nude mice. Mice were randomized to experimental groups 28 days after implantation and were injected intraperitoneally with the same volume of FB23-2 (2 mg/kg) or erastin (10 mg/kg) or vehicle every three days during radiation (4 Gy, once a week). The endpoint of all experiments was tumor size. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [185] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B] | |||
| Responsed Drug | FB23-2 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C666-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7949 |
| HONE-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8706 | |
| In-vivo Model | Three- to four-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were obtained from Guangxi Medical University Laboratory Animal Center and maintained under SPF housing. NPC cells were resuspended in 100 μl of PBS and injected subcutaneously into the flanks of the nude mice. Mice were randomized to experimental groups 28 days after implantation and were injected intraperitoneally with the same volume of FB23-2 (2 mg/kg) or erastin (10 mg/kg) or vehicle every three days during radiation (4 Gy, once a week). The endpoint of all experiments was tumor size. | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Viral infections [ICD-11: 1D9Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [187] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Viral infections [ICD-11: 1D9Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Response Summary | m6A is the most abundant internal modification described in eukaryotic mRNA and several viral RNA including human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) infection. METTL3/METTL14 m6A writer complex plays a negative role in HRSV infections protein synthesis and viral titers, while m6A erasers FTO and ALKBH5 had the opposite effect. | |||
Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [188] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | |||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Response Summary | FTO was implicated in multiple biological processes, such as cancer cell apoptosis, proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis, cell-cycle, differentiation, stem cell self-renewal and so on. | |||
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [191] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Saikosaponins | Investigative | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Cell-cycle | ||||
In-vitro Model |
C1498 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_3494 |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| MOLM-14 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7916 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| SKNO-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2196 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | Upon the development of leukemic disease (established using a white blood cell (WBC) count), 0.1 mg/kg or 0.5 mg/kg of SsD was intraperitoneally injected three times per week for three consecutive weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO-dependent m6A RNA methylation mediated the anti-leukemic actions of saikosaponin-d, thereby opening a window to develop SsD as an epitranscriptome-base drug for leukemia therapy. SsD showed a broadly-suppressed acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest both in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [192] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Response Summary | A prevalent eukaryotic N6-methyladensosine (m6A) post-transcriptional mark can be "erased" by the m6A demethylase FTO, which is commonly deregulated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). | |||
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [194] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.4] | |||
In-vitro Model |
MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| Ku812 | Chronic myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0379 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| In-vivo Model | All mice had free access to food and water throughout the study. To test the oncogenic potential of FTO gene, K562 parental cells were transfected with FTO expression or control vectors for 6 h, and 5.0 × 106 transfected cells were subcutaneously injected into the bilateral flanks of the nude mice. For therapeutic experiments, K562 nilotinibR cells (1.5 × 106) were injected subcutaneously into the bilateral flanks of the nude mice. To retain the resistance phenotypes, these mice received 1 mg/kg nilotinib twice a week for 4 weeks till the tumor approached ~10 mm3. Then the tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into groups of 3 animals and received intraperitoneal injection of either 5 mg/kg nilotinib, 10 mg/kg rhein alone or their combination in polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG400, Sigma #1546445) and saline (ratio 15:38:47), three injections each week for 5 times in total. | |||
| Response Summary | Developing resistant phenotypes during tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy depends on m6A reduction resulting from FTO overexpression in leukemia cells. | |||
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [195] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
In-vitro Model |
MG-63 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 |
| In-vivo Model | According to the method published previously , exponentially growing MG63 and MG63/DXR were harvested, counted with trypan blue to show cells with at least 95% viability, and then resuspended at a final amount from 5 × 106 to 5 × 103 in 100 uL Matrigel (Corning, NY, USA) before being injected subcutaneously into 5-week-old female nude mice.The mice were monitored once every 3 days until the 60th day, and euthanized humanely after the experiment. | |||
| Response Summary | The transcriptome-wide m6A methylome of osteosarcoma cells enriched by chemotherapy, revealing a tight relationship between m6A methylation and the emergence and maintaining of OSCs. | |||
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [196] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Response Summary | Aberrant expression of demethylase genes, FTO and ALKBH1, has a distinct prognostic value in Gastric cancer patients, indicating that FTO and ALKBH1 play vital roles in GC progression and metastasis. | |||
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [199] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Berberine | Phase 4 | ||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| In-vivo Model | 5 × 105 HCT116 CSCs were subcutaneously injected into the mice similarly as nude mice. Seven days later, 5, 10, or 20 mg/kg Berberine was intraperitoneally injected. The same volume of PBS was injected and considered as negative control. | |||
| Response Summary | Berberine effectively decreased m6A methylation by decreasing beta-catenin and subsequently increased FTO suggests a role of Berberine in modulating stemness and malignant behaviors in colorectal cancer. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [34] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | RC cells SW480 at logarithmic growth phase were prepared into cell suspension with a concentration of about 1 × 107/100 L, which was then injected into the left axilla of nude mice with a 1 ml syringe to establish a subcutaneous mouse xenograft model. Once the tumor volume reached about 50 mm3, the nude mice were injected with miR-96 antagomir or NC antagomir (10 nmol once every 5 days for 5 weeks). After 5 weeks, the mice were euthanized, after which the subcutaneous transplanted tumor was removed, and weighed. | |||
| Response Summary | MiR-96 antagomir could potentially retard the cancerogenesis in colorectal cancer via AMPK subunit alpha-2 (AMPKAlpha2/PRKAA2)-dependent inhibition of FTO and blocking FTO-mediated m6A modification of MYC. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [200] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BEL-7402 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5492 |
| BEL-7404 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6568 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| MHCC97-L | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4973 | |
| LM | Extrarenal rhabdoid tumor of the liver | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B3QF | |
| QGY-7703 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6715 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male BALB/c nude mice (5 weeks old) were subcutaneously inoculated in the right axillary fossa with 200 uL (1 × 106 cells) of SIRT1-overexpressing Hep3B cells, SIRT1- and FTO-overexpressing Hep3B cells, shRNA-SIRT1-transfected HepG2 cells, shRNA-SIRT1- and shRNA-FTO-transfected HepG2 cells, and control cells. | |||
| Response Summary | SIRT1 destabilizes FTO, steering the m6A of downstream molecules and subsequent mRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis. A crucial component of small ubiquitin-related modifiers (SUMOs) E3 ligase, RANBP2, is activated by SIRT1, and it is indispensable for FTO SUMOylation at Lysine (K)-216 site that promotes FTO degradation. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [202] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell Progression | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| Response Summary | FTO facilitates lung adenocarcinoma cell progression by activating cell migration through m6A demethylation. | |||
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [203] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | ||
In-vitro Model |
COV362 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2420 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| OVCAR-5 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1628 | |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | Female nude, athymic, BALB/c-nu/nu mice (6-7 weeks old; Harlan) were injected subcutaneously (s.c.) with serially diluted numbers (5,000, 10,000, or 20,000) of OVCAR5_GFP or OVCAR5_FTO cells mixed with Matrigel (Fisher Scientific). Mice were monitored bi-weekly and time to tumor initiation and tumor growth were recorded. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO-Dependent N 6-Methyladenosine Modifications Inhibit Ovarian Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal by Blocking cAMP Signaling. cAMP pathway as a new FTO target in CSCs, associated with tumor inhibiting functions, and provide key new information on the role of m6A modifications regulated by FTO in the fine tuning of cellular fate in HGSOC. | |||
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [204] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell migration | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| Response Summary | Knockdown of HNRNPA2B1 or FTO prominently inhibited prostate cancer cells migration and invasion in vitro experiment. Determined CBLL1, FTO, YTHDC1, HNRNPA2B1 as crucial m6A regulators of prostate cancer. | |||
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [206] | |||
| Responsed Disease | clear cell renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Response Summary | The m6A-demethylases ALKBH5 and FTO are dysregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and could be used as prognostic biomarkers. ALKBH5 mRNA, as well as ALKBH5 and FTO protein expressions, was significantly downregulated in ccRCC compared to normal tissue and most of the other studied tumour entities. | |||
Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [209] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes [ICD-11: 5A10-5A14] | |||
| Response Summary | The content of m6A was highly associated with the risk of T2DM, and the increased mRNA expression of FTO is responsible for the reduction of m6A, which can further cause the complications of T2DM. | |||
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [210] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
In-vitro Model |
N1E-115 | Mouse neuroblastoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0451 |
| NIH 3T3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0594 | |
| In-vivo Model | For high-fat-diet treatment, 3-week-old male mice were randomly divided into three groups: two experimental groups freely fed with HFD of 60% fat, 20% carbohydrate, and 20% protein (Cat#: D12492, Research Diets) or KD of 89.5% fat, 0.1% carbohydrate, and 10.4% protein (Cat#: D12369B, Research Diets), and the control group fed with SD of 10% fat, 70% carbohydrate, and 20% protein (Cat#: D12450B, Research Diets), respectively. The mice were allowed free access to water and food.For fasting treatment, 3-month-old male mice were randomly divided into two groups: the fasting group with only free access to water for 48 h and the control group allowed free access to water and SD. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO fails to bind to its own promoter that promotes FTO expression in the hypothalamus of high-fat diet-induced obese and 48-h fasting mice, suggesting a disruption of the stable expression of this gene.ketogenic diet-derived ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) transiently increases FTO expression in both mouse hypothalamus and cultured cells. | |||
Metabolic disorders [ICD-11: 5D2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [211] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Metabolic disorders [ICD-11: 5D2Z] | |||
| Pathway Response | AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
C2C12 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0188 |
| In-vivo Model | Sixteen 10-wk-old male C57BL/6 J mice [wild-type (WT) mice] and six 10-wk-old male obese C57BL/6Job/ob (OB) mice were purchased from Nanjing Biomedical Research Institute of Nanjing University. WT mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (8 mice/group): normal chow diet (ND) and high-fat diet (HFD) groups. The ND group was fed with a normal chow diet containing10% fat, 20% protein and 70% carbohydrate. The HFD group was fed a HFD containing 45% fat, 20% protein and 35% carbohydrate. OB mice were fed with ND. All mice were housed at 22 ± 1 ℃ under a 12-h light cycle with free access to water and diet during the experiment. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO-dependent demethylation of mRNA m6A methylation was involved in the regulation of skeletal muscle lipid accumulation by the AMPK signalling pathway. | |||
Secondary stereotypy [ICD-11: 8A07]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [212] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Secondary stereotypy [ICD-11: 8A07] | |||
| Response Summary | Inhibition of m6A RNA demethylation by small-molecule drugs, as presented here, has therapeutic potential and provides tools for the identification of disease-modifying m6A RNAs in neurogenesis and neuroregeneration. Small-molecule inhibitors of the RNA m6A demethylases FTO potently support the survival of dopamine neurons. | |||
Alzheimer disease [ICD-11: 8A20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [213] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Alzheimer disease [ICD-11: 8A20] | |||
| Cell Process | Synaptic or neuron development and growth | |||
| Response Summary | The alterations of m6A RNA methylation in alzheimer's disease and in C57BL/6 mice were investigated using high-throughput sequencing. The expression of the m6A methyltransferase METTL3 was elevated and that of the m6A demethylase FTO was decreased in AD mice. | |||
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [215] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| In-vivo Model | 36 male C57BL/6J mice (20-22 g, 2-month-old) were purchased from SPF (Beijing) biotechnology co., Ltd (Beijing, China) and maintained in the specific pathogen-free (SPF) animal laboratory with a 12/12 h light/dark cycle with free access to food and water. The mice were randomly assigned into six groups (n = 6 per group): (1) sham-operated group (Sham), (2) MCAO 6 h, (3) MCAO 12 h, (4) MCAO 1 d, (5) MCAO 3 d, and (6) MCAO 7 d. | |||
Neurological disorders due to toxicity [ICD-11: 8D43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [216] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neurological disorders due to toxicity [ICD-11: 8D43] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Arsenite | Phase 2 | ||
In-vitro Model |
PC-12 Adh | Rat adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_F659 |
| In-vivo Model | The animals were kept in standard laboratory polycarbonate cages in controlled ambient temperature at 23℃ ± 1℃ with relative humidity of 50% ± 10%, and a light-dark cycle of 12/12 h. The mice had free access to standardized pellet food and tap water. After 1-week of habituation, the animals were randomly divided into the following 4 groups: control group, 0.5 mg/l arsenite group, 5 mg/l arsenite group and 50 mg/l arsenite group (n = 16 per group). The mice were exposed to arsenite via drinking water for 6 months. | |||
| Response Summary | Targeting the m6A demethylase FTO in the prevention or intervention against arsenite-related neurodegenerative diseases. | |||
Visual impairment [ICD-11: 9D90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [217] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vision impairment [ICD-11: 9D90] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| In-vivo Model | After general anesthesia with an intraperitoneal injection of ketamine (80 mg/kg) and xylazine (4 mg/kg), topical application of 0.5% proparacaine ophthalmic solution was conducted. Three sutures (10-0 nylon) were placed intrastromally between the limbus and corneal center at the 4, 8, and 12 o'clock positions. Topical norfloxacin was applied after surgery. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO regulates pathological ocular angiogenesis by controlling endothelial cell function in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Pathological ocular angiogenesis commonly results in visual impairment or even blindness. | |||
Ototoxic hearing loss [ICD-11: AB53]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [218] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ototoxic hearing loss [ICD-11: AB53] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Cell Process | Oxidative stress | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEI-OC1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_D899 |
| Response Summary | MA2, which is a highly selective inhibitor of FTO, has a protective effect and improves the viability of HEI-OC1 cells after cisplatin treatment, and they provide new insights into potential therapeutic targets for the amelioration of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [218] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ototoxic hearing loss [ICD-11: AB53] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Cell Process | Oxidative stress | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEI-OC1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_D899 |
| Response Summary | MA2, which is a highly selective inhibitor of FTO, has a protective effect and improves the viability of HEI-OC1 cells after cisplatin treatment, and they provide new insights into potential therapeutic targets for the amelioration of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. | |||
Presbycusis [ICD-11: AB54]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [219] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Presbycusis [ICD-11: AB54] | |||
Cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [220] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43.7] | |||
| In-vivo Model | Leptin receptor-deficient (db/db) mice and control mice (db/ +) were purchased from Shanghai Model Organisms Center, which genetic background is C57BL/6J. All mice were used for experiments at 8-12 weeks old and were housed in constant 24 degrees cages with a 12 h alternating light/dark cycle and free access to water and food. To construct a diabetic heart disease model (DCM), mice were continuously fed to 24 weeks of age, then euthanized, hearts collected in 1.5 ml RNase-free centrifuge tubes, immediately immersed in liquid nitrogen to prevent RNA degradation, and finally stored at 80℃. Five pairs of db/db and db/ + heart samples were selected for RNA sequencing, and the remaining samples were saved for validation. | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of FTO in diabetic cardiomyopathy(DCM) model mice improved cardiac function by reducing myocardial fibrosis and myocyte hypertrophy. | |||
Congestive heart failure [ICD-11: BD10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [221] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Congestive heart failure [ICD-11: BD10] | |||
| In-vivo Model | We quantified m6A levels in RNA extracted from failing human (both ischemic and non-ischemic), pig and mouse (post-myocardial infarction ischemic) hearts and compared them to m6A in non-failing human and sham surgical controls respectively. We detected significantly elevated levels of m6A in both total and polyA+ RNA extracted from human, pig and mouse failing left ventricular (LV) explants compared to non-failing or sham. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO-dependent cardiac m6A methylome in cardiac contraction during heart failure and provides a novel mechanistic insight into the therapeutic mechanisms of FTO. | |||
Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [222] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Abdominal aortic aneurysm [ICD-11: BD50.4] | |||
| Cell Process | Inflammatory infiltrates | |||
| Neovascularization | ||||
In-vitro Model |
PBMCs (Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are isolated from peripheral blood and identified as any blood cell with a round nucleus) | |||
| SMCs (Aneurysmal smooth muscle cells) | ||||
| Response Summary | YTHDF3 represented an even greater risk of rupture. Regarding the cellular location, METTL14 seemed to be associated with inflammatory infiltrates and neovascularization. Furthermore, a strong correlation was seen between FTO and aneurysmal smooth muscle cells (SMCs), YTHDF3, and macrophage infiltrate. The results also reveal the important roles of m6A modulators, including YTHDF3, FTO, and METTL14, in the pathogenesis of human human abdominal aortic aneurysm(AAA) and provide a new view on m6A modification in AAA. | |||
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [223] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Sunitinib | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
hiPSCs (Urinary epithelial cell-derived hiPSCs) | |||
| CMECs (Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells ) | ||||
| CFs (Cardiac Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Response Summary | The RNA demethylase FTO was downregulated, whereas METTL14 and WTAP were upregulated. Furthermore, gain- and loss-of-function studies substantiated that FTO is cardioprotective in TKI(Sunitinib). | |||
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [224] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Betaine | Approved | ||
| In-vivo Model | Eight adult female C57BL/6 mice from the same pool of litters were housed at 22 ± 1 ℃ with 12-h light cycle and were mated with their male siblings. The female mice were fed with a low-fat diet supplemented with betaine from mating and throughout gestation and lactation. Litters were culled to five males per dam. Thirty offspring weaned at the age of day 21 and then were randomly assigned to three groups fed with either a low-fat diet (LF), high-fat diet (HF), or high-fat diet supplemented with betaine (HB) for 6 weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | A novel FTO-dependent function of m(6)A is involve in the hepatoprotective effects of betaine. betaine supplementation across adolescence could protect mice from high-fat-induced lipid accumulation NAFLD in the liver. Moreover, FTO-dependent m6A demethylation is affected by betaine. A novel FTO-dependent function of m(6)A may involve in the hepatoprotective effects of betaine. | |||
Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [225] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z] | |||
| Pathway Response | PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | ||
| Cell Process | Fatty degeneration | |||
| In-vivo Model | A total of 24 male mice were randomly allocated to LFD (low-fat diet), LFDR (low-fat diet + resveratrol), HFD (high-fat diet), and HFDR (high-fat diet + resveratrol) groups for 12 weeks (n = 6/group). | |||
| Response Summary | The beneficial effect of resveratrol on lipid metabolism disorder under HFD is due to a decrease of m6A RNA methylation and an increase of PPARalpha mRNA, providing mechanistic insights into the function of resveratrol in alleviating the disturbance of lipid metabolism in mice. The resveratrol in HFD increased the transcript levels of methyltransferase like 3 (METTL3), alkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5), fat mass and obesity associated protein (FTO), and YTH domain family 2 (YTHDF2), whereas it decreased the level of YTH domain family 3 (YTHDF3) and m6A abundance in mice liver. | |||
Menopausal disorder [ICD-11: GA30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [226] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Premature ovarian failure [ICD-11: GA30.6] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
Hgc (Primary human ovarian granulosa cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | To build the mouse model for POI, cyclophosphamide (CTX) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) was used a high-dose treatment (120 mg/kg, 2 weeks). | |||
| Response Summary | The decreased mRNA and protein expression levels of FTO are responsible for the increase in m6A in POI, which can further increase the risk of complications of POI. FACS was used to measure the levels of proliferation and apoptosis, and siRNA was used to establish FTO and ALKBH5 knockdown cell lines. The m6A content in the RNA from POI patients and POI mice was significantly higher than control groups and that POI was characterized by the content of m6A. | |||
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [228] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61] | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| T-lymphocyte cell line (A type of lymphocyte) | ||||
| Response Summary | Targeting RNA m6A modification is a novel strategy for the treatment of chronic kidney diseases and autophagy. Knockdown of FTO or inhibit the m6A by 3-deazaadenosine blocks the effects of indoxyl sulfate on autophagy activation in cells. | |||
Sex development malformative disorder [ICD-11: LD2A]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [229] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Sex development malformative disorder [ICD-11: LD2A] | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| Response Summary | The inhibition of FTO-mediated up-regulation of m6A could be involved in MEHP-induced Leydig cell apoptosis. | |||
Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 2 (ASB2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.19E-01 p-value: 3.80E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Tretinoin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| RNA degradation (hsa03018) | ||||
| In-vitro Model | K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| Mono-Mac-6 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1426 | |
| Response Summary | FTO enhances leukemic oncogene-mediated cell transformation and leukemogenesis, and inhibits all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced AML cell differentiation, through regulating expression of targets such as Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 2 (ASB2) and RARA by reducing m6A levels in these mRNA transcripts. | |||
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.55E-01 p-value: 1.57E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators in breast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such as Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. | |||
R-2HG
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators in breast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such as Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. | |||
ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 10 (ABCC10)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse hippocampus | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mice hippocampus
Control: Wild type hippocampus
|
GSE94098 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.58E-01 p-value: 2.09E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gefitinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | ABC transporters | hsa02010 | ||
| In-vitro Model | PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were randomized into three groups (n = 7/group), 1 × 107 PC9 cells absorbed exosomes were subcutaneously injected into the Bilateral groin of mice. Treatment began 1 week following injection, the mice were intraperitoneally injected with gefitinib (30 mg/kg/day). | |||
| Response Summary | Not only FTO knockdown enhanced the gefitinib sensitivity of GR cells but also FTO reduction in donor exosomes alleviated the acquired resistance of recipient non-small cell lung cancer PC9 cells. FTO/YTHDF2/ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 10 (ABCC10) axis played a role in intercellular transmission of GR cell-derived exosome-mediated gefitinib resistance. | |||
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
 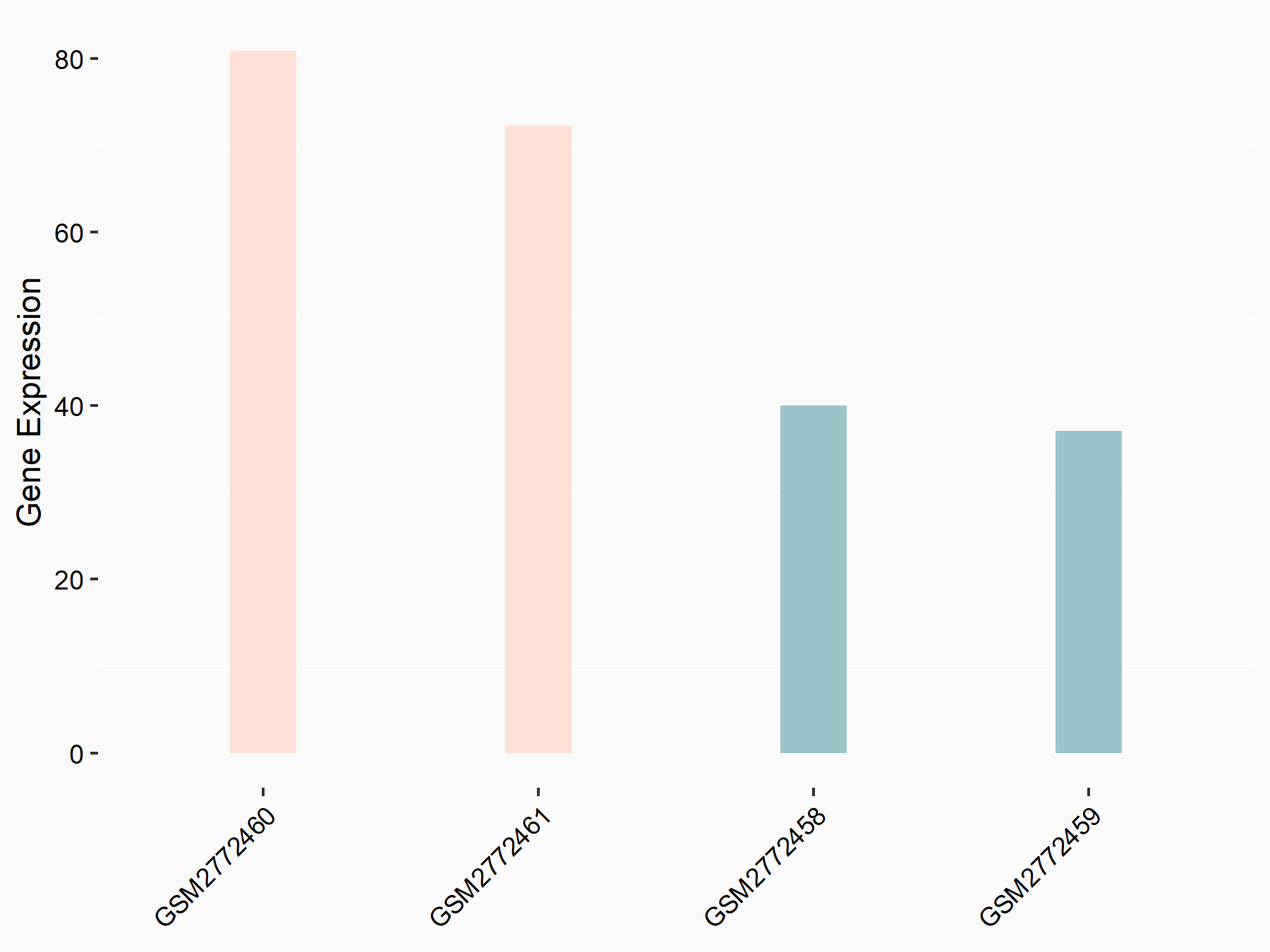 |
logFC: 9.72E-01 p-value: 3.86E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
 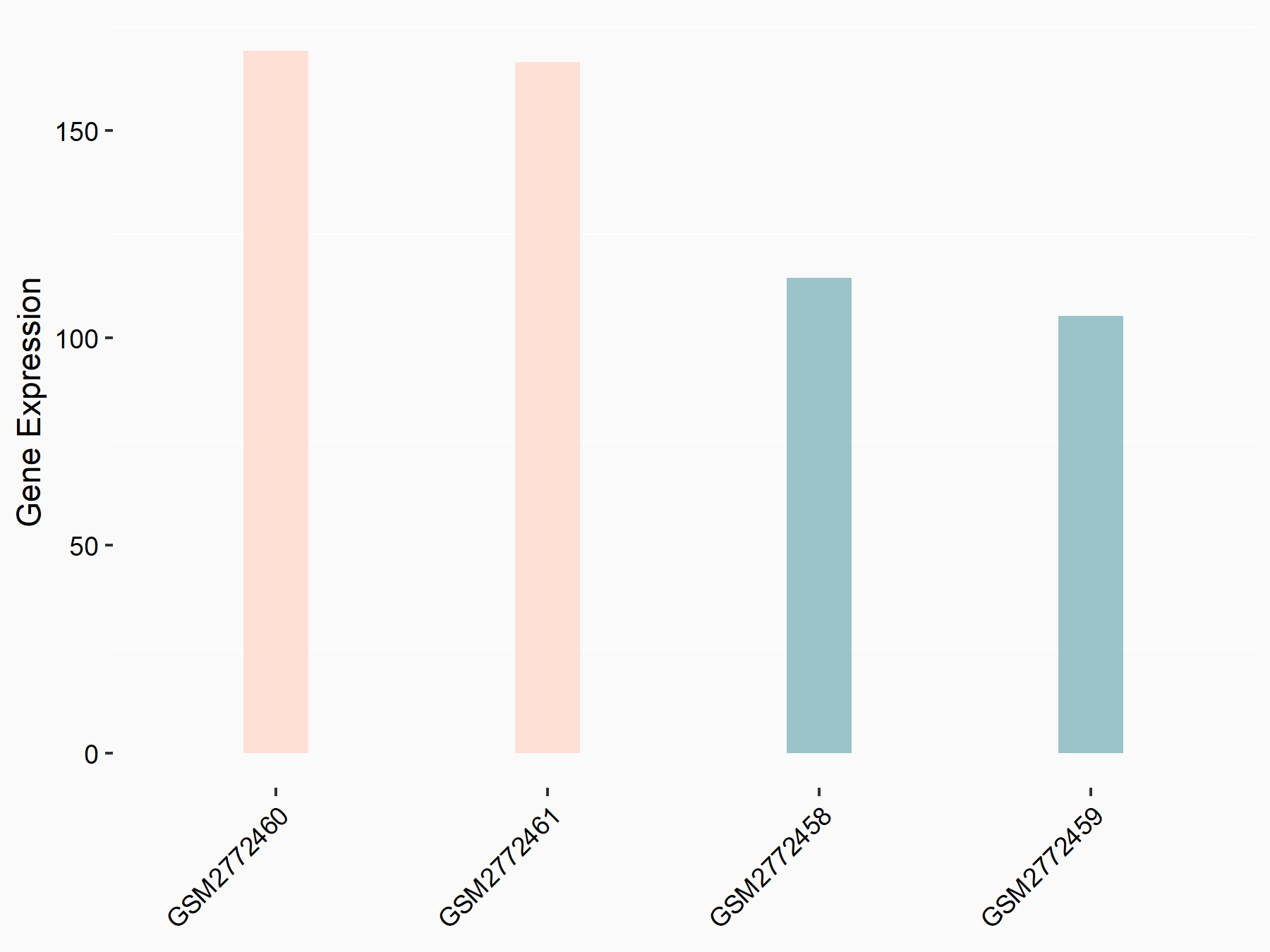 |
logFC: 6.07E-01 p-value: 3.92E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
R-2HG
[Investigative]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia | ICD-11: 2B33.4 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
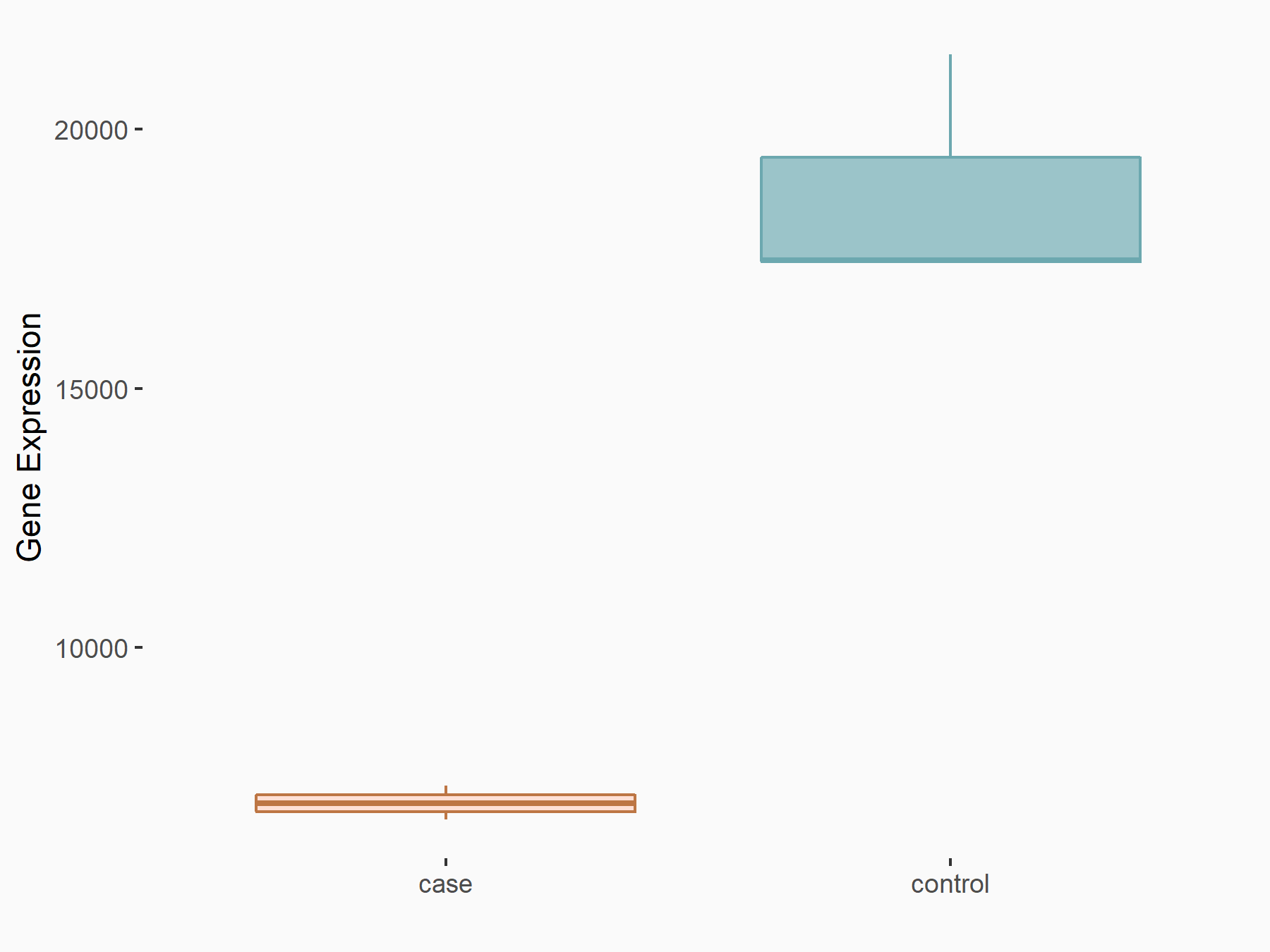  |
logFC: -1.42E+00 p-value: 2.68E-47 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Asparagine inhibitor
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Chloroquine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Meclofenamate sodium
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
CB-839
[Phase 2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
GLS-IN-968
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Cyclin-A2 (CCNA2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 7.89E-01 p-value: 6.22E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Epigallocatechin gallate
[Phase 3]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent Cyclin-A2 (CCNA2) and CDK2 expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16-OVA cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shFTO B16-OVA cells
Control: shNC B16-OVA cells
|
GSE154952 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 7.39E-01 p-value: 1.49E-28 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Epigallocatechin gallate
[Phase 3]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
 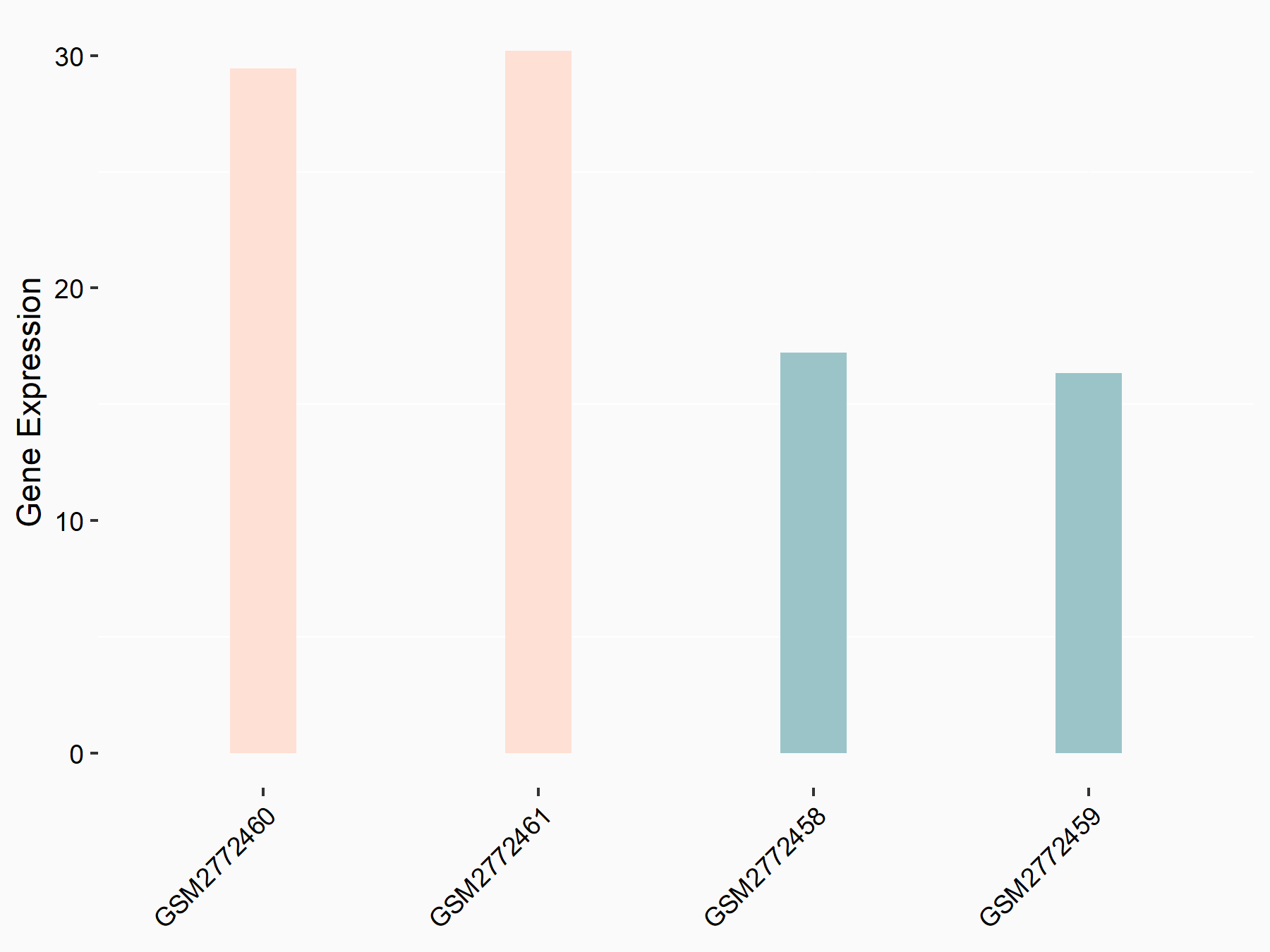 |
logFC: 7.94E-01 p-value: 7.54E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Fluorouracil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Paclitaxel
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Frizzled-10 (FZD10)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse hippocampus | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mice hippocampus
Control: Wild type hippocampus
|
GSE94098 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.03E-01 p-value: 7.74E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
PARPi
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary | ICD-11: 2B5D.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| In-vitro Model | UWB1.289 | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B079 |
| PEO1 | Ovarian cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2686 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 107 PARP inhibitor resistant PEO1 cells were suspended in 200 uL PBS : Matrigel (1:1) unilaterally injected subcutaneously into the right dorsal flank of 6-8 week-old female immunocompromised non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD/SCID) gamma (NSG) mice. When the average tumor size reached ~100 mm3, the mice were then randomized into four groups and treated with vehicle control, Olaparib (50 mg/kg), XAV939 (5 mg/kg) or a combination daily for 18 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Downregulation of m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 was sufficient to increase Frizzled-10 (FZD10) mRNA m6A modification and reduce PARPi sensitivity, the finding elucidates a novel regulatory mechanism of PARPi resistance in EOC by showing that m6A modification of FZD10 mRNA contributes to PARPi resistance in BRCA-deficient EOC cells via upregulation of Wnt/Bete-catenin pathway. | |||
Heat shock factor protein 1 (HSF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -7.09E-01 p-value: 1.48E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bortezomib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Multiple myeloma | ICD-11: 2A83.1 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | RPMI-8226 | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0014 |
| MM1.R | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8794 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 3×106 RPMI8226/MM1R-Luc cells were intravenously injected into NCG mice to establish a disseminated human MM xenograft model. The in vivo antitumor effect of the FTO inhibitor MA2 combined with or without the first-line chemotherapeutic agent BTZ was evaluated as follows: 3 days post xenotransplantation, MA2 (20 mg/kg), or vehicle control was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) daily for 10 days, and BTZ was injected intraperitoneally on days 1, 4, 8, and 11. Mouse serum was collected at specified time points during the treatment, and the tumor burden was monitored by detecting myeloma cell-secreted Lambda light chains via a Human Lambda ELISA Kit (Bethyl Laboratories, No. E88-116). Tumor development was monitored weekly after treatment with an in vivo imaging system (IVIS, SI Imaging, Lago, and LagoX). Luciferin (150 mg/kg, YEASEN, Shanghai, China) was injected intraperitoneally into the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO significantly promotes MM cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting Heat shock factor protein 1 (HSF1)/HSPs in a YTHDF2-dependent manner. FTO inhibition, especially when combined with bortezomib (BTZ) treatment, synergistically inhibited myeloma bone tumor formation and extramedullary spread in NCG mice. | |||
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.83E+00 p-value: 2.17E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Atorvastatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1), downregulated those of KLF2 and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Krueppel-like factor 2 (KLF2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16F10 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout B16F10 cells
Control: B16F10 cells
|
GSE134388 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.68E+00 p-value: 3.25E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Atorvastatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, downregulated those of Krueppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse liver | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mouse liver tissue
Control: Wild type mouse liver tissue
|
GSE125785 | |
| Regulation |
 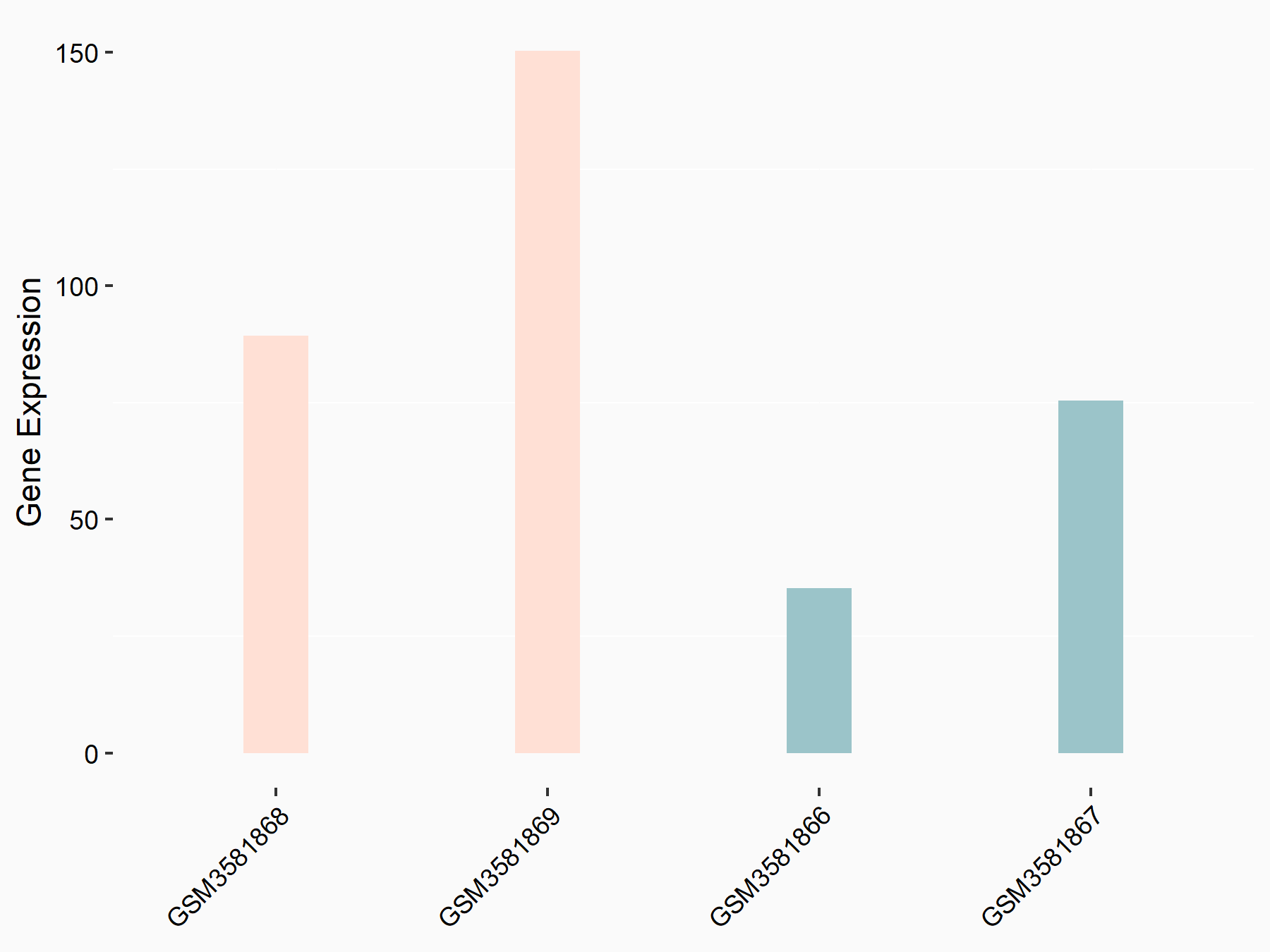 |
logFC: 1.12E+00 p-value: 2.09E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [30] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
R-2HG
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [30] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.81E-01 p-value: 3.45E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
R-2HG
[Investigative]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)/CEBPA signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia | ICD-11: 2B33.4 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)/CEBPA signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
44/ZLD115
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [99] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 |
| KG-1 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0374 | |
FB23
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [99] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 |
| KG-1 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0374 | |
Neutral amino acid transporter B(0) (SLC1A5)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.02E+00 p-value: 5.80E-30 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
GLS-IN-968
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [41] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C90 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | |||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | |||
| In-vitro Model | UMRC2-vec (CCRCC isogenic cell lines that are VHL-deficient) | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic inactivation of FTO using multiple orthogonal approaches revealed that FTO inhibition selectively reduces the growth and survival of VHL-deficient cells in vitro and in vivo. Integrated analysis of transcriptome-wide m6A-seq and mRNA-seq analysis identified the glutamine transporter Neutral amino acid transporter B(0) (SLC1A5) as an FTO target that promotes metabolic reprogramming and survival of VHL-deficient ccRCC cells. GLS1 inhibitors that target mitochondrial glutaminase and the conversion of glutamine to glutamate are currently being evaluated in early-phase clinical trials in ccRCC. These findings identify FTO as a potential HIF-independent therapeutic target for the treatment of VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma. | |||
PDH kinase 1 (PDK1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -7.19E-01 p-value: 8.18E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Temozolomide
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [43] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma | ICD-11: 2A00.00 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Citrate cycle | hsa00020 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| Cell Process | Aerobic glycolysis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| SHG-44 | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6728 | |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| Response Summary | Long noncoding RNA just proximal to X-inactive specific transcript facilitates aerobic glycolysis and temozolomide chemoresistance by promoting stability of PDH kinase 1 (PDK1) mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner in glioblastoma multiforme cells. JPX interacted with N6-methyladenosine (m6A) demethylase FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) and enhanced FTO-mediated PDK1 mRNA demethylation. | |||
Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.53E-01 p-value: 1.38E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [53] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Response Summary | The m6A changes caused by FTO influence the stability of ULK1 transcripts, likely through a YTHDF2-dependent manner.Under both basal and rapamycin-induced autophagy conditions, depletion of FTO significantly reduced the formation of GFP-LC3B puncta. The level of Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)/SQSTM1 (an autophagy substrate) was higher in FTO-knockdown cells than that in control cells. FTO specifically upregulates the ULK1 protein abundance. ULK1 mRNA undergoes m6A modification in the 3'-UTR and the m6A-marked ULK1 transcripts can further be targeted for degradation by YTHDF2. | |||
Canagliflozin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [117] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Macroscopic changes of size of the kidney | ICD-11: MF54.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase ULK1 (ULK1/ATG1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -6.13E-01 p-value: 1.25E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [53] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Response Summary | The m6A changes caused by FTO influence the stability of ULK1 transcripts, likely through a YTHDF2-dependent manner.Under both basal and rapamycin-induced autophagy conditions, depletion of FTO significantly reduced the formation of GFP-LC3B puncta. The level of p62/SQSTM1 (an autophagy substrate) was higher in FTO-knockdown cells than that in control cells. FTO specifically upregulates the Serine/threonine-protein kinase ULK1 (ULK1) protein abundance. ULK1 mRNA undergoes m6A modification in the 3'-UTR and the m6A-marked ULK1 transcripts can further be targeted for degradation by YTHDF2. | |||
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [55] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 |
| SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 5 × 106 cells in 200 ul PBS were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of nude mice. After injection, cisplatin treatment was initiated on day 5. Mice were injected with 5 mg/kg cisplatin or PBS solution in the abdominal cavity once a week for 3 weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of FTO reversed cisplatin resistance of SGC-7901/DDP cells both in vitro and in vivo, which was attributed to the inhibition of Serine/threonine-protein kinase ULK1 (ULK1)-mediated autophagy. These findings indicate that the FTO/ULK1 axis exerts crucial roles in cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. | |||
Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial (SOD2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 8.09E-01 p-value: 6.85E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bortezomib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [56] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Multiple myeloma | ICD-11: 2A83.1 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Response Summary | FTO promotes Bortezomib resistance via m6A-dependent destabilization of Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial (SOD2) expression in multiple myeloma. | |||
Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
 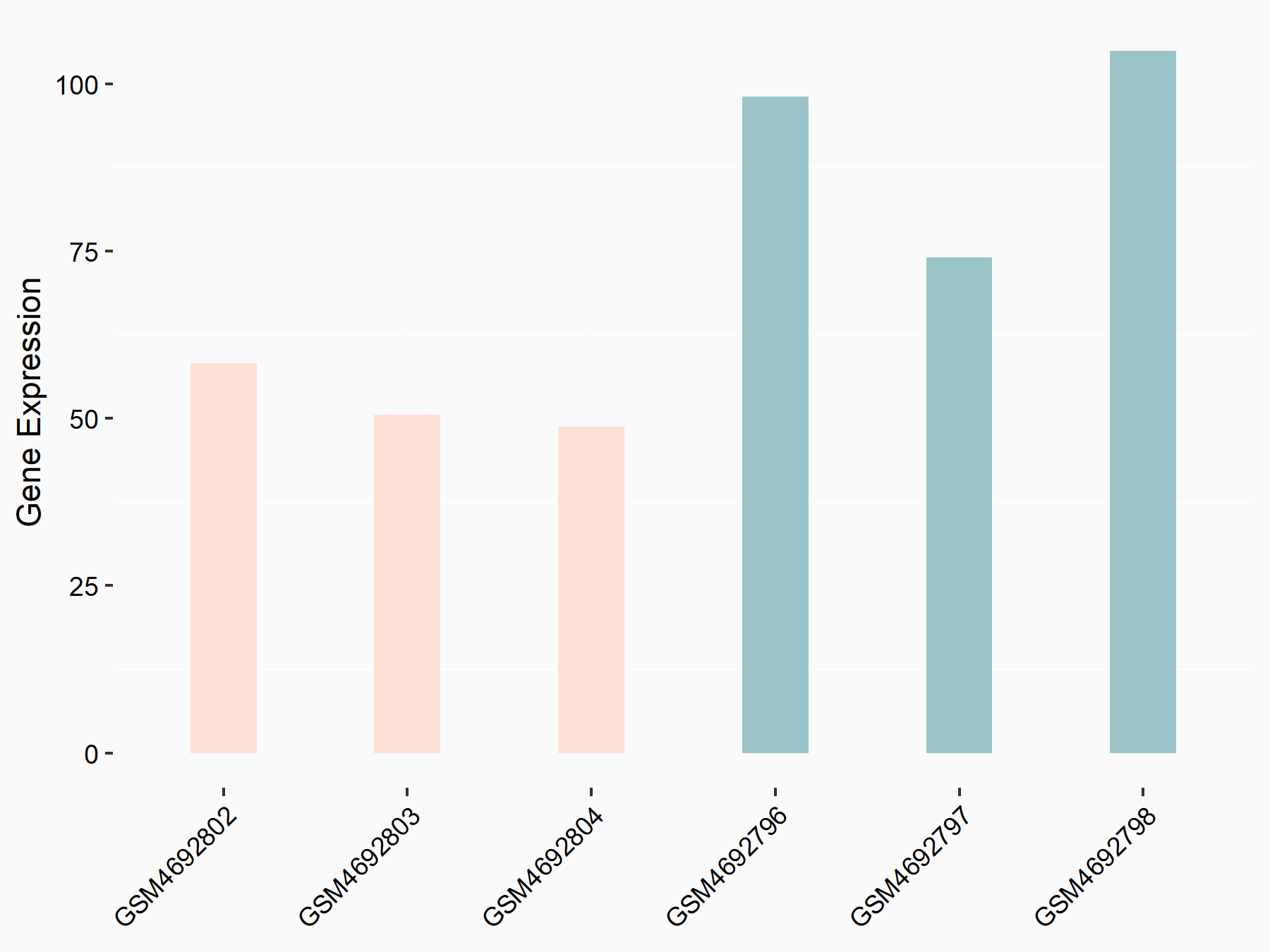 |
logFC: -8.13E-01 p-value: 2.61E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse hippocampus | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mice hippocampus
Control: Wild type hippocampus
|
GSE94098 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.17E-01 p-value: 3.60E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Atorvastatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM1) and ICAM-1, downregulated those of KLF2 and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)
Dac51
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes | ICD-11: 5A10-5A14 | ||
| In-vitro Model | MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53)
Erianin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [73] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C90 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
| In-vivo Model | Induced AKI in c57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal cisplatin injection and treated the animal with vehicle or an FTO inhibitor meclofenamic acid (MA) for 3 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Meclofenamic acid increased Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) mRNA and protein levels in AKI both in vitro and in vivo, and FTO overexpression reduced p53 expression and reversed the MA-induced p53 increase in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury Acute kidney injury. | |||
Meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
| In-vivo Model | Induced AKI in c57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal cisplatin injection and treated the animal with vehicle or an FTO inhibitor meclofenamic acid (MA) for 3 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Meclofenamic acid increased Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) mRNA and protein levels in AKI both in vitro and in vivo, and FTO overexpression reduced p53 expression and reversed the MA-induced p53 increase in cisplatin-induced Acute kidney injury. | |||
Constitutive NOS (eNOS)
Atorvastatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, downregulated those of KLF2 and Constitutive NOS (eNOS), and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1)
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [82] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)
Cytarabine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [85] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| In-vivo Model | Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Vst/Vst (NPG) mice (6 weeks old) were divided into three groups and implanted with 4 × 106 cells of control (MV4-11 NC) or FTO-knockdown (MV4-11 KD-1 or KD-2) by tail vein injection, respectively. | |||
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Fluorouracil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Paclitaxel
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)
PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) (PDCD1), CXCR4, and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA)
Tretinoin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| RNA degradation (hsa03018) | ||||
| In-vitro Model | K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| Mono-Mac-6 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1426 | |
| Response Summary | FTO enhances leukemic oncogene-mediated cell transformation and leukemogenesis, and inhibits all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced AML cell differentiation, through regulating expression of targets such as ASB2 and Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) by reducing m6A levels in these mRNA transcripts. | |||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
Asparagine inhibitor
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Chloroquine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Meclofenamate sodium
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
CB-839
[Phase 2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
GLS-IN-968
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
Doxil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [119] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| Response Summary | Decreased doxorubicin resistance by Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) knockdown was abolished by FTO overexpression and decreased doxorubicin sensitivity by STAT3 overexpression was reversed by FTO knockdown, indicating that FTO was implicated in STAT3-mediated doxorubicin resistance and impairment of doxorubicin sensitivity of BC cells. | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 (USP7)
P22077
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [125] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H522 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1567 | |
| HSAEC (Human small airway epithelial cells) | ||||
| RERF-LC-A1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4402 | |
| NCI-H1882 | Lung small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1504 | |
| NCl-H466 (Human lung cancer cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Equal numbers of A549 cells expressing either control or shFTO were injected subcutaneously, within 30 min of harvesting, over the right and left flanks in male nu/nu mice between 4 and 6 weeks of age. | |||
| Response Summary | The m6A demethylase FTO promotes the growth of Non-small cell lung cancer cells by increasing the expression of USP7.Genetic knockdown or pharmacological inhibition (P5091 or P22027) of Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 (USP7) reduced the proliferation rate of lung cancer cells and decreased the capacity of colony formation of lung cancer cells in vitro, whereas lung cancer cells growth inhibition by FTO knockdown is restored by overexertion of USP7. | |||
P5091
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [125] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H522 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1567 | |
| HSAEC (Human small airway epithelial cells) | ||||
| RERF-LC-A1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4402 | |
| NCI-H1882 | Lung small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1504 | |
| NCl-H466 (Human lung cancer cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Equal numbers of A549 cells expressing either control or shFTO were injected subcutaneously, within 30 min of harvesting, over the right and left flanks in male nu/nu mice between 4 and 6 weeks of age. | |||
| Response Summary | The m6A demethylase FTO promotes the growth of Non-small cell lung cancer cells by increasing the expression of USP7.Genetic knockdown or pharmacological inhibition (P5091 or P22027) of Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 (USP7) reduced the proliferation rate of lung cancer cells and decreased the capacity of colony formation of lung cancer cells in vitro, whereas lung cancer cells growth inhibition by FTO knockdown is restored by overexertion of USP7. | |||
Ubiquitin-like protein ATG12 (ATG12)
Dac51
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes | ICD-11: 5A10-5A14 | ||
| In-vitro Model | MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
microRNA 155 (MIR155)
Temozolomide
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [133] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| In-vitro Model | A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Previously prepared U87 cells (5 × 106 cells, 60 uL) stably infected with miRNA were injected subcutaneously in the right flank of the mice, whereas control U87 cells infected with empty vector were injected in the left flank. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Temozolomide by Targeting MYC-microRNA 155 (MIR155)/miR-23a Cluster-MXI1 Feedback Circuit in Glioma. | |||
microRNA 23a (MIR23A)
Temozolomide
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [133] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| In-vitro Model | A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Previously prepared U87 cells (5 × 106 cells, 60 uL) stably infected with miRNA were injected subcutaneously in the right flank of the mice, whereas control U87 cells infected with empty vector were injected in the left flank. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Temozolomide by Targeting MYC-miR-155/microRNA 23a (MIR23A) Cluster-MXI1 Feedback Circuit in Glioma. | |||
Apoptosis regulatory protein Siva (SIVA1)
Fluorouracil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [139] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| MC-38 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_B288 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the tumor metastasis mouse model, 5-week-old C57BL/6 mice were randomly grouped and injected with 5 × 105 Control or shFTO stable MC38 cells via tail vein. Drug administration was adopted after 48 h. Drug administration (intraperitoneally): DMSO, 5-FU (50 mg/kg every 2 days) or Rhein (10 mg/kg every 2 days). To detect lung metastasis, mice were killed 2 weeks after tumor cell injection. Lung tissues were harvested and fixed with 4% PFA for paraffin-embedded section and lung metastases were detected with Nikon microscopy. For tumor intraperitoneal mouse model, 2 × 106 Dox-shCtrl, Dox-shFTO stable HCT8/5-FU cells were injected into 5-week-old male BALB/C nude mice. Drug administration was adopted after 48 h. Drug administration (intraperitoneally): DMSO, 5-FU (50 mg/kg every 2 days) or FB23-2 (10 mg/kg every 2 days). For tumor intraperitoneal mouse model, 5 × 105 shCtrl, shFTO-1, shFTO-2 stable MC38 cells were injected into 5-week-old C57BL/6 mice. Drug administration was adopted after 48 h. Drug administration (intraperitoneally): DMSO, 5-FU (50 mg/kg every 2 days) or Rhein (10 mg/kg every 2 days). | |||
Autophagy-related protein 9A (ATG9A)
Dac51
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes | ICD-11: 5A10-5A14 | ||
| In-vitro Model | MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 (NEDD4)
Gemcitabine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [150] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Human Pancreatic Nestin-Expressing cells (Human Pancreatic Nestin-Expressing cells) | |||
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| COLO 357 | Pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0221 | |
| In-vivo Model | Female athymic BALB/C nude mice received a subcutaneous injection of 5 × 106 cells into the axilla (4 weeks old, 18-20 g). The tumor volume (V) was calculated each week using the formula V = (W2 L)/2 after measuring the tumor width (W) and length (L). After the injection of cancer cells, for the gemcitabine treatment cohort, mice were injected with gemcitabine (120 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich) intraperitoneally and weekly according to previous studies . | |||
F-box only protein 32 (FBXO32)
3-deazidenosine
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [152] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Certain specified disorders of muscle | ICD-11: FB32.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
R-2HG
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [152] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Certain specified disorders of muscle | ICD-11: FB32.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Glypican-4 (GPC4)
FB23-2
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [156] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Uveitis | ICD-11: 9A96 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model |
HMC3
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_II76 |
Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane protein FLRT3 (FLRT3)
Gefitinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2)
Nicotine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [170] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Blood Pressure | ICD-11: BA00 | ||
| In-vivo Model | SCLC cells were collected, and cell suspensions were prepared at a concentration of 1 × 106 cells per 100 μL PBS and injected subcutaneously into nude mice. When the tumour volume reached 60 mm3, mice were randomly divided into control and treatment groups with five mice in each group. The mice in the treatment group were treated regularly, and chemotherapy drugs (CDDP 3 mg/kg and VP16 2 mg/kg) were administered via intraperitoneal injection. | |||
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT)
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [171] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
Peroxiredoxin-5, mitochondrial (PRDX5)
FB23-2
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [173] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
Polyunsaturated fatty acid lipoxygenase ALOX12 (ALOX12)
Erianin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [73] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C90 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Prolyl endopeptidase FAP (FAP)
VS-6063
[Phase 2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [177] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| HCC827 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2063 | |
| PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | |
| SK-MES-1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0630 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| In-vivo Model | The Laboratory Animal Center of Soochow University provided female BALB/c nude mice (5 weeks old). Mice were kept under specific pathogen-free conditions. They were injected intravenously (i.v.) with FTO-overexpressing and control A549 cells (1.8 × 106 cells/mouse) to establish the in vivo model of NSCLC metastasis, and were then gavaged with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (25 mg/kg, daily) or the FAK inhibitor defactinib (VS6063) (Cat#S7654, Selleck, USA) (25 mg/kg, daily) beginning in the fifth week after injection. The mice were euthanized eight weeks after being inoculated, and their lungs were taken out and preserved in Bouin's solution for macroscopic investigation of metastatic nodules. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung tissues was used to look for micrometastatic foci. | |||
Prostacyclin synthase (PTGIS)
Gefitinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Protein Atg16l2 (ATG16L2)
Dac51
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetes | ICD-11: 5A10-5A14 | ||
| In-vitro Model | MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
Threonylcarbamoyladenosine tRNA methylthiotransferase (CDKAL1)
Fluorouracil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [182] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
Transducin-like enhancer protein 1 (TLE1)
Phenethyl isothiocyanate
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [184] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 |
| NCI-H226 | Pleural epithelioid mesothelioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1544 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were purchased from the Cancer Institute of the Chinese Academy of Medical Science (Beijing, China). Mice were randomly divided into two groups (eight mice per group), and 3×106 H1299 or H1299-LV-FTO-KD cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank of each mouse. For each group, four mice were treated with PEITC (100 mg/kg) intraperitoneally every two days for 14 days beginning the fifth week after cell injection, while the other four mice were treated with PBS as a control. At the end of the experiment, mice were euthanized, and tumor tissues were dissected for further analysis. Tumor weights were measured, and volumes were calculated (V = D/2 × d2, V: volume; D: longitudinal diameter; d: latitudinal diameter). | |||
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1 (SIRPA)
Gefitinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Ubiquitin thioesterase OTUB1 (OTUB1)
Erastin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [185] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6B | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | C666-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7949 |
| HONE-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8706 | |
| In-vivo Model | Three- to four-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were obtained from Guangxi Medical University Laboratory Animal Center and maintained under SPF housing. NPC cells were resuspended in 100 μl of PBS and injected subcutaneously into the flanks of the nude mice. Mice were randomized to experimental groups 28 days after implantation and were injected intraperitoneally with the same volume of FB23-2 (2 mg/kg) or erastin (10 mg/kg) or vehicle every three days during radiation (4 Gy, once a week). The endpoint of all experiments was tumor size. | |||
FB23-2
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [185] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6B | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | C666-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7949 |
| HONE-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8706 | |
| In-vivo Model | Three- to four-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were obtained from Guangxi Medical University Laboratory Animal Center and maintained under SPF housing. NPC cells were resuspended in 100 μl of PBS and injected subcutaneously into the flanks of the nude mice. Mice were randomized to experimental groups 28 days after implantation and were injected intraperitoneally with the same volume of FB23-2 (2 mg/kg) or erastin (10 mg/kg) or vehicle every three days during radiation (4 Gy, once a week). The endpoint of all experiments was tumor size. | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Arsenite
[Phase 2]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [186] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HBE (Human bronchial epithelial cell line) | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification on RNA was significantly increased in arsenite-transformed cells and this modification was synergistically regulated by METTL3, METTL14, WTAP and FTO. Demonstrated the significant role of m6A in the prevention of tumor occurrence and progression induced by arsenite. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [216] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neurological disorders due to toxicity | ICD-11: 8D43 | ||
| In-vitro Model | PC-12 Adh | Rat adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_F659 |
| In-vivo Model | The animals were kept in standard laboratory polycarbonate cages in controlled ambient temperature at 23℃ ± 1℃ with relative humidity of 50% ± 10%, and a light-dark cycle of 12/12 h. The mice had free access to standardized pellet food and tap water. After 1-week of habituation, the animals were randomly divided into the following 4 groups: control group, 0.5 mg/l arsenite group, 5 mg/l arsenite group and 50 mg/l arsenite group (n = 16 per group). The mice were exposed to arsenite via drinking water for 6 months. | |||
| Response Summary | Targeting the m6A demethylase FTO in the prevention or intervention against arsenite-related neurodegenerative diseases. | |||
Saikosaponins
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [191] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Cell-cycle | ||||
| In-vitro Model | C1498 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_3494 |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| MOLM-14 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7916 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| SKNO-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2196 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | Upon the development of leukemic disease (established using a white blood cell (WBC) count), 0.1 mg/kg or 0.5 mg/kg of SsD was intraperitoneally injected three times per week for three consecutive weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | FTO-dependent m6A RNA methylation mediated the anti-leukemic actions of saikosaponin-d, thereby opening a window to develop SsD as an epitranscriptome-base drug for leukemia therapy. SsD showed a broadly-suppressed acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest both in vitro and in vivo. | |||
Berberine
[Phase 4]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [199] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| In-vivo Model | 5 × 105 HCT116 CSCs were subcutaneously injected into the mice similarly as nude mice. Seven days later, 5, 10, or 20 mg/kg Berberine was intraperitoneally injected. The same volume of PBS was injected and considered as negative control. | |||
| Response Summary | Berberine effectively decreased m6A methylation by decreasing beta-catenin and subsequently increased FTO suggests a role of Berberine in modulating stemness and malignant behaviors in colorectal cancer. | |||
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [218] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ototoxic hearing loss | ICD-11: AB53 | ||
| Cell Process | Oxidative stress | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEI-OC1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_D899 |
| Response Summary | MA2, which is a highly selective inhibitor of FTO, has a protective effect and improves the viability of HEI-OC1 cells after cisplatin treatment, and they provide new insights into potential therapeutic targets for the amelioration of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. | |||
Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [218] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ototoxic hearing loss | ICD-11: AB53 | ||
| Cell Process | Oxidative stress | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEI-OC1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_D899 |
| Response Summary | MA2, which is a highly selective inhibitor of FTO, has a protective effect and improves the viability of HEI-OC1 cells after cisplatin treatment, and they provide new insights into potential therapeutic targets for the amelioration of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. | |||
Sunitinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [223] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| In-vitro Model | hiPSCs (Urinary epithelial cell-derived hiPSCs) | |||
| CMECs (Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells ) | ||||
| CFs (Cardiac Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Response Summary | The RNA demethylase FTO was downregulated, whereas METTL14 and WTAP were upregulated. Furthermore, gain- and loss-of-function studies substantiated that FTO is cardioprotective in TKI(Sunitinib). | |||
Betaine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [224] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | ICD-11: DB92 | ||
| In-vivo Model | Eight adult female C57BL/6 mice from the same pool of litters were housed at 22 ± 1 ℃ with 12-h light cycle and were mated with their male siblings. The female mice were fed with a low-fat diet supplemented with betaine from mating and throughout gestation and lactation. Litters were culled to five males per dam. Thirty offspring weaned at the age of day 21 and then were randomly assigned to three groups fed with either a low-fat diet (LF), high-fat diet (HF), or high-fat diet supplemented with betaine (HB) for 6 weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | A novel FTO-dependent function of m(6)A is involve in the hepatoprotective effects of betaine. betaine supplementation across adolescence could protect mice from high-fat-induced lipid accumulation NAFLD in the liver. Moreover, FTO-dependent m6A demethylation is affected by betaine. A novel FTO-dependent function of m(6)A may involve in the hepatoprotective effects of betaine. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
RNA modification
m6A Target: RNA cytosine C(5)-methyltransferase NSUN2 (NSUN2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00016 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA cytosine C(5)-methyltransferase NSUN2 (NSUN2) | |
| Regulated Target | Secreted frizzled related protein 1 (SFRP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
m6A Target: Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00027 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Gln (anticodon TTG) 1-1 (TRQ-TTG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Drug | AVI-5126 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00029 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Arg (anticodon CCG) 1-1 (TRR-CCG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Drug | AVI-5126 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00031 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Thr (anticodon CGT) 1-1 (TRT-CGT1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Drug | AVI-5126 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00045 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Drug | AVI-5126 | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein D1 (FOXD1)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00033 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Gln (anticodon TTG) 1-1 (TRQ-TTG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00035 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Arg (anticodon CCG) 1-1 (TRR-CCG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00037 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Thr (anticodon CGT) 1-1 (TRT-CGT1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00046 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | Forkhead box protein D1 (FOXD1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
m6A Target: Small ribosomal subunit protein mS38 (AURKAIP1)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00039 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Gln (anticodon TTG) 1-1 (TRQ-TTG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00041 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Arg (anticodon CCG) 1-1 (TRR-CCG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00043 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Thr (anticodon CGT) 1-1 (TRT-CGT1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00047 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | Small ribosomal subunit protein mS38 (AURKAIP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
m6A Target: Copper-transporting ATPase 1 (ATP7A)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00048 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | Copper-transporting ATPase 1 (ATP7A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
m6A Target: DNA excision repair protein ERCC-5 (ERCC5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00049 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | DNA excision repair protein ERCC-5 (ERCC5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
m6A Target: NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00479 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 155 (MIR155) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00518 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 221 (MIR221) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
m6A Target: Protein c-Fos (FOS)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00519 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 221 (MIR221) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00536 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 26a-1 (MIR26A1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
m6A Target: hsa-mir-22
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00633 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase B2 (ADARB2) | |
| Regulated Target | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00634 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Zinc finger protein SNAI1 (SNAI1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00635 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA cytosine C(5)-methyltransferase NSUN2 (NSUN2) | |
| Regulated Target | H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
m6A Target: microRNA 576 (MIR576)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00655 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00656 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit DKC1 (DKC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Pseudouridine | |
DNA modification
m6A Target: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha/PPARA)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02019 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02020 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02021 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
m6A Target: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02052 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Ossification of spinal ligaments | |
m6A Target: Glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02078 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02082 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
m6A Target: Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 (CREB1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02079 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02083 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
m6A Target: BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor (NTRK2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02080 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02084 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
m6A Target: Neurotrophic factor BDNF precursor form (BDNF)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02081 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02085 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
m6A Target: Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02111 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02112 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
Histone modification
m6A Target: HOXC13 antisense RNA (HOXC13-AS)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03068 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03086 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Diabetic retinopathy | |
| Drug | FB23-2 | |
m6A Target: Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03124 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Vorinostat | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05215 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Trichostatin A | |
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03179 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Ageing-related disease | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06001 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Ageing-related disease | |
m6A Target: Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03198 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 dimethylation (H3K4me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03199 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | |
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (G9a)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03231 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (EHMT2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Neuropathic pain | |
m6A Target: Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03431 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03447 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4)
| In total 6 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03432 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Rapamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03433 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | GLS-IN-968 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03434 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | CB-839 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03435 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03436 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Chloroquine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03437 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | |
m6A Target: Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
| In total 6 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03438 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Rapamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03439 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | GLS-IN-968 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03440 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | CB-839 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03441 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03442 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Chloroquine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03443 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | |
m6A Target: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03444 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03445 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03446 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Metastasis-associated protein MTA1 (MTA1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03448 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Apoptosis regulatory protein Siva (SIVA1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03449 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Fluorouracil | |
m6A Target: Hexokinase-2 (HK2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03450 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Maternally expressed 3 (MEG3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05951 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Abortion | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Target: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05072 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Urothelial cancer associated 1 (UCA1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | DOX-induced cardiotoxicity | |
m6A Target: Dynamin-1-like protein (DRP1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05099 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | ZNFX1 antisense RNA 1 (ZFAS1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute ischemic stroke | |
m6A Target: Circ_GPR137B
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05119 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-4739 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05120 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_GPR137B | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-4739 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Dickkopf-related protein 2 (DKK2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05125 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_CELF1 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Myocardial Fibrosis | |
m6A Target: Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
| In total 10 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05127 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-let-7b-5p | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05163 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 858 (LINC00858) | |
| Regulated Target | Zinc finger protein 184 (ZNF184) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05181 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-218-5p | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05182 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0001739 (Circ_ZNF277) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-218-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05183 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | AC159540.1 | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-218-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05237 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05251 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05320 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-96 | |
| Regulated Target | Protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 2 (PRKAA2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05437 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 23a (MIR23A) | |
| Regulated Target | Max-interacting protein 1 (MXI1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Brain cancer | |
| Drug | Temozolomide | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05438 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 155 (MIR155) | |
| Regulated Target | Max-interacting protein 1 (MXI1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Brain cancer | |
| Drug | Temozolomide | |
m6A Target: Estrogen receptor (ESR1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05171 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-3492 | |
| Regulated Target | Estrogen receptor (ESR1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Intraflagellar transport protein 80 homolog (IFT80)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05179 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | H2AZ2 pseudogene 1 (H2AZ2P1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma | |
m6A Target: Zinc finger protein SNAI1 (SNAI1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05201 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | GATA6 antisense RNA 1 (head to head) (GATA6-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
m6A Target: Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05225 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | piR-17560 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 (SERCA2a/ATP2A2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05226 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cardiac conduction regulatory RNA (CCRR) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myocardial infarction | |
m6A Target: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 (USP7)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05235 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | P5091 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05236 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05249 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | P5091 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05250 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor E2F1 (E2F1)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05238 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05242 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05252 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05256 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05239 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05253 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 10 (ABCC10)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05240 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05254 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
m6A Target: Protein kinase C-binding protein NELL2 (NELL2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05241 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05255 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05243 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05257 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05646 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5) | |
| Regulated Target | Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Prolyl endopeptidase FAP (FAP)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05244 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | VS-6063 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05258 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | VS-6063 | |
m6A Target: Transducin-like enhancer protein 1 (TLE1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05245 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Phenethyl isothiocyanate | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05259 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Phenethyl isothiocyanate | |
m6A Target: Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane protein FLRT3 (FLRT3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05246 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05260 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
m6A Target: Prostacyclin synthase (PTGIS)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05247 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05261 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
m6A Target: Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1 (SIRPA)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05248 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05262 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Gefitinib | |
m6A Target: Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05314 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | FTO intronic transcript 1 (FTO-IT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Glucose transporter type 1 (SLC2A1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05315 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | FTO intronic transcript 1 (FTO-IT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05338 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-27a-3p | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Glioblastoma multiforme | |
m6A Target: PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1a/PPARGC1A)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05346 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 155 (MIR155) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | |
m6A Target: Myosin heavy chain associated RNA transcript (MHRT)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05472 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Myosin heavy chain associated RNA transcript (MHRT) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Congestive heart failure | |
| Drug | Doxorubicin | |
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05477 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Kidney failure | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05514 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05567 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 384 (MIR384) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
m6A Target: Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05478 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Kidney failure | |
m6A Target: Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2/LINC00022)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05519 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2/LINC00022) | |
| Regulated Target | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
m6A Target: HOXC13 antisense RNA (HOXC13-AS)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05520 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | HOXC13 antisense RNA (HOXC13-AS) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: microRNA 576 (MIR576)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05536 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 576 (MIR576) | |
| Regulated Target | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-181b-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05579 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-181b-3p | |
| Regulated Target | ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 5B (ARL5B) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: pri-miR-10a
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05603 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | pri-miR-10a | |
| Regulated Target | Myotubularin related protein 3 (MTMR3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Brain cancer | |
m6A Target: AC008440.5 (AC008)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05619 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | AC008440.5 (AC008) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-328-3p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Osteoarthritis | |
m6A Target: microRNA 155 (MIR155)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05651 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 155 (MIR155) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury | |
m6A Target: Circ_SETD2
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05658 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_SETD2 | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-181a-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pre-eclampsia | |
m6A Target: pri-miR-3591
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05685 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 3591 | |
| Regulated Target | Protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 2 (PRKAA2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Osteoarthritis | |
m6A Target: Maternally expressed 3 (MEG3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05727 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Maternally expressed 3 (MEG3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Acute ischemic stroke | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05830 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Maternally expressed 3 (MEG3) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Abortion | |
m6A Target: Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1139 (LINC01139)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05748 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1139 (LINC01139) | |
| Regulated Target | Minichromosome maintenance complex component 3 (MCM3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-515-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05772 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-515-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Osteoarthritis | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-383-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05775 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-383-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Integrin subunit alpha 3 (ITGA3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-mir-22
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05779 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-mir-22 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: microRNA 7-1 (MIR7-1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05780 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 7-1 (MIR7-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: MIRLET7E
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05781 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MIRLET7E | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05872 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_RAB11FIP1 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
m6A Target: Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme ATG7 (ATG7)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05873 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_RAB11FIP1 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
m6A Target: CAP-Gly domain-containing linker protein 3 (CLIP3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05874 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 145 (MIR145) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Glioblastoma | |
m6A Target: PDH kinase 1 (PDK1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05968 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long non-coding RNA just proximal to the X-inactive specific transcript (JPX) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Glioblastoma multiforme | |
| Drug | Temozolomide | |
Xenobiotics Compound(s) Regulating the m6A Methylation Regulator
| Compound Name | MA2 | Approved |
|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid (MA)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| Description |
MA2, which is a highly selective inhibitor of FTO, has a protective effect and improves the viability of HEI-OC1 cells after cisplatin treatment, and they provide new insights into potential therapeutic targets for the amelioration of cisplatin-inducedototoxicity.
|
[218] |
| Compound Name | Rapamycin | Approved |
| Synonyms |
Rapamune; Rapamycin (Sirolimus); AY-22989; Rapammune; sirolimusum; WY-090217; RAPA; Antibiotic AY 22989; AY 22989; UNII-W36ZG6FT64; CCRIS 9024; CHEBI:9168; SILA 9268A; W36ZG6FT64; HSDB 7284; C51H79NO13; NSC 226080; DE-109; NCGC00021305-05; DSSTox_CID_3582; DSSTox_RID_77091; DSSTox_GSID_23582; Cypher; Supralimus; Wy 090217; Perceiva; RAP; RPM; Rapamycin from Streptomyces hygroscopicus; SIIA 9268A; LCP-Siro; MS-R001; Rapamune (TN); Rapamycin (TN); Sirolimus (RAPAMUNE); Rapamycin C-7, analog 4; Sirolimus (USAN/INN); Sirolimus [USAN:BAN:INN]; Sirolimus, Rapamune,Rapamycin; Heptadecahydro-9,27-dihydroxy-3-[(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy; 23,27-Epoxy-3H-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclohentriacontine; 23,27-Epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine; 23,27-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29; 3H-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone; Sirolimus (MTOR inhibitor)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
The m6A changes caused by FTO influence the stability of ULK1 transcripts, likely through a YTHDF2-dependent manner.Under both basal and rapamycin-induced autophagy conditions, depletion of FTO significantly reduced the formation of GFP-LC3B puncta. The level ofp62/SQSTM1 (an autophagy substrate) was higher in FTO-knockdown cells than that in control cells. FTO specifically upregulates the ULK1 protein abundance. ULK1 mRNA undergoes m6A modification in the 3'-UTR and the m6A-marked ULK1 transcripts can further be targeted for degradation by YTHDF2.
|
[53] |
| Compound Name | Meclofenamic Acid | Approved |
| Synonyms |
Arquel; Meclofenamate; Acide meclofenamique; Acido meclofenamico; Acidum meclofenamicum; Meclophenamic acid; CL 583; INF 4668; Acide meclofenamique [INN-French]; Acido meclofenamico [INN-Spanish]; Acidum meclofenamicum [INN-Latin]; INF-4668; Meclomen (free acid); Meclofenamic acid (USAN/INN); Meclofenamic acid [USAN:INN:BAN]; N-(2,6-Dichloro-3-methylphenyl)anthranilic acid; N-(2,6-Dichloro-m-tolyl)anthranilic acid; N-(3-Methyl-2,6-dichlorophenyl)anthranilic acid; 2-((2,6-Dichloro-3-methylphenyl)amino)benzoic acid; 2-(2,6-Dichloro-3-methylphenyl)aminobenzoic acid; 2-(2,6-dichloro-3-methylanilino)benzoic acid; 2-[(2,6-dichloro-3-methylphenyl)amino]benzoic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especiallyLILRB4. FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibitacute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability.
|
[30] |
| Compound Name | Fluorescite | Approved |
| Synonyms |
Funduscein-25; Ak-fluor 10%; Ak-fluor 25%; Fluorescite
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especiallyLILRB4. FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibitacute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability.
|
[30] |
| Compound Name | Comtan | Approved |
| Synonyms |
Comtan; Comtess; Entacapona; Entacaponum; Novartis brand of entacapone; Orion brand of entacapone; KB475572; OR 611; COM-998; Comtan (TN); Entacapona [INN-Spanish]; Entacapone [USAN:INN]; Entacaponum [INN-Latin]; OR-611; Stalevo (TN); Entacapone (JAN/USAN/INN); N,N-diethyl-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl) acrylamide; (2E)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethylprop-2-enamide; (E)-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethyl-2-propenamide; (E)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitro-phenyl)-N,N-diethyl-prop-2-enamide; (E)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethylprop-2-enamide; (E)-alpha-Cyano-N,N-diethyl-3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrocinnamamide; 2-Cyano-N,N-diethyl-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)propenamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators inbreast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such asBcl-2 and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis.
|
[4] |
| Compound Name | Berberine | Phase 4 |
| Synonyms |
Berberin; Umbellatine; UNII-0I8Y3P32UF; 0I8Y3P32UF; CHEBI:16118; EINECS 218-229-1; Berberal; BRN 3570374; ST055798; 9,10-Dimethoxy-2,3-(methylenedioxy)-7,8,13,13a-tetrahydroberbinium; Benzo(g)-1,3-benzodioxolo(5,6-a)quinolizinium, 5,6-dihydro-9,10-dimethoxy-; 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium; Berbamine sulphate acid; CHEMBL12089; 7,8,13,13a-tetradehydro-9,10-dimethoxy-2,3-(methylenedioxy)berbinium; BERBINIUM, 7,8,13,13a-TETRAHYDRO-9,10-DIMETHOXY-2,3-(METHYLE
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Berberine effectively decreased m6A methylation by decreasing beta-catenin and subsequently increased FTO suggests a role of Berberine in modulating stemness and malignant behaviors incolorectal cancer.
|
[199] |
| Compound Name | Bisantrene | Phase 3 |
| Synonyms |
Bisantrenum; CL 216942; CHEMBL25336; NSC 337766; 39C34M111K; N-[(E)-[10-[(E)-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylhydrazinylidene)methyl]anthracen-9-yl]methylideneamino]-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-amine; 9,10-Bis((2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)anthracene; Bisantrene [INN]; Bisantrenum [INN-Latin]; 9,10-Bis(2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)anthracene; Bisantreno [INN-Spanish]; NSC337766; NSC-337766; BRN 0966309; 9,10-Anthracenedicarboxaldehyde, bis((4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)hydrazone)-; 9,10-Anthracendicarbaldehyde bis(2-imidazolin-2-ylhydrazon); 9,10-Anthracenedicarboxaldehyde, bis[(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)hydrazone], dihydrochloride; SCHEMBL8906393; 9,10-bis((E)-(2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)anthracene; EX-A2382; ZINC1550957; BDBM50060768; CCG-35603; MFCD01743164; CS-6132; AS-75775; N-[(E)-[10-[(E)-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylhydrazono)methyl]-9-anthryl]methyleneamino]-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-amine; HY-100875; 186B342; BRD-K64298650-300-01-5; 9,10-Anthracenedicarboxaldehyde Bis(2-imidazolin-2-yl-hydrazone); 9,10-Anthracenedicarbaldehyde bis(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylhydrazone); anthracene-9,10 bis-carbaldehyde 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylhydrazone; 9,10-anthracenedicarboxaldehyde Bis[(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2yl)hydrazone); 9,10-Anthracenedicarboxaldehyde, bis(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylhydrazone),dihydrochloride; N-Anthracen-9-yl methylene N''-[(bis)4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-2-yl)-hydrazine; N-Anthracen-bis-9,10-ylmethylene-N''-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-hydrazine(bisantrene); 10-imino(4,5-dihydro-1H-2-imidazolamine)methyl-9-anthrylmethan-(4,5-dihydro-1H-2-imidazolamine)imine; Bis((4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)hydrazone)-9,10-anthracenedicarboxaldehyde dihydrochloride; x N-4,5-dihydro-1H-2-imidazolamine-10-iminomethyl-9-anthrylmethanimine-4,5-dihydro-1H-2-imidazolamine (Bisantrene)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especiallyLILRB4. FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibitacute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability.
|
[30] |
| Compound Name | Brequinar | Phase 2 |
| Synonyms |
6-Fluoro-2-(2'-fluoro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-3-methylquinoline-4-carboxylic acid; brequinarum [Latin]; Brequinar [INN]; Biphenquinate; 6-fluoro-2-(2'-fluorobiphenyl-4-yl)-3-methylquinoline-4-carboxylic acid; Brequinarum [INN-Latin]; UNII-5XL19F49H6; C23H15F2NO2; NSC-368390; NSC 368390; 6-fluoro-2-[4-(2-fluorophenyl)phenyl]-3-methylquinoline-4-carboxylic acid; PHEZJEYUWHETKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N; Dup 785; 5XL19F49H6; 6-FLUORO-2-(2'-FLUORO-1,1'-BIPHENYL-4-YL)-3-METHYLQUINOLINE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID; brequinarum
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especiallyLILRB4. FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibitacute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability.
|
[30] |
| Compound Name | 3DZA | Terminated |
| Synonyms |
Cc3Ado; BW-91Y78; 3DZA; 4-Amino-1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators inbreast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such asBcl-2 and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis.
|
[4] |
| Compound Name | FB23 | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
FB23; 2243736-35-6; 2-[[2,6-bis(chloranyl)-4-(3,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)phenyl]amino]benzoic acid; CHEMBL4572939; SCHEMBL23261118; BCP33227; EX-A3402; FB-23;FB 23; s6291; HY-137187; CS-0136974; A936869; 2-[[2,6-Dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethyl-4-isoxazolyl)phenyl]amino]benzoic acid; 8S3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 = 60 nM
|
[230] |
| Compound Name | (Z)-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-2-pyrazin-2-ylprop-2-enenitrile | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4448030; SCHEMBL20100848
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 250 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | 5-[(Z)-1-cyano-2-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)ethenyl]pyrazine-2-carboxylic acid | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4563060; SCHEMBL21932996
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 300 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | 2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)-N-[2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]aniline | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4532629
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 = 400 nM
|
[230] |
| Compound Name | (Z)-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-2-pyrimidin-4-ylprop-2-enenitrile | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4527360; SCHEMBL20100853
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 500 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | (Z)-3-amino-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethylprop-2-enamide | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4567049; SCHEMBL20100829
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 500 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | (Z)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-3-hydroxy-N-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)prop-2-enamide | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4435468; SCHEMBL20100862
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 500 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | (Z)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxyprop-2-enamide | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4461072; SCHEMBL20100822
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 500 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-pyrimidin-4-ylprop-2-enenitrile | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4467308; SCHEMBL20100828
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 500 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazin-2-ylprop-2-enenitrile | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4529597; SCHEMBL20100823
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 500 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | 2-[2,6-Dichloro-4-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)anilino]benzoic acid | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4563024
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 = 700 nM
|
[230] |
| Compound Name | (Z)-2-(azetidine-1-carbonyl)-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-3-hydroxyprop-2-enenitrile | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4458750; SCHEMBL20100880
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 750 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | 5-[(E)-1-cyano-2-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-2-hydroxyethenyl]pyrazine-2-carboxylic acid | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4463923; SCHEMBL21933009
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 750 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | (Z)-3-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-2-(piperidine-1-carbonyl)prop-2-enenitrile | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4590326; SCHEMBL20100883
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 750 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-pyridin-2-ylprop-2-enenitrile | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4569935; SCHEMBL20100854
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 <= 750 nM
|
[231] |
| Compound Name | Beta-hydroxybutyrate | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
3-hydroxybutanoate; beta-hydroxybutyrate; beta-hydroxybutanoate; 3-OH butyrate; 3-OH-butyrate; beta-hydroxy-n-butyrate; UNII-FG2UN5EP9V; FG2UN5EP9V; DL-3-Hydroxybutyrate; DTXSID9040976; CHEBI:37054; BDBM50270275; Butanoic acid, 3-hydroxy-, ION(1-); Q27117026; 151-03-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
FTO fails to bind to its own promoter that promotes FTO expression in the hypothalamus ofhigh-fat diet-induced obese and 48-h fasting mice, suggesting a disruption of the stable expression of this gene.ketogenic diet-derived ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) transiently increases FTO expression in both mouse hypothalamus and cultured cells.
|
[210] |
| Compound Name | FB23-2 | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
FB23-2; 2243736-45-8; 2-((2,6-Dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)-N-hydroxybenzamide; 2-[2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)anilino]-N-hydroxybenzamide; CHEMBL4567838; SCHEMBL23261120; BCP31164; EX-A3403; MFCD32174281; s8837; HY-127103; CS-0093102; FB23-2(FTO Demethylase inhibitor FB23-2); D81008; A936868; FB-23-2; FB 23-2; FB232; FB-232; FB 232; 2-{[2,6-Dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)phenyl]amino}-N-hydroxybenzamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
FTO is a druggable target and that targeting FTO by small-molecule inhibitors(FB23 and FB23-2) holds potential to treatacute myeloid leukemia.
|
[193] |
| Compound Name | DEHP | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
DEHP; 117-81-7; BIS(2-ETHYLHEXYL)PHTHALATE; Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate; Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; Diethylhexyl phthalate; 2-Ethylhexyl phthalate; Di-sec-octyl phthalate; Octyl phthalate; Fleximel; Octoil; Ethylhexyl phthalate; Palatinol AH; Celluflex DOP; Vestinol AH; Bisoflex DOP; Kodaflex DOP; Staflex DOP; Truflex DOP; Flexol DOP; Vinicizer 80; Bisoflex 81; Eviplast 80; Eviplast 81; Hercoflex 260; RC plasticizer DOP; Compound 889; Witcizer 312; Platinol dop; Di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate; Nuoplaz dop; Platinol ah; Hatcol dop; Reomol dop; Pittsburgh PX-138; Sansocizer DOP; Ergoplast FDO; Monocizer DOP; Plasthall DOP; Flexol plasticizer DOP; Mollan O; Jayflex DOP; Sicol 150; Ergoplast FDO-S; Di(2-ethylhexyl)orthophthalate; Good-rite gp 264; Reomol D 79P; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate; Di(ethylhexyl) phthalate; Bis(ethylhexyl) phthalate; Rcra waste number U028; Px-138; Phthalic acid dioctyl ester; NCI-C52733; Di(2-ethylhexyl) o-phthalate; Phthalic acid di(2-ethylhexyl) ester; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester; DOP; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) 1,2-benzenedicarboxylate; UNII-C42K0PH13C; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) o-phthalate; Phthalic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester; CHEBI:17747; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester; Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester; Phthalic Acid Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Ester; Bis-(2-ethylhexyl)ester kyseliny ftalove; C42K0PH13C; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, 1,2-bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester; DTXSID5020607; Etalon; Bis-(2-ethylhexyl)ester kyseliny ftalove [Czech]; Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; BIS-(2-ETHYLHEXYL) PHTHALATE; NCGC00091499-05; Sconamoll DOP; Diacizer DOP; Kodaflex DEHP; 15495-94-0; Etalon (plasticizer); Sansocizer R 8000; Caswell No. 392K; Dioctylphthalate; Behp; Di-2-ethylhexylphthalate; Diplast O; ESBO-D 82; Ergoplast FDO; Ergoplast FDO-S; Etalon; Phthalic acid, bis-2-ethylhexyl ester; DOF [Russian plasticizer]; SMR000777878; CCRIS 237; Ethyl hexyl phthalate; HSDB 339; Di(2-ethylhexyl) orthophthalate; Bis-(2-ethylhexyl)ester kyseliny ftalove (czech); EINECS 204-211-0; NSC 17069; Diethylhexylphthalate (Bis-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate); RCRA waste no. U028; Union carbide flexol 380; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 295200; BRN 1890696; AI3-04273; DAF 68; Palatinol DOP; Polycizer DOP; Merrol DOP; Palatinol AH-L; Hatco DOP; Vinycizer 80; Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP); N-Dioctyl phthalate; MFCD00009493; Corflex 400; Dioctyl phthalate, 99%; DSSTox_CID_607; 1, bis(ethylhexyl) ester; Epitope ID:140107; EC 204-211-0; WLN: 8OVR BVO8; Di(2-Ethylhexyl phthalate); DSSTox_RID_75688; DSSTox_GSID_20607; SCHEMBL20271; 14C -DEHP; 8033-53-2; MLS001333173; MLS001333174; MLS002454397; Dioctyl phthalate, >=99.5%; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis-(1-ethylhexyl) ester; CHEMBL1242017; SCHEMBL21733281; HMS2233C15; HMS3374J09; AMY40790; HY-B1945; NSC17069; Tox21_400084; Bis(2-ethylhexyl)ester phthalic acid; NSC-17069; s3360; AKOS024318875; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-[13C6]; Phthalic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl ester); MCULE-4692716107; NCGC00091499-01; NCGC00091499-02; NCGC00091499-04; NCGC00091499-06; NCGC00091499-07; CAS-117-81-7; I887; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylate; CS-0014050; FT-0624576; FT-0663286; P0297; WLN: 4Y2 & 1OVR BVO1Y4 & 2; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, Selectophore(TM); C03690; A937603; Q418492; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid bis-(1-ethylhexyl) ester; benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester; BRD-A89471977-001-05-2; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate 100 microg/mL in Methanol; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate 5000 microg/mL in Methanol; F0001-0292; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, SAJ first grade, >=98.0%; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, PESTANAL(R), analytical standard; Phthalic acid, bis-2-ethylhexyl ester 10 microg/mL in Cyclohexane; Plastic additive 01, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, certified reference material, TraceCERT(R); Plastic additive 14, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester, labeled with carbon-14; 50885-87-5; 82208-43-3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
DEHP worsened testicular histology, decreased testosterone concentrations, downregulated expression of spermatogenesis inducers, enhanced oxidative stress, inhibited theNrf2-mediated antioxidant pathway, and increased apoptosis in testes. DEHP is a common environmental endocrine disrupting chemical that inducesmale reproductive disorders. Additionally, DEHP increased global levels of m6A RNA modification and altered the expression of two important RNA methylation modulator genes, FTO and YTHDC2.
|
[110] |
| Compound Name | Rhein | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
Monorhein; Rheic acid; Rhubarb Yellow; Cassic acid; 4,5-Dihydroxyanthraquinone-2-carboxylic acid; Chrysazin-3-carboxylic acid; 4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxylic acid; NSC 38629; Rheinic acid; 1,8-Dihydroxyanthraquinone-3-carboxylic acid; dipropionyl rhein; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-carboxyanthraquinone; UNII-YM64C2P6UX; Rhein(Monorhein); 2-Anthracenecarboxylic acid, 9,10-dihydro-4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-; CCRIS 5129; 9,10-Dihydro-4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-2-anthracenecarboxylic acid; C15H8O6
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especiallyLILRB4. FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibitacute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability.
|
[30] |
| Compound Name | MO-I-500 | Investigative |
| Description |
Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especiallyLILRB4. FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibitacute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability.
|
[30] |
| Compound Name | R-2HG | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
(R)-2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid; 13095-47-1; D-2-Hydroxyglutaric acid; (R)-2-hydroxyglutaric acid; (R)-Hydroxyglutarate; (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate; Pentanedioic acid, 2-hydroxy-, (2R)-; CHEMBL1614745; CHEBI:32796; D-2-Hydroxyglutarate; Glutaric acid, 2-hydroxy-; d-alpha-hydroxyglutaric acid; D-Hydroxyglutarate; 2HG; D-a-Hydroxyglutarate; 2-hydroxy-D-Glutarate; (R)-a-Hydroxyglutarate; delta-2-Hydroxyglutarate; D-a-Hydroxyglutaric acid; 2-hydroxy-delta-Glutarate; D-; A-Hydroxyglutaric acid; (2R)-hydroxyglutaric acid; 2-hydroxy-D-Glutaric acid; (R)-alpha-Hydroxyglutarate; delta-alpha-Hydroxyglutarate; SCHEMBL8032; (R)-a-Hydroxyglutaric acid; delta-2-Hydroxyglutaric acid; (R)-2-hydroxy-Pentanedioate; 2-hydroxy-delta-Glutaric acid; (R)-alpha-Hydroxyglutaric acid; delta-alpha-Hydroxyglutaric acid; (R)-2-hydroxy-Pentanedioic acid; DTXSID80897218; ZINC402968; BDBM50361471; AKOS027325193; FD21404; BS-50252; HY-113038; CS-0059411; C01087; 93397C3E-3CE9-4FEA-A2ED-8F6FA59A1FEA; Q27104222; Z2217110365; 636-67-9
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especiallyLILRB4. FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibitacute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability.
|
[30] |
| Compound Name | Mehp | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
Mehp; Mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; PHTHALIC ACID MONO-2-ETHYLHEXYL ESTER; Mono(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate; 2-Ethylhexyl hydrogen phthalate; Monoethylhexyl phthalate; MONO-2-ETHYLHEXYL PHTHALATE; Mono-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate; 2-(2-ethylhexoxycarbonyl)benzoic acid; (2-Ethylhexyl) hydrogen phthalate; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, mono(2-ethylhexyl) ester; 2-{[(2-ethylhexyl)oxy]carbonyl}benzoic acid; Monoethylhexyl phthalic acid; Phthalic acid, mono-(2-ethylhexyl) ester; CHEBI:17243; PHTHALIC ACID MONOOCTYL ESTER; Phthalic acid mono-2-ethylhexylester; Phthalic acid, mono-2-ethylhexyl ester; NCGC00090773-04; 1276197-22-8; BAR 1; Phthalate, mono(2-ethylhexyl); CCRIS 1742; 2-([(2-Ethylhexyl)oxy]carbonyl)benzoic acid; rac Mono(ethylhexyl) Phthalate-d4; EINECS 224-477-1; mono(ethylhexyl) phthalate; mono-ethylhexyl; Mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; rac Mono(ethylhexyl) Phthalate; monoethylhexylphthalate; mono-ethylhexylphthalate; DSSTox_CID_5680; Phthalic acid, 2-ethylhexyl ester (6CI,7CI); DSSTox_RID_77879; DSSTox_GSID_25680; phthalicacidmonoethylhexylester; phthalicacid,2-ethylhexylester; SCHEMBL472689; mono-(2-ethyl)hexyl phthalate; PHTHALICACIDMONOETHYLHEXYL; CHEMBL1867438; DTXSID2025680; Monoethylhexyl phthalate (mEHP); phthalic acid, 2-ethylhexyl ester; Mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-d4; ACT03365; Tox21_400076; MFCD00041500; AKOS015902975; CS-W019178; HY-W018392; 2-(2-ethylhexyloxycarbonyl)benzoic acid; PHTHALICACIDMONO-2-ETHYLEXYLESTER; NCGC00090773-01; NCGC00090773-02; NCGC00090773-03; NCGC00090773-05; NCGC00090773-06; DS-16446; CAS-4376-20-9; DB-007821; 2-[(2S)-2-ethylhexoxy]carbonylbenzoic acid; FT-0600523; Phthalic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester liquid; Phthalic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester, 97%; W6291; C03343; Phthalic acid hydrogen 1-(2-ethylhexyl) ester; 2-([(2-Ethylhexyl)oxy]carbonyl)benzoic acid #; A826416; Phthalic acid 1-hydrogen 2-(2-ethylhexyl) ester; phthalic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester, AldrichCPR; 1,2-benzenedicarboxylicacid,mono(2-ethylhexyl)ester; BRD-A18246003-001-01-1; Q26841225; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, mono(2-ethylhexyl) ester (9CI); Phthalic acid, mono-2-ethylhexyl ester 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
The inhibition of FTO-mediated up-regulation of m6A could be involved in MEHP-inducedLeydig cell apoptosis.
|
[229] |
| Compound Name | Cycloleucine | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
1-Aminocyclopentanecarboxylic acid; 52-52-8; 1-Aminocyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid; Cycloleucin; 1-Amino-1-cyclopentanecarboxylic acid; 1-Amino-1-carboxycyclopentane; 1-Amino-cyclopentanecarboxylic acid; CYCLO-LEUCINE; Cyclopentanecarboxylic acid, 1-amino-; NSC 1026; CB 1639; X 201; UNII-0TQU7668EI; 1-Aminocyclopentanecarboxylate; HSDB 5195; WR 14,997; NSC1026; 1-amino cyclopentane carboxylic acid; EINECS 200-144-6; BRN 0636626; aminocyclopentanecarboxylic acid; Cyclopentanecarboxylic acid, 1-amino-, L-; AI3-26442
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Studies of the aberrant expression of m6A mediators inbreast cancer revealed that they were associated with different BC subtypes and functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, the cell cycle, migration, and metastasis, through several factors and signaling pathways, such asBcl-2 and the PI3K/Akt pathway, among others. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and a series of inhibitors that target FTO were reported to have potential for the treatment of BC by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis.
|
[4] |
| Compound Name | 4-amino-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
4-amino-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 4-Amino-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 3-Quinolinecarboxylicacid, 4-amino-; 4-aminoquinoline-3-carboxylic; SCHEMBL436714; DTXSID10470018; BBL031107; MFCD08705653; STK660776; ZINC14982158; AKOS002326679; MCULE-8408161492; SB67440; VS-10248; DB-081679; BB 0222277; CS-0248109; FT-0748901; Y9812; EN300-39148; J-514466; F2183-0223; Z398556732
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Inhibition of m6A RNA demethylation by small-molecule drugs, as presented here, has therapeutic potential and provides tools for the identification of disease-modifying m6A RNAs inneurogenesis and neuroregeneration. Small-molecule inhibitors of the RNA m6A demethylases FTO potently support the survival of dopamine neurons.
|
[212] |
References