m6A Regulator Information
General Information of the m6A Regulator (ID: REG00006)
| Regulator Name | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N6-adenosine-methyltransferase non-catalytic subunit; hMETTL14; KIAA1627
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | METTL14 | ||||
| Sequence |
MDSRLQEIRERQKLRRQLLAQQLGAESADSIGAVLNSKDEQREIAETRETCRASYDTSAP
NAKRKYLDEGETDEDKMEEYKDELEMQQDEENLPYEEEIYKDSSTFLKGTQSLNPHNDYC QHFVDTGHRPQNFIRDVGLADRFEEYPKLRELIRLKDELIAKSNTPPMYLQADIEAFDIR ELTPKFDVILLEPPLEEYYRETGITANEKCWTWDDIMKLEIDEIAAPRSFIFLWCGSGEG LDLGRVCLRKWGYRRCEDICWIKTNKNNPGKTKTLDPKAVFQRTKEHCLMGIKGTVKRST DGDFIHANVDIDLIITEEPEIGNIEKPVEIFHIIEHFCLGRRRLHLFGRDSTIRPGWLTV GPTLTNSNYNAETYASYFSAPNSYLTGCTEEIERLRPKSPPPKSKSDRGGGAPRGGGRGG TSAGRGRERNRSNFRGERGGFRGGRGGAHRGGFPPR Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | MT-A70-like family | ||||
| Function |
The METTL3-METTL14 heterodimer forms a N6-methyltransferase complex that methylates adenosine residues at the N(6) position of some mRNAs and regulates the circadian clock, differentiation of embryonic stem cells and cortical neurogenesis. In the heterodimer formed with METTL3, METTL14 constitutes the RNA-binding scaffold that recognizes the substrate rather than the catalytic core. N6-methyladenosine (m6A), which takes place at the 5'-[AG]GAC-3' consensus sites of some mRNAs, plays a role in mRNA stability and processing. M6A acts as a key regulator of mRNA stability by promoting mRNA destabilization and degradation (By similarity). In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), m6A methylation of mRNAs encoding key naive pluripotency-promoting transcripts results in transcript destabilization (By similarity). M6A regulates spermatogonial differentiation and meiosis and is essential for male fertility and spermatogenesis (By similarity). M6A also regulates cortical neurogenesis: m6A methylation of transcripts related to transcription factors, neural stem cells, the cell cycle and neuronal differentiation during brain development promotes their destabilization and decay, promoting differentiation of radial glial cells (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 57721 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Regulator Type | WRITER ERASER READER | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
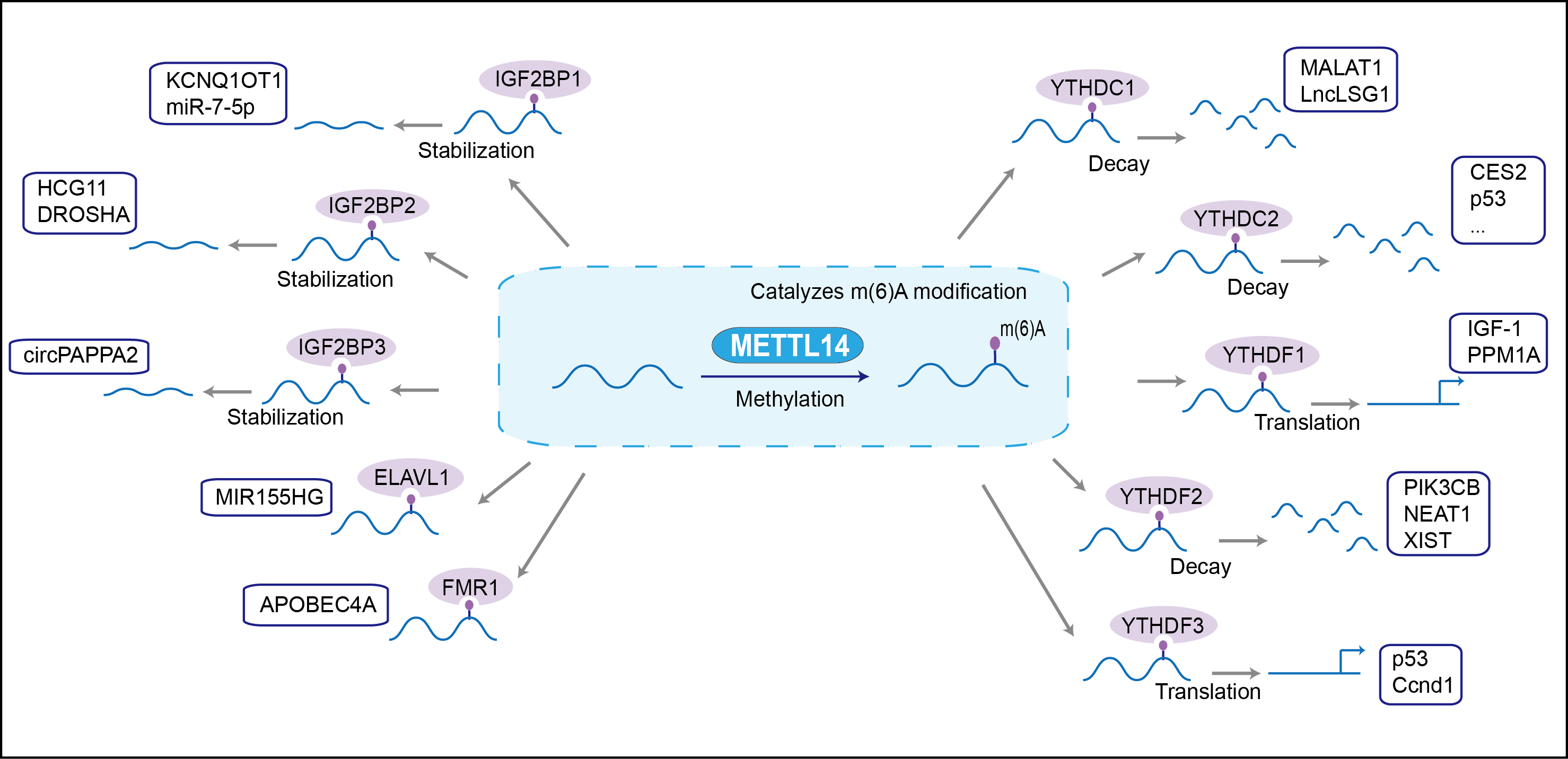
|
|||||
| Target Genes | Click to View Potential Target Genes of This Regulator | ||||
Full List of Target Gene(s) of This m6A Regulator and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
METTL14 can regulate the m6A methylation of following target genes, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulted from the regulation of certain target gene.
Browse Target Gene related Disease
Browse Target Gene related Drug
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
 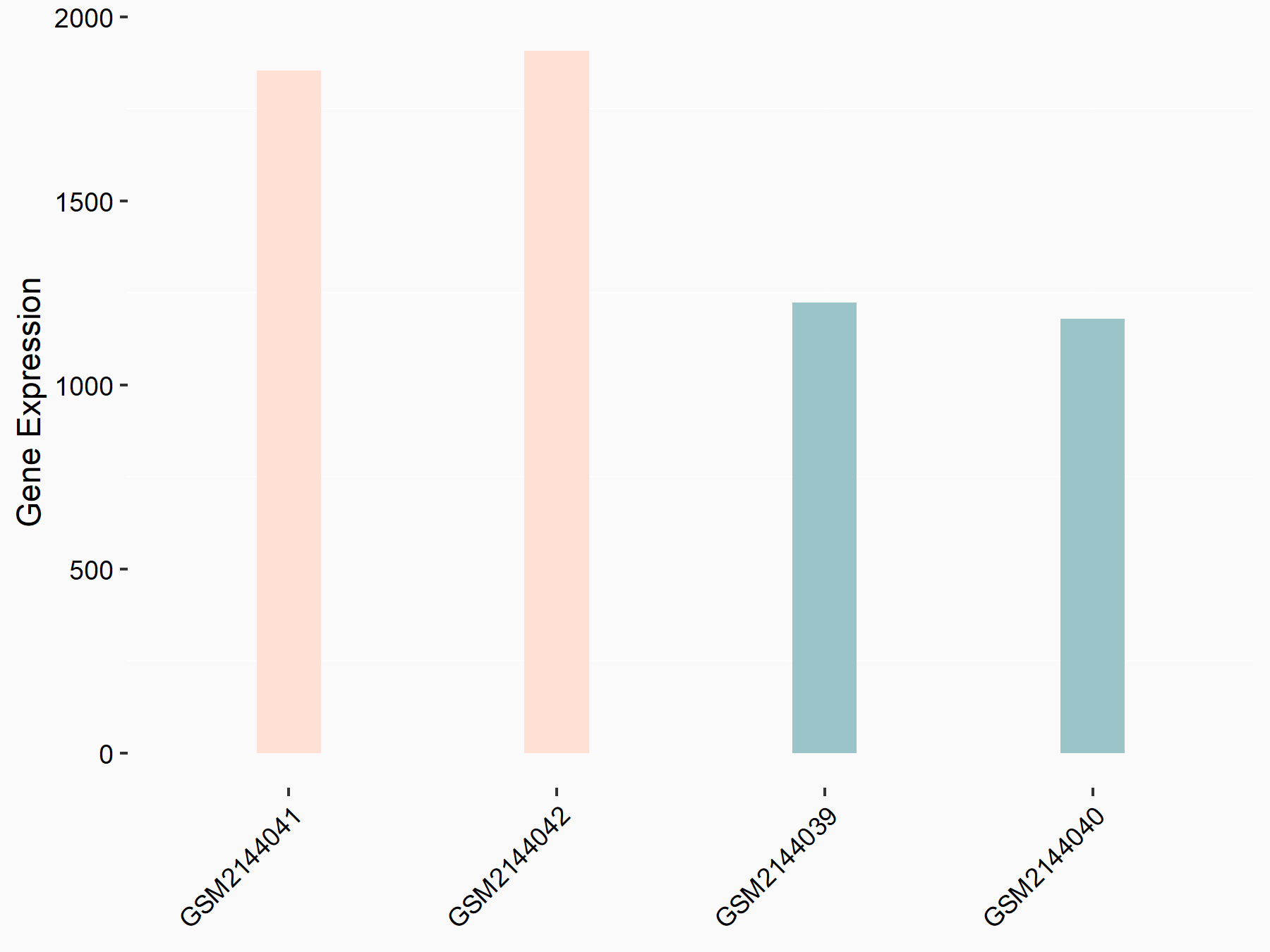 |
logFC: 6.46E-01 p-value: 1.74E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| EA.hy 926 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3901 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were randomly divided into control, Ad-sh-NC, and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups (10 mice per group). The mice in the control group were fed a normal diet, while the Ad-sh-NC and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups were fed a high-fat diet (20% fat and 0.25% cholesterol). Furthermore, 300 uL of constructed sh-NC or sh-METTL14 adenovirus was injected every 3 weeks into the caudal veins of mice from the Ad-sh-NC or Ad-sh-METTL14 groups, respectively. The constructed vectors were obtained from HanBio Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All mice were sacrificed after 24 weeks and the aortas were separated for further experiments. | |||
| Response Summary | Knocking down METTL14 could inhibit the development of atherosclerosis in high-fat diet-treated APOE mice. After transfection with si-METTL14, the Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) expression level and the viability of ox-LDL-incubated cells increased, whereas the apoptosis rate and the expressions of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 decreased. However, the effect of METTL14 knockdown was reversed by p65 overexpression. | |||
Arrestin domain-containing protein 4 (ARRDC4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
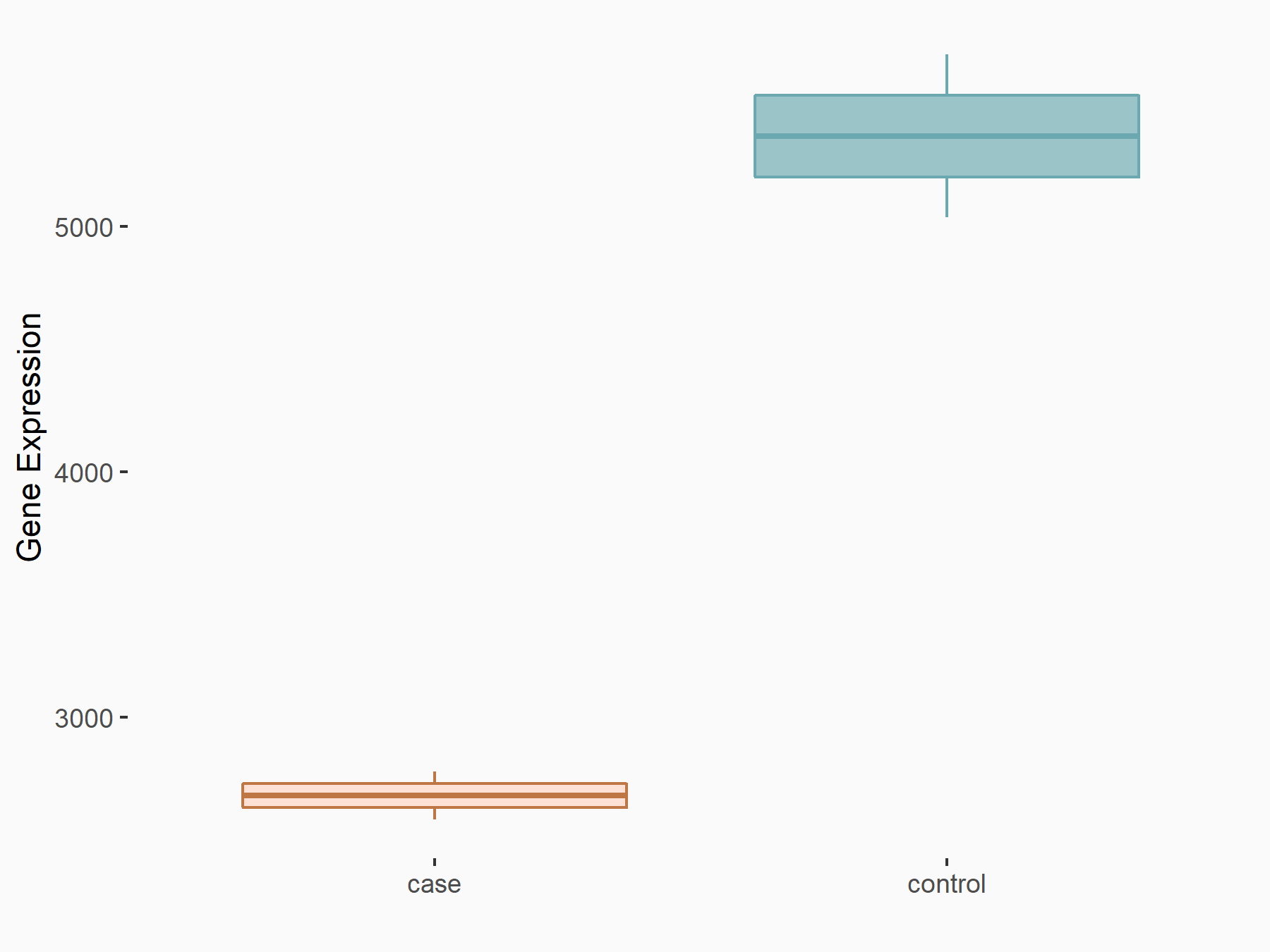 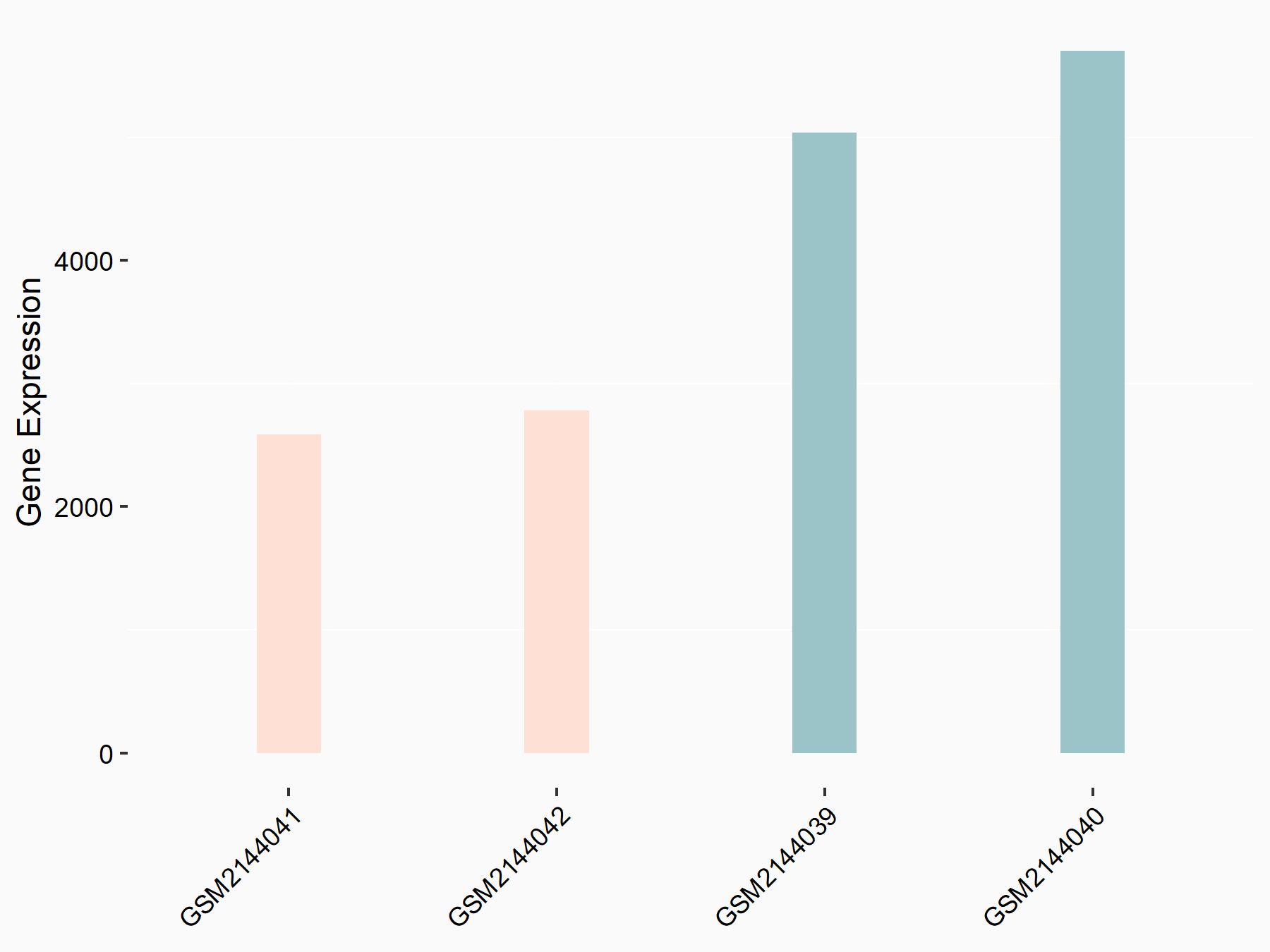 |
logFC: -1.00E+00 p-value: 7.16E-13 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mRNA surveillance pathway | hsa03015), RNA degradation | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 | |
| NCM460 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0460 | |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| HCT 15 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0292 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| In-vivo Model | Equal amount of HCT116 cells (2 × 106) stably expression of relevant plasmids was injected into the right flank of mice, tumor bulks was monitored once a week after injection and volumes were counted as 0.5 × a2 × b (a and b respectively indicated short and long diameter of tumor). | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of METTL14 significantly enhanced Arrestin domain-containing protein 4 (ARRDC4) mRNA stability relying on the "reader" protein YHTDF2 dependent manner in colorectal cancer. | |||
ATP-citrate synthase (ACLY)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
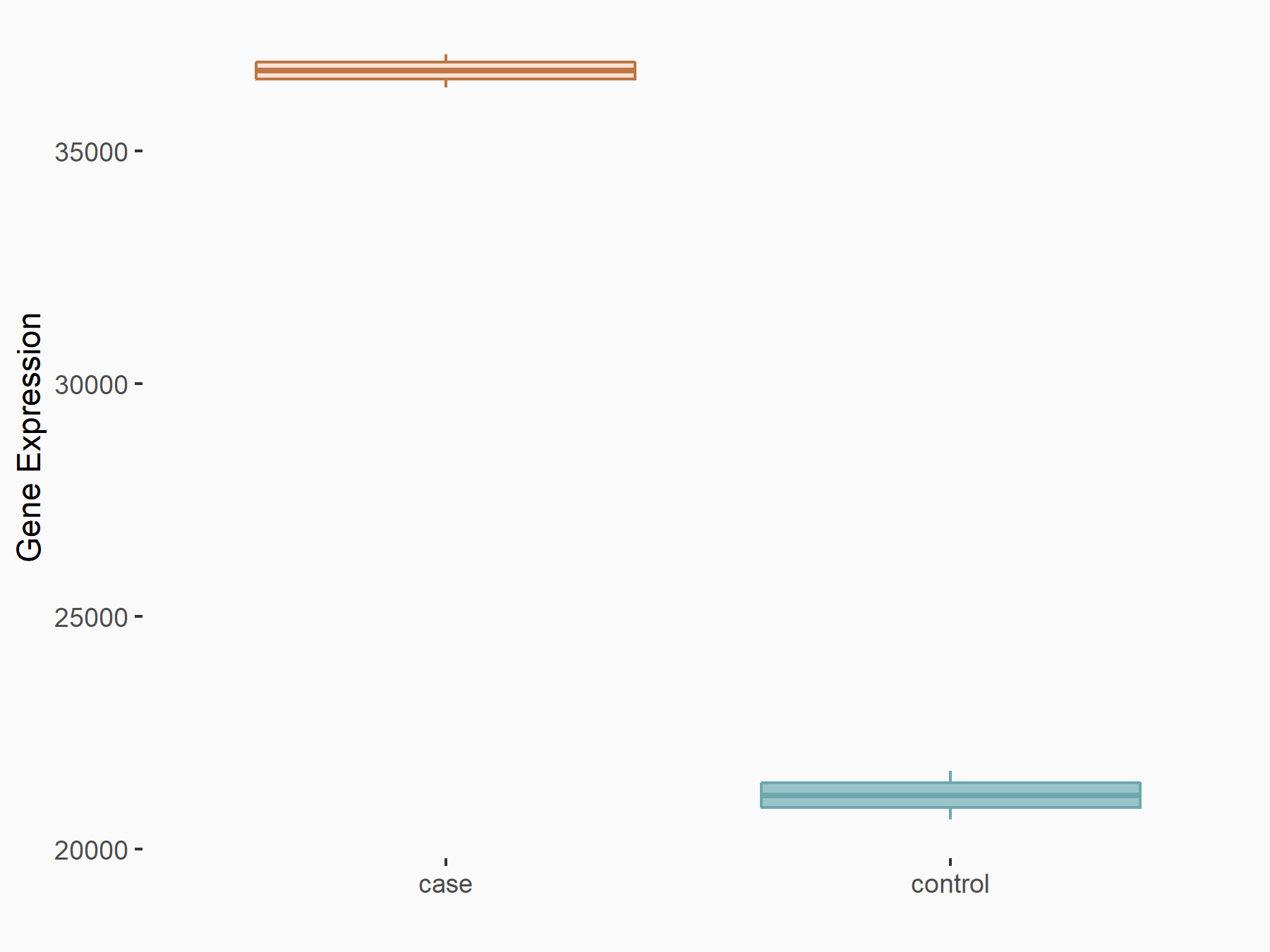  |
logFC: 7.95E-01 p-value: 2.66E-12 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Glycerolipid metabolism | hsa00561 | ||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
LM3 | Malignant neoplasms | Mus musculus | CVCL_D269 |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice with a Tmem30a deletion specifically in pancreatic beta cells were generated as previously described. Mice developed with NAFLD were named for Tmem30a-associated NAFLD (TAN) mice. The littermate mice with genotypes of Tmem30aloxP/loxP were used as controls. | |||
| Response Summary | Targeting METTL3/14 in vitro increases protein level of ATP-citrate synthase (ACLY) and SCD1 as well as triglyceride and cholesterol production and accumulation of lipid droplets. These findings demonstrate a new NAFLD mouse model that provides a study platform for DM2-related NAFLD and reveals a unique epitranscriptional regulating mechanism for lipid metabolism via m6A-modified protein expression of ACLY and SCD1. | |||
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
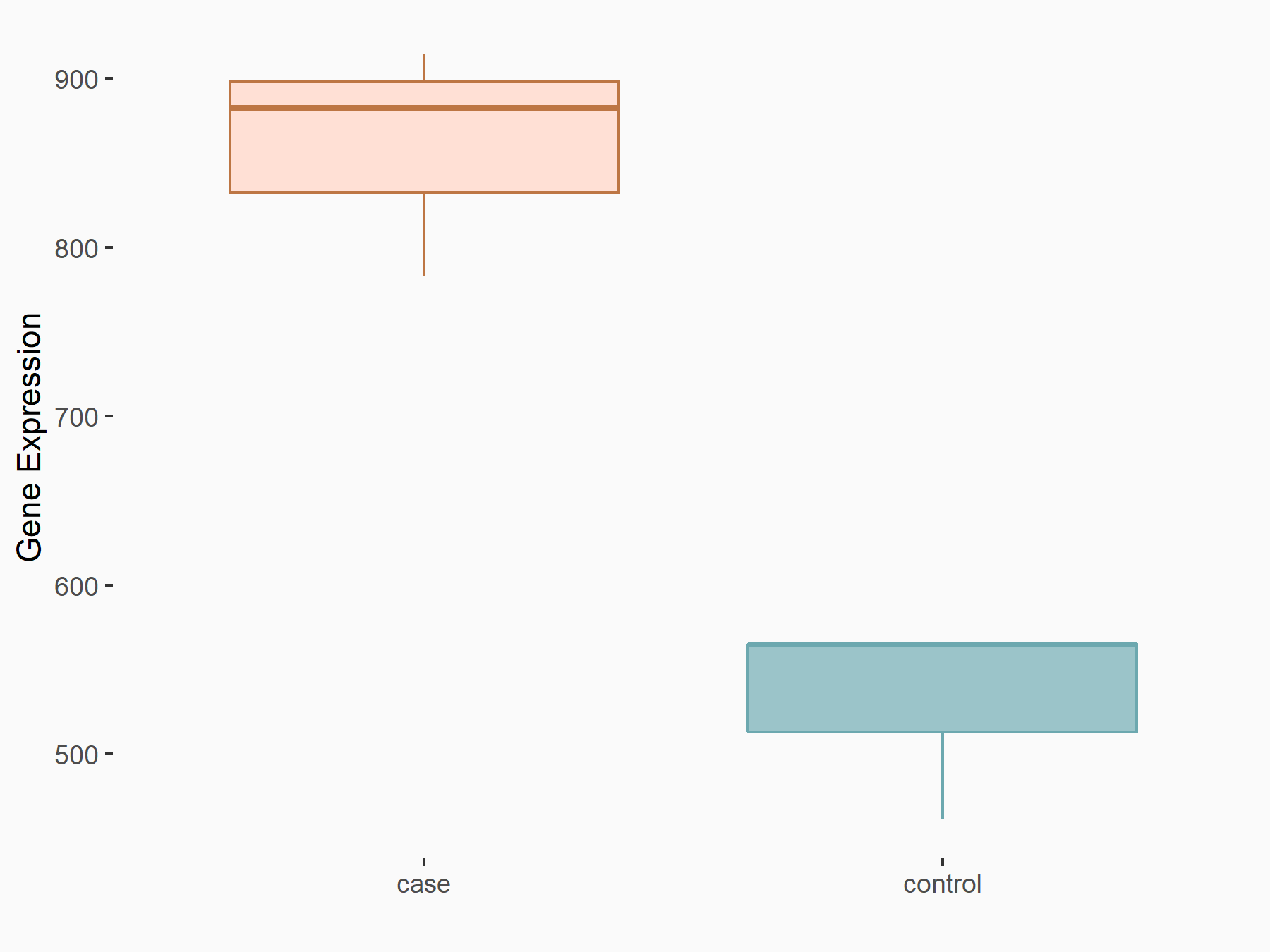  |
logFC: 7.03E-01 p-value: 9.23E-10 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Response Summary | LNC942-METTL14-C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)/CYP1B1 signaling axis, which provides new targets and crosstalk m6A epigenetic modification mechanism for breast cancer prevention and treatment. | |||
Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
C-X-C motif chemokine 10 (Cxcl10)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | CT26 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout CT26 cells
Control: CT26 cells
|
GSE142589 | |
| Regulation |
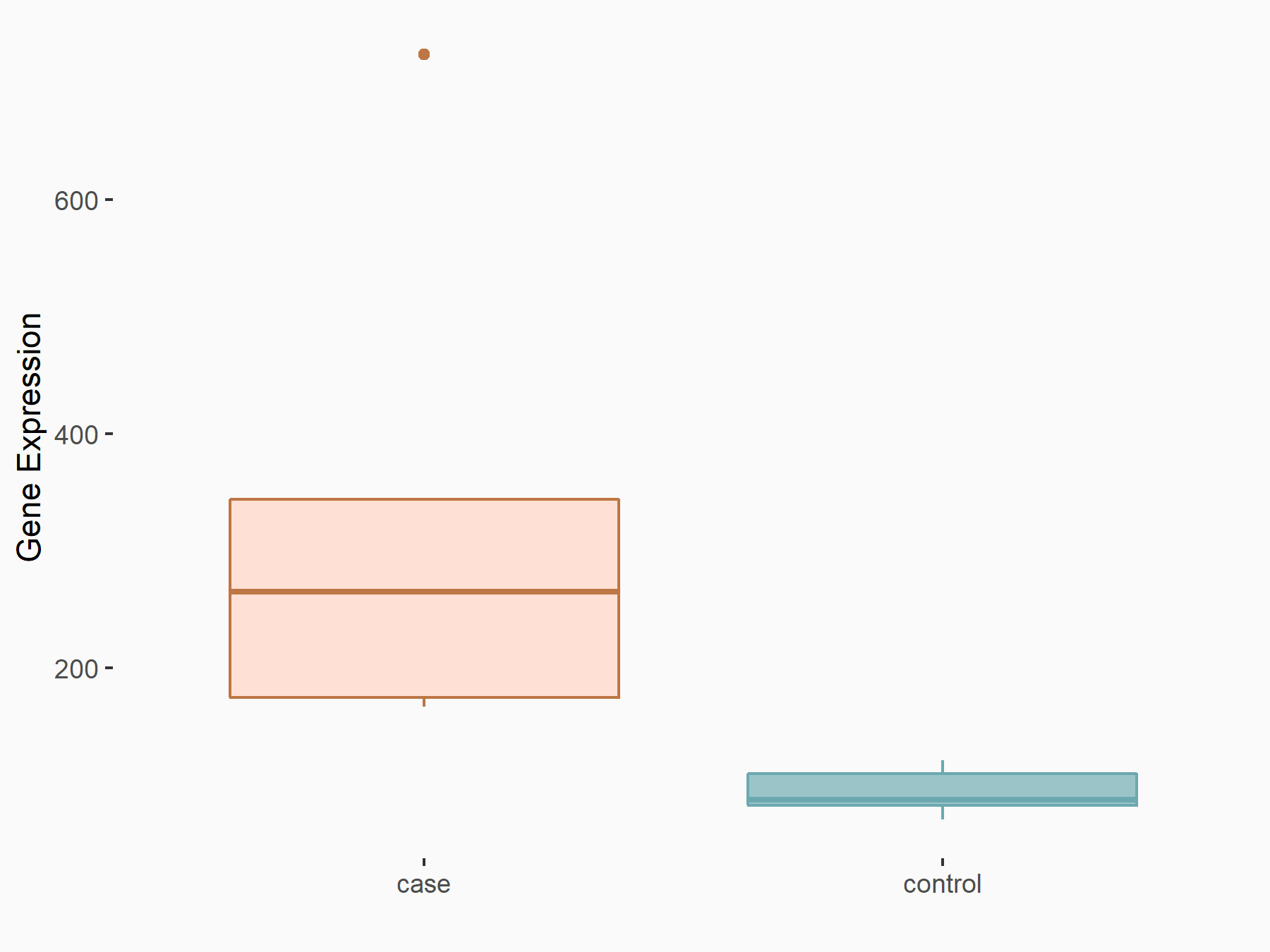 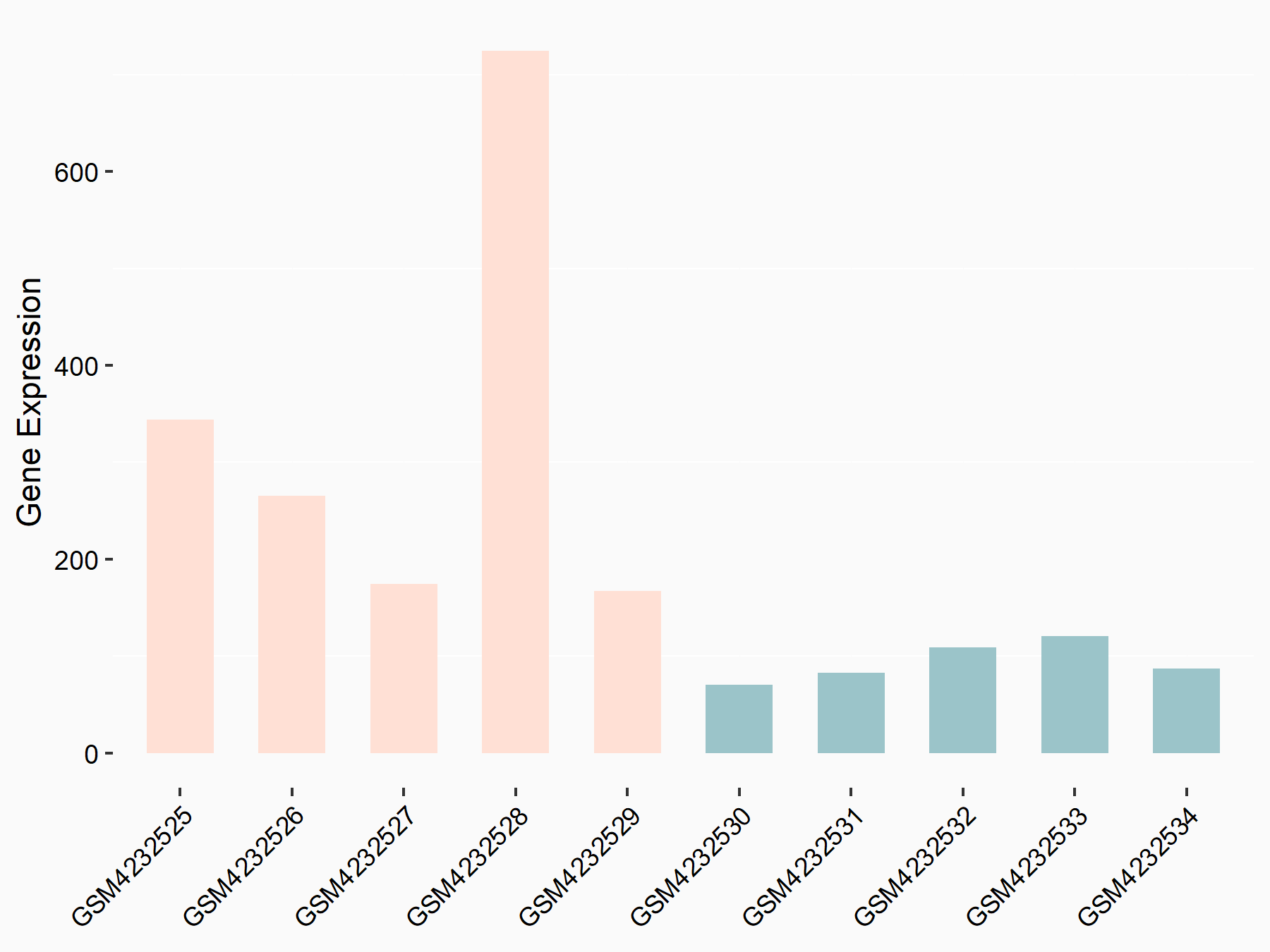 |
logFC: 1.83E+00 p-value: 1.84E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
In-vitro Model |
CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and C-X-C motif chemokine 10 (Cxcl10) in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Stat1 and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
C-X-C motif chemokine 9 (Cxcl9)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | CT26 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout CT26 cells
Control: CT26 cells
|
GSE142589 | |
| Regulation |
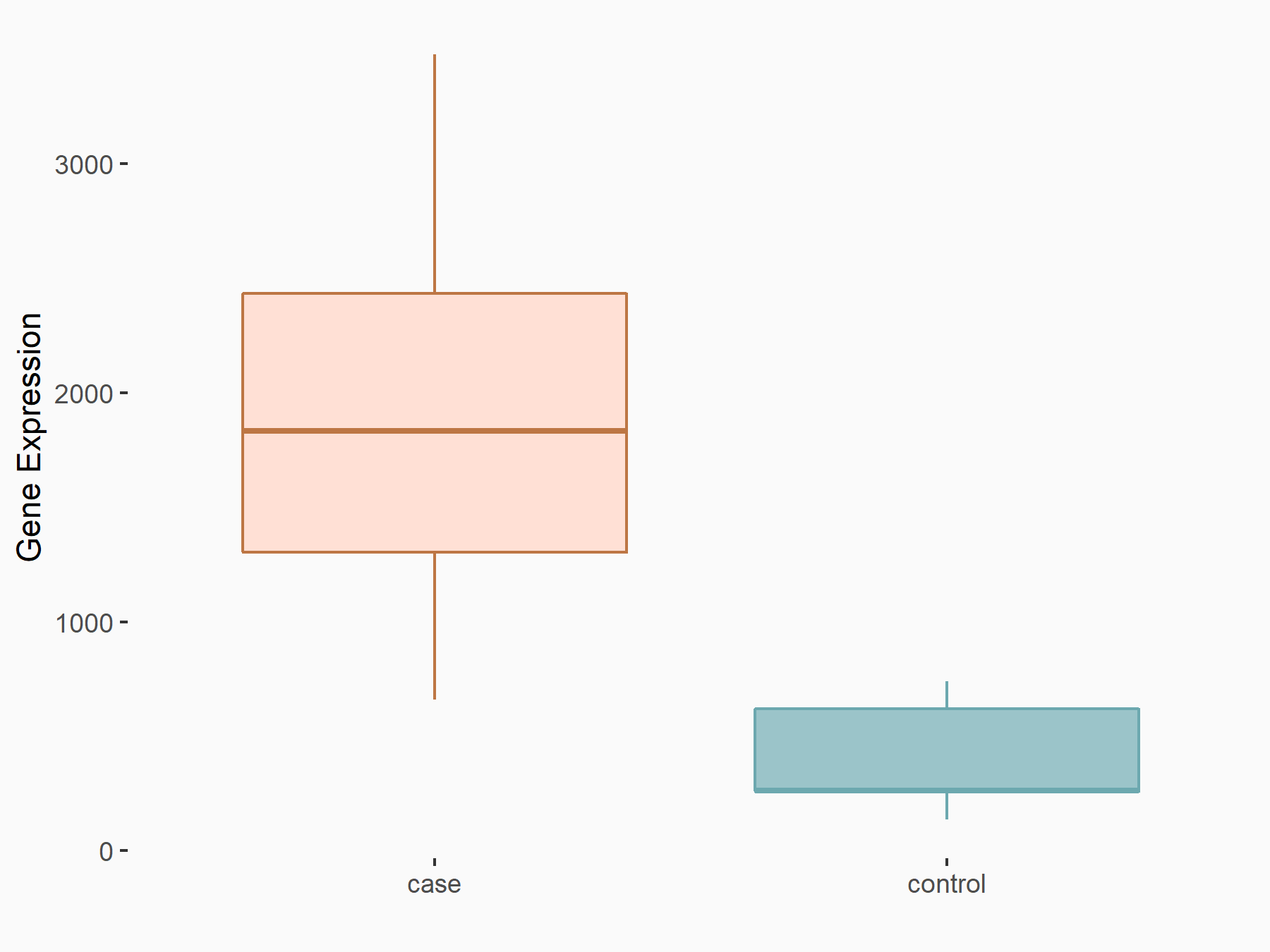 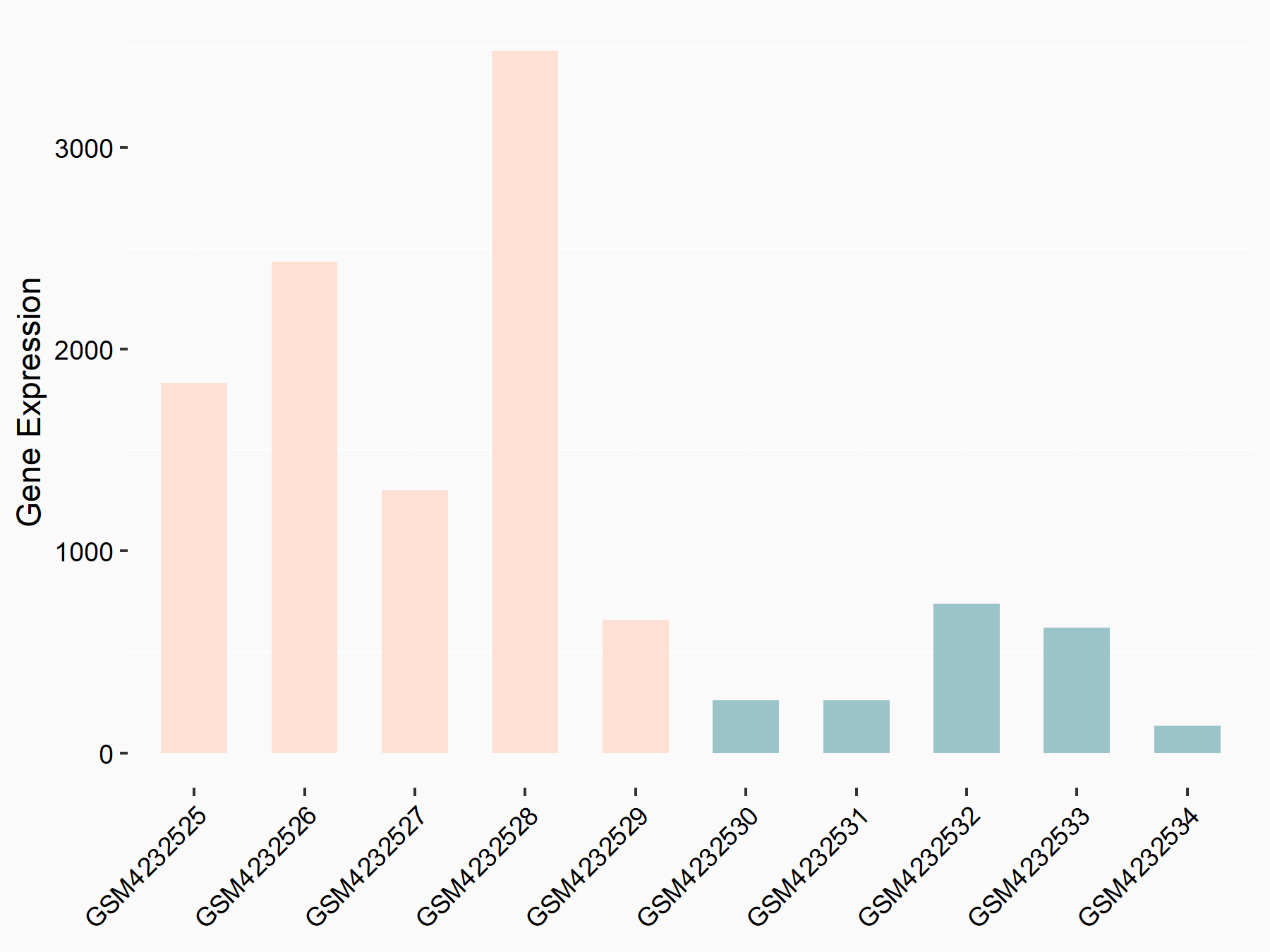 |
logFC: 2.27E+00 p-value: 1.06E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
In-vitro Model |
CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, C-X-C motif chemokine 9 (Cxcl9), and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Stat1 and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CAMKK2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
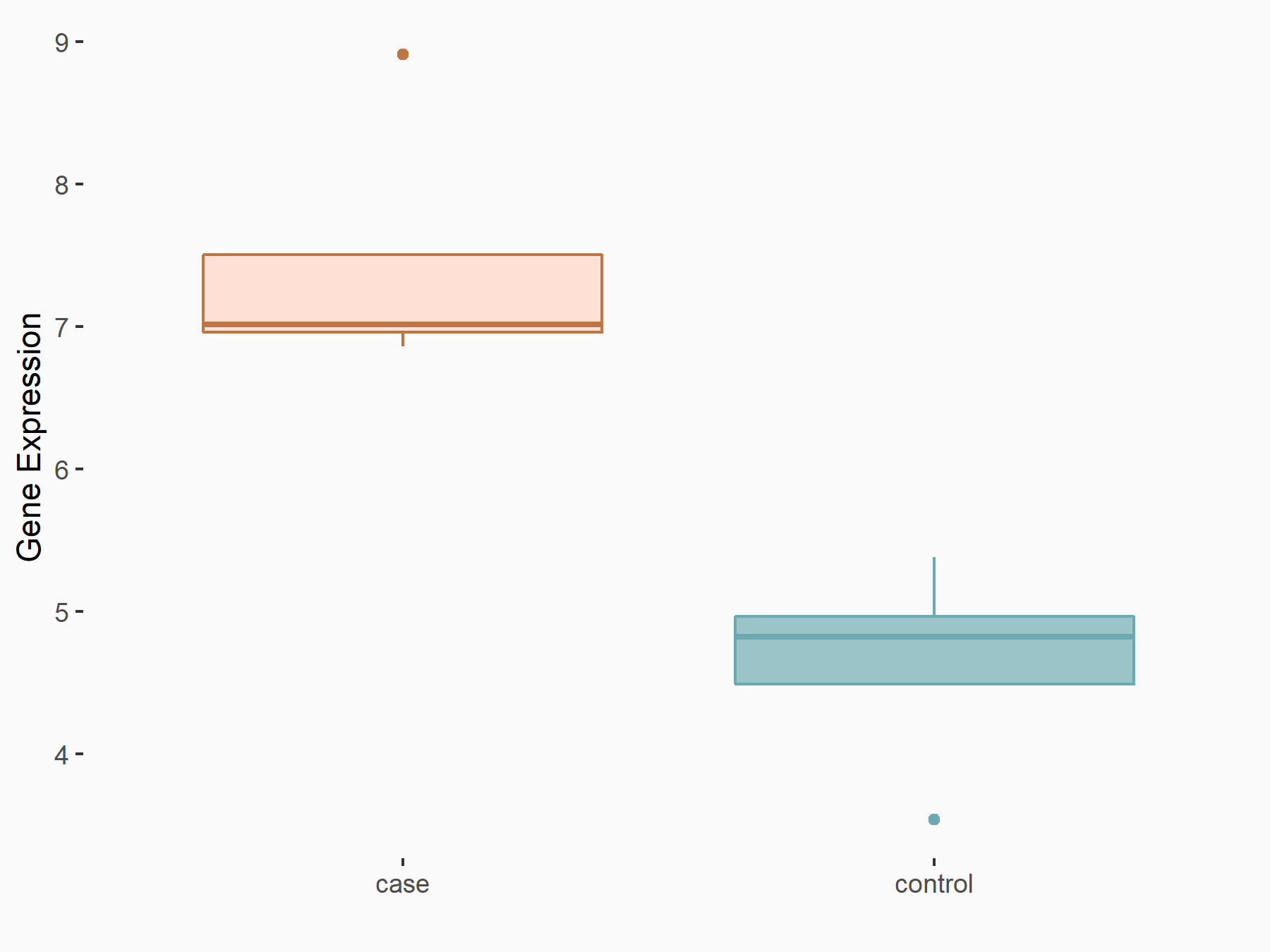 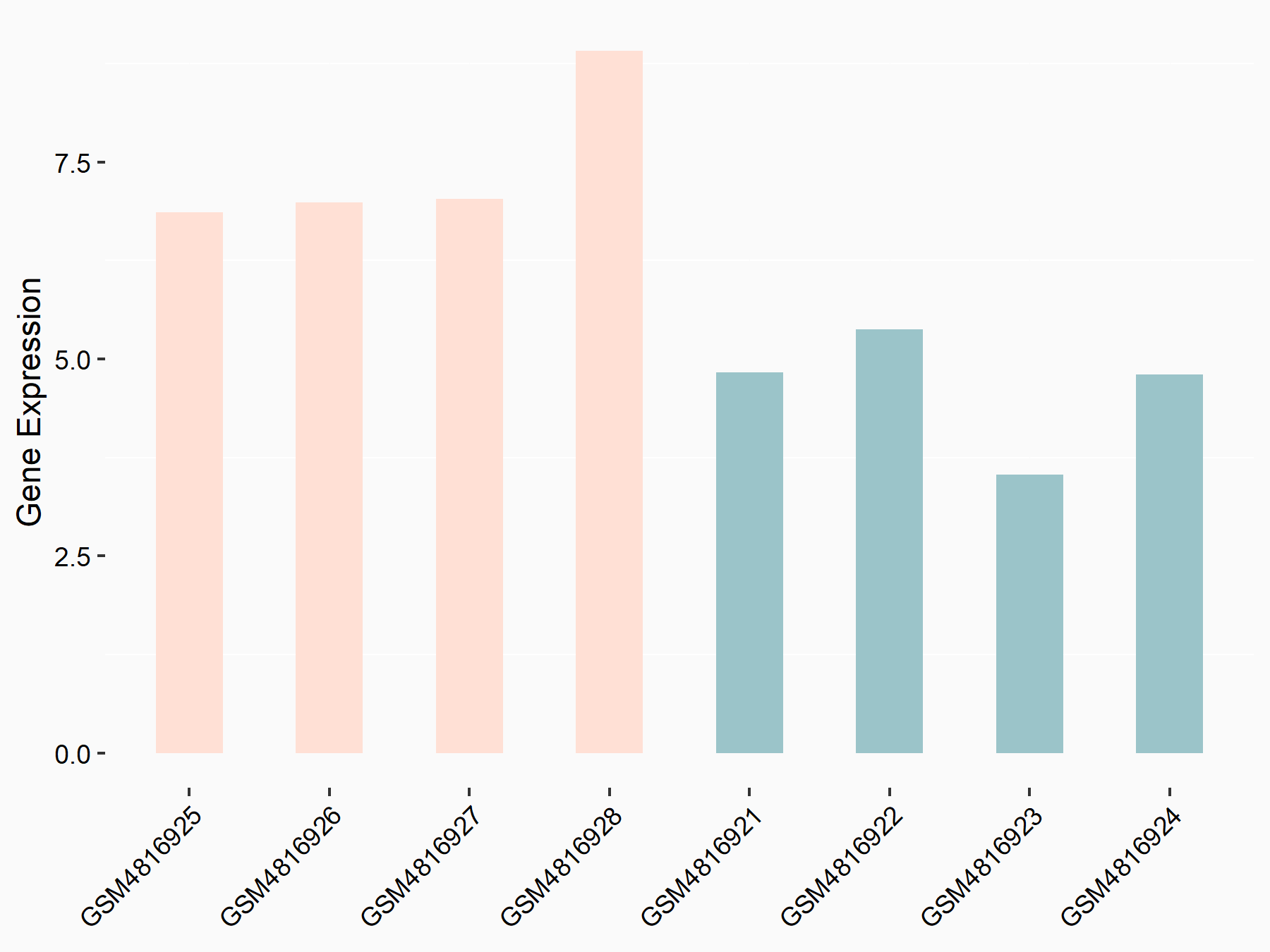 |
logFC: 5.88E-01 p-value: 3.22E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Azoospermia [ICD-11: GB04.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| In-vivo Model | Male SPF BALB/c mice (qls02-0202) were purchased from Qinglongshan animal breeding farm. Mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation and testes were obtained for following histopathological analyses. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification promoted translation of PPM1A (protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform), a negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, but decreased expression of Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CAMKK2) (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta), a positive AMPK regulator, by reducing its RNA stability. Similar regulation of METTL14, ALKBH5, and m6A was also observed in LCs upon treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin (HsCG). Knock down of YTHDF1 failed to change the expression of CAMKK2 Providing insight into novel therapeutic strategies by exploiting m6A RNA methylation as targets for treating azoospermatism and oligospermatism patients with reduction in serum testosterone. | |||
Caspase-3 (CASP3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
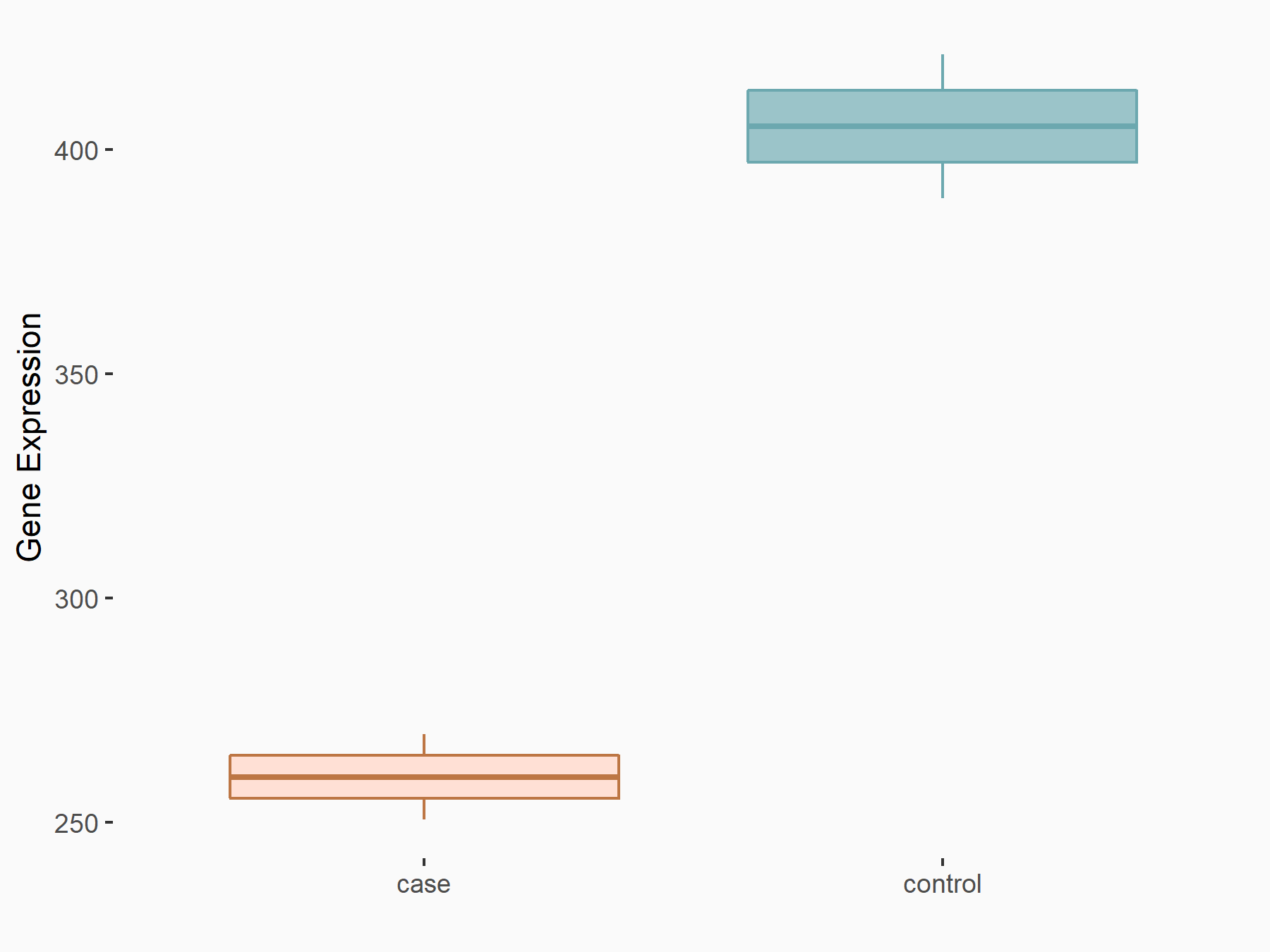 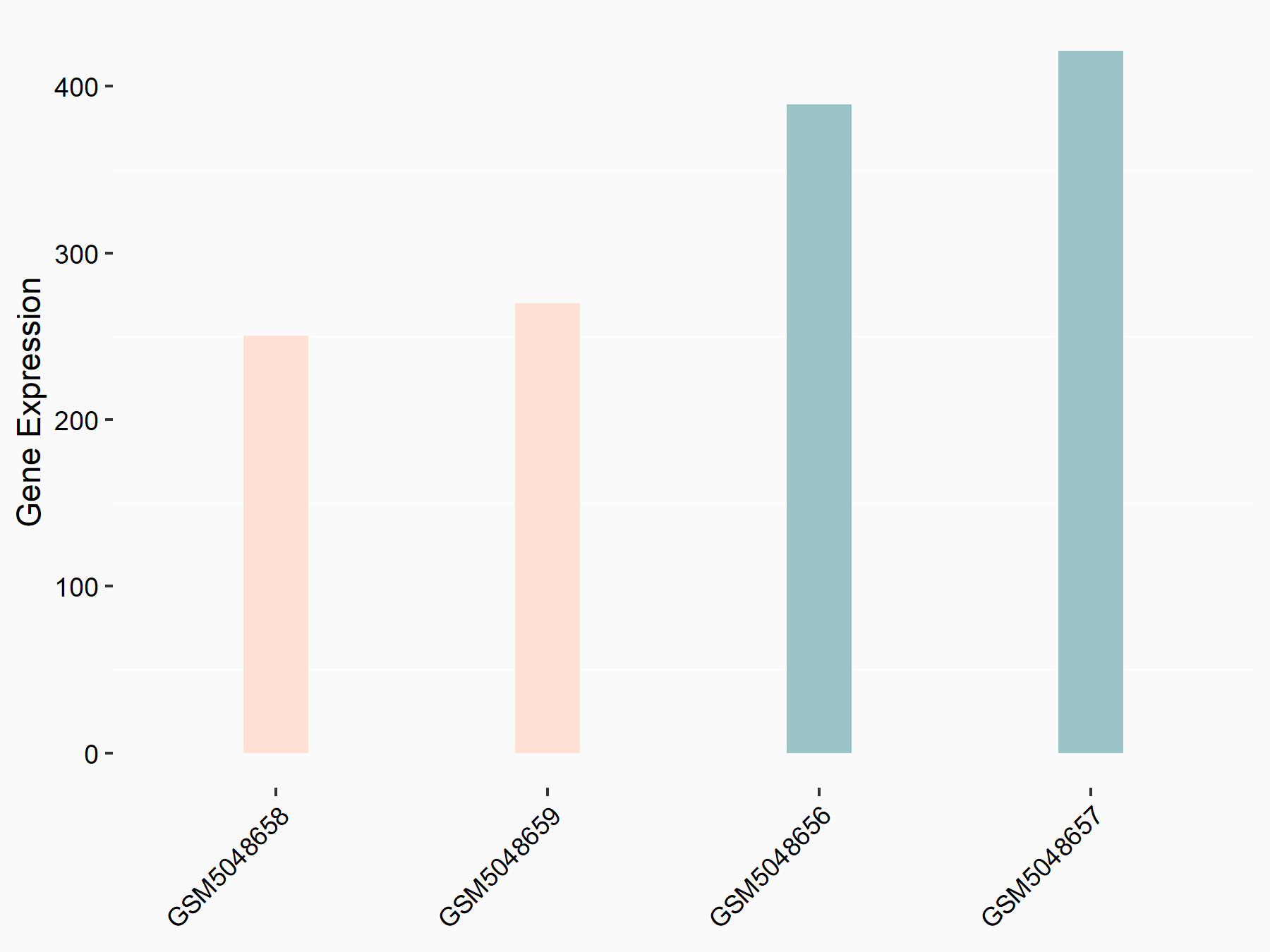 |
logFC: -6.38E-01 p-value: 2.86E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
143B | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 |
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 | |
| Response Summary | METTL14 can promote osteosarcoma cell apoptosis, inhibit cell viability, and have a tumor suppressor effect on osteosarcoma. METTL14 finally achieves apoptosis by activating Caspase-3 (CASP3). | |||
Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
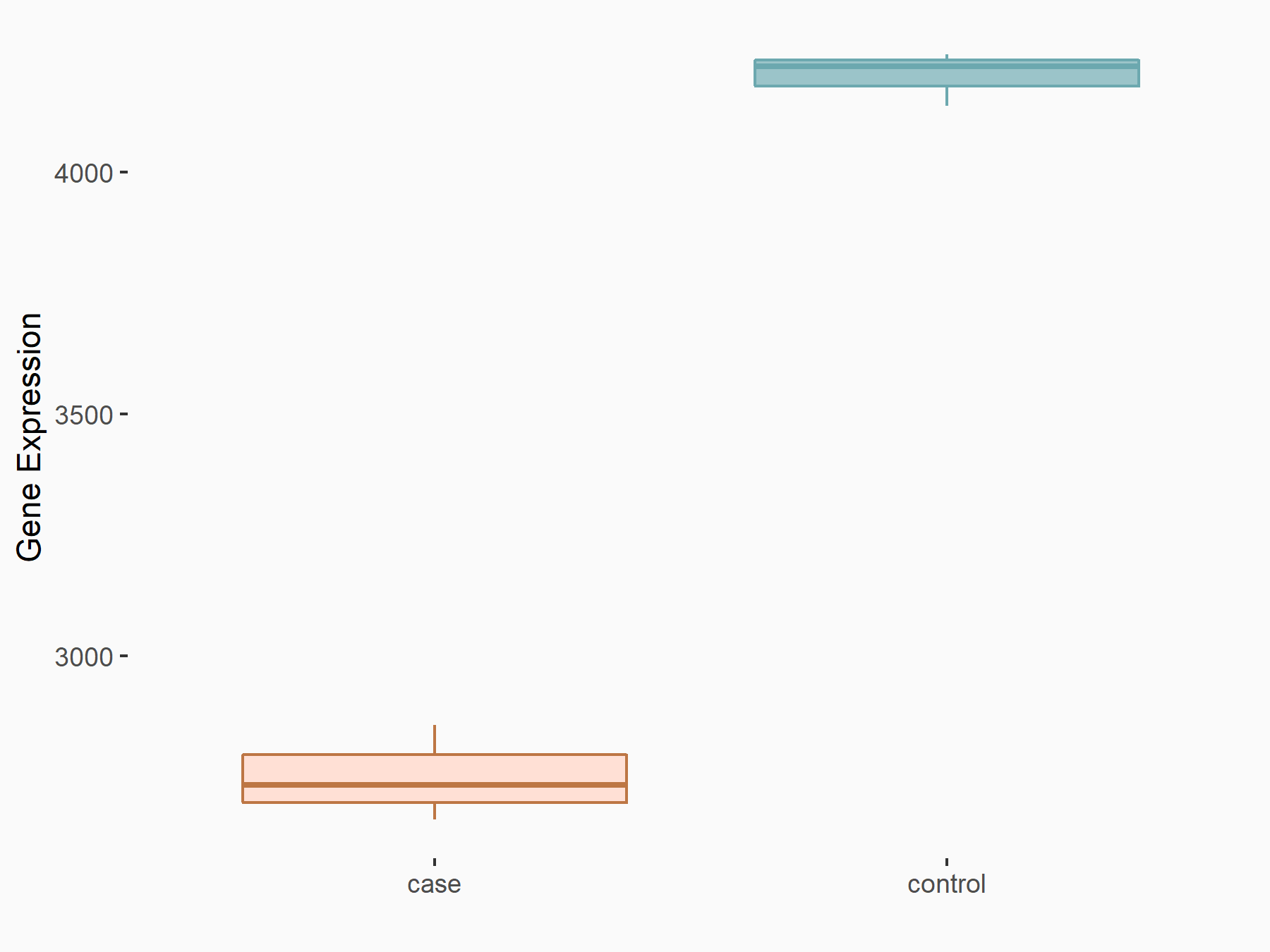 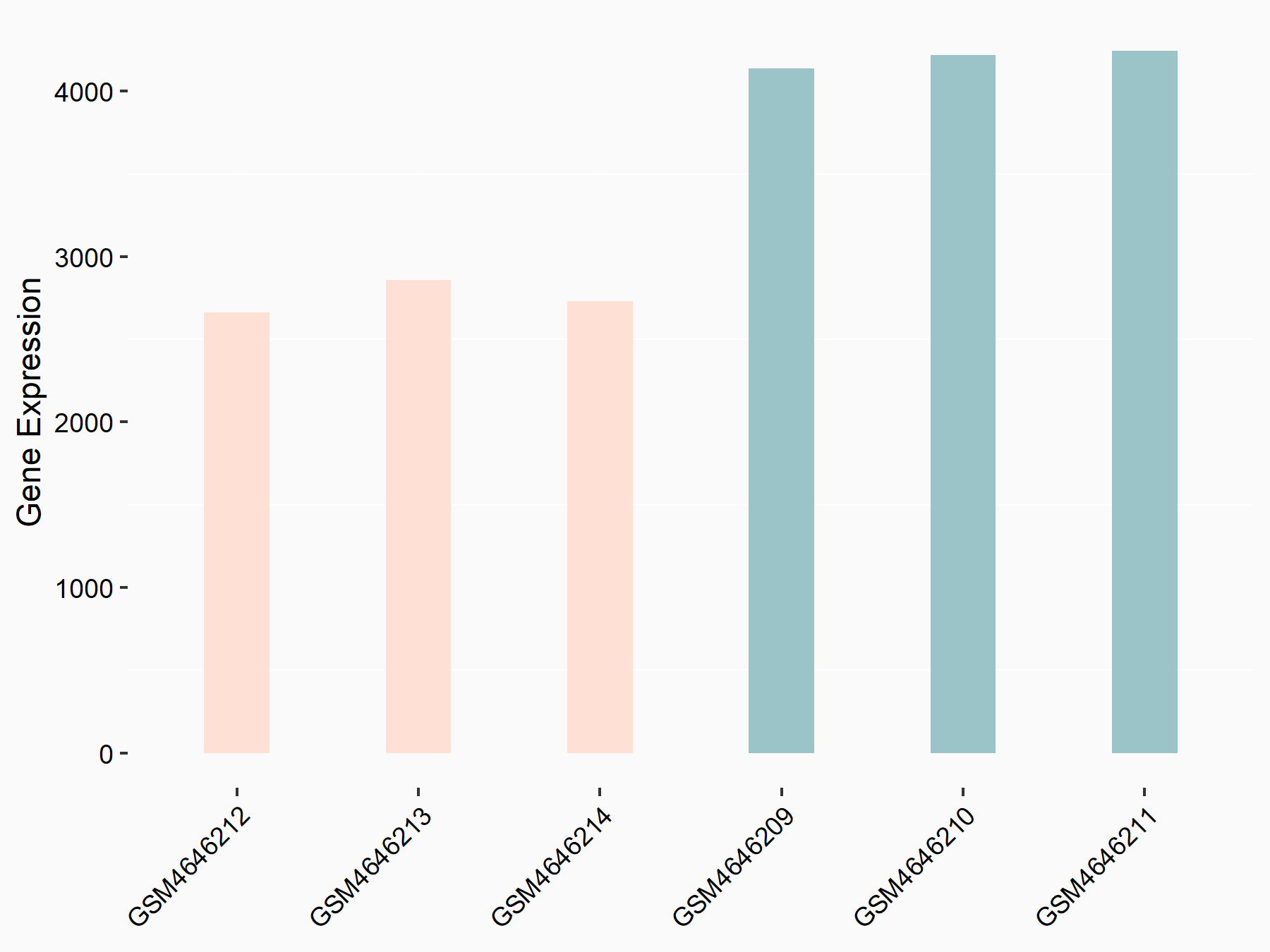 |
logFC: -6.10E-01 p-value: 2.52E-16 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Pertuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Trastuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tucatinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
Neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (Primary myocyte cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | C57BL/6 mouse hearts were subjected to ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in vivo as described previously (Bock-Marquette et al., 2004; Song et al., 2015; Brocard et al., 2017). I/R injury in mice was induced by 45-min ischemia, followed by 7-day and 4-week reperfusion in a loss-of-function study (Figure 1) and gain-of-function study (Figure 2), respectively. In brief, mice were anesthetized with 2% avertin (0.1 ml/10g body weight; Sigma-Aldrich Corporation, United States) through intraperitoneal injection. To generate I/R injury, the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) was ligated with 7-0 nylon for 45 min and then was removed. For the sham group, a suture was passed under the LAD but without ligation. According to the experimental requirements, at different time points of cardiac I/R, the mice were anesthetized for assessing heart function by echocardiographic measurement. All the mice survived during the process of I/R injury after the operation. | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 resulted in enhanced levels of Wnt1 m6A modification and Wnt1 protein but not its transcript level.Furthermore, Mettl14 overexpression blocked I/R-induced downregulation of Wnt1 and Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin) proteins, whereas Mettl14 hearts exhibited the opposite results. Mettl14 attenuates cardiac I/R injury by activating Wnt/Bete-catenin in an m6A-dependent manner, providing a novel therapeutic target for ischemic heart disease. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
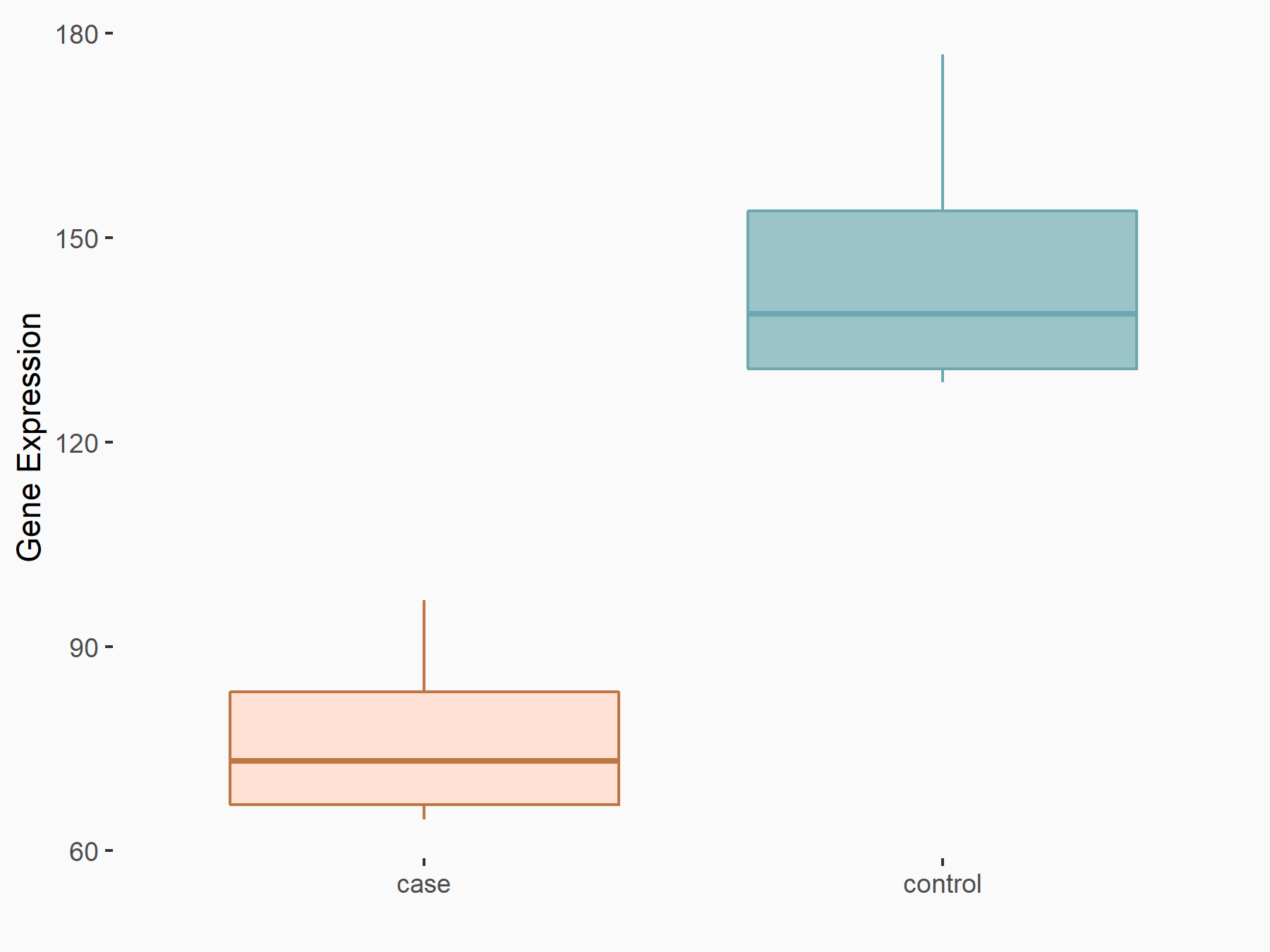 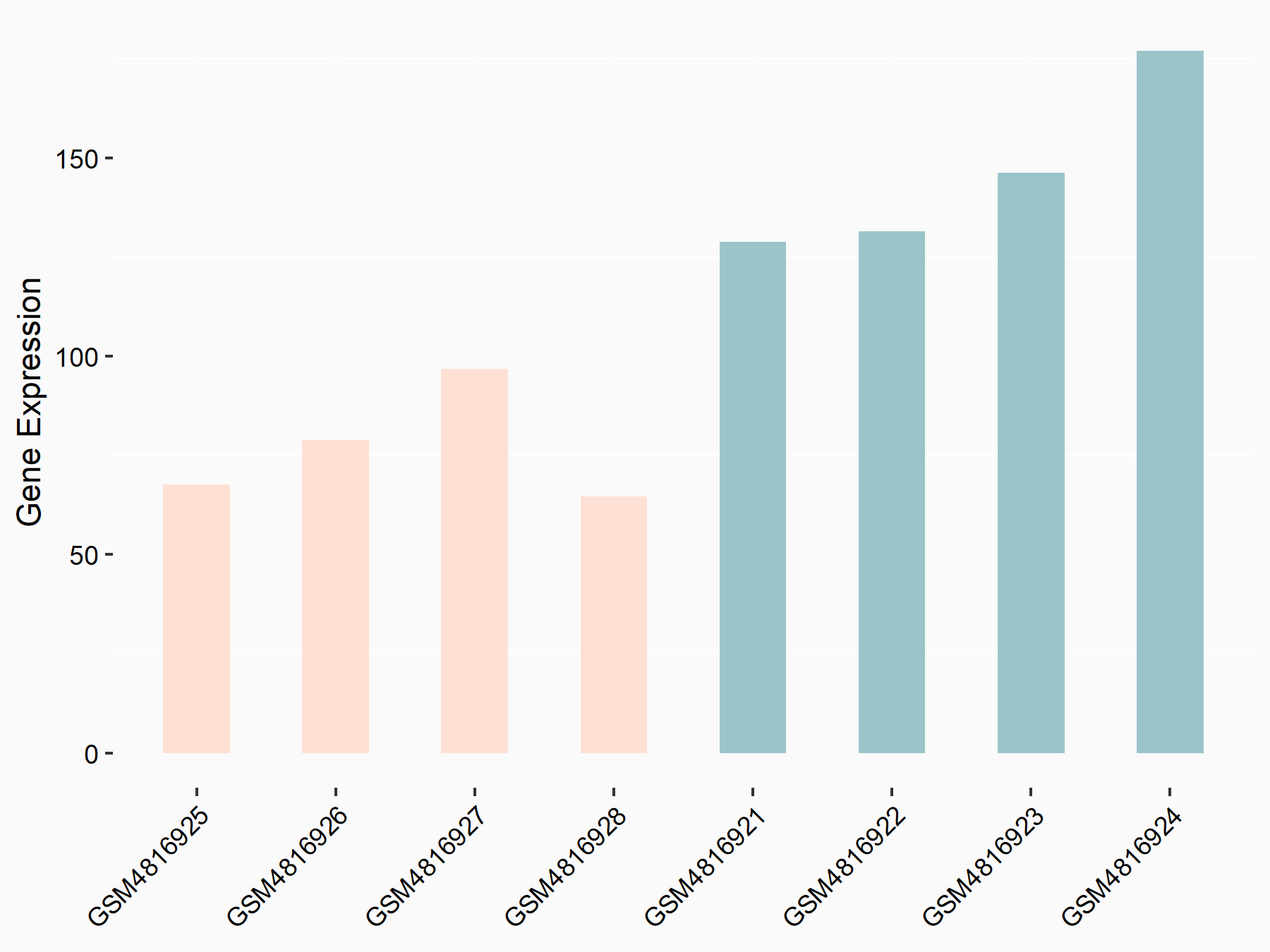 |
logFC: -9.21E-01 p-value: 1.04E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Cells in G7/M phase decreased | ||||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| MOLT-4 | Adult T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0013 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 play an oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia(AML) by targeting mdm2/p53 signal pathway. The knockdown of METTL3 and METTL14 in K562 cell line leads to several changes in the expression of p53 signal pathway, including the upregulation of p53, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A/Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A)), and downregulation of mdm2. | |||
Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [65] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 TP53(-/-) | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_HD97 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
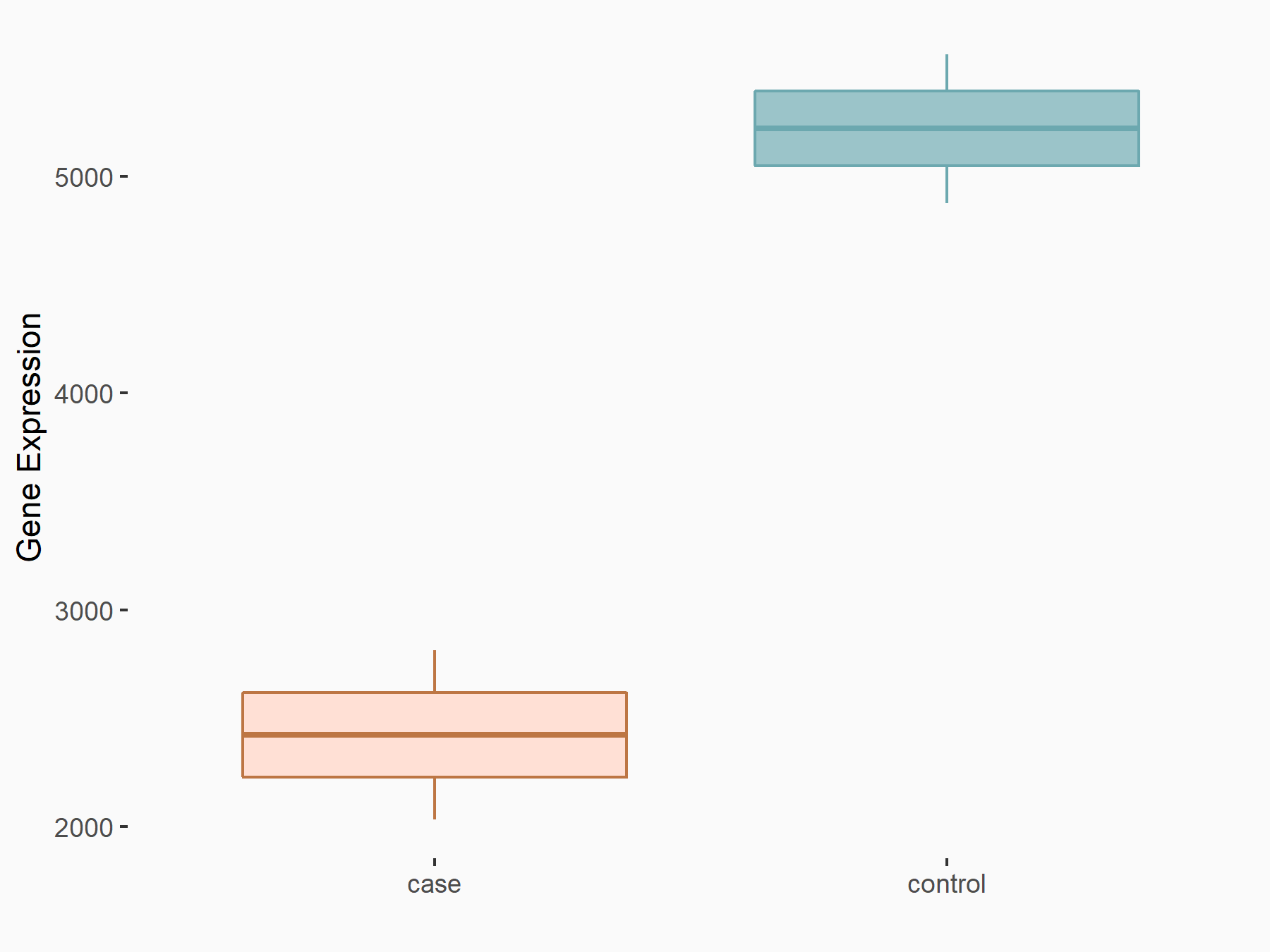  |
logFC: -1.11E+00 p-value: 3.96E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| BEL-7402 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5492 | |
| 7721 (Human hepatic malignant cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 5 × 105 stable SLC7A11-knockdown HCCLM3 cells or SLC7A11-vector cells were injected subcutaneously into BALB/C nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 induced m6A modification at 5'UTR of Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11) mRNA, which in turn underwent degradation relied on the YTHDF2-dependent pathway. Identify the HIF-1alpha /METTL14/YTHDF2/SLC7A11 axis as a potential therapeutic target for the HCC interventional embolization treatment. | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Pertuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Trastuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tucatinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
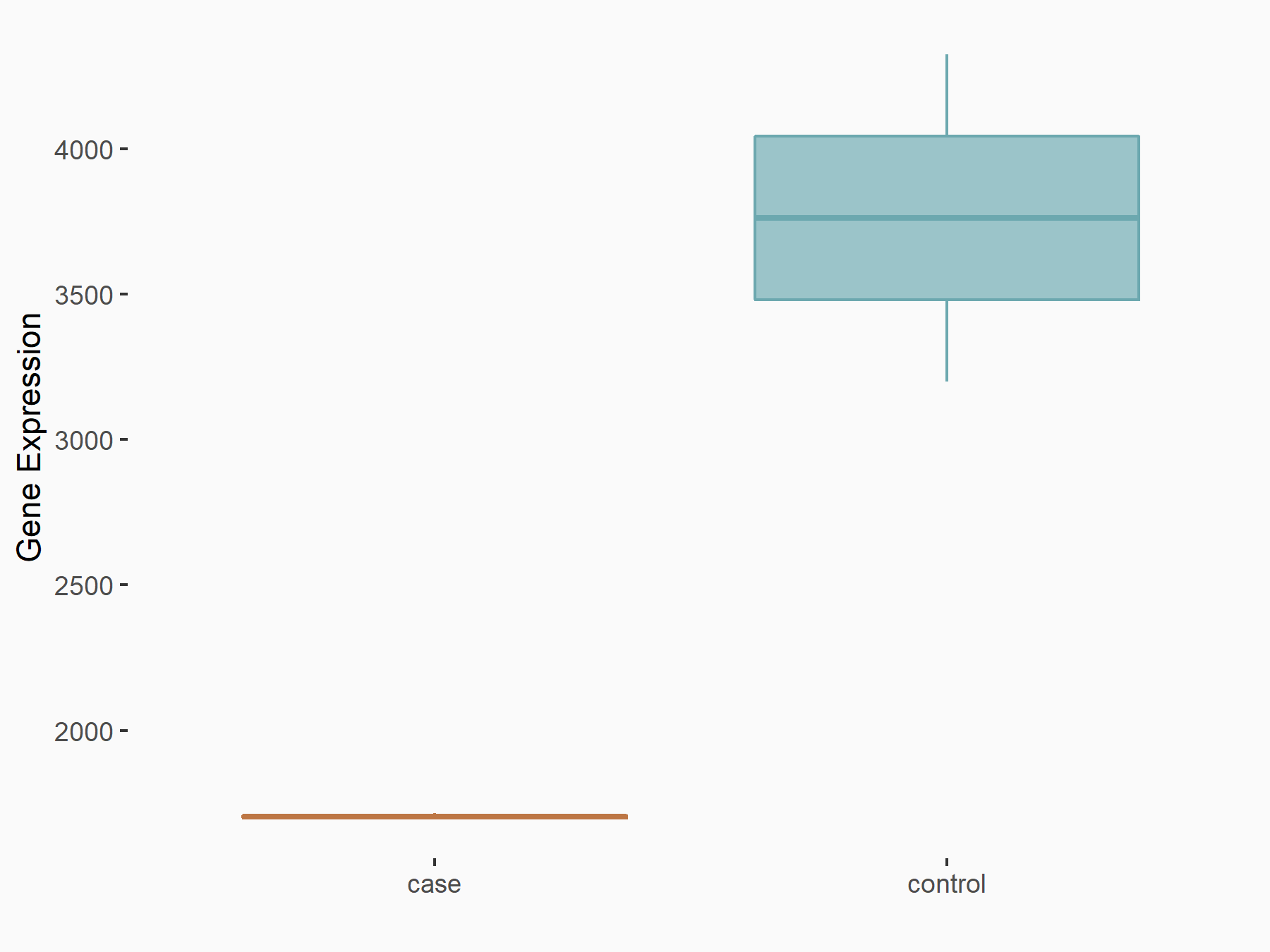  |
logFC: -1.14E+00 p-value: 9.74E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Response Summary | LNC942-METTL14-CXCR4/Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) signaling axis, which provides new targets and crosstalk m6A epigenetic modification mechanism for breast cancer prevention and treatment. | |||
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [66] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| End1/E6E7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3684 | |
| In-vivo Model | To examine the effects of piRNA-14633 on subcutaneous xenograft growth, BALB/c nude mice (Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology) were subcutaneously injected with 0.1 mL of cell suspension containing 2 × 106 cells. Tumor volume (mm3) was measured every 4 days using a Vernier caliper and calculated as 0.4 x (short length)2 × long length. | |||
Dexamethasone-induced Ras-related protein 1 (RASD1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
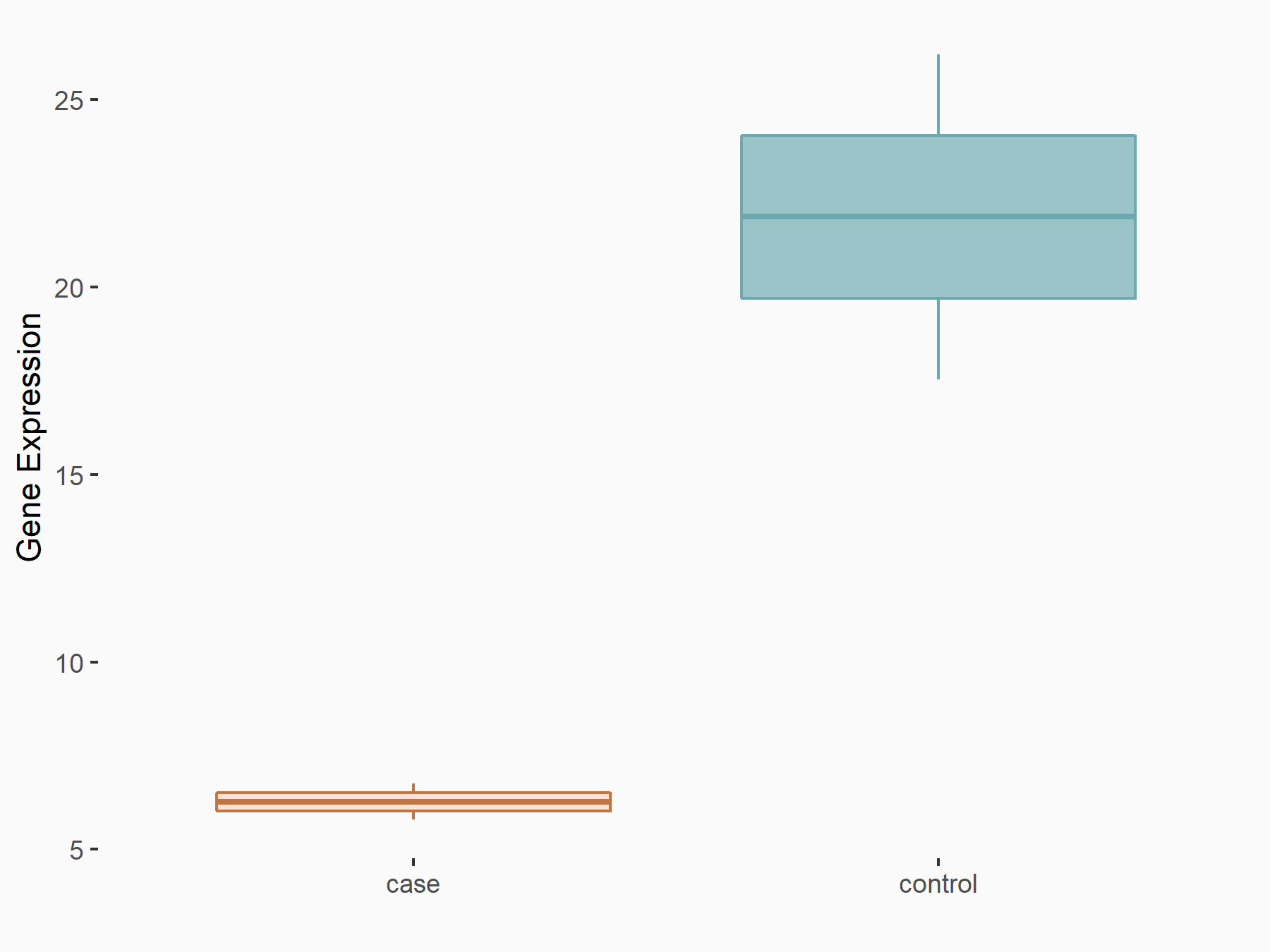  |
logFC: -1.81E+00 p-value: 2.87E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Injuries of spine or trunk [ICD-11: ND51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injuries of spine or trunk [ICD-11: ND51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
In-vitro Model |
C8-D1A | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_6379 |
| C8-B4 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_6378 | |
| In-vivo Model | An incision was made in the skin along the medial dorsal line to the aponeurotic and muscular planes, and the posterior vertebral arches were exposed from T8 to T12. Under the dissection stereomicroscope, 3-mm-long laminectomy was performed on the caudal end of T10 vertebra and the rostral end of T11 vertebra. The Infinite Horizons impactor (Infinite Horizons, L.L.C., Lexington, KY, USA) was adopted to produce the contusion SCI using a force of 60 kdyn/cm2. The SCI model rats were established and randomly assigned to SCI model group, ant-NC (negative control, SCI rats treated with lentiviral (lv)-shRNA NC of Mettl14) group and ant-Mettl14 group (SCI rats treated with lv-shRNA of Mettl14). Rats were subjected to laminectomy and then treated with lv-shRNA Mettl14/lv-shRNA-NC (50 ul/day, 100 nmoL/mL; RiboBio, Guangzhou, China) via an intrathecal injection through lumbar puncture for 3 days (0, 1, and 2 days) after 15 min of SCI modelling. In addition, the unmodeled rats were set as sham group. | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14-mediated m6A modification inhibited Dexamethasone-induced Ras-related protein 1 (RASD1) and induced the apoptosis of spinal cord neurons in SCI by promoting the transformation of pri-miR-375 to mature miR-375. | |||
DNA damage-binding protein 2 (DDB2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
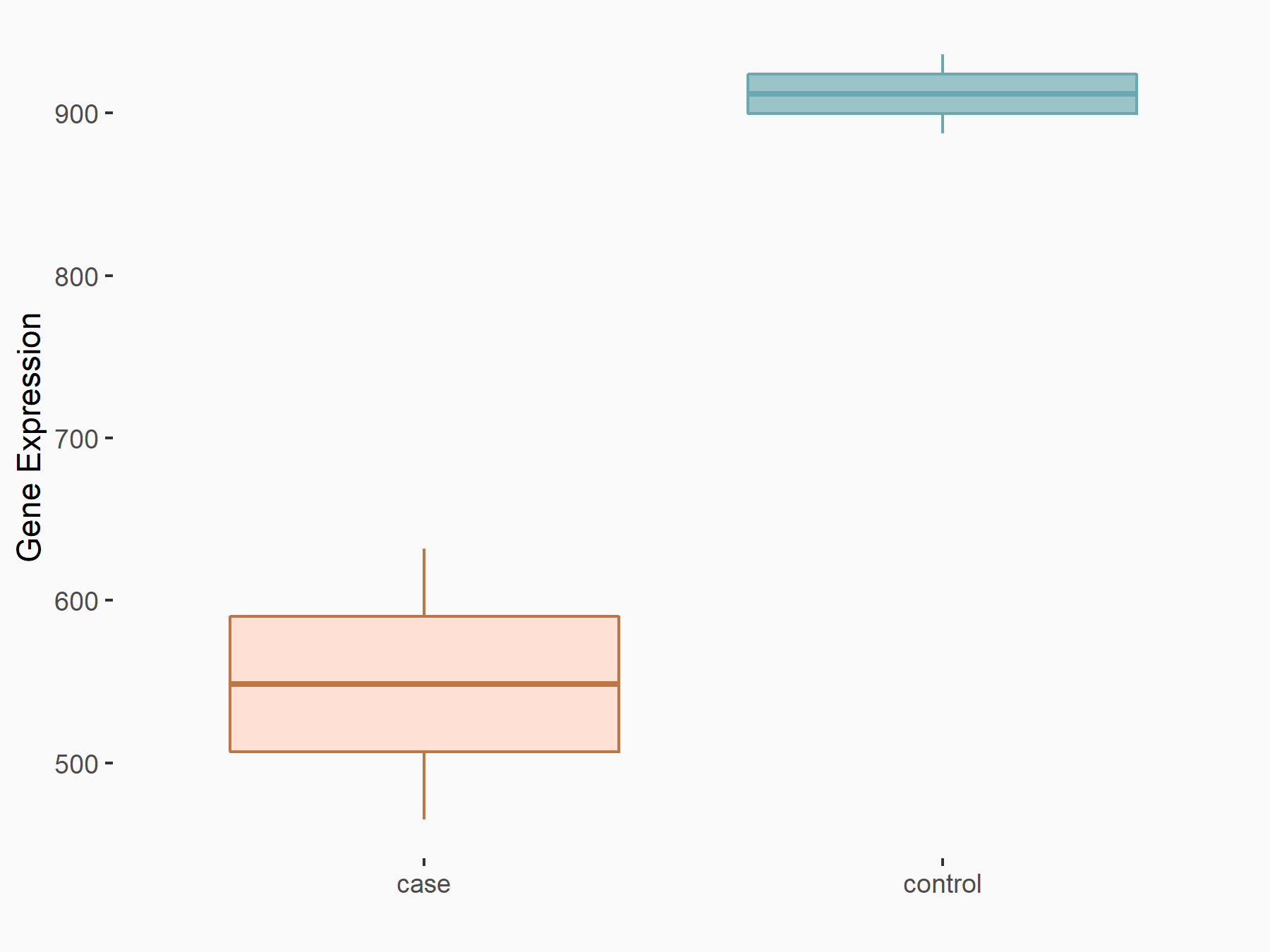  |
logFC: -7.35E-01 p-value: 7.54E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Skin tumour [ICD-11: 2F92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Skin tumour [ICD-11: 2F92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | Genome repair | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
NHEK (Normal human epithelial keratinocytes) | |||
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 | |
| A-431 | Skin squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0037 | |
| Response Summary | METTL14 knockdown decreases GGR and DNA damage-binding protein 2 (DDB2) abundance. Conversely, overexpression of wild-type METTL14 but not its enzymatically inactive mutant increases GGR and DDB2 abundance. METTL14 is a target for selective autophagy and acts as a critical epitranscriptomic mechanism to regulate GGR and suppress UVB-induced skin tumorigenesis. | |||
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
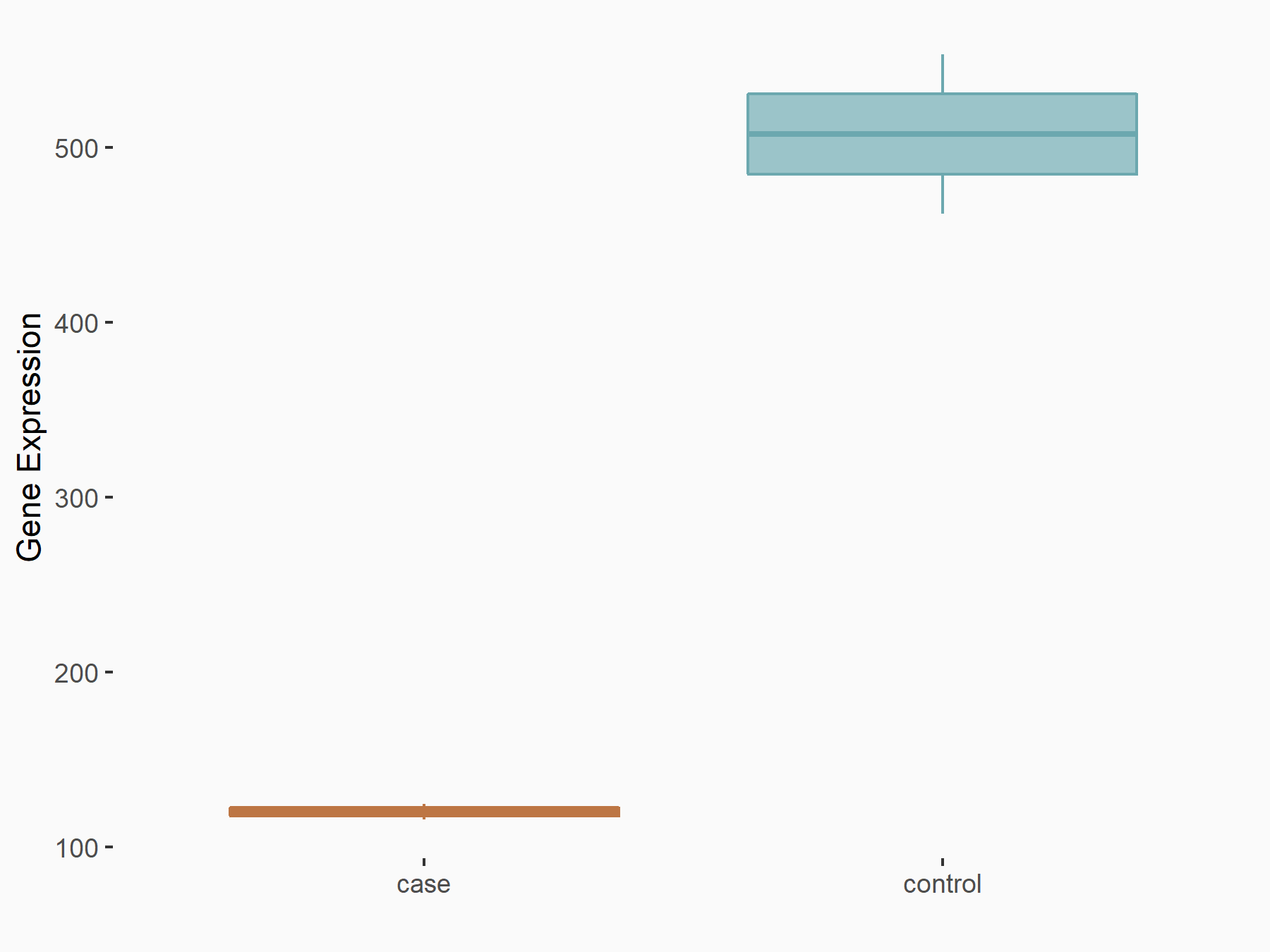 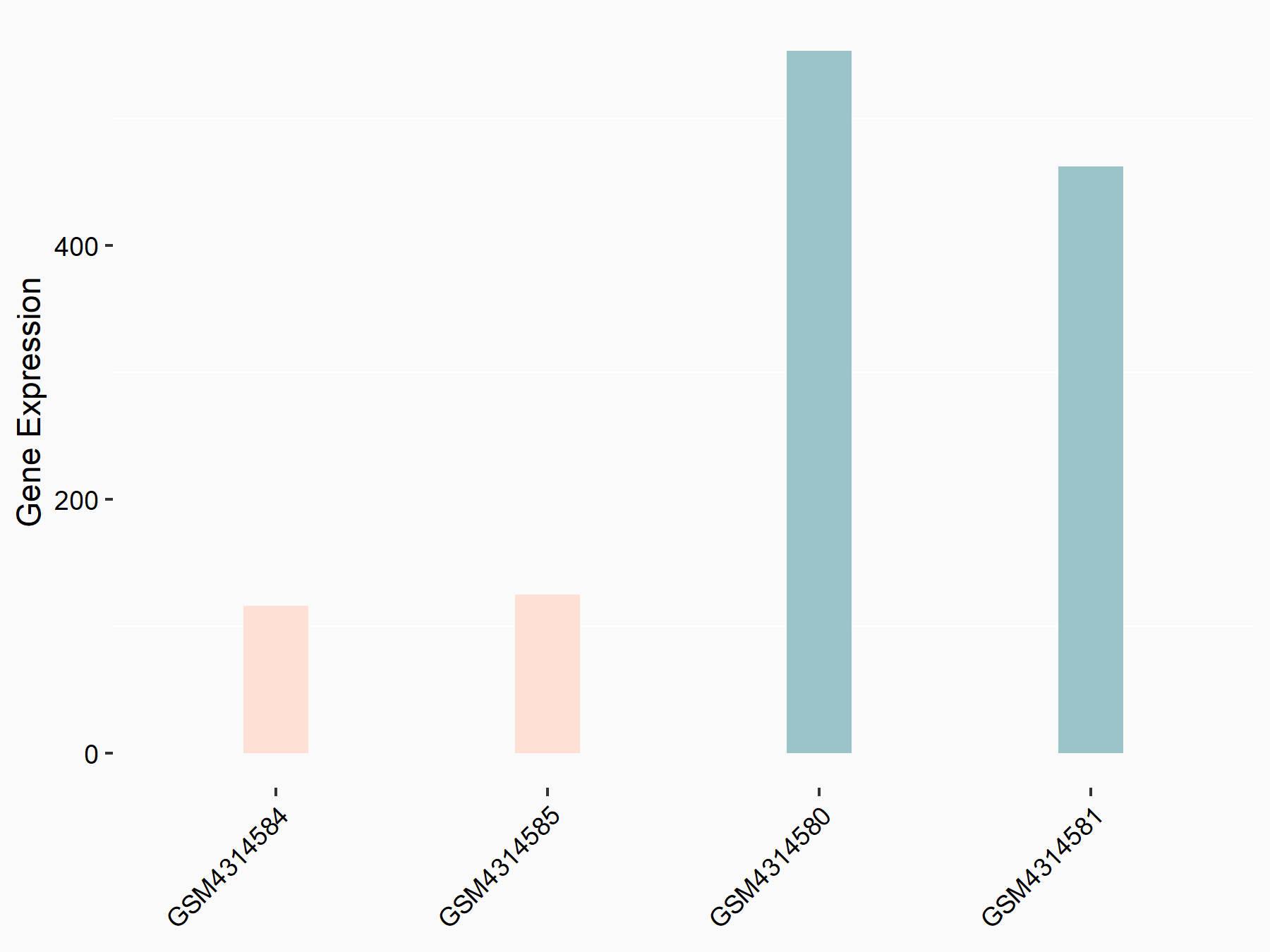 |
logFC: -2.08E+00 p-value: 8.68E-26 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [14] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Ubiquitination degradation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP) mRNA decay through its 3' UTR N6-methyladenosine (m6A) to inhibit its downstream pro-apoptotic target gene expression, suppress ER proteotoxic liver disease. UPR induces METTL14 expression by competing against the HRD1-ER-associated degradation (ERAD) machinery to block METTL14 ubiquitination and degradation. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [68] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Regorafenib | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | After one week of acclimatization, the nude mice were randomly divided into 5 groups (n = 3): Control, vehicle + oe-NC, vehicle + oe-CHOP, Regorafenib + oe-NC, and Regorafenib + oe-CHOP. The Control group was injected with untreated SK-Hep-1 cells. The vehicle + oe-NC group and Regorafenib + oe-NC group were injected with SK-Hep-1 cells transfected with oe-NC. vehicle + oe-CHOP group and Regorafenib + oe-CHOP group were injected with SK-Hep-1 cells transfected with oe-CHOP. | |||
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM7 (TRIM7)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
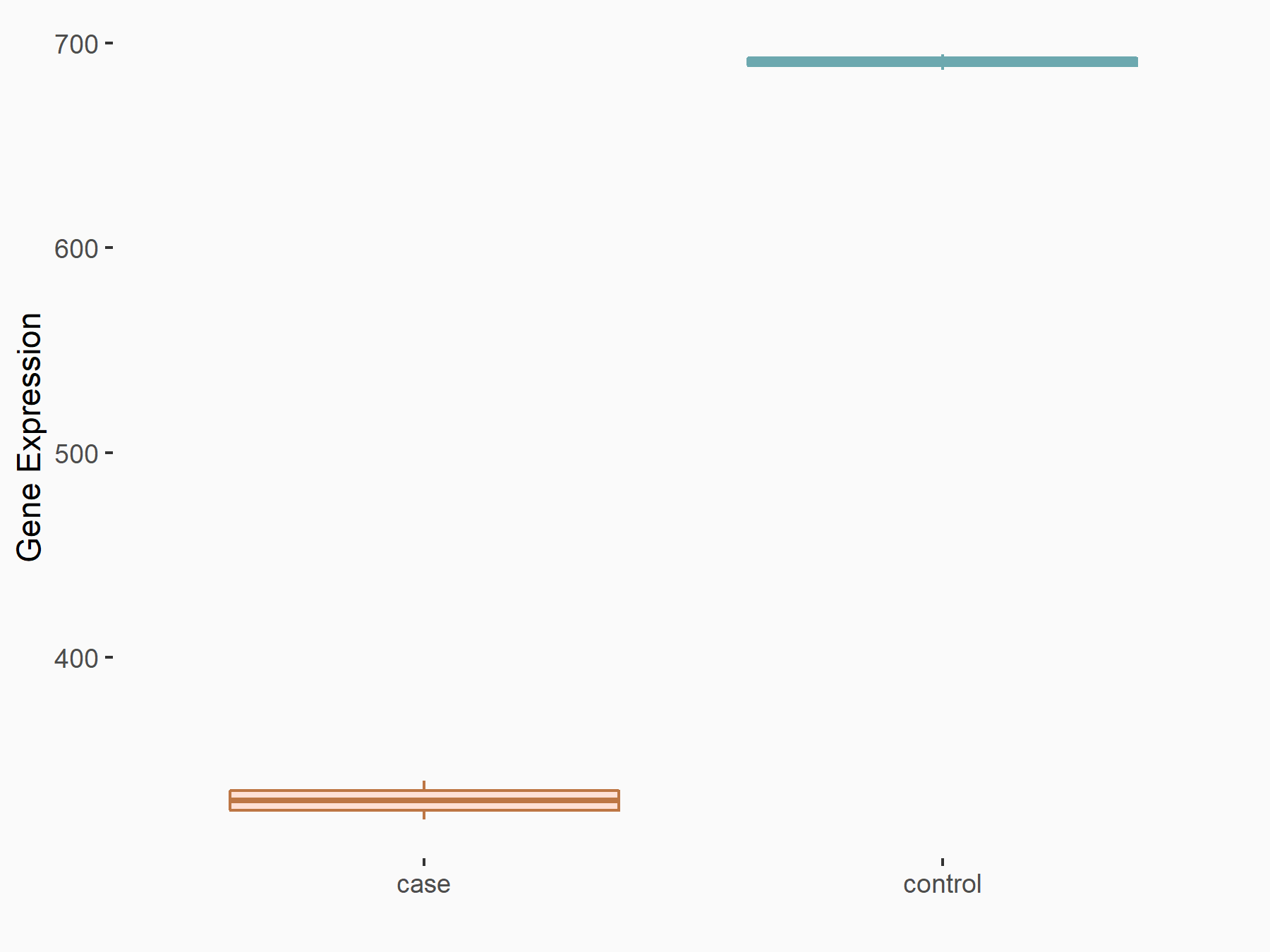 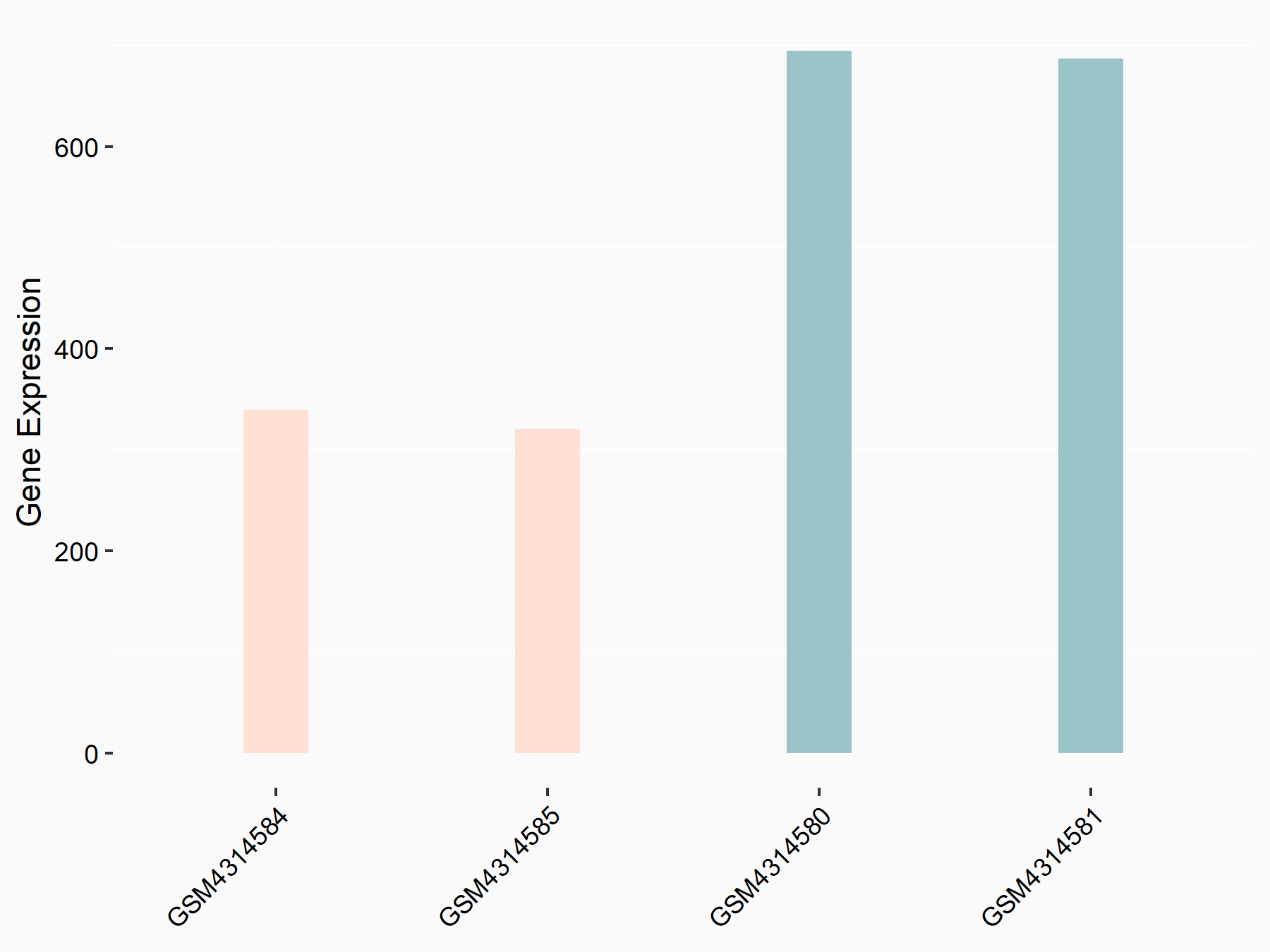 |
logFC: -1.06E+00 p-value: 1.08E-12 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [15] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasome pathway degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| SaOS-2 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0548 | |
| MG-63 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 | |
| HOS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0312 | |
| hFOB 1.19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3708 | |
| In-vivo Model | MG63 cells transduced with lentivirus expressing shTRIM7 or shNC, and SAOS2 cells transduced with lentivirus expressing TRIM7, BRMS1, TRIM7 plus BRMS1 or control vector, were injected via the tail vein into the nude mice (1 × 106 cells/mouse) (n = 11 per group). | |||
| Response Summary | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM7 (TRIM7) mRNA stability was regulated by the METTL3/14-YTHDF2-mRNA in a decay-dependent manner. TRIM7 plays a key role in regulating metastasis and chemoresistance in osteosarcoma through ubiquitination of BRMS1. | |||
ELAV-like protein 1 (HuR/ELAVL1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
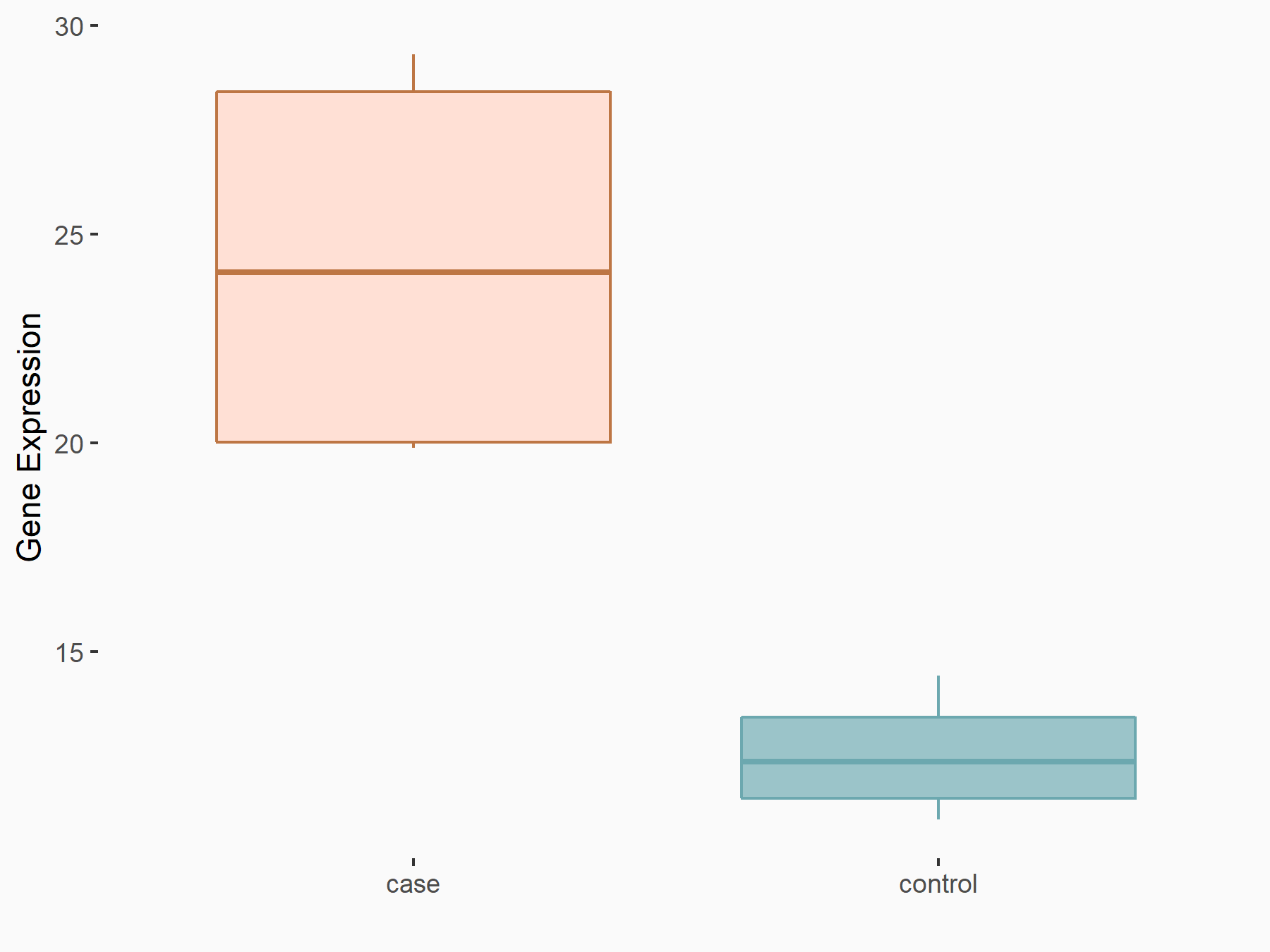  |
logFC: 8.91E-01 p-value: 1.25E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [16] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor xenograft studies, MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with scrambled-siRNA or METTL14-siRNA or ALKBH5-siRNA (2 × 106) were mixed with Matrigel and injected subcutaneously in the flank of 6-week-old female athymic nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 and ALKBH5 determine the m6A status of target genes by controlling each other's expression and by inhibiting m6A reader YTHDF3 (YTH N 6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 3), which blocks RNA demethylase activity. ALKBH5/METTL14 constitute a positive feedback loop with RNA stability factor ELAV-like protein 1 (HuR/ELAVL1) to regulate the stability of target transcripts. This study unveils a previously undefined role for m6A in cancer and shows that the collaboration among writers-erasers-readers sets up the m6A threshold to ensure the stability of progrowth/proliferation-specific genes, and protumorigenic stimulus. | |||
Elongation factor 1-alpha 2 (EEF1A2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
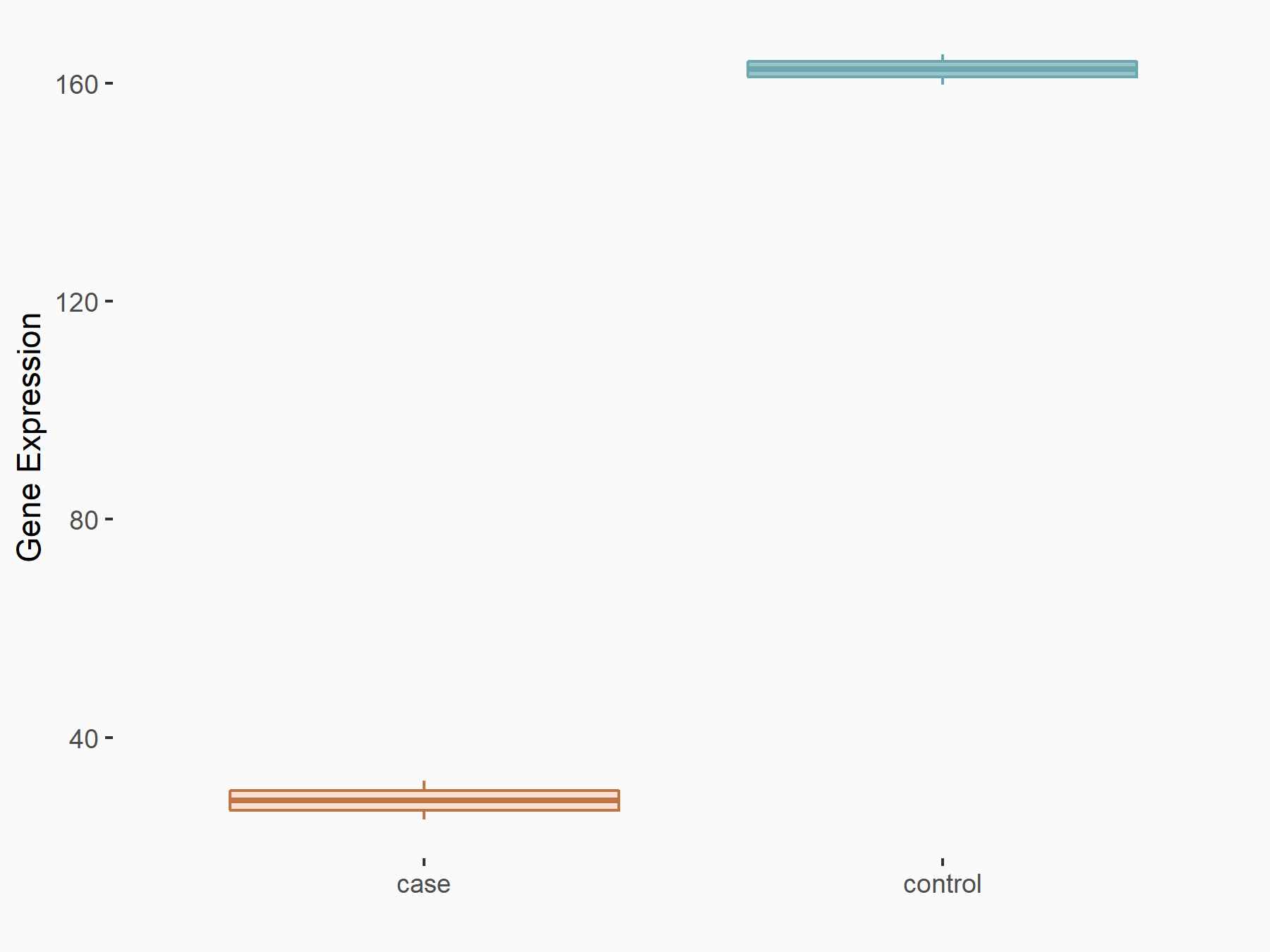  |
logFC: -2.52E+00 p-value: 5.01E-13 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Injuries of spine or trunk [ICD-11: ND51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injuries of spine or trunk [ICD-11: ND51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | Specifically, rats were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of 4% pentobarbital sodium (35 mg/kg) after weight measurement. To expose the posterior vertebral arch from T8 to T12, an incision was subsequently made on the skin along the dorsomedial line to the aponeurosis and muscle plane. Laminectomy (3 mm) was performed from the caudal end of the T10 vertebra to the caudal end of the T11 vertebra under a dissection stereomicroscope. Infinite Horizons impactor (Infinite Horizons, L.L.C., Lexington, KY, USA) was utilized to induce contusion SCI at the force of 60 kdyn/cm . The incision was sutured, followed by intramuscular injection of 20000 units of penicillin once a day for three days. Incisions of rats in the sham group (N = 10) were sutured after skin incision without modeling surgery and related treatment. SCI rat model was established and SCI rats were assigned to the following groups (N = 10 per group): SCI group (SCI treatment), SCI + sh-NC group (injected with silencing negative control lentivirus after SCI treatment), SCI + sh-METTL14 + sh-EEF1A2 group (injected with silencing EEF1A2 and silencing METTL14 lentivirus after SCI treatment), SCI + oe-NC group (injected with overexpressed EEF1A2 NC lentivirus after SCI treatment), SCI + oe-EEF1A2 group (injected with overexpressed EEF1A2 lentivirus after SCI treatment), SCI + oe-EEF1A2 + H2O group [injected with overexpressed EEF1A2 lentivirus and treated with 50 mg/kg (i.p.) H2O after SCI treatment] and SCI + oe-EEF1A2 + Perifosine group [injected with overexpressed EEF1A2 lentivirus and treated with 50 mg/kg (i.p.) Perifosine after SCI treatment . Lentivirus treatment was conducted three days following laminectomy (on day 0, 1, and 2). sh-NC, sh-METTL14, sh-EEF1A2, oe-NC, and oe-EEF1A2 lentivirus (50 uL/day, 100 nmoL/mL; RiboBio, Guangzhou, China) were intrathecally injected through lumbar puncture for 15 min per day. | |||
| Response Summary | Silencing METTL14 repressed apoptosis of spinal cord neurons and attenuated spinal cord injury by inhibiting m6A modification of Elongation factor 1-alpha 2 (EEF1A2) and activating the Akt/mTOR pathway. | |||
Engulfment and cell motility protein 1 (ELMO1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
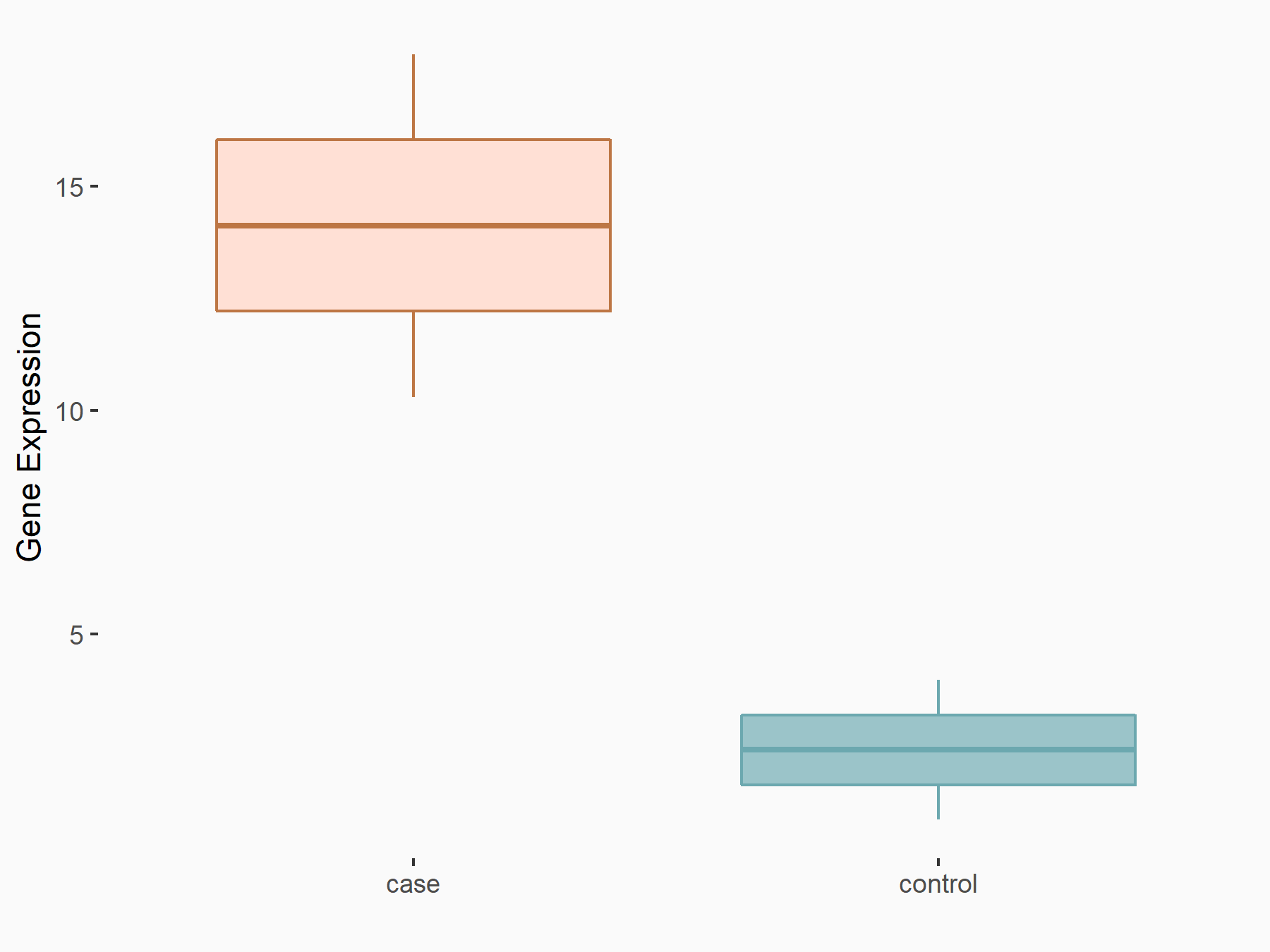  |
logFC: 2.58E+00 p-value: 2.13E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Inflammatory spondyloarthritis [ICD-11: FA92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ankylosing spondylitis [ICD-11: FA92.0Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RNA degradation | hsa03018 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The SKG mice were randomly divided into three groups: a PBS group, an Av-NC group, and an Av-ELMO1 group. The SKG mice in the Av-ELMO1 group were treated with 5 × 1010 Av-ELMO1 via intravenous tail vein injection at the time of disease induction, and the SKG mice in the Av-NC group or PBS group were separately treated with equal amounts of control adenoviruses or PBS. | |||
| Response Summary | TNF-alpha leads to increased expression of ELMO1 in AS-MSC, which is mediated by a METTL14 dependent m6A modification in Engulfment and cell motility protein 1 (ELMO1) 3'UTR. Higher ELMO1 expression of AS-MSC is found in vivo in AS patients. | |||
Ephrin type-B receptor 2 (ERK/EPHB2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
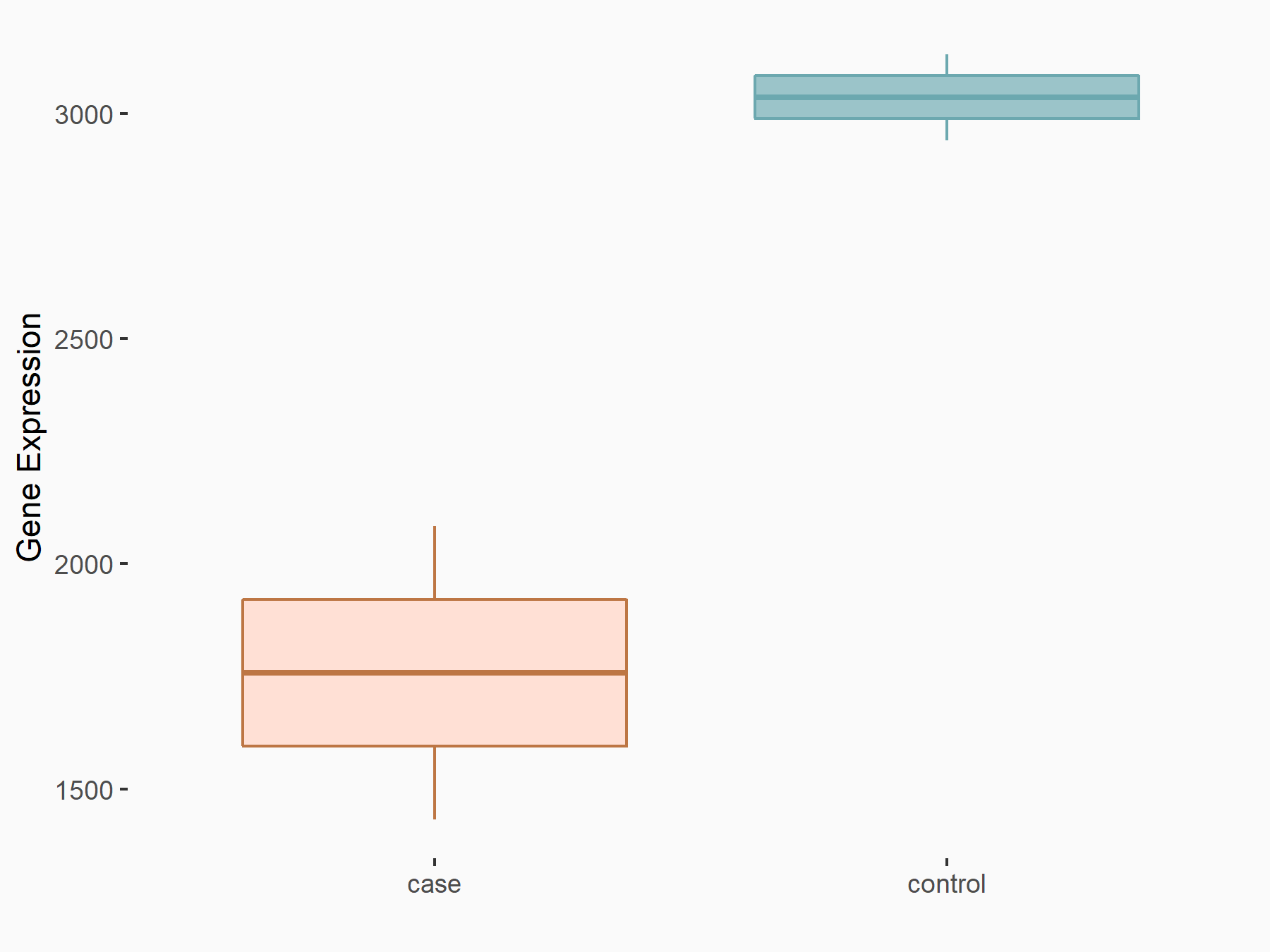  |
logFC: -7.89E-01 p-value: 4.97E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| C2C12 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0188 | |
| In-vivo Model | For mouse muscle injury and regeneration experiment, tibialis anterior (TA) muscles of 6-week-old male mice were injected with 25 uL of 10 uM cardiotoxin (CTX, Merck Millipore, 217503), 0.9% normal saline (Saline) were used as control. The regenerated muscles were collected at day 1, 3, 5, and 10 post-injection. TA muscles were isolated for Hematoxylin and eosin staining or frozen in liquid nitrogen for RNA and protein extraction. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A writers METTL3/METTL14 and the m6A reader YTHDF1 orchestrate MNK2 expression posttranscriptionally and thus control Ephrin type-B receptor 2 (ERK/EPHB2) signaling, which is required for the maintenance of muscle myogenesis and contributes to regeneration. | |||
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
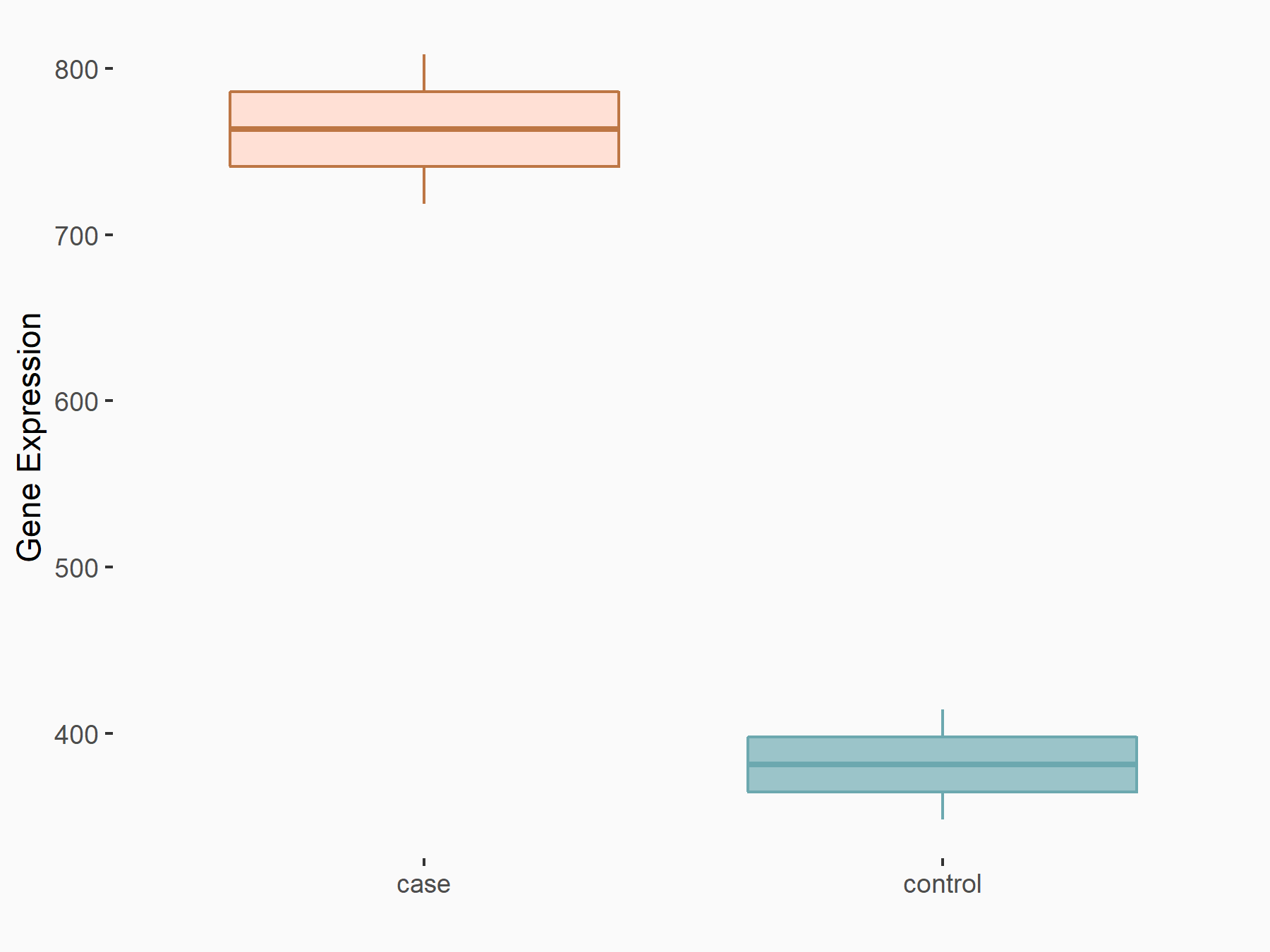  |
logFC: 1.00E+00 p-value: 2.28E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
YY-8103 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_WY40 |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the lung metastasis model, stably transfected HepG2 cells (1 × 106/0.1 mL DMEM) were injected into each nude mouse through the tail vein. Five weeks later, mice were euthanized, and the lung tissues were collected. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 was found to inhibit HCC cell migration, invasion, and EMT through modulating Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
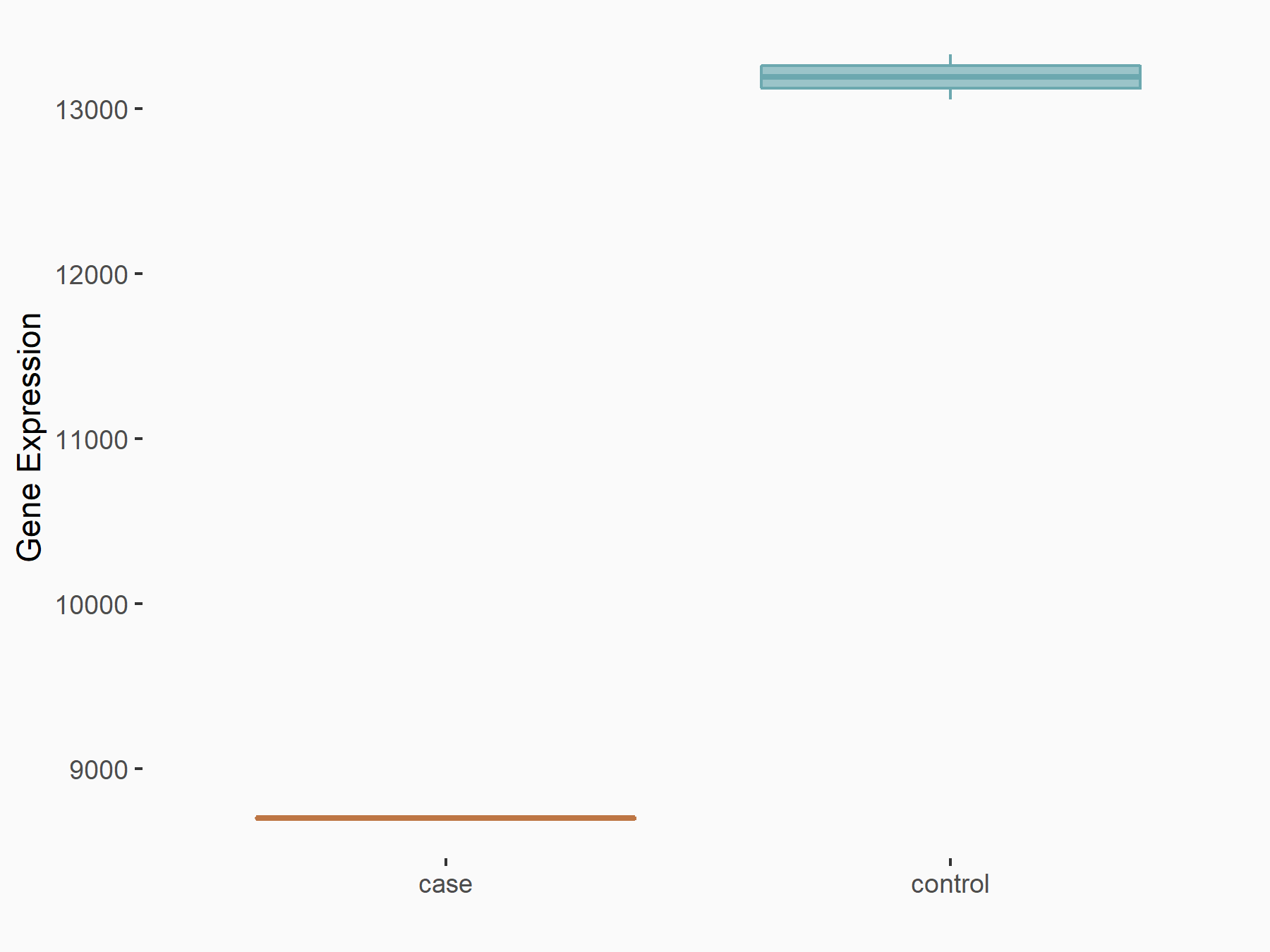  |
logFC: -6.00E-01 p-value: 2.49E-44 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
CAL-33 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1108 |
| HN-6 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8129 | |
| HSC-3 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1288 | |
| In-vivo Model | Specific pathogen-free (SPF) female NOD/SCID mice (5-6 weeks old) were randomly distributed into two groups: the OECtrl group and the OEMETTL14 groups. Phosphate buffer (200 uL) containing approximately 5 × 107 HSC3 or CAL33 cells was subcutaneously injected into the inner thigh of each mouse. The mice were euthanized two weeks after injection, and the tumour xenografts were harvested, photographed, weighed, and fixed. | |||
| Response Summary | The study identified the mechanism by which rapamycin affects autophagy via regulating METTL14, which provides a new idea for a potential targeted therapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma. METTL14 mediated Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) expression via m6A modification and regulated autophagy levels and biological functions in oral squamous cell carcinoma. | |||
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
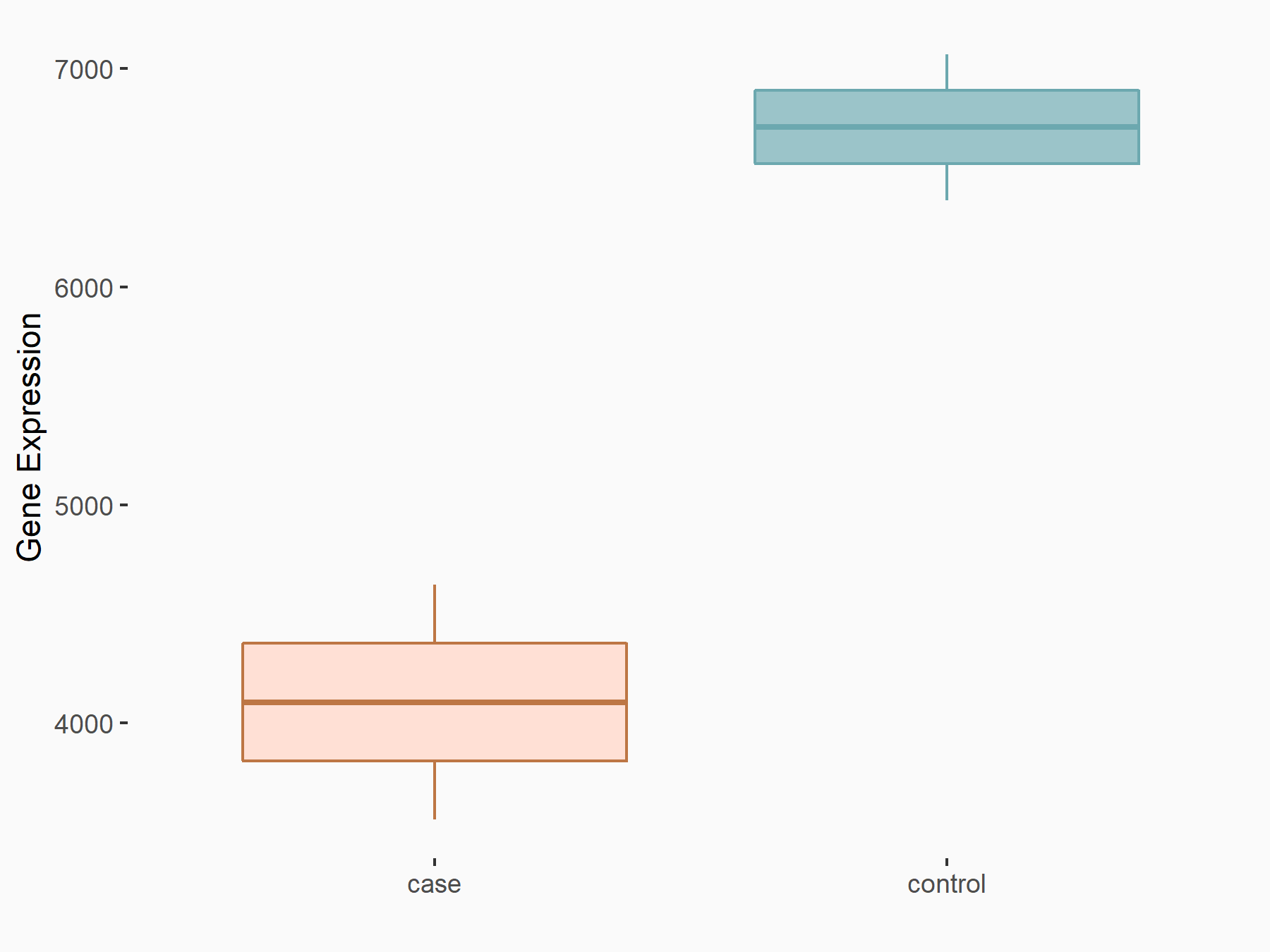  |
logFC: -7.17E-01 p-value: 3.71E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Pertuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Trastuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tucatinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
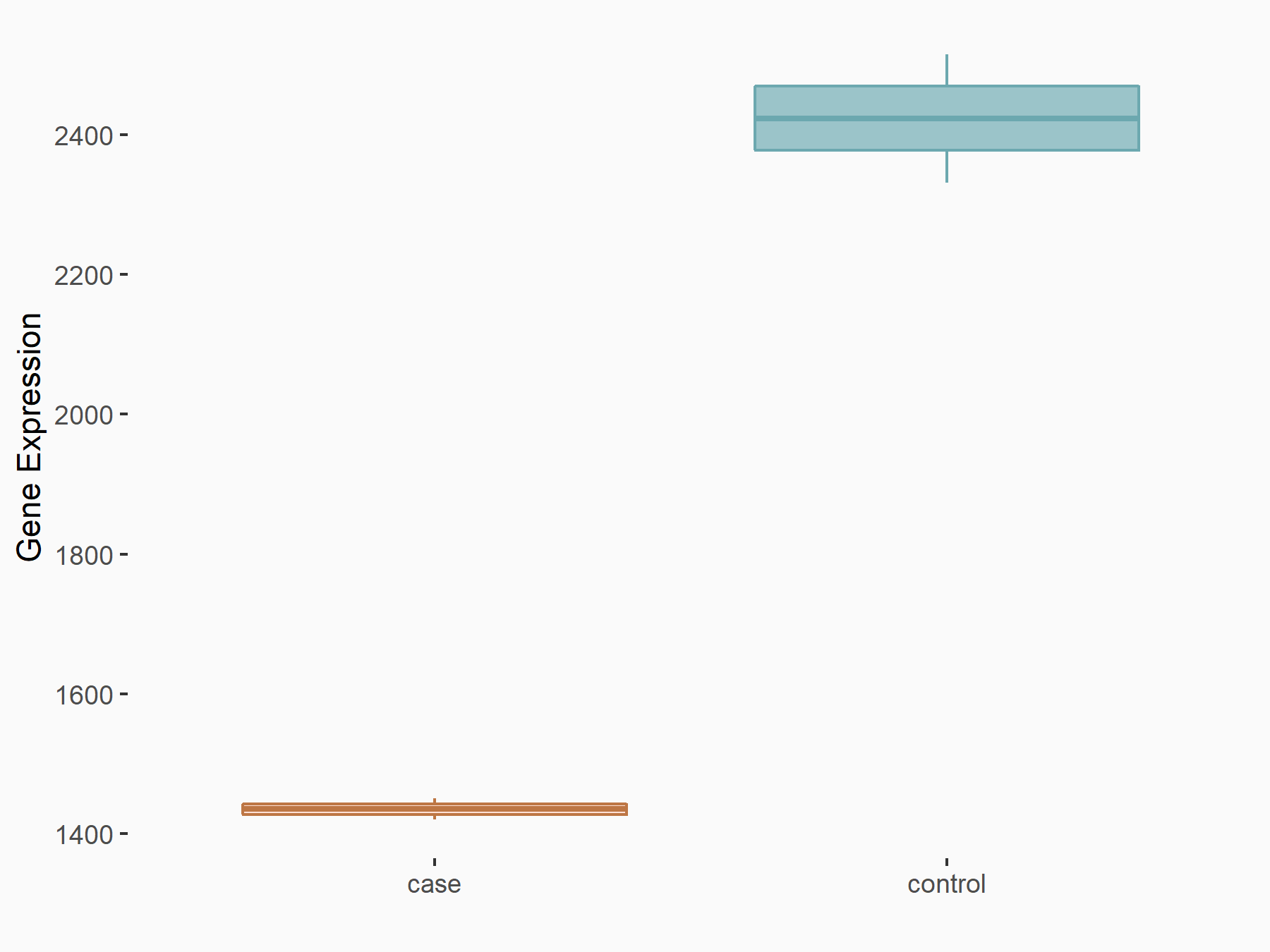  |
logFC: -7.56E-01 p-value: 2.27E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Herpes infection [ICD-11: 1F00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Herpes infection [ICD-11: 1F00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| In-vivo Model | METTL14+/- mice are generated by mating wild-type mice (C57/BL6 background) with METTL14+/- mice. METTL14+/-/APOE-/- healthy offspring mice are produced by heterozygous METTL14+/- mice and heterozygous APOE-/- mice by Mendelian ratios. APOE-/- mice and C57/BL6 mice were purchased from Model Animal Research Center of Nanjing (Nanjing, Jiangsu, China). All mice were housed in the Laboratory Animals Center of the Henan Provincial People's Hospital, with controlled temperature and humidity and a 12:12-hour dark-light cycle, and were provided water and mouse chow ad libitum. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) expression by enhancing its m6A modification and inducing endothelial cell inflammatory response as well as atherosclerotic plaque formation. | |||
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14-/+ mice are generated by mating wild-type mice (C57/BL6 background) with Mettl14-/+ mice. Mettl14-/+/APOE-/- healthy offspring mice are produced by heterozygous Mettl14-/+ mice and heterozygous APOE-/- mice by Mendelian ratios. APOE-/- mice and C57/BL6 mice were purchased from Model Animal Research Center of Nanjing (Nanjing, Jiangsu, China). All mice were housed in the Laboratory Animals Center of the Henan Provincial People's Hospital, with controlled temperature and humidity and a 12:12-hour dark-light cycle, and were provided water and mouse chow ad libitum. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) expression by enhancing its m6A modification and inducing endothelial cell inflammatory response as well as atherosclerotic plaque formation. | |||
Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
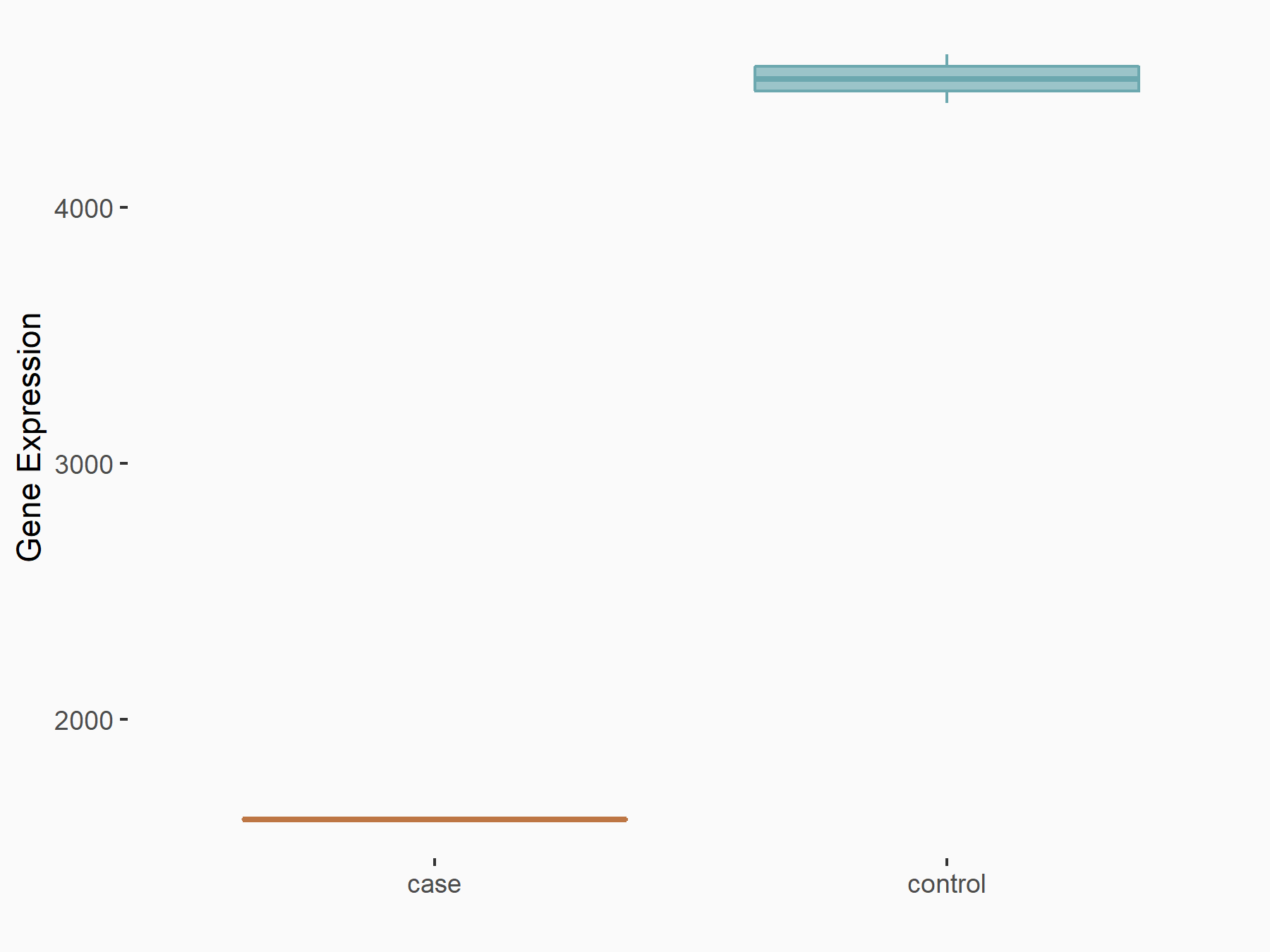 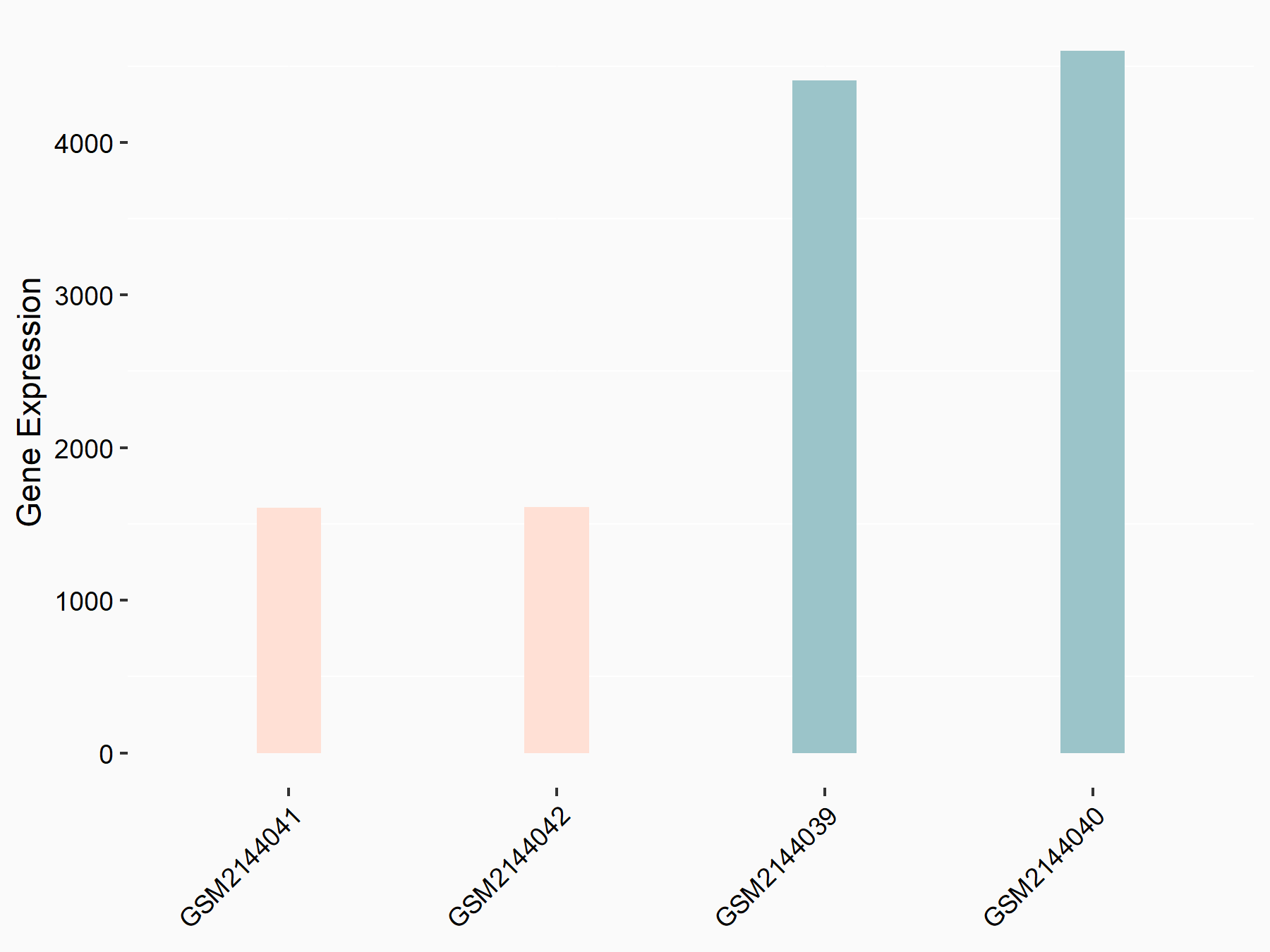 |
logFC: -1.48E+00 p-value: 5.68E-29 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [23] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
HTR-8/SVneo | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7162 |
| HTR-8 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_D728 | |
| Response Summary | Global RNA m6A methylation and METTL14 expression were significantly increased in placental tissues obtained from patients with preeclampsia. Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3) inhibition effectively prevented the impairment of trophoblast proliferation and invasion, and diminished the induction of trophoblast autophagy and apoptosis in METTL14-overexpressing HTR-8/SVneo cells. | |||
Inflammatory spondyloarthritis [ICD-11: FA92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [71] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ankylosing spondylitis [ICD-11: FA92.0Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
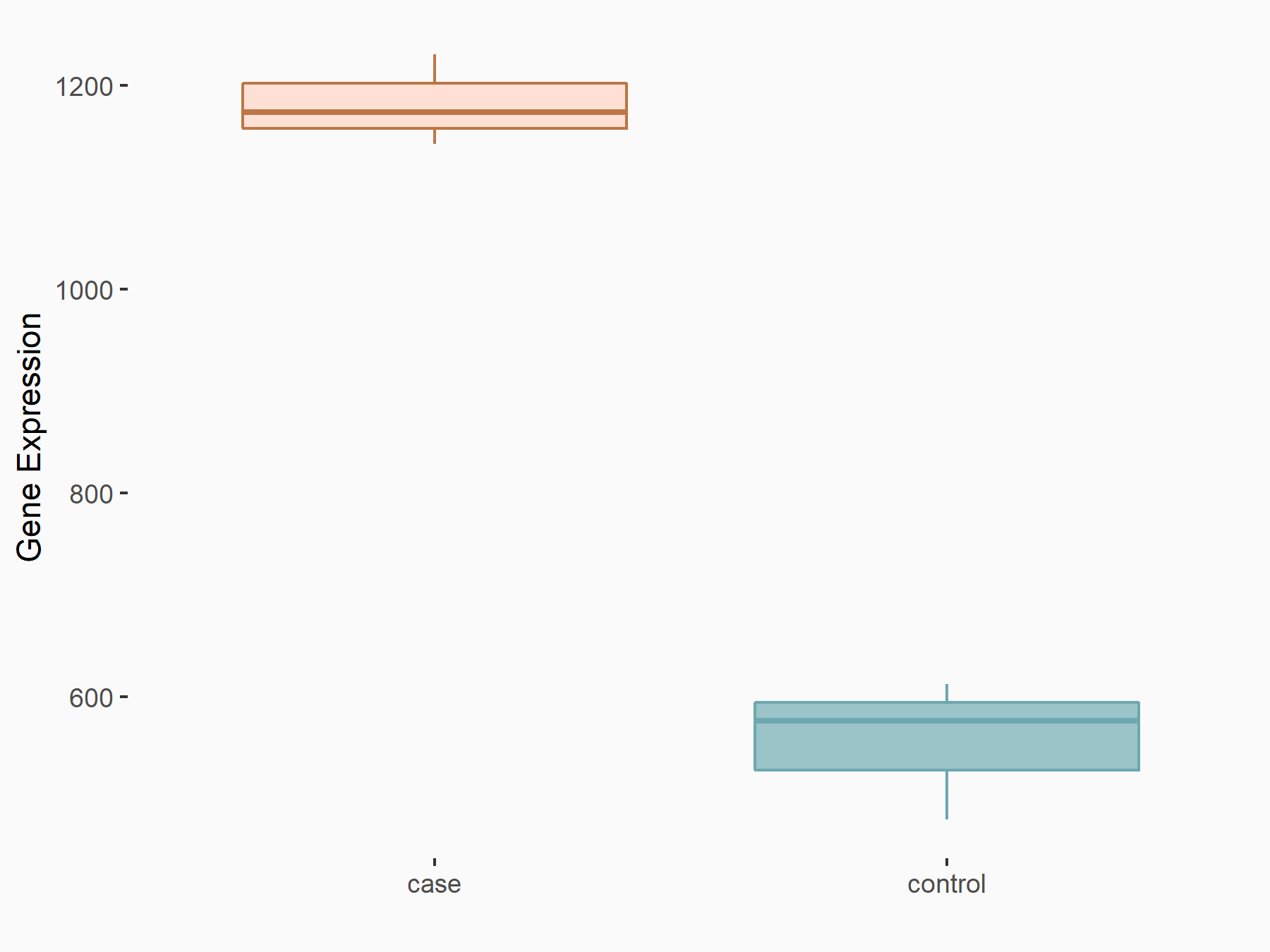 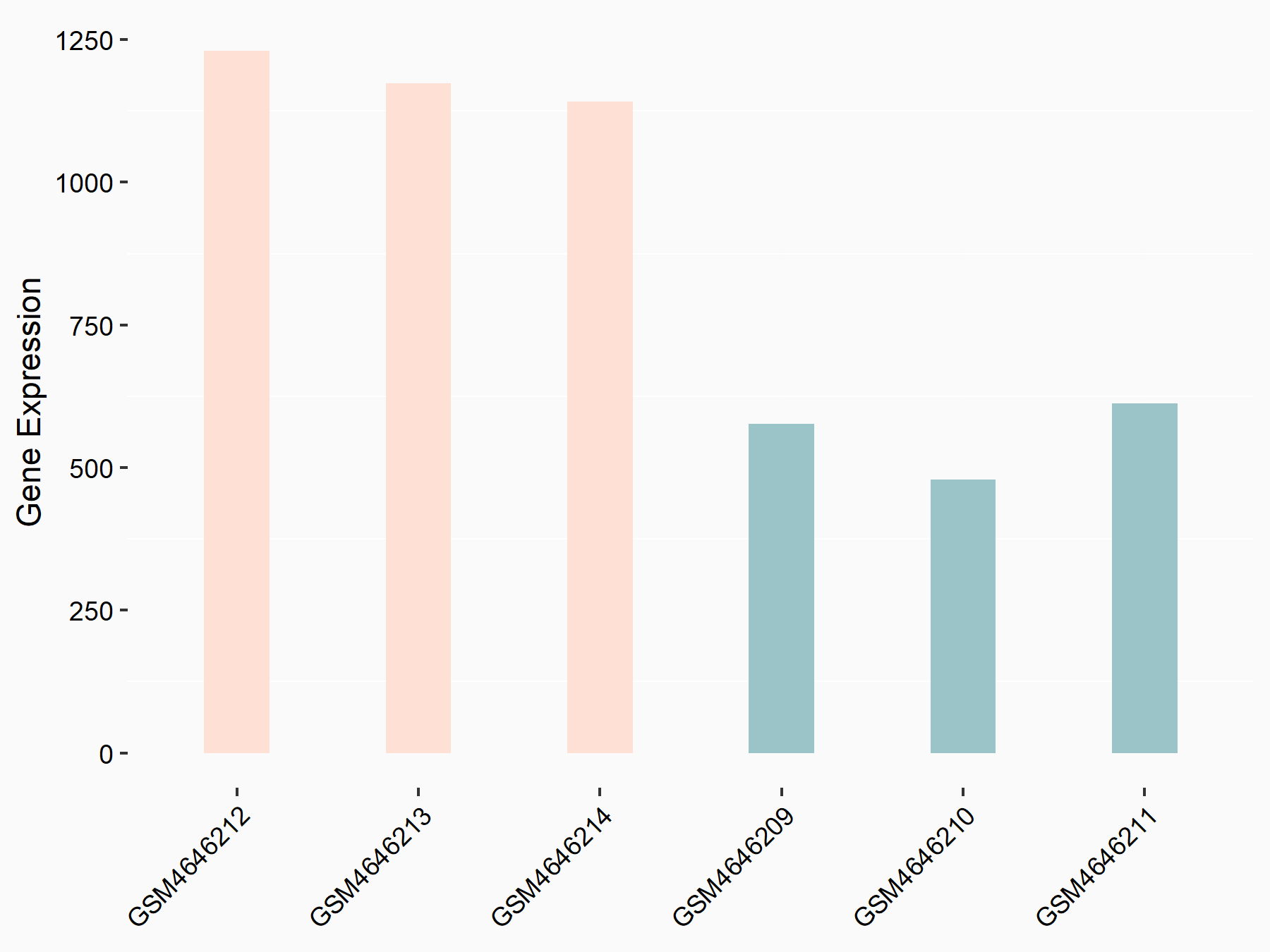 |
logFC: 1.08E+00 p-value: 1.69E-24 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Pertuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B) and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Trastuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B) and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tucatinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B) and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
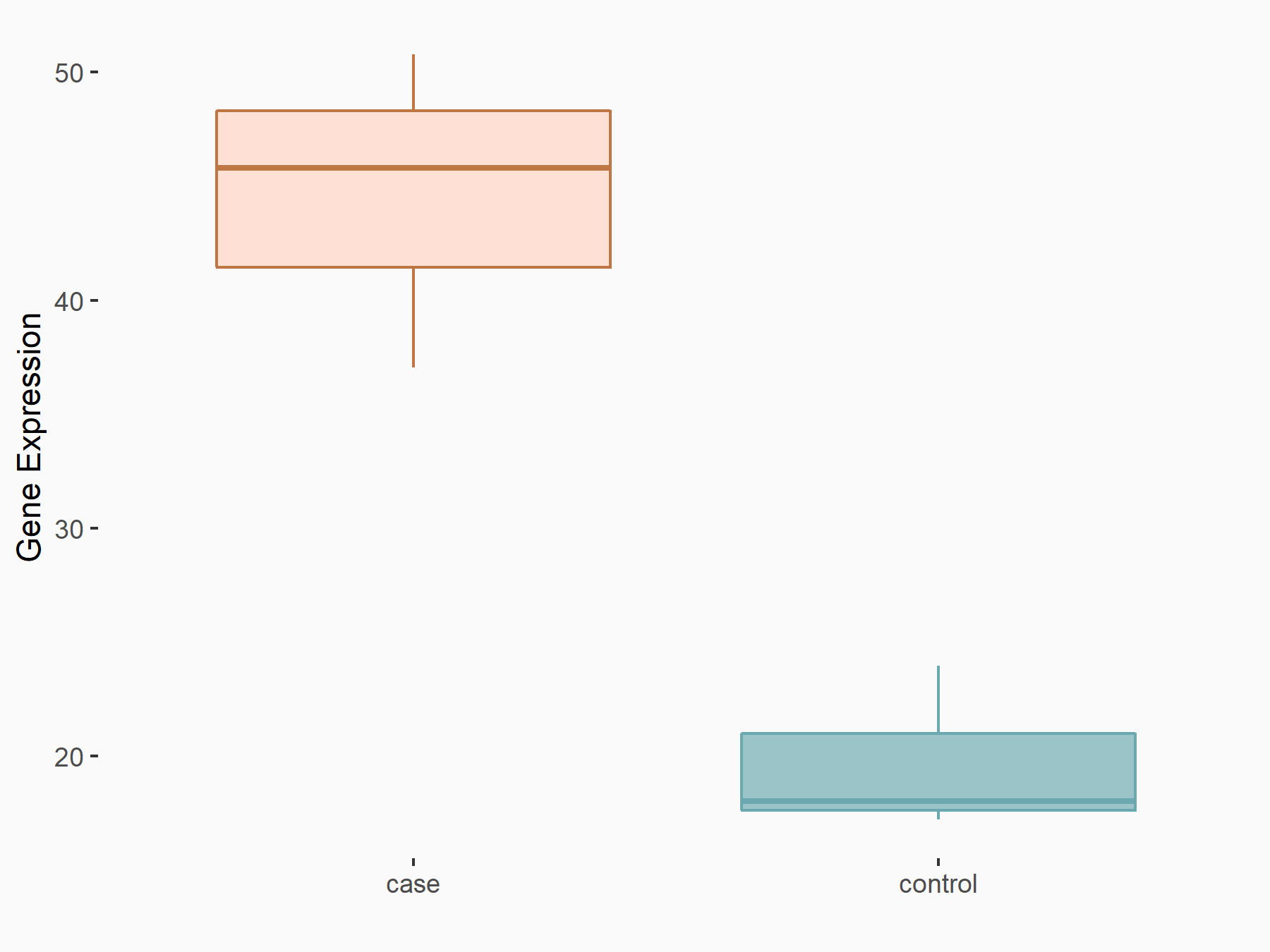  |
logFC: 1.20E+00 p-value: 8.44E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [24] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Response Summary | Findings show that METTL3 and METTL14 were up-regulated in preeclampsia(PE). Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A) is involved in the pathophysiology of PE as its mRNA and protein expression is regulated by m6A modification. | |||
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-gamma (HNF3gamma/FOXA3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
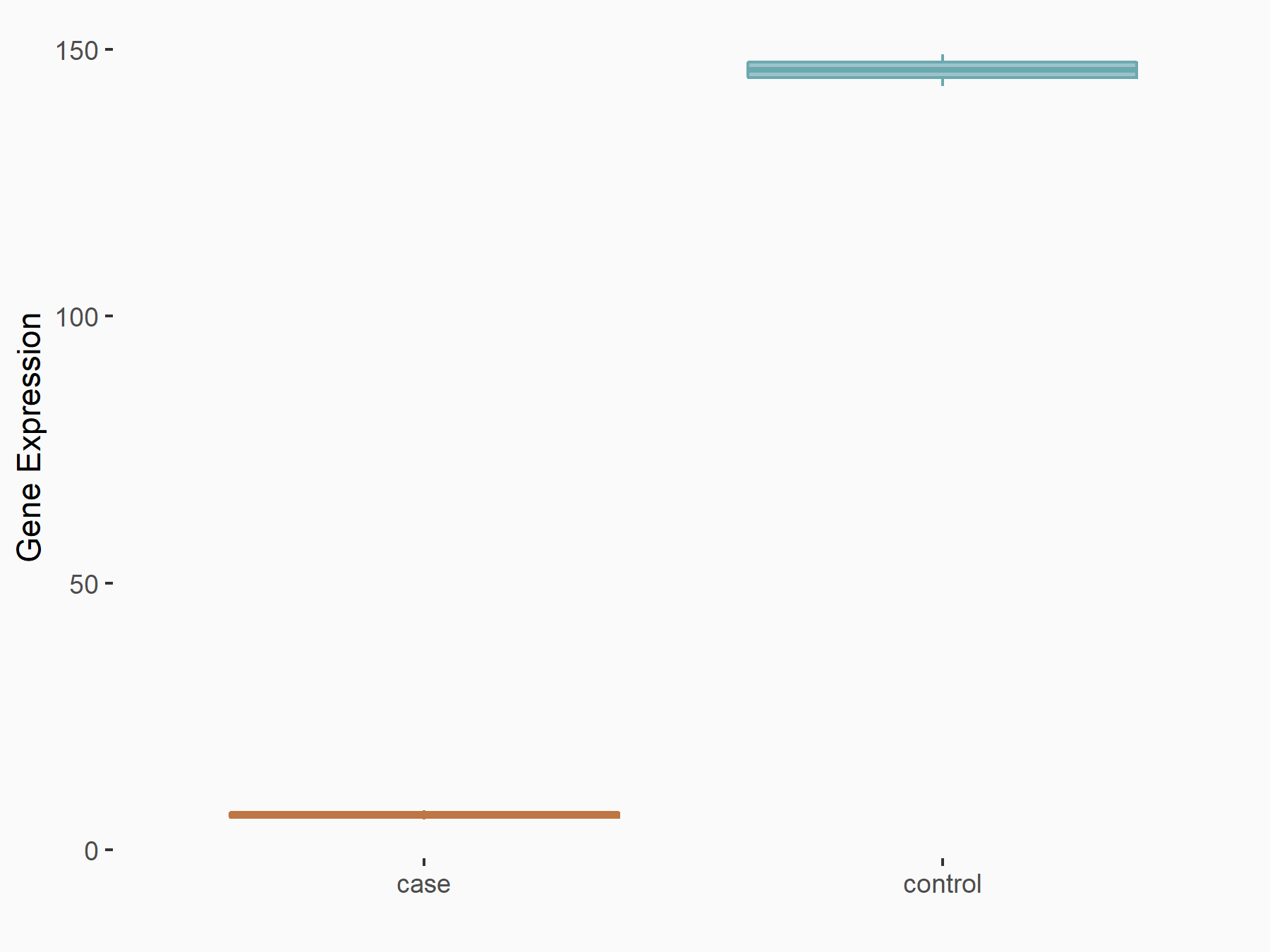  |
logFC: -4.46E+00 p-value: 6.08E-19 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Sorafenib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Membrane transport | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| In-vivo Model | When xenografted tumor growth reached 500 mm3, the mice were subjected to intratumoral injection of Ad-con or Ad-HNF3γ every other day. For the PDX model, fresh patient HCC tissues were cut into fragments with a volume of 3 × 3 mm3 and then implanted subcutaneously into the flanks of nude mice. The mice were given sorafenib (30 mg/kg) or vehicle orally twice a week for 24 days. | |||
| Response Summary | The Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-gamma (HNF3gamma/FOXA3) reduction in hepatocellular carcinoma could be mediated by METTL14-dependent m6A methylation of HNF3-Gamma mRNA. HNF3-Gamma plays an essential role in HCC differentiation and serves as a therapeutic target and predictor of sorafenib benefit in patients. | |||
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
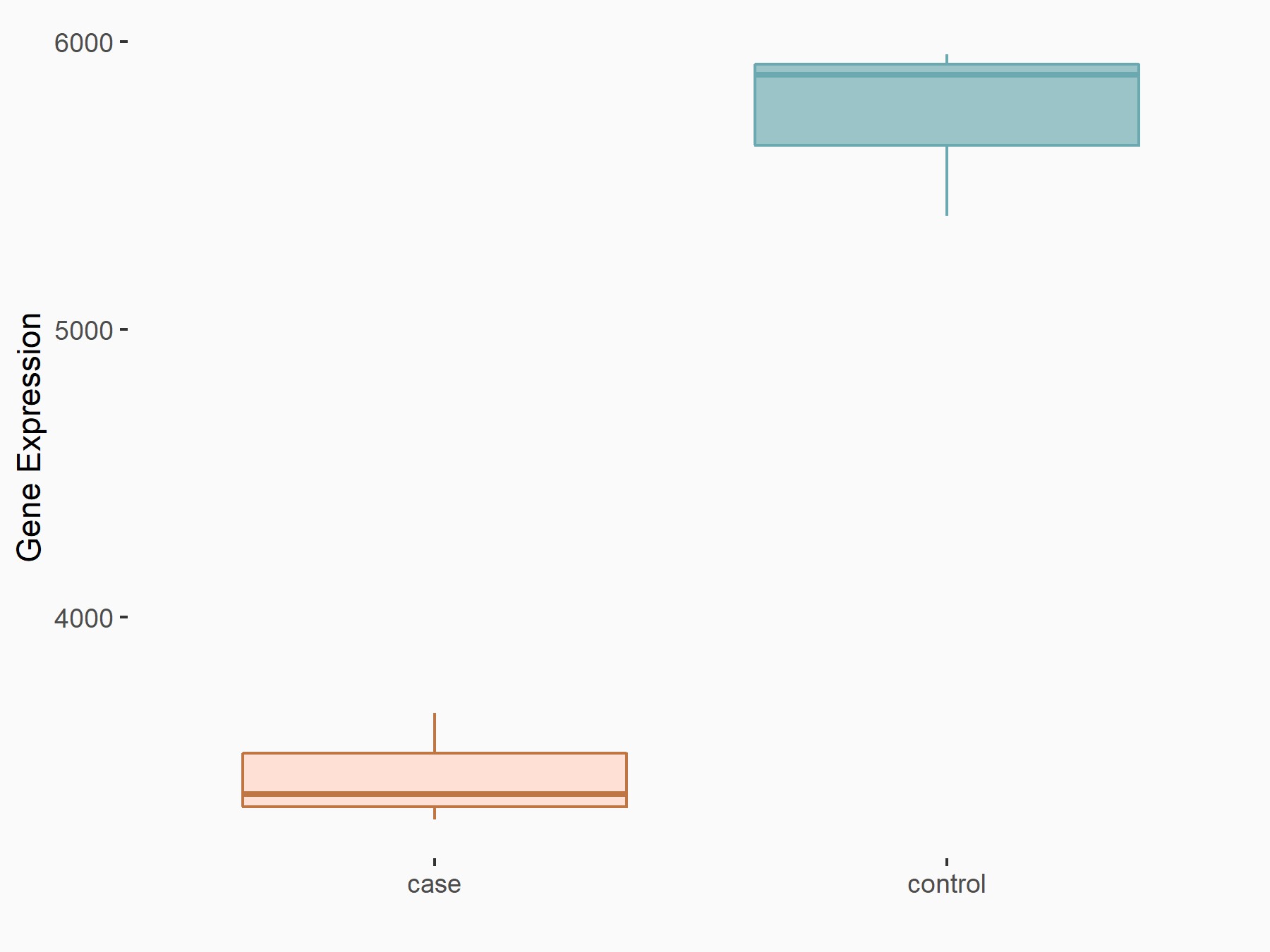  |
logFC: -7.37E-01 p-value: 4.88E-20 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [26] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair and mitochondrial stress | |||
In-vitro Model |
Mouse fibroblasts (Major cellular components of loose connective tissue) | |||
| Response Summary | The long-lived endocrine mutants - Snell dwarf, growth hormone receptor deletion and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A knockout - all show increases in the N6-adenosine-methyltransferases (METTL3/14) that catalyze 6-methylation of adenosine (m6A) in the 5' UTR region of select mRNAs. In addition, these mice have elevated levels of YTHDF1, which recognizes m6A and promotes translation by a cap-independent mechanism. Augmented translation by cap-independent pathways facilitated by m6A modifications contribute to the stress resistance and increased healthy longevity of mice with diminished GH and Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signals. | |||
Integrin beta-4 (ITGB4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
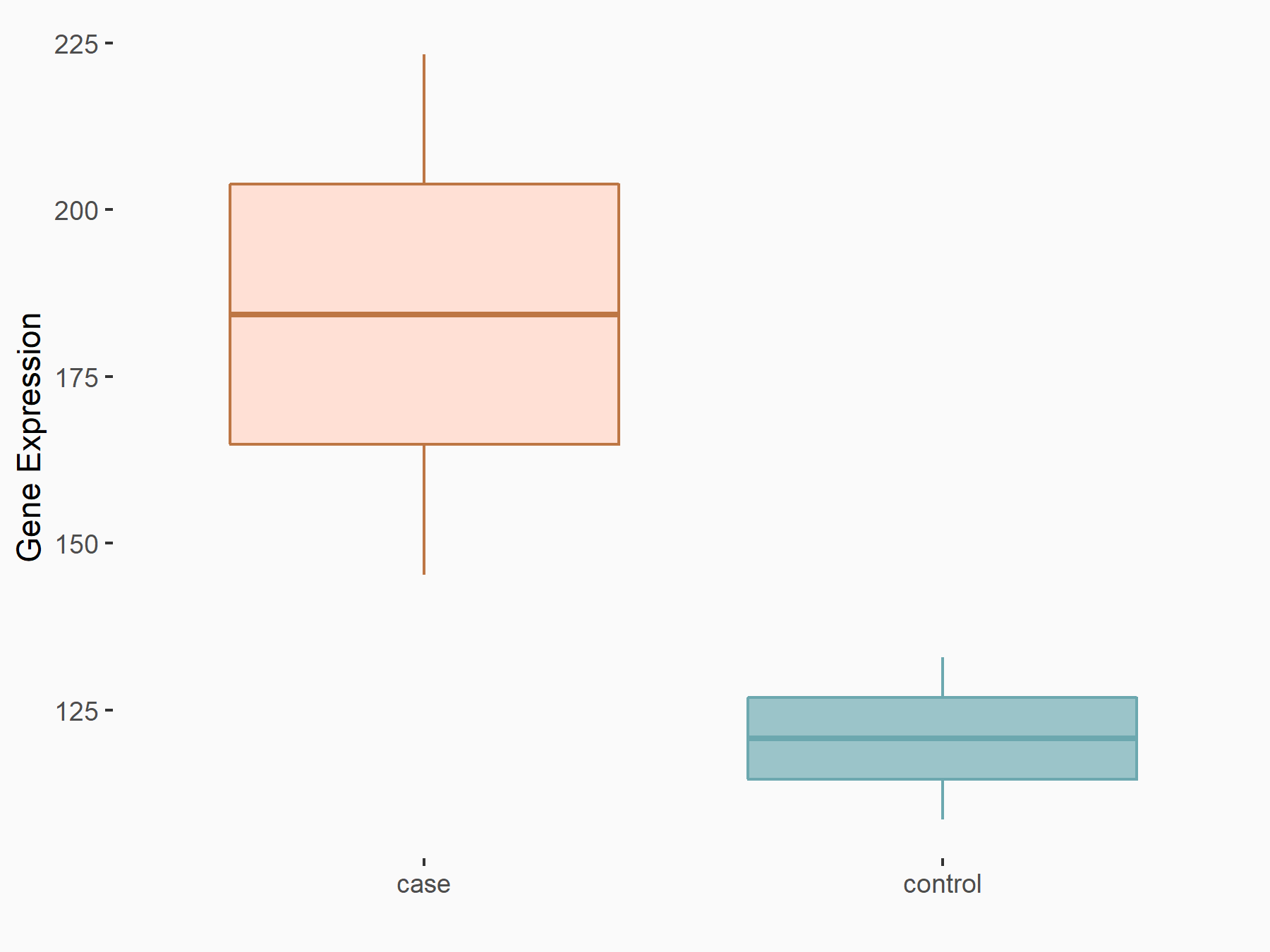  |
logFC: 6.11E-01 p-value: 3.31E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
OS-RC-2 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1626 |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| 769-P | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1050 | |
| In-vivo Model | Each group included 3 mice. 1.0 × 106 stably transfected ACHN cells in 150 uL were injected into a tail vein of each mouse, 45 days after which lungs were excised from the sacrificed mice and stained by Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) Staining. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of METTL14 promoted ccRCC cell migration, invasiveness and metastasis as well as stimulating the EMT process and the PI3K/AKT signal by overexpressing Integrin beta-4 (ITGB4). | |||
Interferon beta (IFNB1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
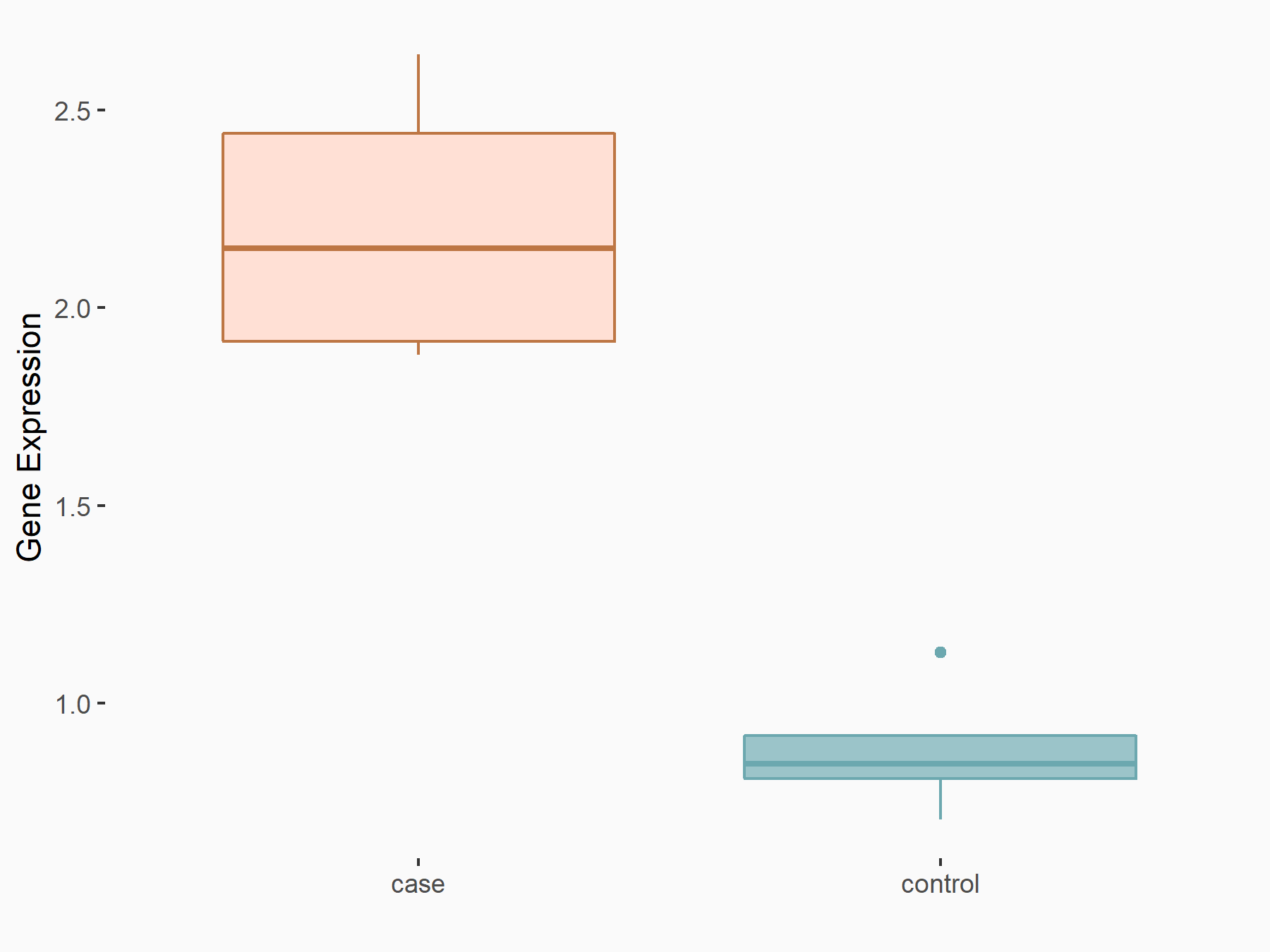 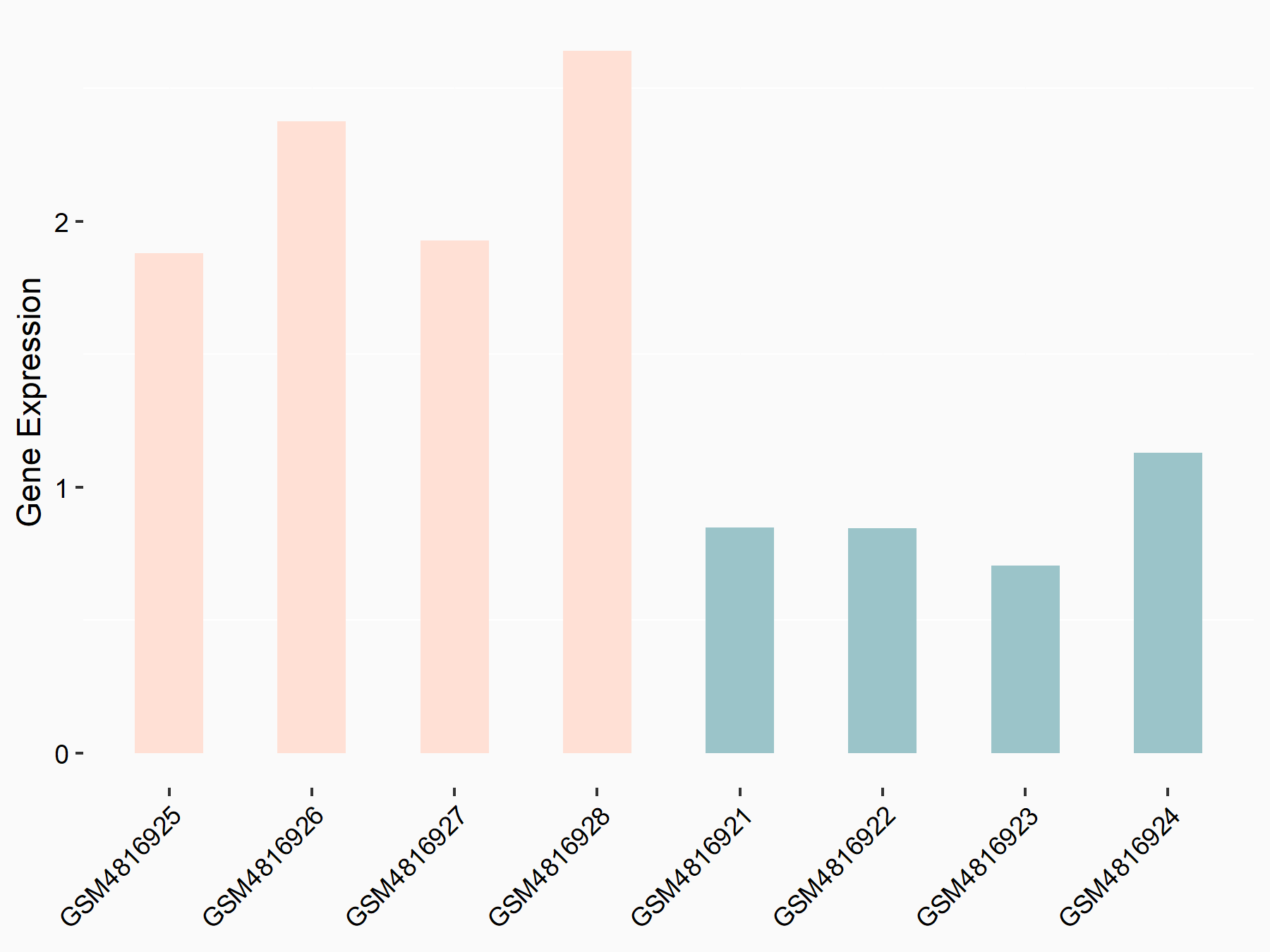 |
logFC: 7.66E-01 p-value: 2.22E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Papillomaviruses [ICD-11: 1D9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [28] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Unspecified viral infection [ICD-11: 1D9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
Innate immunity [ICD-11: 4A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [28] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Innate immunity [ICD-11: 4A00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | CT26 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout CT26 cells
Control: CT26 cells
|
GSE142589 | |
| Regulation |
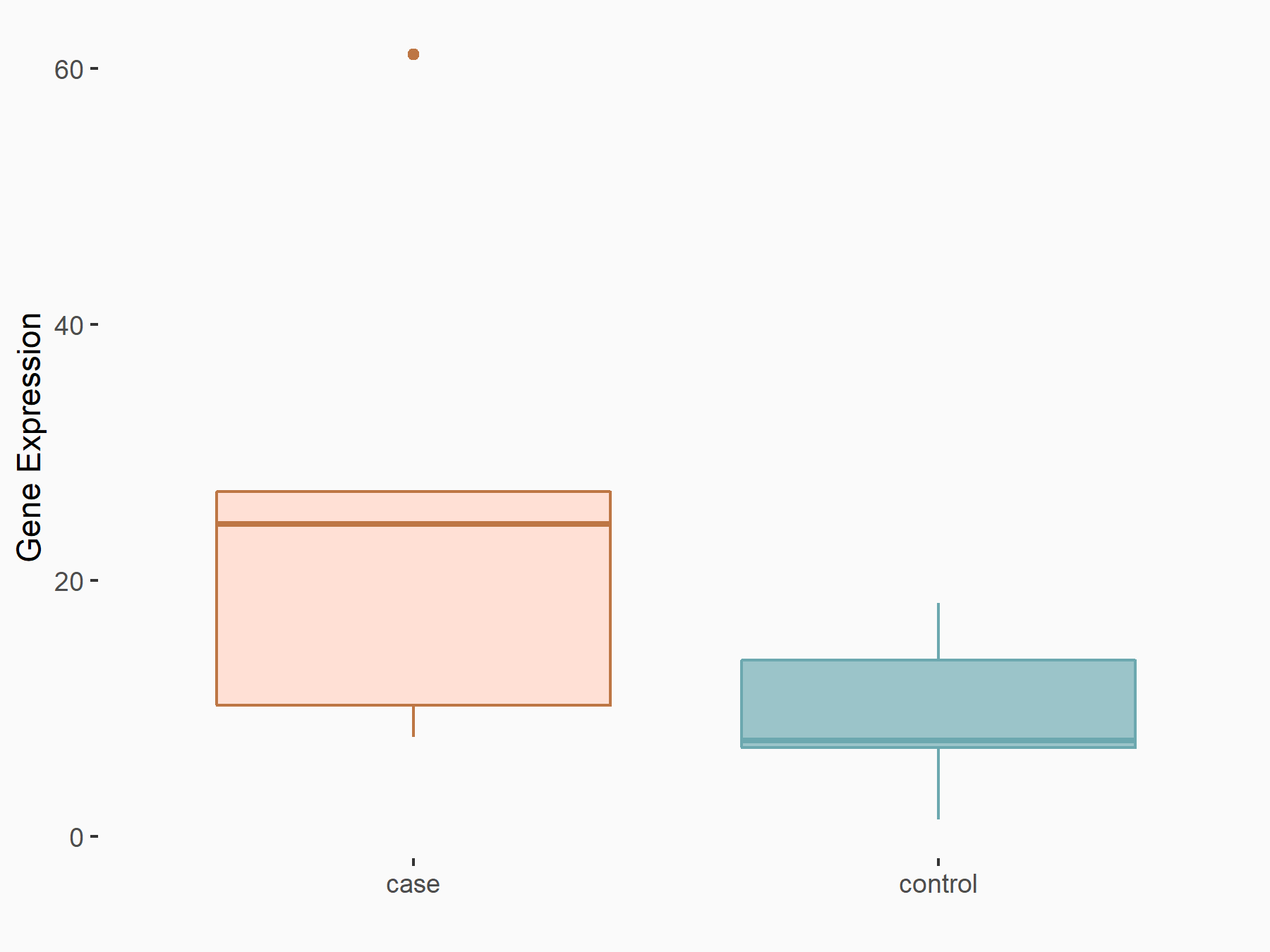 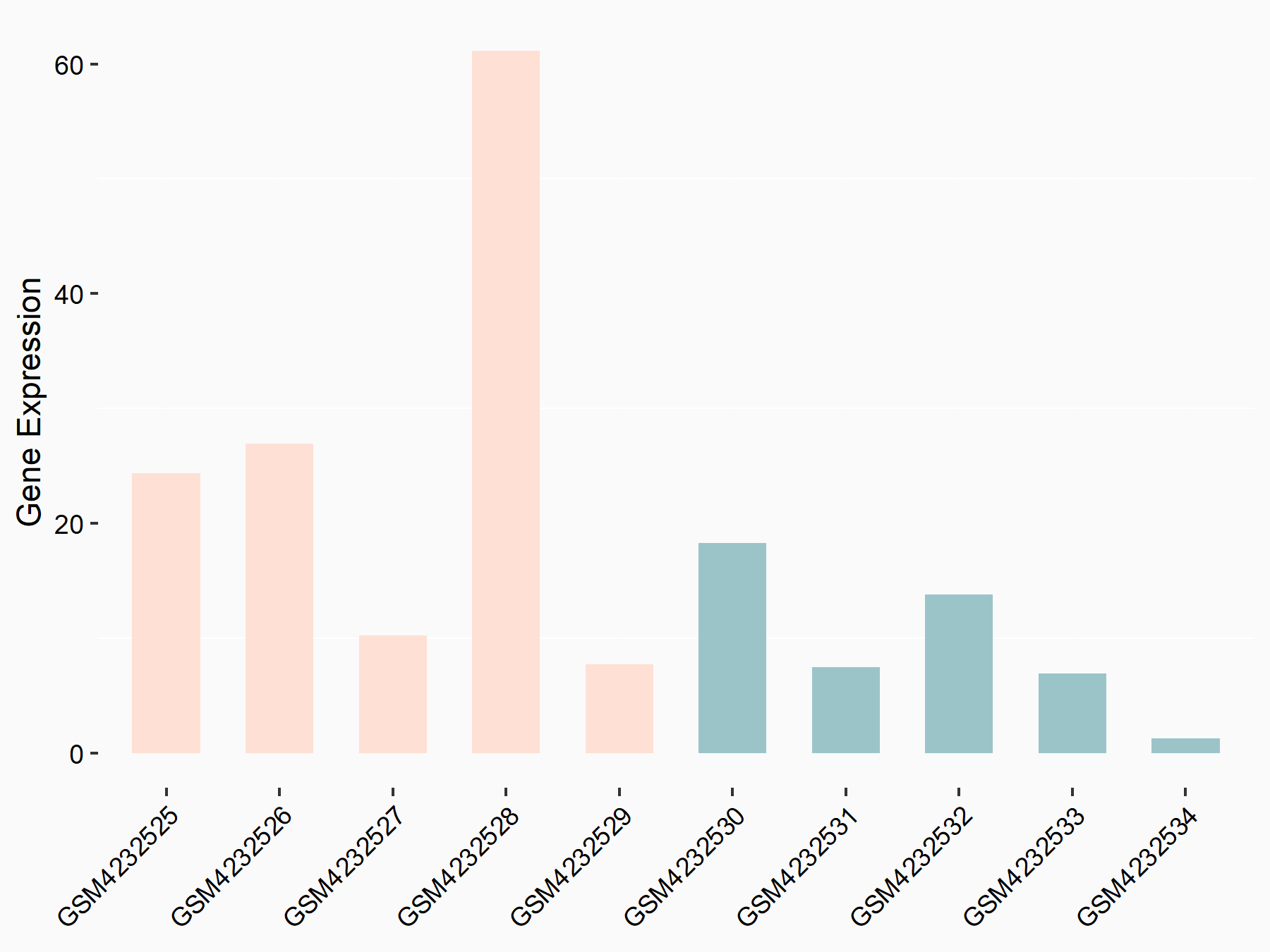 |
logFC: 1.52E+00 p-value: 1.96E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
In-vitro Model |
CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Stat1 and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
Interferon regulatory factor 1 (Irf1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | CT26 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout CT26 cells
Control: CT26 cells
|
GSE142589 | |
| Regulation |
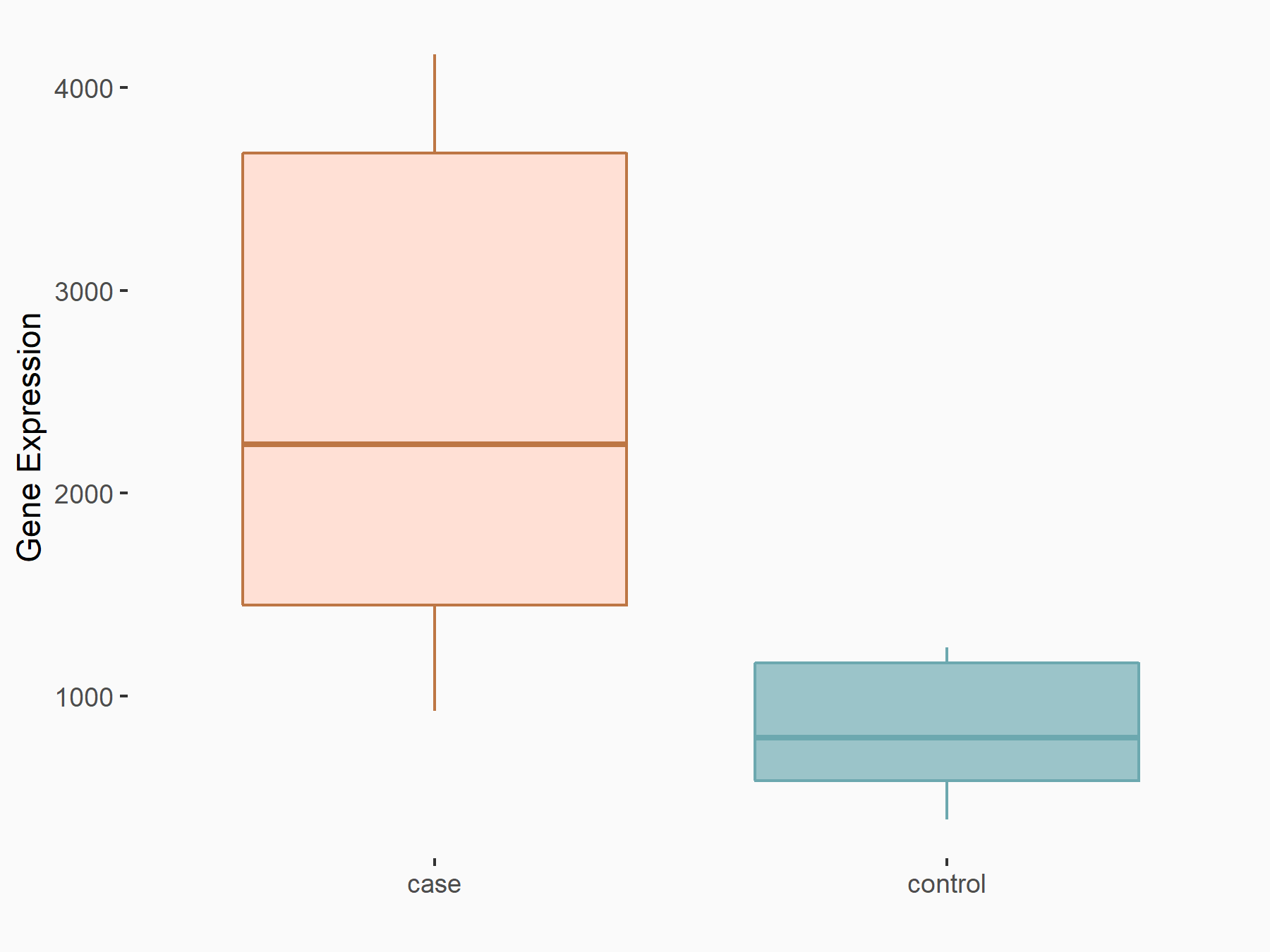 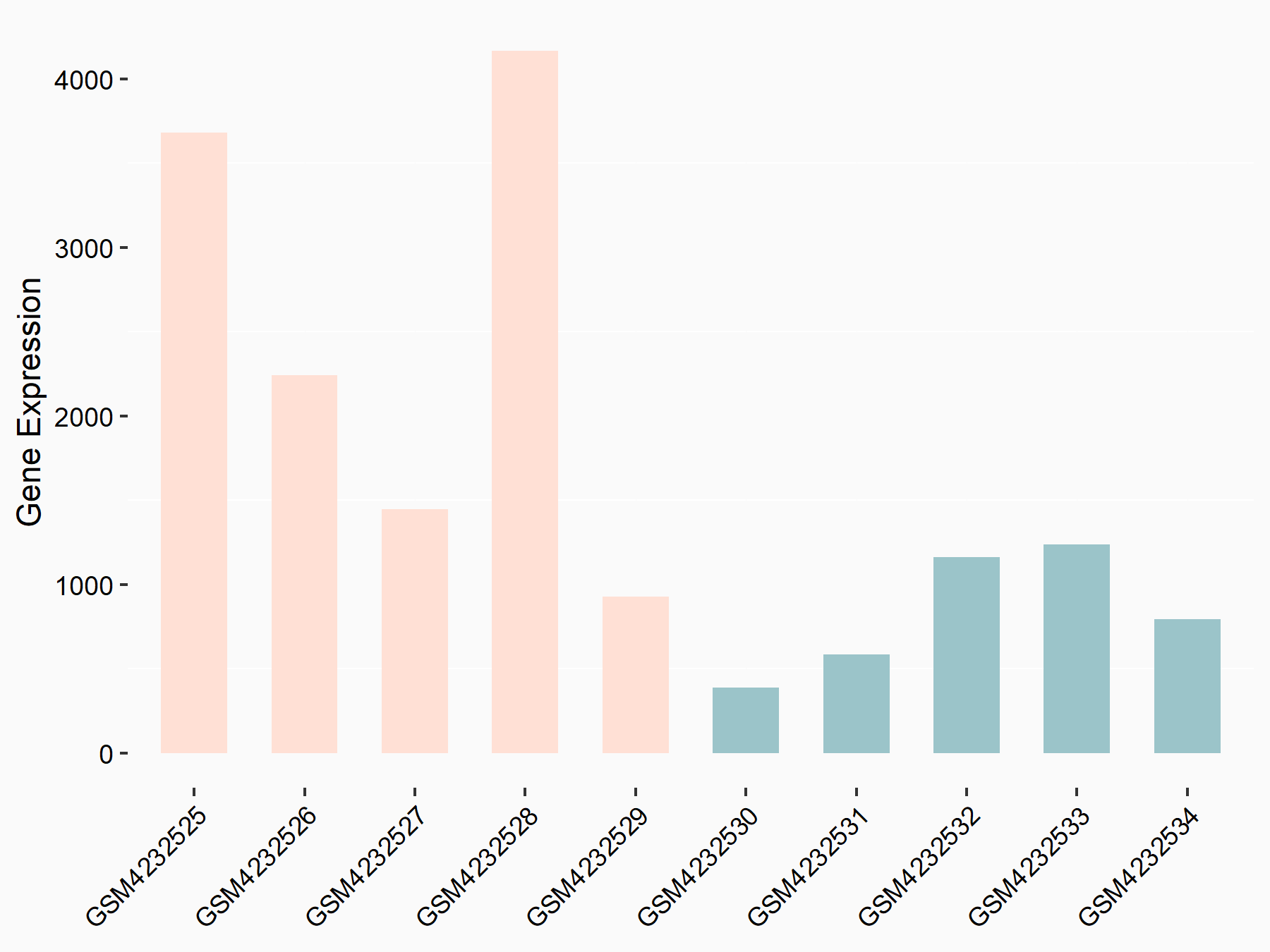 |
logFC: 1.58E+00 p-value: 1.17E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
In-vitro Model |
CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Stat1 and Interferon regulatory factor 1 (Irf1) mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
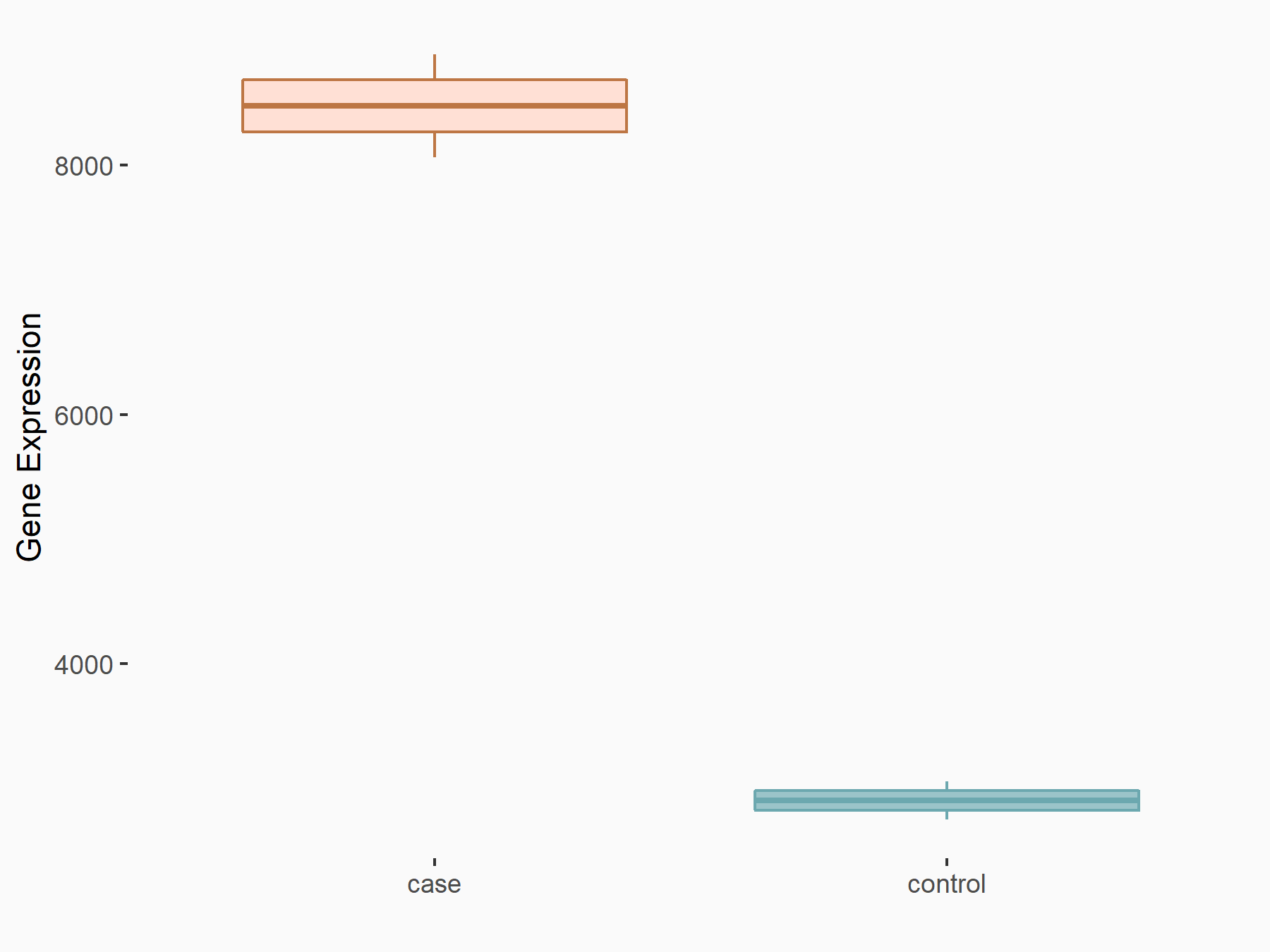 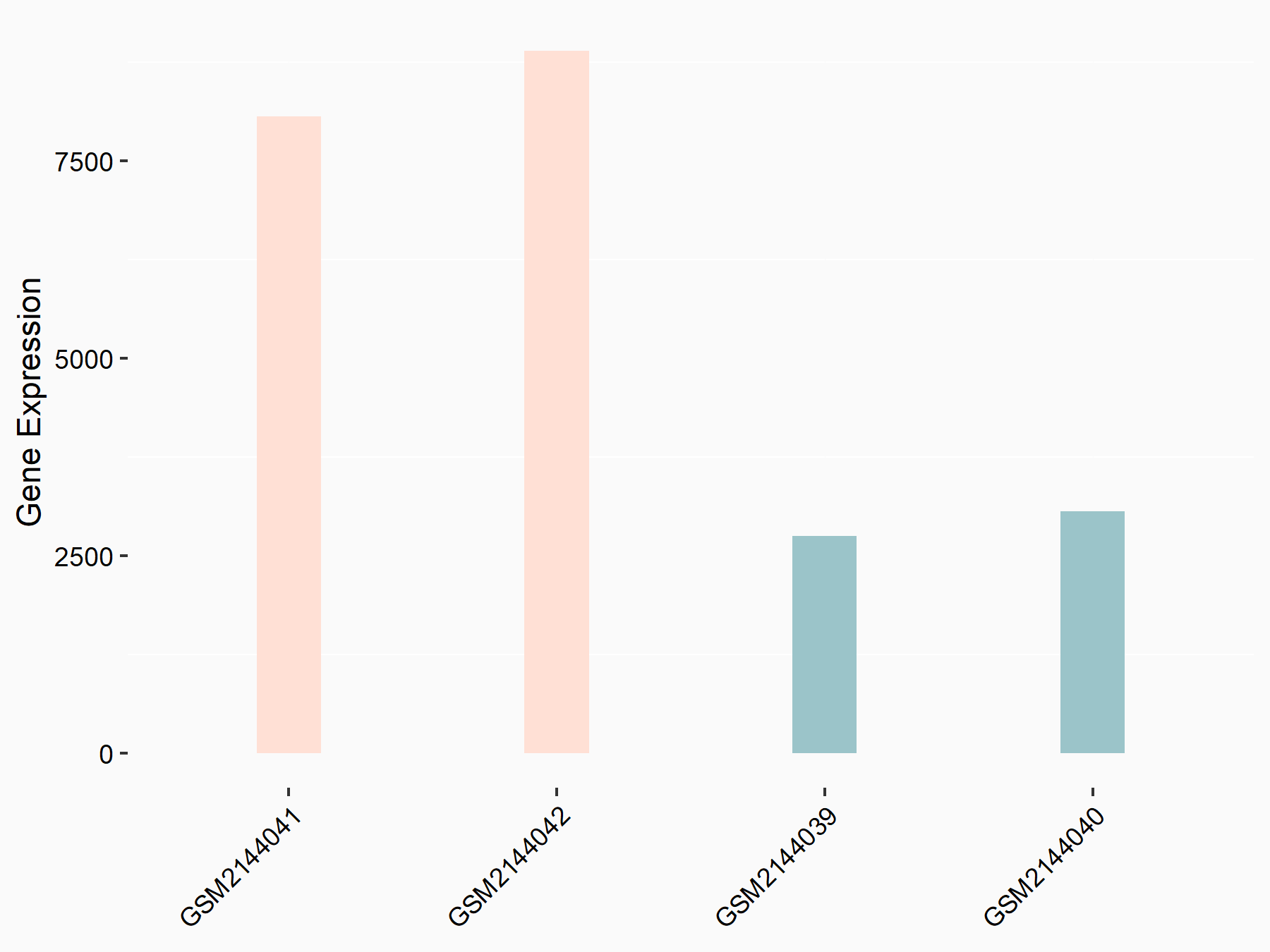 |
logFC: 1.55E+00 p-value: 4.20E-30 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | ||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14 heterozygous mice (Mettl14-/+) were established from C57/BL6 mice by Cyagen Biosciences, Inc. (Suzhou, Jiangsu, China), using CRISPR/Cas9-based targeting and homology-directed repair. C57/BL6 and APOE-/- mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). Mettl14-/+APOE-/- mice were generated by breeding Mettl14-/+ mice with APOE-/- mice. Eight- to 10-week-old male APOE-/- (WT) mice and Mettl14-/+APOE-/- (KO) mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (D12108C, Opensource diets) for 12 weeks. Then, the mice were euthanized for further analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 gene knockout significantly reduced the inflammatory response of macrophages and the development of atherosclerotic plaques, Mettl14 plays a vital role in macrophage inflammation in atherosclerosis via the NF-Kappa-B/Interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling pathway. | |||
Krueppel-like factor 4 (KLF4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
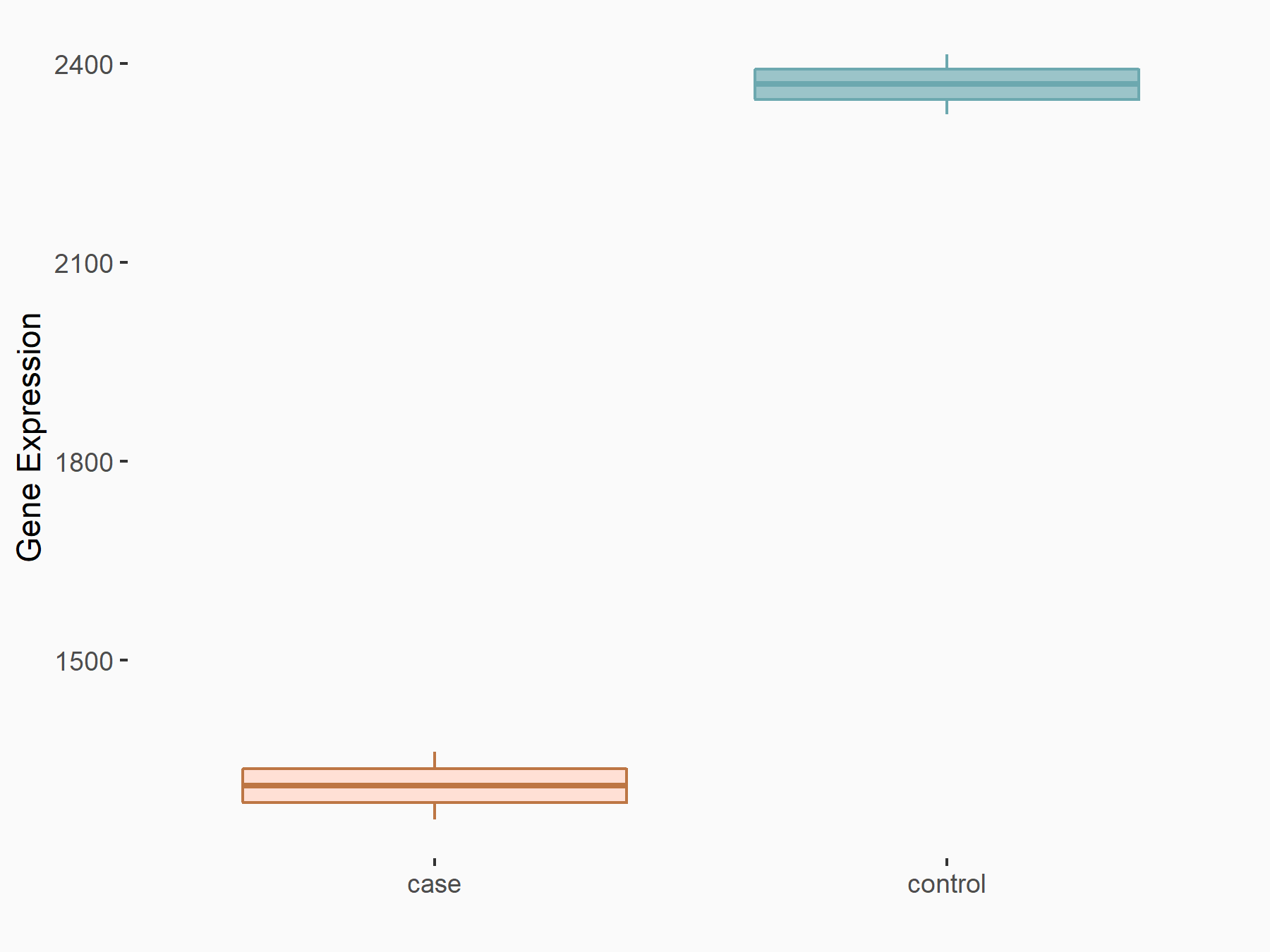 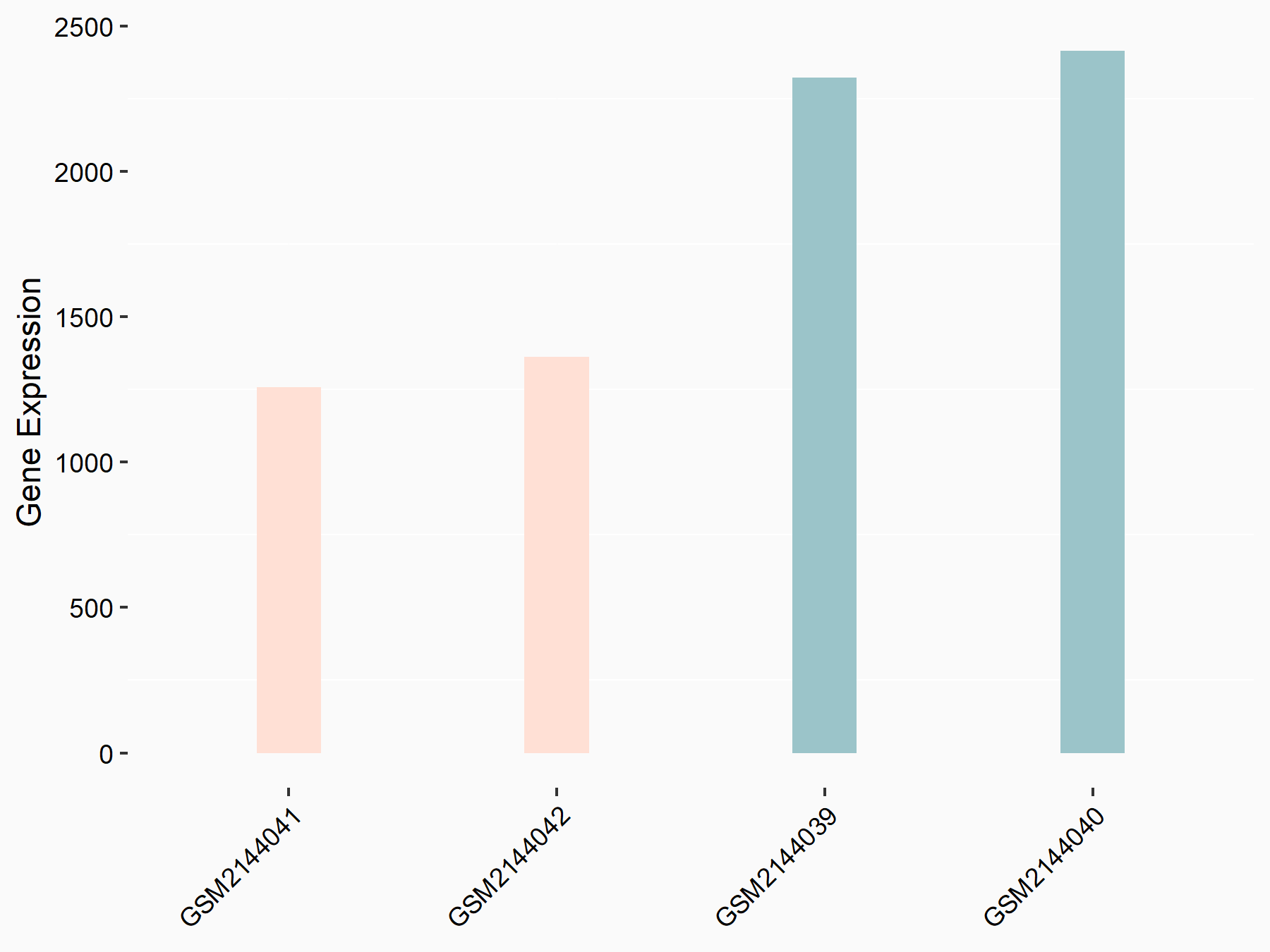 |
logFC: -8.55E-01 p-value: 7.89E-09 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [30] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| In-vivo Model | In vivo, the group of HCT116 cells labeled with luciferase were surgically injected into the spleen of nude mice. After 2 months, the nude mice were subjected to D-luciferin injection and the luciferase signals were monitored and quantified. | |||
| Response Summary | The expression of METTL14 was downregulated in CRC cells and METTL14 could inhibit the metastasis of CRC cells. MeCP2 could bind to METTL14 to coregulate tumor suppressor Krueppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) expression through changing m6 A methylation modification. | |||
Meltrin-beta (ADAM19)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
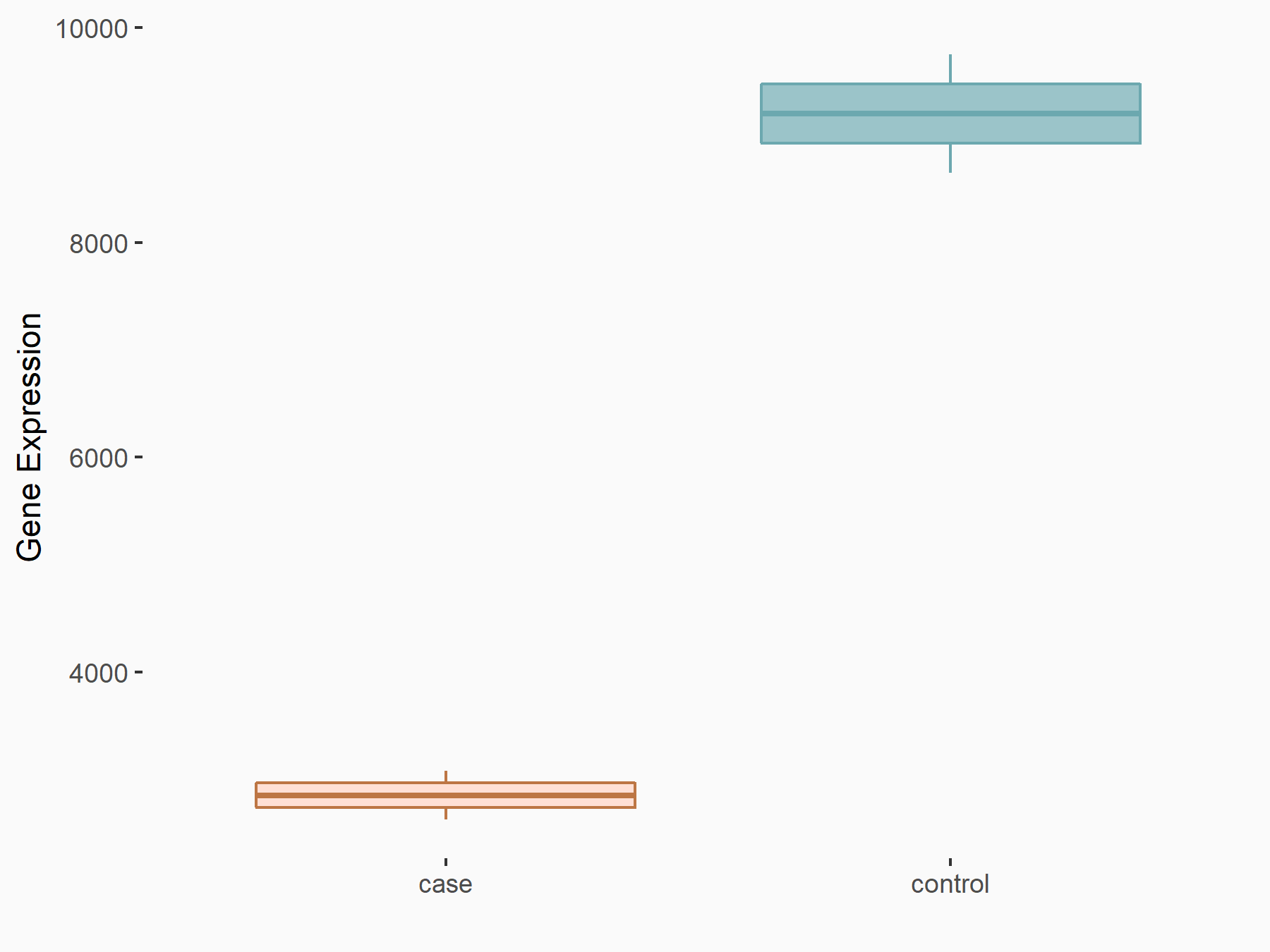 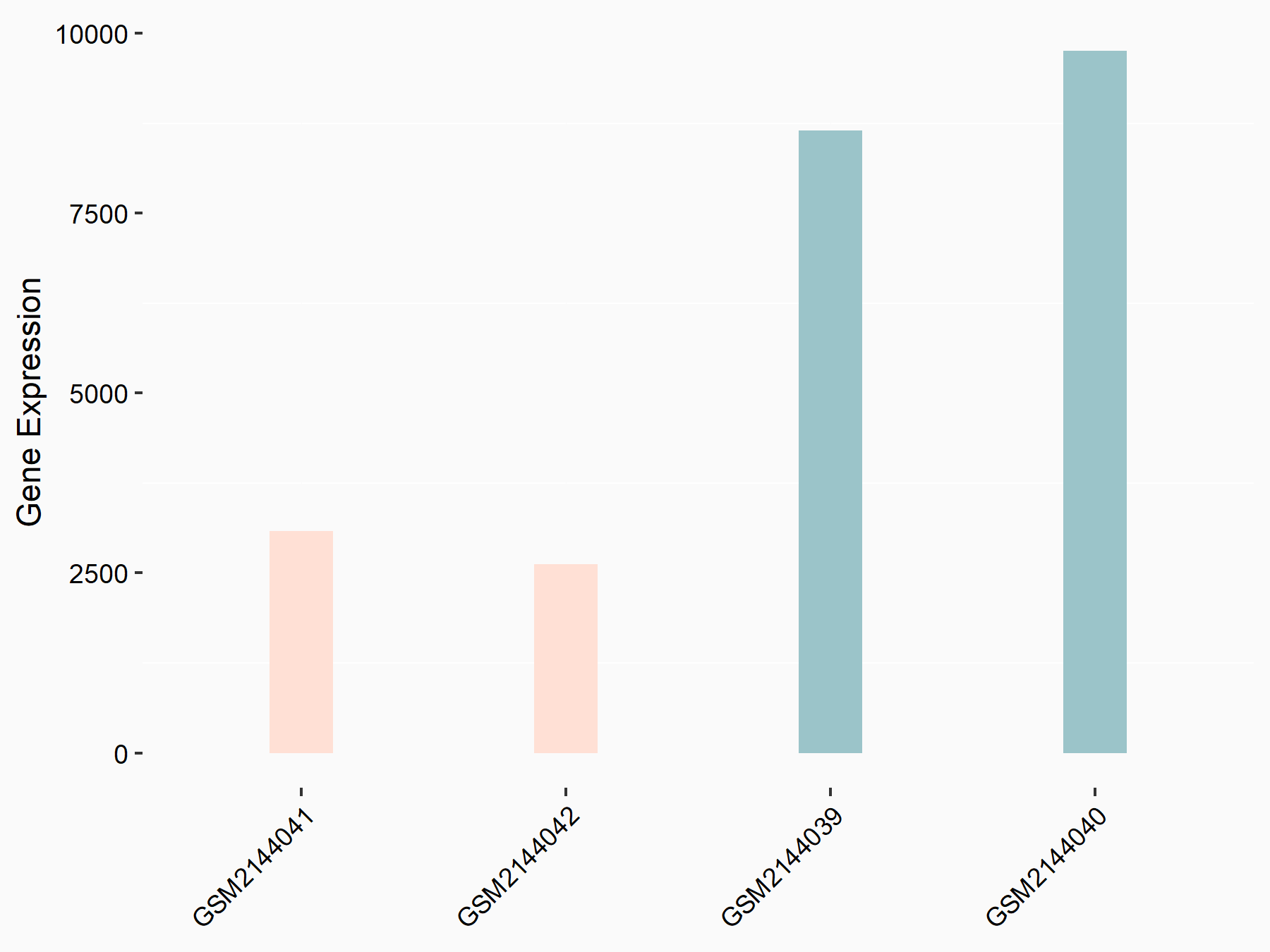 |
logFC: -1.69E+00 p-value: 2.38E-31 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [31] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cells growth | |||
| Cells self-renewal | ||||
| Tumorigenesis | ||||
| MicroRNAs in cancer (hsa05206) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
GSC | Glioma | Epinephelus akaara | CVCL_M752 |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 105 dissociated cells in 2 uL PBS were injected into the following site (anteroposterior [AP] +0.6 mm, mediolateral [ML] +1.6 mm, and dorsoventricular [DV] 2.6 mm) with a rate of 1 uL/min. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of METTL3 or METTL14 induced changes in mRNA m6A enrichment and altered mRNA expression of genes (e.g., Meltrin-beta (ADAM19)) with critical biological functions in GSCs. Treatment with MA2, a chemical inhibitor of FTO, dramatically suppressed GSC-induced tumorigenesis and prolonged lifespan in GSC-grafted animals. | |||
Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
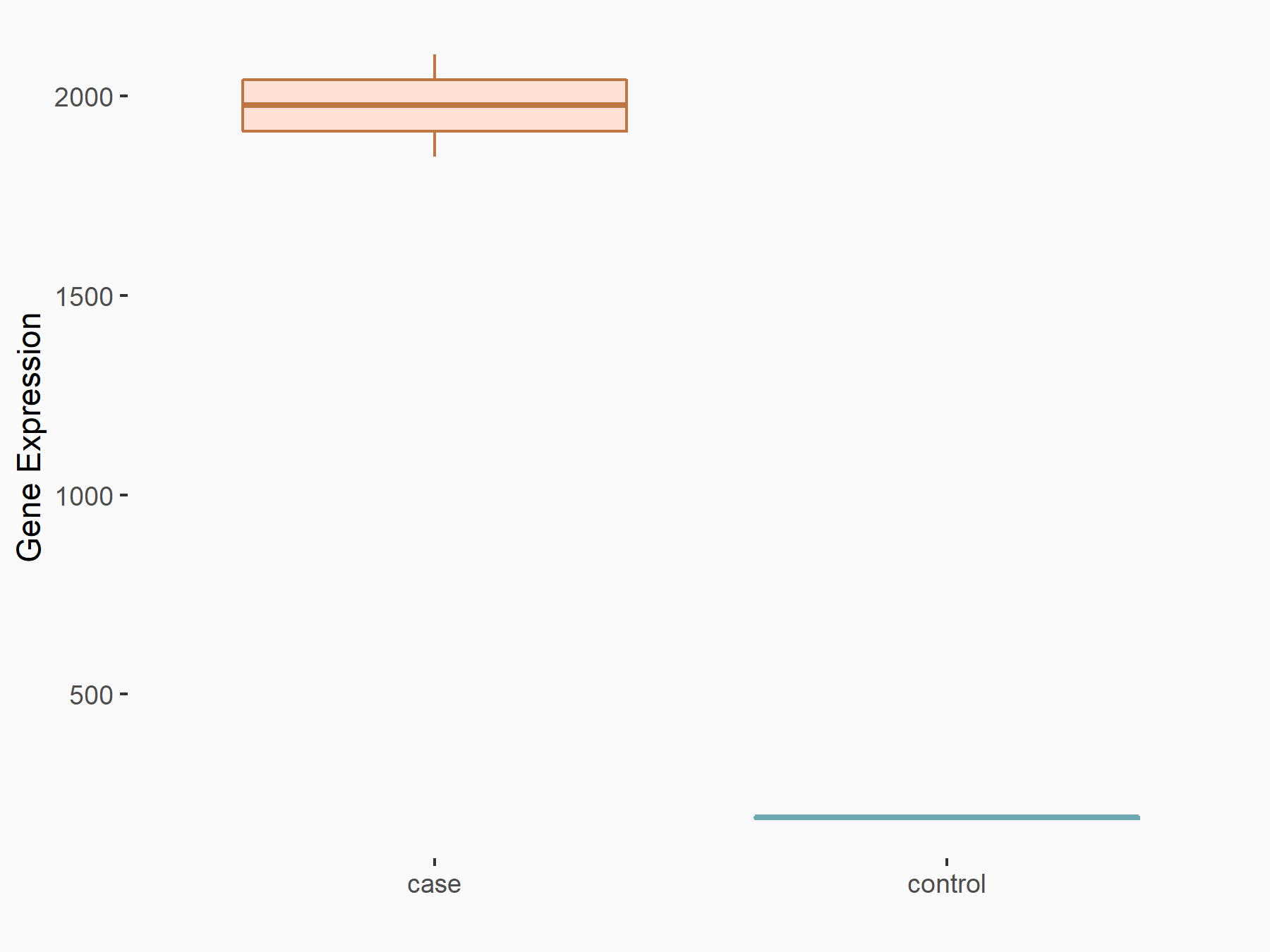 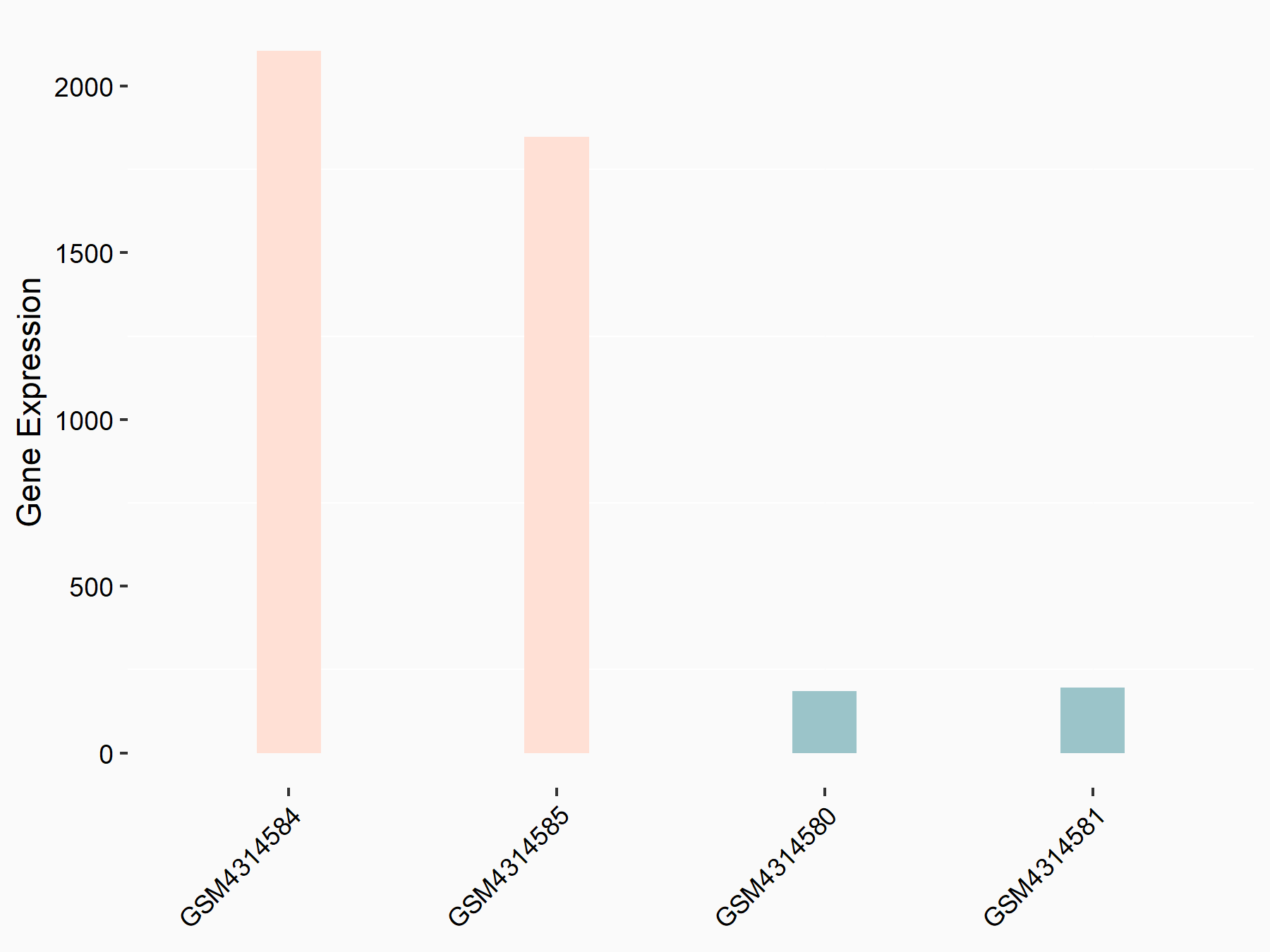 |
logFC: 3.37E+00 p-value: 1.21E-131 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Disorders of the retina [ICD-11: 9B70-9C0Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [32] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Disorders of the retina [ICD-11: 9B70-9C0Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
ARPE-19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0145 |
| Response Summary | The expression of METTL14 is significantly reduced in patients with retinitis pigmentosa (RP). METTL14 regulates the expression of Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) via the modification of m6A, resulting in the dysregulation of NEUROD1 and pathologic changes in RPE cells. | |||
Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
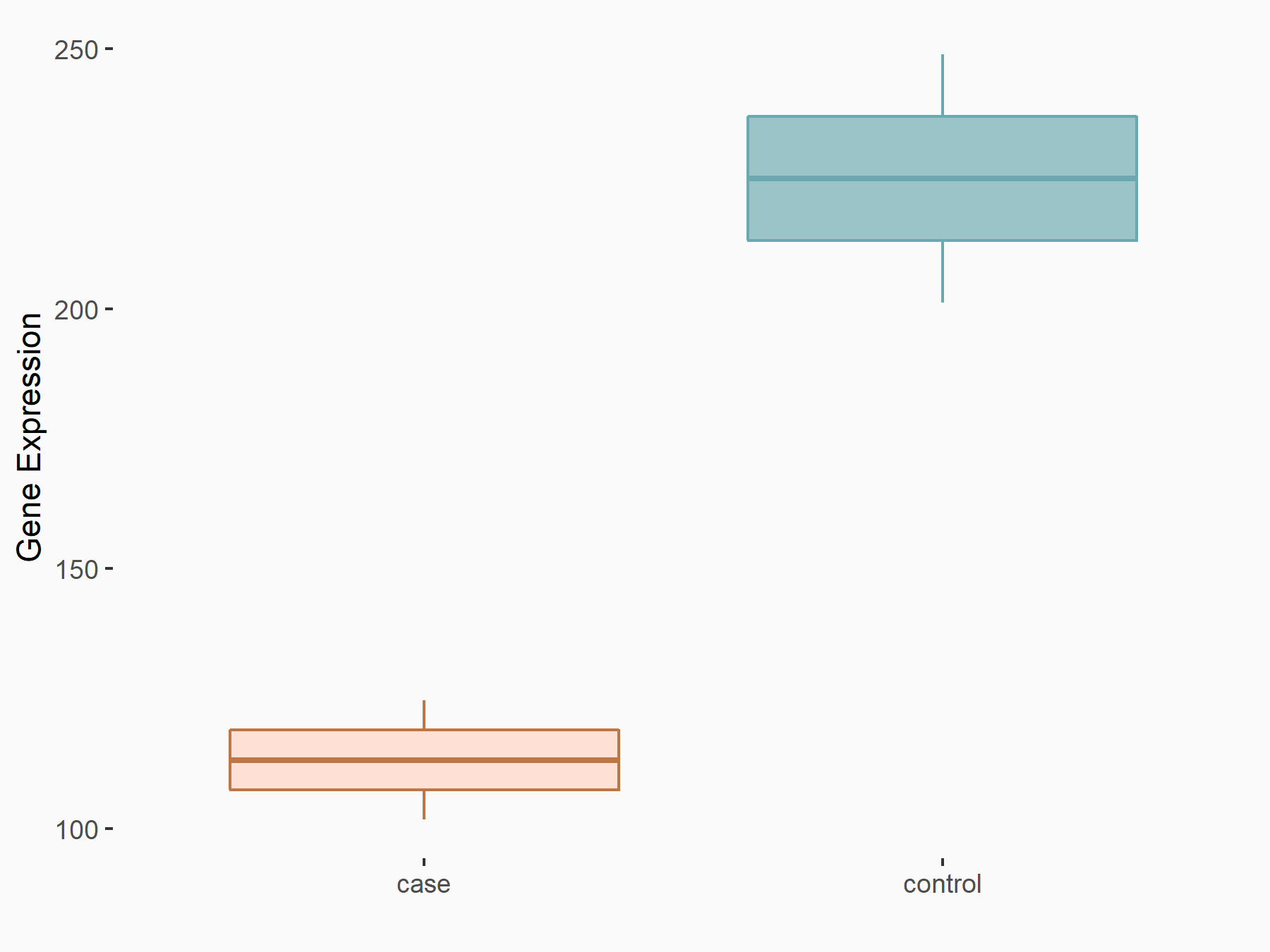 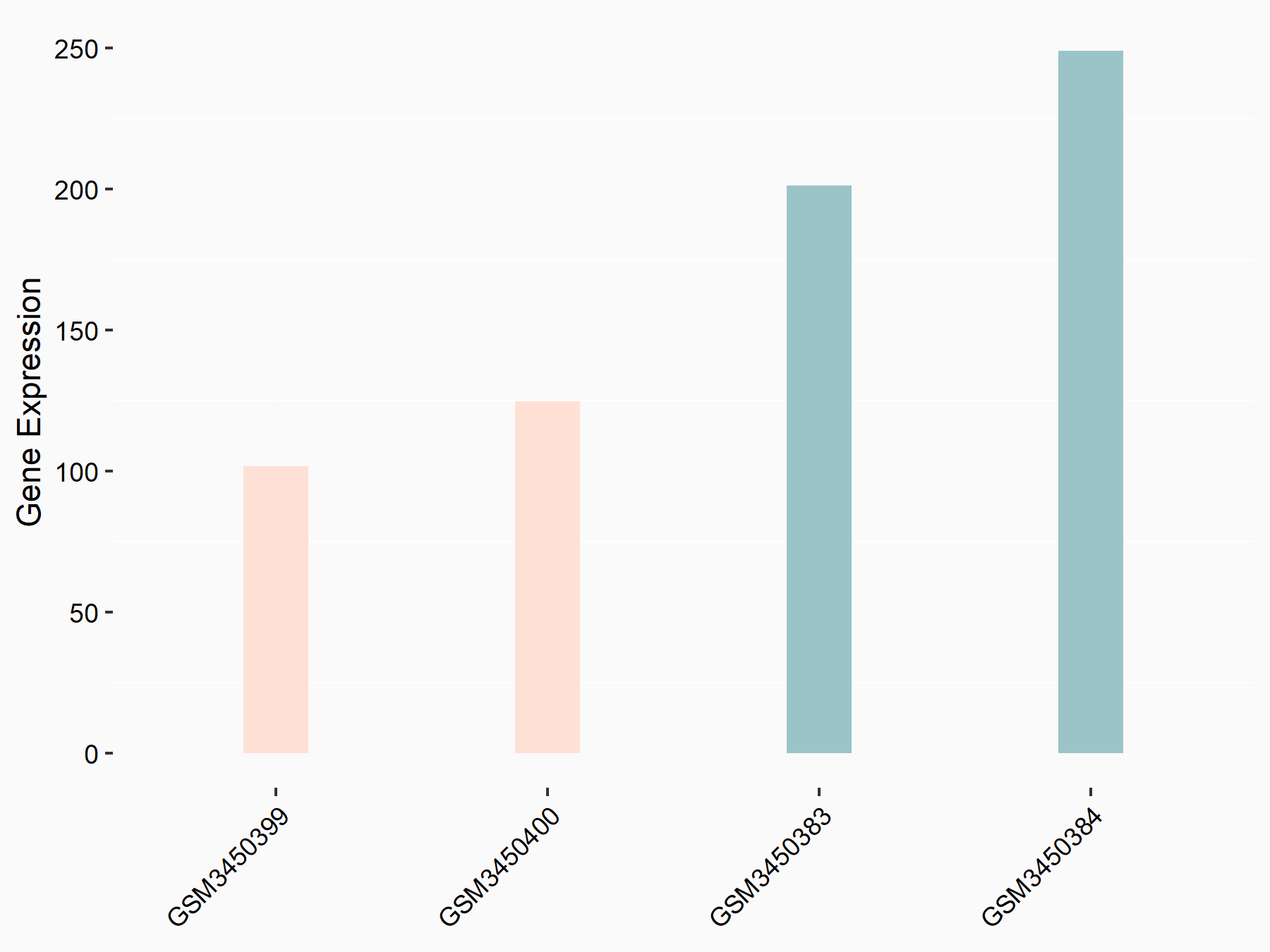 |
logFC: -9.93E-01 p-value: 1.46E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [33] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
RGM1 | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0499 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the purpose of enhancing the overall randomization of the experiment, a random comparison table had been employed. Accordingly, 5-wk-old male nude athymic BALB/c nu/nu mice (Slack, Shanghai, China) were randomly divided into two parts including a control group (NC) and the experimental group METTL14-OE. For developing subcutaneous xeno transplantation model, 5 × 106 HGC-27 cells stably transfected with NC or METTL14 overexpression were subcutaneously incorporated for 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. The mice experienced euthanasia after 27 days of inoculation and obtained xenografts's mass was obtained. Tumor volume over three days was obtained. To create mouse STAD liver metastasis orthotopic tumor model, 1 × 106 HGC-27 cells under stable transfection with NC or METTL14 overexpression were added to subserosal gastric wall of BALB/c nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis of Stomach Adenocarcinoma via stabilization of Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN) mRNA expression. Therefore, METTL14 is a potential biomarker of prognosis and therapeutic targets for Stomach Adenocarcinoma. | |||
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [34] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Response Summary | Upregulation of METTL14 inhibited ccRCC cells proliferation and migration in vitro. Overexpression of METTL14 increased the m6A enrichment of Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN), and promoted Pten expression. METTL14-enhanced Pten mRNA stability was dependent on YTHDF1. | |||
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [35] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK-2 [Human kidney] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 |
| In-vivo Model | Twenty mice were randomly divided into three groups: normal mice group (N), diabetic mice group (DM), and diabetic mice administrated with TSA group (DM + TSA). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14-regulated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway via Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN) affected HDAC5-mediated EMT of renal tubular cells in diabetic kidney disease. | |||
Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
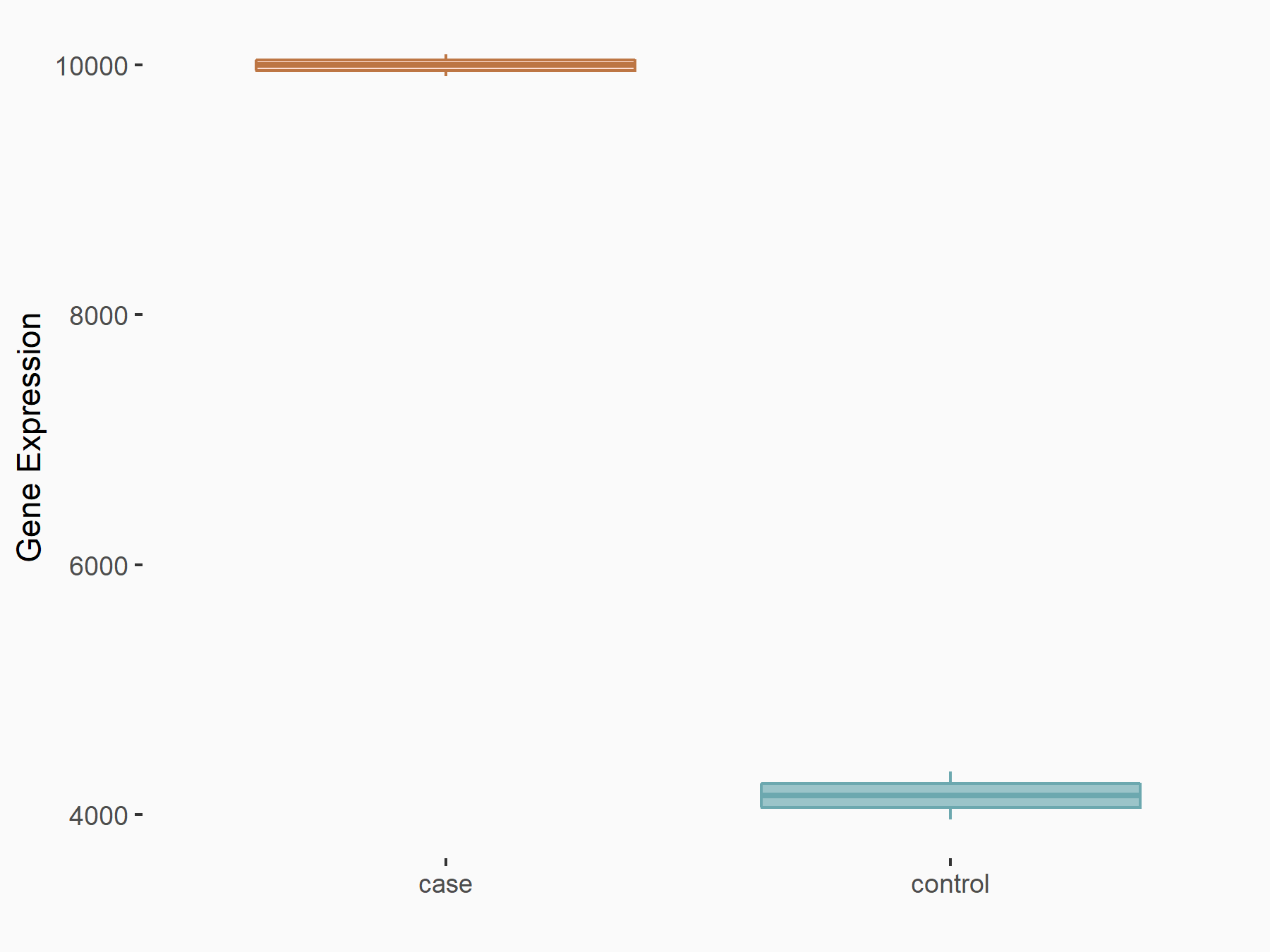 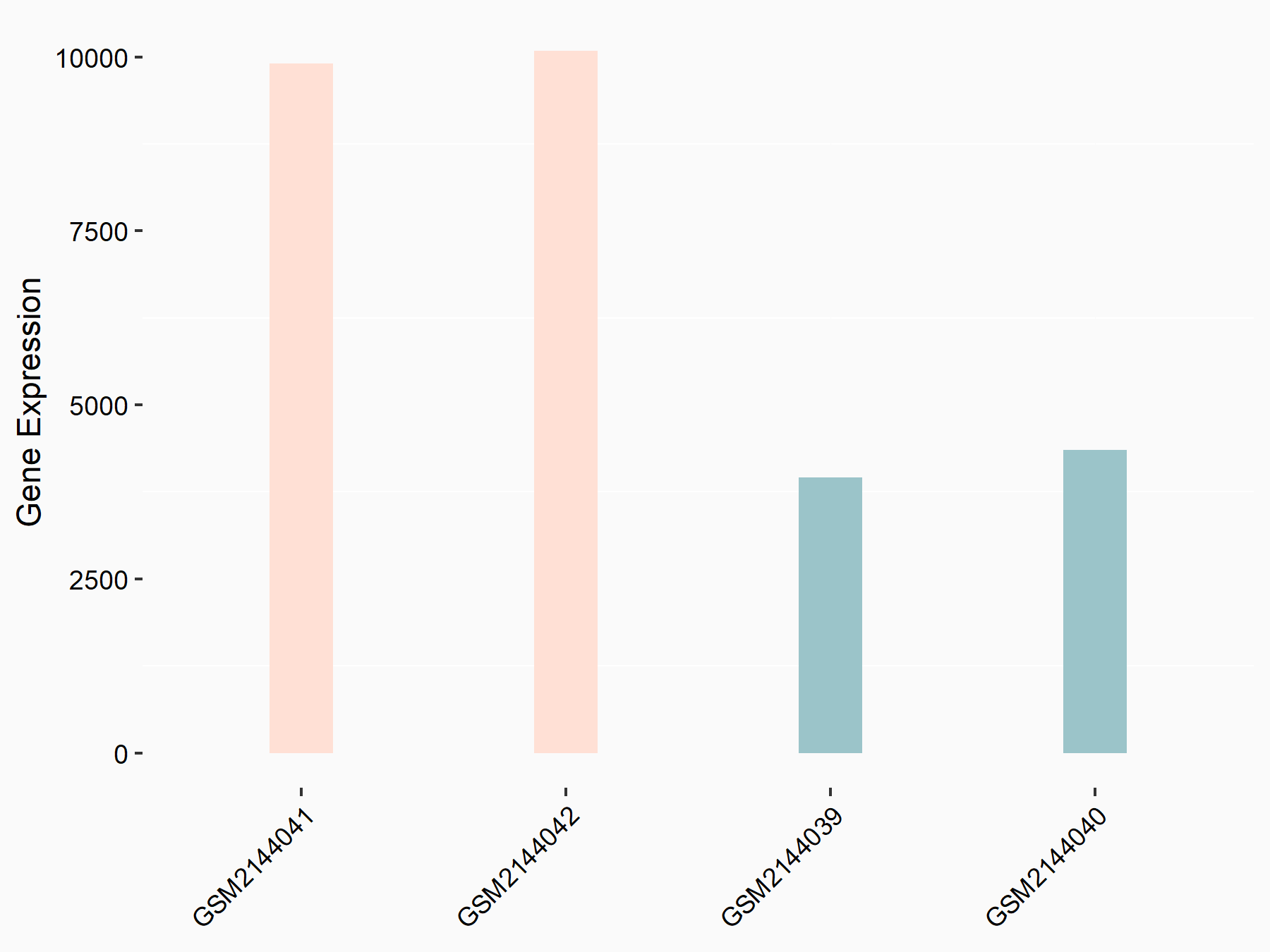 |
logFC: 1.27E+00 p-value: 6.21E-24 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [36] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell survival/proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HSPC (Human hematopoietic stem cell) | ||||
| MNC (Cord blood pluripotent stem cells) | ||||
| OP9 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4398 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | Lin- HSPCs were purified from BM of wildtype mice and 0.1×106 cells were seeded in 2 mL OP9 medium onto the OP9 cells with the addition of 10 ng/mL mouse IL-3, 10 ng/mL human IL-6, 10 ng/mL mouse IL-7, 10 ng/mL mouse Flt-3L, and 50 ng/mL mouse stem cell factor (SCF). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 in normal myelopoiesis and AML pathogenesis, as featured by blocking myeloid differentiation and promoting self-renewal of normal HSPCs and LSCs/LICs. METTL14 exerts its oncogenic role by regulating its mRNA targets (e.g., MYB and Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)) through m6A modification, while the protein itself is negatively regulated by SPI1. | |||
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
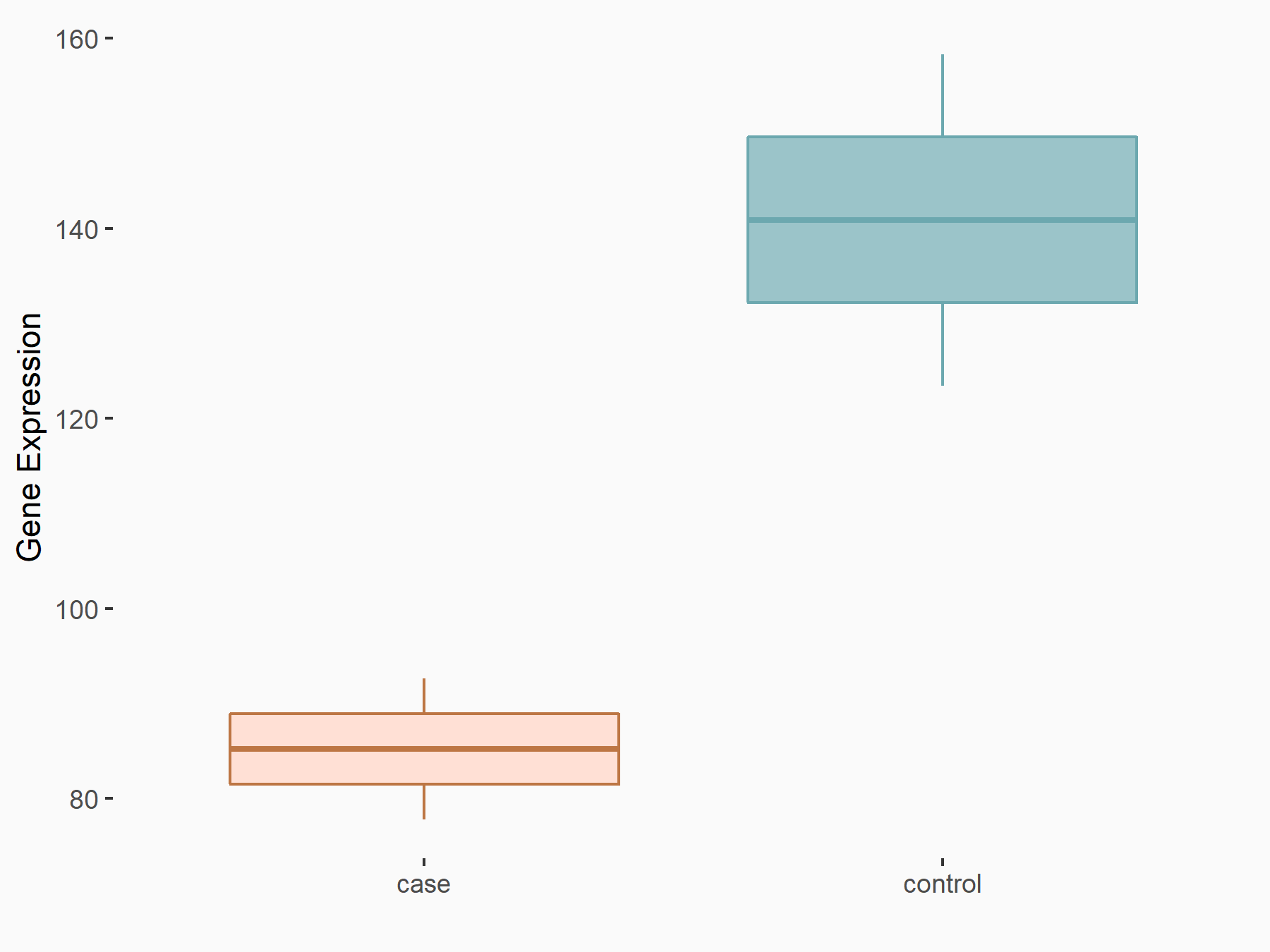 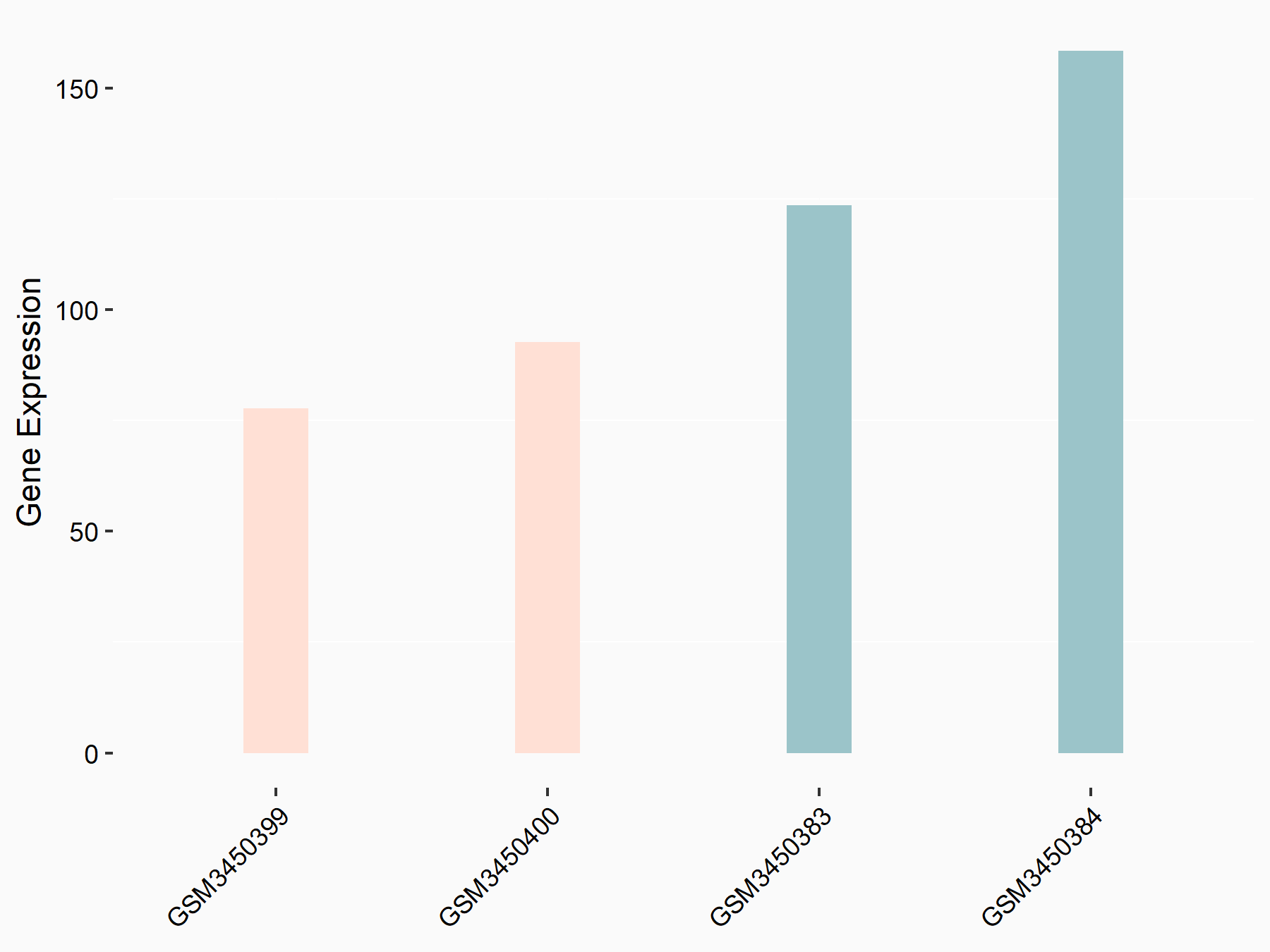 |
logFC: -7.26E-01 p-value: 1.60E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [37] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Doxil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
Conditionally immortalized human podocytes (Podocytes) | |||
| In-vivo Model | To establish mice model with ADR nephropathy, adult male C57BL/6J mice (8-12 weeks of age) were purchased from Animal Center of Fudan University and injected with 19.5 mg/kg ADR (D1515, Sigma-Aldrich, St-Louis, MO, USA) intravenously via tail vein. | |||
| Response Summary | The elevated m6A RNA levels and the most upregulated METTL14 expression in kidneys of mice with adriamycin and diabetic nephropathy. METTL14-dependent RNA m6A modification contributes to podocyte injury through posttranscriptional regulation of NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) mRNA, which provide a potential approach for the diagnosis and treatment of podocytopathies. | |||
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [80] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Neurogenic differentiation factor 1 (NEUROD1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
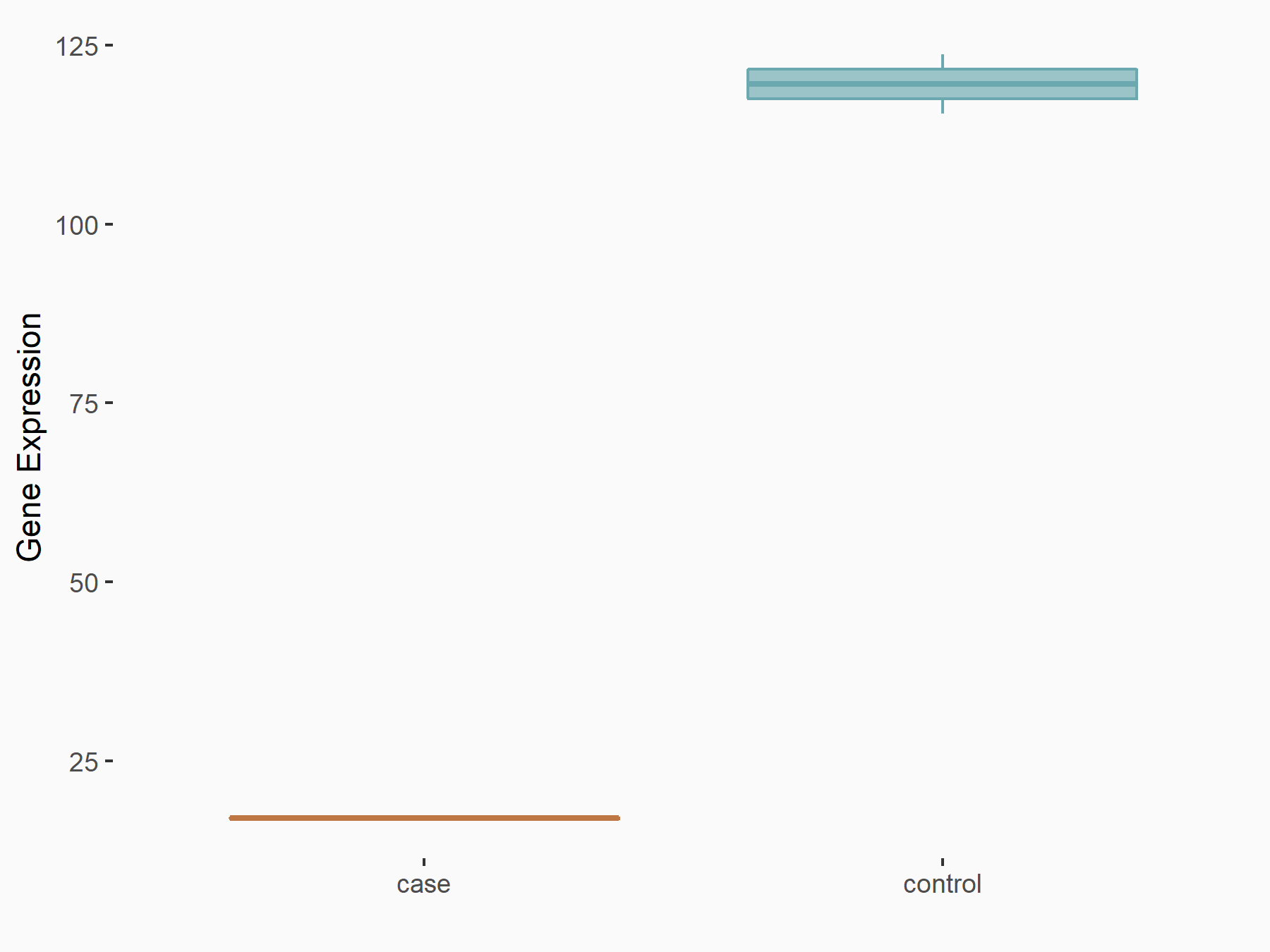 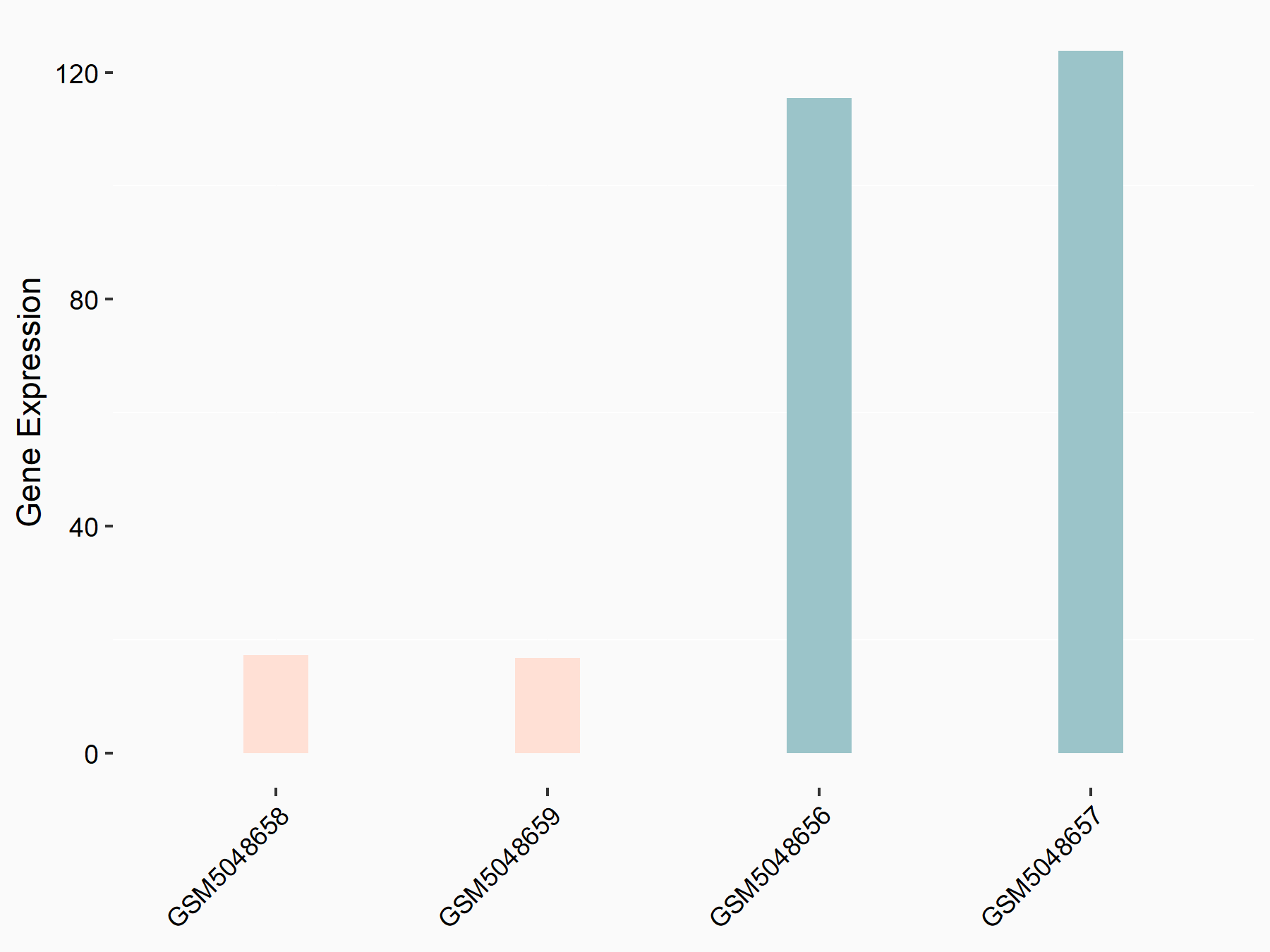 |
logFC: -2.82E+00 p-value: 1.42E-13 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Disorders of the retina [ICD-11: 9B70-9C0Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [32] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Disorders of the retina [ICD-11: 9B70-9C0Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
ARPE-19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0145 |
| Response Summary | The expression of METTL14 is significantly reduced in patients with retinitis pigmentosa (RP). METTL14 regulates the expression of MAP2 via the modification of m6A, resulting in the dysregulation of Neurogenic differentiation factor 1 (NEUROD1) and pathologic changes in RPE cells. | |||
Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
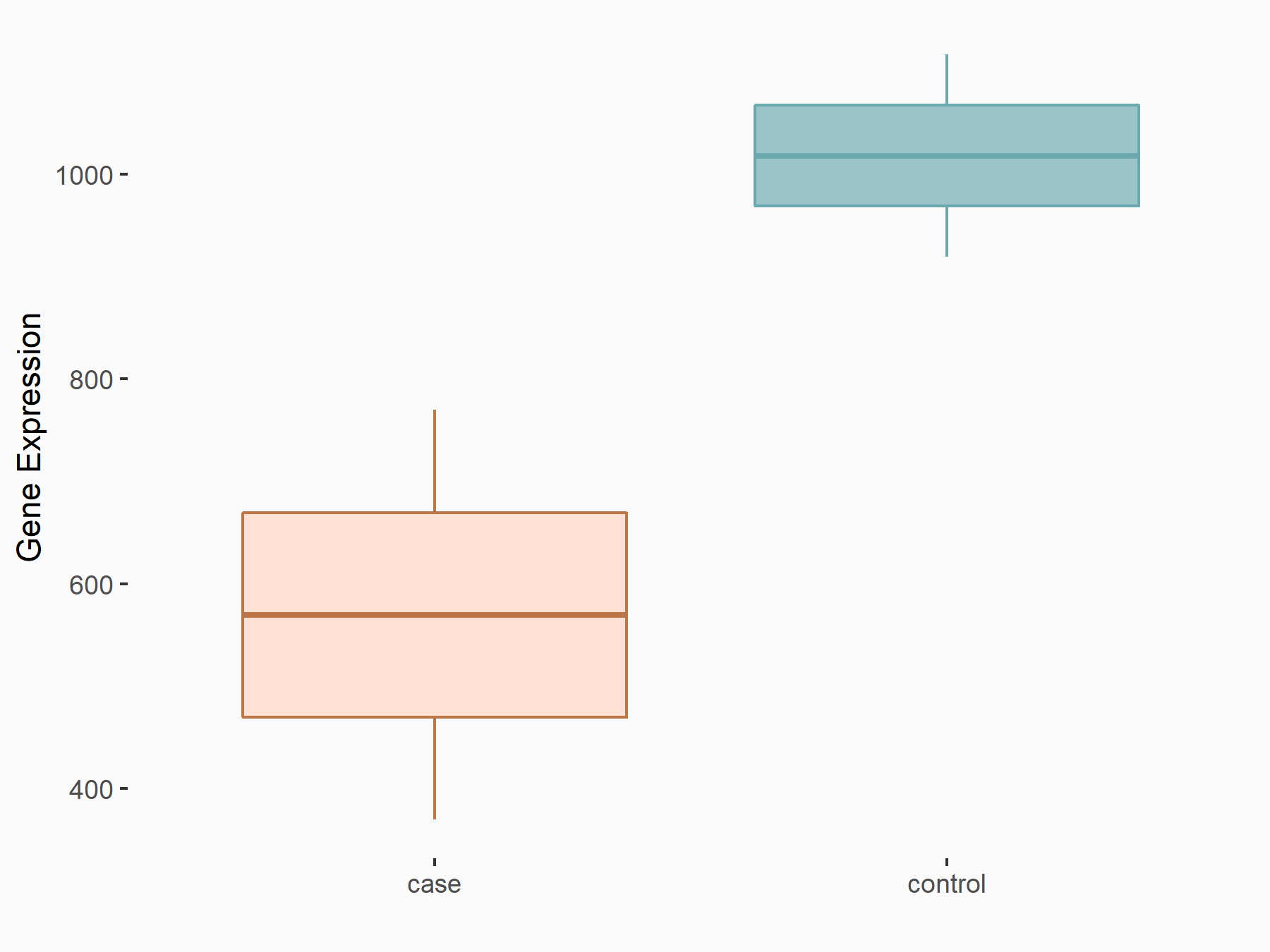 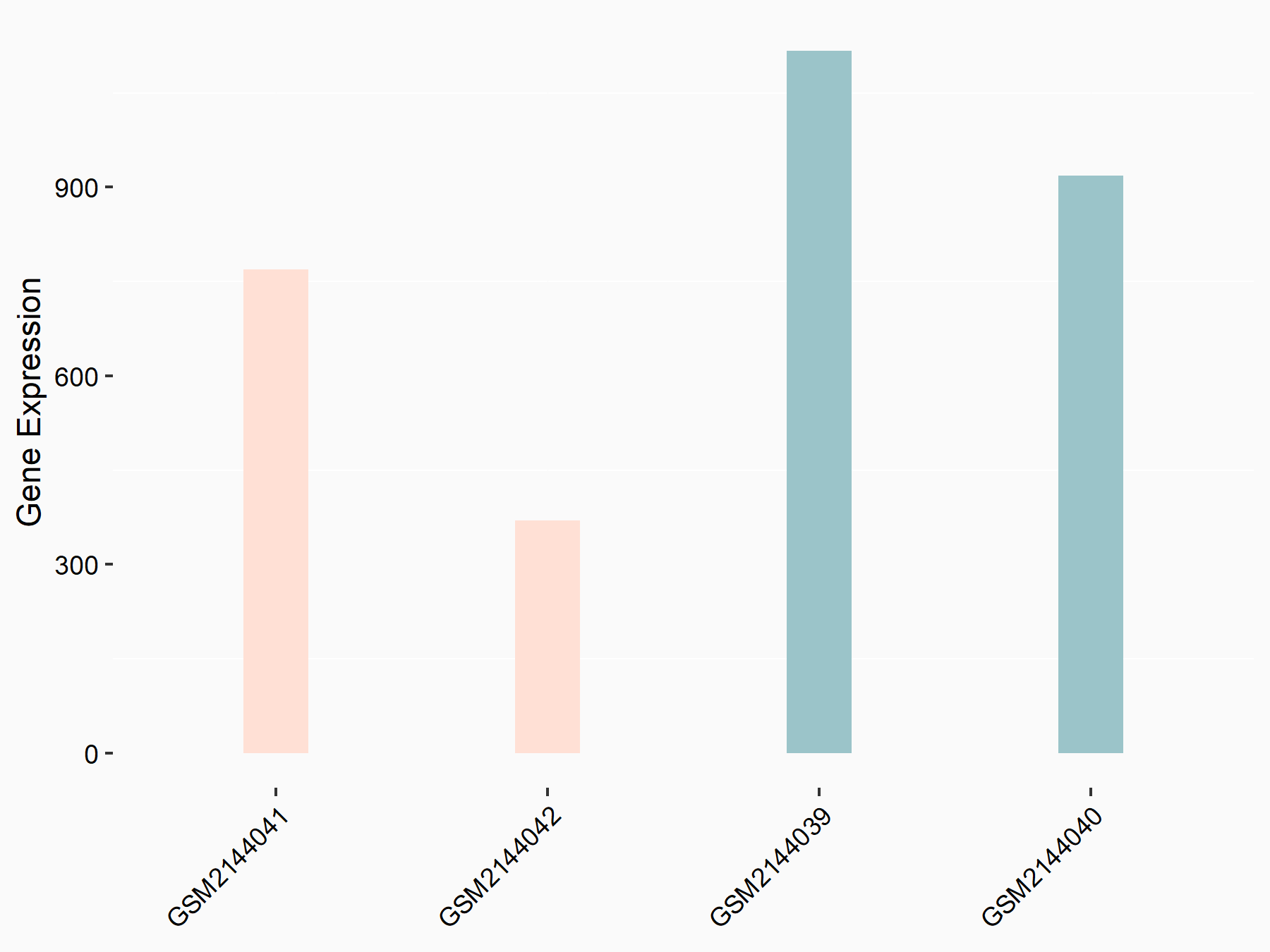 |
logFC: -8.37E-01 p-value: 6.43E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [38] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Self-renewal | ||||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
Primary bladder cancer cells (Obtained from bladder cancer patients) | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 and m6A modification participate in the RNA stability of Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) mRNA. Notch1 plays an essential role in bladder tumorigenesis and bladder TIC self-renewal. | |||
NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (Nfkbia)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
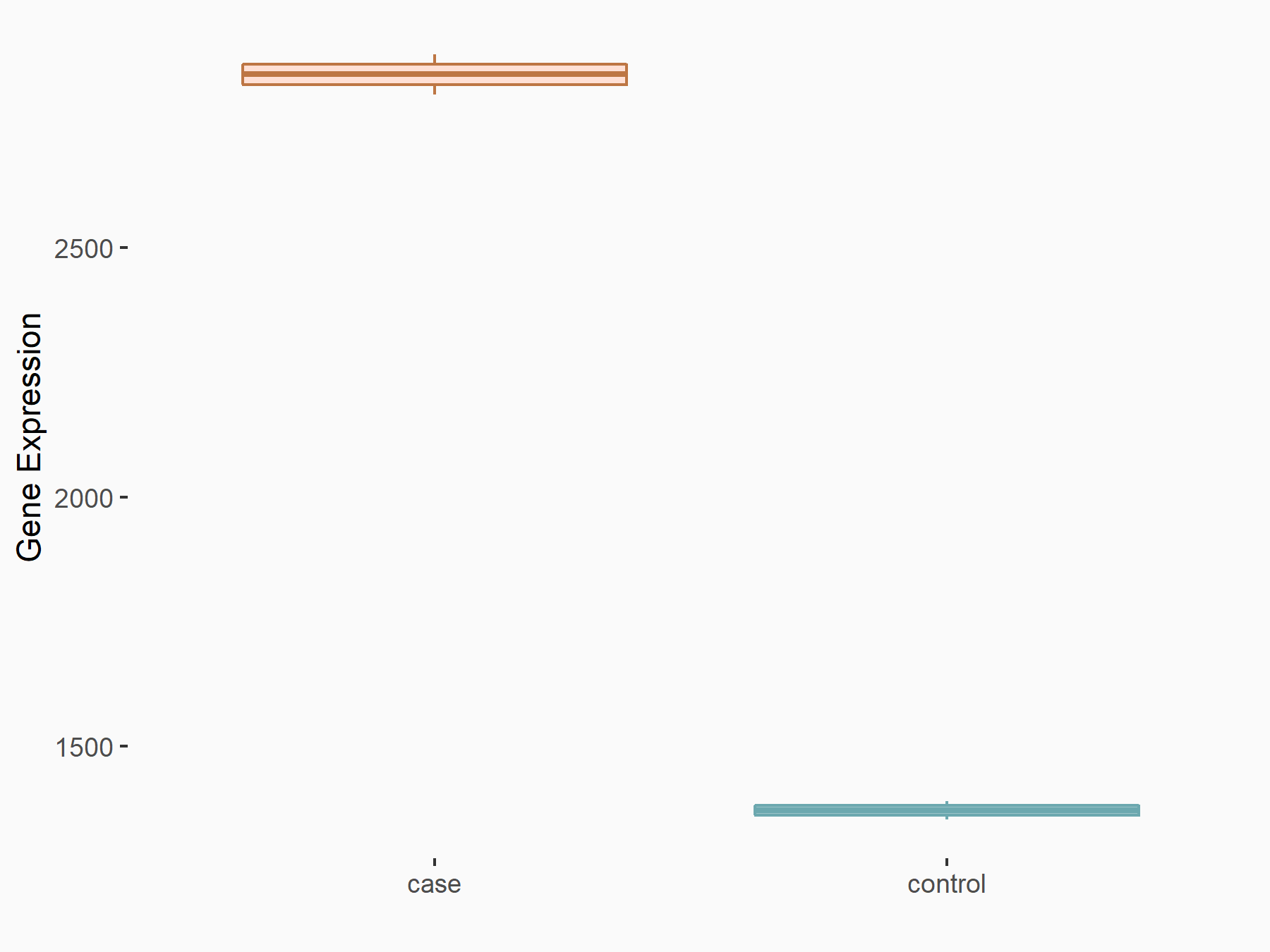 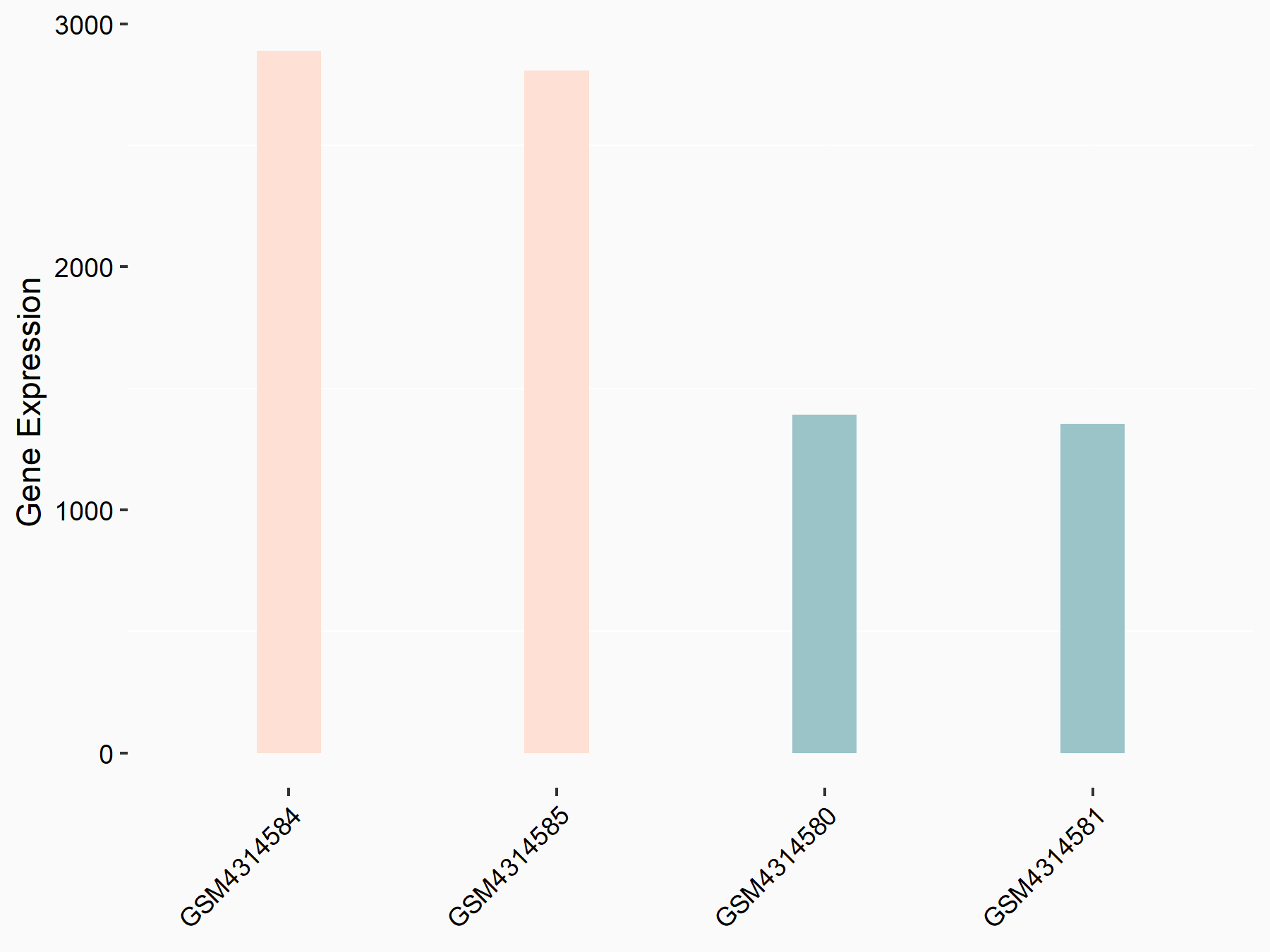 |
logFC: 1.05E+00 p-value: 4.32E-28 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Inflammatory bowel disease [ICD-11: DD7Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [39] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Inflammatory bowel disease [ICD-11: DD7Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14f/f mice were generated as previously described with CRISPR-Cas9 technology by insertion of two loxp sites into Mettl14 genome loci. Mettl14f/f mice without Villin-Cre were used as WT controls (Mettl14 WT) for Mettl14 KO mice. Mettl14f/f mice were crossed with Lgr5-eGFP-IRES-creERT2 (Lgr5-Cre) mice to generate Mettl14 depletion in Lgr5+ stem cells. | |||
| Response Summary | Colonic mucosal barrier dysfunction is one of the major causes of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mettl14 restricted colonic epithelial cell death by regulating the stability of NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (Nfkbia) mRNA and modulating the NF-Kappa-B pathway,suggesting that m6A modification could be a potential therapeutic target for IBD. | |||
Nucleosome-remodeling factor subunit BPTF (BPTF)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
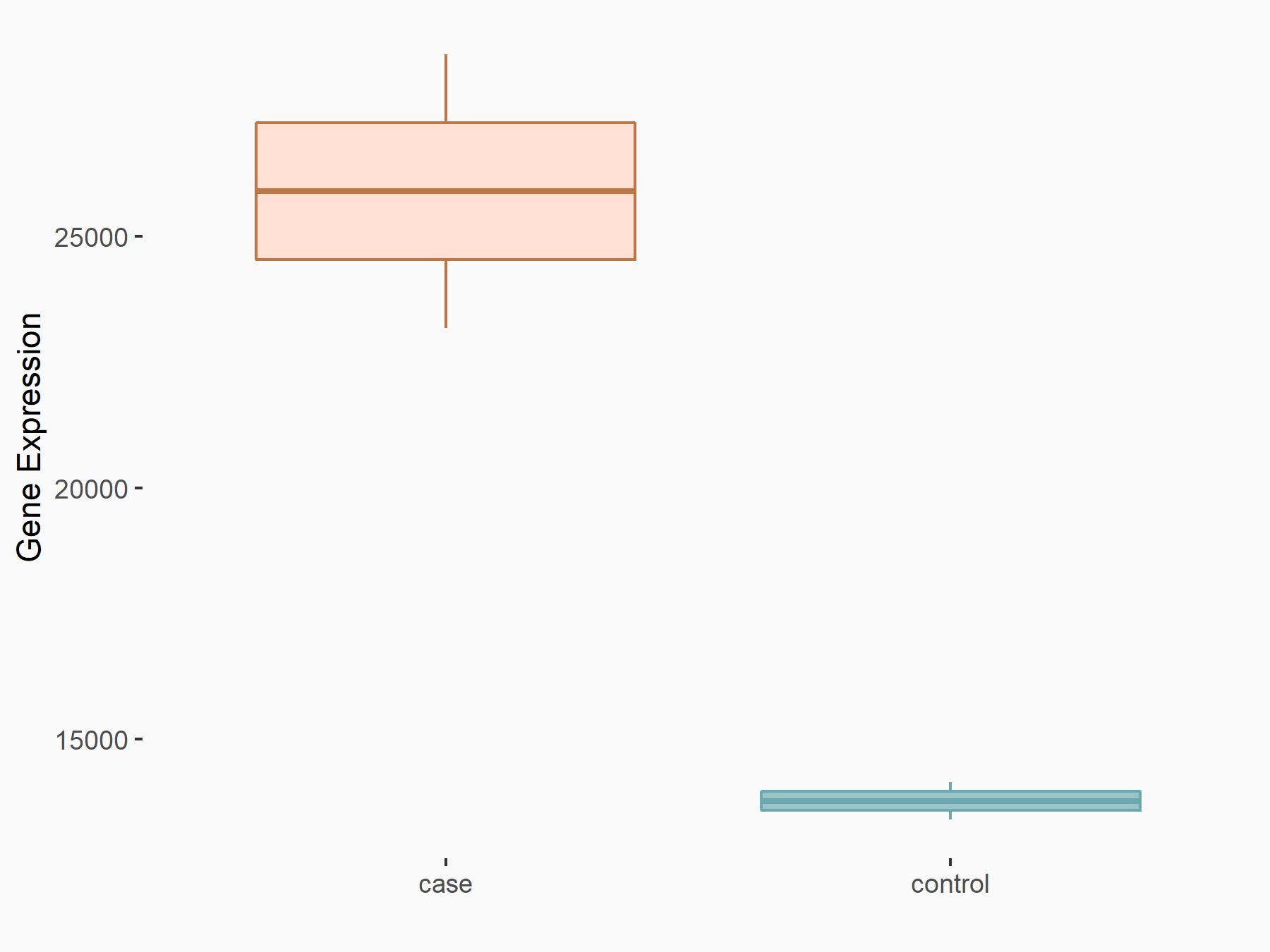 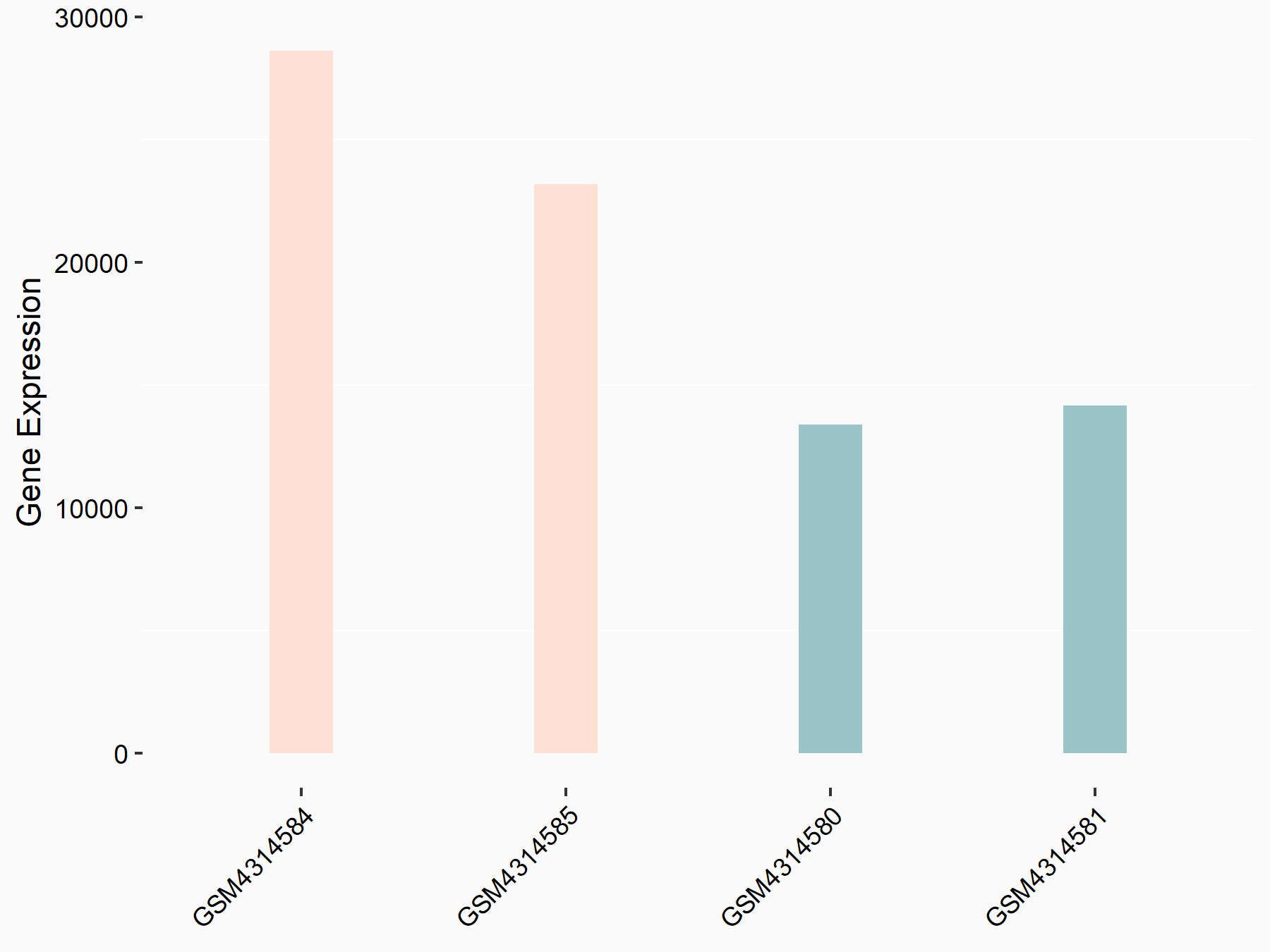 |
logFC: 9.11E-01 p-value: 2.73E-20 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [40] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Glycerolipid metabolism | hsa00561 | ||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
In-vitro Model |
RenCa | Mouse kidney carcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_2174 |
| Caki-1 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0234 | |
| ACHN | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1067 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | To generate a highly metastatic orthotopic xenograft model, 1 × 105 luciferase-expressing Renca cells (Luc-Renca) in 25 ul of 2:1 (v/v) PBS:Matrigel were injected into the right sub-renal capsule of the kidney of BALB/c mice (4 mice/group). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 deficiency promoted RCC metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, METTL14-mediated m6A modification negatively regulated the mRNA stability of Nucleosome-remodeling factor subunit BPTF (BPTF) and depended on BPTF to drive lung metastasis. | |||
p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22 (PERP)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
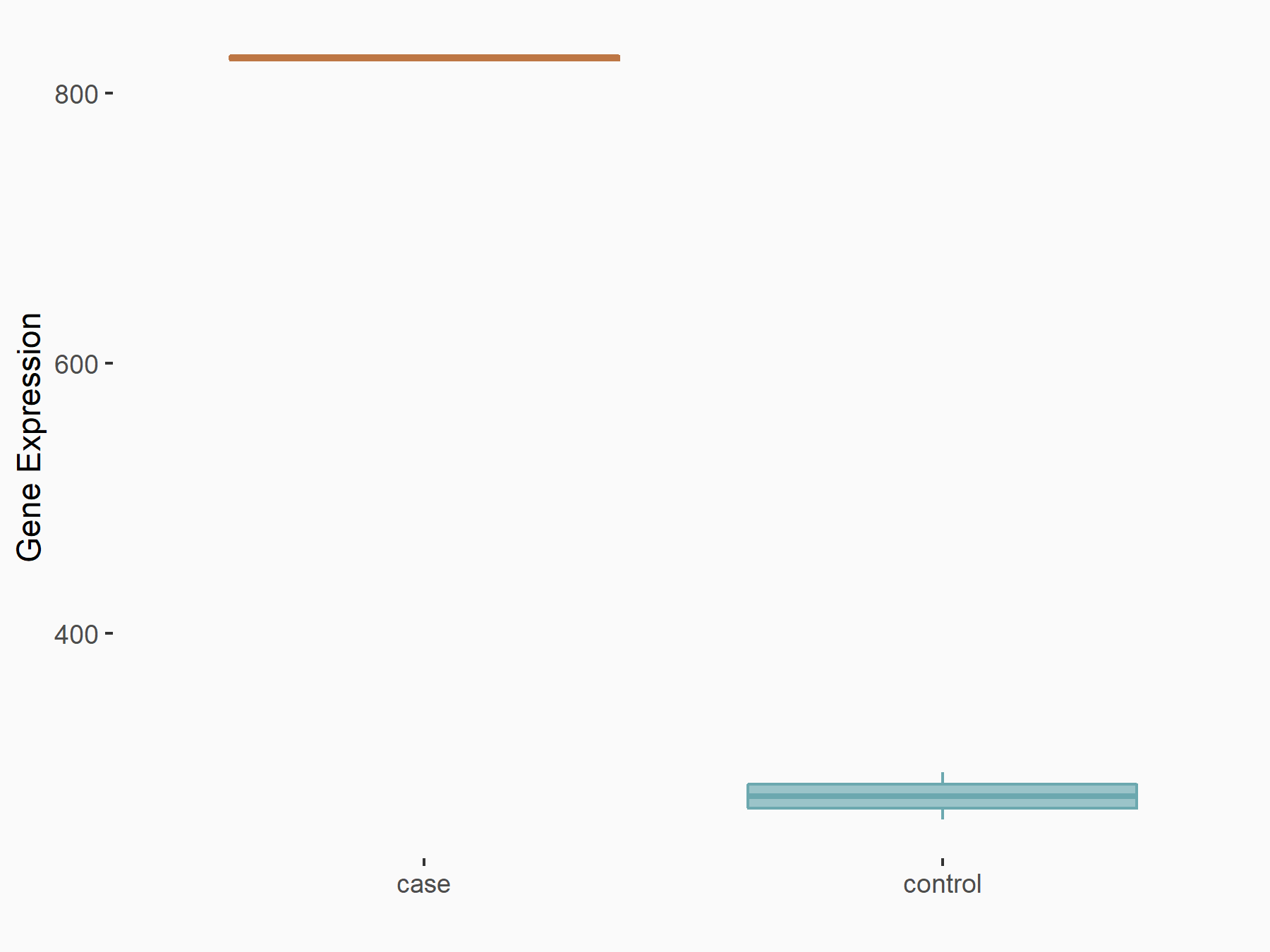  |
logFC: 1.56E+00 p-value: 2.67E-25 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [41] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Panc 03.27 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1635 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous transplantation model, 100 uL of 1 × 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the right armpit of BALB/c nude mice. Animal weight and tumor diameter were measured once a week from the time of implantation.For the pancreatic cancer orthotopic implantation model, 200 uL of Panc02-lucifer cells (2 × 107) were injected into the pancreas in mice anesthetized and laparotomized. After 4 weeks, the mice were anesthetized and injected with 150 mg/kg d-luciferin, via the tail vein.For the liver metastasis model, BALB/c nude mice received 2 × 106 cells (in 100 uL DMEM), directly injected into the spleen. Their body weight was measured once a week from the time of implantation. | |||
| Response Summary | The upregulation of METTL14 leads to the decrease of p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22 (PERP) levels via m6A modification, promoting the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer; therefore METTL14 is a potential therapeutic target for its treatment. | |||
PHLPP-like (PHLPP2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
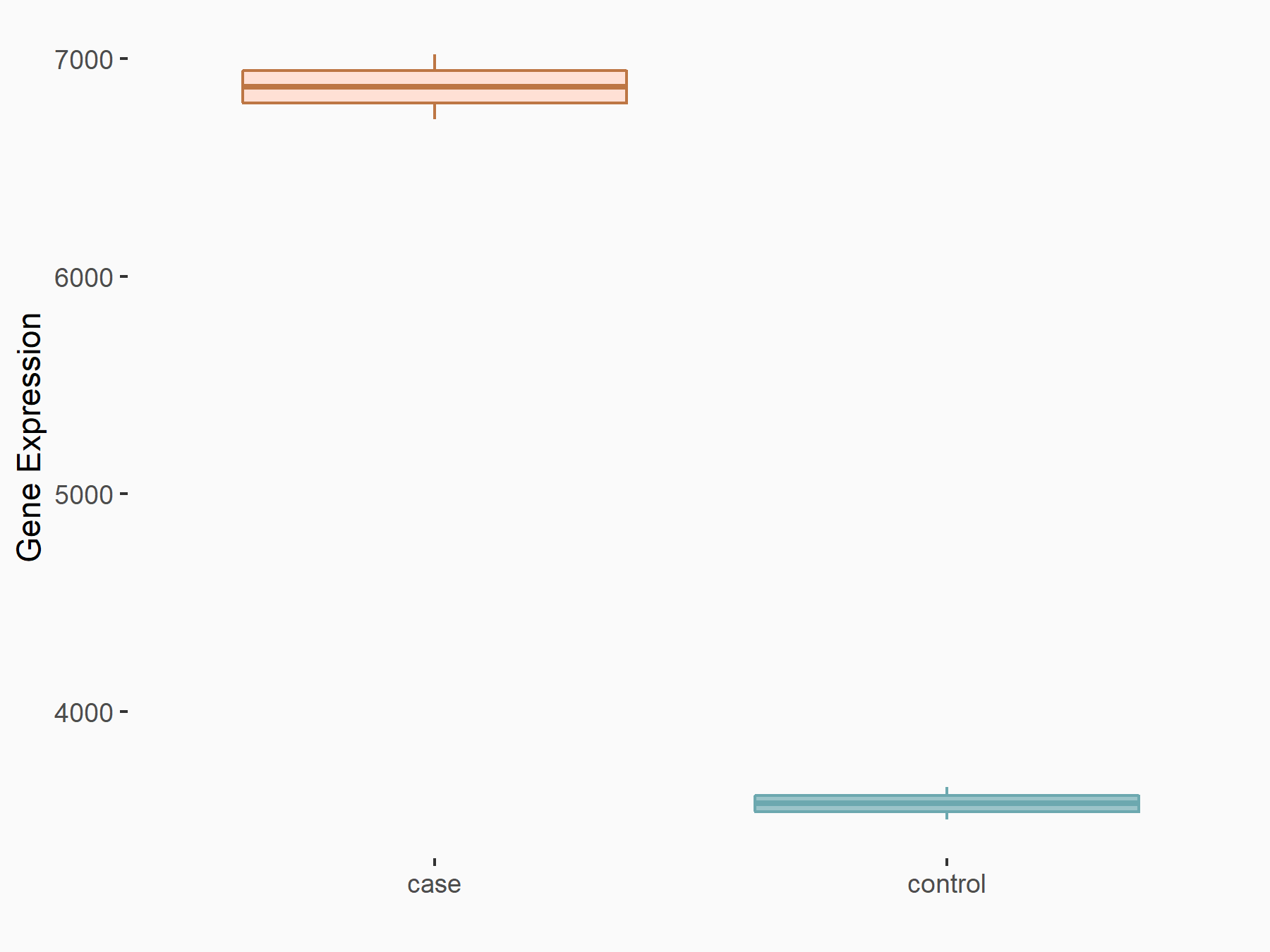  |
logFC: 9.41E-01 p-value: 4.99E-14 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [42] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and tumorigenicity | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEC-1-A | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0293 |
| RL95-2 | Endometrial adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0505 | |
| T HESCs | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C464 | |
| In-vivo Model | 4×106 HEC-1-A endometrial cancer cells (shCtrl, shMETTL3, wild-type, METTL14+/-, or METTL14+/- rescued with wild-type or mutant METTL14) were injected intraperitoneally into 5 week old female athymic nude mice (Foxn1nu, Harlan; n=10 per group). | |||
| Response Summary | About 70% of endometrial tumours exhibit reductions in m6A methylation that are probably due to either this METTL14 mutation or reduced expression of METTL3. Reductions in m6A methylation lead to decreased expression of the negative AKT regulator PHLPP-like (PHLPP2) and increased expression of the positive AKT regulator mTORC2. these results reveal reduced m6A mRNA methylation as an oncogenic mechanism in endometrial cancer and identify m6A methylation as a regulator of AKT signalling. | |||
PI3-kinase subunit alpha (PI3k/PIK3CA)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
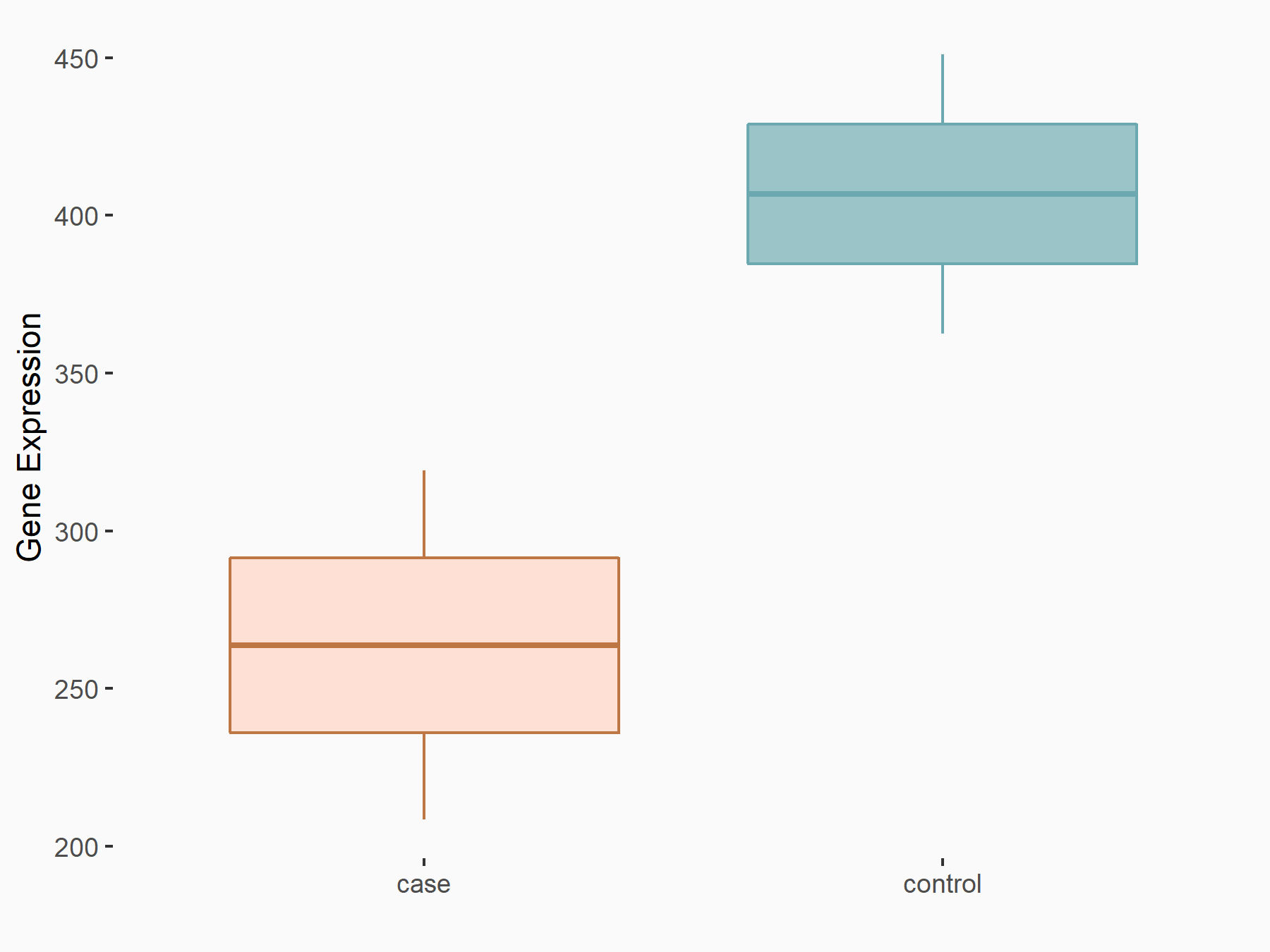 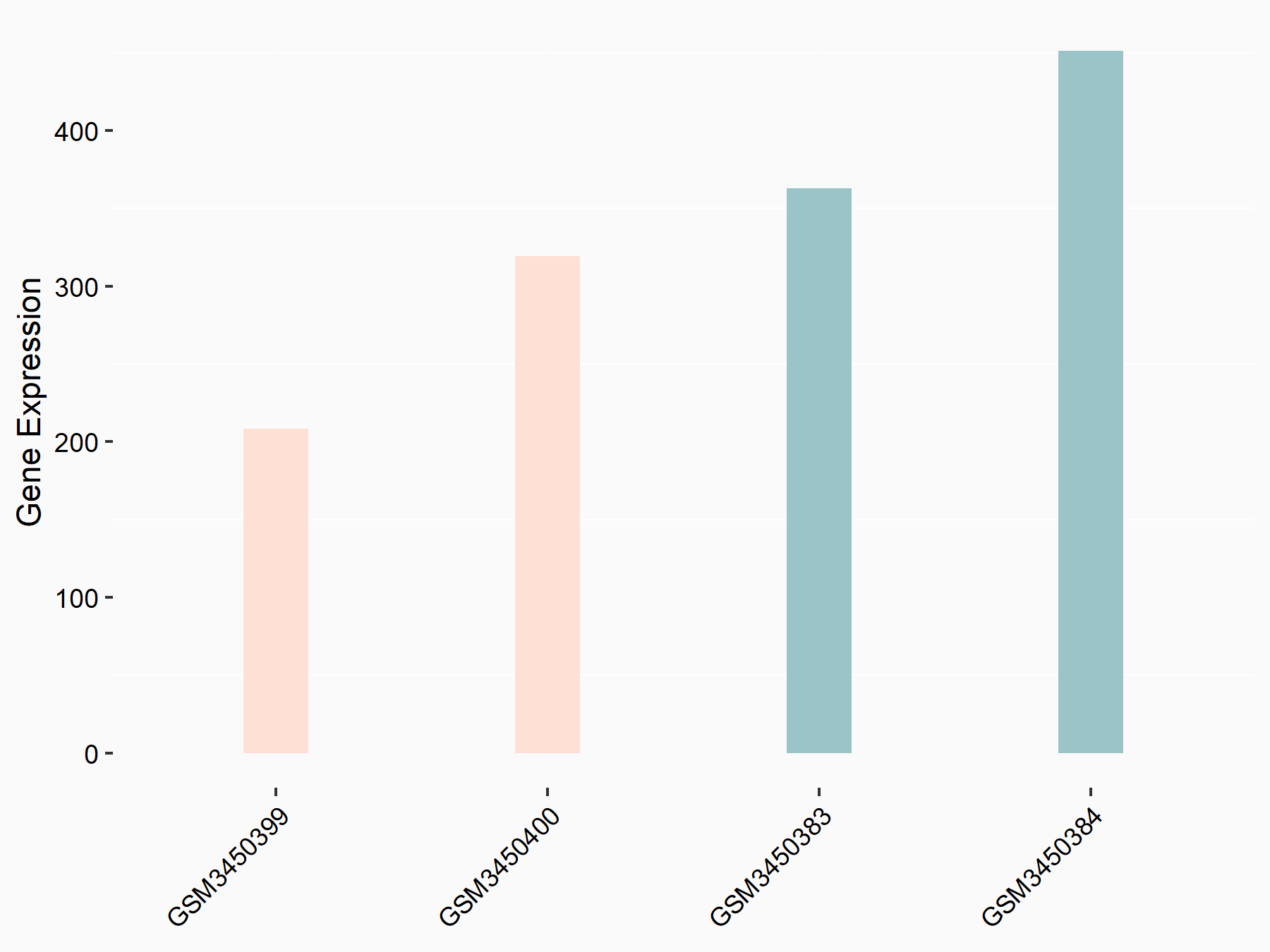 |
logFC: -6.28E-01 p-value: 7.56E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [43] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| Response Summary | The m6A modification level was decreased in GC and METTL14 was a key regulator resulting in m6A disorder in GC. METTL14 overexpression suppressed GC cell proliferation and aggression by deactivating the PI3-kinase subunit alpha (PI3k/PIK3CA)/AKT/mTOR pathway and the EMT pathway, respectively. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
YY-8103 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_WY40 |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the lung metastasis model, stably transfected HepG2 cells (1 × 106/0.1 mL DMEM) were injected into each nude mouse through the tail vein. Five weeks later, mice were euthanized, and the lung tissues were collected. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 was found to inhibit HCC cell migration, invasion, and EMT through modulating EGFR/PI3-kinase subunit alpha (PI3k/PIK3CA)/AKT signaling pathway in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
PI3-kinase subunit beta (PIK3CB)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
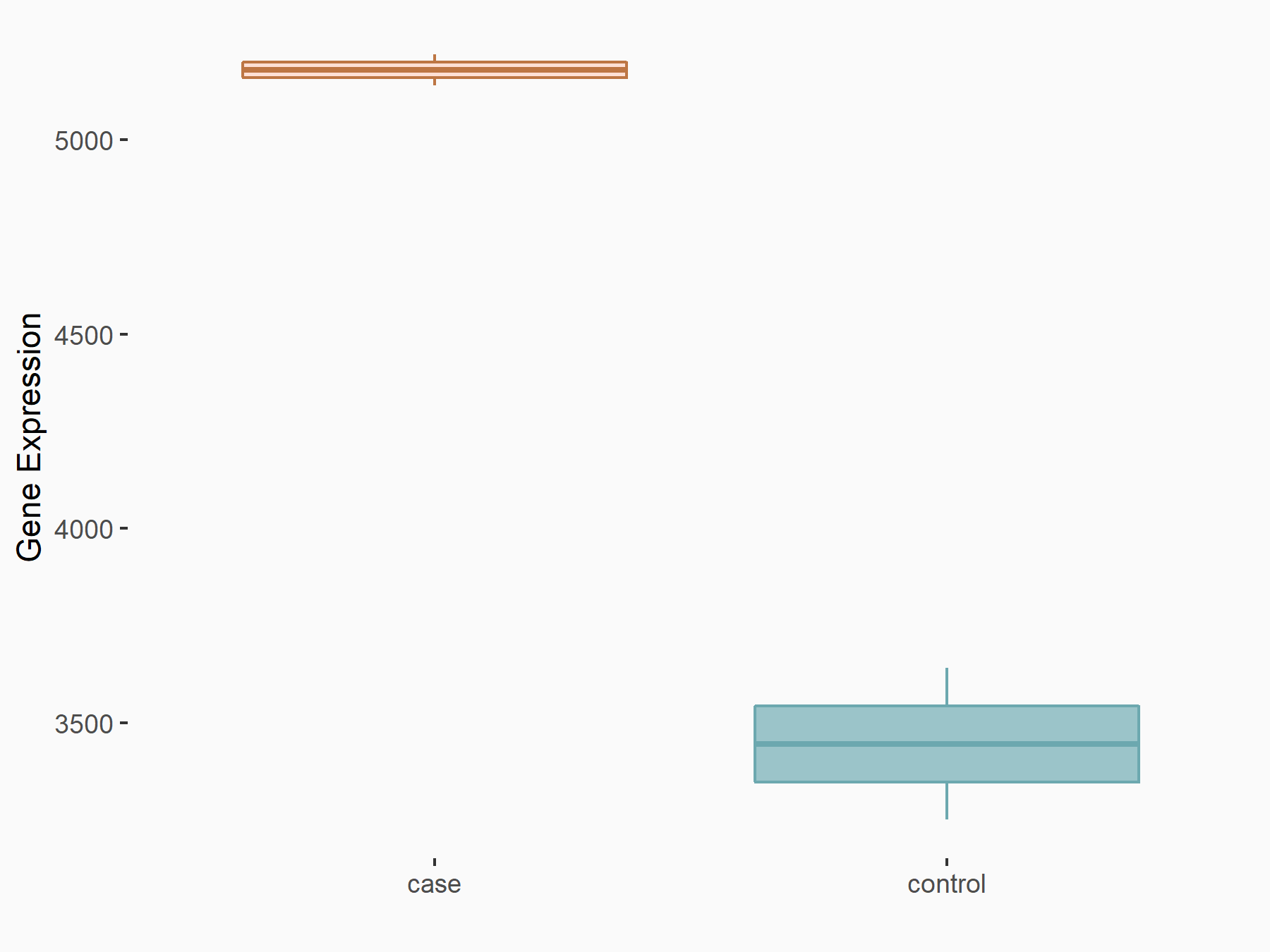 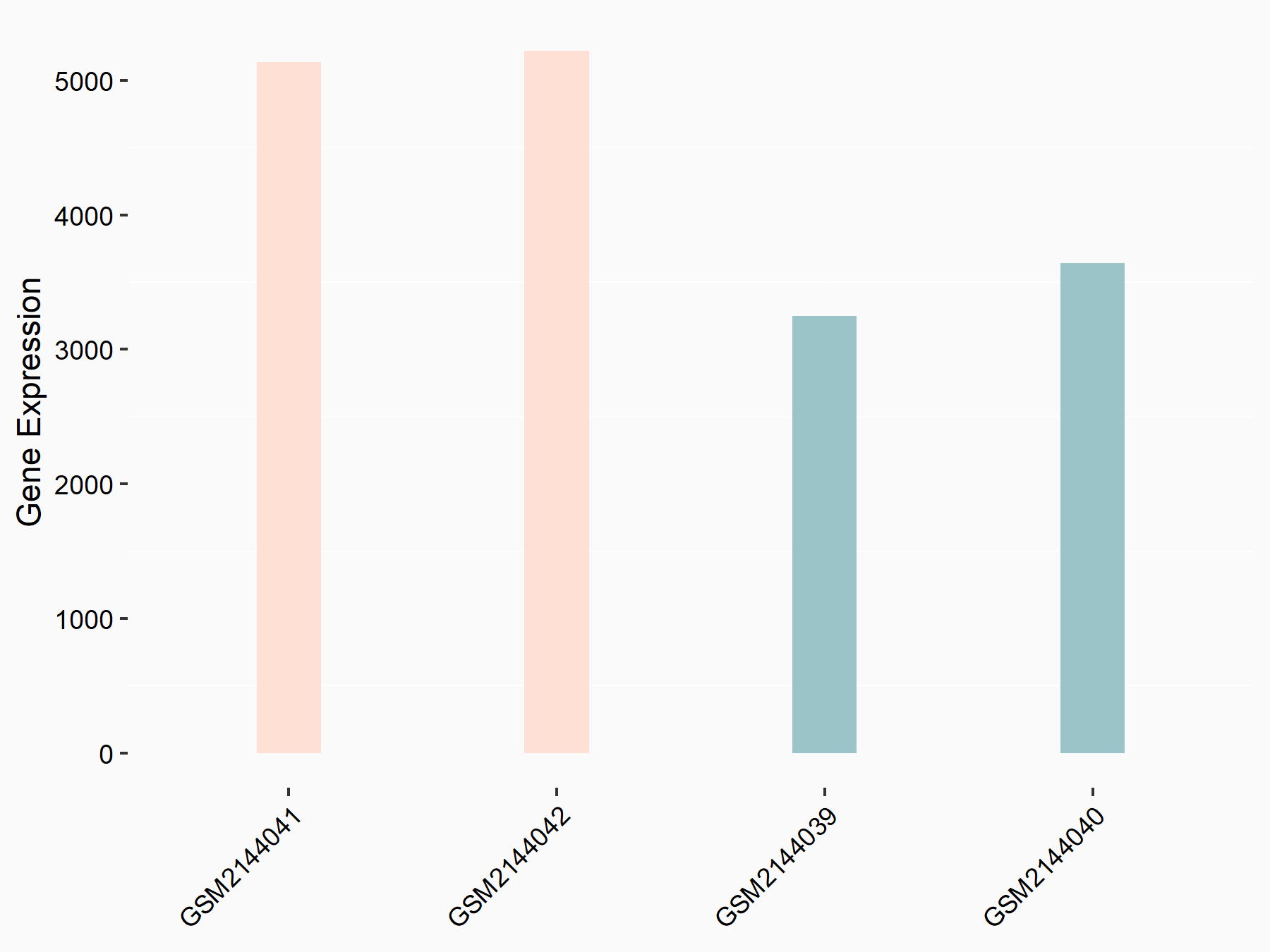 |
logFC: 5.88E-01 p-value: 1.08E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [44] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Responsed Drug | AZD6482 | Terminated | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| In-vivo Model | Established cohorts of mice bearing tumour xenografts driven by PTEN-deficient BxPC-3 and PANC-1 cells with PIK3CB overexpression. When tumours grew to ~300 mm3, mice were grouped and administered with vehicle (DMSO) or KIN-193 via intraperitoneal injection (20 mg/kg) once daily. | |||
| Response Summary | N6-methyladenosine mRNA methylation of PIK3CB regulates AKT signalling to promote PTEN-deficient pancreatic cancer progression. Rs142933486 is significantly associated with the overall survival of PDAC by reducing the PIK3CB m6A level, which facilitated its mRNA and protein expression levels mediated by the m6A 'writer' complex (METTL13/METTL14/WTAP) and the m6A 'reader' YTHDF2. KIN-193, a PI3-kinase subunit beta (PIK3CB)-selective inhibitor, is shown to serve as an effective anticancer agent for blocking PTEN-deficient PDAC. | |||
Proline-rich AKT1 substrate 1 (AKT1S1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
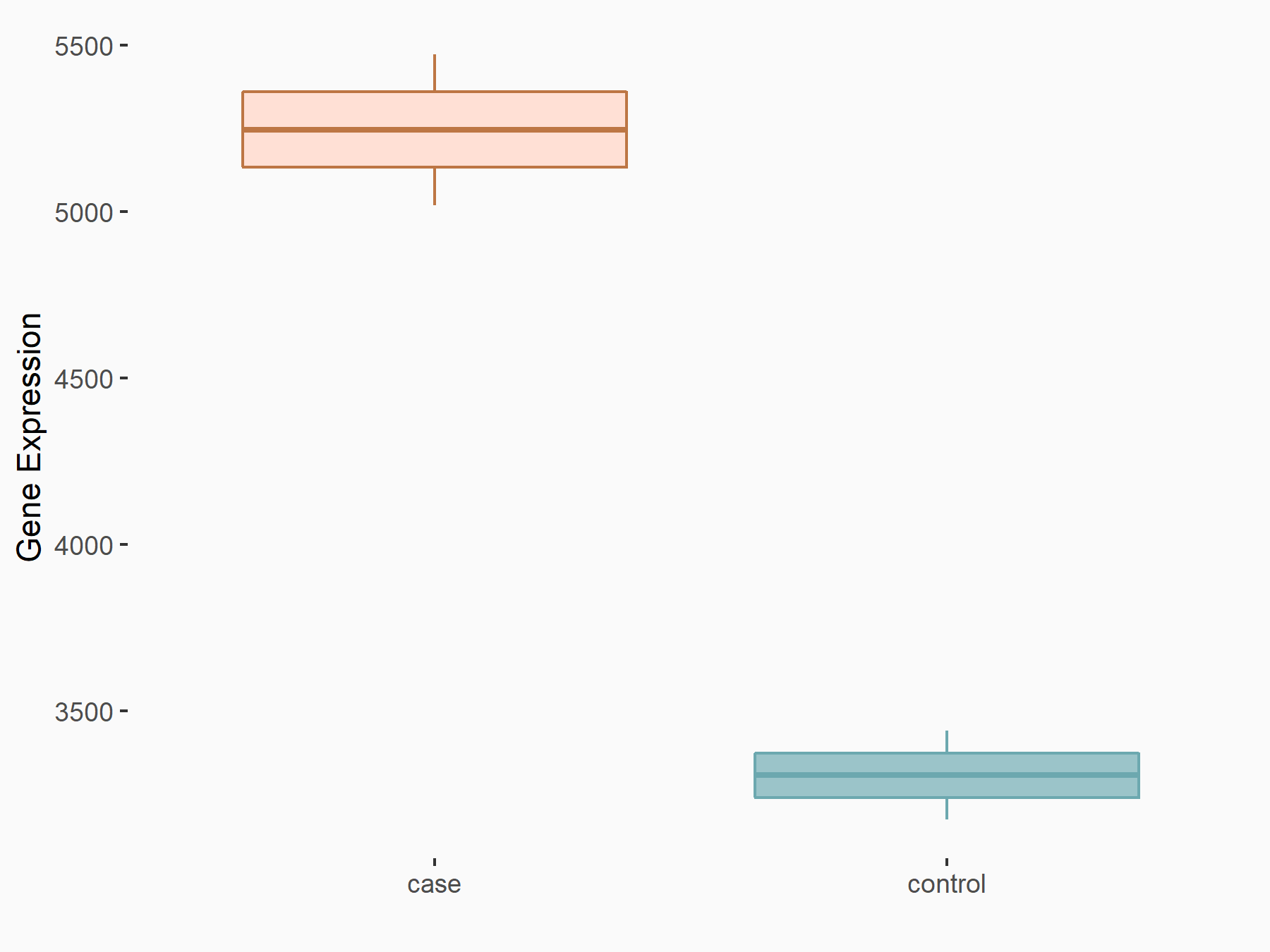 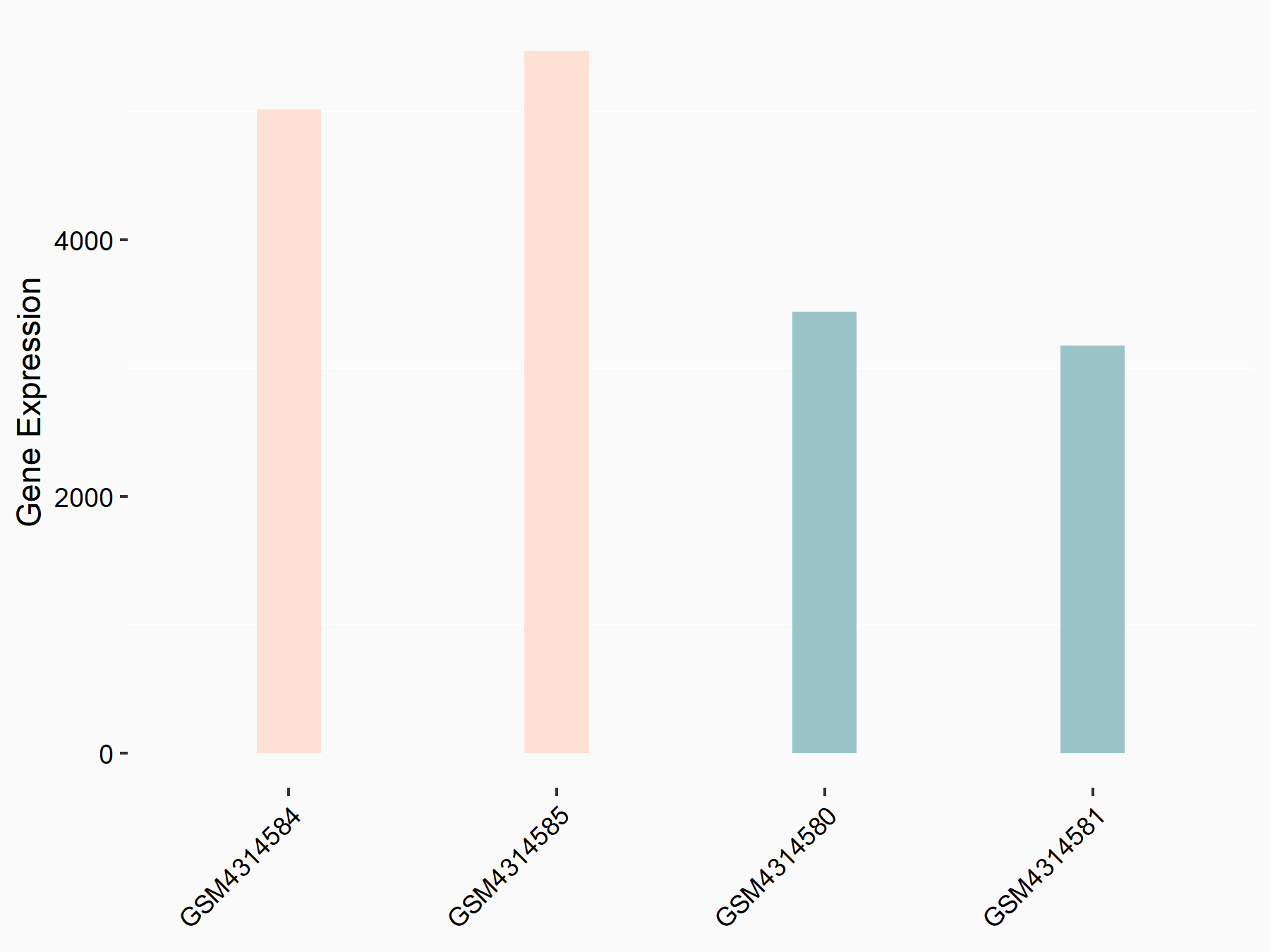 |
logFC: 6.65E-01 p-value: 2.87E-13 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [45] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| MKN28 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1416 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| Response Summary | METTL14-mediated m6A modification of circORC5 suppresses gastric cancer progression by regulating miR-30c-2-3p/Proline-rich AKT1 substrate 1 (AKT1S1) axis. METTL14 was downregulated in GC tissue samples and its low expression acted as a prognostic factor of poor survival in patients with GC. | |||
Protein phosphatase 1A (PPM1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
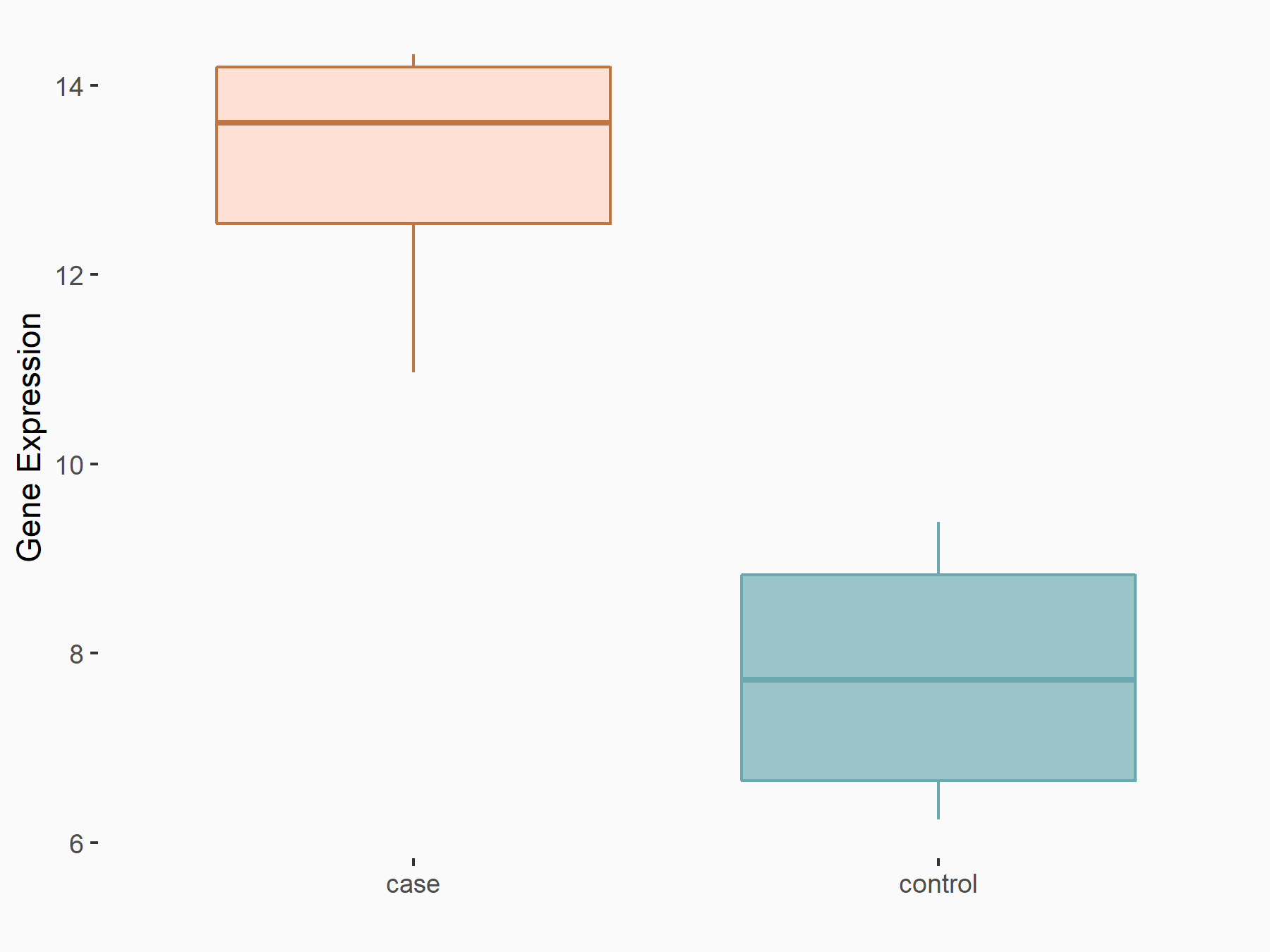 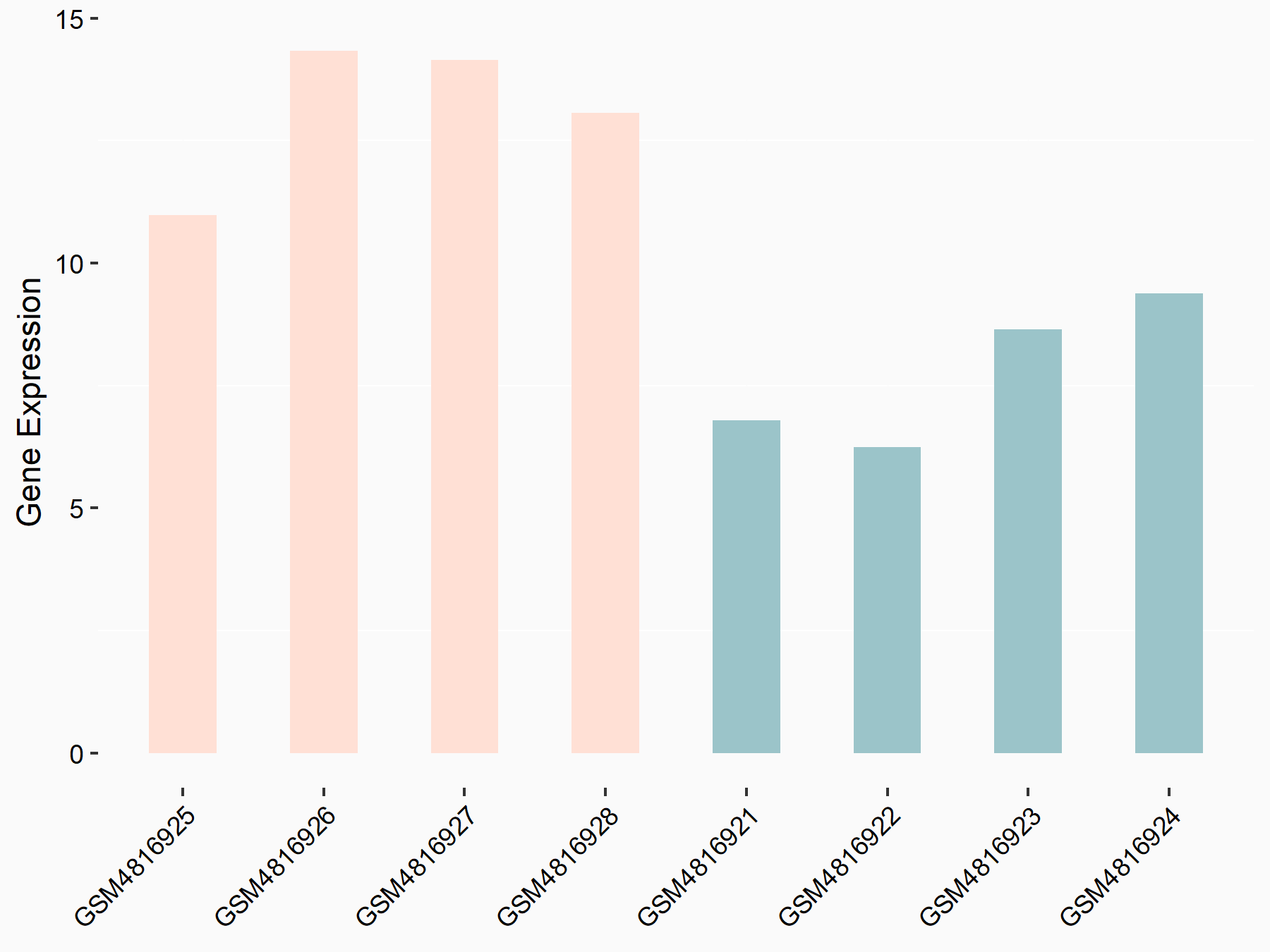 |
logFC: 6.97E-01 p-value: 2.44E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Azoospermia [ICD-11: GB04.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| In-vivo Model | Male SPF BALB/c mice (qls02-0202) were purchased from Qinglongshan animal breeding farm. Mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation and testes were obtained for following histopathological analyses. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification promoted translation of Protein phosphatase 1A (PPM1A) (protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform), a negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, but decreased expression of CAMKK2 (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta), a positive AMPK regulator, by reducing its RNA stability. Similar regulation of METTL14, ALKBH5, and m6A was also observed in LCs upon treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin (HsCG). Knock down of YTHDF1 failed to change the expression of CAMKK2 Providing insight into novel therapeutic strategies by exploiting m6A RNA methylation as targets for treating azoospermatism and oligospermatism patients with reduction in serum testosterone. | |||
Putative C->U-editing enzyme APOBEC-4 (APOBEC4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | CT26 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout CT26 cells
Control: CT26 cells
|
GSE142589 | |
| Regulation |
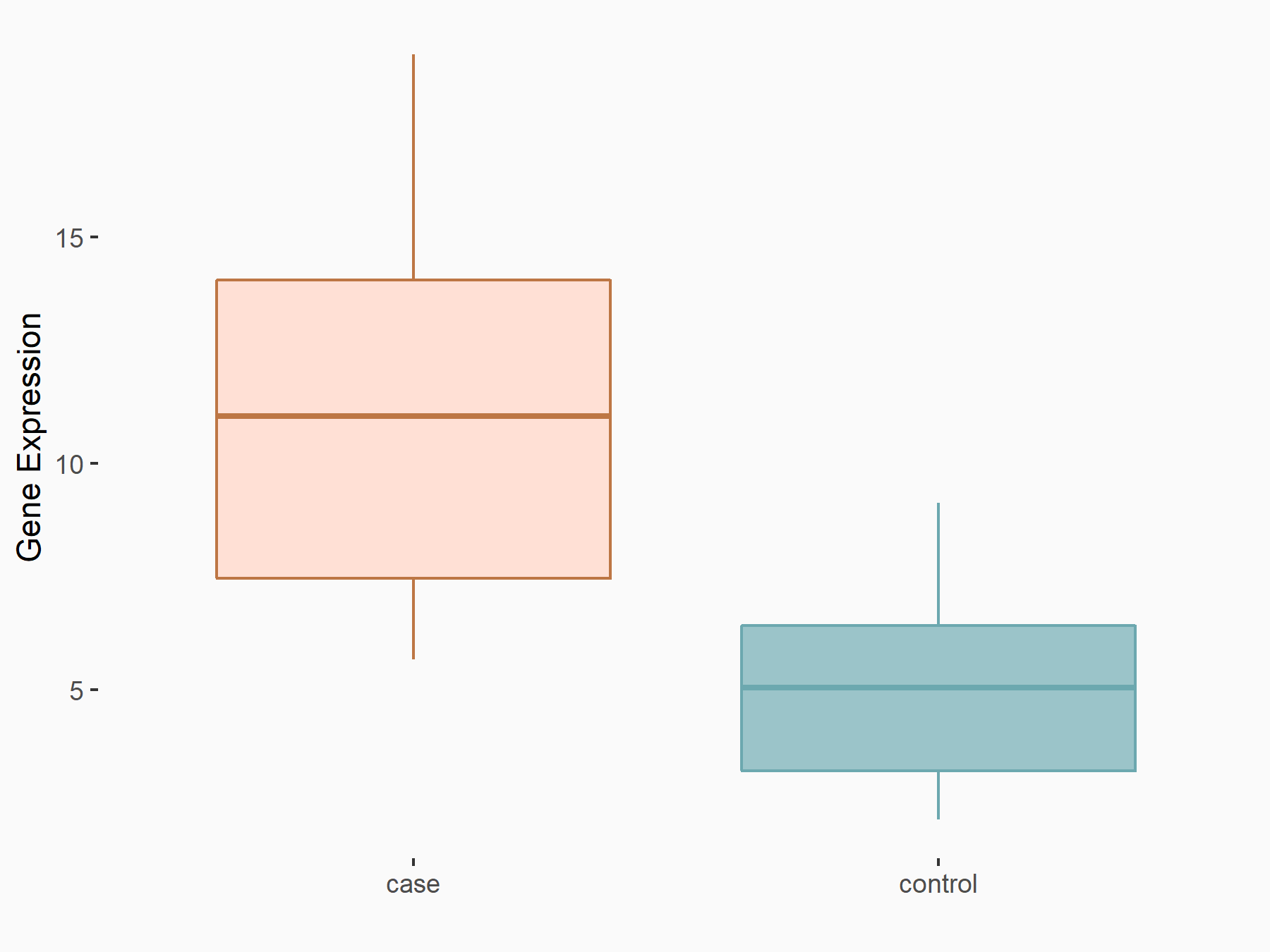 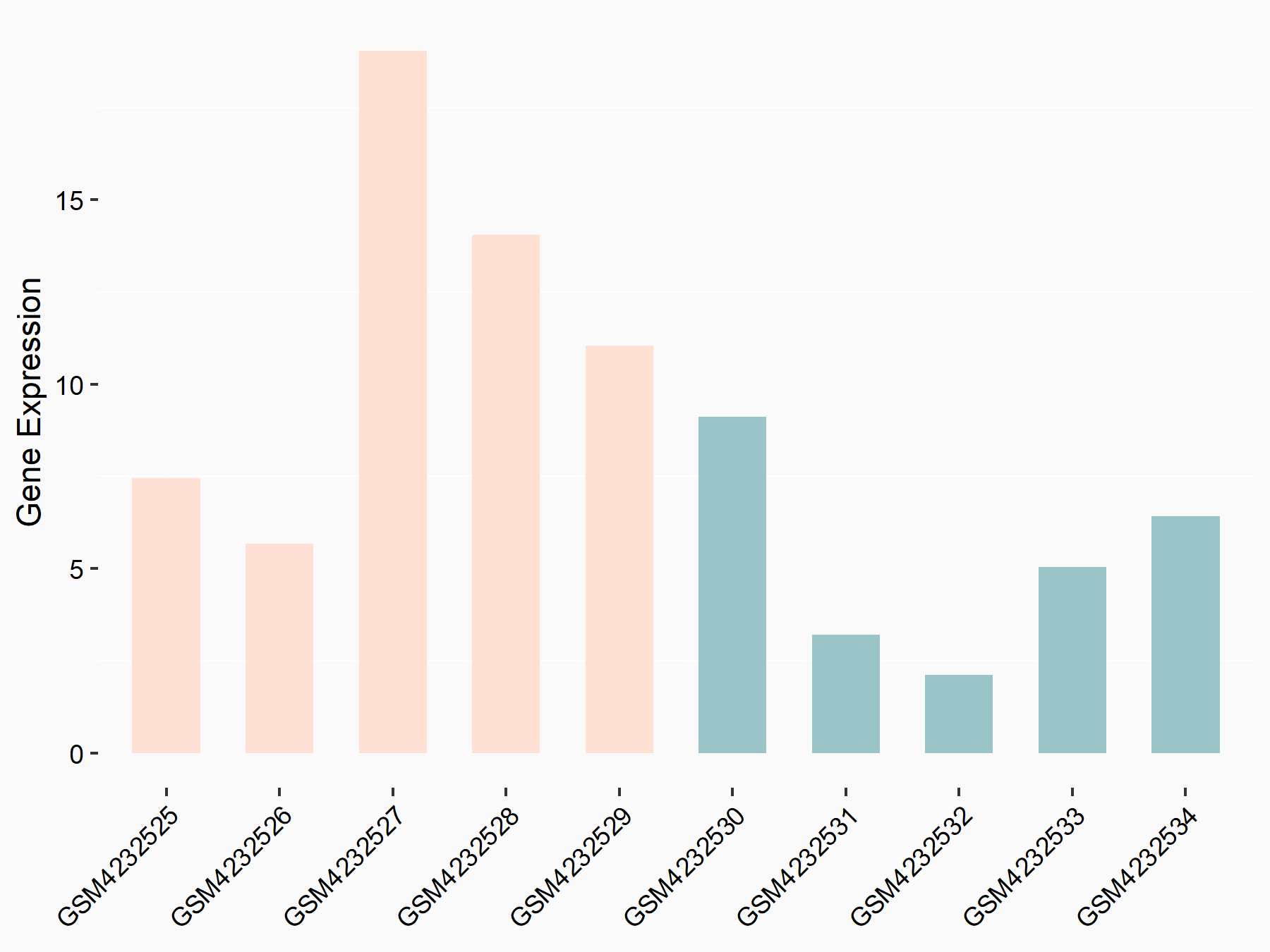 |
logFC: 1.15E+00 p-value: 4.95E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [46] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEY | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0297 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| Response Summary | Putative C->U-editing enzyme APOBEC-4 (APOBEC4) was found to be significantly correlated with m6A regulators such as WTAP, METTL14, ZC3H13, RBM15B, and FMR1. APOBEC3A was identified as a protective factor from comprehensive analyses based on the immune microenvironment and genomic instability of ovarian cancer. APOBEC3A had the potential to serve as a promising prognostic biomarker for foretelling the survival and immunotherapy response of ovarian cancer patients. | |||
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
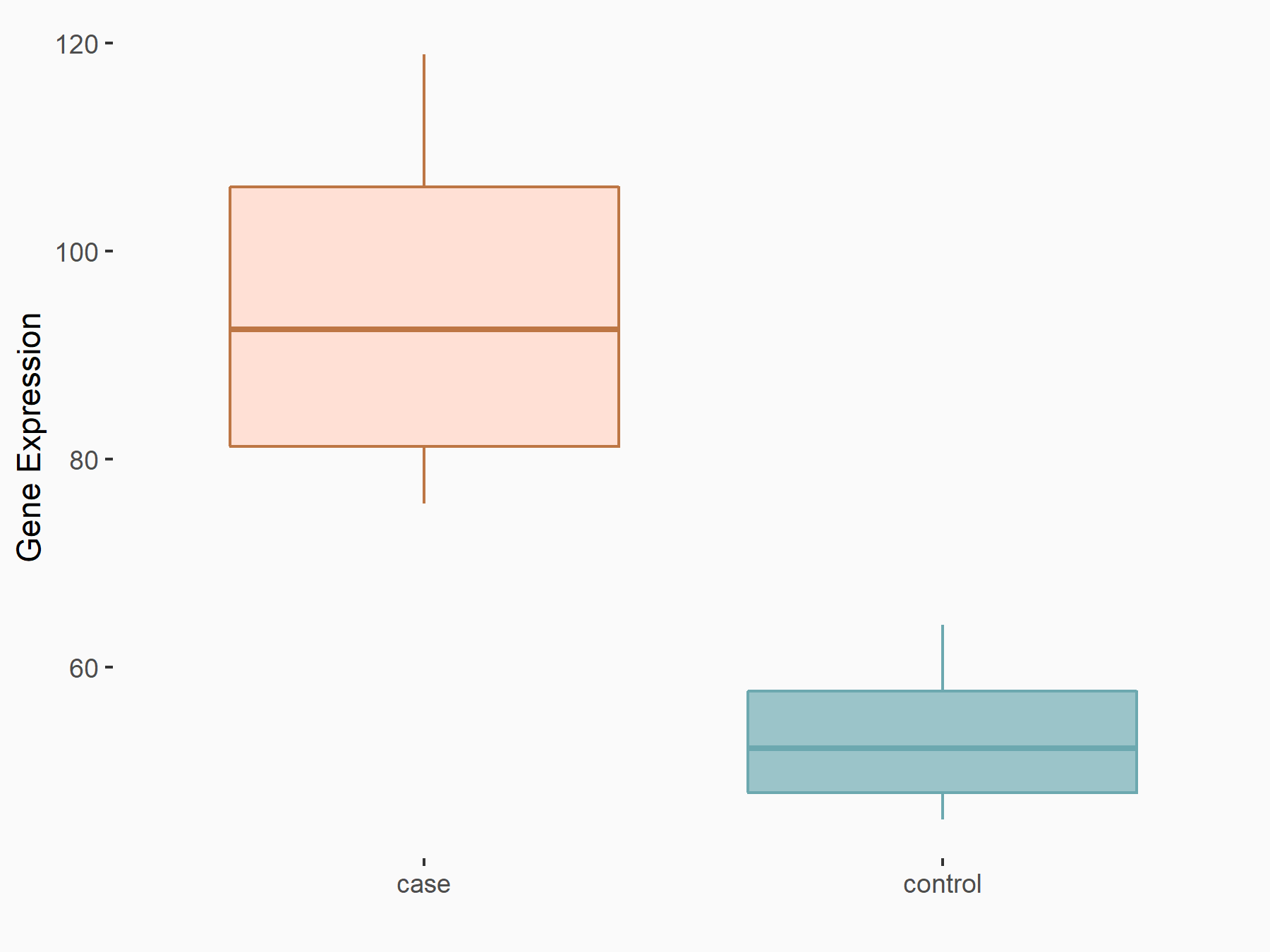 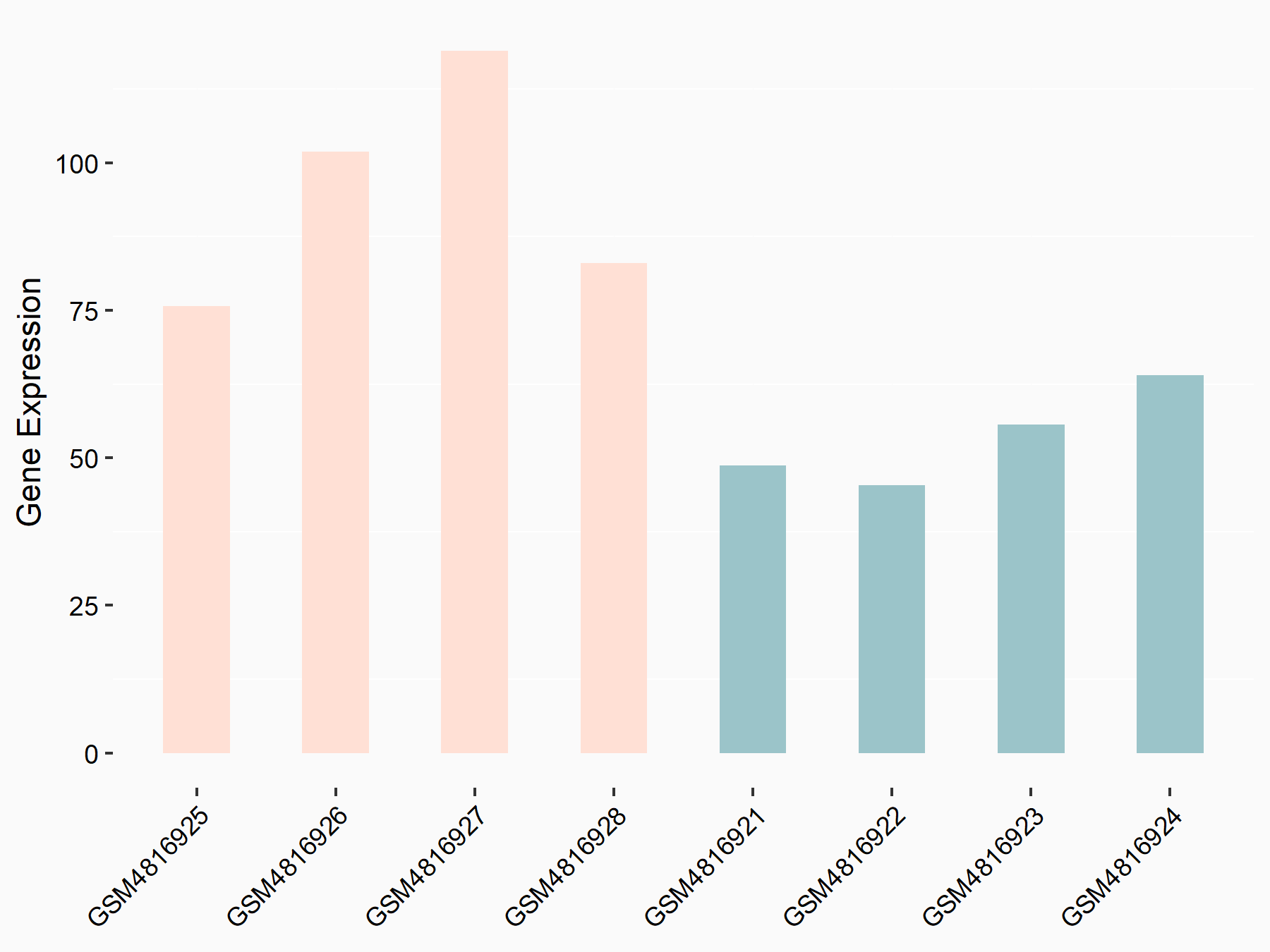 |
logFC: 8.08E-01 p-value: 3.19E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [43] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| Response Summary | The m6A modification level was decreased in GC and METTL14 was a key regulator resulting in m6A disorder in GC. METTL14 overexpression suppressed GC cell proliferation and aggression by deactivating the PI3K/RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)/mTOR pathway and the EMT pathway, respectively. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
YY-8103 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_WY40 |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the lung metastasis model, stably transfected HepG2 cells (1 × 106/0.1 mL DMEM) were injected into each nude mouse through the tail vein. Five weeks later, mice were euthanized, and the lung tissues were collected. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 was found to inhibit HCC cell migration, invasion, and EMT through modulating EGFR/PI3K/RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) signaling pathway in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
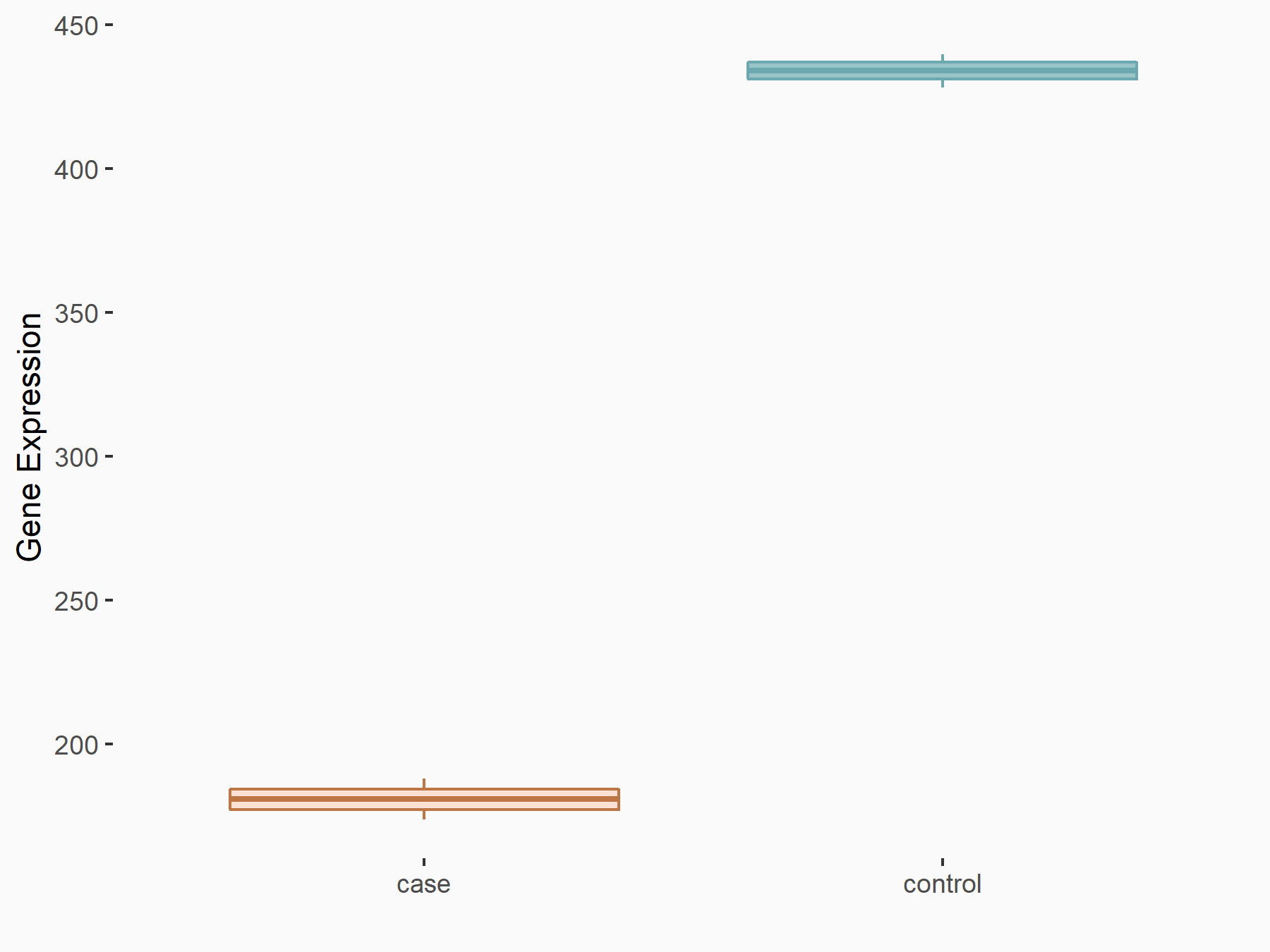 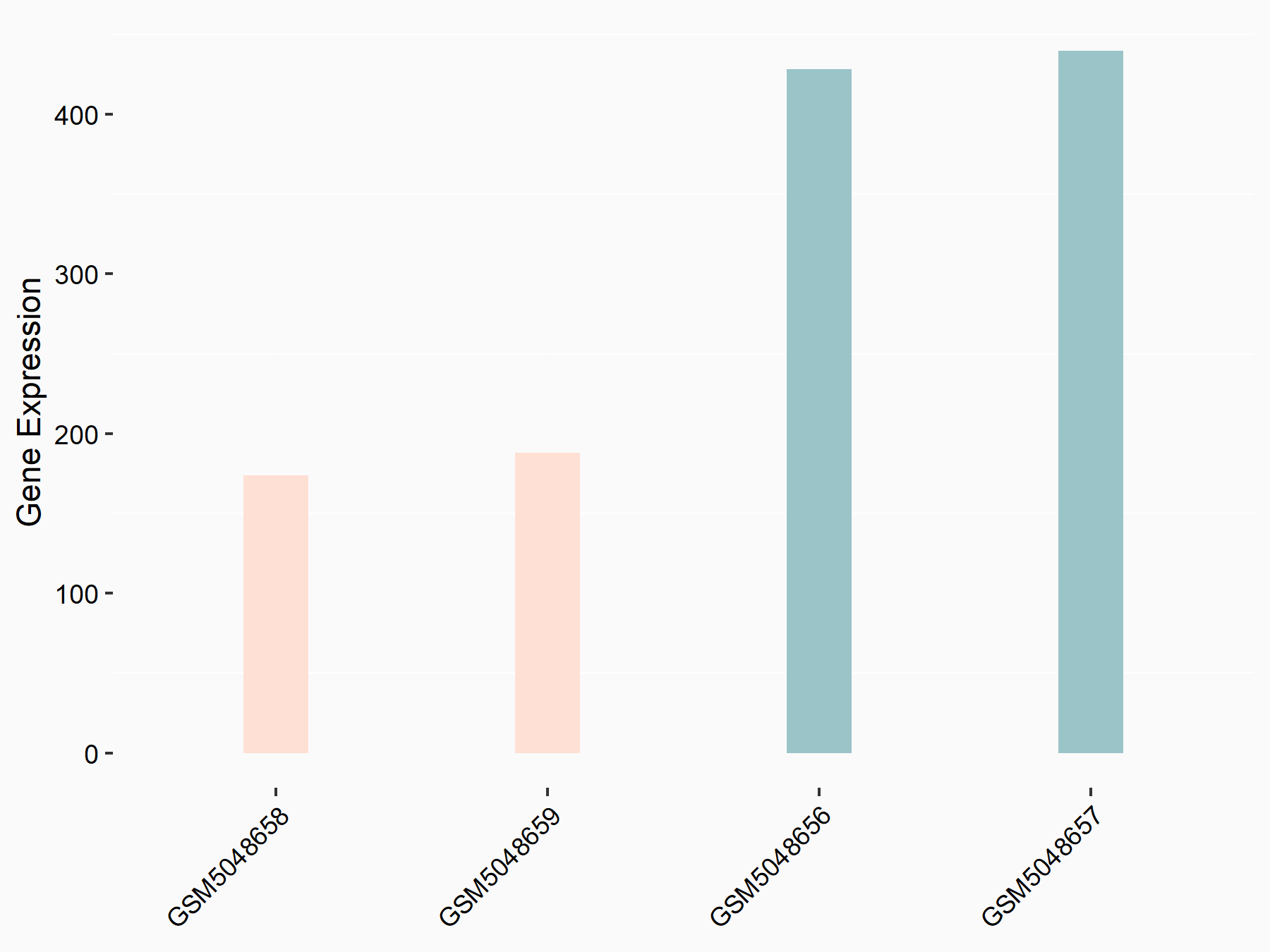 |
logFC: -1.26E+00 p-value: 3.52E-15 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute viral hepatitis [ICD-11: 1E50]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [47] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis B [ICD-11: 1E50.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
In-vitro Model |
Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
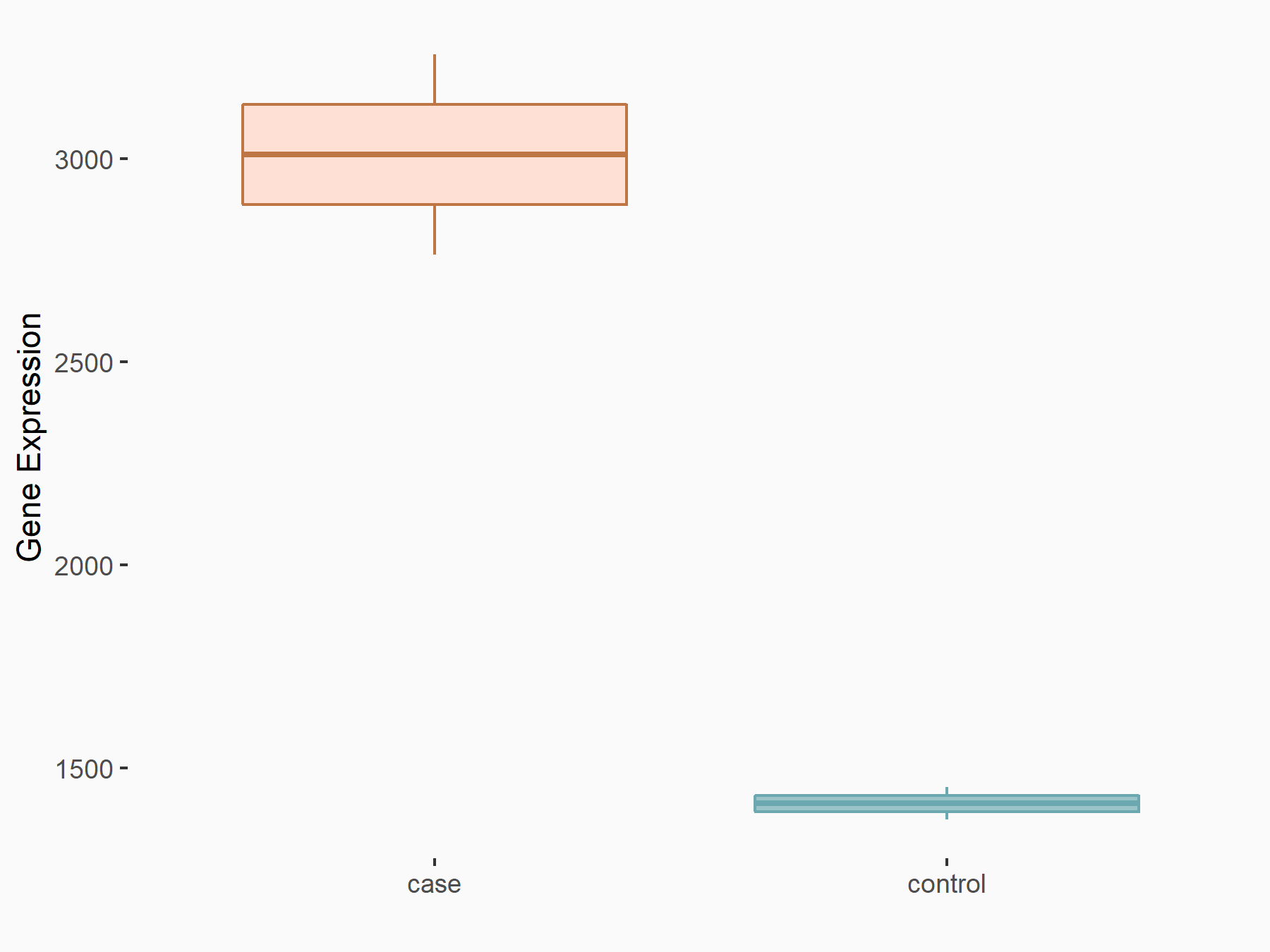 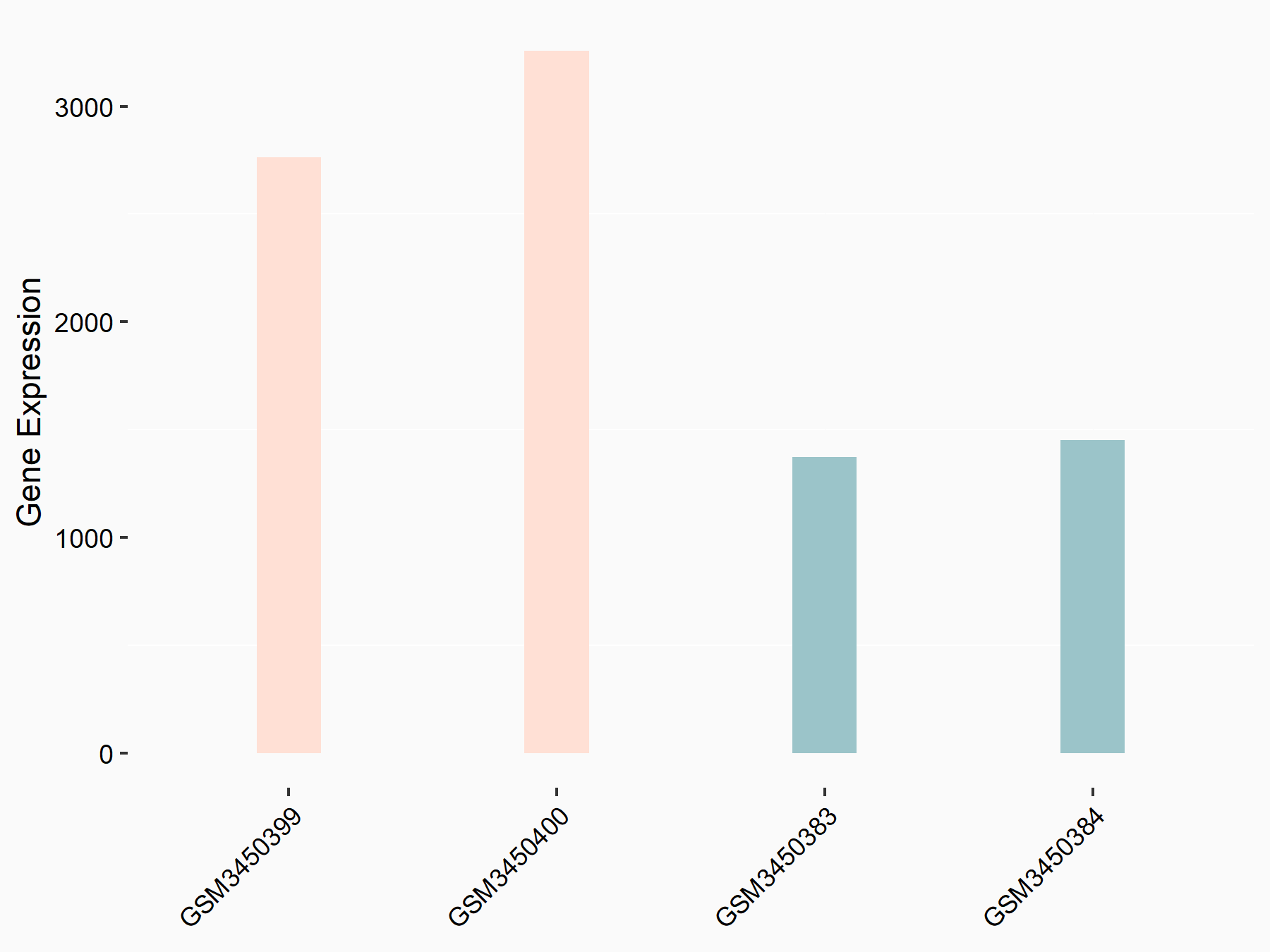 |
logFC: 1.09E+00 p-value: 8.51E-14 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Pertuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1) signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Trastuzumab | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1) signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tucatinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
In-vitro Model |
ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1) signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
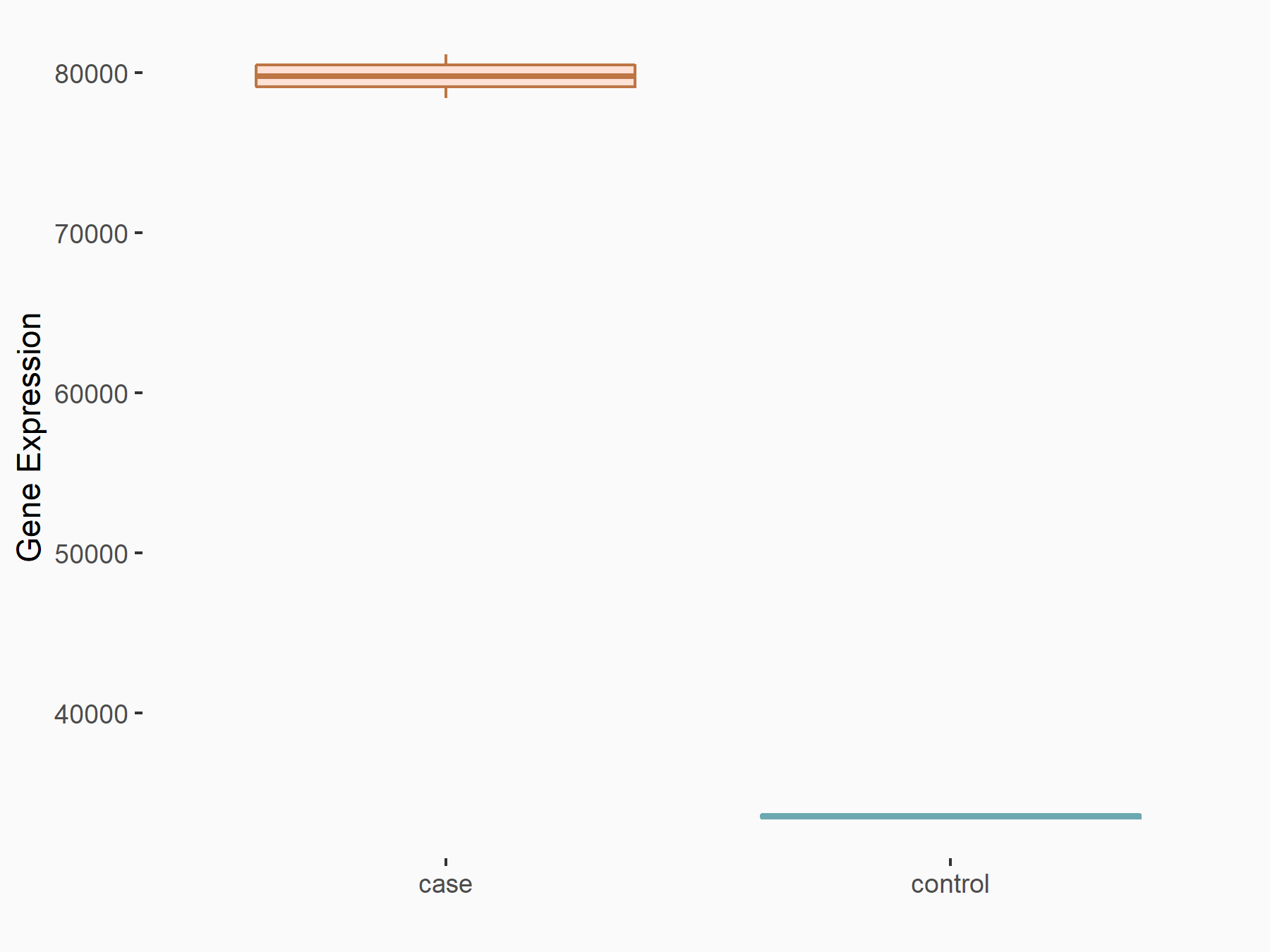 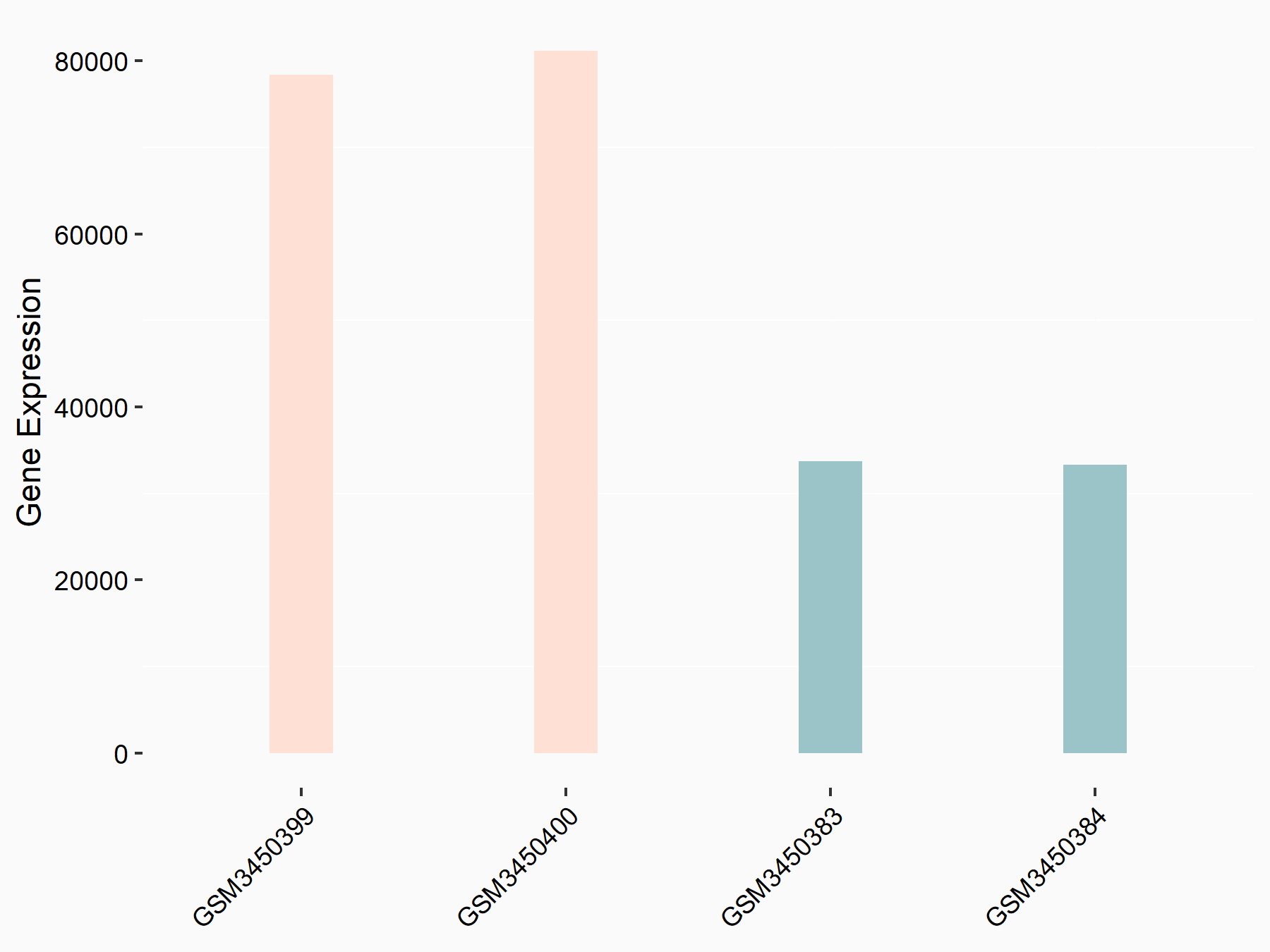 |
logFC: 1.25E+00 p-value: 7.56E-25 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Glycerolipid metabolism | hsa00561 | ||
| Cell Process | Lipid metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
LM3 | Malignant neoplasms | Mus musculus | CVCL_D269 |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice with a Tmem30a deletion specifically in pancreatic beta cells were generated as previously described. Mice developed with NAFLD were named for Tmem30a-associated NAFLD (TAN) mice. The littermate mice with genotypes of Tmem30aloxP/loxP were used as controls. | |||
| Response Summary | Targeting METTL3/14 in vitro increases protein level of ACLY and Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) as well as triglyceride and cholesterol production and accumulation of lipid droplets. These findings demonstrate a new NAFLD mouse model that provides a study platform for DM2-related NAFLD and reveals a unique epitranscriptional regulating mechanism for lipid metabolism via m6A-modified protein expression of ACLY and SCD1. | |||
Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [91] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [92] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
Tastin (TROAP)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | IL7H6 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout IL7H6 cells
Control: Wild type IL7H6 cells
|
GSE151071 | |
| Regulation |
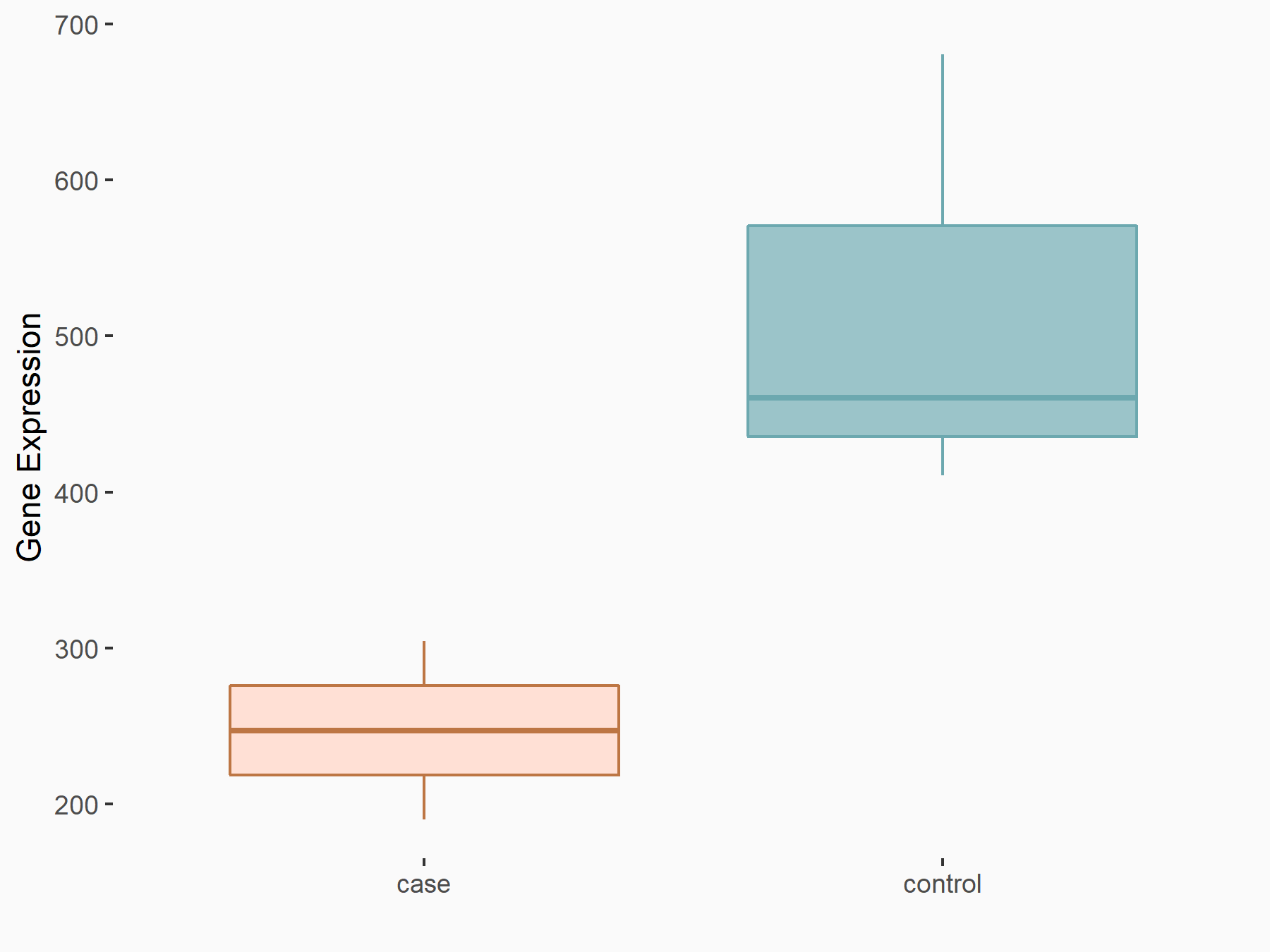 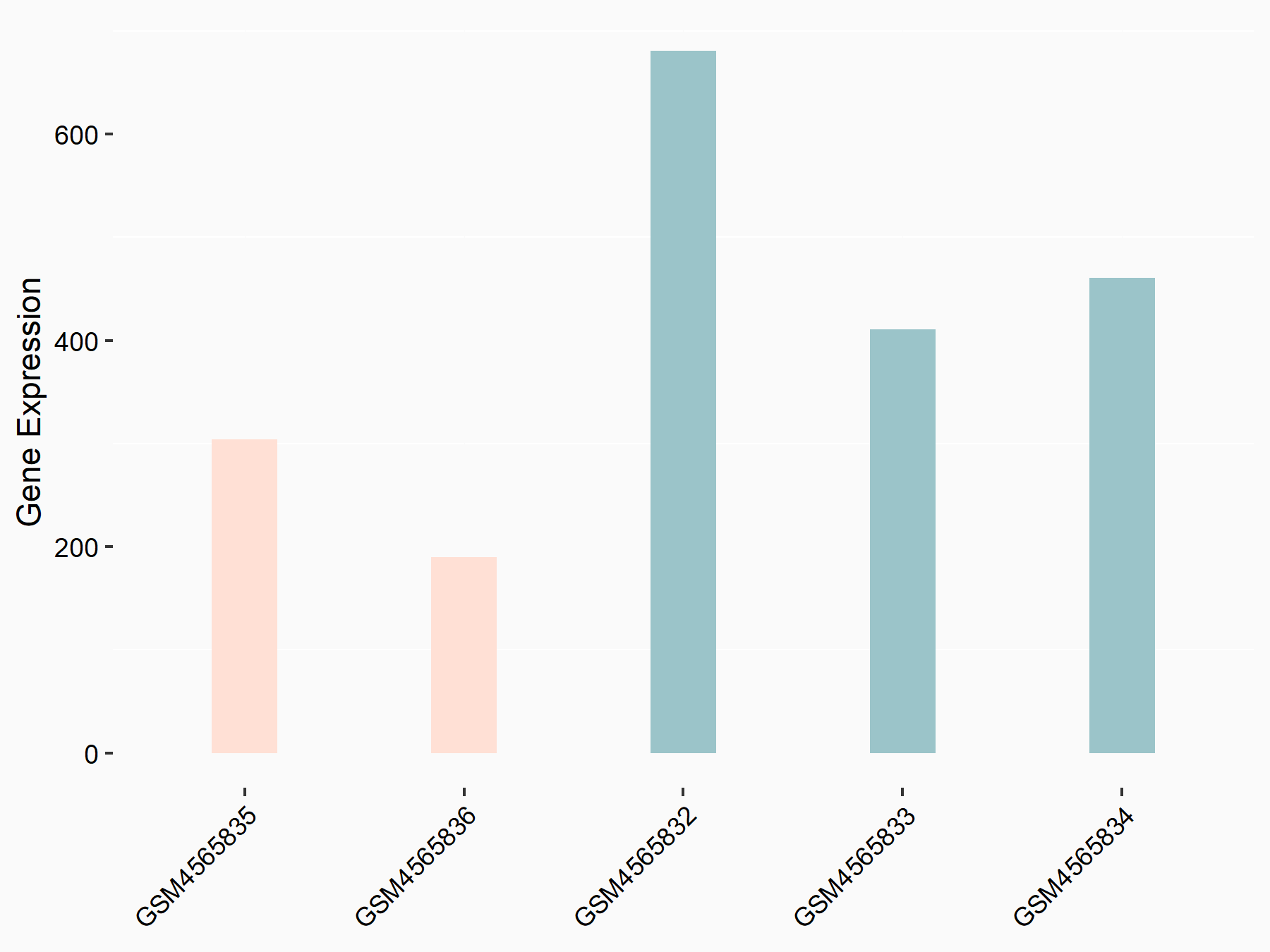 |
logFC: -1.07E+00 p-value: 3.99E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [48] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 | |
| In-vivo Model | KOV-3 cells (1 ×106) stable transfected with METTL14 or control lentivirus, were injected subcutaneously into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 overexpression decreased ovarian cancer proliferation by inhibition of Tastin (TROAP) expression via an m6A RNA methylation-dependent mechanism. | |||
Thrombospondin-1 (THBS1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
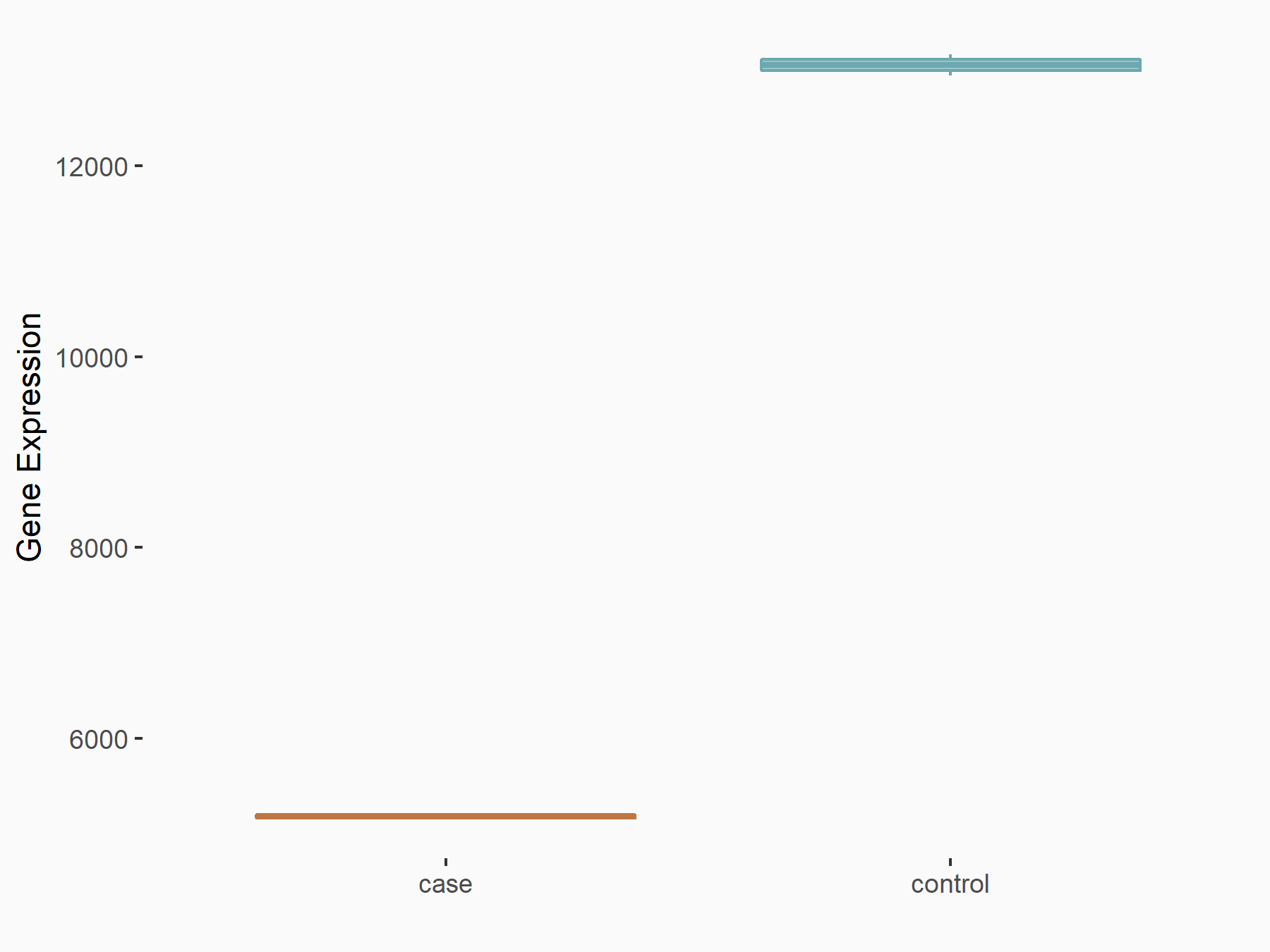 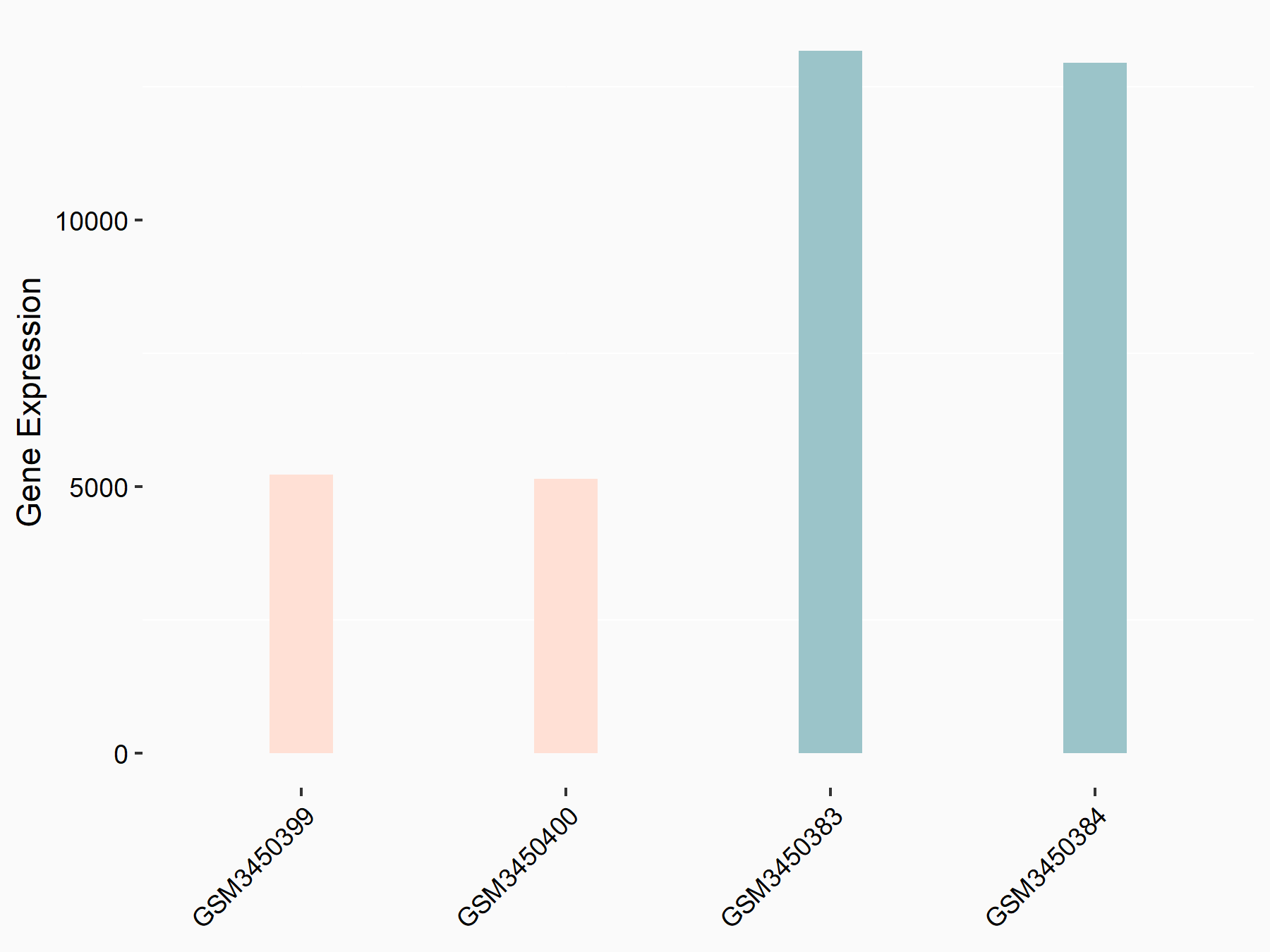 |
logFC: -1.33E+00 p-value: 7.54E-27 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [49] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RNA degradation | hsa03018 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| In-vivo Model | Stably transfected shMETTL14 and shNC DU145 cells (5×106 cells) suspended in a mixture of 100uL PBS were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of male nude BALB/C mice (6-8 weeks old) to induce tumor formation. | |||
| Response Summary | In prostate cancer, METTL14 downregulated Thrombospondin-1 (THBS1) expression in an m6A-dependent manner, which resulted in the recruitment of YTHDF2 to recognize and degrade Thrombospondin 1 (THBS1) mRNA. | |||
TNF receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
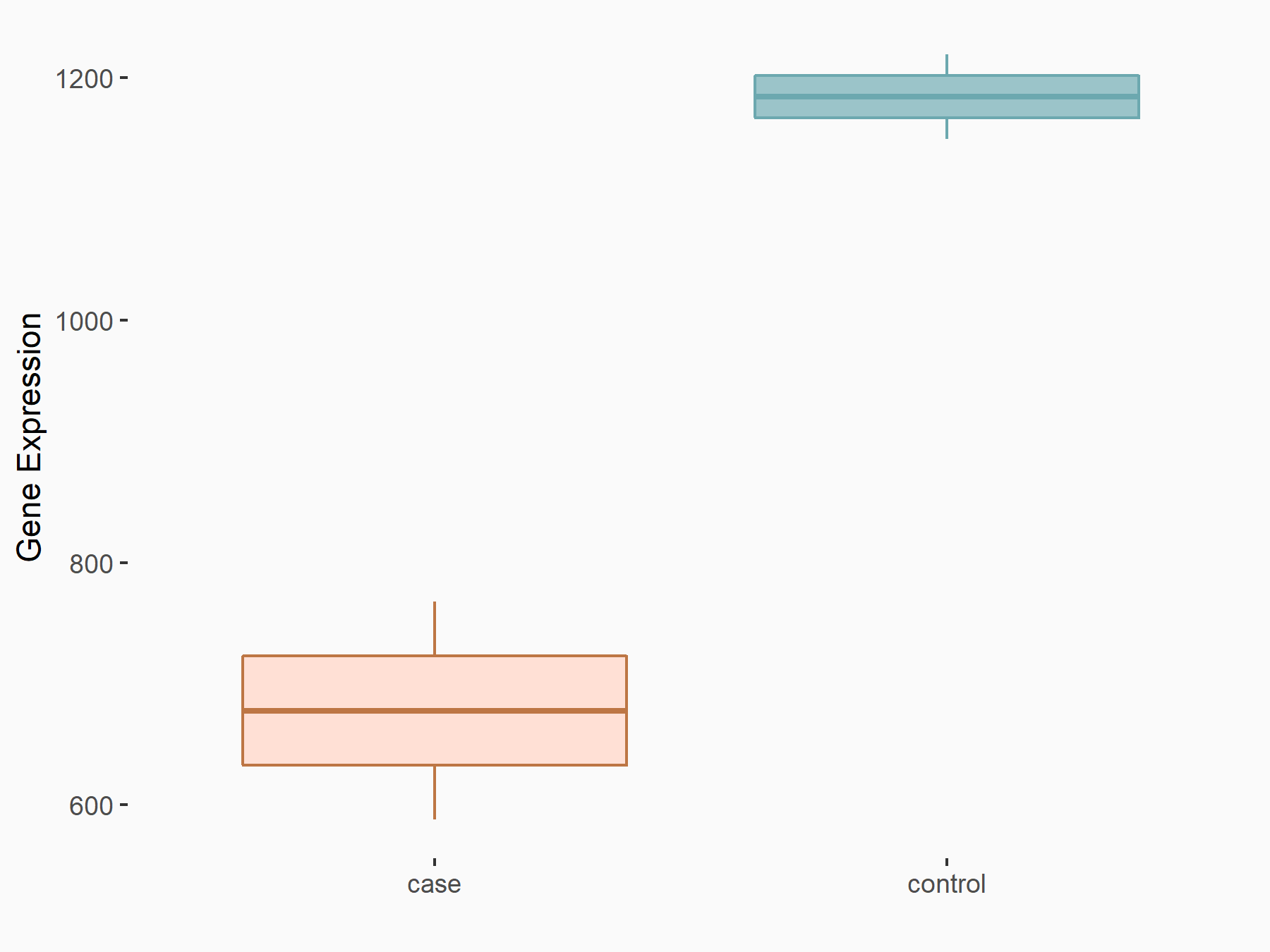 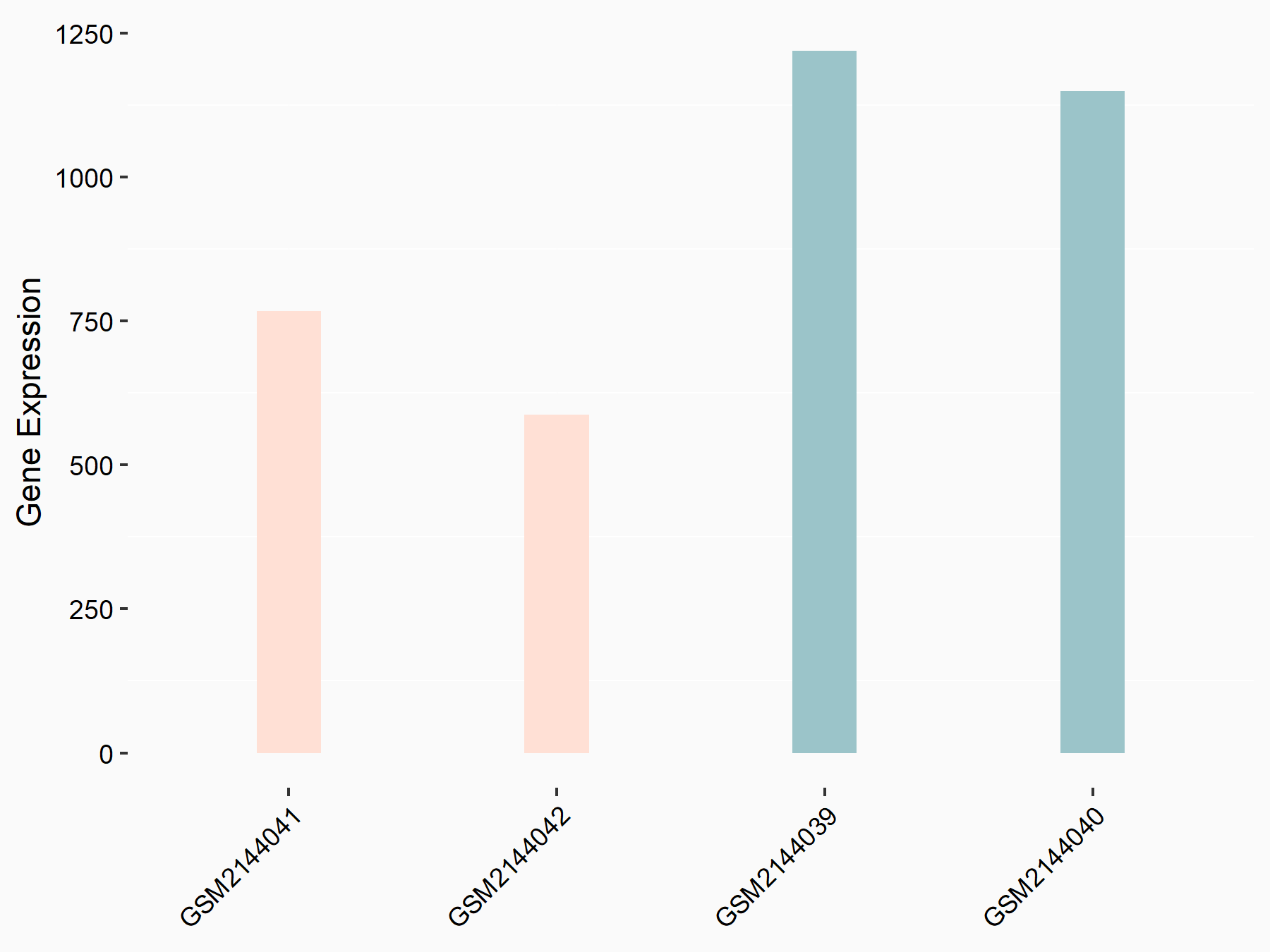 |
logFC: -8.04E-01 p-value: 5.72E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [50] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Sunitinib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
OS-RC-2 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1626 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the xenograft tumor model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 100 uL PBS were subcutaneously inoculated in the right flank of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. For the ccRCC orthotopic implantation model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 30 uL Matrigel were injected under the renal capsule of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 6 weeks, the anesthetized mice were intraperitoneally injected with D-luciferin (Yeason) and imaged using an in vivo imaging system to detect tumor growth and metastasis. For the lung metastasis model, approximately 5 × 105 ccRCC cells suspended in PBS were injected into the tail vein of 5-week-old mice. After 6-8 weeks, mice were anesthetized and lung metastasis was imaged as above. | |||
| Response Summary | In renal cell carcinoma, overexpression of TNF receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) promotes sunitinib resistance by modulating apoptotic and angiogenic pathways in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
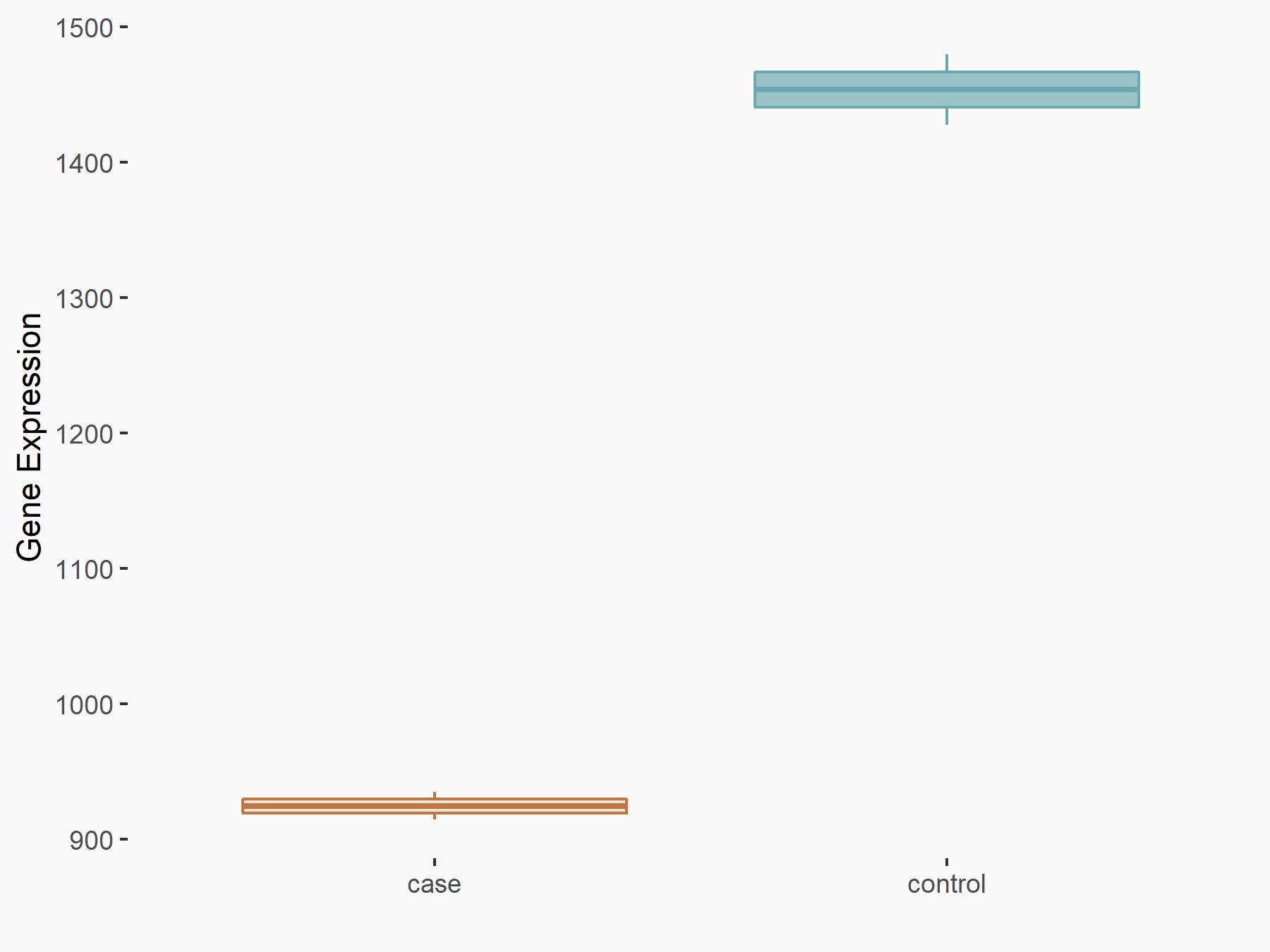  |
logFC: -6.53E-01 p-value: 4.62E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Doxil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Olaparib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
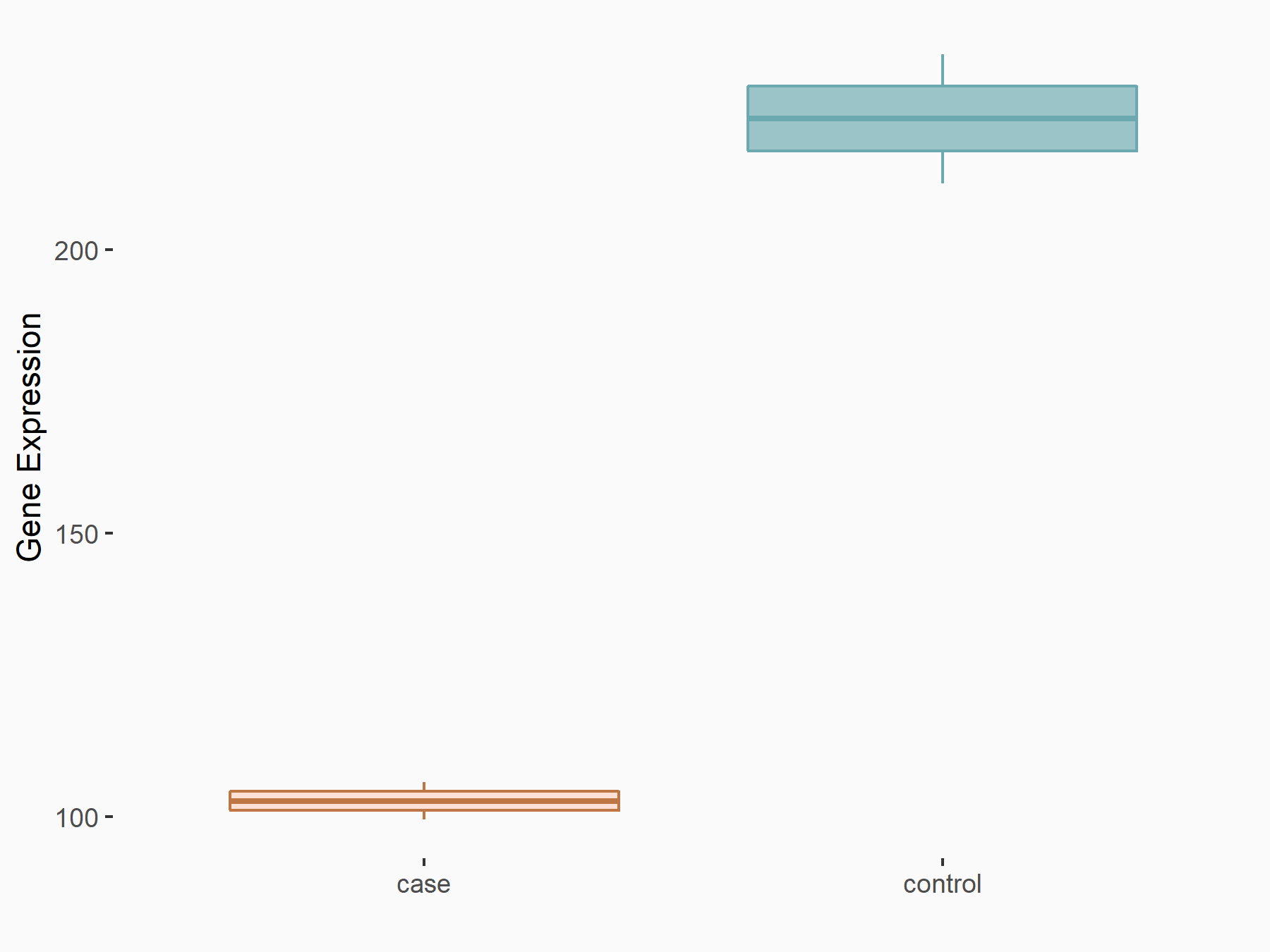  |
logFC: -1.12E+00 p-value: 2.46E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
In-vitro Model |
CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
Transcription factor p65 (RELA)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
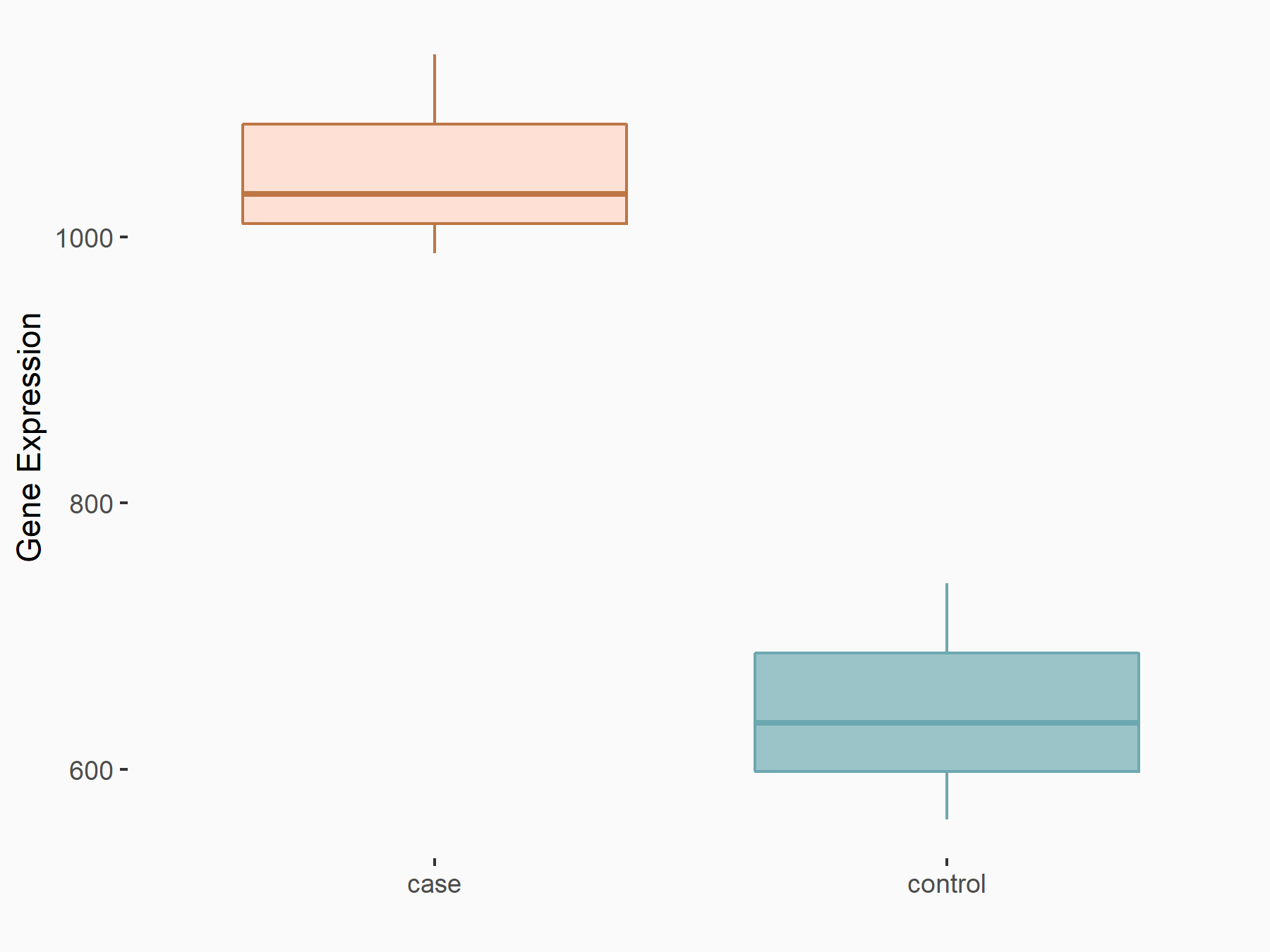  |
logFC: 7.00E-01 p-value: 8.41E-10 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| EA.hy 926 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3901 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were randomly divided into control, Ad-sh-NC, and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups (10 mice per group). The mice in the control group were fed a normal diet, while the Ad-sh-NC and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups were fed a high-fat diet (20% fat and 0.25% cholesterol). Furthermore, 300 uL of constructed sh-NC or sh-METTL14 adenovirus was injected every 3 weeks into the caudal veins of mice from the Ad-sh-NC or Ad-sh-METTL14 groups, respectively. The constructed vectors were obtained from HanBio Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All mice were sacrificed after 24 weeks and the aortas were separated for further experiments. | |||
| Response Summary | Knocking down METTL14 could inhibit the development of atherosclerosis in high-fat diet-treated APOE mice. After transfection with si-METTL14, the bcl-2 expression level and the viability of ox-LDL-incubated cells increased, whereas the apoptosis rate and the expressions of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 decreased. However, the effect of METTL14 knockdown was reversed by Transcription factor p65 (RELA) overexpression. | |||
Transcription factor SOX-4 (SOX4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
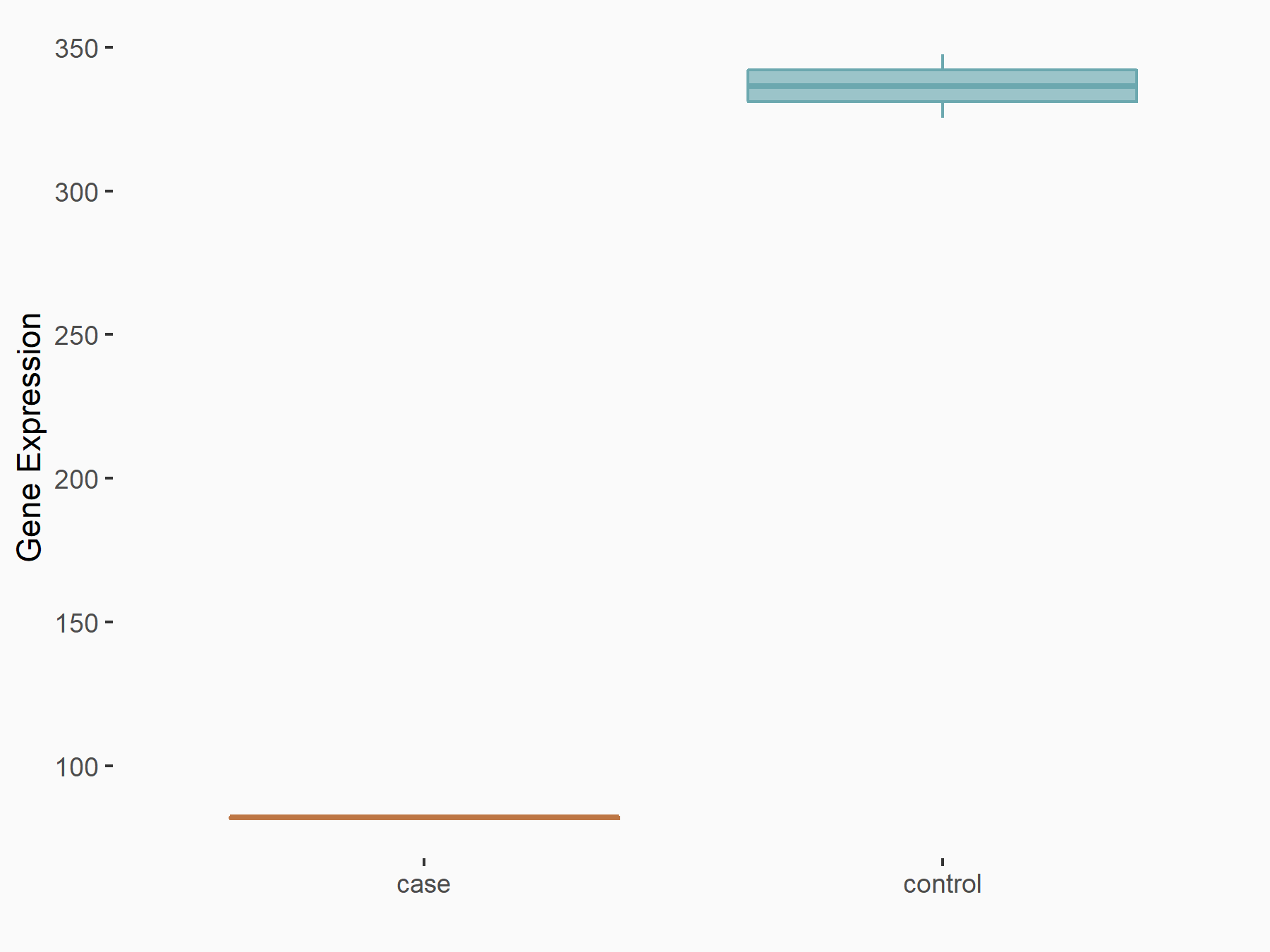  |
logFC: -2.04E+00 p-value: 4.12E-17 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [52] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell migration | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| NCM460 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0460 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 transfected HCT116 cells in 0.2 ml PBS were injected into the tail vein of nude mice which were randomly divided into nine groups (eight mice per group). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 inhibited colorectal cancer malignant process partly through Transcription factor SOX-4 (SOX4)-mediated EMT process and PI3K/Akt signals. | |||
Transcriptional activator Myb (MYB)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
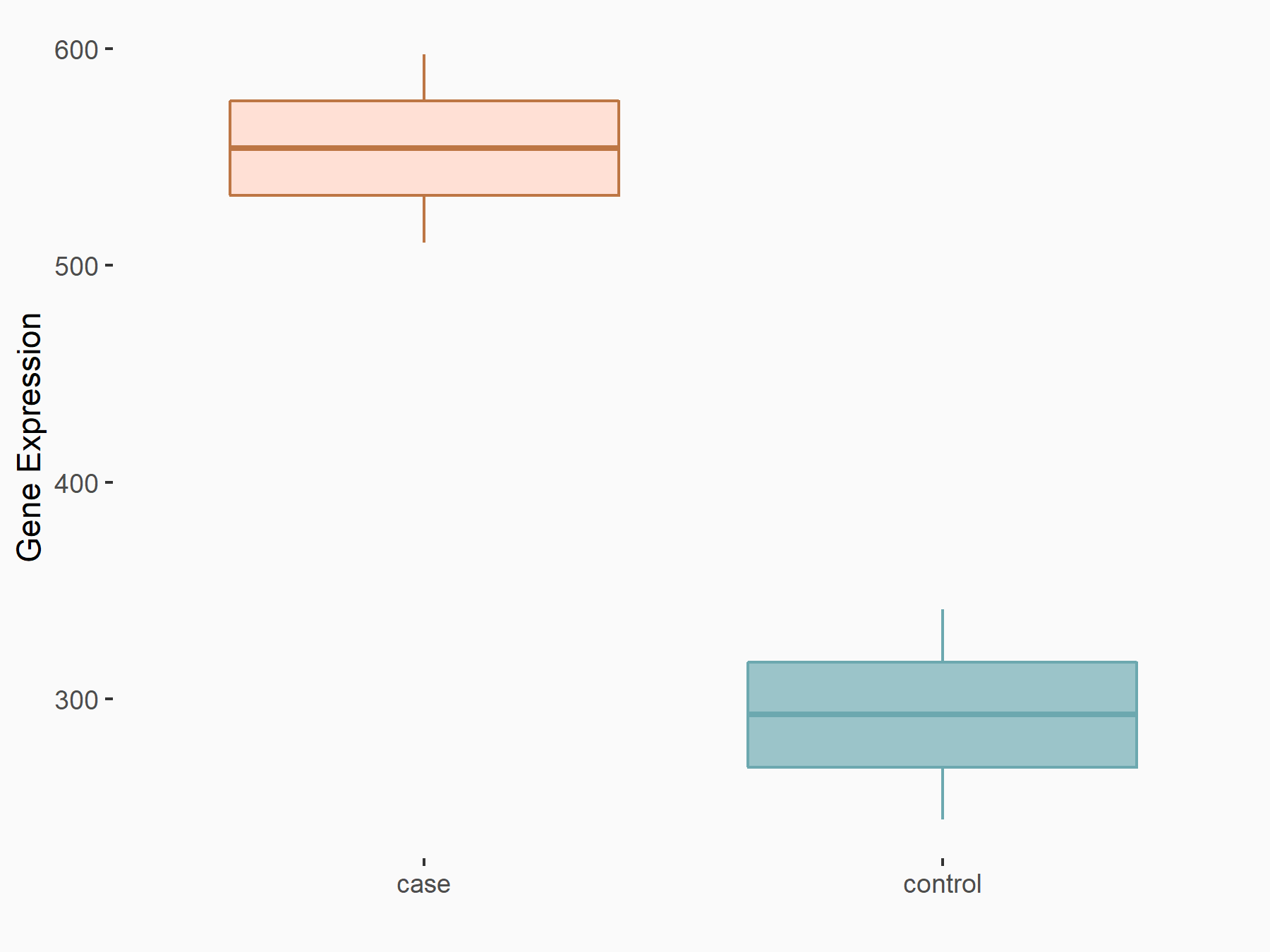  |
logFC: 9.21E-01 p-value: 4.44E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [36] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell survival/proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HSPC (Human hematopoietic stem cell) | ||||
| MNC (Cord blood pluripotent stem cells) | ||||
| OP9 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4398 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | Lin- HSPCs were purified from BM of wildtype mice and 0.1×106 cells were seeded in 2 mL OP9 medium onto the OP9 cells with the addition of 10 ng/mL mouse IL-3, 10 ng/mL human IL-6, 10 ng/mL mouse IL-7, 10 ng/mL mouse Flt-3L, and 50 ng/mL mouse stem cell factor (SCF). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 in normal myelopoiesis and AML pathogenesis, as featured by blocking myeloid differentiation and promoting self-renewal of normal HSPCs and LSCs/LICs. METTL14 exerts its oncogenic role by regulating its mRNA targets (e.g., Transcriptional activator Myb (MYB) and MYC) through m6A modification, while the protein itself is negatively regulated by SPI1. | |||
Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
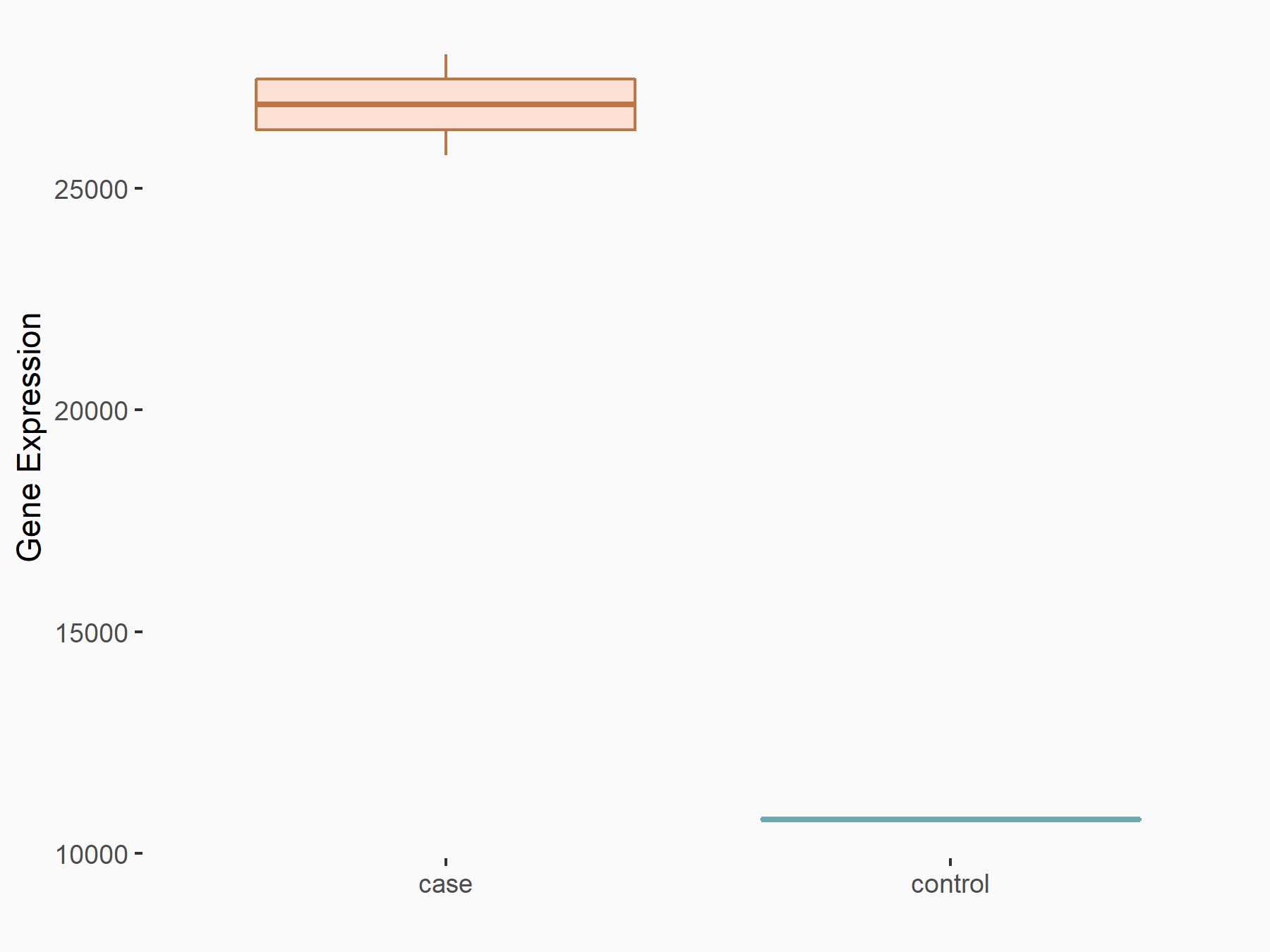  |
logFC: 1.32E+00 p-value: 8.59E-29 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Urinary/pelvic organs injury [ICD-11: NB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [53] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of kidney [ICD-11: NB92.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes renal ischemic reperfusion injury via suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1). | |||
Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [95] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C6Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Tribbles homolog 2 (TRIB2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
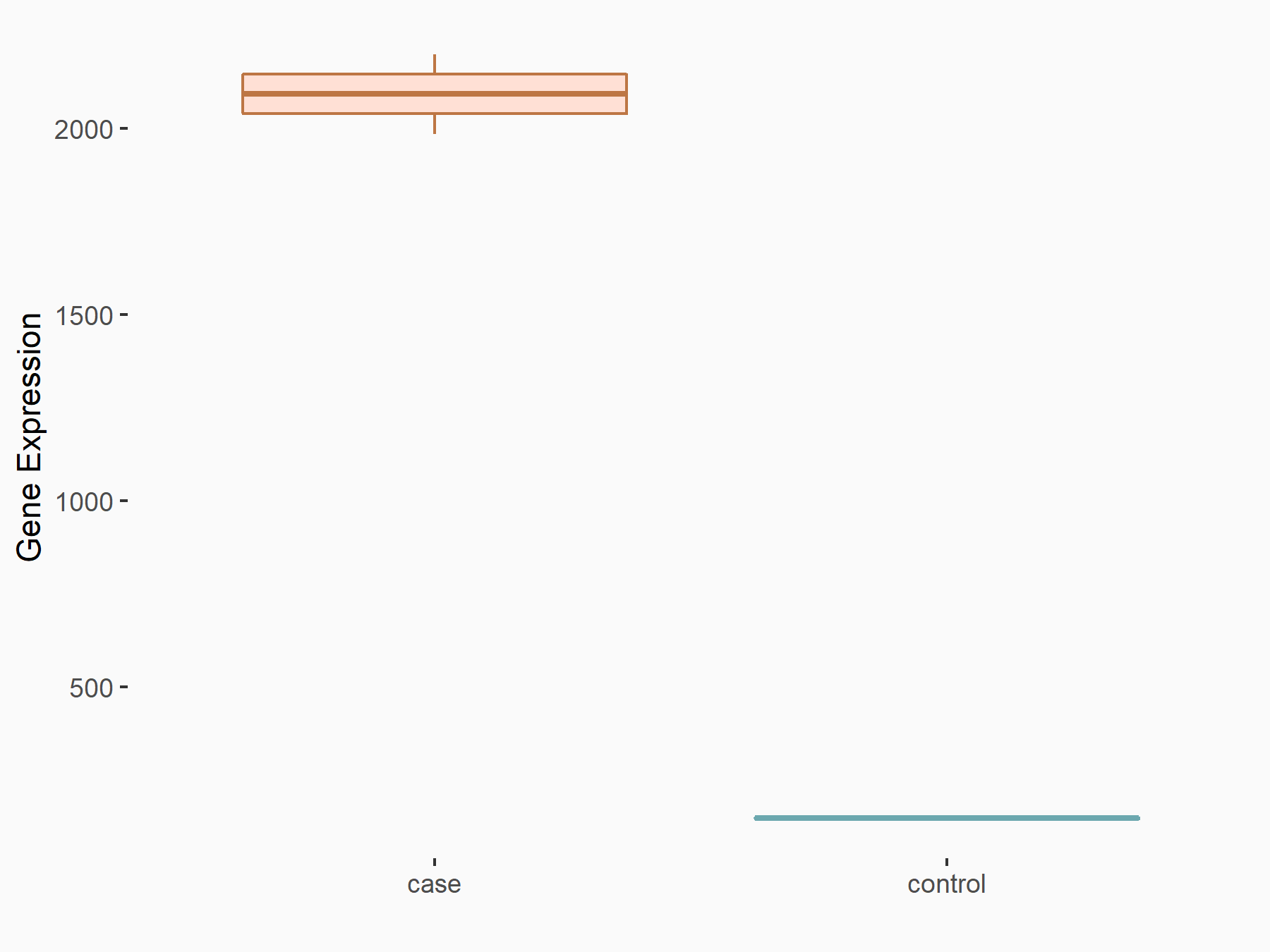 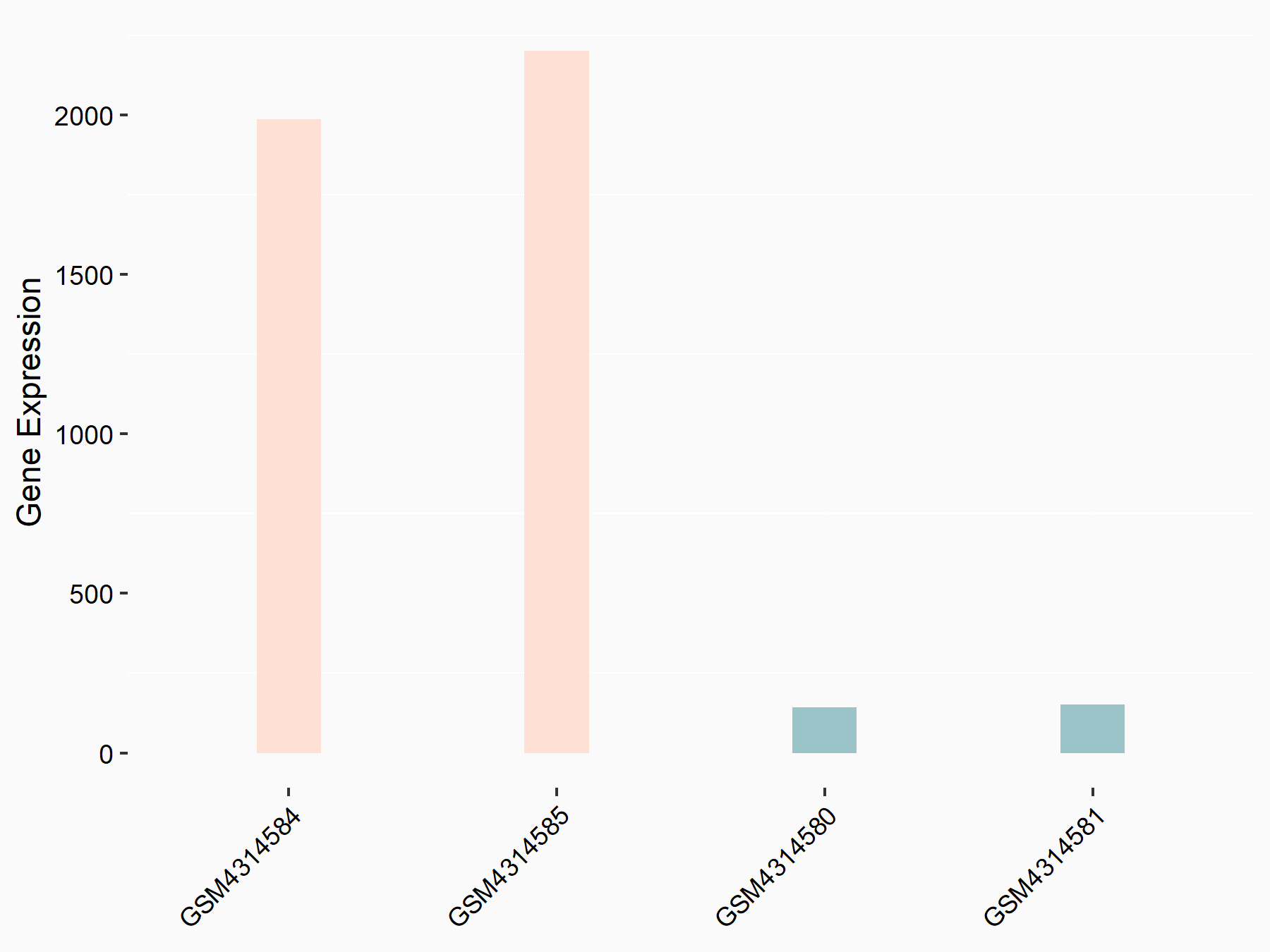 |
logFC: 3.83E+00 p-value: 1.54E-161 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasome pathway degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 |
| KYSE-410 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1352 | |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| HET-1A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3702 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 | |
| CVCL_E307 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_E307 | |
| In-vivo Model | Fresh PDX tumor samples collected from two established PDX models (PDX #07 with high TRIB2 expression and PDX #12 with low TRIB2, passages three to four) were minced and subcutaneously implanted into the flanks of 3- to 4-week-old female BALB/c nude mice (Jiesijie Laboratory Animals). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14, an m6A RNA methyltransferase downregulated in ESCC, suppresses Tribbles homolog 2 (TRIB2) expression via miR-99a-5p-mediated degradation of TRIB2 mRNA by targeting its 3' untranslated region, whereas TRIB2 induces ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of METTL14 in a COP1-dependent manner. | |||
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF/TNF-alpha)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | CT26 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout CT26 cells
Control: CT26 cells
|
GSE142589 | |
| Regulation |
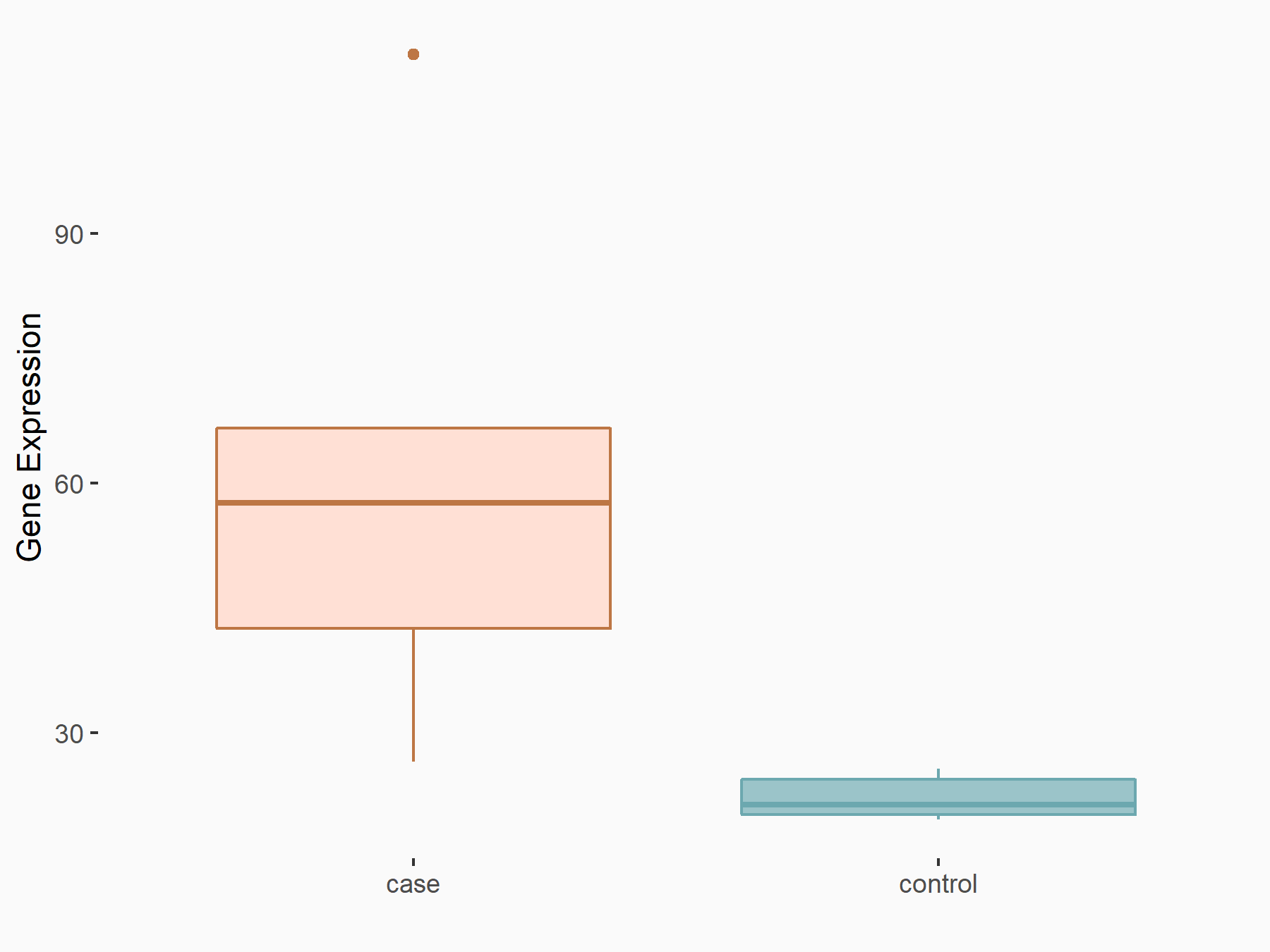 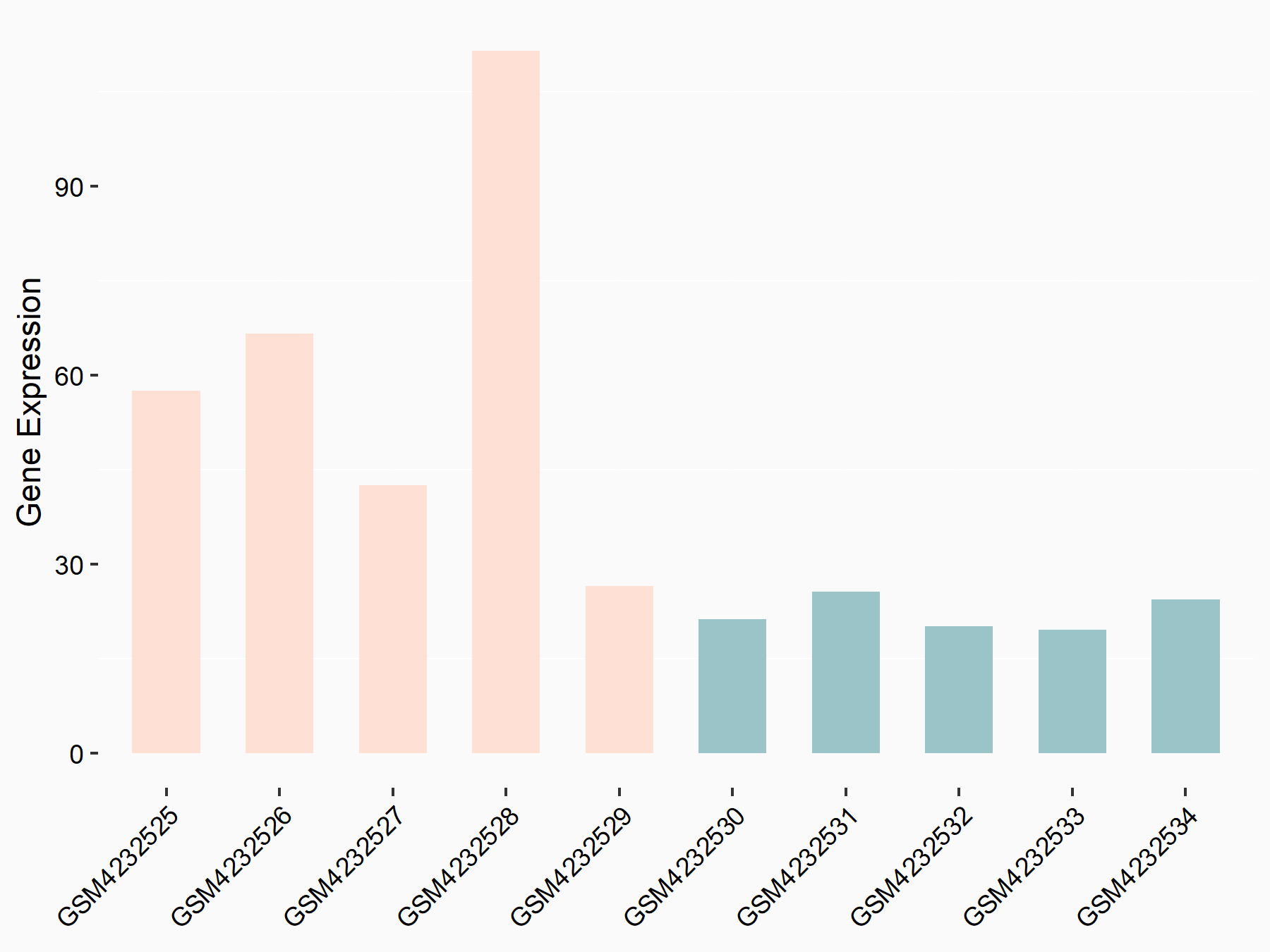 |
logFC: 1.47E+00 p-value: 1.57E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [55] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | hsa04933 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HRGECs cell line (Human glomerular microvascular endothelial cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | After adaptive feeding for 1 week, db/db mice were randomly divided into five groups (n = 6): db/db group, db/db + rAAV group, db/db + rAAV-METTL14 group, db/db + rAAV-klotho group, and db/db + rAAV-METTL14 + rAAV-klotho group. Except db/db group, the other four groups were injected with recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) control, rAAV mediated delivery of METTL14 (rAAV-METTL14), or/and rAAV mediated delivery of klotho (rAAV-klotho) respectively via tail vein. Six db/m mice were chosen as the normal control. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 could aggravated high glucose-induced glomerular endothelial cell injury and diabetic nephropathy through m6A modification of alpha-klotho. METTL14 silence decreased the levels of ROS, Tumor necrosis factor (TNF/TNF-alpha) and IL-6 and cell apoptosis. | |||
Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 (TIE1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
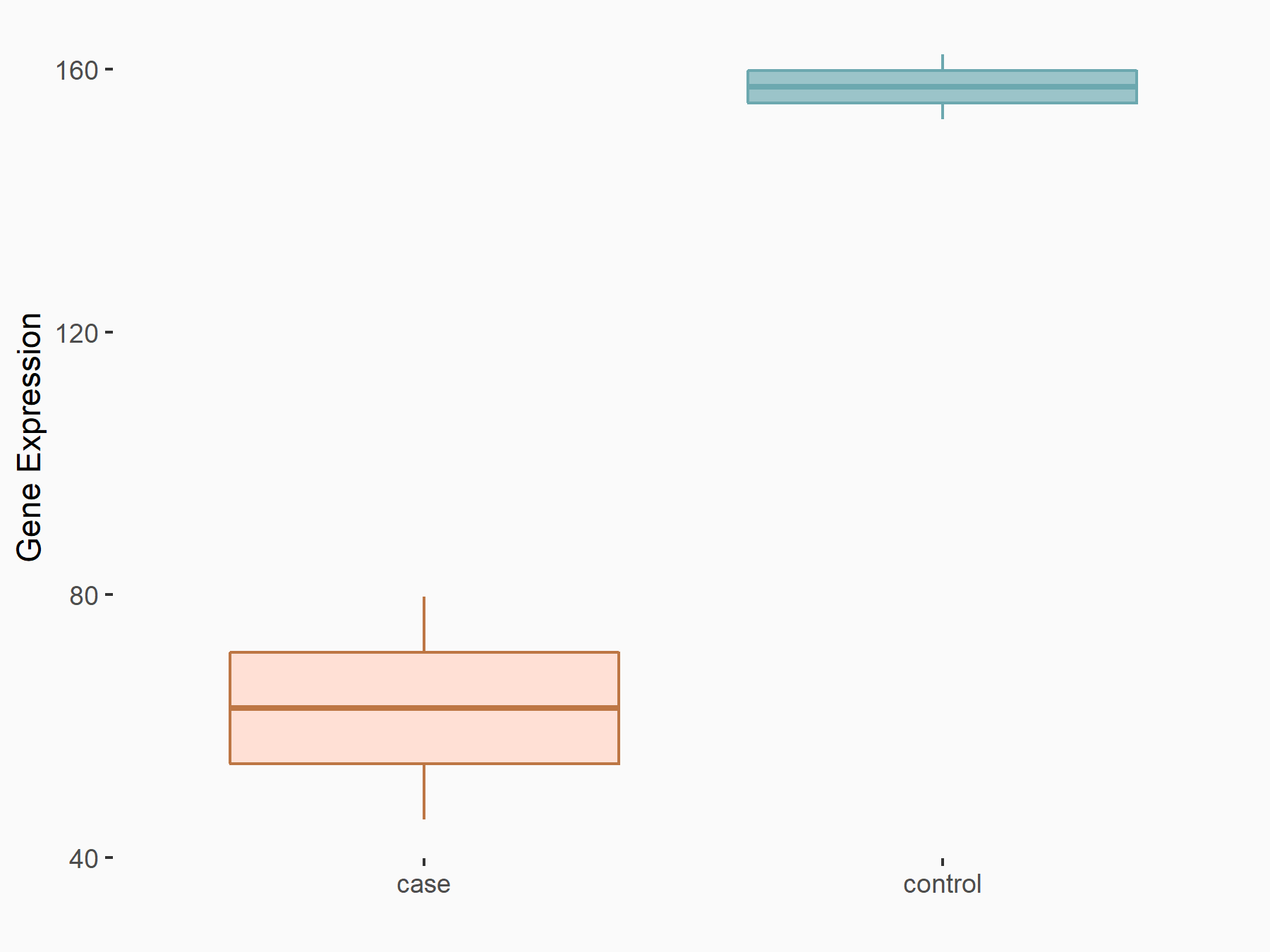 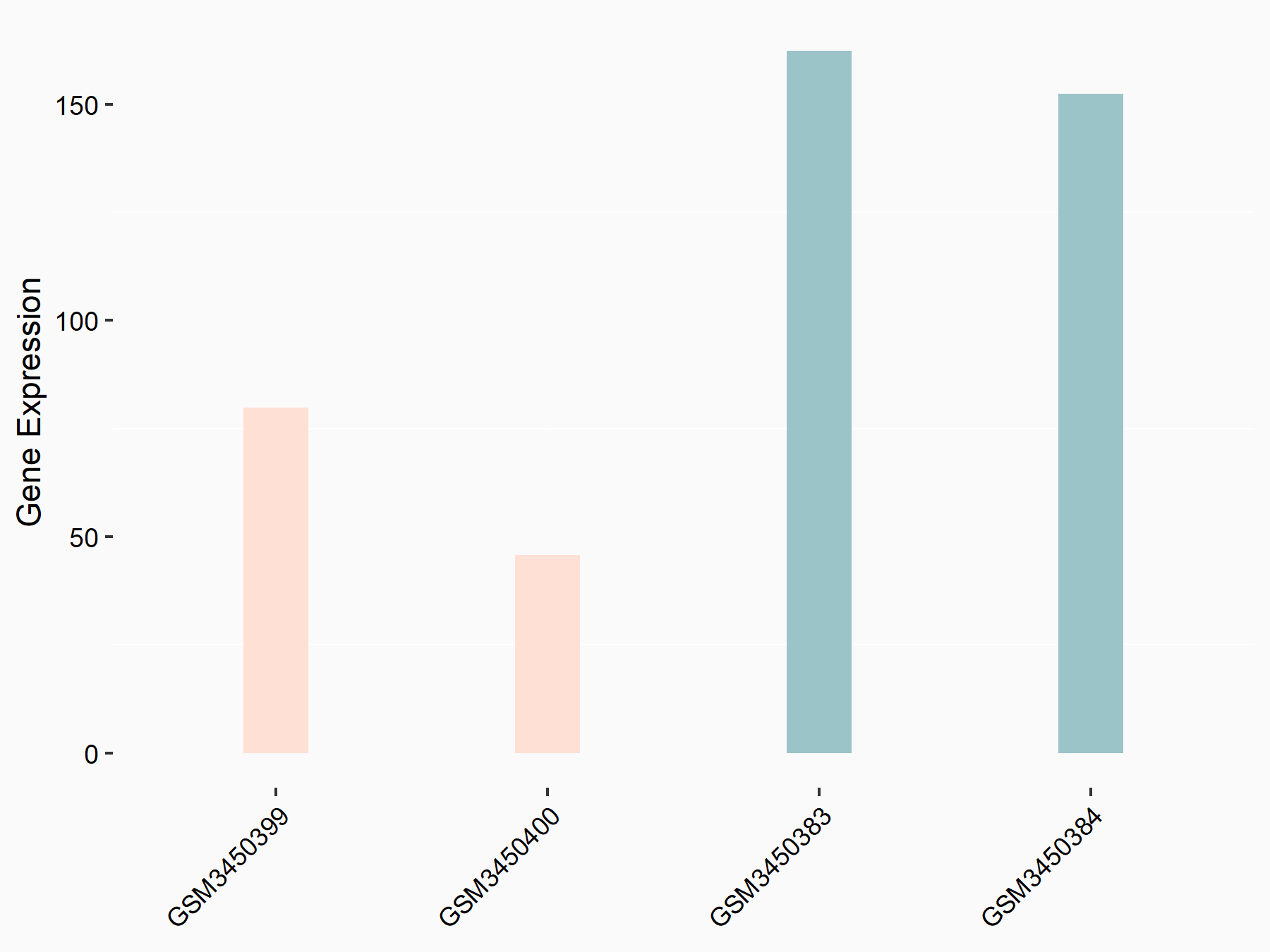 |
logFC: -1.32E+00 p-value: 5.08E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Haemorrhoids [ICD-11: DB60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [56] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Haemorrhoids [ICD-11: DB60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| Response Summary | The overexpression of miR-4729 in vascular endothelial cells decreased the global mRNA methylation and TIE1 mRNA 3'UTR-specific site methylation by silencing METTL14 expression, reducing Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 (TIE1) mRNA stability, down-regulating the TIE1/VEGFA signal molecular loop expression, and weakening angiogenesis ability. MiR-4729 regulates TIE1 mRNA m6A modification and angiogenesis in hemorrhoids by targeting METTL14. | |||
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6 (PTPN6)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | IL7H6 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout IL7H6 cells
Control: Wild type IL7H6 cells
|
GSE151071 | |
| Regulation |
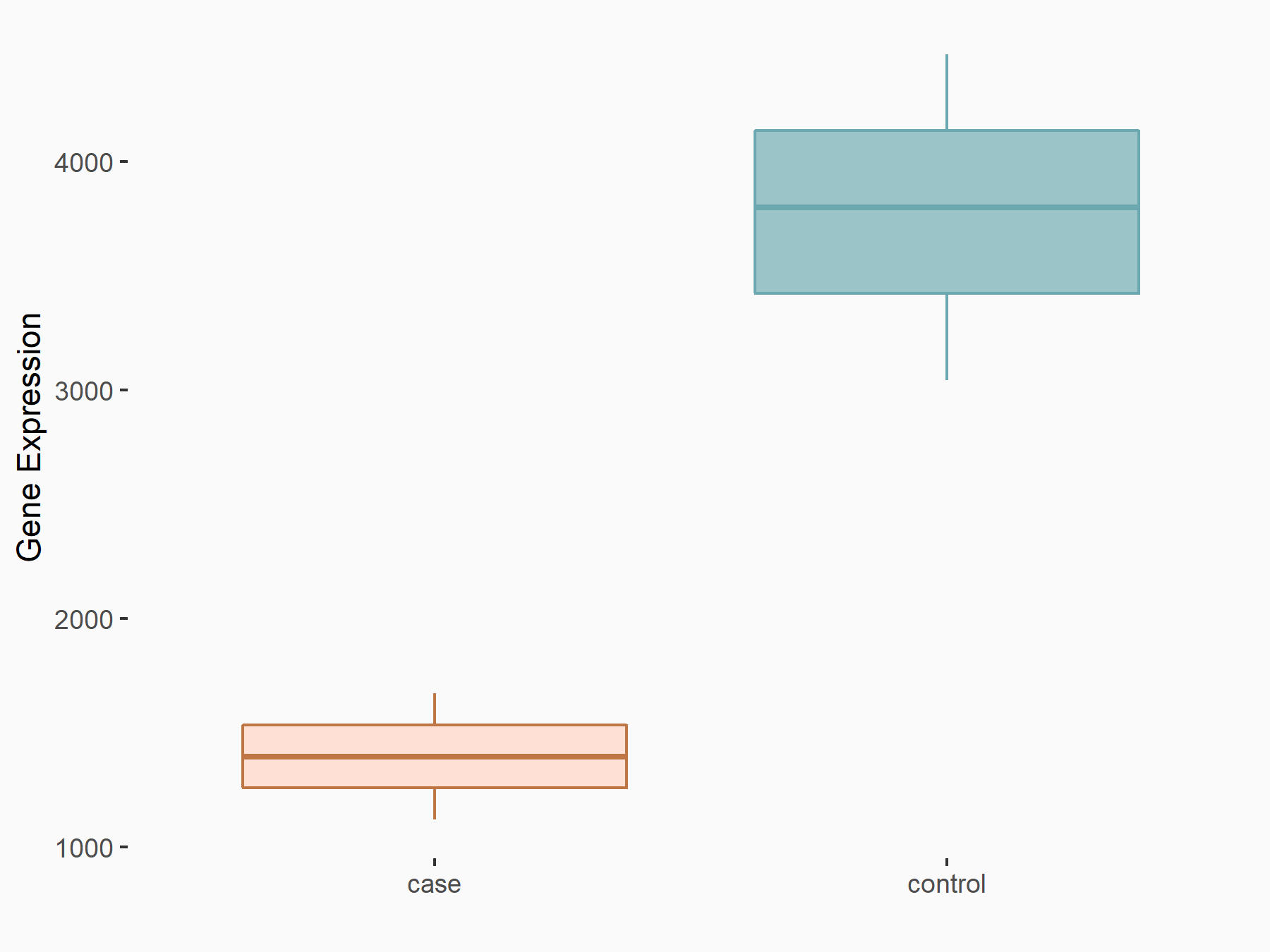 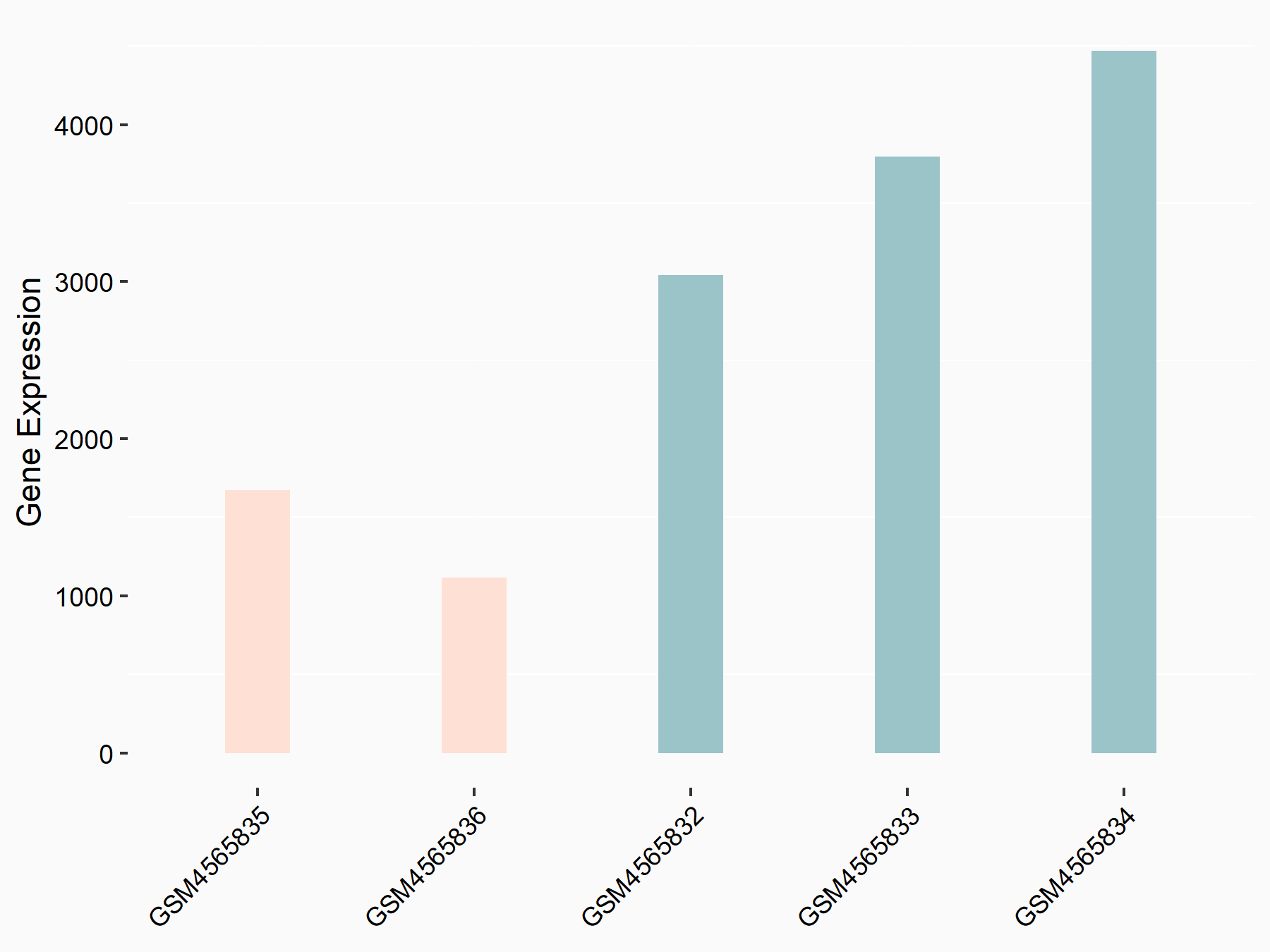 |
logFC: -1.44E+00 p-value: 2.37E-10 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteonecrosis [ICD-11: FB81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [57] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteonecrosis, unspecified [ICD-11: FB81.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
BMSCs (BMSCs were obtained from the femurs and tibias of 2-3-week-old Sprague-Dawley male rats (Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University)) | |||
| Response Summary | Imbalanced osteogenic/adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells BMSCs is considered the core pathological characteristic of SONFH. METTL14 regulated Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6 (PTPN6) expression by increasing PTPN6 mRNA stability in an m6A-dependent manner. Moreover, PTPN6 knockdown abrogated the beneficial effects of METTL14 overexpression on BMSCs. | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 48 (USP48)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
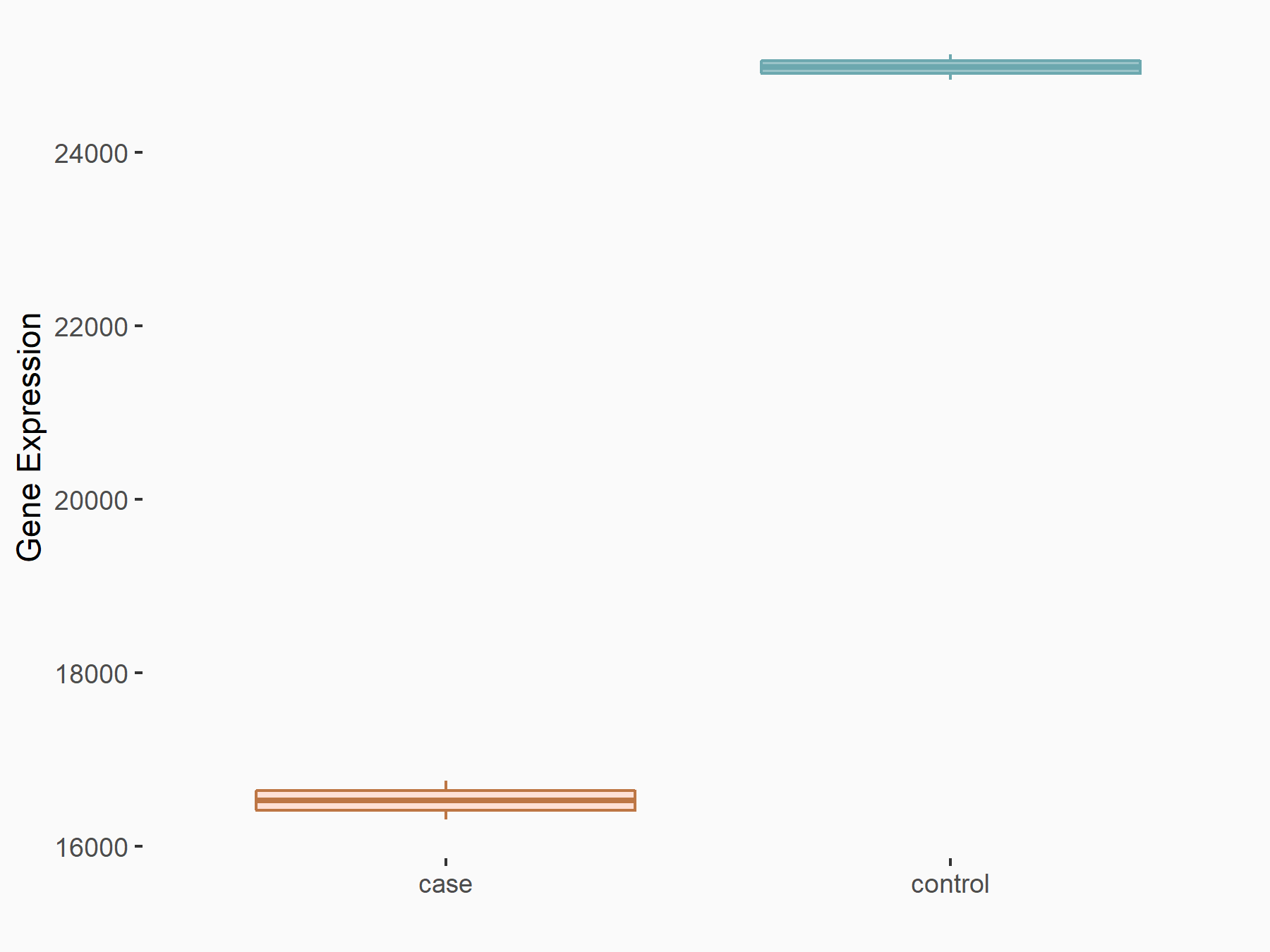 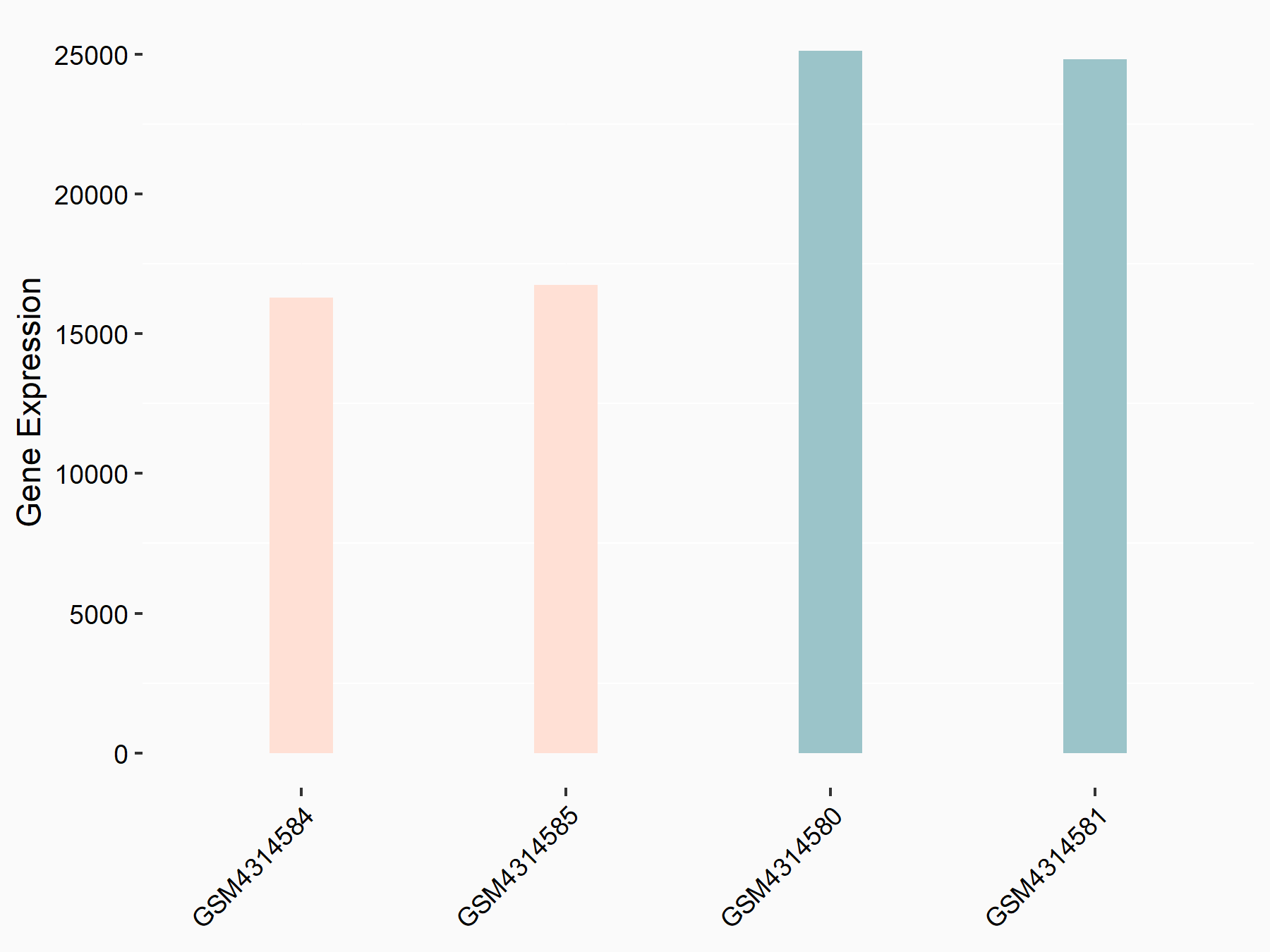 |
logFC: -5.96E-01 p-value: 3.62E-16 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [58] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| Glycolysis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BEL-7404 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6568 |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| In-vivo Model | Hepatocyte-specific knockout USP48 was obtained by crossing Alb-Cre mice with USP48flox/flox mice. | |||
| Response Summary | Methyltransferase-like 14 (Mettl14)-induced m6A modification participated in the regulation of Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 48 (USP48) in hepatocellular carcinoma by maintaining USP48 mRNA stability. This work uncovers the tumor-suppressive function of the Mettl14-USP48-SIRT6 axis via modulation of glycolysis, providing new insights into the critical roles of metabolic activities in HCC and identifying an attractive target for future treatment studies. | |||
HLA complex group 11 (HCG11)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
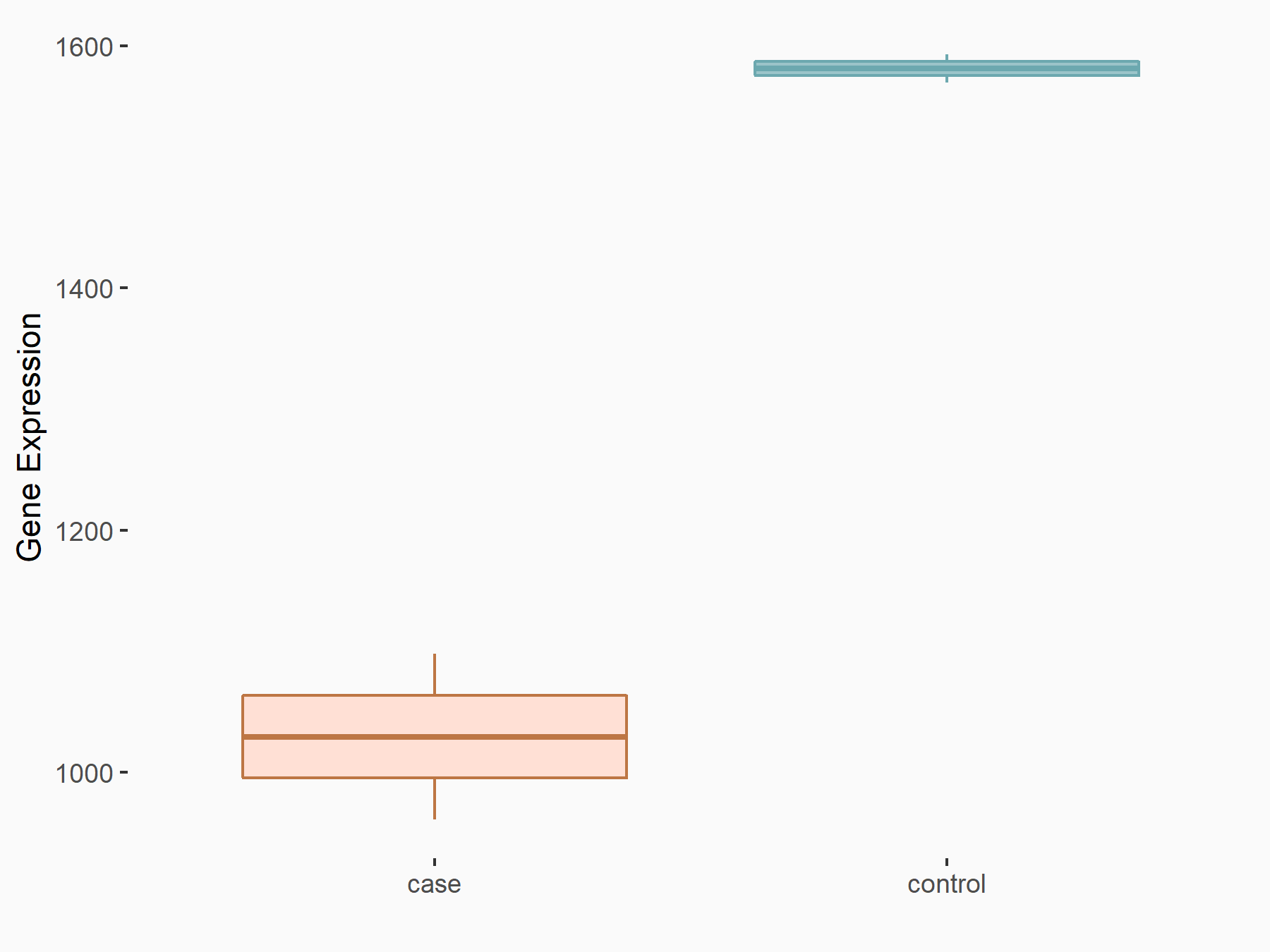 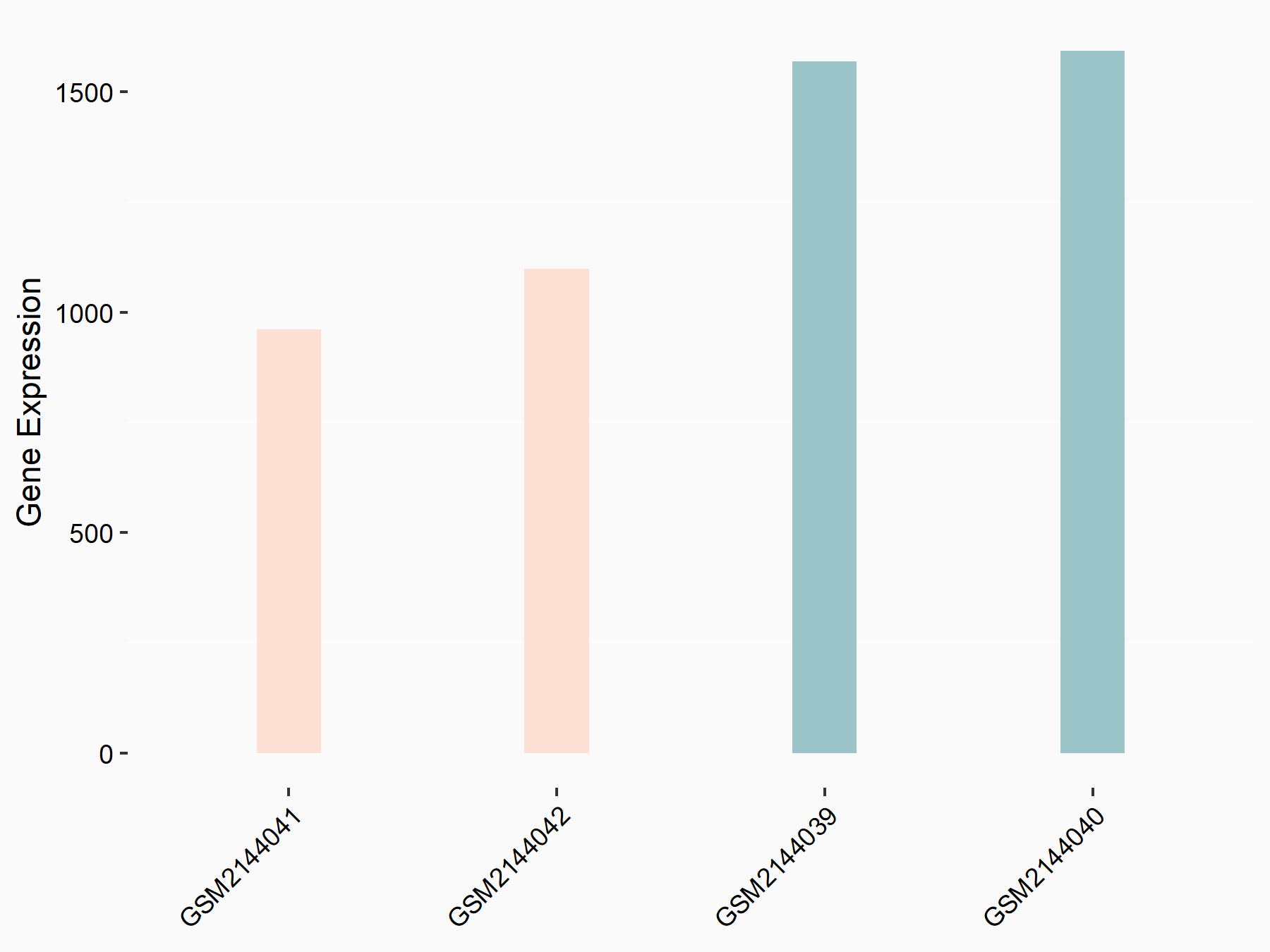 |
logFC: -6.19E-01 p-value: 1.66E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [59] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stabilization | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| HBE (Human bronchial epithelial cell line) | ||||
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| NCI-H522 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1567 | |
| PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | |
| In-vivo Model | LUAD cells stably HCG11 and/or LATS1 overexpressed or silenced were subcutaneously injected into the flank of the BALB/c nude mice (male, 4 weeks old). | |||
| Response Summary | HLA complex group 11 (HCG11) mediated by METTL14 inhibited the growth of lung adenocarcinoma via IGF2BP2/LATS1. The m6A modification of HCG11 promoted its nuclear exportation and binding by Insulin Like Growth Factor 2 MRNA Binding Protein 2 (IGF2BP2), resulting in increased stability. | |||
Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
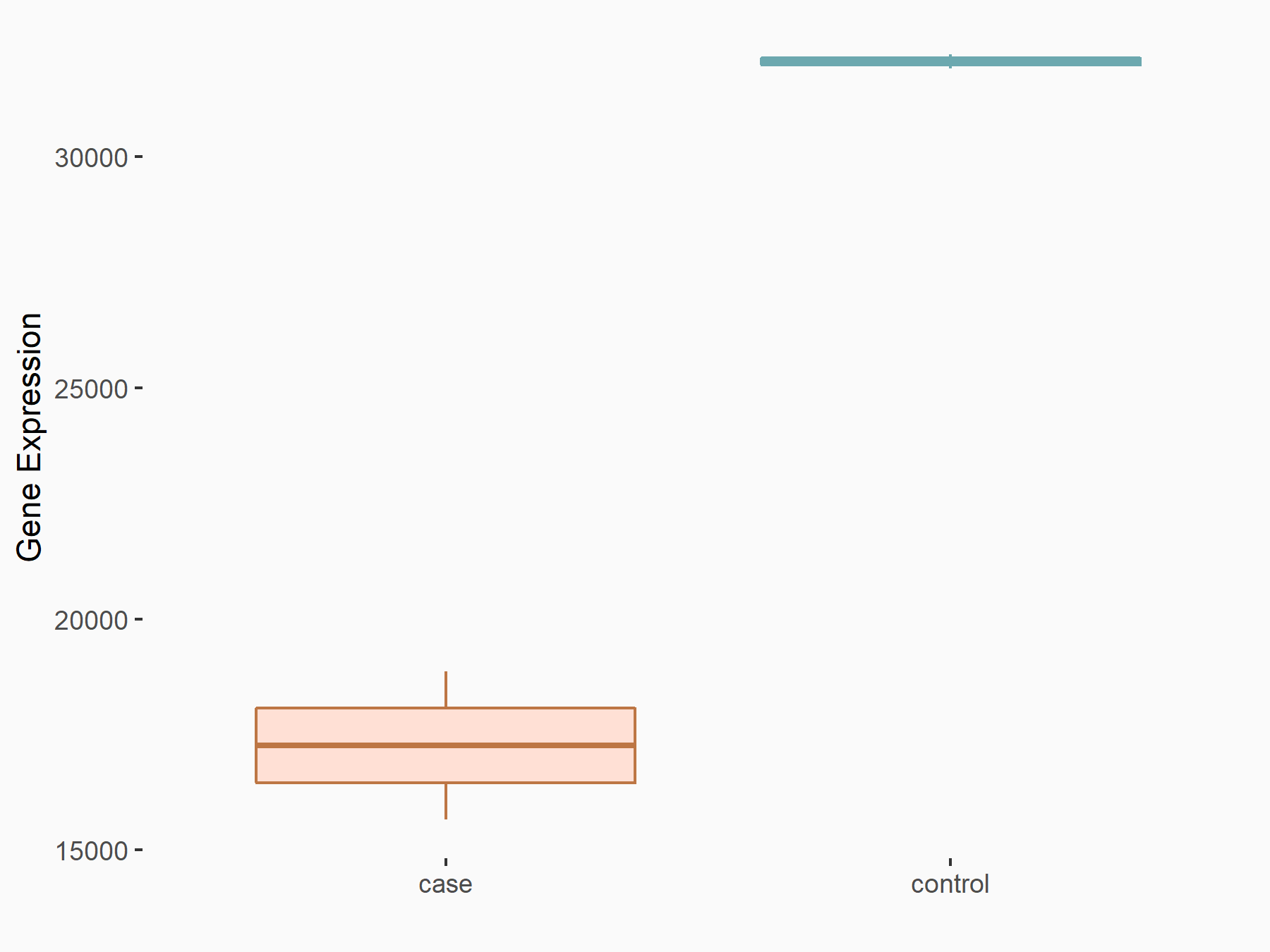 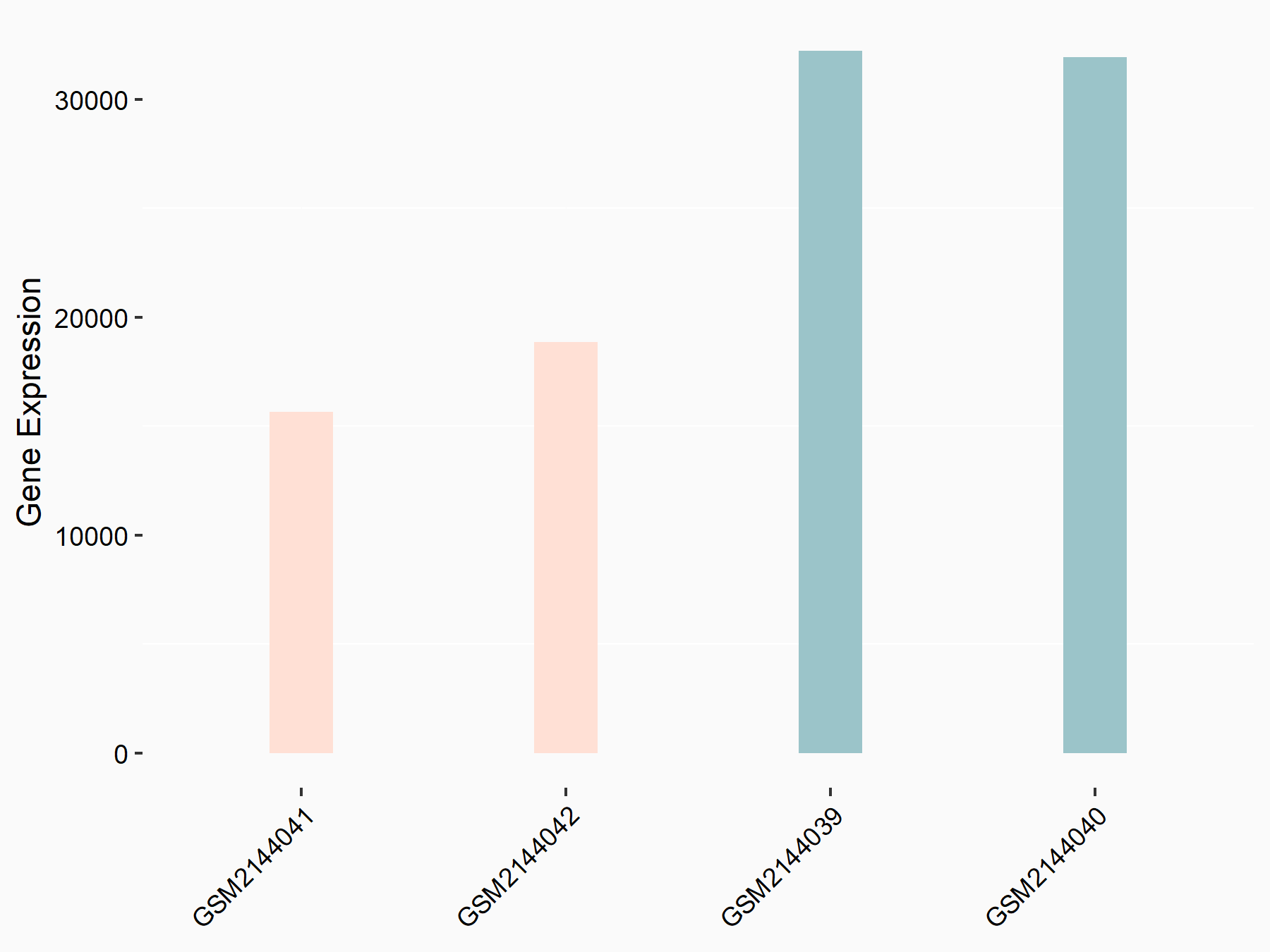 |
logFC: -8.94E-01 p-value: 3.90E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [60] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
769-P | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1050 |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mouse subcutaneous xenograft and lung metastasis experiments were carried out with six 4-week-old male BALB/c nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In renal cell carcinoma, YTHDF2 accelerated the degradation of Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)_1 by selectively recognizing METTL14-mediated m6A marks on Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)_1. | |||
Coronary atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BA52]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [103] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Coronary atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BA52.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [103] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Aspartate--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic (DARS)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [61] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
In-vitro Model |
SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| End1/E6E7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3684 | |
| DoTc2 4510 | Cervical carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1181 | |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
| C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 | |
| Response Summary | DARS-AS1 was validated to facilitate DARS translation via recruiting METTL3 and METTL14, which bound with DARS mRNA Aspartate--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic (DARS) mRNA 5' untranslated region (5'UTR) and promoting its translation. The present study demonstrated that the 'HIF1-Alpha/DARS-AS1/DARS/ATG5/ATG3' pathway regulated the hypoxia-induced cytoprotective autophagy of cervical cancer(CC) and is a promising target of therapeutic strategies for patients afflicted with CC. | |||
Basic leucine zipper transcriptional factor ATF-like 2 (BATF2)
Malignant neoplasms tongue [ICD-11: 2B62]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [62] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant neoplasms tongue [ICD-11: 2B62.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SCC-15 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1681 |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c nude mice (aged 4-6 weeks) were fed under specific pathogen-free conditions at 26-28°C under 40-60% humidity. For tumorigenicity assay in vivo, CAL-27 cells transfected with BATF2 overexpression plasmids or empty plasmids or untreated CAL-27 cells were subcutaneously inoculated into the right armpit of mice. Following 4 weeks, mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation under isoflurane anesthesia and neoplasms were isolated and weighted. The volume of neoplasms was monitored once a week. For the in vivo metastasis model, the tail vein of mice was intravenously injected with BATF2-overexpressed or control CAL-27 cells or untreated CAL-27 cells. | |||
Cadherin-1 (CDH1)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [64] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
In-vitro Model |
Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 |
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53)
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Cells in G6/M phase decreased | ||||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| MOLT-4 | Adult T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0013 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 play an oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia(AML) by targeting mdm2/Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) signal pathway. The knockdown of METTL3 and METTL14 in K562 cell line leads to several changes in the expression of p53 signal pathway, including the upregulation of p53, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A/p21), and downregulation of mdm2. | |||
Cytochrome P450 2C8 (CYP2C8)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | hsa00982 | ||
| Cell Process | Drug-metabolizing | |||
In-vitro Model |
HepaRG | Hepatitis C infection | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9720 |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| Response Summary | In the Hepatocellular carcinoma cells YTHDC2 promotes CYP2C8 mRNA degradation via recognizing the m6A in CYP2C8 mRNA, which is installed by METTL3/14 and removed by FTO. | |||
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 (Mdm2)
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Cells in G5/M phase decreased | ||||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| MOLT-4 | Adult T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0013 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 play an oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia(AML) by targeting E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 (Mdm2)/p53 signal pathway. The knockdown of METTL3 and METTL14 in K562 cell line leads to several changes in the expression of p53 signal pathway, including the upregulation of p53, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A/p21), and downregulation of mdm2. | |||
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM11 (TRIM11)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [69] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Epithelial splicing regulatory protein 2 (ESRP2)
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [70] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination | |||
In-vitro Model |
OS-RC-2 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1626 |
| Caki-1 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0234 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the xenograft tumor model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 100 uL PBS were subcutaneously inoculated in the right flank of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. For the ccRCC orthotopic implantation model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 30 uL Matrigel were injected under the renal capsule of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 6 weeks, the anesthetized mice were intraperitoneally injected with D-luciferin (Yeason) and imaged using an in vivo imaging system to detect tumor growth and metastasis. For the lung metastasis model, approximately 5 × 105 ccRCC cells suspended in PBS were injected into the tail vein of 5-week-old mice. After 6-8 weeks, mice were anesthetized and lung metastasis was imaged as above. | |||
| Response Summary | The expression of METTL14 was negatively correlated to the prognosis, stage, and ccRCC tumor grade. Lnc-LSG1 could be regulated by METTL14. Lnc-LSG1 can directly bind to Epithelial splicing regulatory protein 2 (ESRP2) protein and promote ESRP2 degradation via facilitating ESRP2 ubiquitination. | |||
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha (HNF1A/TCF1)
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [72] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MC3T3-E1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0409 |
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A)
Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [73] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | |
Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (LASP1)
Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [75] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2)
Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [42] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEC-1-A | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0293 |
| In-vivo Model | 4×106 HEC-1-A endometrial cancer cells (shCtrl, shMETTL3, wild-type, METTL14+/-, or METTL14+/- rescued with wild-type or mutant METTL14) were injected intraperitoneally into 5 week old female athymic nude mice (Foxn1nu, Harlan; n=10 per group). | |||
| Response Summary | About 70% of endometrial tumours exhibit reductions in m6A methylation that are probably due to either this METTL14 mutation or reduced expression of METTL3. Reductions in m6A methylation lead to decreased expression of the negative AKT regulator PHLPP2 and increased expression of the positive AKT regulator Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2). these results reveal reduced m6A mRNA methylation as an oncogenic mechanism in endometrial cancer and identify m6A methylation as a regulator of AKT signalling. | |||
MAP kinase signal-integrating kinase 2 (MNK2)
Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Muscular dystrophies [ICD-11: 8C70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| C2C12 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0188 | |
| In-vivo Model | For mouse muscle injury and regeneration experiment, tibialis anterior (TA) muscles of 6-week-old male mice were injected with 25 uL of 10 uM cardiotoxin (CTX, Merck Millipore, 217503), 0.9% normal saline (Saline) were used as control. The regenerated muscles were collected at day 1, 3, 5, and 10 post-injection. TA muscles were isolated for Hematoxylin and eosin staining or frozen in liquid nitrogen for RNA and protein extraction. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A writers METTL3/METTL14 and the m6A reader YTHDF1 orchestrate MAP kinase signal-integrating kinase 2 (MNK2) expression posttranscriptionally and thus control ERK signaling, which is required for the maintenance of muscle myogenesis and contributes to regeneration. | |||
Microprocessor complex subunit DGCR8 (DGCR8)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [76] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Tumor metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCC-1664 cell line (Primary HCC cells) | |||
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male athymic BALB/c nude mice (5 weeks old) were used. Subcutaneous tumor growth assays, liver metastasis model, and tail vein injection model were performed as described.Metastases were detected using the IVIS@Lumina II system (Caliper Life Sciences, Hopkinton, MA) 10 minutes after intraperitoneal injection of 4.0 mg luciferin (Gold Biotech) in 50 uL of saline. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 interacts with the microprocessor protein Microprocessor complex subunit DGCR8 (DGCR8) and positively modulates the primary microRNA 126 process in an m6 A-dependent manner. microRNA 126 inhibits the repressing effect of METTL14 in Hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. | |||
NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3)
Insulin resistance [ICD-11: 5A44]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [77] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Insulin resistance [ICD-11: 5A44] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 |
Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [78] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80] | |||
Injury of other or unspecified intrathoracic organs [ICD-11: NB32]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [79] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of other or unspecified intrathoracic organs [ICD-11: NB32.3] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were divided into four groups: sham group, cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) group, CLP + lentivirus short hairpin RNA NC (lv-shNC) group, CLP + lentivirus short hairpin RNA METTL14 (lv-shMETTL4) group. The CLP assay was used to establish the sepsis-induced ALI model. In brief, mice were fasted for 12 h before surgery and were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate (3 mL/kg). Mice were fixed in a supine position, and after abdominal disinfection, an incision of about 1 cm was made along the midline of the abdominal wall. Then, the cecum was separated and penetrated using 18-gauge needle for three times. After that, the punctured cecum was returned to the abdominal cavity, and the abdominal incision was sutured layer by layer. The mice in the sham group were subjected to the same procedure without puncture treatment. For METTL14 knockdown globally, lentivirus (lv) containing shMETTL14 and shNC (0.2 ml, 1 × 109 pfu/ml) were injected into the caudal vein 4 days before modeling, respectively. | |||
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-6 (SIRT6)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [58] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| Glycolysis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BEL-7404 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6568 |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| In-vivo Model | Hepatocyte-specific knockout USP48 was obtained by crossing Alb-Cre mice with USP48flox/flox mice. | |||
| Response Summary | Methyltransferase-like 14 (Mettl14)-induced m6A modification participated in the regulation of USP48 in hepatocellular carcinoma by maintaining USP48 mRNA stability. This work uncovers the tumor-suppressive function of the Mettl14-USP48-NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-6 (SIRT6) axis via modulation of glycolysis, providing new insights into the critical roles of metabolic activities in HCC and identifying an attractive target for future treatment studies. | |||
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1)
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | ||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14 heterozygous mice (Mettl14-/+) were established from C57/BL6 mice by Cyagen Biosciences, Inc. (Suzhou, Jiangsu, China), using CRISPR/Cas9-based targeting and homology-directed repair. C57/BL6 and APOE-/- mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). Mettl14-/+APOE-/- mice were generated by breeding Mettl14-/+ mice with APOE-/- mice. Eight- to 10-week-old male APOE-/- (WT) mice and Mettl14-/+APOE-/- (KO) mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (D12108C, Opensource diets) for 12 weeks. Then, the mice were euthanized for further analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 gene knockout significantly reduced the inflammatory response of macrophages and the development of atherosclerotic plaques, Mettl14 plays a vital role in macrophage inflammation in atherosclerosis via the Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1)/IL-6 signaling pathway. | |||
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [81] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [ICD-11: DB92.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
KCs (Mouse Kupffer cells (BeNa Culture Collection, Beijing, China; BNCC340733)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | At 8 weeks of age, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were challenged with LPS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; L2880, single intraperitoneal injection at 5 mg/kg, n = 3) or CCl4 (10%, Macklin, Shanghai, China; C805332, intraperitoneal injection at 5 mL/kg diluted with corn oil, twice per week for 4 weeks, n = 3). The corresponding control groups were treated with single intraperitoneal injection of saline (n = 3) or intraperitoneal injection of corn oil twice per week for 4 weeks (n = 3), respectively. Two hours after LPS injection and 4 weeks after CCl4 treatment, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were etherized and the primary KCs were isolated from liver according to a previously published method. | |||
| Response Summary | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) acts as transcription factor to transactivate METTL3/METTL14 genes upon LPS challenge, leading to global RNA m6A hypermethylation. m6A modification in TGF-beta1 upregulation, which helps to shed light on the molecular mechanism of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH) progression. | |||
P2X purinoceptor 6 (P2RX6)
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [82] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW839 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3604 |
| SN12C-PM6 | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9549 | |
| OS-RC-2 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1626 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the in vivo metastasis assays, luciferase labeled OS-RC-2 cells stably expressing OE-P2RX6 or pWPI-vector were injected into the tail vein of 5 weeks old BALB/c nude mice (Sipper-BK laboratory animal Company, Shanghai, China). | |||
| Response Summary | In RCC, METTL14 implicated m6A modification in RCC and down-regulated P2X purinoceptor 6 (P2RX6) protein translation. | |||
Pescadillo homolog (PES1)
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [84] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.2] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Decrease of S phase | |||
In-vitro Model |
U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| LAMA-84 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0388 | |
| KCL-22 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2091 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase complex METTL3/METTL14 is upregulated in CML patients and that is required for proliferation of primary CML cells and CML cell lines sensitive and resistant to the TKI imatinib. METTL3 directly regulates the level of Pescadillo homolog (PES1) protein identified as an oncogene in several tumors. These results point to METTL3 as a novel relevant oncogene in CML and as a promising therapeutic target for TKI resistant CML. | |||
PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1a/PPARGC1A)
Diabetic [ICD-11: 5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [85] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic [ICD-11: 5A14] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Arsenite | Phase 2 | ||
In-vitro Model |
L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 |
Proto-oncogene Wnt-1 (Wnt1)
Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
Neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (Primary myocyte cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | C57BL/6 mouse hearts were subjected to ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in vivo as described previously (Bock-Marquette et al., 2004; Song et al., 2015; Brocard et al., 2017). I/R injury in mice was induced by 45-min ischemia, followed by 7-day and 4-week reperfusion in a loss-of-function study (Figure 1) and gain-of-function study (Figure 2), respectively. In brief, mice were anesthetized with 2% avertin (0.1 ml/10g body weight; Sigma-Aldrich Corporation, United States) through intraperitoneal injection. To generate I/R injury, the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) was ligated with 7-0 nylon for 45 min and then was removed. For the sham group, a suture was passed under the LAD but without ligation. According to the experimental requirements, at different time points of cardiac I/R, the mice were anesthetized for assessing heart function by echocardiographic measurement. All the mice survived during the process of I/R injury after the operation. | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 resulted in enhanced levels of Proto-oncogene Wnt-1 (Wnt1) m6A modification and Wnt1 protein but not its transcript level. Furthermore, Mettl14 overexpression blocked I/R-induced downregulation of Wnt1 and Bete-catenin proteins, whereas Mettl14 hearts exhibited the opposite results. Mettl14 attenuates cardiac I/R injury by activating Wnt/Bete-catenin in an m6A-dependent manner, providing a novel therapeutic target for ischemic heart disease. | |||
Protocadherin Fat 4 (FAT4)
Melanoma of uvea [ICD-11: 2D0Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [86] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma of uvea [ICD-11: 2D0Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Mel290 | Uveal melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C304 |
| OMM2.3 | Uveal melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C306 | |
| OMM-1 | Uveal melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6939 | |
| CRMM-1 | Conjunctival melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M593 | |
| CRMM-2 | Conjunctival melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M594 | |
| CM2005.1 | Conjunctival melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M592 | |
| MuM-2B | Uveal melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3447 | |
| 92-1 [Human uveal melanoma] | Uveal melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8607 | |
| ARPE-19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0145 | |
| A-375 | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0132 | |
| SK-MEL-28 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0526 | |
| PIG1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S410 | |
Ras-related protein Rab-22A (RAB22A)
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [87] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
RB1-inducible coiled-coil protein 1 (RB1CC1/FIP200)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [88] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
CAL-33 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1108 |
| In-vivo Model | Thirty-six specific pathogen-free male BALB/c-nude mice (age, 5-6 weeks) were randomly assigned to the groups: CAL33/shMETTL14#2, CAL33/shMETTL14#3, CAL33/shNC and HSC3/shMETTL14#2, HSC3/shMETTL14#3, HSC3/shNC (n = 6 per group). Fifty microliters of PBS buffer containing approximately 1 × 106 cells was injected into the left tongue under 2% pentobarbital sodium intraperitoneal injection anesthesia to establish a tumor xenograft. The weight of the mice was measured every 3 days after one week until they lost more than 15% of their body weight in a short period of time. | |||
Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Paclitaxel | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | STM2457 | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [43] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| Response Summary | The m6A modification level was decreased in GC and METTL14 was a key regulator resulting in m6A disorder in GC. METTL14 overexpression suppressed GC cell proliferation and aggression by deactivating the PI3K/AKT/Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) pathway and the EMT pathway, respectively. | |||
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [90] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
In-vitro Model |
GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male nude mice (age: 4 weeks) were obtained from Charles River (Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China). For tumorigenesis analysis, AGS cells (1 × 106) with stable knockdown of AGAP2-AS1 or scramble, were injected into mice. Next, we detected and measured the tumor volume each week. The weight of the tumor in each nude mouse was also measured at 4 weeks after injection. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to detect Ki67- and caspase-3- positive cells in the tumor. | |||
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3)
Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [93] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | |||
TNF alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3)
Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [94] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||
| In-vivo Model | All animal experiments were performed in accordance with Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines. Six- to eight-week-old male DBA/1J mice (n = 5 per group) were purchased from the Shanghai Laboratory Animal Center, Chinese Academy of Science. All of mice were fed in the specific pathogen free-animal laboratory of the Experimental Animal Center of Fujian Medical University. Animals were housed under controlled conditions with a 12-hour light/dark cycle and with food/water access ad libitum. | |||
Ubiquitin domain-containing protein TINC (TINCR)
Cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [96] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43.7] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
neonatal ventricular myocytes (Mouse hearts were enzymatically digested to acquire the primary neonatal ventricular myocytes) | |||
| H9c2(2-1) | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0286 | |
| In-vivo Model | The diabetic model was constructed by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (65 mg/kg), which imitates a model of type 1 diabetes. The fasting blood glucose was measured one week after injection. Only rats with glucose levels higher than 16.7 mmol/L were defined as diabetic. Cardiac function was investigated seven days following the last treatment, and the heart tissues were then isolated for expression analyses. The lentivirus vector used for silencing or overexpressing specific genes were dissolved in 50uL saline at the concentration of 1 × 109 TU with one dose after the animal model was established. NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950 (10 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected 30 min before streptozotocin treatment. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 suppressed pyroptosis and diabetic cardiomyopathy via downregulating lncRNA Ubiquitin domain-containing protein TINC (TINCR), which further decreased the expression of key pyroptosis-related protein, NLRP3. | |||
Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme ATG7 (ATG7)
Retinopathy [ICD-11: 9B71]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [97] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Retinopathy [ICD-11: 9B71] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Seven-day-old C57BL/6J mice and their lactating mothers were exposed to a 75 % oxygen environment in a chamber for a period of 5 days. Subsequently, the mice were transferred to normal room air (21 % oxygen) at postnatal day 12 (P12) and kept under these conditions for an additional 5 days. At P17, the mice were sacrificed by 10 min following an intraperitoneal injection of a mixture of ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg), and their eyes were enucleated and processed for immunostaining or immunoblotting. | |||
H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19)
Abnormalities of breathing [ICD-11: MD11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [98] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Abnormalities of breathing [ICD-11: MD11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell viability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
H9c2(2-1) | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0286 |
| In-vivo Model | In vivo myocardial I/R injury was performed by 60 min of ligation of LAD followed by 5 h of reperfusion. | |||
| Response Summary | Either knockdown of METTL3 or METTL14 notably reversed the hypoxic preconditioning-induced enhancement of cell viability, anti-apoptosis ability, and H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) expression. | |||
LncRNA activating regulator of DKK1 (LNCAROD)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [99] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Proteasome | hsa03050 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasomal degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C666-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7949 |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| FaDu | Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1218 | |
| HK1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE27 | |
| NP69 (A human immortalized nasopharyngeal epithelial) | ||||
| Tca8113 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6851 | |
| Response Summary | The N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification mediated by METTL3 and METTL14 enhanced the stability of LncRNA activating regulator of DKK1 (LNCAROD) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. LNCAROD is stabilized by m6A methylation and promotes cancer progression via forming a ternary complex with HSPA1A and YBX1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. | |||
Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1320 (LINC01320)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [100] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| MKN7 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1417 | |
| MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 | |
| NCI-N87 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1603 | |
| Response Summary | In gastric cancer, METTL14 was involved in the m6A modification of LINC01320 and induced the up-regulation of Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1320 (LINC01320). | |||
Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [101] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Blood malignancies [ICD-11: 2B33.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Oncogenic fusion protein expression | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| In-vivo Model | The NOD-SCID mice were intravenously (tail vein) implanted with sh-RNA-established NB4 cells. Direct injection of 5 × 106 shRNA-transformed NB4 cells into 150 uL of PBS was performed to establish intravenous (tail vein) leukemia. | |||
| Response Summary | MALAT1 hijacks both chimeric mRNAs and fusion protein in nuclear speckles during chromosomal translocation and mediates colocalization with METTL14 in an oncogenic fusion protein such as PML-RARalpha. Reducing MALAT1 or m6A methyltransferases and the 'reader' YTHDC1 result in the universal retention of distinct oncogenic gene (PML-RARalpha) mRNAs in nucleus. Targeting the lncRNA-triggered autoregulatory loop to disrupt chimeric mRNA transport represents a new common paradigm for treating blood malignancies. | |||
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [102] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 |
| SCC-15 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1681 | |
| Hs 680.Tg | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0842 | |
| FaDu | Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1218 | |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| In-vivo Model | Lentiviruses containing sh-METTL-14 and its negative control (RiboBio Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) were transduced into CAL27 cells and stably transduced cells were screened using puromycin. CAL27 cells (3 × 106 cells/mouse) were subcutaneously inoculated into the posterior flank of each mouse (N = 12/group). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 and lncRNA Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) were upregulated, and miR-224-5p was downregulated in OSCC tissues and cells. METTL14 induced m6A modification of MALAT1 to upregulate MALAT1. | |||
X inactive specific transcript (XIST)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas [ICD-11: 2A81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [104] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas [ICD-11: 2A81] | |||
In-vitro Model |
OCI-Ly3 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma activated B-cell type | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8800 |
| OCI-Ly10 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8795 | |
| SU-DHL-2 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma activated B-cell type | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9550 | |
| U-2932 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1896 | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [105] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Tumorigenicity and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| NCM460 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0460 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | For liver metastasis model, mice were anaesthetized and an incision was made through the skin and peritoneum to expose the spleen. 1 × 106 HCT116 cells were injected into the spleen (n = 4 each group). | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, knockdown of METTL14 substantially abolished m6A level of X inactive specific transcript (XIST) and augmented XIST expression. m6A-methylated XIST was recognized by YTHDF2, a m6A reader protein, to mediate the degradation of XIST. | |||
ZNFX1 antisense RNA 1 (ZFAS1)
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [87] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
microRNA 211 (MIR211)
Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [106] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
CCRF-CEM | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0207 |
| H9 | Sezary syndrome | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1240 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| SUP-T1 | Childhood T lymphoblastic lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1714 | |
| In-vivo Model | Subcutaneously injected with 5 × 106 Jurkat cells and fed under Specific Pathogen Free (SPF) conditions. One week later, tumor mass was injected once a week with Agomir NC, Agomir-211, Antagomir NC and Antagomir 211, respectively, for three weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | microRNA 211 (MIR211) is a novel tumor suppressor in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma,it regulated by METTL14. Targeting of miR-211/TCF12 axis is a potential treatment for T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma patients. | |||
microRNA 375 (MIR375)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [107] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell growth and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | Six-week-old BALB/c nude mice were purchased from the College of Veterinary Medicine, Yang Zhou University. For the xenografted tumor model, 1 × 107 HCT116 cells in 0.2 mL PBS were subcutaneously injected into BALB/c nude mice, which were randomly divided into four groups (six mice per group). The volume of the tumors was calculated with the following equation: V = 0.5 × (length × width2). For metastasis experiments, 2 × 106 cells in 0.2 mL PBS were injected into the tail vein of nude mice, which were randomly divided into four groups (six mice per group). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 suppressed Colorectal cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion via the microRNA 375 (MIR375)/YAP1 and miR-375/SP1 pathways. | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [108] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Injuries of spine or trunk [ICD-11: ND51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injuries of spine or trunk [ICD-11: ND51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
In-vitro Model |
C8-D1A | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_6379 |
| C8-B4 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_6378 | |
| In-vivo Model | An incision was made in the skin along the medial dorsal line to the aponeurotic and muscular planes, and the posterior vertebral arches were exposed from T8 to T12. Under the dissection stereomicroscope, 3-mm-long laminectomy was performed on the caudal end of T10 vertebra and the rostral end of T11 vertebra. The Infinite Horizons impactor (Infinite Horizons, L.L.C., Lexington, KY, USA) was adopted to produce the contusion SCI using a force of 60 kdyn/cm2. The SCI model rats were established and randomly assigned to SCI model group, ant-NC (negative control, SCI rats treated with lentiviral (lv)-shRNA NC of Mettl14) group and ant-Mettl14 group (SCI rats treated with lv-shRNA of Mettl14). Rats were subjected to laminectomy and then treated with lv-shRNA Mettl14/lv-shRNA-NC (50 ul/day, 100 nmoL/mL; RiboBio, Guangzhou, China) via an intrathecal injection through lumbar puncture for 3 days (0, 1, and 2 days) after 15 min of SCI modelling. In addition, the unmodeled rats were set as sham group. | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14-mediated m6A modification inhibited RASD1 and induced the apoptosis of spinal cord neurons in SCI by promoting the transformation of pri-miR-375 to mature microRNA 375 (MIR375). | |||
microRNA 93 (MIR93)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [109] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1106 cells/100 L NSCLC cell suspension (oe-NC group, oe-METTL14 + oe-NC group, oe-METTL14 + oe-TXNIP group) were injected into the tail vein. Twenty-four nude mice (8 in each group) were employed. Following the 56th post-injection day, mice were decapitated by decortication. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was used to identify tumor metastases in the mouse lung tissue . | |||
hsa-miR-146a-5p
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [110] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell migration and invasion | |||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
In-vitro Model |
MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, hsa-miR-146a-5p modulated by METTL14 promoted cell migration and invasion. | |||
hsa-miR-19a-3p
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [111] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell migration and invasion | |||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
In-vitro Model |
ASVEC cell line (Atherosclerotic vascular endothelial cells) | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 increased the m6A modification of pri-miR-19a and promoted the processing of mature hsa-miR-19a-3p, thus promoting the proliferation and invasion of atherosclerotic vascular endothelial cells. | |||
hsa-miR-21-5p
Abortion [ICD-11: JA00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [112] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Abortion [ICD-11: JA00.0] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HTR-8 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_D728 |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c mice (female) and C57BL/6 mice (male) (8-12 weeks-old, 20-22 g) were obtained from the Shanghai Laboratory Animal Center (Shanghai, China). Pregnancy day 0.5 (E0.5) was determined by measuring the vaginal plug. The m6A inhibitor, 3-deazaadenosine (40 μL at a concentration of 10 mg/kg dissolved in physiological saline; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was injected into the uterine cavity using a small catheter (Instech Laboratories, Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA) at E6.5, E5.5, and E4.5, respectively, whereas the control group was injected with an equal volume of saline solution. Mice were sacrificed at E10.5, embryo resorption was measured and photographed, and the placentas were collected. The resorbed embryos were small (<20 % of the average size), appeared dark with unclear boundaries between the fetus and the placenta, and showed necrosis. | |||
hsa-miR-30c-1-3p
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [113] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | miRNA maturation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | The cells (1 × 106) were re-suspended in normal saline and mixed with 25% Matrigel matrix (50 uL) at a 1:1 ratio and subcutaneously injected into the right groin of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 was remarkably downregulated in LC tissues and cell lines. METTL14 mediated the maturation of hsa-miR-30c-1-3p. | |||
hsa-miR-30c-2-3p
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [45] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| MKN28 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1416 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| Response Summary | METTL14-mediated m6A modification of circORC5 suppresses gastric cancer progression by regulating hsa-miR-30c-2-3p/AKT1S1 axis.METTL14 was downregulated in GC tissue samples and its low expression acted as a prognostic factor of poor survival in patients with GC. | |||
hsa-miR-380-3p
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [114] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
HPDE | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4376 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| In-vivo Model | The PC cell line PANC1 was subcutaneously injected into the dorsal flank of the mice at the concentration of 1 × 106 cells per mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | hsa-miR-380-3p was enriched with m6A modifications, and elimination of m6A modifications by deleting METTL3 and METTL14 synergistically suppressed miR-380-3p expressions in pancreatic cancer cells. | |||
hsa-miR-99a-5p
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasome pathway degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 |
| KYSE-410 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1352 | |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| HET-1A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3702 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 | |
| CVCL_E307 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_E307 | |
| In-vivo Model | Fresh PDX tumor samples collected from two established PDX models (PDX #07 with high TRIB2 expression and PDX #12 with low TRIB2, passages three to four) were minced and subcutaneously implanted into the flanks of 3- to 4-week-old female BALB/c nude mice (Jiesijie Laboratory Animals). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14, an m6A RNA methyltransferase downregulated in ESCC, suppresses TRIB2 expression via hsa-miR-99a-5p-mediated degradation of TRIB2 mRNA by targeting its 3' untranslated region, whereas TRIB2 induces ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of METTL14 in a COP1-dependent manner. | |||
hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [115] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Protein export | hsa03060 | ||
| Cell Process | Eukaryotic translation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| RT-4 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0036 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | Chose 4-week-old female BALB/c nude mice for tumor xenograft experiments, which randomly were divided into four groups (n = 5 per group). Bladder cancer cells (3 × 106) were subcutaneously injected into the right axilla of the nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | Circ0008399 bound WTAP to promote formation of the WTAP/METTL3/METTL14 m6A methyltransferase complex, reduce cisplatin sensitivity in bladder cancer, implicating the potential therapeutic value of targeting this axis. | |||
hsa_circ_0089552 (circ_NOTCH1)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [116] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| In-vivo Model | Thirty-two 6 week-old female nude mice divided into four groups (n = 8 per group) for injections of H1299 cells transfected with (a) pLKO.1 + pWPI, (b) shcircNOTCH1 + pWPI, (c) pLKO.1 + oeGPER and (d) shcircNOTCH1 + oeGPER. | |||
| Response Summary | GPER promotes non-small-cell lung cancer cell growth by regulating YAP1-TEAD/QKI/circNOTCH1/m6A methylated NOTCH1 signalling. Further exploration of the mechanism demonstrated that GPER could up-regulate hsa_circ_0089552 (circNOTCH1), which could compete with NOTCH1 mRNA for METTL14 binding. | |||
AC026356.1
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [117] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Cells (2 × 104) were seeded onto 12-well plates and cultured in serum-free 1640 medium. Cell spheroids were documented and quantified using an inverted microscope (Olympus, Japan) after two weeks. | |||
Alpha-actinin-4 (ACTN4)
SARS-CoV-2 [ICD-11: XN109]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [118] | |||
| Responsed Disease | SARS-CoV-2 [ICD-11: XN109] | |||
Alpha-synuclein (SNCA)
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [119] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SN4741
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_S466 |
| In-vivo Model | Male nude mice (6 weeks old) were purchased from the Shanghai Laboratory Animal Central (Shanghai, China). 95D cells (1 × 107) transfected with sh-HNRNPA2B1 or sh-NC lentiviruses were injected subcutaneously into the right flanks of mice. After 8 weeks, the mice were sacrificed, and the xenografted tumors were collected for hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and IHC analysis. | |||
Amino acid transporter heavy chain SLC3A2 (SLC3A2)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [120] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 22 (ANKRD22)
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [121] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Aspartyl/asparaginyl beta-hydroxylase (ASPH)
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [122] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-CS
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0F27 |
| In-vivo Model | The adenovirus-mediated silencing METTL14 (ad-sh-METTL14) or negative control vectors were designed and packaged by GenePharma (Shanghai, China). All mice (18 mice in each group) were euthanized at 20 weeks of age by injection of pentobarbital sodium (250 mg/kg). | |||
BET1-like protein (BET1L)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [123] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous xenotransplantation, 3- to 4-week-old male BALB/c nude mice were randomly divided into groups (8 mice per group) and injected in the back flank with 100 μL of 1.0 × 107 suspended cells. | |||
C-C motif chemokine 5 (CCL5)
Gestational diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: JA63]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [124] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gestational diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: JA63] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Fentanyl | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 |
| Capan-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0237 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
Calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (CALCOCO1)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Paclitaxel | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | STM2457 | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
Caldesmon (CALD1)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [125] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
CCN family member 2 (CTGF)
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [126] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SV40 MES 13
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_5368 |
| NRK-52E | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0468 | |
Circ_FUT8
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [127] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| THLE-3 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3804 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male BALb/c nude mice (three mice per group) were bought from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center, and indicated HCC cells were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of nude mice at 2 × 106 cells per site. | |||
Circ_GFR-Alpha-1
Female reproductive system disorders [ICD-11: SC4Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [128] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Female reproductive system disorders [ICD-11: SC4Y] | |||
| Pathway Response | Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| FGSCs cell line (Female Germline Stem Cells) | ||||
| Response Summary | Circ_GFR-Alpha-1 promotes female germline stem cells self-renewal by acting as a ceRNA that sponges miR-449, leading to enhanced GFRalpha-1 expression and activation of the GDNF signaling pathway. circGFRalpha-1 acts as a ceRNA based on METTL14-mediated cytoplasmic export through the GGACU motif. | |||
Circ_ORC5
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [45] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| MKN28 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1416 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| Response Summary | METTL14-mediated m6A modification of Circ_ORC5 suppresses gastric cancer progression by regulating miR-30c-2-3p/AKT1S1 axis. METTL14 was downregulated in GC tissue samples and its low expression acted as a prognostic factor of poor survival in patients with GC. | |||
Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-5 (ATF5)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [129] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Dickkopf-related protein 3 (DKK3)
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [130] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic nephropathy [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK-2 [Human kidney] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 |
| In-vivo Model | Female mice (8 weeks old, 20-25 g) on a C57BL/6J background were fasted for 12 h but were allowed to drink water freely. They were then injected intraperitoneally with 50 mg/kg body weight of freshly dissolved STZ in sterile PBS for four consecutive days. Mice were given sterile PBS alone in the same way as an untreated control. The mice's blood glucose levels were assessed two weeks after their most recent treatment. Mice that exhibited glucose levels greater than 200 mg/dL were classified as successful hyperglycemic models and were utilized in subsequent studies. Five months after the final dose of STZ, the mice were euthanized, and the renal tissues were collected for pathological examination to confirm the successful establishment of the model of diabetes nephropathy induced by hyperglycemia. All animal experiments were performed according to the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the China Pharmaceutical University. Isoflurane was used to anesthetize mice. | |||
Dynamin-1-like protein (DRP1)
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [131] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR1 (UBR1)
Injuries of spine or trunk [ICD-11: ND51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [132] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Spinal cord injury [ICD-11: ND51.2] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PC-12 | Lung papillary adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S979 |
| In-vivo Model | After anesthetization with an intraperitoneal injection of ketamine (80 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg), none of the rats had obvious abdominal distention, ascites, discomfort, or pain. Laminectomy was performed at T8-T10 (counting from top to bottom; from the 8th thoracic vertebra to the 10th thoracic vertebra). The spine was immobilized with a stereotaxic device, and the exposed spinal cord was severely injured at the center between T8 and T10 by a 5-g weight dropping freely from a height of 8 cm (Perot et al., 1987; Ray et al., 2000). After surgery, the rats were carefully nursed and fed and their urine was squeezed three times a day until reflex bladder emptying was established. Successful modeling was defined as (1) rapid retraction of the whole body, (2) rapid edema and congestion on the surface of the local spinal cord, (3) intact spinal dura mater, (4) flaccid paralysis of the hindlimbs, and (5) survival. Rats that underwent unsuccessful modeling were replaced. The SCI (1 d), SCI (7 d), and SCI (14 d) groups were killed on first, seventh, and 14th day after modeling, respectively, while the other groups were killed on the 14th day. Most operations in the sham group were the same as those in the SCI group, with no spinal cord contusions. The SCI + LV-NC, SCI + LV-UBR1, SCI + sh-NC, and SCI + sh-METTL14 groups were given lentiviral tail vein injections (once every 3 d, virus titers of 108 TU/ml; GenePharma) 3 d before SCI modeling. | |||
Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [133] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| In-vivo Model | The KYSE-150 cells were subcutaneously inoculated on the right side at a dosage of 106 cells per mouse. After the tumor grew to approximately 50 mm3, mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 6): Control, CisR-exo, Cis, and Cis + CisR-exo. Then, normal saline or cisplatin (20 mg/kg; twice a week) was intratumorally injected alone or combined with CisR-exos (10 μg; once every two days). | |||
Frizzled-2 (FZD2)
Diabetic [ICD-11: 5A14]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [134] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic [ICD-11: 5A14] | |||
In-vitro Model |
CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
Hamartin (TSC1)
Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [135] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Coptisine | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
| In-vivo Model | Sixty mice were disposed in 6 groups randomly by using spss25.0 software after an adaption period of one week (n = 10): control, DSS model, 5-ASA (200 mg/kg) +DSS, coptisine 25 mg/kg + DSS (COP-l), coptisine 50 mg/kg + DSS (COP-M) and coptisine 100 mg/kg + DSS (COP-H). The dosages of 5-ASA and COP were implemented in accordance with the previous report. | |||
Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [136] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR)
Disorders due to use of opioids [ICD-11: 6C43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [137] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Disorders due to use of opioids [ICD-11: 6C43.1] | |||
| Responsed Drug | MM-102 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
hsa-mir-19a
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [111] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Interleukin-12 subunit beta (IL12B)
Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [138] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46] | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
Interleukin-13 (IL13)
Allergy [ICD-11: 4A8Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [139] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Allergy [ICD-11: 4A8Z] | |||
Asthma [ICD-11: CA23]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [139] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Asthma [ICD-11: CA23] | |||
Intraflagellar transport protein 80 homolog (IFT80)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [140] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HN4 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_IS30 |
| HN-6 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8129 | |
| WSU-HN30 | Pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5525 | |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| SCC-9 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1685 | |
| SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 | |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| In-vivo Model | To determine whether lnc-H2AFV-1 overexpression could enhance tumorigenicity in vivo, 1 × 106 HN6 cells stably transduced with LV-lnc-H2AFV-1 or LV-NC were subcutaneously injected into the right and left flanks of six mice. | |||
JmjC domain-containing protein 8 (JMJD8)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [141] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
Lnc_LSG1
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [70] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination | |||
In-vitro Model |
OS-RC-2 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1626 |
| Caki-1 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0234 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the xenograft tumor model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 100 uL PBS were subcutaneously inoculated in the right flank of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. For the ccRCC orthotopic implantation model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 30 uL Matrigel were injected under the renal capsule of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 6 weeks, the anesthetized mice were intraperitoneally injected with D-luciferin (Yeason) and imaged using an in vivo imaging system to detect tumor growth and metastasis. For the lung metastasis model, approximately 5 × 105 ccRCC cells suspended in PBS were injected into the tail vein of 5-week-old mice. After 6-8 weeks, mice were anesthetized and lung metastasis was imaged as above. | |||
| Response Summary | The expression of METTL14 was negatively correlated to the prognosis, stage, and ccRCC tumor grade. Lnc-LSG1 could be regulated by METTL14. Lnc_LSG1 can directly bind to ESRP2 protein and promote ESRP2 degradation via facilitating ESRP2 ubiquitination. | |||
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2747 (LINC02747)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [142] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 941 (LINC00941)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [143] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| In-vivo Model | PANC-1 cells were stably transfected with LV-METTL14, LV-NC, sh-METTL14, sh-NC, or sh-LINC00941. A mixture of 2×106 cells and 100 μL PBS was injected into the spleen of every BALB/c nude mouse. After two months of housing in a sterile environment, the mice were sacrificed. Their liver tissues were removed for hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. | |||
Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B)
Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [144] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [145] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
miR-6858
Lichen planus [ICD-11: EA91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [146] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lichen planus [ICD-11: EA91.4] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Mitochondrial fission 1 protein (FIS1)
Cognitive impairment [ICD-11: MB21]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [147] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cognitive impairment [ICD-11: MB21] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Neuro-2a | Mouse neuroblastoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0470 |
| In-vivo Model | To investigate chronic Cd-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and neurotoxicity in vivo, C57BL/6J mice were randomly assigned to 2 groups: (i) control group mice (n = 20) and (ii) Cd exposure group mice (n = 20). | |||
Neurotrophic factor BDNF precursor form (BDNF)
Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury [ICD-11: NA07]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [149] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury [ICD-11: NA07] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Xuefu Zhuyu decoction | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (body weight 220 g-250 g) were acquired from Hunan Silaike Jingda Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (Changsha, China, license No. SCXK (XIANG) 2016-0002). They were housed under specific pathogen-free conditions in the Department of Laboratory Animals, Central South University (Changsha, China, license No. SYXK (XIANG) 2015-0017). All rats were kept in air-conditioned animal quarters under standard conditions (50 ± 10% relative humidity, 12-h light/dark cycle, 22 ± 2 °C), with ad libitum water and food. | |||
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [64] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
In-vitro Model |
Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 |
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATC1)
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [150] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
| MC3T3-E1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0409 | |
Paired box protein Pax-6 (PAX6)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [151] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
In-vitro Model |
BV-2 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0182 |
| In-vivo Model | C57BL/6 mice were anesthetized intraperitoneally with 1% sodium pentobarbital (100 mg/kg). The mouse was placed on a thermostatic blanket to maintain the rectal temperature at 37.0°C± 0.5°C during surgery. The left common carotid artery (CCA), external carotid artery (ECA), and internal carotid artery (ICA) were exposed through a midline incision in the cervico abdominal region. The CCA was ligated distally with surgical nylon monofilament. | |||
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP], mitochondrial (PCK2)
Hepatic inflammation [ICD-11: DB97]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [152] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatic inflammation [ICD-11: DB97] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase GPX4 (GPX4)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [153] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.1] | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| In-vivo Model | For xenograft establishment, six-week-old female athymic nude mice (n = 6 per group) were used, following ethical guidelines approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Each mouse received subcutaneous injections in the flank region with 1 × 10^6 cells suspended in 100 μL of serum-free medium, either sh-METTL3-transfected A549 cells or sh-NC-transfected controls. Tumour growth was monitored bi-dimensionally every week using callipers, with tumour volume calculated using the formula (length × width^2)/2. After 4 weeks, the mice were anaesthetised and euthanized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium (100 mg/kg). The tumours were weighted and used for HE and Immunohistochemistry staining. | |||
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [154] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
| In-vivo Model | Female 8-week-old Wistar rats (weighed 200 ± 20 g) were housed under a 12-h light/dark cycle with temperature and humidity (23 ± 1°C and 52 ± 2%) maintained, and they had free access to food and tap water. After 1 week of adaptive feeding, rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 40 mg/kg of sodium thiopental. A rat model of OA was established according to the reference.32 Iodoacetate causes joint pathology via the inhibition of glycolysis, thereby targeting the avascular cartilage and causing chondrocyte death.33 With the left leg flexed at a 90° angle at the knee, 2 mg of monosodium iodoacetate (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA) was injected through the patellar ligament between the tibia and the femur using a 26GX3/8 needle at a volume of 25 μL. Control rats received an intra-articular injection of sterile saline (25 μL) alone. After recovery, the animals were returned to cages. Seven days after injection, the cartilages in the control and OA groups were collected for gene expression analysis. | |||
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [155] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Polyamine-transporting ATPase 13A3 (ATP13A3)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [156] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCoEpiC (Healthy colon epithelial HCoEpiC cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | The nude mice were randomly assigned to two groups consisting of six mice each. We injected transformed cells (P0 and P40) into the flank of each mouse in 0.1 mL of sterile PBS to form xenograft tumors. The tumor volume was measured every 2 or 3 days (volume = length × width2 × 1/2). The tumors were resected, imaged, and weighed after the mice were sacrificed. One piece of each tumor tissue was fixed in 4% (v/v) paraformaldehyde for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining, and the remaining tissue was stored at -80 °C. | |||
pri-miR-17
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [157] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Fluorouracil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 | |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| NCM460 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0460 | |
Progestin and adipoQ receptor family member 3 (PAQR3)
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [158] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic nephropathy [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
In-vitro Model |
GEC
|
N.A. | Epinephelus tauvina | CVCL_S009 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
Protein disulfide-isomerase (P4HB)
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [159] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Responsed Drug | ICARIIN | Investigative | ||
| In-vivo Model | After anesthesia with ketamine-xylazine(intraperitoneal injection, 60 and 5 mg/kg, respectively), the rats were operated to remove the bilateral ovaries. For the rats in the Sham group, only the fat around the ovaries was surgically removed. Four weeks after the operation, the animals were orally treated with ICA (250 mg/kg) daily for 10 weeks . | |||
Pseudorabies Virus (PRV)
Rabies [ICD-11: 1C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [160] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rabies [ICD-11: 1C82] | |||
| Responsed Drug | 3-deazidenosine | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PK-15
|
N.A. | Sus scrofa | CVCL_2160 |
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 (RIP3)
Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [161] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Abdominal aortic aneurysm [ICD-11: BD50.4] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha-Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha (PML-RARalpha)
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [101] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Blood malignancies [ICD-11: 2B33.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell differentiation | |||
Rho GTPase-activating protein 12 (ARHGAP12)
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [122] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-CS
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0F27 |
| In-vivo Model | The adenovirus-mediated silencing METTL14 (ad-sh-METTL14) or negative control vectors were designed and packaged by GenePharma (Shanghai, China). All mice (18 mice in each group) were euthanized at 20 weeks of age by injection of pentobarbital sodium (250 mg/kg). | |||
RNA-binding protein Nova-2 (NOVA2)
Hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis [ICD-11: DB93]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [162] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis [ICD-11: DB93] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
SET-binding protein (SETBP1)
Myelodysplastic neoplasms [ICD-11: 2A4Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [163] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Myelodysplastic neoplasms [ICD-11: 2A4Z] | |||
| In-vivo Model | In the first in vivo experiment focused on investigating the role of METTL14 in MDS cell proliferation in vivo, the MDS-L-luc cells were transduced with the Dox-inducible shMETTL14 (shMETTL14_Tet-on). After treatment with 2 μg/mL puromycin for a duration of 4 days, a total of 2.5 × 106 selected cells were injected via the tail vein into irradiated female NCG-M mice aged 8-10 weeks (GemPharmatech, China) to establish cell line-derived xenograft (CDX) models. On day 14 post transplantation, 20 mice were randomly assigned to two groups and treated with either Dox or vehicle. A total of 2 mg Dox was dissolved in water and administered by gastric lavage once a day. Five mice from each group underwent in vivo chemiluminescence imaging on day 14, 21, and 28 after receiving intraperitoneal injection of luciferin (Promega, USA). Their overall survival (OS) was also observed and documented. The remaining five mice from each group were utilized to assess the proportions of human CD45+cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood on day 28 through flow cytometry analysis. | |||
Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 3 (SLC2A3)
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [164] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
In-vitro Model |
MC3T3-E1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0409 |
| In-vivo Model | Female C57BL/6 mice, aged eight weeks, were selected for the study. The mice were divided into three groups with six mice per group. After intramuscular anesthesia (xylazine 10 mg/kg, ketamine 100 mg/kg), two groups underwent bilateral ovariectomy (OVX), while the remaining group had a sham operation. Ovariectomized mice were administered weekly intratibial injections of Mettl14 overexpression adenovirus containing at a concentration of 109 plaque-forming unit per injection, for a duration of 8 weeks. The mice were humanely euthanized one week after the final injection, and their tibia were gathered for further analysis. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Tongji University (NO: TJBH00823101). All the experimental methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines. All experimental procedures involving mice were carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the ARRIVE guidelines (Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments). | |||
Spindlin-2A (SPIN2A)
Vascular Calcification [ICD-11: BE2Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [165] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular Calcification [ICD-11: BE2Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 | |
|
NCTC clone 929
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_0462 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
SREBF2 antisense RNA 1 (SREBF2-AS1)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Sorafenib | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| SNU-398 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0077 | |
| THLE-2 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3803 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
Taurine up-regulated 1 protein (TUG1)
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [167] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic nephropathy [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
TNF and HNRNPL related immunoregulatory long non-coding RNA (THRIL)
Injury of other or unspecified intrathoracic organs [ICD-11: NB32]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [168] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of other or unspecified intrathoracic organs [ICD-11: NB32.3] | |||
| Responsed Drug | LPS | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
Transcription factor SOX-6 (SOX6)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [169] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Transcription factor SOX-9 (SOX9)
Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [170] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||
Transmembrane protein 127 (TMEM127)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [171] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Approximately 1 × 106 viable MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were resuspended in 1:1 ratio in 50 μl medium and 50 μl matrigel (Corning, 354234) and injected orthotopically into the fourth mammary fat pad of each mouse. After injection, tumor size was measured twice a week using an electronic caliper. Tumor volumes were calculated with the formula: volume = (L × W2)/2, where L is the tumor length and W is the tumor width measured in millimeters. | |||
TRHDE antisense RNA 1 (TRHDE-AS1)
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [172] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
In-vitro Model |
RWPE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3791 |
| 22Rv1 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1045 | |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| LNCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0395 | |
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 38 (USP38)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [173] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c nude mice were purchased from the Slac Laboratories (Shanghai, China) and randomly divided into two groups. The xenograft mouse model was generated via tail-vein injection of METTL14-expressing T24 cells (5 × 105 cells per mouse) into experimental mice while those injected with pcDNA3.1 empty vector transfected cells as control. | |||
Zinc finger protein PLAGL2 (PLAGL2)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [174] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| In-vivo Model | Twenty BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks) were randomly assigned to sh-NC, sh-METTL14, sh-METTL14+oe-NC, and sh-METTL14+oe-PLAGL2, with 5 mice in each group. Mice were raised under sterile conditions of ambient room temperature of 26-28°C, the humidity of 40-60%, and alternating day and night for 10 h/14 h. The Mice were fed sterile food and water. After 1 week of adaptive feeding, A549 cells that transfected with sh-NC, sh-METTL14, oe-NC, and oe-PLAGL2 were subcutaneously injected. The cell concentration was 5 × 106/mL, and 200 μL was injected. | |||
Zinc finger protein RFP (TRIM27)
Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [175] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
Zinc transporter ZIP9 (SLC39A9)
Periodontitis [ICD-11: DA0C]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [176] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Periodontitis [ICD-11: DA0C] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Viral infections [ICD-11: 1D9Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [178] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Viral infections [ICD-11: 1D9Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Response Summary | m6A is the most abundant internal modification described in eukaryotic mRNA and several viral RNA including human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) infection. METTL3/METTL14 m6A writer complex plays a negative role in HRSV infections protein synthesis and viral titers, while m6A erasers FTO and ALKBH5 had the opposite effect. | |||
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [179] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Response Summary | Some SNPs in the METTL14 gene are associated with predisposition to neuroblastoma. | |||
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [180] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
In-vitro Model |
MG-63 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 |
| In-vivo Model | According to the method published previously , exponentially growing MG63 and MG63/DXR were harvested, counted with trypan blue to show cells with at least 95% viability, and then resuspended at a final amount from 5 × 106 to 5 × 103 in 100 uL Matrigel (Corning, NY, USA) before being injected subcutaneously into 5-week-old female nude mice.The mice were monitored once every 3 days until the 60th day, and euthanized humanely after the experiment. | |||
| Response Summary | The transcriptome-wide m6A methylome of osteosarcoma cells enriched by chemotherapy, revealing a tight relationship between m6A methylation and the emergence and maintaining of OSCs. | |||
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [181] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HOK | Normal | Hexagrammos otakii | CVCL_YE19 |
| HN-6 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8129 | |
| HN-5 | Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8128 | |
| HN-15 | Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity | Homo sapiens | CVCL_W297 | |
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 are overexpressed in OSCC tissues and in the HN6 OSCC cell line that promotes cell proliferation. Overexpressed METTL3 or METTL14 is found to be an independent prognostic factor for short overall survival in patients with OSCC. | |||
Rectum cancer [ICD-11: 2B92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [182] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rectum cancer [ICD-11: 2B92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair | |||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
| Response Summary | The m6A RNA methylation regulators, specifically YTHDC2 and METTL14, were significantly down-regulated and were potential prognostic biomarkers in rectal cancer. | |||
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [183] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gemcitabine | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| Hs 766T | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0334 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | |
| In-vivo Model | NOD/SCID mice (6-week-old) were injected (subcutaneously in both flanks) with 5.0 x 106 PANC-1 GemR cells (infected with scr or METTL14 shRNA) per mouse suspended in 50 ul PBS and mixed with equal volume of growth factor reduced matrigel. One week after injection, we started measuring tumor size at the indicated times. Tumor size was calculated by 0.5 × (long diameter) × (short diameter)2. The mice were treated with vehicle or 100 mg/kg gemcitabine intraperitoneally twice a week. | |||
| Response Summary | Suppression of METTL14 obviously increased the sensitivity of gemcitabine in resistant cells. This study suggested that METTL14 is a potential target for chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [184] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
In-vitro Model |
SK-MES-1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0630 |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| 16HBE14o- | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0112 | |
| Response Summary | Silencing of METTL14 suppressed non-small cell lung cancer malignancy by inhibiting Twist-mediated activation of AKT signaling. | |||
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [185] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
CRL-11731D cell line (Human ovarian cancer cell) | |||
| TOV-112D | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3612 | |
| Response Summary | METTL3 can regulate m6A methylation independently of METTL14 and WTAP in endometrioid epithelial ovarian cancer. | |||
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [186] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
In-vitro Model |
SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 |
| C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 | |
| Response Summary | Up-regulation of METTL14 acted as an adverse prognostic factor for overall survival in cervical cancer patients. These study suggest an important oncogenic role of METTL14 in the growth and invasion of both HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancer cells. | |||
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [187] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | |||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Response Summary | It is plausible that VHL-HIF-METTL3/14 pathways are involved in the m6A regulation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells, and PI3K-mTOR as well as p53 signaling pathways are possible downstream targets of m6A in ccRCC. | |||
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [188] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder urothelial carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C94.2] | |||
In-vitro Model |
UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| TCCSUP | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1738 | |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| RT-112 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1670 | |
| MGH-U3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9827 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
| Response Summary | METTL14 as a key component for m6 A RNA deposit and that it is closely related to BlCa progression, playing an important role in tumor aggressiveness. | |||
Hematological disorders [ICD-11: 3C0Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [189] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hematological disorders [ICD-11: 3C0Z] | |||
| Response Summary | This reviewed summarize and discuss recent findings regarding the biological functions and underlying mechanisms of m6A modification(i.e., the METTL3/METTL14/WTAP complex and other cofactor proteins) and the associated machinery in normal hematopoiesis and the initiation, progression, and drug response of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a major subtype of leukemia usually associated with unfavorable prognosis. | |||
Lupus erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [190] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lupus erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings suggested decreased YTHDF2 that was associated with disease activity play an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE, METTL14 and ALKBH5 were concomitantly decreased. | |||
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [191] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Cell Process | Mitotic clonal expansion | |||
In-vitro Model |
3T3F442A | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0122 |
| 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 | |
| COS (From the African green monkey cell line (CV-1).) | ||||
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Mice were anesthetized after 24 h of fasting, and 5 U of human insulin (Humalin R; Eli Lilly) was injected into the inferior vena cava. After 5 min, the liver and hind limb muscles were dissected and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
| Response Summary | WTAP, coupled with METTL3 and METTL14, is increased and distributed in nucleus by the induction of adipogenesis dependently on RNA in vitro Knockdown of each of these three proteins leads to cell cycle arrest and impaired adipogenesis associated with suppression of cyclin A2 upregulation during MCE, whose knockdown also impairs adipogenesis. | |||
Glucose intolerance [ICD-11: 5C61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [192] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glucose Intolerance [ICD-11: 5C61.Y] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Tamoxifen | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were fed a normal chow diet (Harlan Teklad) and maintained in a standard 12-hour light/12-hour dark cycle. At the age of 10 weeks, both male and female mice were intraperitoneally injected with 250 L (20 mg/mL) tamoxifen every other day for three times to delete Mettl14 in Beta-cells. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests were performed on mice at the age of 15 weeks after a 5-hour fast (2 g/kg dextrose). Insulin levels were measured at 0, 15, and 30 minutes after glucose challenge by using the Ultra Sensitive Mouse Insulin ELISA Kit .Insulin tolerance tests were performed after a 5-hour fast by administering human recombinant insulin (0.75 U/kg). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 deficiency in beta-cells induces glucose intolerance and a decrease in insulin secretion.To define the role of m6A in regulating the beta-cell function, the study generated beta-cell METTL14-specific knockout (beta-KO) mice by tamoxifen administration. beta-cell mass in beta-KO mice was related to beta-cell proliferation and also observed elevated mRNA and protein levels of Ire1-alpha and sXBP-1 in beta-KO islets. | |||
Epilepsy due to structural or metabolic conditions or diseases [ICD-11: 8A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [193] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Epilepsy due to structural or metabolic conditions or diseases [ICD-11: 8A60.5] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Betaine | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated with a single i.p. injection of pentylenetetrazol (PTZ, Sigma-Aldrich, P6500) at a dose of 50 mg/kg to establish the animal model of acute seizures [16]. Betaine (Sigma-Aldrich, B2629) was dissolved in normal saline, and administrated at a dose of 200 mg/kg or 600 mg/kg, i.p., to mice for 15 days before PTZ injection in reference to a previous study. | |||
Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [194] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Abdominal aortic aneurysm [ICD-11: BD50.4] | |||
| Cell Process | Inflammatory infiltrates | |||
| Neovascularization | ||||
In-vitro Model |
PBMCs (Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are isolated from peripheral blood and identified as any blood cell with a round nucleus) | |||
| SMCs (Aneurysmal smooth muscle cells) | ||||
| Response Summary | YTHDF3 represented an even greater risk of rupture. Regarding the cellular location, METTL14 seemed to be associated with inflammatory infiltrates and neovascularization. Furthermore, a strong correlation was seen between FTO and aneurysmal smooth muscle cells (SMCs), YTHDF3, and macrophage infiltrate. The results also reveal the important roles of m6A modulators, including YTHDF3, FTO, and METTL14, in the pathogenesis of human human abdominal aortic aneurysm(AAA) and provide a new view on m6A modification in AAA. | |||
Vascular Calcification [ICD-11: BE2Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [195] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular Calcification [ICD-11: BE2Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HASMC cell line (Primary human artery smooth muscle cell) | |||
| In-vivo Model | The experimental rats received intraperitoneal injection with IS at a dosage of 100 mg/kg/48 h for 8,16,24 weeks. The control rats (n = 5) received same volume of phosphate-buffered saline injection every 48 h for 8,16,24 weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 expression increases in calcific arteries and in HASMCs induced by indoxyl sulfate, thereby increasing the m6A level in RNA and decreasing the vascular repair function.METTL14 m6A regulates vascular calcification induced by indoxyl sulfate. | |||
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [196] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Sunitinib | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
hiPSCs (Urinary epithelial cell-derived hiPSCs) | |||
| CMECs (Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells ) | ||||
| CFs (Cardiac Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Response Summary | The RNA demethylase FTO was downregulated, whereas METTL14 and WTAP were upregulated. Furthermore, gain- and loss-of-function studies substantiated that FTO is cardioprotective in TKI(Sunitinib). | |||
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [197] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
GC-1 spg | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_8872 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mouse GC-1 spg cells were treated with the ester form of meclofenamic acid (MA2) to inhibit the demethylase activity of FTO. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, METTL14, ALKBH5 and YTHDC2 are involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis. MA2 affected CDKs expression through the m6A-dependent mRNA degradation pathway, and thus repressed spermatogonial proliferation. Additionally, mutation of the predicted m6A sites in the Cdk2-3'UTR could mitigated the degradation of CDK2 mRNA after MA2 treatment. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [198] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04] | |||
In-vitro Model |
Pachytene/diplotene spermatocyte (Prepared from undifferentiated mouse spermatogonial cells) | |||
| Preleptotene spermatocyte (Prepared from undifferentiated mouse spermatogonial cells) | ||||
| Round spermatid. (Prepared from undifferentiated mouse spermatogonial cells) | ||||
| Type A1 spermatogonia (Prepared from undifferentiated mouse spermatogonial cells) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | All mice described above were maintained on the C57BL/6J (B6) background. Mettl3- and Mettl14-floxed mice (Mettl3flox/flox and Mettl14flox/flox) were then bred with germ cell-specific expressed Cre mice including Vasa-Cre mouse line (Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, Maine, USA) and Stra8-GFPCre mouse line for excising the loxP-flanked exon 4 and exon 2 to generate germ cell-specific Mettl3 and Mettl14KO mice, respectively. Germ cell-specific Mettl3 and Mettl14 double KO mice were obtained by crossing Mettl3flox/floxMettl14flox/flox with Mettl3flox/+Mettl14flox/+ or Mettl3flox/+Mettl14flox/flox carried germ cell-specific expressed Cre mice. | |||
| Response Summary | Combined deletion of Mettl3 and Mettl14 in advanced germ cells with Stra8-GFPCre disrupts spermiogenesis, whereas mice with single deletion of either Mettl3 or Mettl14 in advanced germ cells show normal spermatogenesis. | |||
Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [144] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Inflammatory response [ICD-11: MG46] | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
 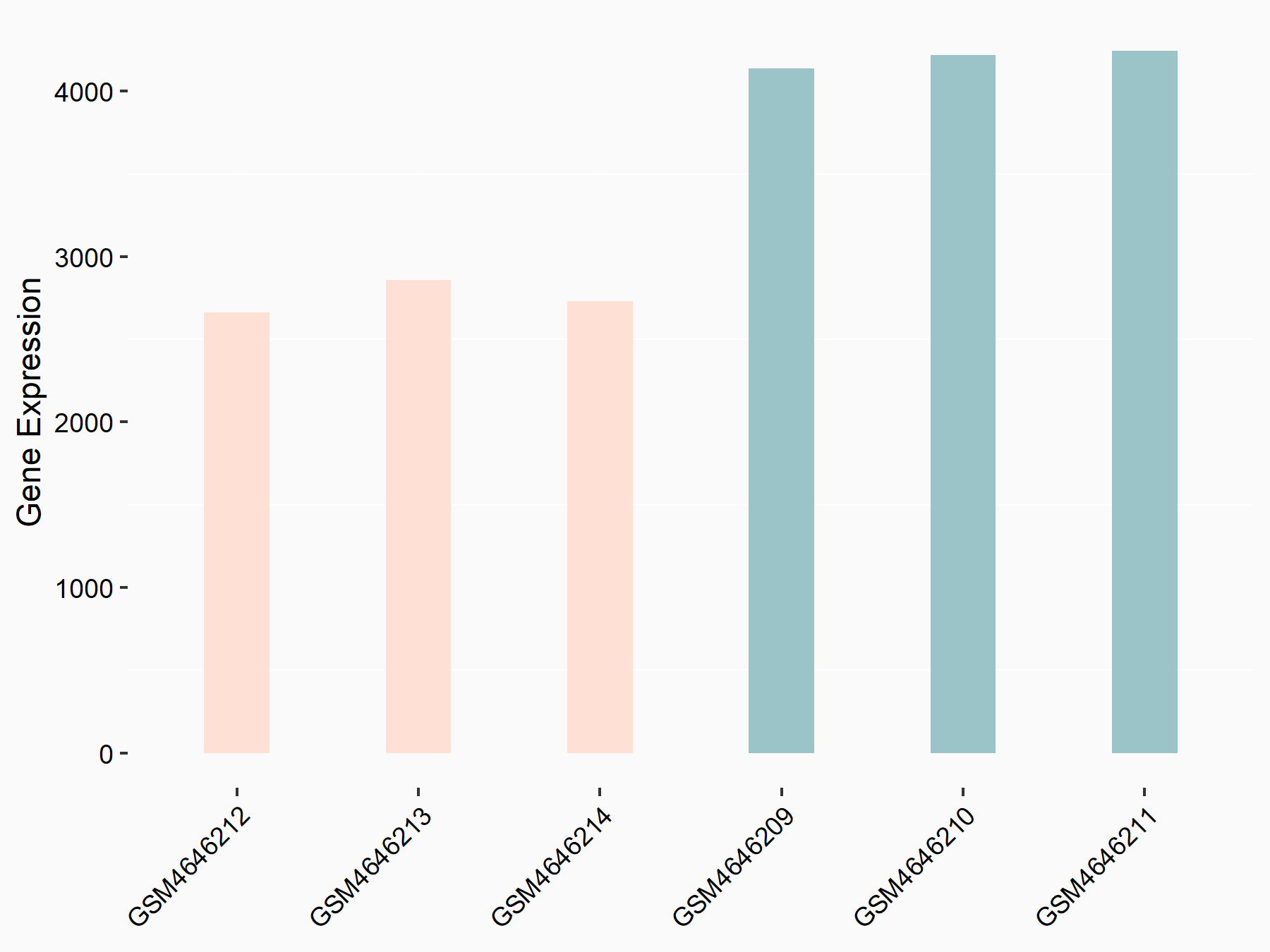 |
logFC: -6.10E-01 p-value: 2.52E-16 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pertuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Trastuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Tucatinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
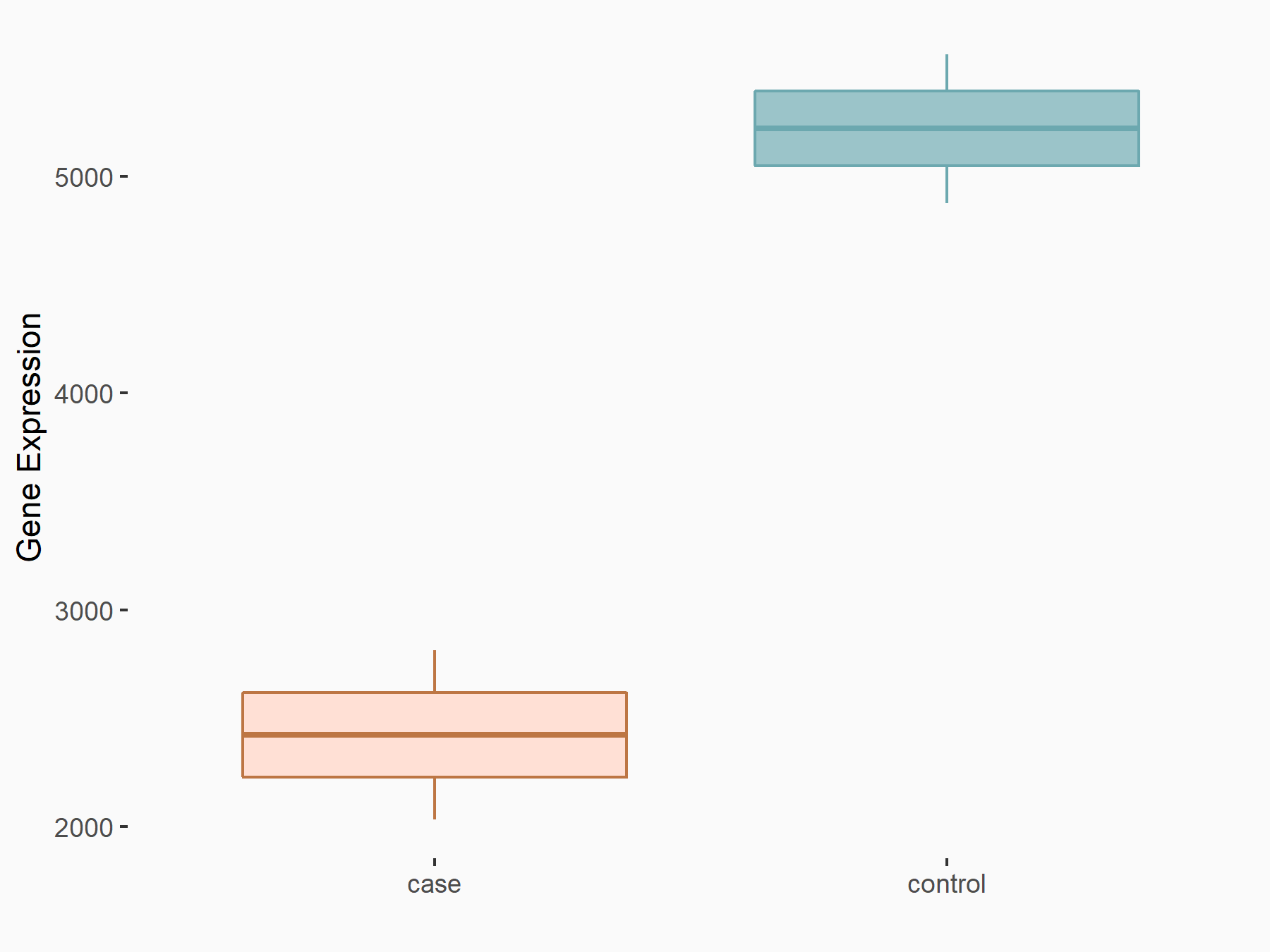 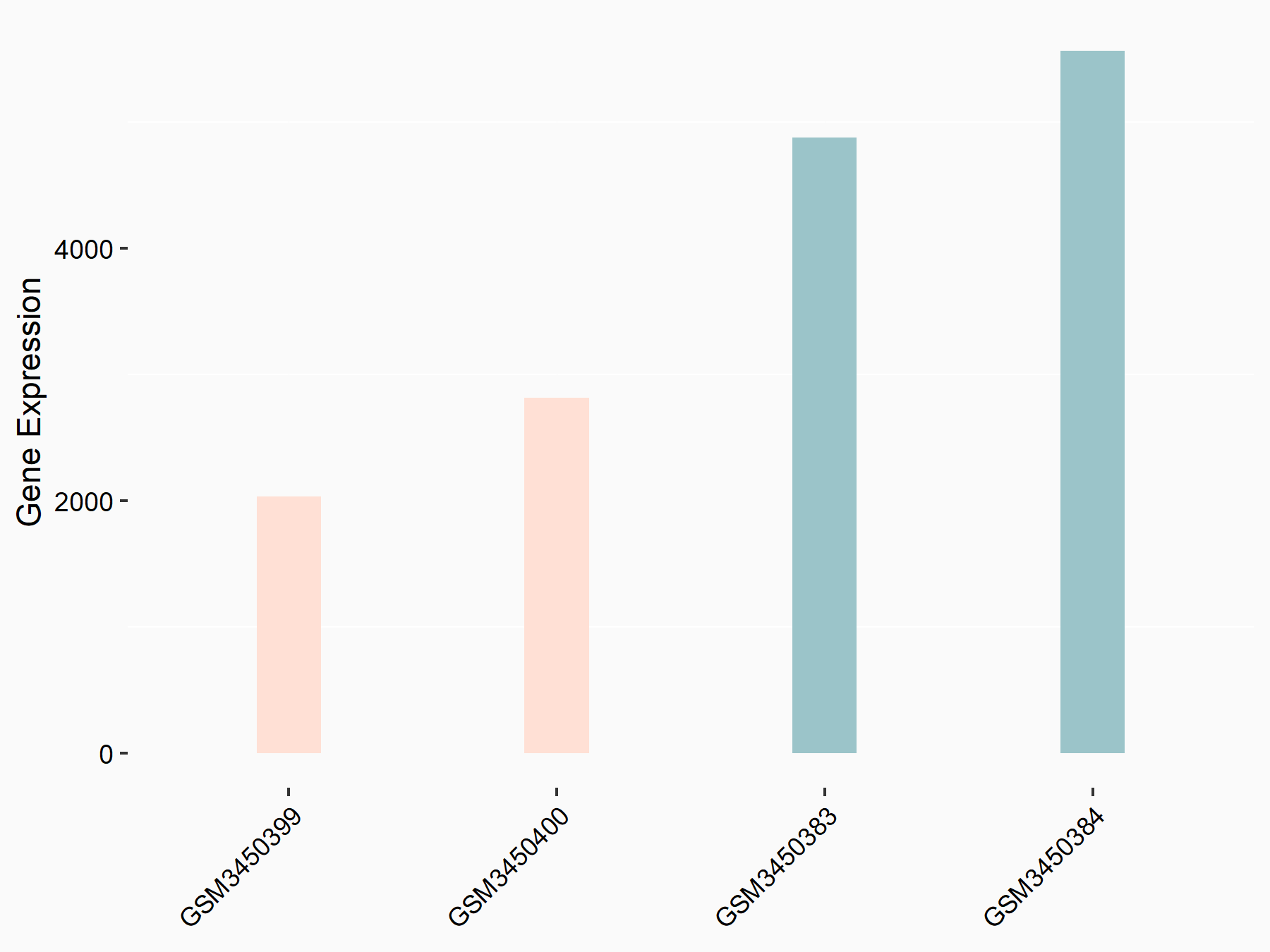 |
logFC: -1.11E+00 p-value: 3.96E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pertuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Trastuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Tucatinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
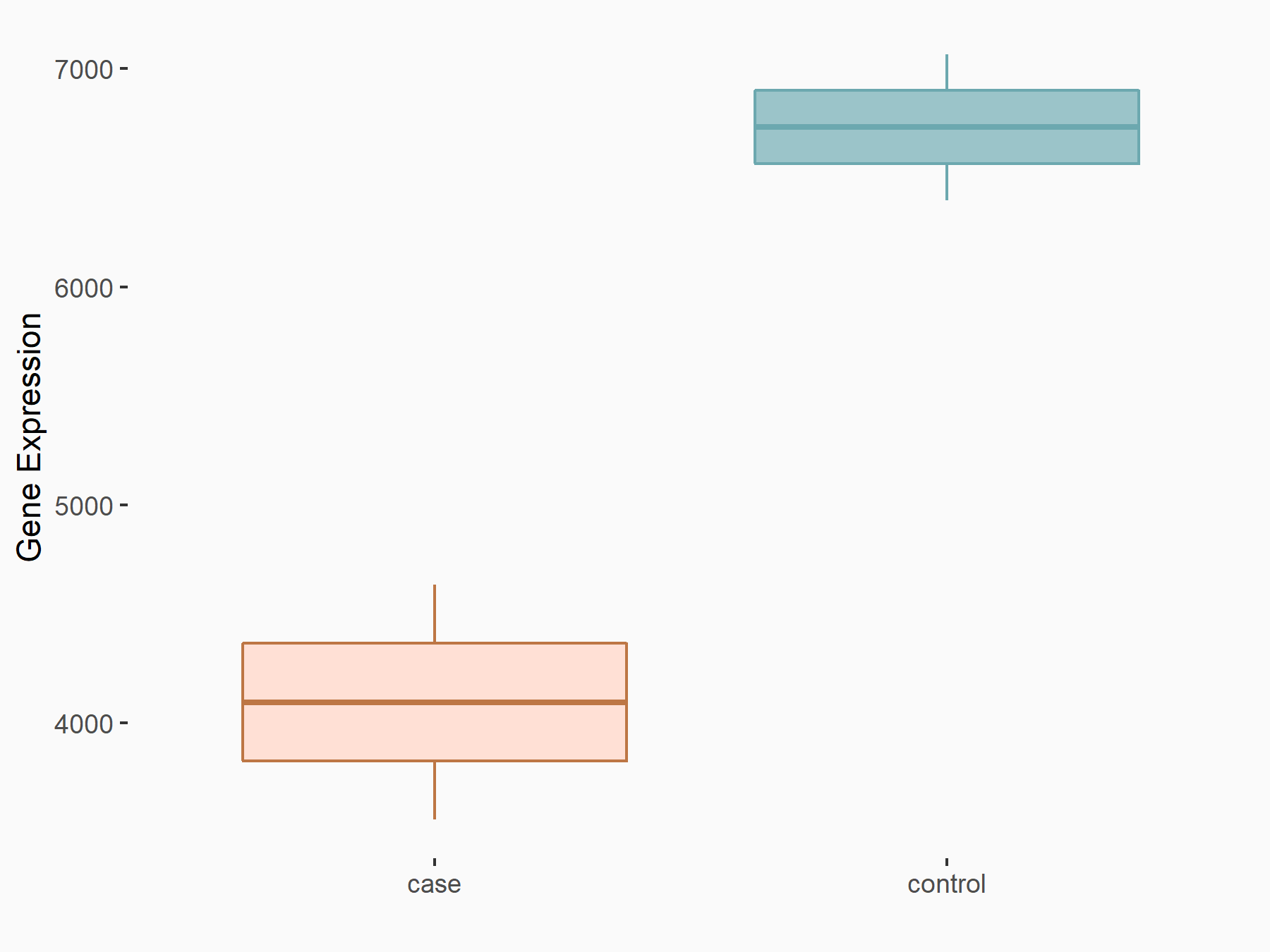 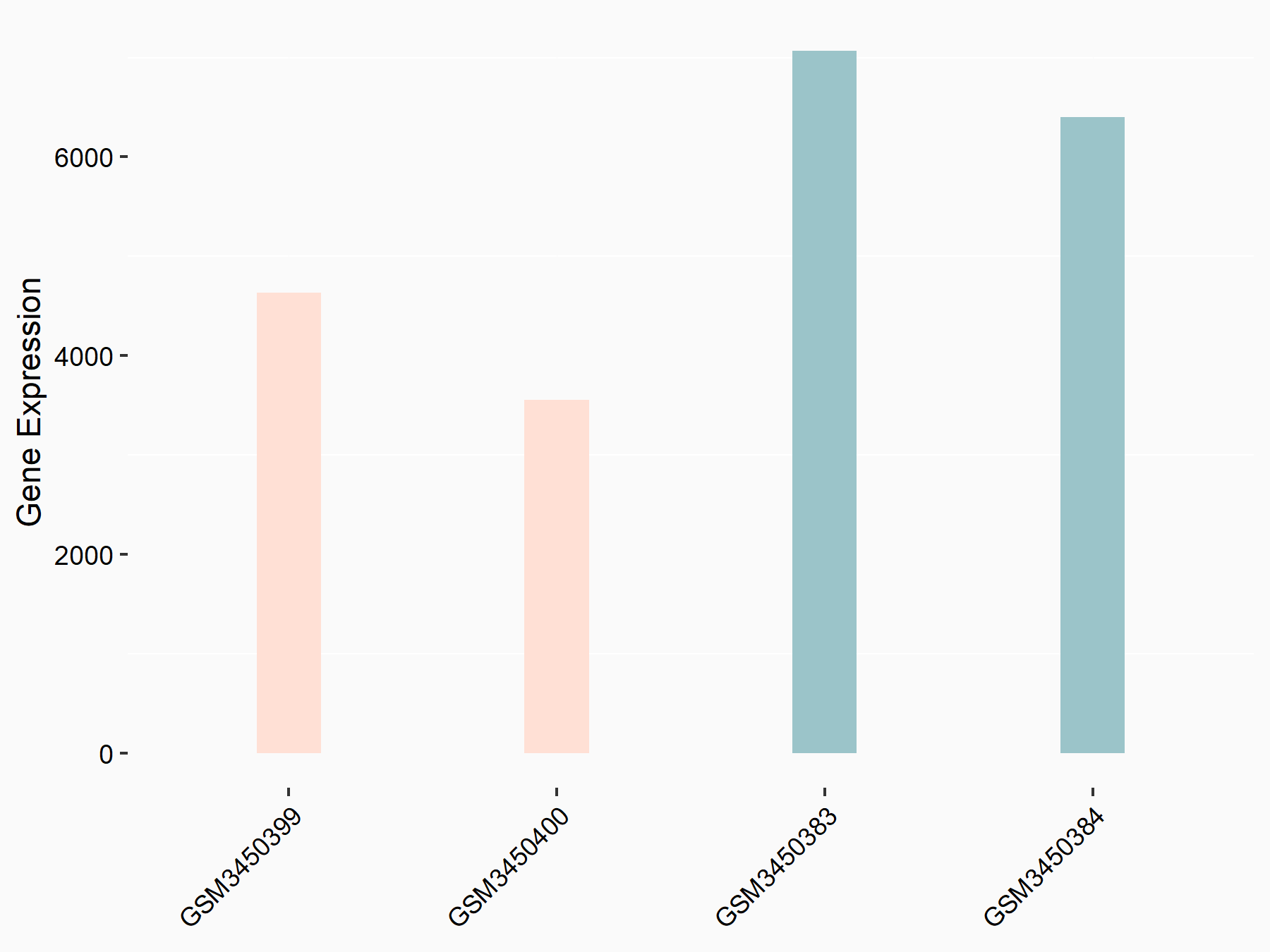 |
logFC: -7.17E-01 p-value: 3.71E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pertuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Trastuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Tucatinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
 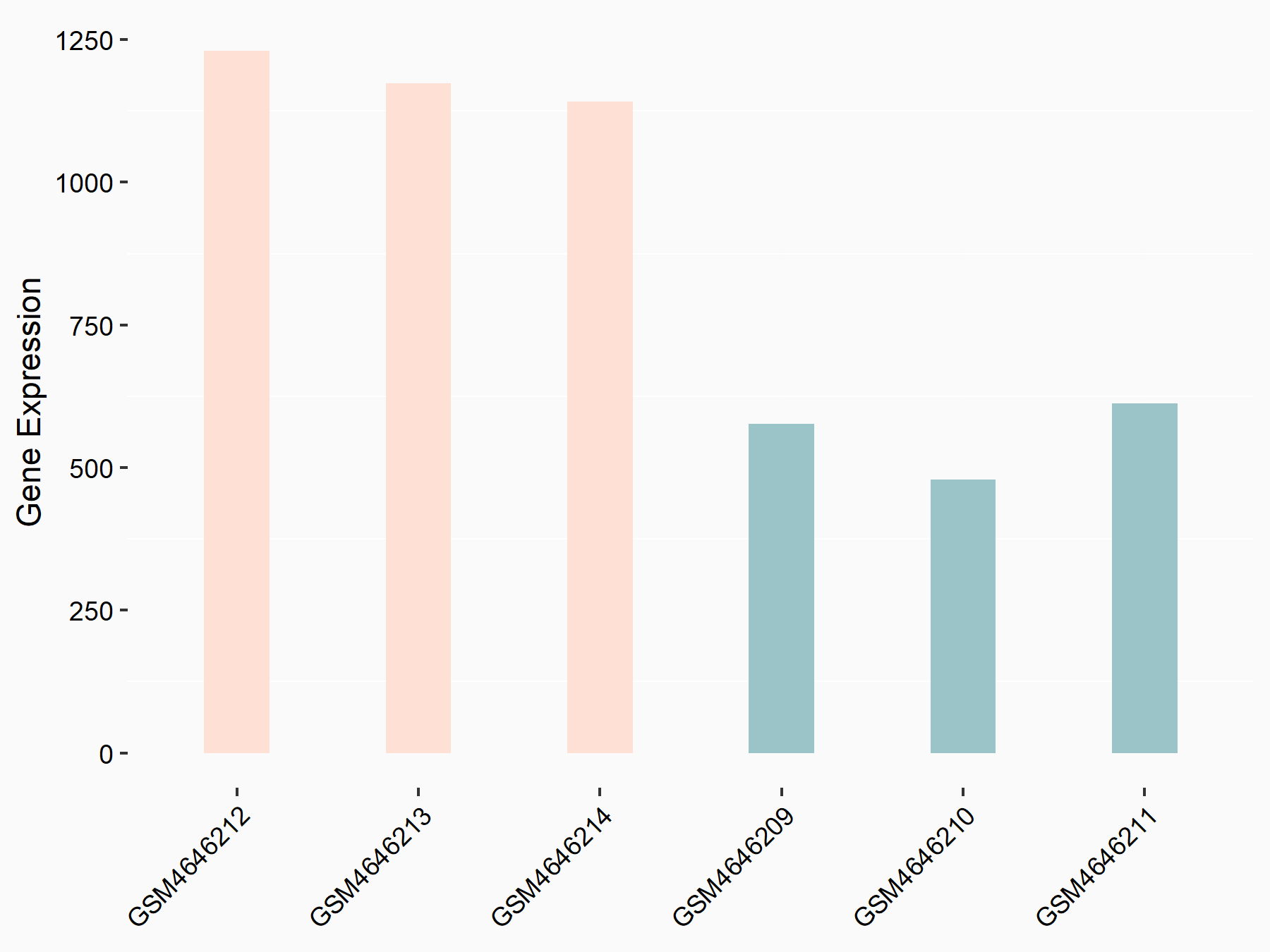 |
logFC: 1.08E+00 p-value: 1.69E-24 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pertuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B) and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Trastuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B) and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Tucatinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B) and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/FPN1 signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-gamma (HNF3gamma/FOXA3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
 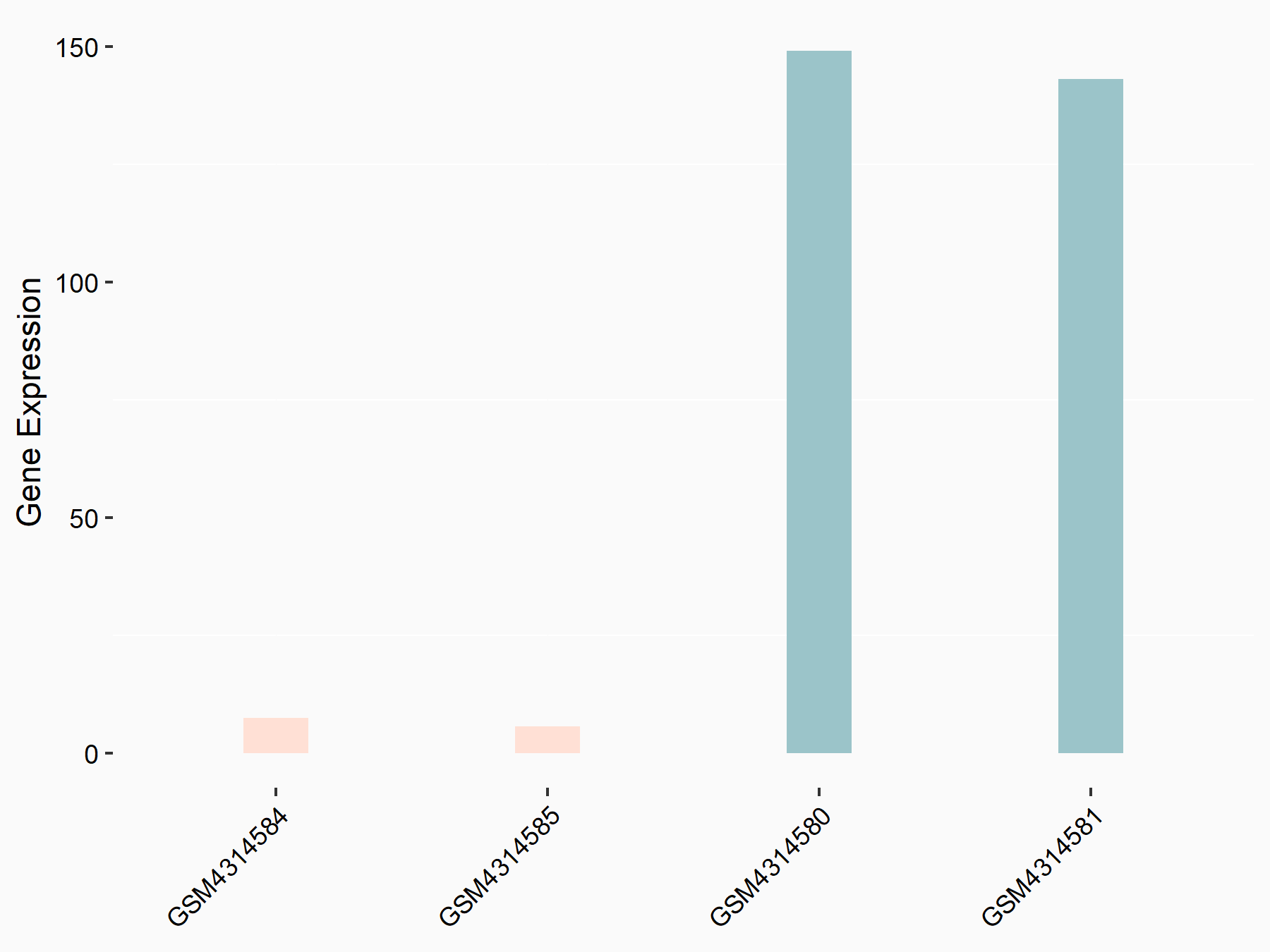 |
logFC: -4.46E+00 p-value: 6.08E-19 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Sorafenib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Membrane transport | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| In-vivo Model | When xenografted tumor growth reached 500 mm3, the mice were subjected to intratumoral injection of Ad-con or Ad-HNF3γ every other day. For the PDX model, fresh patient HCC tissues were cut into fragments with a volume of 3 × 3 mm3 and then implanted subcutaneously into the flanks of nude mice. The mice were given sorafenib (30 mg/kg) or vehicle orally twice a week for 24 days. | |||
| Response Summary | The Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-gamma (HNF3gamma/FOXA3) reduction in hepatocellular carcinoma could be mediated by METTL14-dependent m6A methylation of HNF3-Gamma mRNA. HNF3-Gamma plays an essential role in HCC differentiation and serves as a therapeutic target and predictor of sorafenib benefit in patients. | |||
Meltrin-beta (ADAM19)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
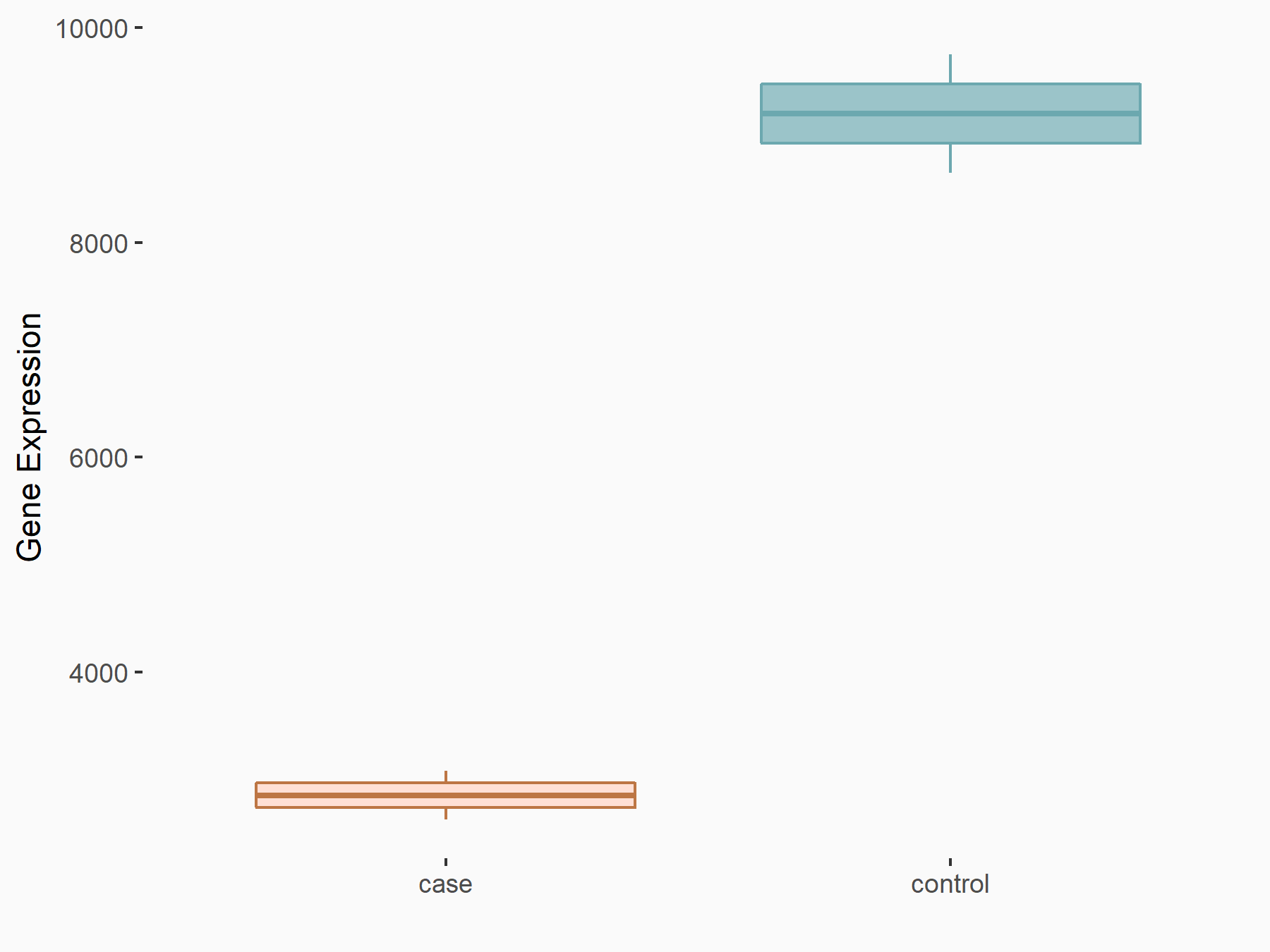 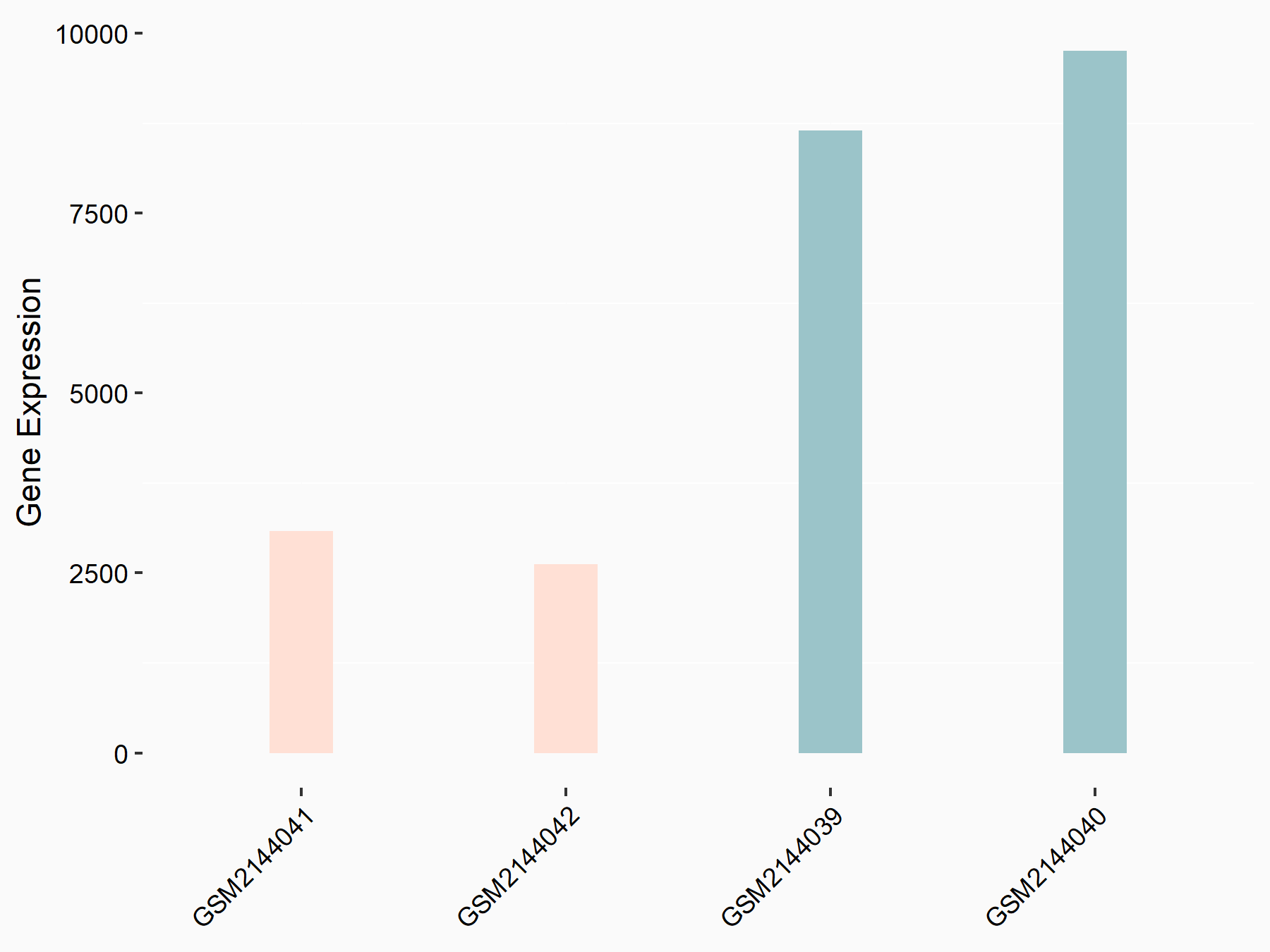 |
logFC: -1.69E+00 p-value: 2.38E-31 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [31] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma | ICD-11: 2A00.00 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cells growth | |||
| Cells self-renewal | ||||
| Tumorigenesis | ||||
| MicroRNAs in cancer (hsa05206) | ||||
| In-vitro Model | GSC | Glioma | Epinephelus akaara | CVCL_M752 |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 105 dissociated cells in 2 uL PBS were injected into the following site (anteroposterior [AP] +0.6 mm, mediolateral [ML] +1.6 mm, and dorsoventricular [DV] 2.6 mm) with a rate of 1 uL/min. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of METTL3 or METTL14 induced changes in mRNA m6A enrichment and altered mRNA expression of genes (e.g., Meltrin-beta (ADAM19)) with critical biological functions in GSCs. Treatment with MA2, a chemical inhibitor of FTO, dramatically suppressed GSC-induced tumorigenesis and prolonged lifespan in GSC-grafted animals. | |||
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
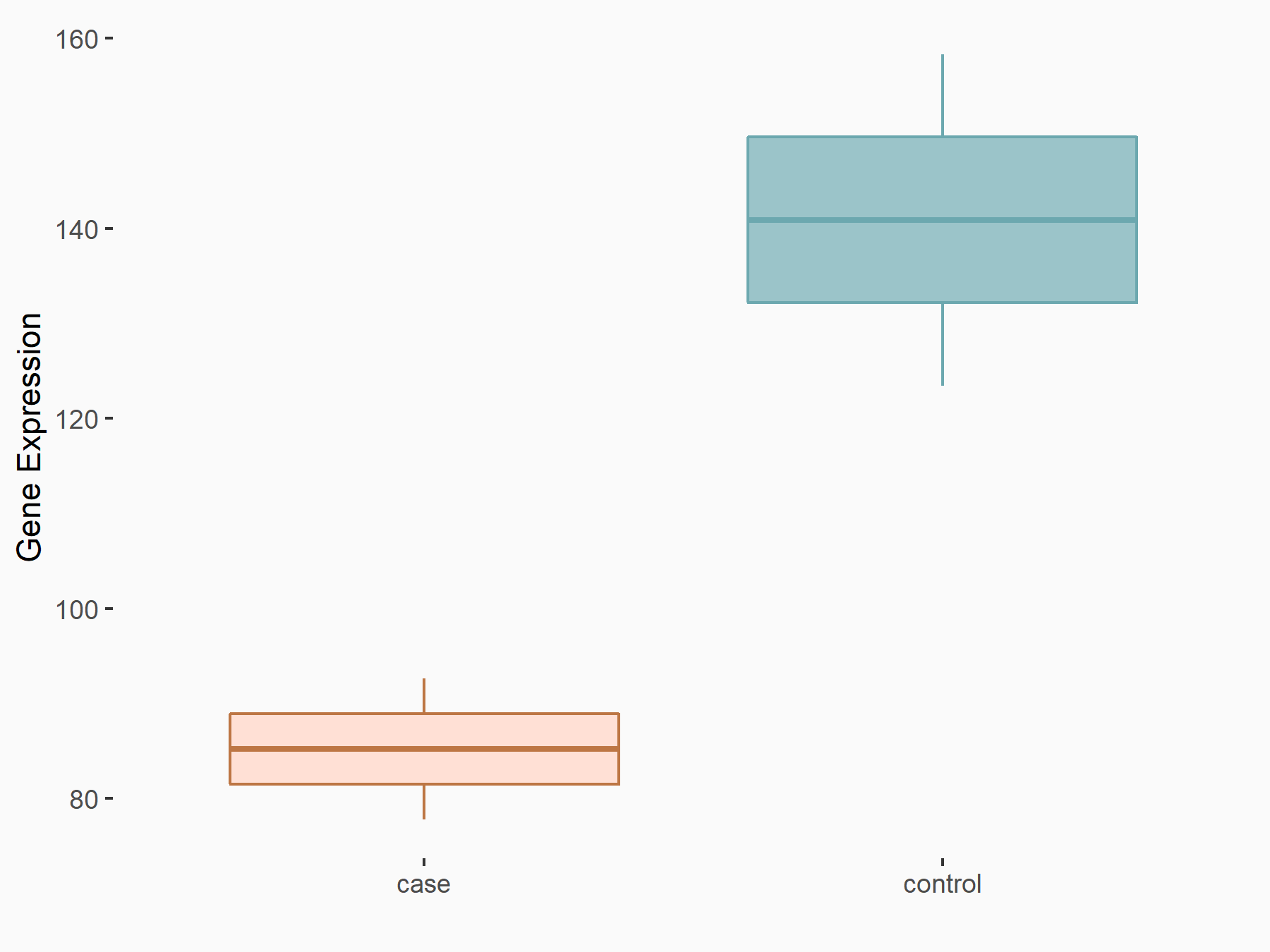 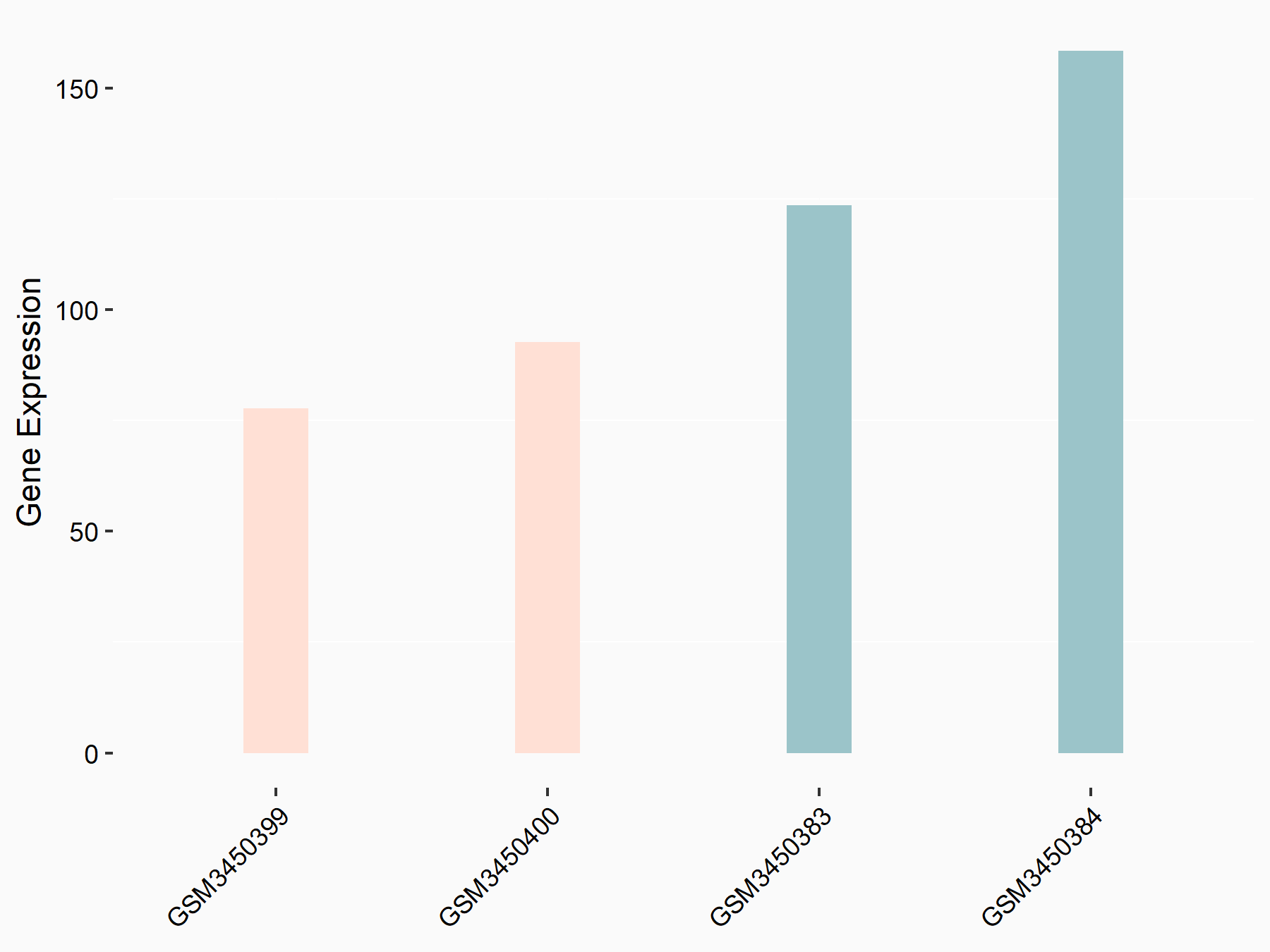 |
logFC: -7.26E-01 p-value: 1.60E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Doxil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [37] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease | ICD-11: GB61.Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | Conditionally immortalized human podocytes (Podocytes) | |||
| In-vivo Model | To establish mice model with ADR nephropathy, adult male C57BL/6J mice (8-12 weeks of age) were purchased from Animal Center of Fudan University and injected with 19.5 mg/kg ADR (D1515, Sigma-Aldrich, St-Louis, MO, USA) intravenously via tail vein. | |||
| Response Summary | The elevated m6A RNA levels and the most upregulated METTL14 expression in kidneys of mice with adriamycin and diabetic nephropathy. METTL14-dependent RNA m6A modification contributes to podocyte injury through posttranscriptional regulation of NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) mRNA, which provide a potential approach for the diagnosis and treatment of podocytopathies. | |||
PI3-kinase subunit beta (PIK3CB)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
 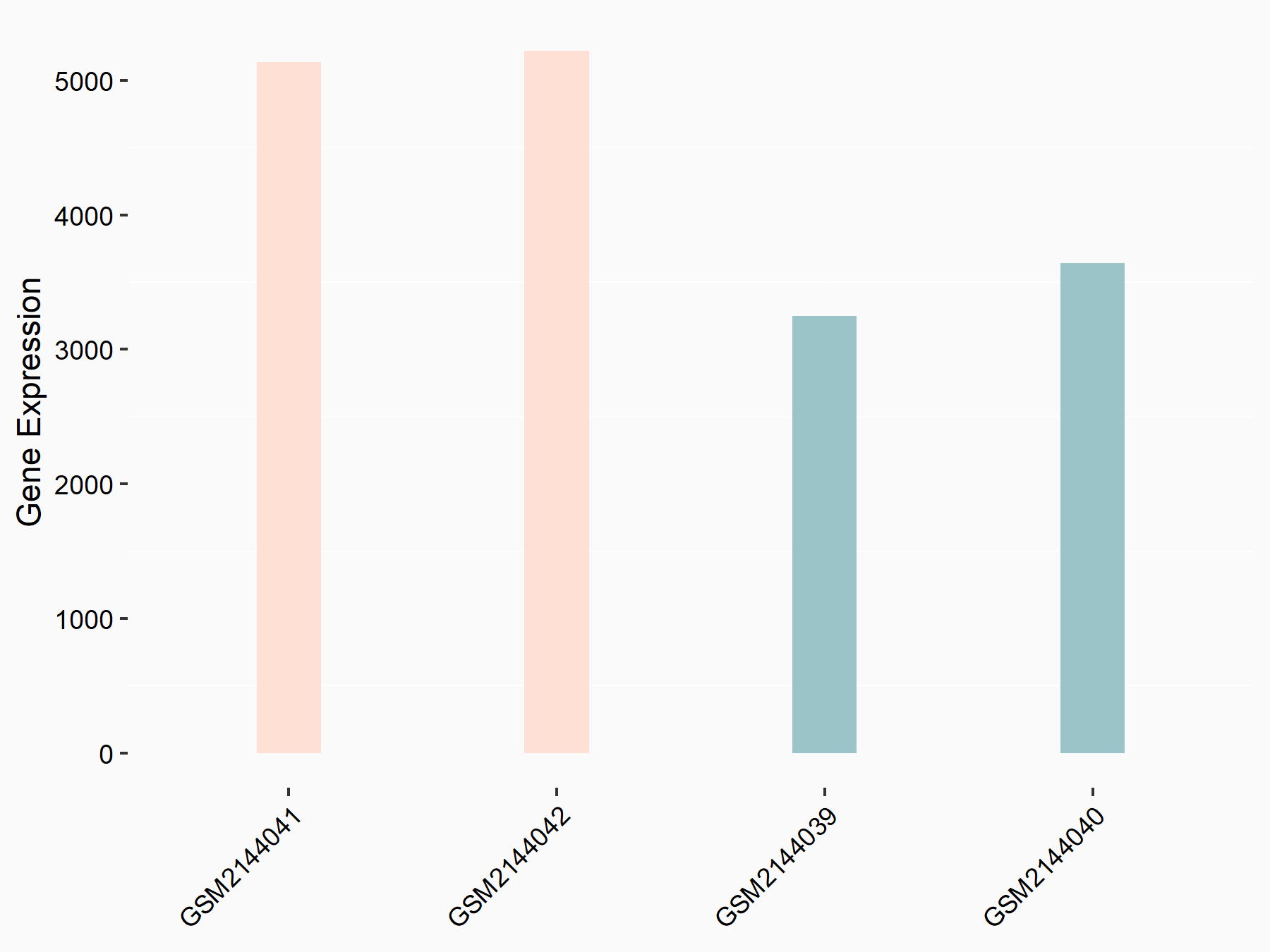 |
logFC: 5.88E-01 p-value: 1.08E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
AZD6482
[Terminated]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [44] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
| In-vitro Model | BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| In-vivo Model | Established cohorts of mice bearing tumour xenografts driven by PTEN-deficient BxPC-3 and PANC-1 cells with PIK3CB overexpression. When tumours grew to ~300 mm3, mice were grouped and administered with vehicle (DMSO) or KIN-193 via intraperitoneal injection (20 mg/kg) once daily. | |||
| Response Summary | N6-methyladenosine mRNA methylation of PIK3CB regulates AKT signalling to promote PTEN-deficient pancreatic cancer progression. Rs142933486 is significantly associated with the overall survival of PDAC by reducing the PIK3CB m6A level, which facilitated its mRNA and protein expression levels mediated by the m6A 'writer' complex (METTL13/METTL14/WTAP) and the m6A 'reader' YTHDF2. KIN-193, a PI3-kinase subunit beta (PIK3CB)-selective inhibitor, is shown to serve as an effective anticancer agent for blocking PTEN-deficient PDAC. | |||
Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | HepG2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL14 HepG2 cells
Control: shCtrl HepG2 cells
|
GSE121949 | |
| Regulation |
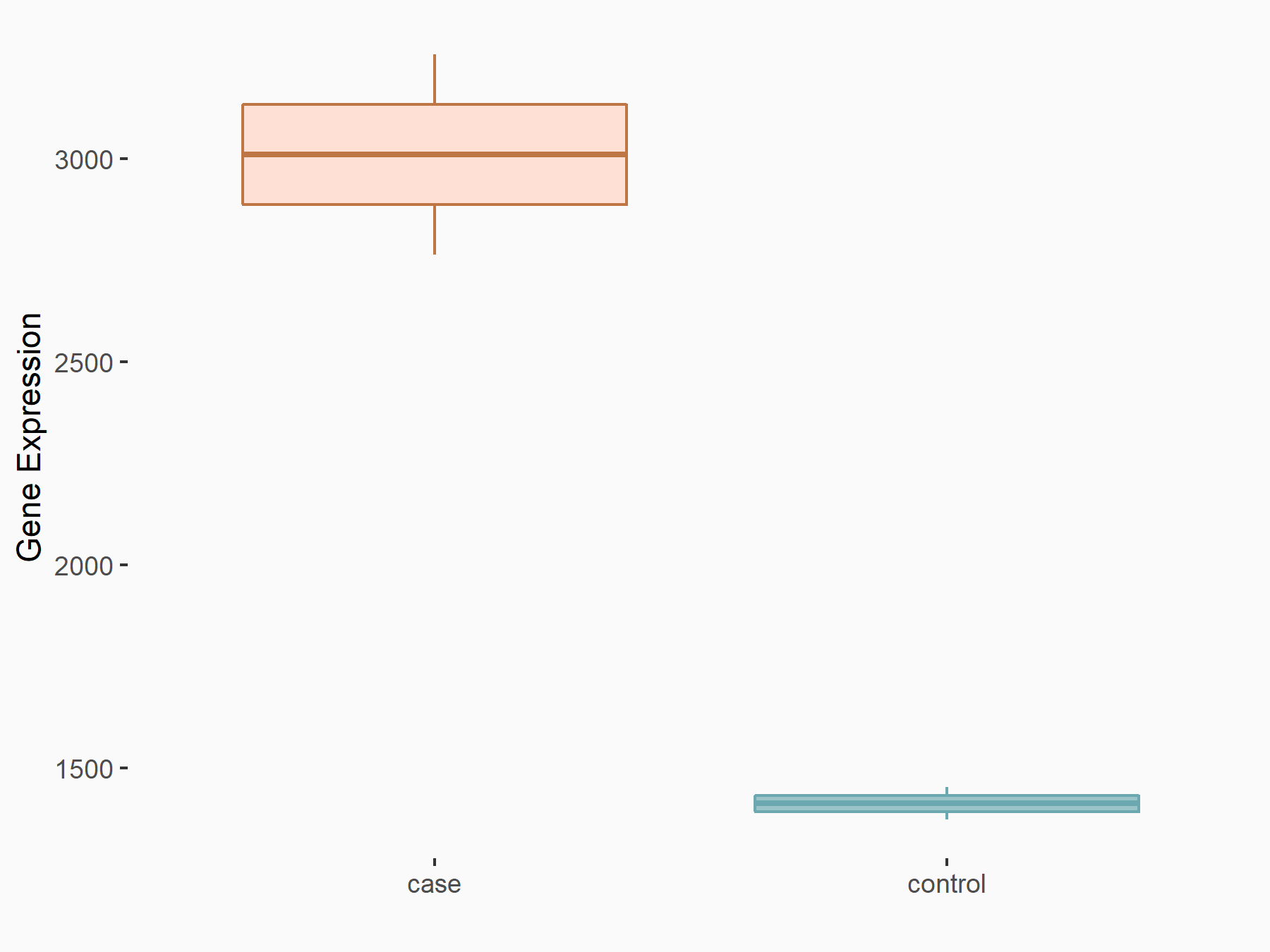 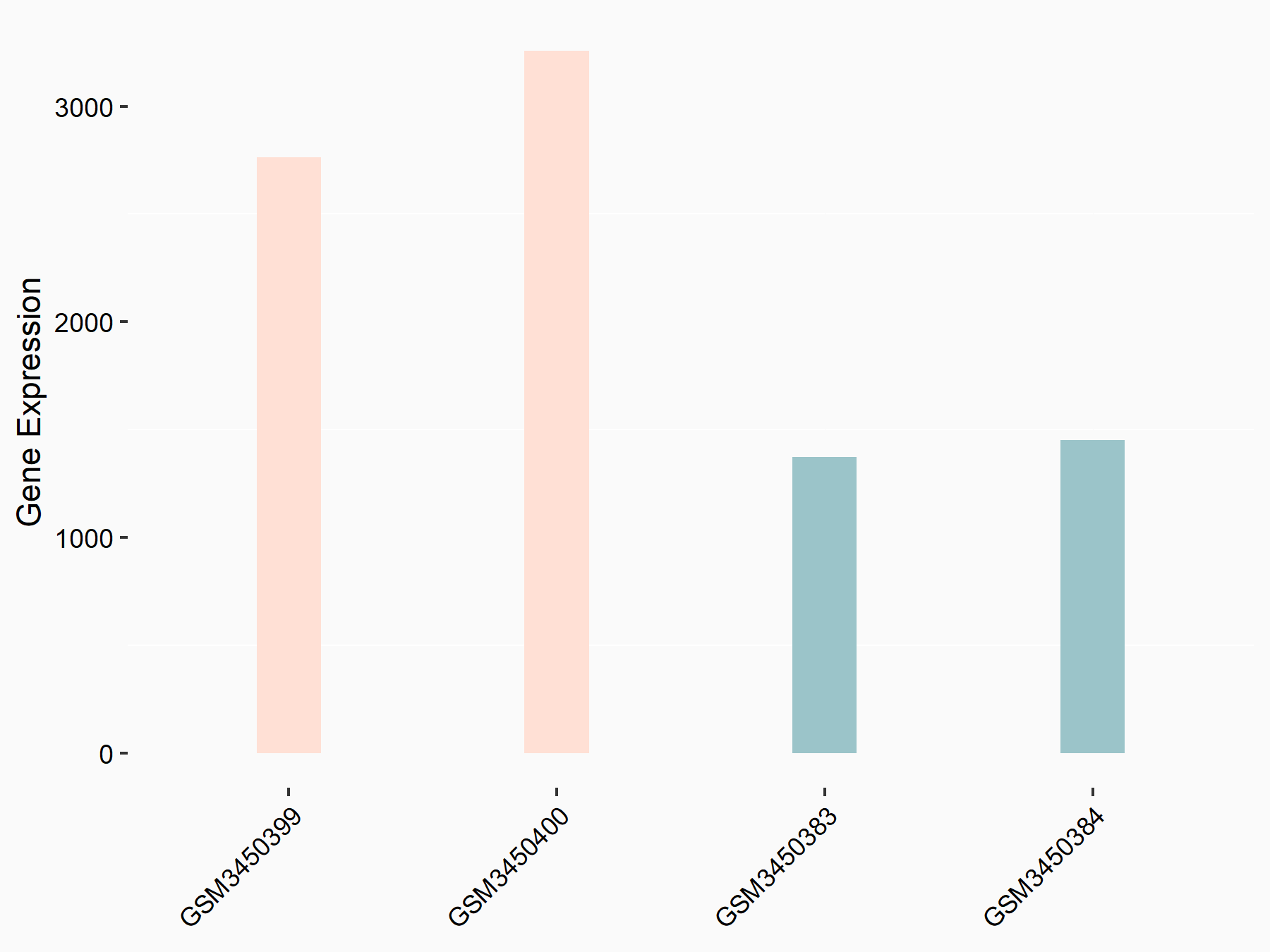 |
logFC: 1.09E+00 p-value: 8.51E-14 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pertuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1) signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Trastuzumab
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1) signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
Tucatinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutathione synthesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ZR-75-1 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-361 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | |
| AU565 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1074 | |
| In-vivo Model | Luciferase-labeled rSKBR3 and MDA-MB-361 cells (1 × 107 cells) mixed with 1:1 Matrigel (Corning, 356237) were subcutaneously injected into the fat pads of mice. After a tumor was palpable, the mice were randomized into four groups (five mice per group), and they were treated with vehicle, trastuzumab (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration), roblitinib (30 mg/kg, oral administration), or a combination of both drugs. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-hypomethylation regulated FGFR4 phosphorylates GSK-3beta and activates beta-catenin/TCF4-SLC7A11/Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1) signaling to drive anti-HER2 resistance. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly increased the expression level of FGFR4 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. FGFR4 reduced the sensitivity of HER2-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab plus pertuzumab or tucatinib. These results pinpoint a mechanism of anti-HER2 resistance and provide a strategy for overcoming resistance via FGFR4 inhibition in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. | |||
TNF receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
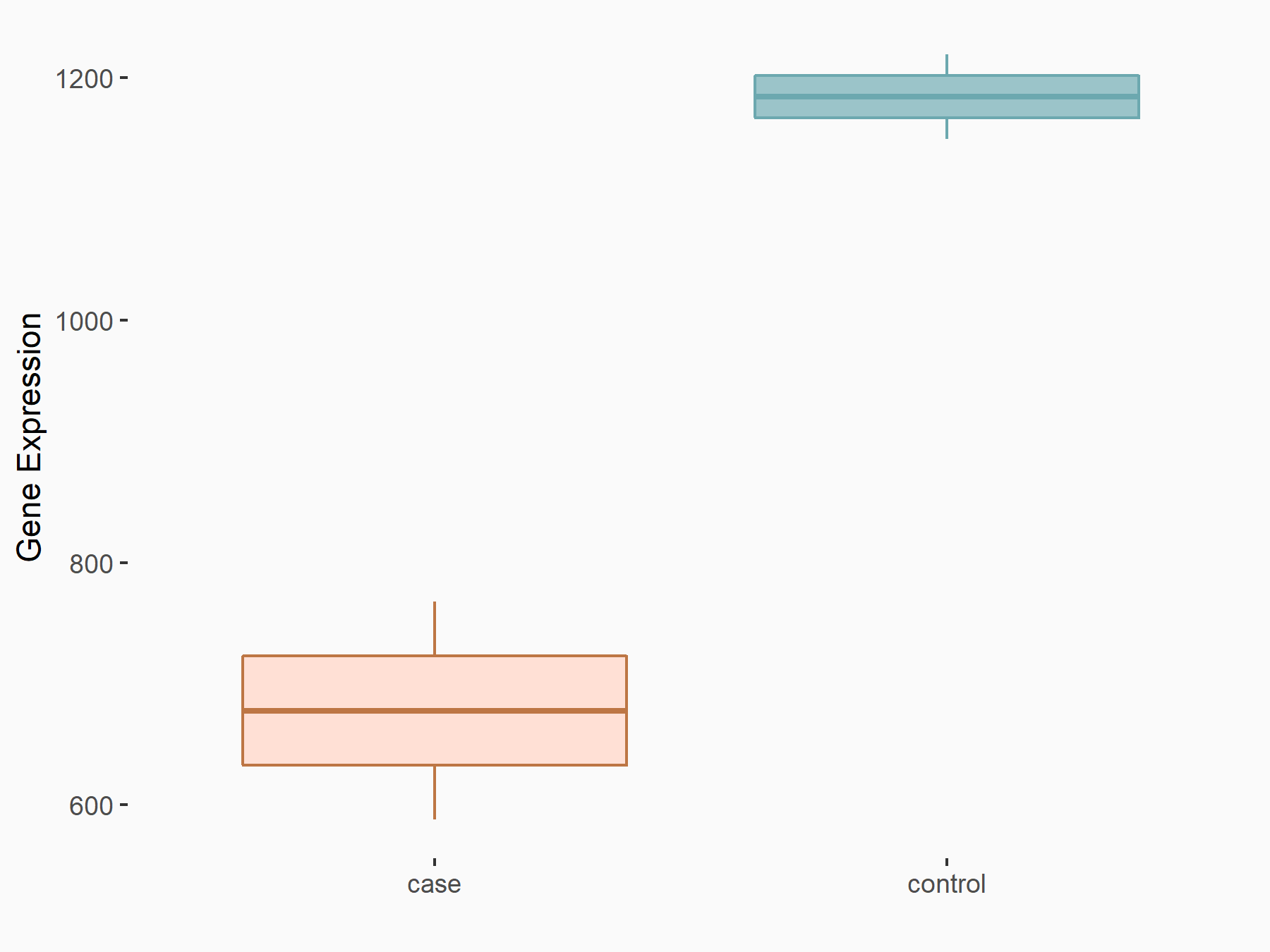 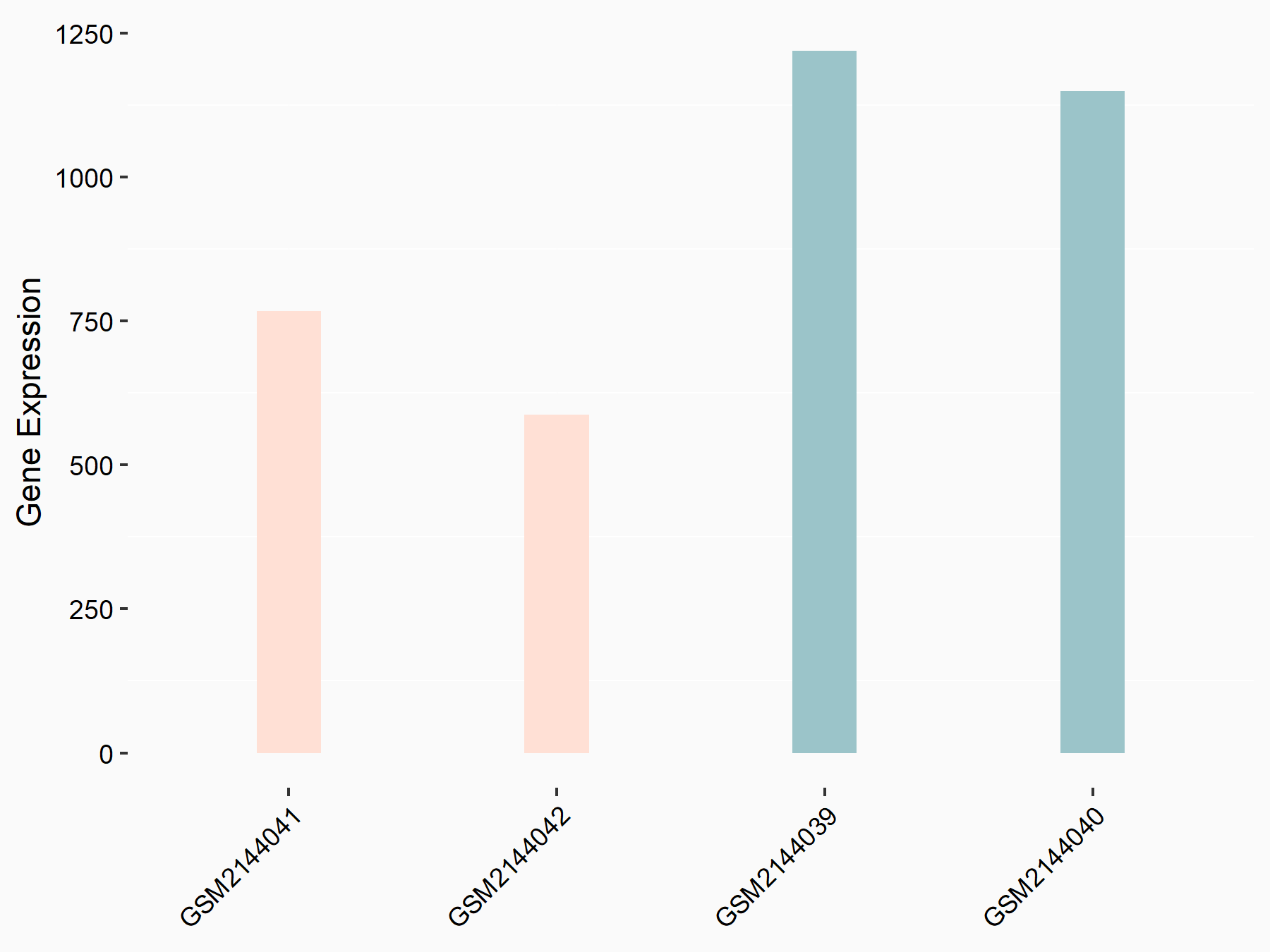 |
logFC: -8.04E-01 p-value: 5.72E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Sunitinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [50] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C90 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | OS-RC-2 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1626 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the xenograft tumor model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 100 uL PBS were subcutaneously inoculated in the right flank of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. For the ccRCC orthotopic implantation model, approximately 1 × 106 ccRCC cells suspended in 30 uL Matrigel were injected under the renal capsule of 5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 6 weeks, the anesthetized mice were intraperitoneally injected with D-luciferin (Yeason) and imaged using an in vivo imaging system to detect tumor growth and metastasis. For the lung metastasis model, approximately 5 × 105 ccRCC cells suspended in PBS were injected into the tail vein of 5-week-old mice. After 6-8 weeks, mice were anesthetized and lung metastasis was imaged as above. | |||
| Response Summary | In renal cell carcinoma, overexpression of TNF receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) promotes sunitinib resistance by modulating apoptotic and angiogenic pathways in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
 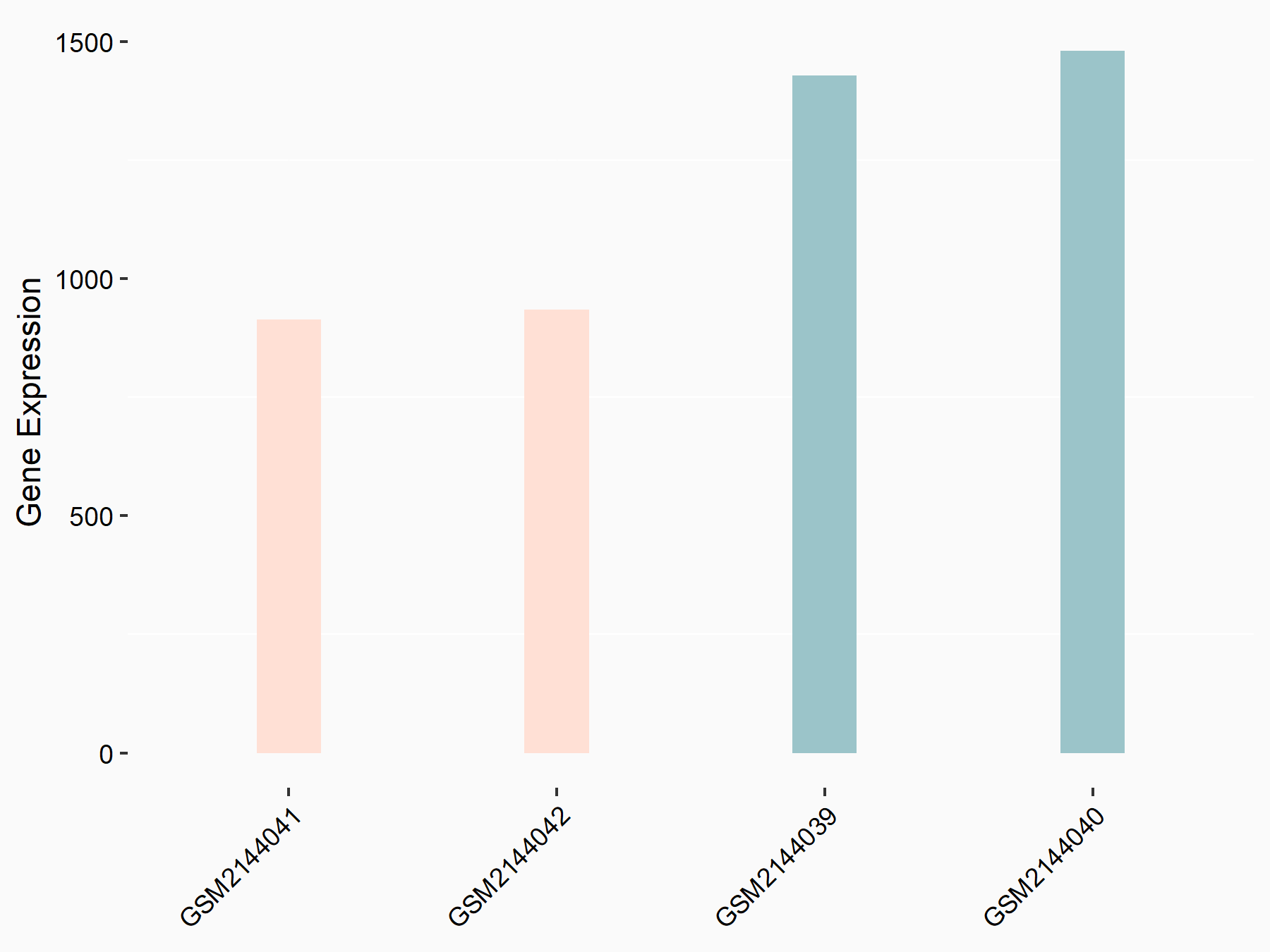 |
logFC: -6.53E-01 p-value: 4.62E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
Doxil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
Olaparib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP)
Regorafenib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [68] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | After one week of acclimatization, the nude mice were randomly divided into 5 groups (n = 3): Control, vehicle + oe-NC, vehicle + oe-CHOP, Regorafenib + oe-NC, and Regorafenib + oe-CHOP. The Control group was injected with untreated SK-Hep-1 cells. The vehicle + oe-NC group and Regorafenib + oe-NC group were injected with SK-Hep-1 cells transfected with oe-NC. vehicle + oe-CHOP group and Regorafenib + oe-CHOP group were injected with SK-Hep-1 cells transfected with oe-CHOP. | |||
Pancreas/duodenum homeobox protein 1 (Pdx1)
Bisphenol F
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [83] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1a/PPARGC1A)
Arsenite
[Phase 2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [85] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic | ICD-11: 5A14 | ||
| In-vitro Model | L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 |
Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)
Paclitaxel
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
STM2457
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3)
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [115] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Protein export | hsa03060 | ||
| Cell Process | Eukaryotic translation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| RT-4 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0036 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | Chose 4-week-old female BALB/c nude mice for tumor xenograft experiments, which randomly were divided into four groups (n = 5 per group). Bladder cancer cells (3 × 106) were subcutaneously injected into the right axilla of the nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | Circ0008399 bound WTAP to promote formation of the WTAP/METTL3/METTL14 m6A methyltransferase complex, reduce cisplatin sensitivity in bladder cancer, implicating the potential therapeutic value of targeting this axis. | |||
C-C motif chemokine 5 (CCL5)
Fentanyl
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [124] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gestational diabetes mellitus | ICD-11: JA63 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 |
| Capan-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0237 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
Calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (CALCOCO1)
Paclitaxel
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
STM2457
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | The experimental mice were housed in an SPF-grade animal laboratory at a temperature of approximately 25 °C, a humidity range of 50%, and an average daylight duration of 12 h. BALB/C female mice at 5-7 weeks of age were taken and prepared for tumor-bearing. After the mice were sacrificed, their tissues were collected, weighed and immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. | |||
Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2)
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [133] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer | ICD-11: 2B70 | ||
| In-vitro Model | TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| In-vivo Model | The KYSE-150 cells were subcutaneously inoculated on the right side at a dosage of 106 cells per mouse. After the tumor grew to approximately 50 mm3, mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 6): Control, CisR-exo, Cis, and Cis + CisR-exo. Then, normal saline or cisplatin (20 mg/kg; twice a week) was intratumorally injected alone or combined with CisR-exos (10 μg; once every two days). | |||
Hamartin (TSC1)
Coptisine
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [135] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ulcerative colitis | ICD-11: DD71 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
| In-vivo Model | Sixty mice were disposed in 6 groups randomly by using spss25.0 software after an adaption period of one week (n = 10): control, DSS model, 5-ASA (200 mg/kg) +DSS, coptisine 25 mg/kg + DSS (COP-l), coptisine 50 mg/kg + DSS (COP-M) and coptisine 100 mg/kg + DSS (COP-H). The dosages of 5-ASA and COP were implemented in accordance with the previous report. | |||
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR)
MM-102
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [137] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Disorders due to use of opioids | ICD-11: 6C43.1 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 (MAPK13)
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [148] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | 621-101 | Lung lymphangioleiomyomatosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S879 |
|
HEK293-EBNA
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6974 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| UMB1949 | Kidney angiomyolipoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C471 | |
Neurotrophic factor BDNF precursor form (BDNF)
Xuefu Zhuyu decoction
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [149] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury induced by controlled cortical impact injury | ICD-11: NA07 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (body weight 220 g-250 g) were acquired from Hunan Silaike Jingda Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (Changsha, China, license No. SCXK (XIANG) 2016-0002). They were housed under specific pathogen-free conditions in the Department of Laboratory Animals, Central South University (Changsha, China, license No. SYXK (XIANG) 2015-0017). All rats were kept in air-conditioned animal quarters under standard conditions (50 ± 10% relative humidity, 12-h light/dark cycle, 22 ± 2 °C), with ad libitum water and food. | |||
pri-miR-17
Fluorouracil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [157] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 | |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| NCM460 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0460 | |
Protein disulfide-isomerase (P4HB)
ICARIIN
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [159] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis | ICD-11: FB83.1 | ||
| In-vivo Model | After anesthesia with ketamine-xylazine(intraperitoneal injection, 60 and 5 mg/kg, respectively), the rats were operated to remove the bilateral ovaries. For the rats in the Sham group, only the fat around the ovaries was surgically removed. Four weeks after the operation, the animals were orally treated with ICA (250 mg/kg) daily for 10 weeks . | |||
Pseudorabies Virus (PRV)
3-deazidenosine
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [160] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rabies | ICD-11: 1C82 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model |
PK-15
|
N.A. | Sus scrofa | CVCL_2160 |
SREBF2 antisense RNA 1 (SREBF2-AS1)
Sorafenib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [166] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| SNU-398 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0077 | |
| THLE-2 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3803 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
TNF and HNRNPL related immunoregulatory long non-coding RNA (THRIL)
LPS
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [168] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of other or unspecified intrathoracic organs | ICD-11: NB32.3 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
Transmembrane protein 127 (TMEM127)
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [171] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Approximately 1 × 106 viable MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were resuspended in 1:1 ratio in 50 μl medium and 50 μl matrigel (Corning, 354234) and injected orthotopically into the fourth mammary fat pad of each mouse. After injection, tumor size was measured twice a week using an electronic caliper. Tumor volumes were calculated with the formula: volume = (L × W2)/2, where L is the tumor length and W is the tumor width measured in millimeters. | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Arsenite
[Phase 2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [177] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HBE (Human bronchial epithelial cell line) | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification on RNA was significantly increased in arsenite-transformed cells and this modification was synergistically regulated by METTL3, METTL14, WTAP and FTO. Demonstrated the significant role of m6A in the prevention of tumor occurrence and progression induced by arsenite. | |||
Gemcitabine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [183] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| In-vitro Model | PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| Hs 766T | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0334 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | |
| In-vivo Model | NOD/SCID mice (6-week-old) were injected (subcutaneously in both flanks) with 5.0 x 106 PANC-1 GemR cells (infected with scr or METTL14 shRNA) per mouse suspended in 50 ul PBS and mixed with equal volume of growth factor reduced matrigel. One week after injection, we started measuring tumor size at the indicated times. Tumor size was calculated by 0.5 × (long diameter) × (short diameter)2. The mice were treated with vehicle or 100 mg/kg gemcitabine intraperitoneally twice a week. | |||
| Response Summary | Suppression of METTL14 obviously increased the sensitivity of gemcitabine in resistant cells. This study suggested that METTL14 is a potential target for chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. | |||
Tamoxifen
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [192] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glucose Intolerance | ICD-11: 5C61.Y | ||
| In-vitro Model | MIN6 | Mouse insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were fed a normal chow diet (Harlan Teklad) and maintained in a standard 12-hour light/12-hour dark cycle. At the age of 10 weeks, both male and female mice were intraperitoneally injected with 250 L (20 mg/mL) tamoxifen every other day for three times to delete Mettl14 in Beta-cells. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests were performed on mice at the age of 15 weeks after a 5-hour fast (2 g/kg dextrose). Insulin levels were measured at 0, 15, and 30 minutes after glucose challenge by using the Ultra Sensitive Mouse Insulin ELISA Kit .Insulin tolerance tests were performed after a 5-hour fast by administering human recombinant insulin (0.75 U/kg). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 deficiency in beta-cells induces glucose intolerance and a decrease in insulin secretion.To define the role of m6A in regulating the beta-cell function, the study generated beta-cell METTL14-specific knockout (beta-KO) mice by tamoxifen administration. beta-cell mass in beta-KO mice was related to beta-cell proliferation and also observed elevated mRNA and protein levels of Ire1-alpha and sXBP-1 in beta-KO islets. | |||
Betaine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [193] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Epilepsy due to structural or metabolic conditions or diseases | ICD-11: 8A60.5 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated with a single i.p. injection of pentylenetetrazol (PTZ, Sigma-Aldrich, P6500) at a dose of 50 mg/kg to establish the animal model of acute seizures [16]. Betaine (Sigma-Aldrich, B2629) was dissolved in normal saline, and administrated at a dose of 200 mg/kg or 600 mg/kg, i.p., to mice for 15 days before PTZ injection in reference to a previous study. | |||
Sunitinib
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [196] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| In-vitro Model | hiPSCs (Urinary epithelial cell-derived hiPSCs) | |||
| CMECs (Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells ) | ||||
| CFs (Cardiac Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Response Summary | The RNA demethylase FTO was downregulated, whereas METTL14 and WTAP were upregulated. Furthermore, gain- and loss-of-function studies substantiated that FTO is cardioprotective in TKI(Sunitinib). | |||
Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [197] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility | ICD-11: GB04 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In-vitro Model | GC-1 spg | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_8872 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mouse GC-1 spg cells were treated with the ester form of meclofenamic acid (MA2) to inhibit the demethylase activity of FTO. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, METTL14, ALKBH5 and YTHDC2 are involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis. MA2 affected CDKs expression through the m6A-dependent mRNA degradation pathway, and thus repressed spermatogonial proliferation. Additionally, mutation of the predicted m6A sites in the Cdk2-3'UTR could mitigated the degradation of CDK2 mRNA after MA2 treatment. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
RNA modification
m6A Target: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00002 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA cytosine C(5)-methyltransferase NSUN2 (NSUN2) | |
| Regulated Target | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
m6A Target: Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00413 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00414 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00448 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 214 (MIR214) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00512 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-mir-18a | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
m6A Target: X inactive specific transcript (XIST)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00427 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00428 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
m6A Target: Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00435 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyltransferase-like protein 1 (METTL1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 125a (MIR125A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m7G | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00440 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 214 (MIR214) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00474 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 181a-1 (MIR181A1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00476 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 155 (MIR155) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
m6A Target: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00444 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 214 (MIR214) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
m6A Target: High mobility group protein HMGI-C (HMGA2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00467 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 149 (MIR149) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00468 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyltransferase-like protein 1 (METTL1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 149 (MIR149) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m7G → m6A | |
m6A Target: KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00471 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 149 (MIR149) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00472 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyltransferase-like protein 1 (METTL1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 149 (MIR149) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m7G | |
m6A Target: NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00482 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-mir-22 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6Am → m6A | |
m6A Target: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B/p27)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00497 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 222 (MIR222) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00498 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 222 (MIR222) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
m6A Target: Fascin (FSCN1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00542 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 200b (MIR200B) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00543 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 200b (MIR200B) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor SOX-6 (SOX6)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00554 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 122 (MIR122) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-34a
| In total 13 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00611 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 (CCNE1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00612 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 (CCNE1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00613 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET1 (TET1) | |
| Regulated Target | G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 (CCNE1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00614 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00615 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Zinc finger protein SNAI1 (SNAI1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00616 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET3 (TET3) | |
| Regulated Target | Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00617 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00618 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00619 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Pseudouridylate synthase 1 homolog (PUS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Pseudouridine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00620 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | THO complex subunit 4 (ALYREF) | |
| Regulated Target | N-myc proto-oncogene protein (MYCN) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00621 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | Cytochrome c, somatic (CYCS) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00622 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00623 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
m6A Target: microRNA 126 (MIR126)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00624 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00625 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase alkB homolog 3 (ALKBH3) | |
| Regulated Target | Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m1A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00626 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyltransferase-like protein 1 (METTL1) | |
| Regulated Target | Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m7G | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00627 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
m6A Target: hsa-mir-146a
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00628 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00629 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00630 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | THO complex subunit 4 (ALYREF) | |
| Regulated Target | Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00631 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00632 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6Am → m6A | |
m6A Target: microRNA 375 (MIR375)
| In total 6 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00657 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00658 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit DKC1 (DKC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Pseudouridine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00659 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00660 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00661 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6Am → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00662 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyltransferase-like protein 1 (METTL1) | |
| Regulated Target | High mobility group protein HMGI-C (HMGA2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m7G | |
m6A Target: hsa-mir-19a
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00673 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA cytosine C(5)-methyltransferase NSUN2 (NSUN2) | |
| Regulated Target | H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
DNA modification
m6A Target: Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 (NOTCH2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02045 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 (NOTCH2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
m6A Target: SREBF2 antisense RNA 1 (SREBF2-AS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02099 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET1 (TET1) | |
| Regulated Target | Sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2 (SREBF2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: microRNA 375 (MIR375)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02101 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02102 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02103 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP], mitochondrial (PCK2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02114 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET2 (TET2) | |
| Regulated Target | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP], mitochondrial (PCK2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Hepatic inflammation | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-146a-5p
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02203 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02227 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02251 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02204 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02228 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02252 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02205 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02229 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02253 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)
| In total 9 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02206 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02211 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02219 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02230 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02235 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02243 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02254 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02259 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02267 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
m6A Target: Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 9 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02207 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02212 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02220 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02231 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02236 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02244 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02255 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02260 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02268 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
m6A Target: Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (FPN1)
| In total 9 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02208 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02213 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02221 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02232 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02237 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02245 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02256 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02261 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02269 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
m6A Target: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4)
| In total 9 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02209 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02215 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02222 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02233 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02239 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02246 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02257 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02263 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02270 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
m6A Target: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3Beta/GSK3B)
| In total 9 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02210 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02218 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02223 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02234 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02242 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02247 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02258 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Pertuzumab | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02266 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tucatinib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02271 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Trastuzumab | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8)
| In total 9 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02214 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Olaparib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02216 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Cisplatin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02217 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Adriamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02238 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Olaparib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02240 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Cisplatin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02241 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Adriamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02262 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Olaparib | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02264 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Cisplatin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02265 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Adriamycin | |
m6A Target: Transmembrane protein 127 (TMEM127)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02224 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Rapamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02248 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Rapamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02272 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Rapamycin | |
m6A Target: Calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (CALCOCO1)
| In total 6 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02225 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Paclitaxel | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02249 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Paclitaxel | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02273 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Paclitaxel | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05976 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | STM2457 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05978 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | STM2457 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05980 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | STM2457 | |
m6A Target: Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1)
| In total 6 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02226 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Paclitaxel | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02250 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Paclitaxel | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02274 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Paclitaxel | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05977 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | STM2457 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05979 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | STM2457 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05981 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | STM2457 | |
m6A Target: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06014 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Eomesodermin homolog (EOMES) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
m6A Target: Insulin receptor (INSR)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06016 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin receptor (INSR) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
m6A Target: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06018 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
Histone modification
m6A Target: Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains 1 (CBP)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03007 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03009 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03011 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03008 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03010 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03012 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03016 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05997 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
m6A Target: Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03019 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1A (SETD1A)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03027 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1A (SETD1A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1B (SETD1B)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03028 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1B (SETD1B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03029 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor SOX-4 (SOX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03036 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Protocadherin Fat 4 (FAT4)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03051 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Melanoma of uvea | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03052 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9Ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Melanoma of uvea | |
m6A Target: HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03063 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (KDM1A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 monomethylation (H3K4me1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Disorders due to use of opioids | |
| Drug | MM-102 | |
m6A Target: long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2747 (LINC02747)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03064 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: pri-rRNA
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03098 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03099 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H2 (SUV39H2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03116 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 2A (KDM2A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | |
m6A Target: Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03139 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (KDM1A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 dimethylation (H3K4me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 22 (ANKRD22)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03152 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | |
m6A Target: Amino acid transporter heavy chain SLC3A2 (SLC3A2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03156 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Bifunctional arginine demethylase and lysyl-hydroxylase JMJD6 (JMJD6) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H4 arginine 3 symmetric dimethylation (H4R3me2a) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-5 (ATF5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03157 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03206 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Acute ischemic stroke | |
m6A Target: Homeobox protein Hox-A13 (HOXA13)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03229 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | PHD finger protein 20 (PHF20) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
m6A Target: microRNA 375 (MIR375)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03276 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: X inactive specific transcript (XIST)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03277 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03278 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: C-X-C motif chemokine 9 (Cxcl9)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03279 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: C-X-C motif chemokine 10 (Cxcl10)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03280 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03281 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Interferon regulatory factor 1 (Irf1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03282 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Arrestin domain-containing protein 4 (ARRDC4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03283 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Krueppel-like factor 4 (KLF4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03284 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Polyamine-transporting ATPase 13A3 (ATP13A3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03285 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: pri-miR-17
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03286 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Fluorouracil | |
m6A Target: BET1-like protein (BET1L)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03287 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: JmjC domain-containing protein 8 (JMJD8)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03288 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Zinc finger protein PLAGL2 (PLAGL2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03307 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03308 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: pri-miR-93-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03309 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-30c-1-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03493 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Bifunctional arginine demethylase and lysyl-hydroxylase JMJD6 (JMJD6) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H4 arginine 3 symmetric dimethylation (H4R3me2a) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1320 (LINC01320)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03494 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Circ_ORC5
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03495 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-30c-2-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03496 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Proline-rich AKT1 substrate 1 (AKT1S1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03497 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: PI3-kinase subunit alpha (PI3k/PIK3CA)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03498 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03499 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03500 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03501 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03502 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Interleukin-12 subunit beta (IL12B)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06000 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Target: Circ_FUT8
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05121 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-628-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05123 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Urothelial cancer associated 1 (UCA1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Psoriasis | |
m6A Target: NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05148 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-103-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteoporosis | |
m6A Target: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha (HNF1A/TCF1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05149 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-103-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteoporosis | |
m6A Target: Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase GPX4 (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05150 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-103-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteoporosis | |
m6A Target: Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATC1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05151 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-103-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteoporosis | |
m6A Target: Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 3 (SLC2A3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05152 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-103-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteoporosis | |
m6A Target: Protein disulfide-isomerase (P4HB)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05153 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-103-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteoporosis | |
| Drug | ICARIIN | |
m6A Target: Mitochondrial fission 1 protein (FIS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05160 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lnc-Gm10532 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cognitive impairment | |
m6A Target: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05173 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0125169 (Circ_METTL14(11)S) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05352 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 942 (LINC00942) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 38 (USP38)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05174 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-3165 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
m6A Target: Intraflagellar transport protein 80 homolog (IFT80)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05178 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | H2AZ2 pseudogene 1 (H2AZ2P1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma | |
m6A Target: CCN family member 2 (CTGF)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05185 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | AI662270 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Chronic kidney disease | |
m6A Target: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05193 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | piR-14633 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05353 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 942 (LINC00942) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Pancreas/duodenum homeobox protein 1 (Pdx1)
| In total 12 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05194 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-141 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | Bisphenol F | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05195 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200b | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | Bisphenol F | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05196 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200c | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | Bisphenol F | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05984 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-141 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)sulfonylphenol | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05985 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200b | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)sulfonylphenol | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05986 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200c | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)sulfonylphenol | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05987 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-141 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | BPAF | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05988 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200b | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | BPAF | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05989 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200c | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | BPAF | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05990 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-141 | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | Bisphenol A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05991 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200b | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | Bisphenol A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05992 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-200c | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Drug | Bisphenol A | |
m6A Target: Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05202 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-130a-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| Drug | Cisplatin | |
m6A Target: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05325 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | LOC10013.776 (AGAP2-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Pre-mRNA-splicing regulator WTAP (WTAP) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05329 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-26a-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Intervertebral disc degeneration | |
m6A Target: Aspartate--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic (DARS)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05357 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DARS1 antisense RNA 1 (DARS1-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor SOX-9 (SOX9)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05368 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_FTO | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
m6A Target: microRNA 375 (MIR375)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05410 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 375 (MIR375) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05606 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 375 (MIR375) | |
| Regulated Target | Dexamethasone-induced Ras-related protein 1 (RASD1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Injuries of spine or trunk | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05931 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 375 (MIR375) | |
| Regulated Target | Transcription factor SOX-12 (SOX12) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: X inactive specific transcript (XIST)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05421 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | X inactive specific transcript (XIST) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05836 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | X inactive specific transcript (XIST) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas | |
m6A Target: LncRNA activating regulator of DKK1 (LNCAROD)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05426 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | LncRNA activating regulator of DKK1 (LNCAROD) | |
| Regulated Target | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-146a-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05431 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-146a-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-19a-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05435 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-19a-3p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Atherosclerosis | |
m6A Target: H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05451 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Abnormalities of breathing | |
m6A Target: hsa_circ_0089552 (circ_NOTCH1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05453 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0089552 (Circ_NOTCH1) | |
| Regulated Target | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: ZNFX1 antisense RNA 1 (ZFAS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05455 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | ZNFX1 antisense RNA 1 (ZFAS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Ras-related protein Rab-22A (RAB22A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Atherosclerosis | |
m6A Target: Circ_GFR-Alpha-1
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05491 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_GFR-Alpha-1 | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 449a (MIR449A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Female reproductive system disorders | |
m6A Target: Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1320 (LINC01320)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05499 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1320 (LINC01320) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-495-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: microRNA 211 (MIR211)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05500 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 211 (MIR211) | |
| Regulated Target | Transcription factor 12 (TCF12) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Lymphoma | |
m6A Target: HLA complex group 11 (HCG11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05523 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | HLA complex group 11 (HCG11) | |
| Regulated Target | Serine/threonine-protein kinase LATS1 (LATS1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05531 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3) | |
| Regulated Target | Pre-mRNA-splicing regulator WTAP (WTAP) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| Drug | Cisplatin | |
m6A Target: Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05540 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05729 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Krueppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Coronary atherosclerosis | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-380-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05564 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-380-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-99a-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05573 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-99a-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Tribbles homolog 2 (TRIB2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-30c-1-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05578 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-30c-1-3p | |
| Regulated Target | MARCKS-related protein (MARCKSL1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Lnc_LSG1
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05590 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lnc_LSG1 | |
| Regulated Target | Epithelial splicing regulatory protein 2 (ESRP2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | |
m6A Target: Circ_ORC5
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05598 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_ORC5 | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-30c-2-3p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-30c-2-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05599 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-30c-2-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Proline-rich AKT1 substrate 1 (AKT1S1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05624 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-224-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | |
m6A Target: pri-miR-873
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05666 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | pri-miR-873 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: TNF and HNRNPL related immunoregulatory long non-coding RNA (THRIL)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05725 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | TNF and HNRNPL related immunoregulatory long non-coding RNA (THRIL) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Injury of other or unspecified intrathoracic organs | |
| Drug | LPS | |
m6A Target: miR-6858
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05734 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | miR-6858 | |
| Regulated Target | Gasdermin C (GSDMC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Lichen planus | |
m6A Target: Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 941 (LINC00941)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05735 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 941 (LINC00941) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
m6A Target: microRNA 93 (MIR93)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05770 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 93 (MIR93) | |
| Regulated Target | Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: AC026356.1
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05773 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | AC026356.1 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-34a
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05804 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 34a (MIR34A) | |
| Regulated Target | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: OIP5 antisense RNA 1 (OIP5-AS1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05806 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | OIP5 antisense RNA 1 (OIP5-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 98 (MIR98) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05963 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 98 (MIR98) | |
| Regulated Target | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 8 (ADAMTS8) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer | |
m6A Target: KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05813 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-7-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Drug | Doxorubicin | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-21-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05823 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-21-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Abortion | |
m6A Target: TRHDE antisense RNA 1 (TRHDE-AS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05832 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | TRHDE antisense RNA 1 (TRHDE-AS1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| Drug | Propofol | |
m6A Target: SREBF2 antisense RNA 1 (SREBF2-AS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05834 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | SREBF2 antisense RNA 1 (SREBF2-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | FMR1 autosomal homolog 1 (FXR1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Drug | Chidamide | |
m6A Target: Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha-Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha (PML-RARalpha)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05879 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Blood malignancies | |
Xenobiotics Compound(s) Regulating the m6A Methylation Regulator
| Compound Name | MA2 | Approved |
|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid (MA)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| Description |
Knockdown of METTL3 or METTL14 induced changes in mRNA m6A enrichment and altered mRNA expression of genes (e.g.,ADAM19) with critical biological functions inGSCs. Treatment with MA2, a chemical inhibitor of FTO, dramatically suppressed GSC-induced tumorigenesis and prolonged lifespan in GSC-grafted animals.
|
[31] |
| Compound Name | Tamoxifen | Approved |
| Synonyms |
tamoxifen; 10540-29-1; trans-Tamoxifen; Crisafeno; Soltamox; Tamoxifene; Diemon; Tamoxifenum; Tamoxifeno; Tamizam; Istubol; Tamoxen; Citofen; Oncomox; Valodex; Retaxim; Tamoxifene [INN-French]; Tamoxifenum [INN-Latin]; Tamoxifeno [INN-Spanish]; Tamoxifen (Z); Tamoxifen and its salts; Tamoxifen [INN:BAN]; ICI-46474; ICI 47699; TRANS FORM OF TAMOXIFEN; CCRIS 3275; UNII-094ZI81Y45; HSDB 6782; CHEMBL83; EINECS 234-118-0; 1-p-beta-Dimethylaminoethoxyphenyl-trans-1,2-diphenylbut-1-ene; Citofen; Nourytam; Novaldex; Tamone; Tamoxifeno;Tamoxifenum; Tomaxithen; Gen-Tamoxifen; Istubal (TN); Nolvadex (TN); Nolvadex-D; Novo-Tamoxifen; Pms-Tamoxifen; Tamoplex (TN); Tamoxifen (INN); Tamoxifen (TN); Trans-Tamoxifen; Valodex (TN); TAMOXIFEN (TAMOXIFEN CITRATE (54965-24-1)); Trans-2-[4-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethylamine; (Z)-1-(p-Dimethylaminoethoxyphenyl)-1,2-diphenyl-1-butene; (Z)-2-(4-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine; (Z)-2-(4-(1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine; (Z)-2-(para-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethylamine (IUPAC); (Z)-2-[4-(1,2)-DIPHENYL-1-BUTENYL)-PHENOXY]-N,N-DIMETHYLETHANAMINE; (Z)-2-[p-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethylamine; 1-p-beta-Dimethylamino-ethoxyphenyl-trans-1,2-diphenylbut-1-ene; 1-para-beta-Dimethylaminoethoxyphenyl-trans-1,2-diphenylbut-1-ene; 2-[4-[(Z)-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl]phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine; 2-{4-[(1Z)-1,2-diphenylbut-1-en-1-yl]phenoxy}-N,N-dimethylethanamine; Tamoxifen (Hormonal therapy); [3H]tamoxifen
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
METTL14 deficiency inbeta-cells induces glucose intolerance and a decrease in insulin secretion.To define the role of m6A in regulating the beta-cell function, the study generated beta-cell METTL14-specific knockout (beta-KO) mice by tamoxifen administration. beta-cell mass in beta-KO mice was related to beta-cell proliferation and also observed elevated mRNA and protein levels of Ire1-alpha and sXBP-1 in beta-KO islets.
|
[192] |
| Compound Name | N~2~-hexyl-6,7-dimethoxy-N~4~-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)quinazoline-2,4-diamine | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL4086403; SCHEMBL23260478; MS012; BDBM50501525; MS 012; MS-012; N~2~-hexyl-6,7-dimethoxy-N~4~-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)quinazoline-2,4-diamine; 2089617-83-2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50=7±2 nM
|
[199] |
| Compound Name | 6,7-Dimethoxy-N-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-Yl)-2-(Morpholin-4-Yl)quinazolin-4-Amine | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL571717; 6,7-Dimethoxy-N-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-Yl)-2-(Morpholin-4-Yl)quinazolin-4-Amine; 7L6; SCHEMBL15280520; BDBM50300032; NCGC00185861-01; 6,7-dimethoxy-N-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-2-morpholinoquinazolin-4-amine
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50=13 ± 4 nM
|
[199] |
References