m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00451)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
YAP1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | LNCaP cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 LNCaP cells
Control: shControl LNCaP cells
|
GSE147884 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.80E-01 p-value: 6.99E-58 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between YAP1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.22E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 4 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The expression of m6A and METTL3 was upregulated in human gastric cancer tissues and gastric cancer cell lines. m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promoted the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells through the m6A modification of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1). | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3-induced circ1662 promoted colorectal cancer cell invasion and migration by accelerating Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) nuclear transport. Circ1662 enhanced CRC invasion and migration depending on YAP1 and SMAD3. This result implies that circ1662 is a new prognostic and therapeutic marker for CRC metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c nude mice (4 weeks old) were acquired from Vital River Laboratory (Beijing, China). HCT116 cells with stable circ1662 expression (2 × 106 in 100 L of PBS) were injected via the tail vein. After 45 days, the mice were sacrificed. The lung metastatic carcinoma specimens were processed into paraffin-embedded sections for subsequent H&E staining and IHC. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methylation plays a key role in VM formation in HCC. METTL3 and Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) could be potential therapeutic targets via impairing VM formation in anti-metastatic strategies. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell migration and invasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | Homo sapiens (SK-HEP-1-Luc (luciferase labeled) cells were obtained from OBIO (Shanghai, China).) | |||
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1 × 107 SK-HEP-1-Luc-shControl or SK-HEP-1-Luc-shMETTL3 stable cells were suspended in 300 uL of PBS and injected orthotopically into the left liver lobe of nude mice. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF1 | ||
| Cell Line | AGS cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shYTHDF1 AGS
Control: shNC AGS
|
GSE166972 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 3.89E+00 p-value: 1.09E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between YAP1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | Hela | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.35E+00 | GSE63591 |
| In total 3 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of pre-miR-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B51 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 knockdown alleviated the progression of renal fibrosis both in cultured cells induced by transforming growth factor-beta administration and in the UUO mouse model. Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) was accordingly down-regulated when YTHDF1 was inhibited. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kidney disorders | ICD-11: GB90 | ||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF2 | ||
| Cell Line | GSC11 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siYTHDF2 GSC11 cells
Control: siControl GSC11 cells
|
GSE142825 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 7.52E-01 p-value: 2.51E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between YAP1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | Hela | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.34E+00 | GSE49339 |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of pre-miR-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B51 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 knockdown significantly increases the total YAP expression, but inhibits TGF-beta/Smad signaling, indicating that YTHDF2 regulates EMT probably via Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) signaling. YTHDF2 is a new predictive biomarker of development of pancreatic cancer. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cells proliferation | |||
| Cells migration | ||||
| Cells invasion | ||||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| PaTu 8988s | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1846 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 6.87E-01 p-value: 5.76E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Response Summary | Stable knockdown of FTO inhibited OSCC cell viability, colony formation, and tumor growth. Further, FTO depletion increased Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) m6A modification at mRNA 3'-untranslated region, accelerating the degradation of YAP1 mRNA, a well-documented oncogene promoting OSCC progression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO down-expressed in myocardial IRI mice and hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced cardiomyocytes. Moreover, FTO uninstalled the methylation of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) mRNA, and enforced the stability of Yap1 mRNA.The study reveals the role of FTO in H/R-induced myocardial cell injury via m6A-dependent manner, which provided a new approach to improve myocardial IRI. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemic heart disease | ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | Neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (Primary myocyte cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | After anesthesia (50 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium, intraperitoneal injection), the left thorax was cut to expose the heart, and the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery was ligated by 7/0 sterile suture. Myocardial ischemia was induced by 30 min of LAD coronary artery ligation and following 2 h of reperfusion. Sham group mice underwent the same surgical procedure without LAD coronary artery ligation. | |||
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
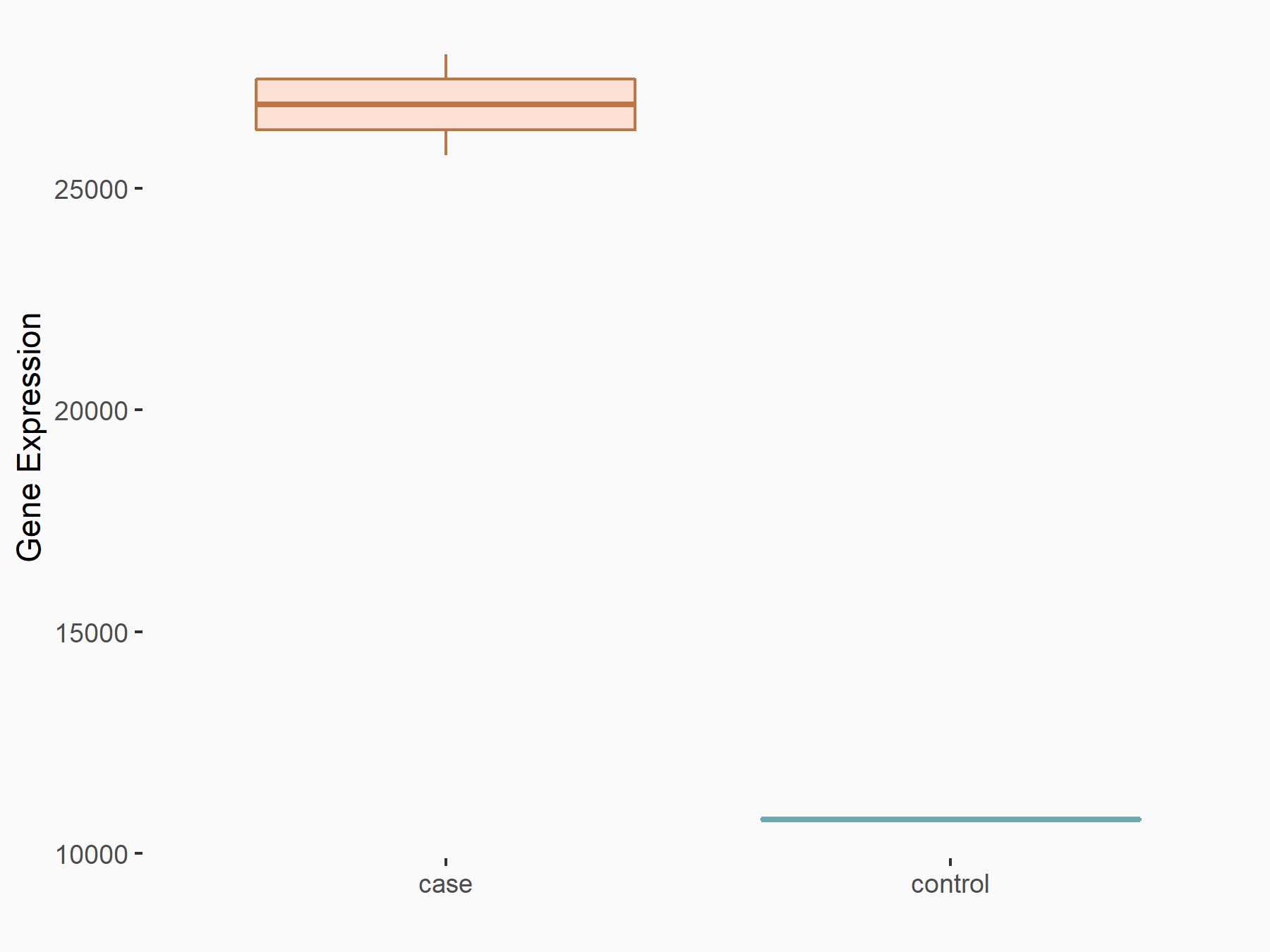  |
logFC: 1.32E+00 p-value: 8.59E-29 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes renal ischemic reperfusion injury via suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1). | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of kidney | ICD-11: NB92.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
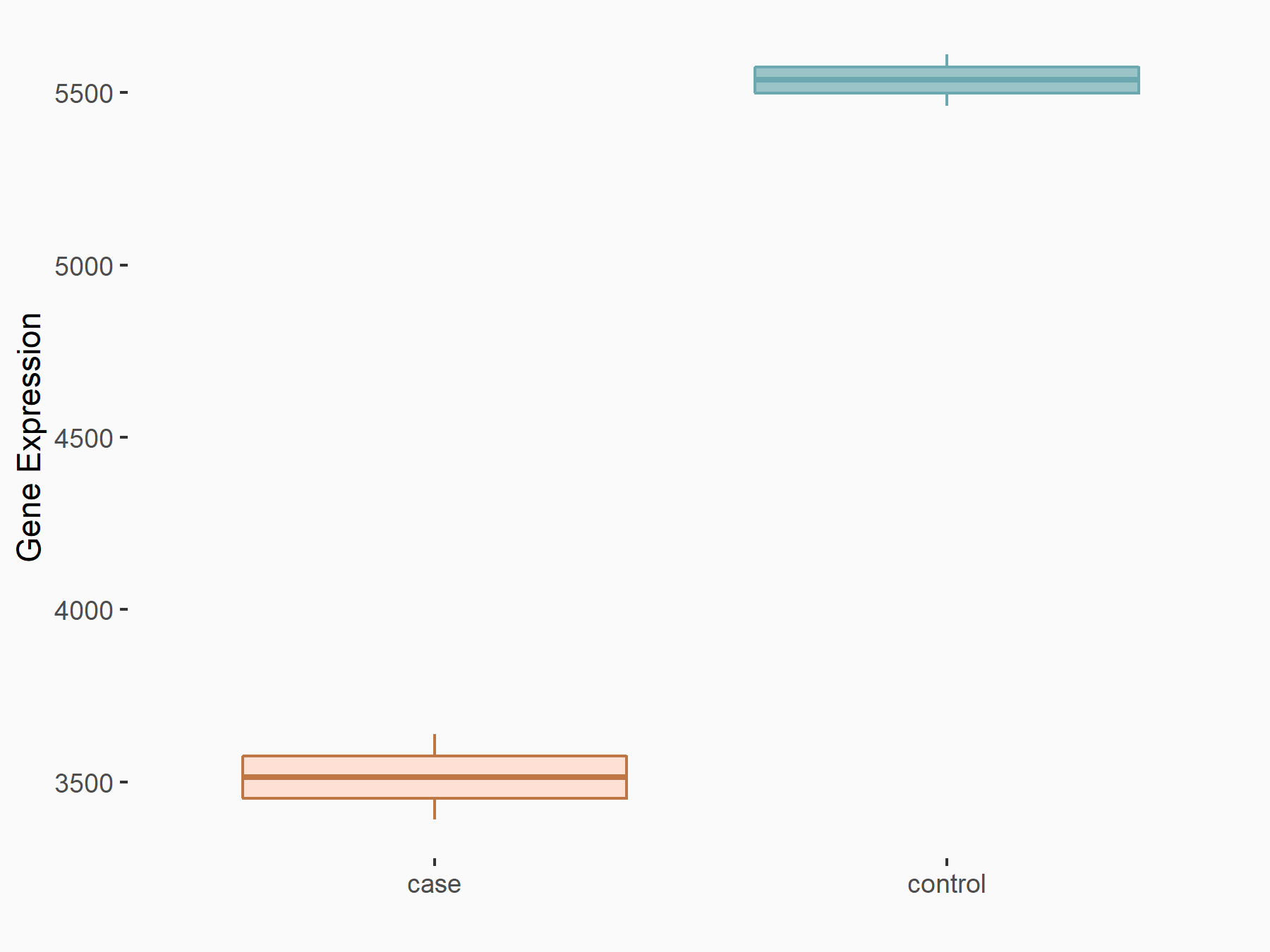  |
logFC: -6.56E-01 p-value: 3.77E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 3 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of pre-miR-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B51 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing YTHDFs-mediated Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression and inhibiting miR-107/LATS2-mediated YAP activity in non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell EMT | ||||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the experiments, mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into indicated groups (five mice per group). To assess the in vivo effects of cycloleucine, the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter from mice and then these xenografted mice were feed with Vehicle or cycloleucine (25 mg/kg twice weekly) and tumor volume were measured every 3 day. Tumor volume was estimated as 0.5 × a2 × b (where a and b represent a tumors short and long diameter, respectively). Mice were euthanized after 7 weeks and the tumors were measured a final time. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation improved the mRNA stability of YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA-binding protein 1 (YTHDF1), thereby increasing its expression, which consequently promoted the translation of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1).This finding suggests a novel potential therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction cardiac regeneration. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction | ICD-11: BA41 | ||
| In-vivo Model | Cas9 and sgRNA were microinjected into the fertilized eggs of C57BL/6J mice, which were then transplanted to obtain positive F0 mice. The statuses of F0 mice were confirmed by PCR and sequencing. Next, positive F0 mice were mated with C57BL/6J mice to yield stable F1 generation mice. F1 and F2 transgenic mice were used in this study. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) [READER]
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between YAP1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | Hela | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.33E+00 | GSE86214 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (EIF3A) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 promoted Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) mRNA translation by interacting with eIF3a in NSCLC. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| In-vitro Model | BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | 3 to 5-week old female BALB/c athymic (NU/NU) nude mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into indicated groups (five mice per group). To assess the in vivo effects of cycloleucine, the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter from mice and then these xenografted mice were feed with Vehicle or cycloleucine (25 mg/kg twice weekly) and tumor volume were measured every 3 day. | |||
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Response Summary | IGF2BP2 activates the expression of ErbB2 by recognizing the m6A of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1), thus affecting the cell cycle of colorectal cancer, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and promoting proliferation. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Temozolomide | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | IGF2BP2 activates the expression of ErbB2 by recognizing the m6A of YAP, thus affecting the cell cycle of CRC, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and promoting proliferation. | |||
YTH domain-containing protein 2 (YTHDC2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Response Summary | High YTHDC2 was strongly positively correlated with high Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) in clinical GC tissues, YTHDC2 is a novel oncogene in GC, which provides the theoretical basis for the strategy of targeting YTHDC2 for GC patients. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| In-vivo Model | They were subcutaneously and caudal vein injected with YTHDC2 knockout AGS cells, respectively. After 7 weeks, the mice were sacrificed and tumor size and lung metastasis nodules were recorded. | |||
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of pre-miR-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of pre-miR-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of pre-miR-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [8] | |||
| Response Summary | Stable knockdown of FTO inhibited OSCC cell viability, colony formation, and tumor growth. Further, FTO depletion increased Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) m6A modification at mRNA 3'-untranslated region, accelerating the degradation of YAP1 mRNA, a well-documented oncogene promoting OSCC progression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The expression of m6A and METTL3 was upregulated in human gastric cancer tissues and gastric cancer cell lines. m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promoted the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells through the m6A modification of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1). | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [20] | |||
| Response Summary | High YTHDC2 was strongly positively correlated with high Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) in clinical GC tissues, YTHDC2 is a novel oncogene in GC, which provides the theoretical basis for the strategy of targeting YTHDC2 for GC patients. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing protein 2 (YTHDC2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| In-vivo Model | They were subcutaneously and caudal vein injected with YTHDC2 knockout AGS cells, respectively. After 7 weeks, the mice were sacrificed and tumor size and lung metastasis nodules were recorded. | |||
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [13] | |||
| Response Summary | IGF2BP2 activates the expression of ErbB2 by recognizing the m6A of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1), thus affecting the cell cycle of colorectal cancer, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and promoting proliferation. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Temozolomide | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | IGF2BP2 activates the expression of ErbB2 by recognizing the m6A of YAP, thus affecting the cell cycle of CRC, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and promoting proliferation. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3-induced circ1662 promoted colorectal cancer cell invasion and migration by accelerating Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) nuclear transport. Circ1662 enhanced CRC invasion and migration depending on YAP1 and SMAD3. This result implies that circ1662 is a new prognostic and therapeutic marker for CRC metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c nude mice (4 weeks old) were acquired from Vital River Laboratory (Beijing, China). HCT116 cells with stable circ1662 expression (2 × 106 in 100 L of PBS) were injected via the tail vein. After 45 days, the mice were sacrificed. The lung metastatic carcinoma specimens were processed into paraffin-embedded sections for subsequent H&E staining and IHC. | |||
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [7] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 knockdown significantly increases the total YAP expression, but inhibits TGF-beta/Smad signaling, indicating that YTHDF2 regulates EMT probably via Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) signaling. YTHDF2 is a new predictive biomarker of development of pancreatic cancer. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cells proliferation | |||
| Cells migration | ||||
| Cells invasion | ||||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| PaTu 8988s | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1846 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methylation plays a key role in VM formation in HCC. METTL3 and Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) could be potential therapeutic targets via impairing VM formation in anti-metastatic strategies. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell migration and invasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | Homo sapiens (SK-HEP-1-Luc (luciferase labeled) cells were obtained from OBIO (Shanghai, China).) | |||
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1 × 107 SK-HEP-1-Luc-shControl or SK-HEP-1-Luc-shMETTL3 stable cells were suspended in 300 uL of PBS and injected orthotopically into the left liver lobe of nude mice. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 5 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [11] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 promoted Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) mRNA translation by interacting with eIF3a in NSCLC. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (EIF3A) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | 3 to 5-week old female BALB/c athymic (NU/NU) nude mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into indicated groups (five mice per group). To assess the in vivo effects of cycloleucine, the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter from mice and then these xenografted mice were feed with Vehicle or cycloleucine (25 mg/kg twice weekly) and tumor volume were measured every 3 day. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [11] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing YTHDFs-mediated Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression and inhibiting miR-107/LATS2-mediated YAP activity in non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell EMT | ||||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the experiments, mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into indicated groups (five mice per group). To assess the in vivo effects of cycloleucine, the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter from mice and then these xenografted mice were feed with Vehicle or cycloleucine (25 mg/kg twice weekly) and tumor volume were measured every 3 day. Tumor volume was estimated as 0.5 × a2 × b (where a and b represent a tumors short and long diameter, respectively). Mice were euthanized after 7 weeks and the tumors were measured a final time. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 5 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [9] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO down-expressed in myocardial IRI mice and hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced cardiomyocytes. Moreover, FTO uninstalled the methylation of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) mRNA, and enforced the stability of Yap1 mRNA.The study reveals the role of FTO in H/R-induced myocardial cell injury via m6A-dependent manner, which provided a new approach to improve myocardial IRI. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | Neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (Primary myocyte cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | After anesthesia (50 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium, intraperitoneal injection), the left thorax was cut to expose the heart, and the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery was ligated by 7/0 sterile suture. Myocardial ischemia was induced by 30 min of LAD coronary artery ligation and following 2 h of reperfusion. Sham group mice underwent the same surgical procedure without LAD coronary artery ligation. | |||
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [12] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation improved the mRNA stability of YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA-binding protein 1 (YTHDF1), thereby increasing its expression, which consequently promoted the translation of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1).This finding suggests a novel potential therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction cardiac regeneration. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Cas9 and sgRNA were microinjected into the fertilized eggs of C57BL/6J mice, which were then transplanted to obtain positive F0 mice. The statuses of F0 mice were confirmed by PCR and sequencing. Next, positive F0 mice were mated with C57BL/6J mice to yield stable F1 generation mice. F1 and F2 transgenic mice were used in this study. | |||
Kidney disorders [ICD-11: GB90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [6] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 knockdown alleviated the progression of renal fibrosis both in cultured cells induced by transforming growth factor-beta administration and in the UUO mouse model. Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) was accordingly down-regulated when YTHDF1 was inhibited. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kidney disorders [ICD-11: GB90] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Urinary/pelvic organs injury [ICD-11: NB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [10] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes renal ischemic reperfusion injury via suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1). | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of kidney [ICD-11: NB92.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 3 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
Temozolomide
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [13] | |||
| Response Summary | IGF2BP2 activates the expression of ErbB2 by recognizing the m6A of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1), thus affecting the cell cycle of colorectal cancer, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and promoting proliferation. | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | IGF2BP2 activates the expression of ErbB2 by recognizing the m6A of YAP, thus affecting the cell cycle of CRC, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and promoting proliferation. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03139 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (KDM1A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 dimethylation (H3K4me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | |
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03140 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (KDM1A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 dimethylation (H3K4me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | |
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03555 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03600 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03658 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Regulator: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05091 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | piR-31115 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05190 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_PACRGL | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Drug | Trans-3,5,4'-trimethoxystilbene | |
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05092 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | piR31115 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00451)
| In total 4 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005167 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102165002-102165003:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | AAAGTGTTGGGATTACAGGCATGAGCCACCATGTCCAGCCG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_24811 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005168 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102172566-102172567:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | TGGCAGCTTTTCTGGGGATTACATGTGTGAGCCACCACACT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_24812 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005169 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102180188-102180189:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | CCGGCTAATTTTGTAGTTTTAGTAGAGATGGGGTTTCACCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526594.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_24813 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005170 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102212118-102212119:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | GTATAAAGACATCACTCAGTATCTGAACACTAGACGCTGTT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_24814 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 3 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE005325 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102110831-102110832:+ | [22] | |
| Sequence | CTGGGTCAGGGGGTGCGCGTCGGGGGAGGCAGAAGCCATGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | m5C-RIP-seq; Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_8882 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE005326 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102231157-102231158:+ | [22] | |
| Sequence | TCTGATGAATTGGAAAGGAGCAAACCAGAAATGGCTTTATT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_8883 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE005327 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102231162-102231163:+ | [22] | |
| Sequence | TGAATTGGAAAGGAGCAAACCAGAAATGGCTTTATTTTCTC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_8884 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 95 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008157 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102110496-102110497:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AGAAAGGGAGGAAGGAAGGAACAAGAAAAGGAAATAAAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000282441.10; rmsk_3640863; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160909 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008158 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102110638-102110639:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TCCCGAGGCGCAGCCGCCAGACCAGTGGAGCCGGGGCGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160910 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008159 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102110728-102110729:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CCCCGGCCCTGAGAGCGAGGACAGCGCCGCCCGGCCCGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160911 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008160 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102110943-102110944:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GGGCAGGGCCCGCCGTCCGGACCCGGGCAACCGGCACCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160912 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008161 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102111026-102111027:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GATCGTGCACGTCCGCGGGGACTCGGAGACCGACCTGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160913 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008162 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102111034-102111035:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ACGTCCGCGGGGACTCGGAGACCGACCTGGAGGCGCTCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160914 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008163 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102111068-102111069:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GCTCTTCAACGCCGTCATGAACCCCAAGACGGCCAACGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160915 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008164 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102111094-102111095:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AGACGGCCAACGTGCCCCAGACCGTGCCCATGAGGCTCCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160916 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008165 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102112625-102112626:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TGTATAGTCTCCTGTCGGAGACCAAAGGGTTTTGGAACTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160917 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008166 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102112641-102112642:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GGAGACCAAAGGGTTTTGGAACTCAGAAAAAATCACTTAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000629586.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160918 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008167 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102112726-102112727:+ | [24] | |
| Sequence | CAATTTAGCTGCTTGCCTAAACACTTCAATTTGTCTTAGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160919 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008168 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102114242-102114243:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TGGGAGCTGTTTCTCCTGGGACACTGACCCCCACTGGAGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160920 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008169 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102114365-102114366:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CAGGTTGGGAGATGGCAAAGACATCTTCTGGTCAGAGATAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160921 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008170 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102162468-102162469:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GTCTTAGTCACATCGATCAGACAACAACATGGCAGGACCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160922 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008171 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102162484-102162485:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TCAGACAACAACATGGCAGGACCCCAGGAAGGCCATGCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160923 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008172 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102162559-102162560:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AGTGCAGCAGAATATGATGAACTCGGCTTCAGGTGAGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160924 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008173 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102186039-102186040:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CCTCTTCCTGATGGATGGGAACAAGCCATGACTCAGGATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160925 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008174 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102186077-102186078:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TGGAGAAATTTACTATATAAACCATAAGAACAAGACCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000629586.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160926 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008175 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102186086-102186087:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TTACTATATAAACCATAAGAACAAGACCACCTCTTGGCTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160927 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008176 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102186091-102186092:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ATATAAACCATAAGAACAAGACCACCTCTTGGCTAGACCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160928 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008177 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102186107-102186108:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CAAGACCACCTCTTGGCTAGACCCAAGGCTTGACCCTCGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160929 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008178 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102186149-102186150:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TGGTAAAGGTTCATCTCAAAACCTTTTTAGATGCTTTTGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526594.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160930 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008179 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102205898-102205899:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TCTTTTCATTTCAGCCATGAACCAGAGAATCAGTCAGAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1299; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000524575.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160931 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008180 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102205929-102205930:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AGTCAGAGTGCTCCAGTGAAACAGCCACCACCCCTGGCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; kidney; H1299; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160932 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008181 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102206052-102206053:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AAGGAGAGGCTGCGGCTGAAACAGCAAGAACTGCTTCGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1299; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160933 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008182 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102206061-102206062:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CTGCGGCTGAAACAGCAAGAACTGCTTCGGCAGGTGAGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160934 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008183 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102223648-102223649:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | CCCTGCGTAGCCAGTTACCAACACTGGAGCAGGATGGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160935 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008184 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102223669-102223670:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CACTGGAGCAGGATGGTGGGACTCAAAATCCAGTGTCTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160936 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008185 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102223714-102223715:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GGATGTCTCAGGAATTGAGAACAATGACGACCAATAGCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160937 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008186 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102227002-102227003:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TTAACTTGAGTCTAGTGCAGACCTGTCTCCTCGCCCACCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000526343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160938 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008187 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102227079-102227080:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TGGAGAATTGAGGCCTTGGGACAAGTAAGTTGTATGGGTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160939 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008188 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102227500-102227501:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CTCTCGAGATGAGAGTACAGACAGTGGACTAAGCATGAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; BGC823; HepG2; U2OS | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000524575.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160940 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008189 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102227507-102227508:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GATGAGAGTACAGACAGTGGACTAAGCATGAGCAGCTACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; BGC823; HepG2; U2OS; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160941 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008190 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102227538-102227539:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCTACAGTGTCCCTCGAACCCCAGATGACTTCCTGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; BGC823; HepG2; U2OS; A549; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160942 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008191 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102227557-102227558:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AACCCCAGATGACTTCCTGAACAGTGTGGATGAGATGGATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; kidney; BGC823; HepG2; U2OS; A549; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160943 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008192 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229732-102229733:+ | [26] | |
| Sequence | AACCAAAGCACCCTGCCCTCACAGCAGAACCGTTTCCCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160944 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008193 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229740-102229741:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CACCCTGCCCTCACAGCAGAACCGTTTCCCAGACTACCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160945 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008194 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229752-102229753:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ACAGCAGAACCGTTTCCCAGACTACCTTGAAGCCATTCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; Huh7; Jurkat; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000528834.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160946 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008195 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229775-102229776:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ACCTTGAAGCCATTCCTGGGACAAATGTGGACCTTGGAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000526343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160947 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008196 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229785-102229786:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CATTCCTGGGACAAATGTGGACCTTGGAACACTGGAAGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000524575.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160948 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008197 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229793-102229794:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GGACAAATGTGGACCTTGGAACACTGGAAGGAGATGGAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; kidney; A549; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160949 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008198 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229815-102229816:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ACTGGAAGGAGATGGAATGAACATAGAAGGAGAGGAGCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; Huh7; Jurkat; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160950 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008199 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229866-102229867:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | GCAGGAAGCTTTGAGTTCTGACATCCTTAATGACATGGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000531439.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160952 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008200 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229878-102229879:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | GAGTTCTGACATCCTTAATGACATGGAGTCTGTTTTGGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000629586.2; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000529029.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160953 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008201 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229928-102229929:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | TAGATAAAGAAAGCTTTCTTACATGGTTATAGAGCCCTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000629586.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160955 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008202 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229953-102229954:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GTTATAGAGCCCTCAGGCAGACTGAATTCTAAATCTGTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000531439.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160956 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008203 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102229986-102229987:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TCTGTGAAGGATCTAAGGAGACACATGCACCGGAAATTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160957 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008204 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230049-102230050:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GCTAATACAGAAAAAGATGAACAAACGTCCAGCAAGATACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000524575.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160959 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008205 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230053-102230054:+ | [27] | |
| Sequence | ATACAGAAAAAGATGAACAAACGTCCAGCAAGATACTTTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.179660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000526343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160960 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008206 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230132-102230133:+ | [26] | |
| Sequence | ATGTATTGCTGACCTCTTTCACAGTTGGCTCTAAAGAATCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000524575.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160962 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008207 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230163-102230164:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TAAAGAATCAAAAGAAAAAAACTTTTTATTTCTTTTGCTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; U2OS; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000528834.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160963 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008208 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230188-102230189:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TTATTTCTTTTGCTATTAAAACTACTGTTCATTTTGGGGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; U2OS; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000528834.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160964 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008209 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230294-102230295:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CATTTTAACTAAATACTCAGACTTAGAAGTCAGATGCTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000526343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160968 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008210 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230375-102230376:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TTCCTTTGTCCAGTGGAAAAACATGATTTACTGGTCTGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160969 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008211 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230393-102230394:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | AAACATGATTTACTGGTCTGACAAGCCAAAAATGTTATATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160970 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008212 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230455-102230456:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GATTTGAAGAGATAGCTGAAACCAAGGCTGAAGACTGTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160971 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008213 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230468-102230469:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AGCTGAAACCAAGGCTGAAGACTGTTTTACTTTCAGTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000528834.1; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160972 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008214 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230517-102230518:+ | [26] | |
| Sequence | TCCTAGTGCTATCATTAGTCACATAATGACCTTGATTTTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160973 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008215 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230525-102230526:+ | [27] | |
| Sequence | CTATCATTAGTCACATAATGACCTTGATTTTATTTTAGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.839113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160974 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008216 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230561-102230562:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGCTTATAAGGCATGAGACAATTTCCATATAAATATAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000526343.5; ENST00000529029.1; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160975 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008217 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230724-102230725:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GGTTGGTTGGTTTTGTCGGAACCTAGGCAAATGACCATATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160976 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008218 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230882-102230883:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ATATACATACACACACCCAAACATAACATTTATAATAGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160979 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008219 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230887-102230888:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | CATACACACACCCAAACATAACATTTATAATAGTGTGGTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160980 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008220 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230985-102230986:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | GCTTTGTATGCATTTAGAATACATGACTAGTAGTTTATATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160981 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008221 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102230990-102230991:+ | [27] | |
| Sequence | GTATGCATTTAGAATACATGACTAGTAGTTTATATTTCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160982 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008222 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102231345-102231346:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | GTAGTTCTCATTTGTAATGAACACATTAACGACTAGATTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160983 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008223 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102231394-102231395:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | CTTCAAGATTGTTCTTACTTACAAGACTTGCTCCTACTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160984 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008224 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102231399-102231400:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AGATTGTTCTTACTTACAAGACTTGCTCCTACTTCTATGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160985 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008225 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102231624-102231625:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | AAAGAGTATTTTTTAAAGGAACAAAACGAGCATGAATTAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160986 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008226 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102231847-102231848:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | AGATTTTTTTCCCCCCAATTACAAAATCTAAGTATTTTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_3641073; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160987 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008227 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232017-102232018:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CTAAGGCTTTTATTAAGAAAACAGCAGAAAGATTAAATCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160988 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008228 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232099-102232100:+ | [27] | |
| Sequence | TAGAGTAGTAATGAAATTCTACCTAGAATGCAAAATTGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.05802381 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160989 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008229 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232129-102232130:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | CAAAATTGGGTATATGAATTACATAGCATGTTGTTGGGATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160990 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008230 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232306-102232307:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | GGTTGTGAAGATTTAGGGGGACCTTGATAGAGAACTTTATA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160991 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008231 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232319-102232320:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TAGGGGGACCTTGATAGAGAACTTTATAAACTTCTTTCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160992 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008232 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232328-102232329:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CTTGATAGAGAACTTTATAAACTTCTTTCTCTTTAATAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160993 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008233 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232349-102232350:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CTTCTTTCTCTTTAATAAAGACTTGTCTTACACCGTGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160994 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008234 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232358-102232359:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | CTTTAATAAAGACTTGTCTTACACCGTGCTGCCATTAAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160995 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008235 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232409-102232410:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | AGAGTTTCAGTCACCTAAGTACACCCACAAAACAATATGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160996 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008236 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232420-102232421:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CACCTAAGTACACCCACAAAACAATATGAATATGGAGATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160997 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008237 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232502-102232503:+ | [27] | |
| Sequence | TGTTGTAGCAGTACTGTGATACCTGGCACAGTGCTTTGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.089839286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160998 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008238 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232554-102232555:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TCTGTACTGACCTGAAGGAGACCTAAGAGTCCTTTCCCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_160999 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008239 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232718-102232719:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TTGAATTGCTTTTACAATAAACCAATTTTATAATCTTTAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161000 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008240 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232753-102232754:+ | [27] | |
| Sequence | TTTAAATTTATCAACTTTTTACATTTGTGTTATTTTCAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161001 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008241 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232790-102232791:+ | [27] | |
| Sequence | AGTCAGGGCTTCTTAGATCTACTTATGGTTGATGGAGCACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161002 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008242 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232808-102232809:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | CTACTTATGGTTGATGGAGCACATTGATTTGGAGTTTCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161003 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008243 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232892-102232893:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTTTAAAGGAAAAATGAACACAGGGAAGTGACTTTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161004 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008244 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232968-102232969:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ATACATGCCTTCTATATGGAACATGGCAGAAAGACTGAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161005 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008245 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102232981-102232982:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | ATATGGAACATGGCAGAAAGACTGAAAAATAACAGTAATTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161006 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008246 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102233039-102233040:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | TCATACCAATCAGTGTTGAAACTCAAACATTGCAAAAGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161007 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008247 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102233045-102233046:+ | [23] | |
| Sequence | CAATCAGTGTTGAAACTCAAACATTGCAAAAGTGGGTGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161008 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008248 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102233099-102233100:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | AACACTTTTCTAGCGTTGGTACATCTGAGAAATGAGTGCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161009 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008249 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102233178-102233179:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | TTGTGGGTGTGCCTATCATAACAATTGTTTTCTGTATCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000615667.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161010 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008250 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102233251-102233252:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | ATTAGAGAATTCTTTAATGCACACTTGTCAAATATATATAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537274.5; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000345877.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161011 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE008251 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:102233339-102233340:+ | [25] | |
| Sequence | TGCTCATATGTTAGGTACTTACATAAATTGTTACATTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000345877.6; ENST00000282441.10; ENST00000615667.4; ENST00000537274.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_161012 | ||
References