m6A-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: M6ADRUG0047)
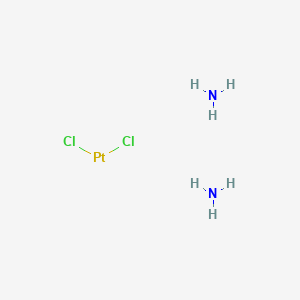
| Name |
Cisplatin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Abiplatin; Biocisplatinum; Briplatin; Cismaplat; Cisplatine; Cisplatino; Cisplatinum; Cisplatyl; Citoplationo; Lederplatin; Neoplatin; Plastin; Platamine; Platidiam; Platinoxan; Randa; Cis-DDP; Cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum; Peyrone's chloride; Peyrone's salt; Cis-Dichlorodiammineplatinum(II); Cis-[PtCl2(NH3)2]; Cis-diamminedichloridoplatinum(II); Trans-diamminedichloridoplatinum(II); (SP-4-1)-diamminedichloridoplatinum; (SP-4-1)-diamminedichloroplatinum; (SP-4-2)-diamminedichloridoplatinum; (SP-4-2)-diamminedichloroplatinum; Cisplatin (Chemotherapy)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status | Approved | [1] | |||
| Structure |
 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
Cl2H6N2Pt
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/2ClH.2H3N.Pt/h2*1H;2*1H3;/q;;;;+2/p-2
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LXZZYRPGZAFOLE-UHFFFAOYSA-L
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Full List of m6A Targets Related to This Drug
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 (AKR1C1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of CDK2, CDK4, p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 (AKR1C1) axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9 (ABCC9)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | TRIM11 regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma drug resistance by positively modulating the Daple/beta-catenin/ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9 (ABCC9) signaling pathway. TRIM11 enhanced the multidrug resistance in NPC by inhibiting apoptosis in vitro and promoting cisplatin (DDP) resistance in vivo. METTL3-mediated m6A modification caused the upregulation of TRIM11 via IGF2BP2 in NPC drug-resistant cells. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6B | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | ABC transporters | hsa02010 | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | |||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| In-vitro Model | CNE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6888 |
| CNE-2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6889 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 2 × 106 cells was mixed with 0.2 ml PBS (pH 7.4) and 30% (v/v) Matrigel matrix (BD Biosciences). | |||
Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase METTL3 regulates autophagy and sensitivity to cisplatin by targeting Autophagy protein 5 (ATG5) in seminoma. The use of autophagy inhibitors 3-MA could reverse the protective effect of METTL3 on TCam-2 cells. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Testicular cancer | ICD-11: 2C80 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Cellular Transport | ||||
| Cellular catabolism | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | Tcam-2/DDP (Cisplatin-resistant TCam-2 cell line) | |||
| TCam-2 | Testicular seminoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_T012 | |
Axin-1 (AXIN1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 interference could suppress the EMT of cervical cancer cells and enhance cisplatin chemosensitivity by regulating Axin-1 (AXIN1). | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer | ICD-11: 2C77 | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| In-vitro Model | SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Ect1/E6E7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3679 | |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
| C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 | |
Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of ALKBH5 promoted bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and decreased cisplatin chemosensitivity, ALKBH5 inhibited the progression and sensitized bladder cancer cells to cisplatin through a Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2)-mediated glycolysis pathway in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010) | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
| In-vitro Model | UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| 253J | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7935 | |
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Response Summary | Meclofenamic acid increased Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) mRNA and protein levels in AKI both in vitro and in vivo, and FTO overexpression reduced p53 expression and reversed the MA-induced p53 increase in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury Acute kidney injury. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
| In-vivo Model | Induced AKI in c57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal cisplatin injection and treated the animal with vehicle or an FTO inhibitor meclofenamic acid (MA) for 3 days. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), CDK4, p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of CDK2, Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B/p27)
| In total 2 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Response Summary | The role of YTHDF2 in tumourigenesis and cisplatin-desensitising function by promoting the degradation of Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B/p27) mRNA in an m6 A-dependent manner. YTHDF2 exhibits tumour oncogenic and cisplatin-desensitising properties, which offer insight into the development of novel combination therapeutic strategies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.10 | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Arrest cell cycle at G0/G1 phase | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HuCC-T1 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0324 |
| RBE | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4896 | |
| HCCC-9810 (The intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell lines (HCCC-9810) were purchased from Cellcook Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China).) | ||||
| HIBEC (The normal intrahepatic bile duct cell line (HIBEC) were purchased from Cellcook Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China).) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | For tumour xenograft models, 1 × 107 HuCC-T1 cells in knockdown group or control group were implanted into the right flank of 5-week-old female nude mice. The volumes of tumour were recorded every 4 days by calliper. The volumes were calculated as length × width2/2. For patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model (PDX0075), ICC tissues from a patient, who relapsed in 6 months after R0 resection and subsequent chemotherapy with cisplatin and gemcitabine, were diced into 3 mm3 pieces and transplanted subcutaneously into the right flank of 5-week-old female B-NDG mice. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of CDK2, CDK4, Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B/p27), and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Double-strand break repair protein MRE11 (MRE11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Response Summary | VIRMA has an oncogenic role in germ cell tumor confirming our previous tissue-based study and is further involved in response to cisplatin by interfering with DNA repair. Enhanced response to cisplatin after VIRMA knockdown was related to significant increase in DNA damage (with higher Gamma-H2AX and GADD45B levels) and downregulation of XLF and Double-strand break repair protein MRE11 (MRE11). | |||
| Responsed Disease | Germ cell tumour of testis | ICD-11: 2C80.2 | ||
| Target Regulator | Protein virilizer homolog (VIRMA) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | 2102EP | Embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C522 |
| NCC-IT | Testicular embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1451 | |
| NT2 | Malignant neoplasms | Mus musculus | CVCL_JA57 | |
| TCam-2 | Testicular seminoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_T012 | |
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 6 (DUSP6)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase Wilms' tumor 1-associated protein facilitates cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance in NK/T cell lymphoma by regulating dual-specificity phosphatases 6 expression via m6A RNA methylation. WTAP enhanced Dual specificity protein phosphatase 6 (DUSP6) expression by increasing m6A levels of DUSP6 mRNA transcript, leading to oncogenic functions in NKTCL. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm | ICD-11: 2B33 | ||
| Target Regulator | Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | Normal NK cells (CD3-negative lymphocytes) | |||
| SNK-6 | Nasal type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_A673 | |
| YTS | Lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_D324 | |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM11 (TRIM11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | TRIM11 regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma drug resistance by positively modulating the Daple/beta-catenin/E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM11 (TRIM11) signaling pathway. TRIM11 enhanced the multidrug resistance in NPC by inhibiting apoptosis in vitro and promoting cisplatin (DDP) resistance in vivo. METTL3-mediated m6A modification caused the upregulation of TRIM11 via IGF2BP2 in NPC drug-resistant cells. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6B | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | ABC transporters | hsa02010 | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | |||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | |||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
| In-vitro Model | CNE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6888 |
| CNE-2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6889 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 2 × 106 cells was mixed with 0.2 ml PBS (pH 7.4) and 30% (v/v) Matrigel matrix (BD Biosciences). | |||
Fibrinogen alpha chain (FGA)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A plays an important role in cisplatin induced acute kidney injury and berberine alleviates this process. Cisplatin induced an increase in Slc12a1 protein levels and a decrease in Fibrinogen alpha chain (FGA) and Havcr1 protein levels. However, berberine pretreatment reversed these effects. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic processes | |||
| Cell death | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vivo Model | This study investigated the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylome of kidneys from three mouse groups: C57 mice (controls), those with CI-AKI (injury group, IG), and those pretreated with berberine (treatment group, TG). | |||
G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of CDK2, CDK4, p27, and G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1), and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVCR1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A plays an important role in cisplatin induced acute kidney injury and berberine alleviates this process. Cisplatin induced an increase in Slc12a1 protein levels and a decrease in FGA and Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVCR1) protein levels. However, berberine pretreatment reversed these effects. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic processes | |||
| Cell death | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vivo Model | This study investigated the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylome of kidneys from three mouse groups: C57 mice (controls), those with CI-AKI (injury group, IG), and those pretreated with berberine (treatment group, TG). | |||
Histone H2AX (H2AX)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Response Summary | VIRMA has an oncogenic role in germ cell tumor confirming our previous tissue-based study and is further involved in response to cisplatin by interfering with DNA repair. Enhanced response to cisplatin after VIRMA knockdown was related to significant increase in DNA damage (with higher Histone H2AX (H2AX) and GADD45B levels) and downregulation of XLF and MRE11. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Germ cell tumour of testis | ICD-11: 2C80.2 | ||
| Target Regulator | Protein virilizer homolog (VIRMA) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | 2102EP | Embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C522 |
| NCC-IT | Testicular embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1451 | |
| NT2 | Malignant neoplasms | Mus musculus | CVCL_JA57 | |
| TCam-2 | Testicular seminoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_T012 | |
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [14] | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of IGFBP3 induced apoptosis and enhanced cisplatin response in vitro and confirmed that the suppression is in part by blocking Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signaling. IGFBP3 is effective in lung cancer cells with high IGF1 signaling activity and imply that relevant biomarkers are essential in selecting lung cancer patients for IGF1-targeted therapy. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | ||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) | READER | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 |
| HCC2429 | Lung non-small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5132 | |
| In-vivo Model | Paired littermates of F2 (Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-:KrasG12D/+) were sacrificed ranging from ages 4 to 7 months. After preliminary analysis of F2 mice, we sacrificed 5-month-old Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-KrasG12D/+ mice that had been backcrossed to S129 background for representative analysis. The lung tissue was immediately removed after the mice were sacrificed and visible pleural nodules were counted directly. | |||
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of CDK2, CDK4, p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1)-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Negative growth regulatory protein MyD118 (GADD45B)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Response Summary | VIRMA has an oncogenic role in germ cell tumor confirming our previous tissue-based study and is further involved in response to cisplatin by interfering with DNA repair. Enhanced response to cisplatin after VIRMA knockdown was related to significant increase in DNA damage (with higher Gamma-H2AX and Negative growth regulatory protein MyD118 (GADD45B) levels) and downregulation of XLF and MRE11. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Germ cell tumour of testis | ICD-11: 2C80.2 | ||
| Target Regulator | Protein virilizer homolog (VIRMA) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | 2102EP | Embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C522 |
| NCC-IT | Testicular embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1451 | |
| NT2 | Malignant neoplasms | Mus musculus | CVCL_JA57 | |
| TCam-2 | Testicular seminoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_T012 | |
Non-homologous end-joining factor 1 (NHEJ1/XLF)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Response Summary | VIRMA has an oncogenic role in germ cell tumor confirming our previous tissue-based study and is further involved in response to cisplatin by interfering with DNA repair. Enhanced response to cisplatin after VIRMA knockdown was related to significant increase in DNA damage (with higher Gamma-H2AX and GADD45B levels) and downregulation of Non-homologous end-joining factor 1 (NHEJ1/XLF) and MRE11. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Germ cell tumour of testis | ICD-11: 2C80.2 | ||
| Target Regulator | Protein virilizer homolog (VIRMA) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | 2102EP | Embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C522 |
| NCC-IT | Testicular embryonal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1451 | |
| NT2 | Malignant neoplasms | Mus musculus | CVCL_JA57 | |
| TCam-2 | Testicular seminoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_T012 | |
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of CDK2, CDK4, p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [16] | |||
| Response Summary | ZC3H13 overexpression sensitized to cisplatin and weakened metabolism reprogramming of HCC cells, ZC3H13-induced m6A modified patterns substantially abolished Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM) mRNA stability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Target Regulator | Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 13 (ZC3H13) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
| In-vitro Model | SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [17] | |||
| Response Summary | ARHGAP5-AS1 also stabilized ARHGAP5 mRNA in the cytoplasm by recruiting METTL3 to stimulate m6A modification of Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5) mRNA. As a result, ARHGAP5 was upregulated to promote chemoresistance and its upregulation was also associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. downregulation of ARHGAP5-AS1 in resistant cells evidently reversed the resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs including cisplatin (DDP), ADM, and 5-FU. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Transport and catabolism | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 |
| SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase ULK1 (ULK1/ATG1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of FTO reversed cisplatin resistance of SGC-7901/DDP cells both in vitro and in vivo, which was attributed to the inhibition of Serine/threonine-protein kinase ULK1 (ULK1)-mediated autophagy. These findings indicate that the FTO/ULK1 axis exerts crucial roles in cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 |
| SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 5 × 106 cells in 200 ul PBS were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of nude mice. After injection, cisplatin treatment was initiated on day 5. Mice were injected with 5 mg/kg cisplatin or PBS solution in the abdominal cavity once a week for 3 weeks. | |||
Solute carrier family 12 member 1 (SLC12A1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A plays an important role in cisplatin induced acute kidney injury and berberine alleviates this process. Cisplatin induced an increase in Solute carrier family 12 member 1 (SLC12A1) protein levels and a decrease in FGA and Havcr1 protein levels. However, berberine pretreatment reversed these effects. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic processes | |||
| Cell death | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vivo Model | This study investigated the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylome of kidneys from three mouse groups: C57 mice (controls), those with CI-AKI (injury group, IG), and those pretreated with berberine (treatment group, TG). | |||
Transcription factor AP-2 gamma (TFAP2C)
| In total 2 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 potentiates resistance to cisplatin through m6A modification of Transcription factor AP-2 gamma (TFAP2C) in seminoma. Enhanced stability of TFAP2C mRNA promoted seminoma cell survival under cisplatin treatment burden probably through up-regulation of DNA repair-related genes. IGF2BP1 binds to TFAP2C and enhances TFAP2C mRNA stability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Testicular cancer | ICD-11: 2C80 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair | |||
| In-vitro Model | TCam-2 | Testicular seminoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_T012 |
| In-vivo Model | Male mice were subcutaneously injected with tumour cells near the limbs to establish xenografts (1 × 106/mouse, 0.2 mL for each injection site; METTL3-overexpressing TCam-2/CDDP cells were inoculated once at the initial time and IGF2BP1-inhibited TCam-2/CDDP cells were inoculated every 3 days). | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 potentiates resistance to cisplatin through m6A modification of Transcription factor AP-2 gamma (TFAP2C) in seminoma. Enhanced stability of TFAP2C mRNA promoted seminoma cell survival under cisplatin treatment burden probably through up-regulation of DNA repair-related genes. IGF2BP1 binds to TFAP2C and enhances TFAP2C mRNA stability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Testicular cancer | ICD-11: 2C80 | ||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair | |||
| In-vitro Model | TCam-2 | Testicular seminoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_T012 |
| In-vivo Model | Male mice were subcutaneously injected with tumour cells near the limbs to establish xenografts (1 × 106/mouse, 0.2 mL for each injection site; METTL3-overexpressing TCam-2/CDDP cells were inoculated once at the initial time and IGF2BP1-inhibited TCam-2/CDDP cells were inoculated every 3 days). | |||
Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8)
| In total 2 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Response Summary | In breast cancer, accordingly YTHDF1 knockdown sensitizes breast cancer cells to Adriamycin and Cisplatin as well as Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor. Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) is a target molecule by YTHDF1 which modulates E2F8 mRNA stability and DNA damage repair in a METTL14-dependent manner. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Hs 578T | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0332 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1×106 MDA-MB-231 cells were resuspended in 100 uL PBS with 50% Matrigel (Corning Costar, USA), and injected into the mammary fat pad of the mice. | |||
Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1)
| In total 3 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
Tripartite motif-containing protein 29 (TRIM29)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [23] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-YTHDF1-mediated Tripartite motif-containing protein 29 (TRIM29) upregulation facilitates the stem cell-like phenotype of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. TRIM29 acts as an oncogene to promote the CSC-like features of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer in an m6A-YTHDF1-dependent manner. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Ectopic expression | |||
| In-vitro Model | A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | The specified number of viable SKOV3/DDP cells and SKOV3/DDP cells with TRIM29 knock down were resuspended in 100 uL PBS, injected subcutaneously under the left and right back of 4-week old nude mice respectively (n = 3 per group). | |||
Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 (JAK2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [24] | |||
| Response Summary | The ALKBH5-HOXA10 loop jointly activates the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway by mediating Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 (JAK2) m6A demethylation, promoting epithelial ovarian cancer resistance to cisplatin. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary | ICD-11: 2B5D.0 | ||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HO8910-DDP (HO8910 underwent continuous stepwise exposure to increasing concentrations of cisplatin to create the cisplatin-resistant cell lines HO8910-DDP) | |||
| HO-8910 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6868 | |
| A2780-DDP (A2780 underwent continuous stepwise exposure to increasing concentrations of cisplatin to create the cisplatin-resistant cell line) | ||||
| A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 | |
| In-vivo Model | About 5× 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the axilla of the female athymic BALB/C nude mice (4 week-old, 18-20 g). When the average tumor size reached approximately 100mm3 (after 1 week), mice were then randomized into two groups and treated with cisplatin (5 mg/kg) or normal saline (NS) weekly. | |||
Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 4 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Response Summary | This study highlighted METTL3 as a tumor promoter in Thymic tumors and c-MYC as a promising target to be exploited for the treatment of TET. High expression of c-MYC protein is enabled by lncRNA Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1), which is methylated and delocalized by METTL3. Silencing of METTL3 combined with cisplatin or c-MYC inhibitor induces cell death in TET cells. Blocking of c-MYC by using JQ1 inhibitor cooperates with METTL3 depletion in the inhibition of proliferation and induction of cell death. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Thymic epithelial tumors | ICD-11: 2C27.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell viability and proliferation | |||
| In-vitro Model | T1889 | Thymic undifferentiated carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_D024 |
RMRP
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [26] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A RNA methylation-mediated RMRP stability renders proliferation and progression of non-small cell lung cancer through regulating TGFBR1/SMAD2/SMAD3 pathway. RMRP promoted the cancer stem cells properties and epithelial mesenchymal transition, which promote the resistance to radiation therapy and cisplatin. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | ||
| EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | hsa01521 | |||
| Cell Process | Epithelial mesenchymal transition | |||
hsa-miR-1914-3p
| In total 3 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-hsa-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-hsa-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, YTHDF3, YTHDF1, and eIF3b directly promoted YAP translation through an interaction with the translation initiation machinery. METTL3 knockdown inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to DDP in vivo.m6A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-hsa-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce Non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance and metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into two groups (five mice per group) after the diameter of the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter. Xenografted mice were then administrated with PBS or DDP (3 mg/kg per day) for three times a week, and tumor volume were measured every second day. | |||
hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3)
| In total 3 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Response Summary | Circ0008399 bound WTAP to promote formation of the WTAP/METTL3/METTL14 m6A methyltransferase complex, reduce cisplatin sensitivity in bladder cancer, implicating the potential therapeutic value of targeting this axis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Target Regulator | Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Protein export | hsa03060 | ||
| Cell Process | Eukaryotic translation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| RT-4 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0036 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | Chose 4-week-old female BALB/c nude mice for tumor xenograft experiments, which randomly were divided into four groups (n = 5 per group). Bladder cancer cells (3 × 106) were subcutaneously injected into the right axilla of the nude mice. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Response Summary | Circ0008399 bound WTAP to promote formation of the WTAP/METTL3/METTL14 m6A methyltransferase complex, reduce cisplatin sensitivity in bladder cancer, implicating the potential therapeutic value of targeting this axis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Protein export | hsa03060 | ||
| Cell Process | Eukaryotic translation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| RT-4 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0036 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | Chose 4-week-old female BALB/c nude mice for tumor xenograft experiments, which randomly were divided into four groups (n = 5 per group). Bladder cancer cells (3 × 106) were subcutaneously injected into the right axilla of the nude mice. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Response Summary | Circ0008399 bound WTAP to promote formation of the WTAP/METTL3/METTL14 m6A methyltransferase complex, reduce cisplatin sensitivity in bladder cancer, implicating the potential therapeutic value of targeting this axis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Protein export | hsa03060 | ||
| Cell Process | Eukaryotic translation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| RT-4 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0036 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | Chose 4-week-old female BALB/c nude mice for tumor xenograft experiments, which randomly were divided into four groups (n = 5 per group). Bladder cancer cells (3 × 106) were subcutaneously injected into the right axilla of the nude mice. | |||
Circ_MAP3K4
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Response Summary | Driven by m6A modification, Circ_MAP3K4 encoded circMAP3K4-455aa, protected HCC cells from cisplatin exposure, and predicted worse prognosis of HCC patients. IGF2BP1 facilitates circMAP3K4 peptide translation, then the circMAP3K4 peptide inhibits AIF cleavage and nuclear distribution. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasome pathway degradation | |||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Drug
| In total 32 item(s) under this drug | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02072 | ||
| m6A Regulator | ELAV-like protein 1 (ELAVL1) | |
| m6A Target | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02198 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | |
| m6A Target | Circ_MAP3K4 | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 13 (PTPN13) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02216 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02240 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02264 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Transcription factor E2F8 (E2F8) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03190 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H2 (SUV39H2) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H2 (SUV39H2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03191 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | |
| m6A Target | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H2 (SUV39H2) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H2 (SUV39H2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03472 | ||
| m6A Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| m6A Target | Glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 (CHAC1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03513 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 426 (LINC00426) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03526 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 426 (LINC00426) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03641 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05051 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | ARHGAP5 antisense RNA 1 (head to head) (ARHGAP5-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05107 | ||
| m6A Regulator | RNA-binding protein Musashi homolog 2 (MSI2) | |
| m6A Target | Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 942 (LINC00942) | |
| Regulated Target | Musashi RNA binding protein 2 (MSI2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05202 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-130a-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05269 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | |
| m6A Target | Zinc finger protein RFP (TRIM27) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-136-5p | |
| Regulated Target | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05271 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Transcription factor SOX-2 (SOX2) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_VMP1 | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-524-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05272 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Transcription factor SOX-2 (SOX2) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-524-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05404 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05405 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | |
| m6A Target | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05406 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-1914-3p | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-1914-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05407 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | |
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-1914-3p | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-1914-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05408 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | |
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-1914-3p | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-1914-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05413 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | |
| m6A Target | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 632 (LINC00632) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 632 (LINC00632) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05414 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | |
| m6A Target | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 632 (LINC00632) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 632 (LINC00632) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05415 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | |
| m6A Target | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 632 (LINC00632) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 632 (LINC00632) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05516 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Thymic epithelial tumors | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05529 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) | |
| m6A Target | hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3) | |
| Regulated Target | Pre-mRNA-splicing regulator WTAP (WTAP) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05530 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3) | |
| Regulated Target | Pre-mRNA-splicing regulator WTAP (WTAP) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05531 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0008399 (Circ_RBM3) | |
| Regulated Target | Pre-mRNA-splicing regulator WTAP (WTAP) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05588 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | |
| m6A Target | Circ_MAP3K4 | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_MAP3K4 | |
| Regulated Target | Apoptosis inducing factor mitochondria associated 1 (AIFM1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05713 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 426 (LINC00426) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 426 (LINC00426) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-200a-3p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06023 | ||
| m6A Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| m6A Target | Glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 (CHAC1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
References