m6A-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: M6ADRUG0089)
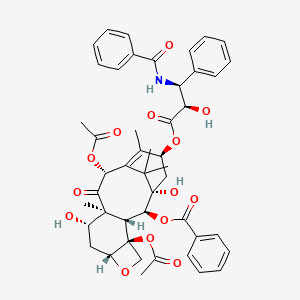
| Name |
Paclitaxel
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Paclitaxel
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status | Approved | [1] | |||
| Structure |
 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
C47H51NO14
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C47H51NO14/c1-25-31(60-43(56)36(52)35(28-16-10-7-11-17-28)48-41(54)29-18-12-8-13-19-29)23-47(57)40(61-42(55)30-20-14-9-15-21-30)38-45(6,32(51)22-33-46(38,24-58-33)62-27(3)50)39(53)37(59-26(2)49)34(25)44(47,4)5/h7-21,31-33,35-38,40,51-52,57H,22-24H2,1-6H3,(H,48,54)/t31-,32-,33+,35-,36+,37+,38-,40-,45+,46-,47+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Full List of m6A Targets Related to This Drug
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Drug
| In total 7 item(s) under this drug | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02225 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (CALCOCO1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02226 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02249 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (CALCOCO1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02250 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02273 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (CALCOCO1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02274 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05665 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | FGD5 antisense RNA 1 (FGD5-AS1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | FGD5 antisense RNA 1 (FGD5-AS1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Endometrial cancer | |
References