m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00470)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
DDIT3
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
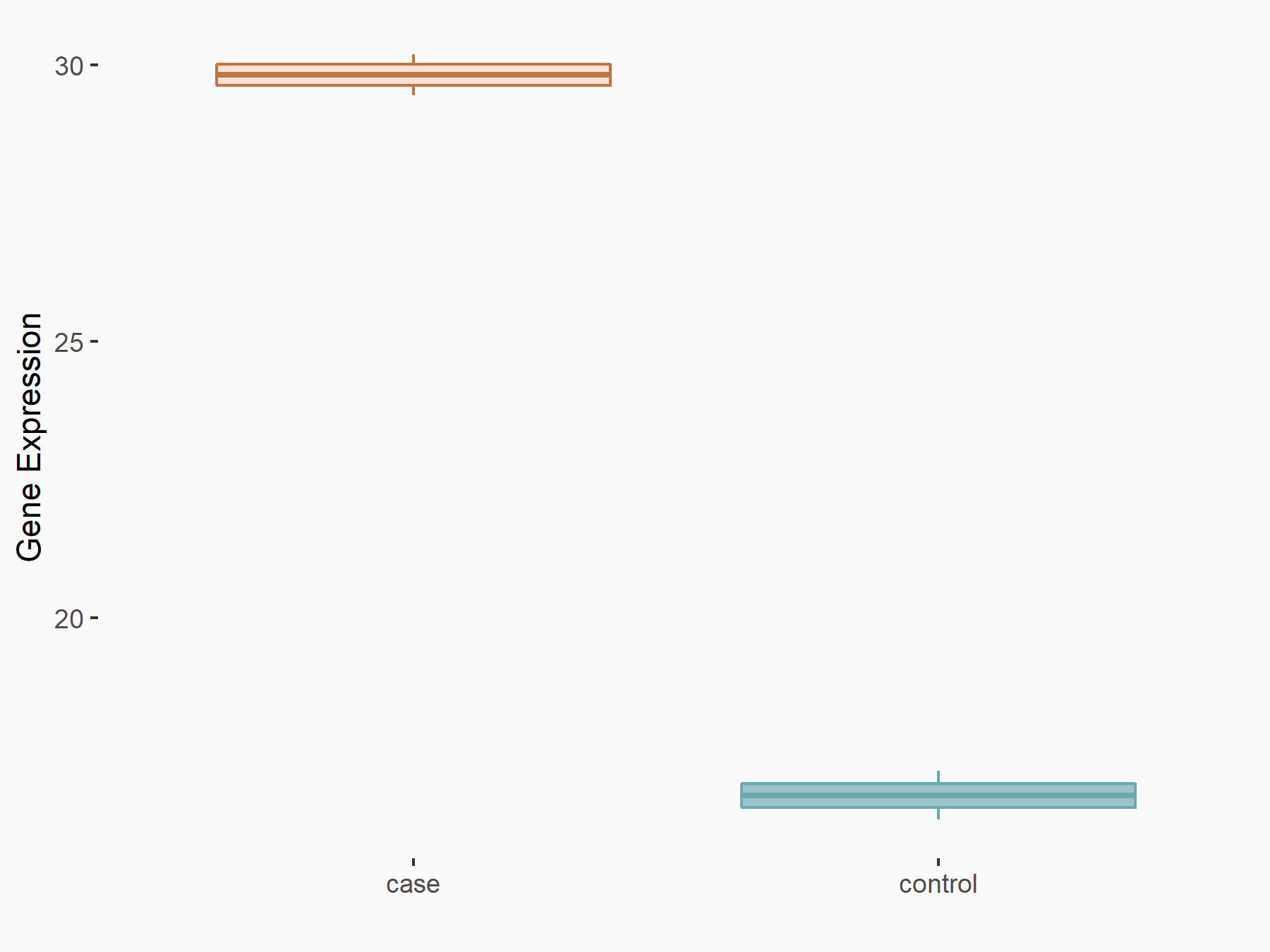  |
logFC: 7.94E-01 p-value: 7.54E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 3 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Fluorouracil | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Paclitaxel | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
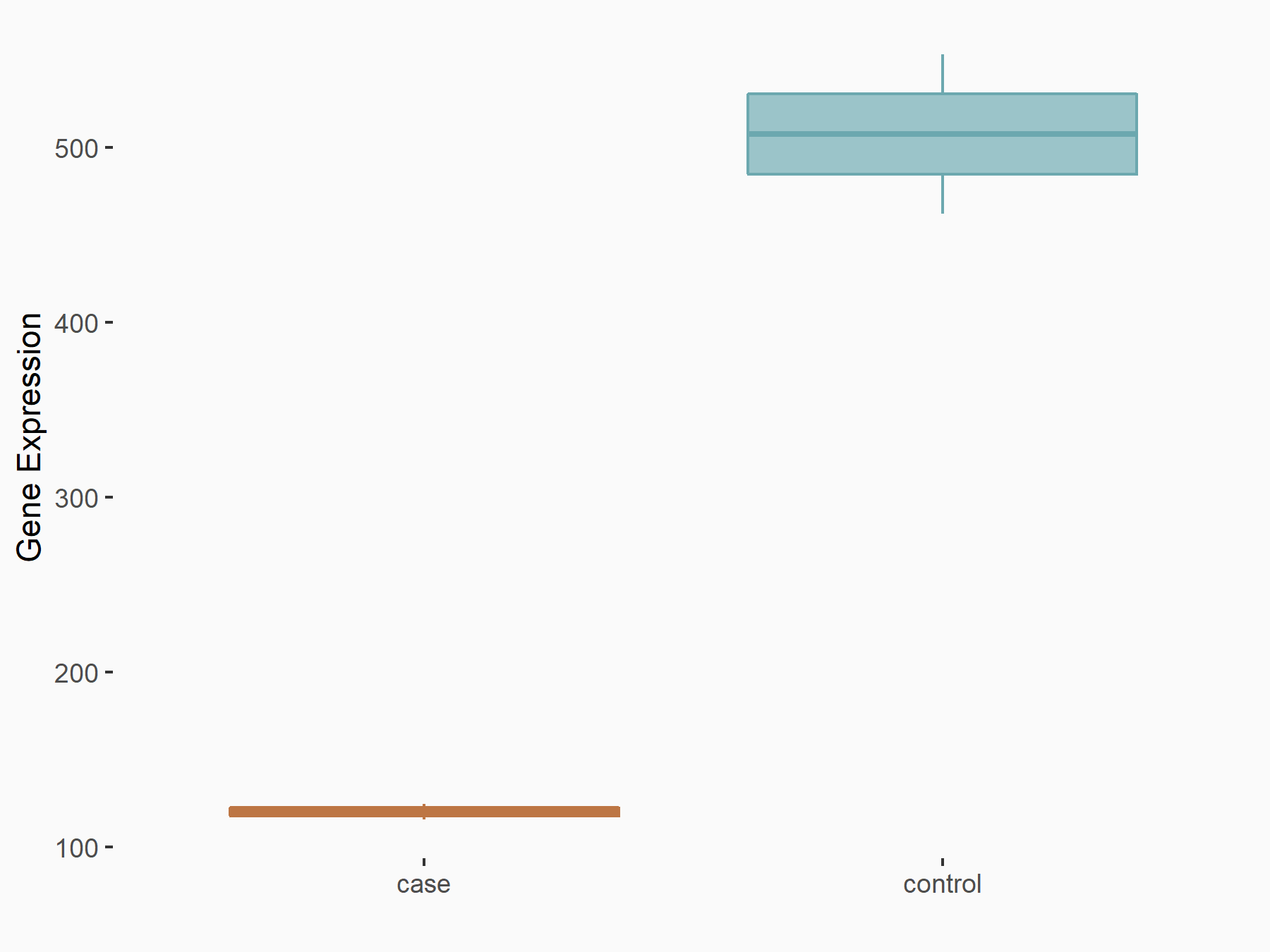  |
logFC: -2.08E+00 p-value: 8.68E-26 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP) mRNA decay through its 3' UTR N6-methyladenosine (m6A) to inhibit its downstream pro-apoptotic target gene expression, suppress ER proteotoxic liver disease. UPR induces METTL14 expression by competing against the HRD1-ER-associated degradation (ERAD) machinery to block METTL14 ubiquitination and degradation. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease | ICD-11: DB9Z | ||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Ubiquitination degradation | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Fluorouracil | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Paclitaxel | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 promotes DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP) mRNA decay through its 3' UTR N6-methyladenosine (m6A) to inhibit its downstream pro-apoptotic target gene expression, suppress ER proteotoxic liver disease. UPR induces METTL14 expression by competing against the HRD1-ER-associated degradation (ERAD) machinery to block METTL14 ubiquitination and degradation. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Ubiquitination degradation | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Fluorouracil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Paclitaxel
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00470)
| In total 28 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013594 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516624-57516625:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGATTGTACATTTATTTATTACTGTCCCTATCTATTAAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547303.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195163 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013595 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516637-57516638:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGCTTGTATATAGAGATTGTACATTTATTTATTACTGTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195164 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013596 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516674-57516675:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGGGGAAGGCTTGGAGTAGACAAAAGGAAAGGTCTCAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195166 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013597 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516702-57516703:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATGATGTGACCCTCAATCCCACATACGCAGGGGGAAGGCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195167 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013598 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516775-57516776:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATCAGTCCCCCACTTGGGCCACACTACCCACCTTTCCCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000551116.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195168 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013599 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516807-57516808:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGAATCTGCACCAAGCATGAACAATTGGGAGCATCAGTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195169 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013600 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516922-57516923:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGAATGAAAGGAAAGTGGCACAGCTAGCTGAAGAGAATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195170 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013601 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516946-57516947:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGCGCATGAAGGAGAAAGAACAGGAGAATGAAAGGAAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195171 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013602 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517000-57517001:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGAACCAGGAAACGGAAACAGAGTGGTCATTCCCCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195172 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013603 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517014-57517015:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGGAAGACCAAGGGAGAACCAGGAAACGGAAACAGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000552740.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195173 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013604 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517025-57517026:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCAGGAGGAAGAGGAGGAAGACCAAGGGAGAACCAGGAAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000552740.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195174 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013605 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517111-57517112:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTGACTGAGGAGGAGCCAGAACCAGCAGAGGTCACAAGCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; MT4; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000552740.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195175 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013606 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517128-57517129:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTGCTTCTCTGGCTTGGCTGACTGAGGAGGAGCCAGAACCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195176 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013607 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517335-57517336:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGAAGCCTGGTATGAGGACCTGCAAGAGGTCCTGTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; A549; Huh7; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195180 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013608 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517372-57517373:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CATTGCCTTTCTCCTTCGGGACACTGTCCAGCTGGGAGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; A549; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7; peripheral-blood; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000547526.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195182 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013609 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517423-57517424:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTGCAGATGTGCTTTTCCAGACTGATCCAACTGCAGAGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; A549; Huh7; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195183 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013610 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517476-57517477:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGCATAGACTGTTTGCTACATGGAGCTTGTTCCAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195185 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013611 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517486-57517487:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTTGCCAACTTGTGGCATAGACTGTTTGCTACATGGAGCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195187 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013612 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517511-57517512:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTACAAAAACAGGCATCAGACCAGCTTGCCAACTTGTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000552740.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195188 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013613 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517522-57517523:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTACAACTTTACCTACAAAAACAGGCATCAGACCAGCTTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195189 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013614 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517562-57517563:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CATAAACAATATGTAAATAAACAGATGTGGCTGTATTCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195190 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013615 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517577-57517578:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TAGCACCAAAGCAGCCATAAACAATATGTAAATAAACAGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195191 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013616 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517662-57517663:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CAAAAATTTTAAACGGCAGGACAGTAAATATTTTAGATGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HEK293T; HeLa; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195192 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013617 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517700-57517701:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCACACCTGAAAGCAGGTAAACTTAACCTACCCTTTTCCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; A549; fibroblasts; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000551116.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195193 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013618 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57517726-57517727:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGAAGGAAGTGTATCTTCATACATCACCACACCTGAAAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000642841.1; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195194 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013619 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57520430-57520431:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCAAAATCAGAGCTGGAACCTGAGGAGAGAGGCGAGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; A549; HEK293T; fibroblasts; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000642841.1; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000346473.7; ENST00000547303.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195195 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013620 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57520506-57520507:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGCGCTCCCGAGGTCAGAGACTTAAGTCTAAGGCACTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; A549; HEK293T; fibroblasts; MM6; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000547526.1; ENST00000552740.5; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195196 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE013621 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57521672-57521673:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGAAAATAGGTGGCCAAACAGAATCGGGTCCACTGGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000623876.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_195197 | ||
Pseudouridine (Pseudo)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: PSESITE000019 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:57516762-57516763:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TTGGGCCACACTACCCACCTTTCCCAGAAGTGGCTACTGAC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000551116.5; ENST00000623876.2; ENST00000547303.5; ENST00000346473.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Pseudo_site_1159 | ||
References