m6A-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: M6ADRUG0005)
| Name |
Fluorouracil
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5-Fluorouracil; 51-21-8; fluorouracil; 5-FU; Fluoroplex; Adrucil; Efudex; Carac; Fluracil; Fluoroblastin; 5-fluoropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione; Kecimeton; Timazin; Carzonal; Efudix; Arumel; Fluril; Queroplex; Fluracilum; Ulup; 5-Fluoracil; Phthoruracil; Fluro Uracil; 5-Fluoro-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione; Ftoruracil; Fluorouracilum; Efurix; Fluri; 5 Fluorouracil; Effluderm (free base); 5-fluoro-1H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione; Fluorouracilo; Fluroblastin; Phtoruracil; 2,4-Dihydroxy-5-fluoropyrimidine; 2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione, 5-fluoro-; Adrucil; Effluderm; Fluorouracile; Fluoruracil; Fluracedyl; Flurodex; Neofluor; Onkofluor; Ribofluor; Tetratogen; URF; Allergan Brand of Fluorouracil; Biosyn Brand of Fluorouracil; CSP Brand of Fluorouracil; Cinco FU; Dakota Brand of Fluorouracil; Dermatech Brand of Fluorouracil; Dermik Brandof Fluorouracil; Ferrer Brand of Fluorouracil; Fluoro Uracile ICN; Fluorouracil GRY; Fluorouracil Mononitrate; Fluorouracil Monopotassium Salt; Fluorouracil Monosodium Salt; Fluorouracil Potassium Salt; Fluorouracil Teva Brand; Fluorouracile Dakota; Fluorouracile [DCIT]; Fluorouracilo Ferrer Far; Gry Brand of Fluorouracil; Haemato Brand of Fluorouracil; Haemato fu; Hexal Brand of Fluorouracil; ICN Brand of Fluorouracil; Inhibits thymilidate synthetase; Medac Brand of Fluorouracil; Neocorp Brand of Fluorouracil; Onkoworks Brand of Fluorouracil; Ribosepharm Brand of Fluorouracil; Riemser Brand of Fluorouracil; Roche Brand of Fluorouracil; Teva Brand of Fluorouracil; F 6627; F0151; IN1335; U 8953; Adrucil (TN); Carac (TN); Dakota, Fluorouracile; Efudex (TN); Fluoro-Uracile ICN; Fluoro-uracile; Fluoro-uracilo; Fluoroplex (TN); Fluorouracil-GRY; Fluorouracilo [INN-Spanish]; Fluorouracilum [INN-Latin]; Haemato-fu; Ro 2-9757; U-8953; Ro-2-9757; Fluorouracil (JP15/USP/INN); Fluorouracil [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; 1-fluoro-1h-pyrimidine-2,4-dione; 2,4-Dioxo-5-fluoropryimidine; 2,4-Dioxo-5-fluoropyrimidine; 5 FU Lederle; 5 FU medac; 5 Fluorouracil biosyn; 5 HU Hexal; 5-FU (TN); 5-FU Lederle; 5-FU medac; 5-Faracil; 5-Fluor-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidindion; 5-Fluor-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidindion [Czech]; 5-Fluor-2,4-dihydroxypyrimidin; 5-Fluor-2,4-dihydroxypyrimidin [Czech]; 5-Fluor-2,4-pyrimidindiol; 5-Fluor-2,4-pyrimidindiol [Czech]; 5-Fluoracil [German]; 5-Fluoracyl; 5-Fluoro-2,4-pyrimidinedione; 5-Fluoropyrimidin-2,4-diol; 5-Fluoropyrimidine-2,4-dione; 5-Fluorouracil-biosyn; 5-Fluoruracil; 5-Fluoruracil [German]; 5-Ftouracyl; 5-HU Hexal; 5-fluoro uracil; 5FU
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status | Approved | [1] | |||
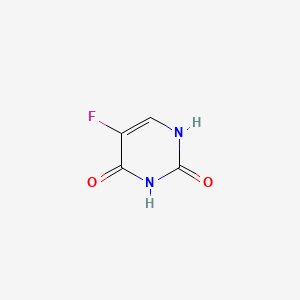
| Structure |
 |
||||
| Formula |
C4H3FN2O2
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C4H3FN2O2/c5-2-1-6-4(9)7-3(2)8/h1H,(H2,6,7,8,9)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
GHASVSINZRGABV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Full List of m6A Targets Related to This Drug
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | KIAA1429 acts as an oncogenic factor in breast cancer by regulating CDK1 in an N6-methyladenosine-independent manner.5'-fluorouracil was found to be very effective in reducing the expression of KIAA1429 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) in breast cancer. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulator | Protein virilizer homolog (VIRMA) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3/CHOP)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of mTORC1 signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein (DDIT3), which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Omeprazole pretreatment could enhance the inhibitory effect of 5-Fu, DDP and TAX on gastric cancer cells. FTO inhibition induced by omeprazole enhanced the activation of Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signal pathway that inhibited the prosurvival autophagy so as to improve the antitumor efficiency of chemotherapeutic drugs on GC cells. Meanwhile, transcript level of DDIT3, which is an apoptosis-related tumor suppressor gene downstream of mTORC1, was regulated by omeprazole-induced FTO silence through an m6A-dependent mechanism. m6A modification and its eraser FTO plays a role in the improvement of chemosensitivity mediated by proton pump inhibitor omeprazole. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
Neurocalcin-delta (NCALD)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 dependent m6A methylation was upregulated in CRC to promote the processing of miR 181d 5p by DGCR8. This led to increased miR 181d 5p expression, which inhibited the 5 FU sensitivity of CRC cells by targeting Neurocalcin-delta (NCALD). | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| In-vivo Model | A tumor-bearing model was established by subcutaneously injecting 100 ul HT29 cells (5×106) followed by an intravenous injection of CAFs-derived exosomes (50 ug/mouse every three days) into the tail vein of the mice. An intraperitoneal injection of 5-FU (50 mg/kg, every week) was administered on day 12. | |||
RAD51-associated protein 1 (RAD51AP1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 augmented 5 FU induced DNA damage and overcame 5 FU resistance in HCT 8R cells, which could be mimicked by inhibition of RAD51-associated protein 1 (RAD51AP1). The present study revealed that the METTL3/RAD51AP1 axis plays an important role in the acquisition of 5 FU resistance in CRC. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Response Summary | ARHGAP5-AS1 also stabilized ARHGAP5 mRNA in the cytoplasm by recruiting METTL3 to stimulate m6A modification of Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5) mRNA. As a result, ARHGAP5 was upregulated to promote chemoresistance and its upregulation was also associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. downregulation of ARHGAP5-AS1 in resistant cells evidently reversed the resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs including cisplatin (DDP), ADM, and 5-FU. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cellular processes | |||
| Cellular transport | ||||
| Cellular catabolism | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 |
| SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | |
Translocation protein SEC62 (SEC62)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Response Summary | Translocation protein SEC62 (SEC62) upregulated by the METTL3-mediated m6A modification promotes the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by binding to beta-catenin and enhancing Wnt signalling. Depletion of Sec62 sensitized the CRC cells to 5-Fu or oxaliplatin treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Protein degradation | |||
| In-vitro Model | DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| In-vivo Model | DLD-1 cells were subcutaneously implanted into 4-6 weeks old female nude mice. When tumors reached a size of about 50 mm3, the nude mice were randomly divided into 6 groups. | |||
LBX2 antisense RNA 1 (LBX2-AS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Response Summary | The increased LBX2 antisense RNA 1 (LBX2-AS1) in CRC was mediated by METTL3-dependent m6A methylation. LBX2-AS1 serves as a therapeutic target and predictor of 5-FU benefit in colorectal cancer patients. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
hsa-miR-181d-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 dependent m6A methylation was upregulated in CRC to promote the processing of miR 181d 5p by DGCR8. This led to increased hsa-miR-181d-5p expression, which inhibited the 5 FU sensitivity of CRC cells by targeting NCALD. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| In-vivo Model | A tumor-bearing model was established by subcutaneously injecting 100 ul HT29 cells (5×106) followed by an intravenous injection of CAFs-derived exosomes (50 ug/mouse every three days) into the tail vein of the mice. An intraperitoneal injection of 5-FU (50 mg/kg, every week) was administered on day 12. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Drug
| In total 20 item(s) under this drug | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02056 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) | |
| m6A Target | . | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Homeobox D10 (HOXD10) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02057 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) | |
| m6A Target | . | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Homeobox D10 (HOXD10) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03286 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | |
| m6A Target | pri-miR-17 | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03351 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | |
| m6A Target | Apoptosis regulatory protein Siva (SIVA1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03449 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| m6A Target | Apoptosis regulatory protein Siva (SIVA1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03558 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Translocation protein SEC62 (SEC62) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03559 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | LBX2 antisense RNA 1 (LBX2-AS1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03564 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | RAD51-associated protein 1 (RAD51AP1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03574 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-181d-5p | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03575 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Neurocalcin-delta (NCALD) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03603 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Translocation protein SEC62 (SEC62) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03604 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | LBX2 antisense RNA 1 (LBX2-AS1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03609 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | RAD51-associated protein 1 (RAD51AP1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03619 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-181d-5p | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03620 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Neurocalcin-delta (NCALD) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03642 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05517 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | LBX2 antisense RNA 1 (LBX2-AS1) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | LBX2 antisense RNA 1 (LBX2-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-422a | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05615 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-181d-5p | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-181d-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Neurocalcin-delta (NCALD) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05975 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) | |
| m6A Target | . | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) | |
| Regulated Target | Homeobox D10 (HOXD10) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05983 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | |
| m6A Target | Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | ARHGAP5 antisense RNA 1 (head to head) (ARHGAP5-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
References