m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00210)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
CDK2
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | B16-OVA cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shFTO B16-OVA cells
Control: shNC B16-OVA cells
|
GSE154952 | |
| Regulation |
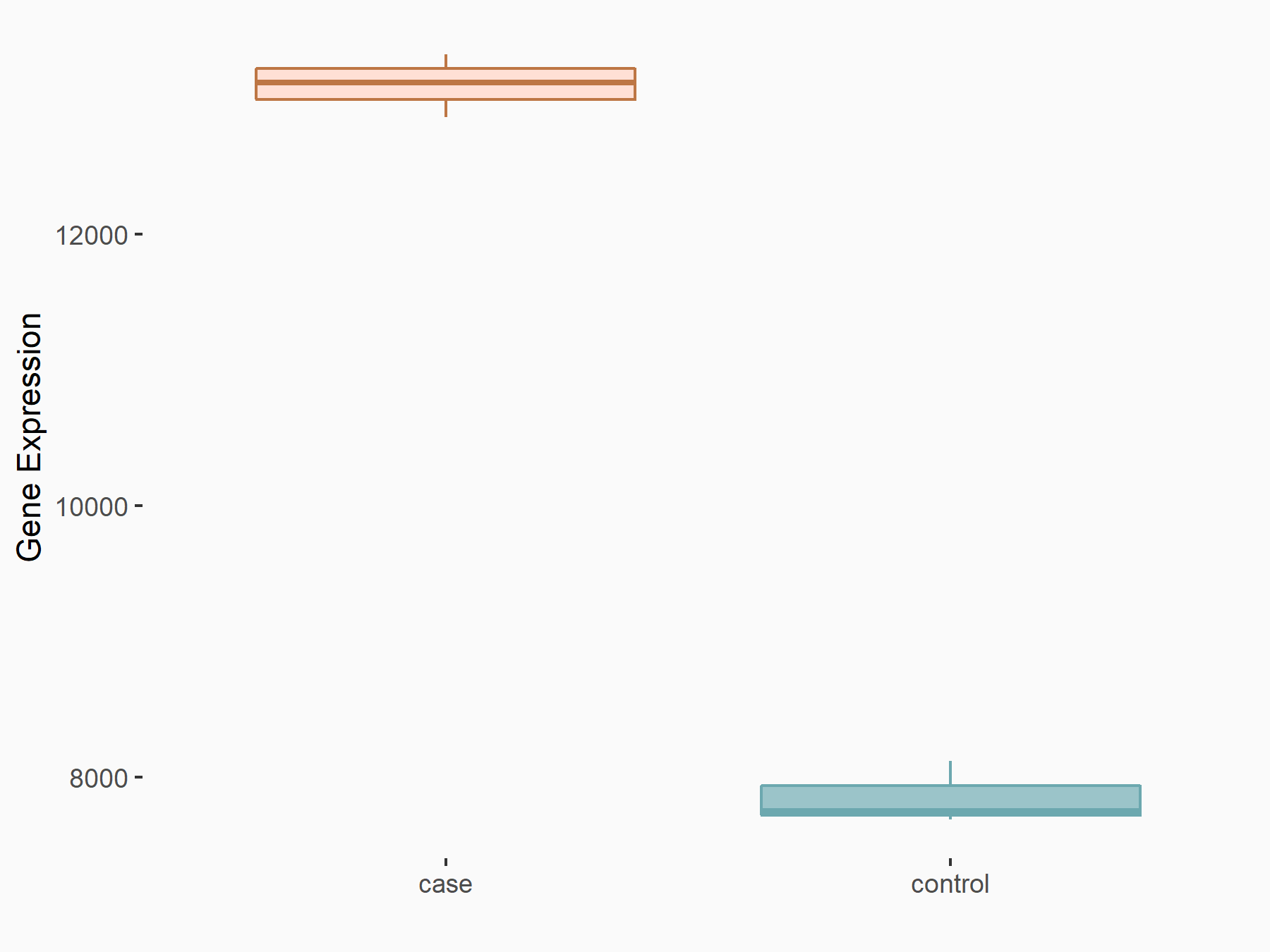 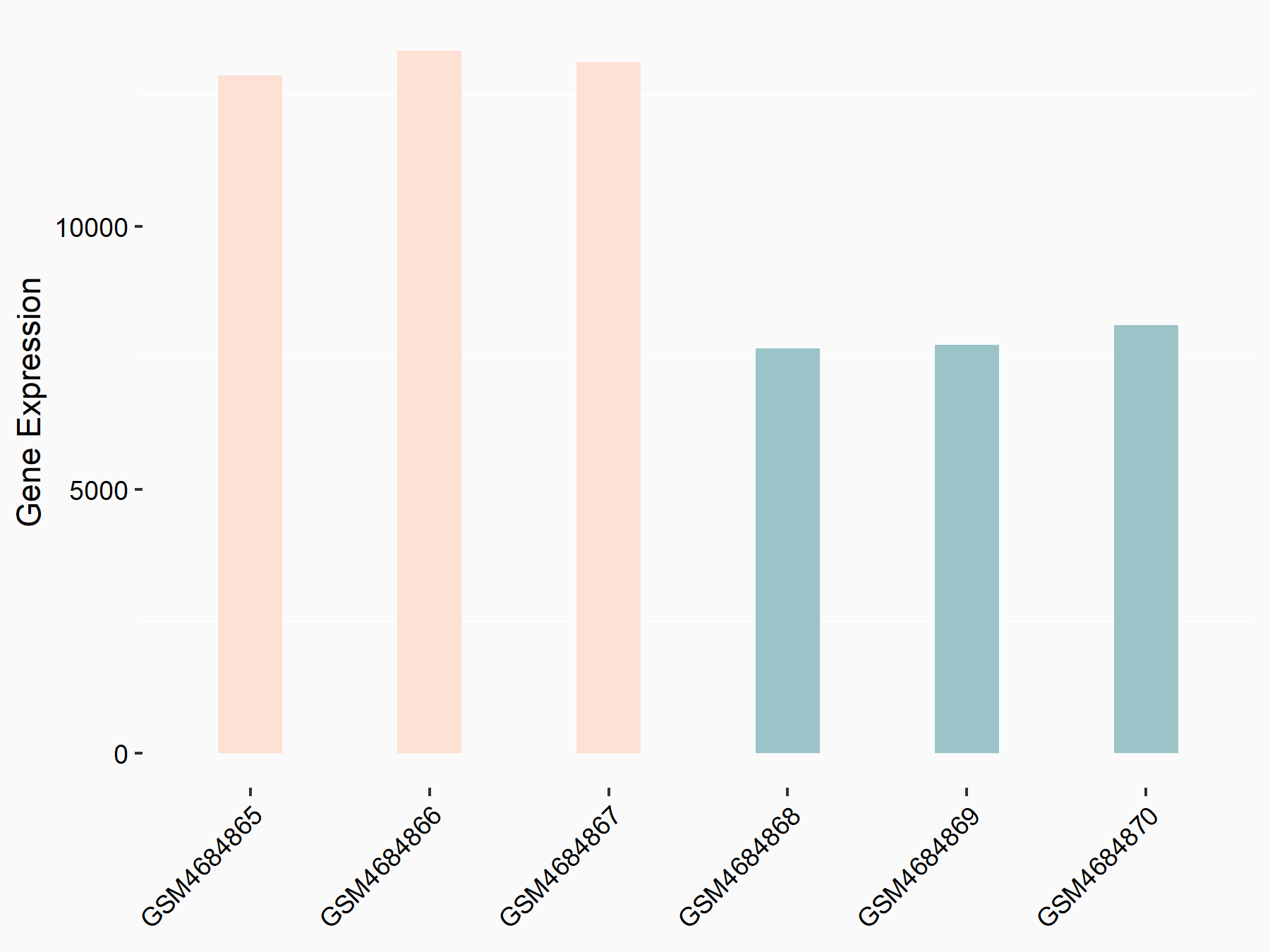 |
logFC: 7.39E-01 p-value: 1.49E-28 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 3 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin gallate | Phase 3 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO knockdown markedly decreased the expression of CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), crucial cell cycle regulators, leading to delayed entry of MDI-induced cells into G2 phase. m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 recognized and decayed methylated mRNAs of CCNA2 and CDK2, leading to decreased protein expression, thereby prolonging cell cycle progression and suppressing adipogenesis. The adipocyte life cycle, including proliferation and adipogenesis, has become a potential target for many bioactive compounds and drugs for the prevention and treatment of obesity. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Arrest cell cycle at S phase | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Metformin could inhibit adipogenesis and combat obesity, metformin could inhibit protein expression of FTO, leading to increased m6A methylation levels of Ccnd1 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)(two crucial regulators in cell cycle). Ccnd1 and Cdk2 with increased m6A levels were recognised by YTHDF2, causing an YTHDF2-dependent decay and decreased protein expressions. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF1 | ||
| Cell Line | AGS cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shYTHDF1 AGS
Control: shControl AGS
|
GSE159425 | |
| Regulation |
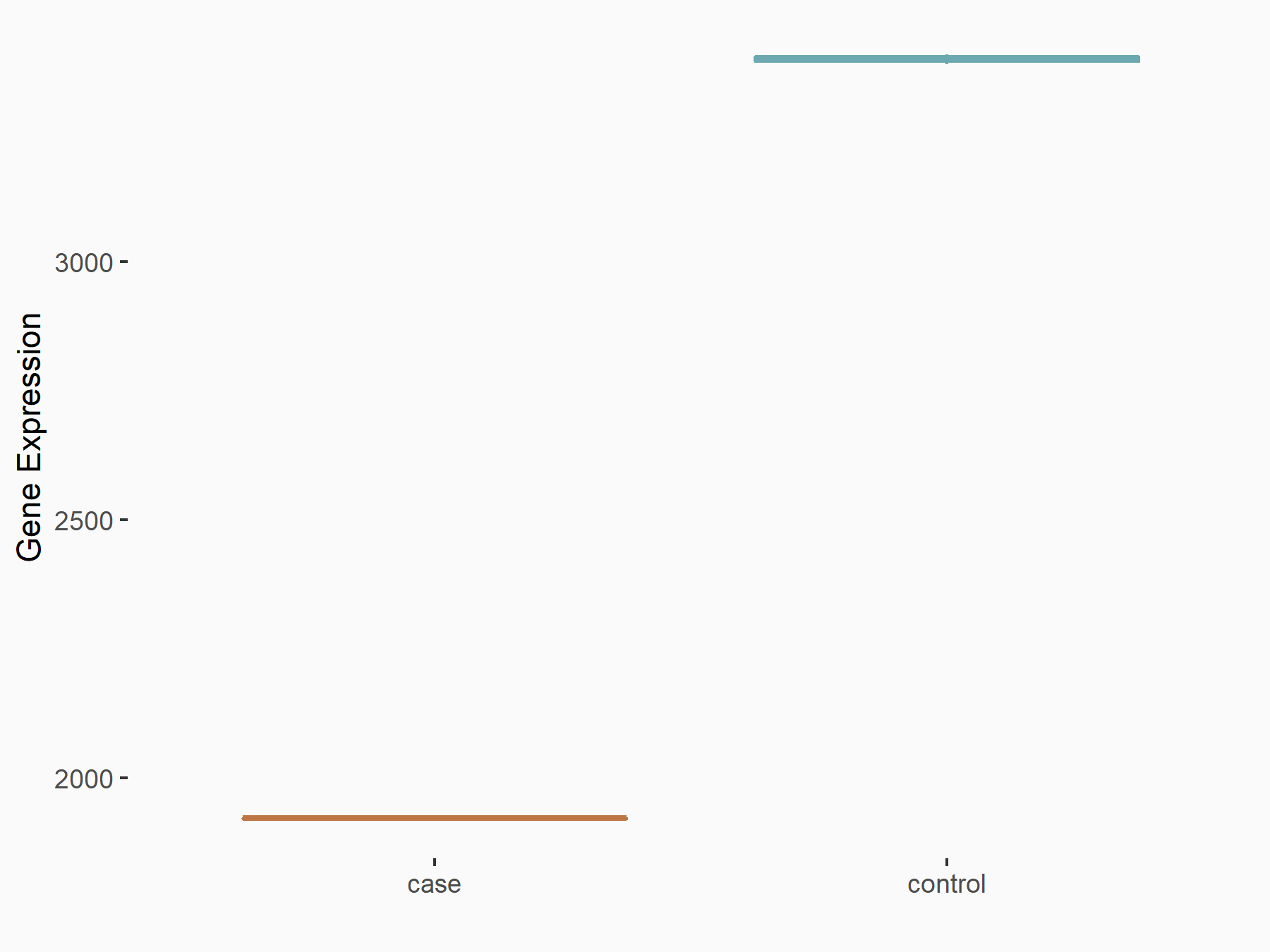 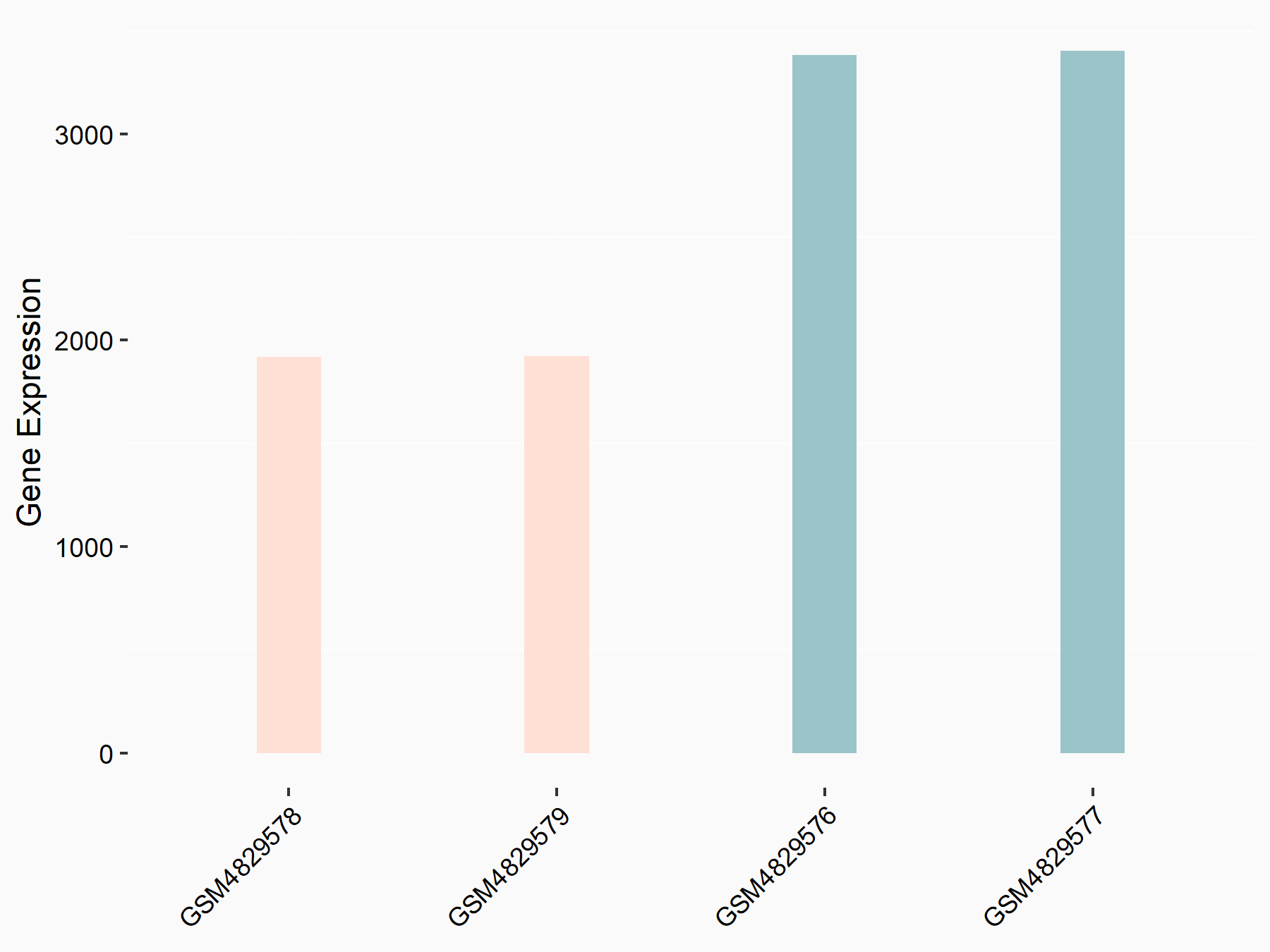 |
logFC: -8.20E-01 p-value: 7.96E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), CDK4, p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| In total 3 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin gallate | Phase 3 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO knockdown markedly decreased the expression of CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), crucial cell cycle regulators, leading to delayed entry of MDI-induced cells into G2 phase. m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 recognized and decayed methylated mRNAs of CCNA2 and CDK2, leading to decreased protein expression, thereby prolonging cell cycle progression and suppressing adipogenesis. The adipocyte life cycle, including proliferation and adipogenesis, has become a potential target for many bioactive compounds and drugs for the prevention and treatment of obesity. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Arrest cell cycle at S phase | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Metformin could inhibit adipogenesis and combat obesity, metformin could inhibit protein expression of FTO, leading to increased m6A methylation levels of Ccnd1 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)(two crucial regulators in cell cycle). Ccnd1 and Cdk2 with increased m6A levels were recognised by YTHDF2, causing an YTHDF2-dependent decay and decreased protein expressions. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), CDK4, p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 6 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin gallate | Phase 3 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO knockdown markedly decreased the expression of CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), crucial cell cycle regulators, leading to delayed entry of MDI-induced cells into G2 phase. m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 recognized and decayed methylated mRNAs of CCNA2 and CDK2, leading to decreased protein expression, thereby prolonging cell cycle progression and suppressing adipogenesis. The adipocyte life cycle, including proliferation and adipogenesis, has become a potential target for many bioactive compounds and drugs for the prevention and treatment of obesity. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Arrest cell cycle at S phase | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Metformin could inhibit adipogenesis and combat obesity, metformin could inhibit protein expression of FTO, leading to increased m6A methylation levels of Ccnd1 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)(two crucial regulators in cell cycle). Ccnd1 and Cdk2 with increased m6A levels were recognised by YTHDF2, causing an YTHDF2-dependent decay and decreased protein expressions. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin gallate | Phase 3 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 5 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO knockdown markedly decreased the expression of CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), crucial cell cycle regulators, leading to delayed entry of MDI-induced cells into G2 phase. m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 recognized and decayed methylated mRNAs of CCNA2 and CDK2, leading to decreased protein expression, thereby prolonging cell cycle progression and suppressing adipogenesis. The adipocyte life cycle, including proliferation and adipogenesis, has become a potential target for many bioactive compounds and drugs for the prevention and treatment of obesity. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| Arrest cell cycle at S phase | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 6 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Metformin could inhibit adipogenesis and combat obesity, metformin could inhibit protein expression of FTO, leading to increased m6A methylation levels of Ccnd1 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)(two crucial regulators in cell cycle). Ccnd1 and Cdk2 with increased m6A levels were recognised by YTHDF2, causing an YTHDF2-dependent decay and decreased protein expressions. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF1 deficiency inhibits Non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor formation through regulating the translational efficiency of Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), CDK4, p27, and cyclin D1, and that YTHDF1 depletion restrains de novo lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) progression. Mechanistic studies identified the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 axis as the downstream mediator of YTHDF1. YTHDF1 high expression correlates with better clinical outcome, with its depletion rendering cancerous cells resistant to cisplatin (DDP) treatment. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| A549-DDP (Human lung adenocarcinoma is resistant to cisplatin) | ||||
| GLC-82 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3371 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H838 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1594 | |
| SPC-A1 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6955 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mice were treated via nasal inhalation of adenovirus carrying Cre recombinase (5 × 106 p.f.u for Ad-Cre, Biowit Inc., Shenzhen, Guangdong), and were then killed at indicated times for gross inspection and histopathological examination. | |||
Epigallocatechin gallate
[Phase 3]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent CCNA2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) expressions mediated by FTO and YTHDF2 contributed to EGCG-induced adipogenesis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Cell Process | Adipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 |
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03086 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Diabetic retinopathy | |
| Drug | FB23-2 | |
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03087 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Diabetic retinopathy | |
| Drug | FB23-2 | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Regulator: Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05345 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-501-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Pre-mRNA-splicing regulator WTAP (WTAP) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Kidney cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00210)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000048 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55966918-55966919:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTACTGGGCCCTGTTTCCCCCTCCTCGGCCCCCGAGAGCCA | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_10322 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000049 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972417-55972418:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATCCCATTTTCCTCTGACGTCCACCTCCTACCCCATAGGAG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_10323 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 40 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013254 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55966809-55966810:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCCTCTGGTGGCGGTCGGGAACTCGGTGGGAGGCGGCAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000556464.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192290 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013255 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55966852-55966853:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | GTTTCAAGTTGGCCAAATTGACAAGAGCGAGAGGTATACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192291 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013256 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55966900-55966901:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TCCCGACCCGGGGCCACGGTACTGGGCCCTGTTTCCCCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.278136905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000553376.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192292 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013257 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55967015-55967016:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCGCTGGCGCTTCATGGAGAACTTCCAAAAGGTGGAAAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; BGC823; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; iSLK; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192296 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013258 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55967063-55967064:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | GGGCACGTACGGAGTTGTGTACAAAGCCAGAAACAAGTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000556464.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192297 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013259 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55967075-55967076:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGTTGTGTACAAAGCCAGAAACAAGTTGACGGGAGAGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000554619.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192298 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013260 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55967120-55967121:+ | [14] | |
| Sequence | GCTTAAGAAAATCCGCCTGGACACGTGAGTGGCCTCTGTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000556464.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192299 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013261 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55967146-55967147:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | GAGTGGCCTCTGTACCCGGGACTCCTAACTGGGGACCTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000555357.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192300 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013262 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55967160-55967161:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | CCCGGGACTCCTAACTGGGGACCTCCTTGATTGTCCCCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000554619.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192301 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013263 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55967878-55967879:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | AGACTGAGGGTGTGCCCAGTACTGCCATCCGAGAGATCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.278136905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000556276.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000556146.1; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000556464.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192302 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013264 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55968065-55968066:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | TAGGCTGCTGGATGTCATTCACACAGAAAATAAACTCTACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000555357.1; ENST00000556276.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000556146.1; ENST00000440311.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192303 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013265 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55968868-55968869:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | ACCTCAGAATCTGCTTATTAACACAGAGGGGGCCATCAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000556276.5; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000556146.1; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000553376.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192304 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013266 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55968895-55968896:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGCCATCAAGCTAGCAGACTTTGGACTAGCCAGAGCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000556276.5; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000556146.1; ENST00000554619.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192305 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013267 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55968933-55968934:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | CTTTTGGAGTCCCTGTTCGTACTTACACCCATGAGGTGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.278136905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000556276.5; ENST00000556146.1; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000555408.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192306 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013268 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55968937-55968938:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | TGGAGTCCCTGTTCGTACTTACACCCATGAGGTGAGTCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000556146.1; ENST00000556464.5; ENST00000556276.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192307 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013269 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55969541-55969542:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | ATATTATTCCACAGCTGTGGACATCTGGAGCCTGGGCTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000554619.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000556276.5; ENST00000556146.1; ENST00000556464.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192308 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013270 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971161-55971162:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | AGTTACTTCTATGCCTGATTACAAGCCAAGTTTCCCCAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000556656.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192310 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013271 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971210-55971211:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | CAAGATTTTAGTAAAGTTGTACCTCCCCTGGATGAAGATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.8355 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000553376.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192311 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013272 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971321-55971322:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CAGGATGAAGGAAGGATGAGACCCTGAAATCTGGGCCTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192312 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013273 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971457-55971458:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | TGGTTTCCTGATTTCTGGGAACACCTGCTGCCCATTTAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192313 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013274 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971542-55971543:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | AATGCTGCACTACGACCCTAACAAGCGGATTTCGGCCAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000556656.5; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000555408.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192314 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013275 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971706-55971707:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTTGGCCTTGGGCTATTTGGACTCAGGTGGGCCCTCTGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000554545.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192315 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013276 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971725-55971726:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GACTCAGGTGGGCCCTCTGAACTTGCCTTAAACACTCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192316 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013277 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971736-55971737:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCCCTCTGAACTTGCCTTAAACACTCACCTTCTAGTCTTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440311.6; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192317 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013278 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971794-55971795:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TACAGGGGTGAAAGGGGGGAACCAGTGAAAATGAAAGGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1B; H1A; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000553376.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192319 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013279 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971831-55971832:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | GAAGTTTCAGTATTAGATGCACTTAAGTTAGCCTCCACCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000554545.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192320 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013280 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971920-55971921:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | AATTTTAAAAAAGCCTTCCTACACGTTAGATTTGCCGTACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192321 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013281 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971922-55971923:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TTTTAAAAAAGCCTTCCTACACGTTAGATTTGCCGTACCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.058863095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192322 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013282 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971985-55971986:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TATTTCCAGTGTTTGGGATGACCAGGATCCCAAGCCTCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.839113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000555408.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192323 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013283 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972011-55972012:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | ATCCCAAGCCTCCTGCTGCCACAATGTTTATAAAGGCCAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000555408.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192324 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013284 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972064-55972065:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTAAGTTGGTGCTTTTGAGAACCAAGTAAAACAAAACCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000553376.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192325 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013285 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972074-55972075:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCTTTTGAGAACCAAGTAAAACAAAACCACTGGGAGGAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000555408.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192326 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013286 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972079-55972080:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGAGAACCAAGTAAAACAAAACCACTGGGAGGAGTCTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000555408.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192327 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013287 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972178-55972179:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | CTCACCTAATAGGCTGGGAGACTGAAGACTCAGCCCGGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192328 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013288 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972276-55972277:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | GGAATCTGGGAGGCCCTGAGACAGGGATTGTGCTTCATTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000555408.5; ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192329 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013289 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972413-55972414:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | CCTGATCCCATTTTCCTCTGACGTCCACCTCCTACCCCATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.833690476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192330 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013290 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972476-55972477:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | GCATCATTTTGAGAATGCTGACACTTTTTCAGGGCTGTGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192331 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013291 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972478-55972479:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | ATCATTTTGAGAATGCTGACACTTTTTCAGGGCTGTGATTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.506922619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192332 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013292 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972541-55972542:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TTTCTTTAAAAGAAGGATGAACAATTATATTTATATTTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192333 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013293 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55972653-55972654:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | CACCTTGGGGTTTTGTAATGACAGTGCTAAAAAAAAAAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000266970.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_192334 | ||
Pseudouridine (Pseudo)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: PSESITE000016 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:55971834-55971835:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | GTTTCAGTATTAGATGCACTTAAGTTAGCCTCCACCACCCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000553376.5; ENST00000554545.1; ENST00000266970.9; ENST00000354056.4; ENST00000555408.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Pseudo_site_1146 | ||
References