m6A Regulator Information
General Information of the m6A Regulator (ID: REG00005)
| Regulator Name | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alkylated DNA repair protein alkB homolog 5; Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase alkB homolog 5; ABH5; OFOXD1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | ALKBH5 | ||||
| Sequence |
MAAASGYTDLREKLKSMTSRDNYKAGSREAAAAAAAAVAAAAAAAAAAEPYPVSGAKRKY
QEDSDPERSDYEEQQLQKEEEARKVKSGIRQMRLFSQDECAKIEARIDEVVSRAEKGLYN EHTVDRAPLRNKYFFGEGYTYGAQLQKRGPGQERLYPPGDVDEIPEWVHQLVIQKLVEHR VIPEGFVNSAVINDYQPGGCIVSHVDPIHIFERPIVSVSFFSDSALCFGCKFQFKPIRVS EPVLSLPVRRGSVTVLSGYAADEITHCIRPQDIKERRAVIILRKTRLDAPRLETKSLSSS VLPPSYASDRLSGNNRDPALKPKRSHRKADPDAAHRPRILEMDKEENRRSVLLPTHRRRG SFSSENYWRKSYESSEDCSEAAGSPARKVKMRRH Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | alkB family | ||||
| Function |
Dioxygenase that demethylates RNA by oxidative demethylation: specifically demethylates N(6)-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA, the most prevalent internal modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) in higher eukaryotes. Can also demethylate N(6)-methyladenosine in single-stranded DNA (in vitro). Requires molecular oxygen, alpha-ketoglutarate and iron. Demethylation of m6A mRNA affects mRNA processing and export. Required for the late meiotic and haploid phases of spermatogenesis by mediating m6A demethylation in spermatocytes and round spermatids: m6A demethylation of target transcripts is required for correct splicing and the production of longer 3'-UTR mRNAs in male germ cells (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 54890 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Regulator Type | WRITER ERASER READER | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
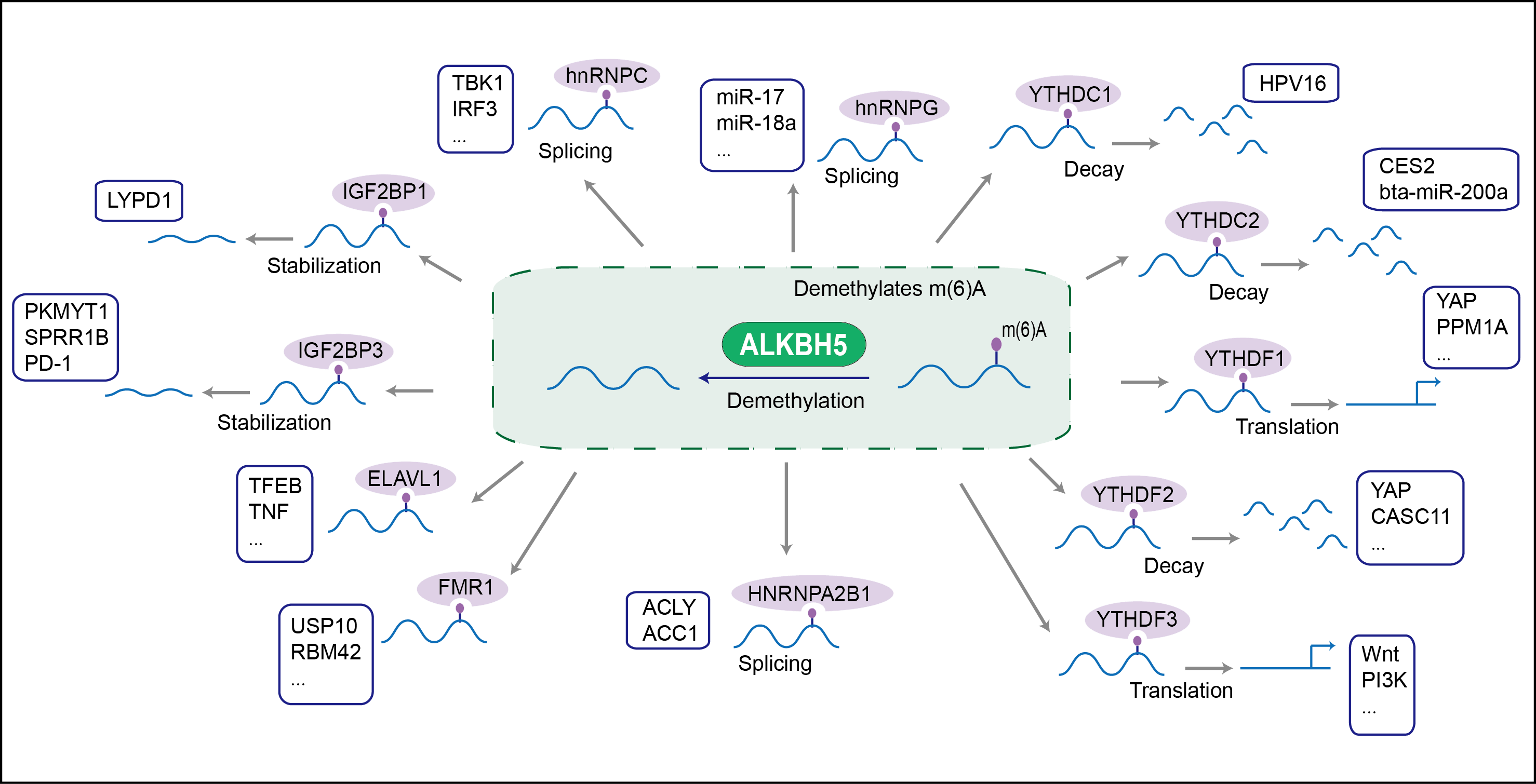
|
|||||
| Target Genes | Click to View Potential Target Genes of This Regulator | ||||
Full List of Target Gene(s) of This m6A Regulator and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
ALKBH5 can regulate the m6A methylation of following target genes, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulted from the regulation of certain target gene.
Browse Target Gene related Disease
Browse Target Gene related Drug
Alpha-enolase (ENO1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | human pluripotent stem cells | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: hILO ALKBH5knockout cells
Control: hILO wild type cells
|
GSE163945 | |
| Regulation |
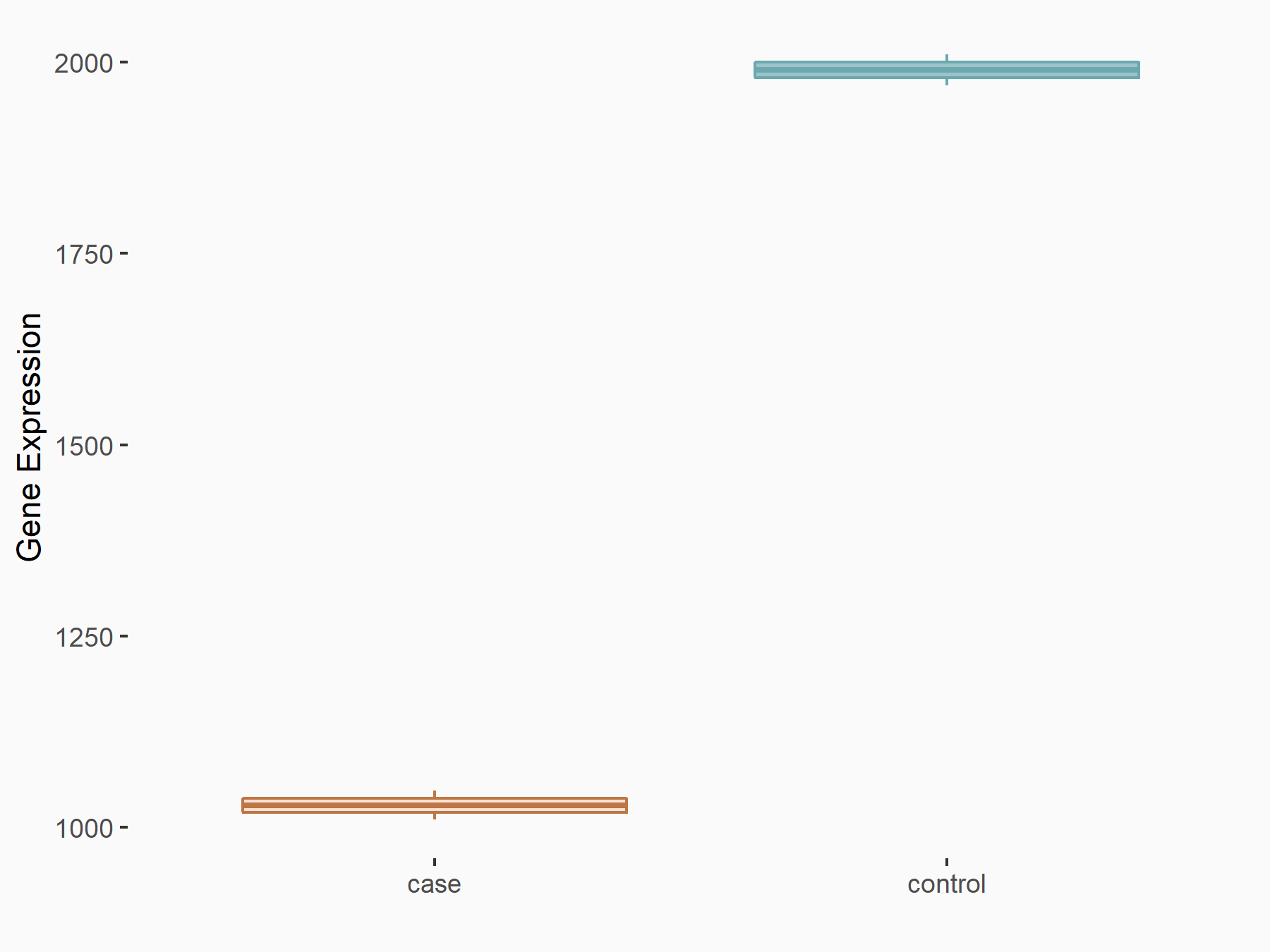  |
logFC: -9.52E-01 p-value: 3.98E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Carbon metabolism | hsa01200 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
In-vitro Model |
PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| NCI-H441 | Lung papillary adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1561 | |
| NCI-H292 | Lung mucoepidermoid carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0455 | |
| NCI-H2030 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1517 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| 3LL | Malignant tumors of the mouse pulmonary system | Mus musculus | CVCL_5653 | |
| HCC827 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2063 | |
| Calu-1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0608 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| A-427 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1055 | |
| 16HBE14o- | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0112 | |
| In-vivo Model | KP and Mettl3-/- mice were bred to generate KPM-/- mice. Afterwards, the KP and KPM-/- mice were intranasally infected under anesthesia with adeno-associated virus type 5 (AAV5) expressing Cre to initiate lung tumorigenesis along with ALKBH5-expressing AAV5 or Empty AAV5 to generate KPE, KPA, KPEM-/- and KPAM-/- spontaneous LUAD mouse models. For generation of LLC-based intra-pulmonary tumor mouse models, 1 × 107 LLC cells were injected into C57BL/6 mice via the tail vein.For cell-derived xenograft (CDX) mouse models, 1.0 × 107 H1299 or 1.5 × 107 H1975 cells were subcutaneously injected into 4-6-week-old athymic nude mice. The tumors were monitored at indicated time points and isolated for further analysis after sacrifice. | |||
| Response Summary | Alpha-enolase (ENO1) positively correlated with METTL3 and global m6A levels, and negatively correlated with ALKBH5 in human Lung adenocarcinoma(LUAD). In addition, m6A-dependent elevation of ENO1 was associated with LUAD progression. | |||
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | CAG cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 CAG cells
Control: shNC CAG cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
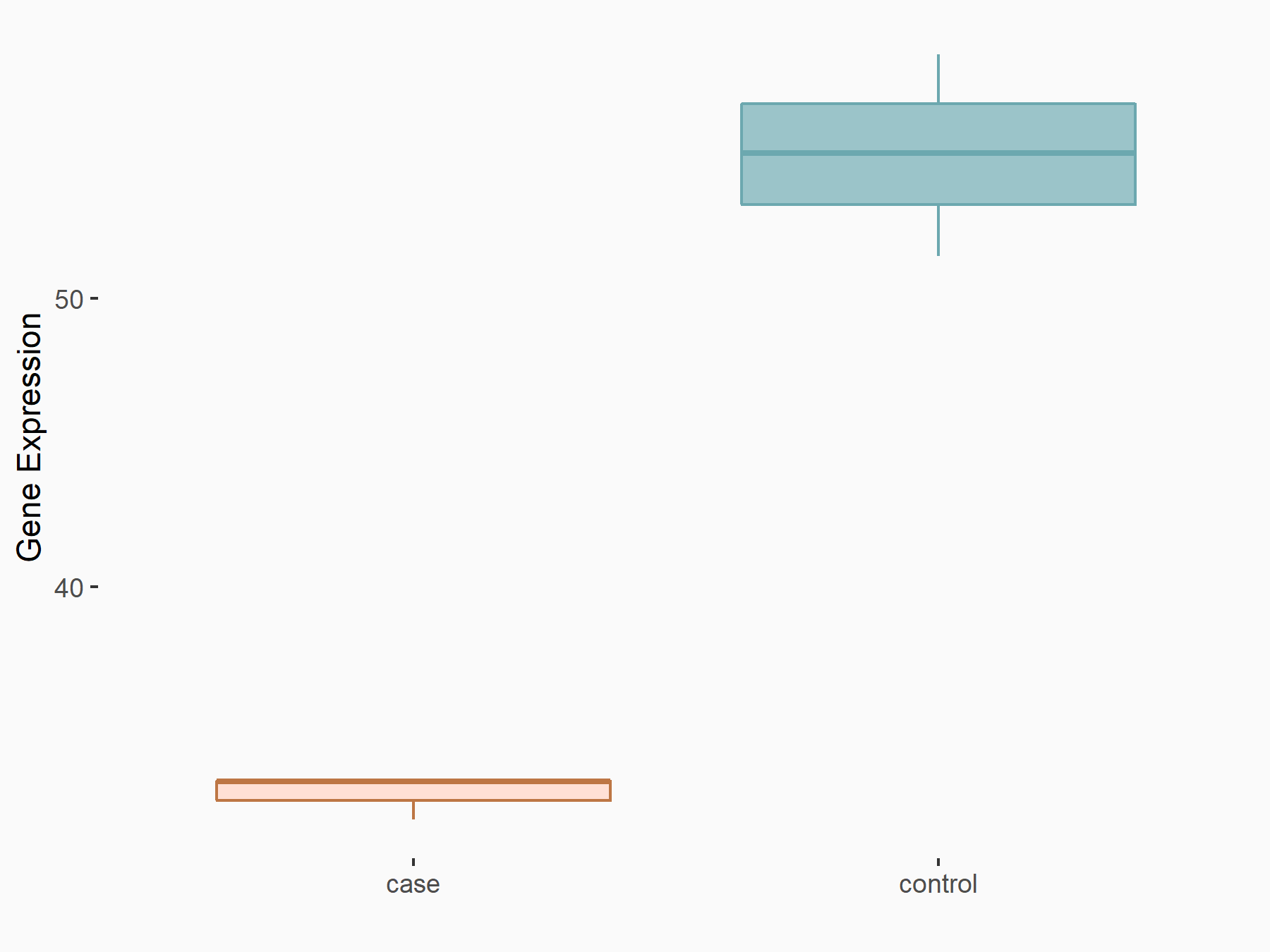 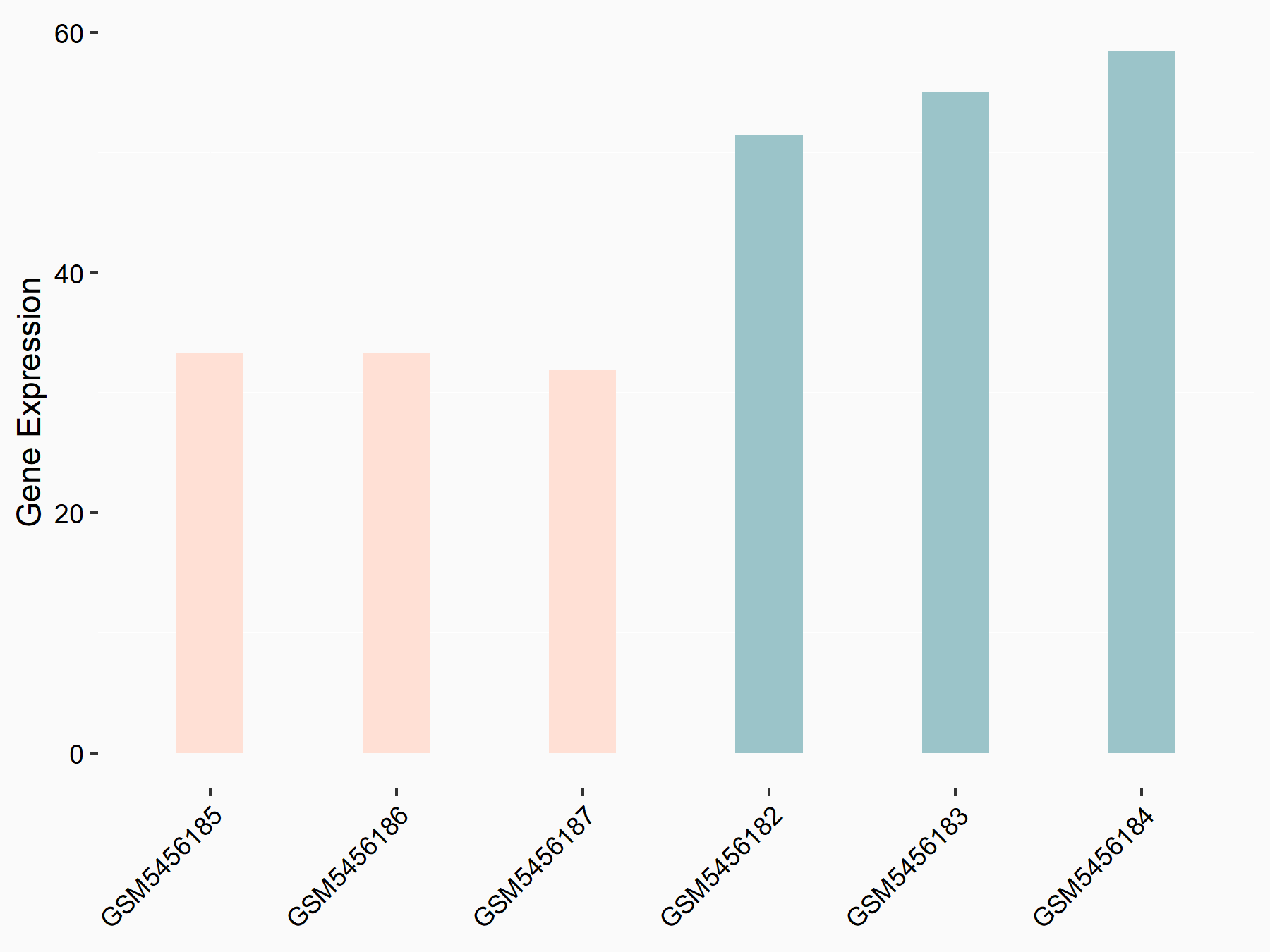 |
logFC: -7.25E-01 p-value: 1.10E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
In-vitro Model |
A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| CoC1 | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6891 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | SKOV3 or A2780 cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral vectors and injected (5 × 106 cells/mouse in 200 uL volume) subcutaneously into the left armpit of 6-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 21 days, the animals were sacrificed to confirm the presence of tumors and weigh the established tumors. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is a tumor-promoting gene in epithelial ovarian cancer, which is involved in the mTOR pathway and Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2)-Beclin1 complex. ALKBH5 activated EGFR-PIK3CA-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. | |||
Aurora kinase B (AURKB)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
 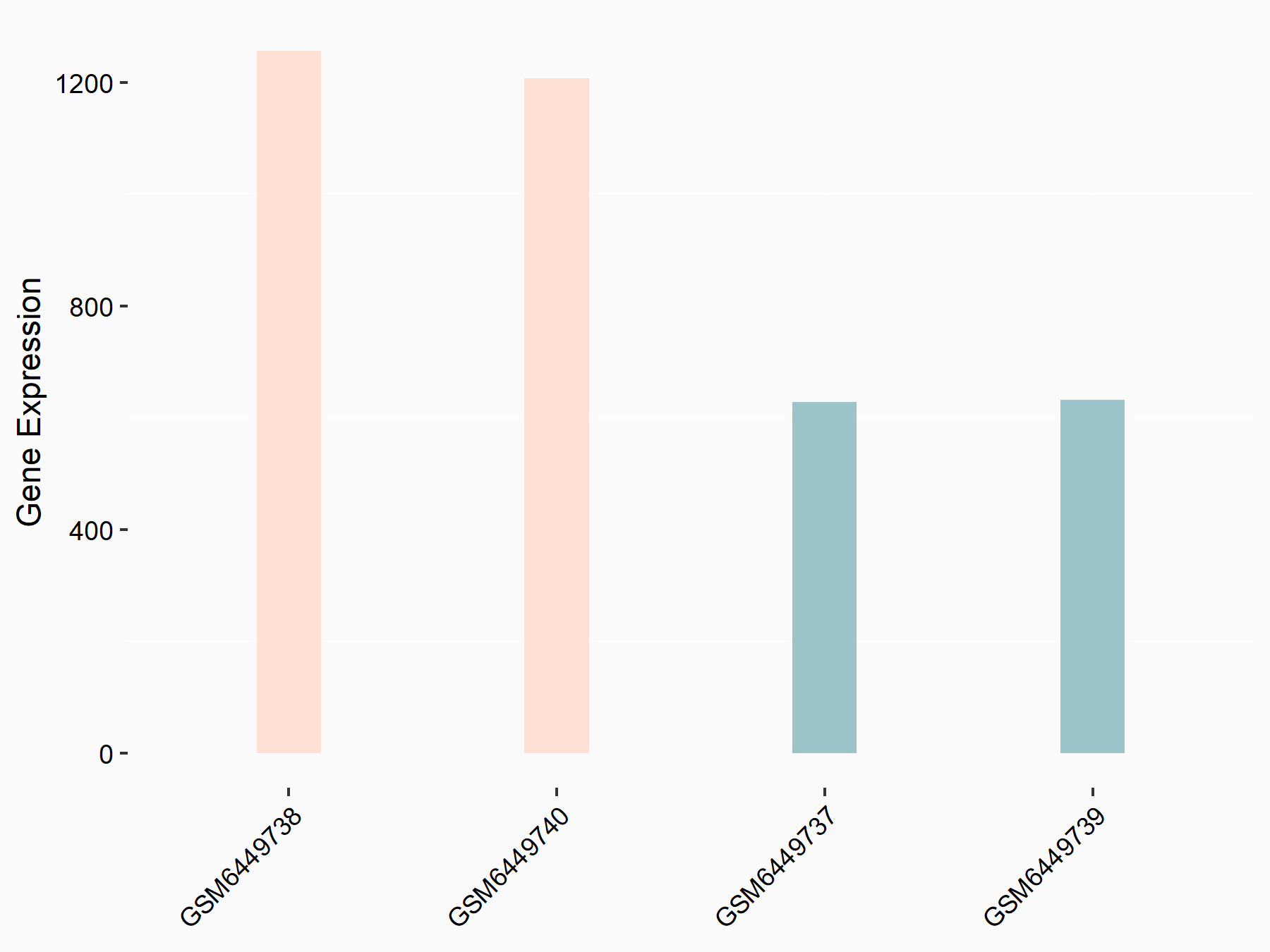 |
logFC: 9.68E-01 p-value: 1.88E-24 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell colony formation | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
769-P | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1050 |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| ACHN | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1067 | |
| Caki-1 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0234 | |
| Caki-2 | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0235 | |
| HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 | |
| In-vivo Model | The nude mice were randomly grouped into 2 groups, of 5 mice each; 786-0 cells (7×106 in 100 L PBS) were stabilized with ALKBH5 knockdown lentiviral transfection vector (shALKBH5) or scramble vector (SCR) via subcutaneous injection into the left armpit of each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 plays a carcinogenic role in renal cell carcinoma by stabilizing Aurora kinase B (AURKB) mRNA in a m6A-dependent manner. | |||
Beclin-1 (BECN1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
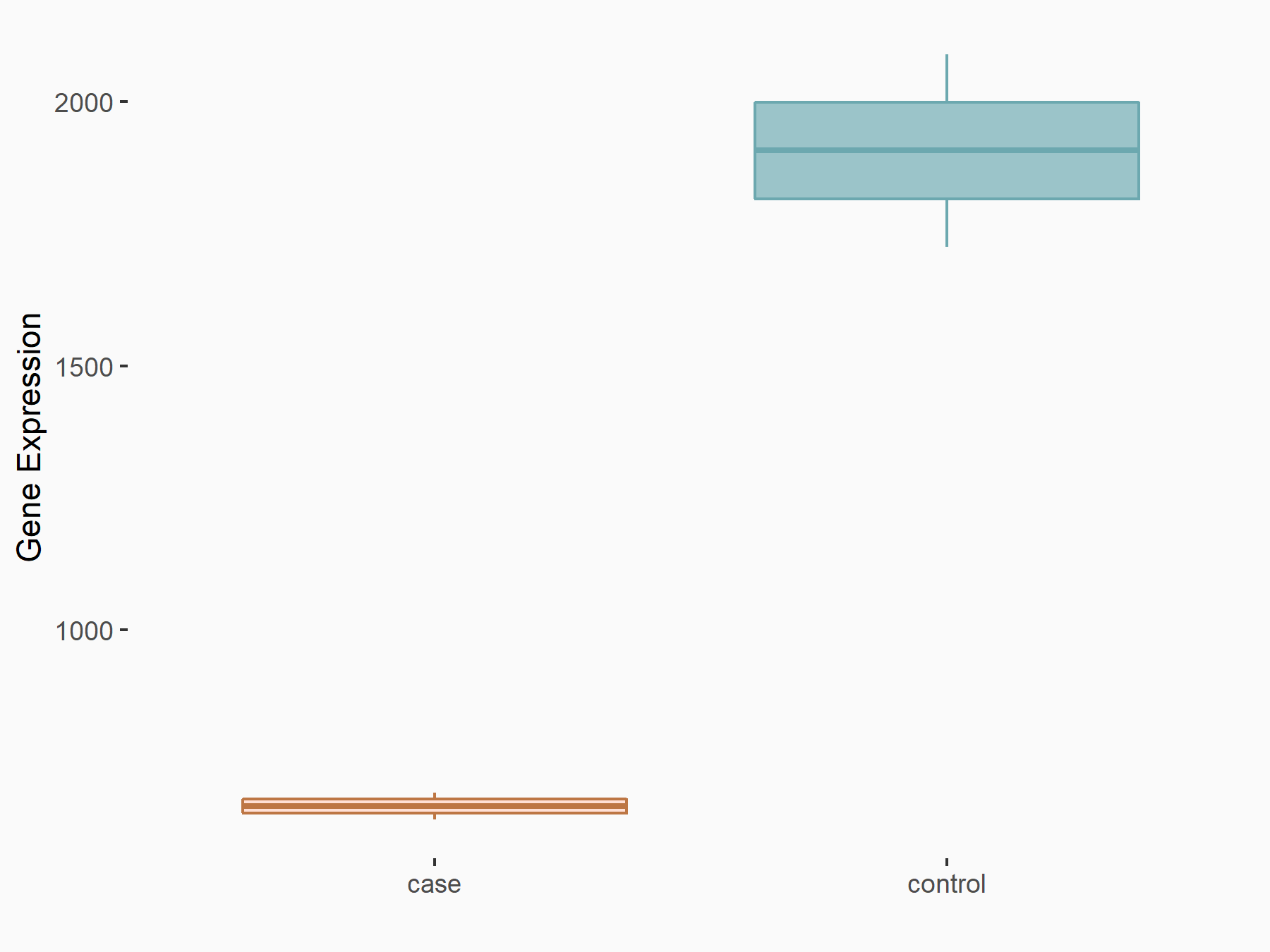 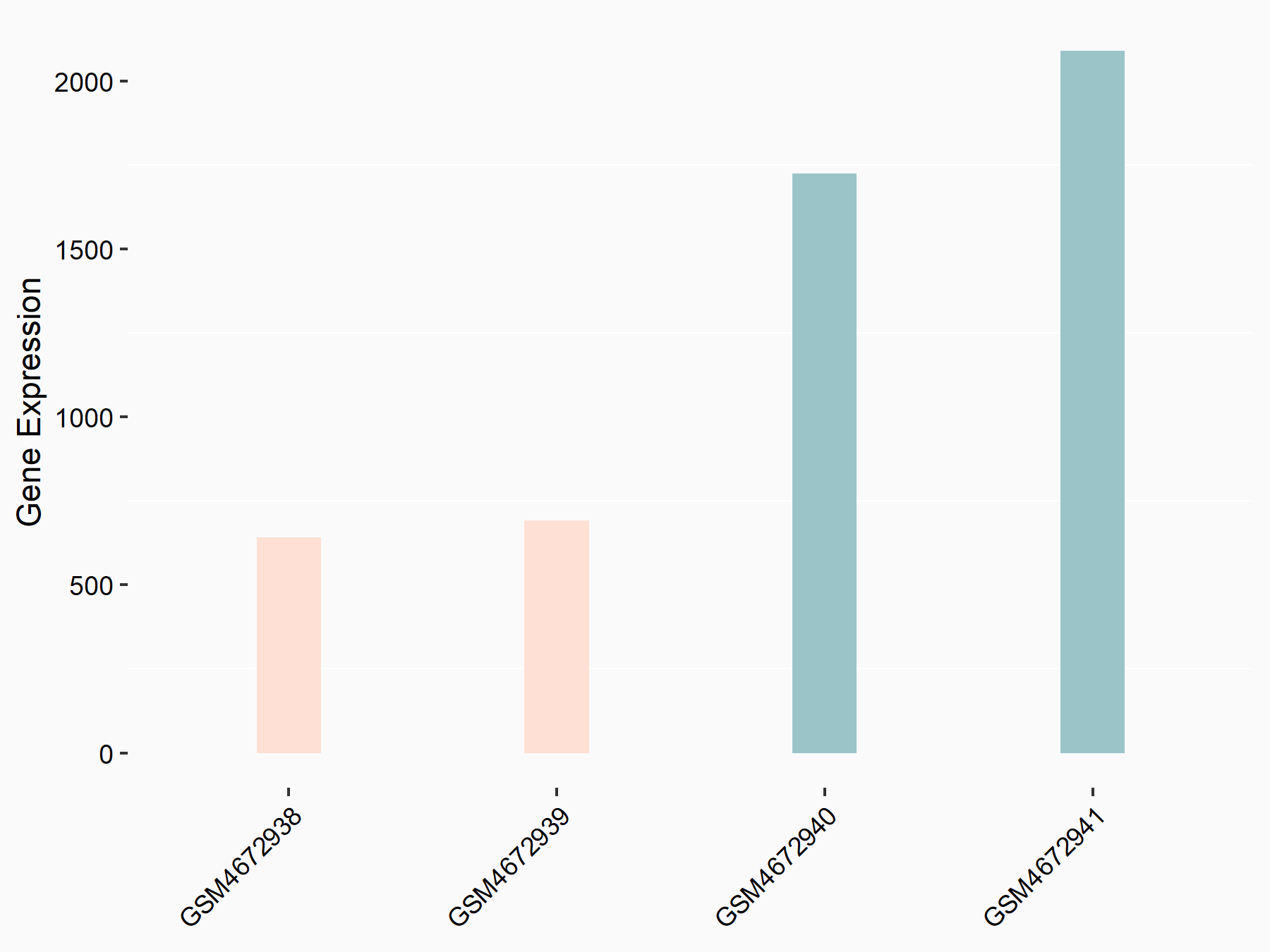 |
logFC: -1.52E+00 p-value: 9.98E-13 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
In-vitro Model |
A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| CoC1 | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6891 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | SKOV3 or A2780 cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral vectors and injected (5 × 106 cells/mouse in 200 uL volume) subcutaneously into the left armpit of 6-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 21 days, the animals were sacrificed to confirm the presence of tumors and weigh the established tumors. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is a tumor-promoting gene in epithelial ovarian cancer, which is involved in the mTOR pathway and BCL-2-Beclin-1 (BECN1) complex. ALKBH5 activated EGFR-PIK3CA-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. | |||
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
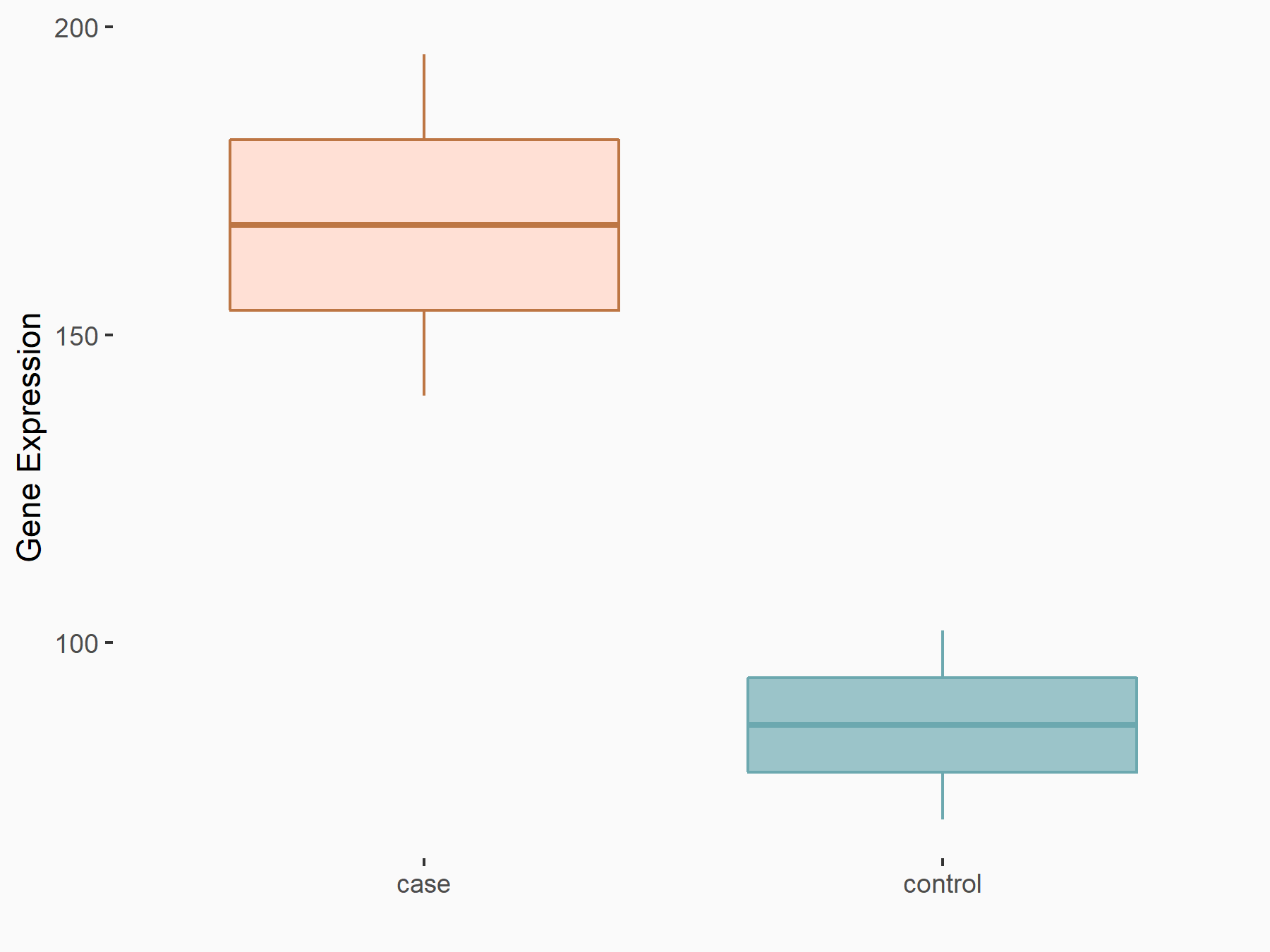 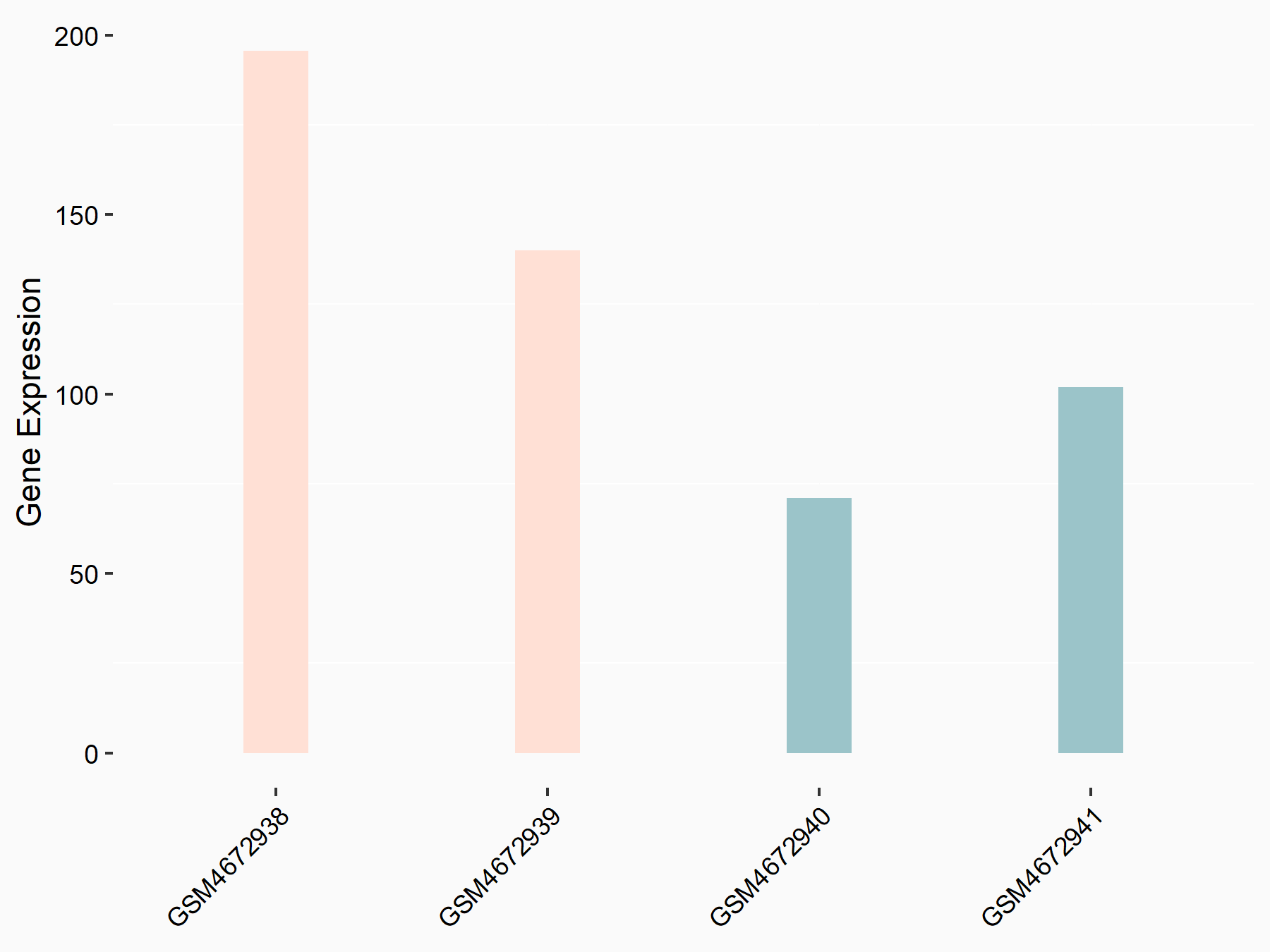 |
logFC: 9.58E-01 p-value: 1.09E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ossification of spinal ligaments [ICD-11: FA83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ossification of spinal ligaments [ICD-11: FA83] | |||
| Responsed Drug | MK22606 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Ossification | |||
In-vitro Model |
Ligamentum flavum cells (Ligamentum flavum cells) | |||
| Response Summary | The overexpression of ALKBH5 led to the activation of p-AKT, and Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) was regulated by ALKBH5 through the AKT signaling pathway. ALKBH5 promoted the osteogenesis of the ligamentum flavum cells through BMP2 demethylation and AKT activation. MK22606 is an AKT inhibitor. Moreover, when ALKBH5 was knocked down in the ligamentum flavum cells, p-AKT was inhibited when compared with that in the overexpressed ALKBH5 and control groups. | |||
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
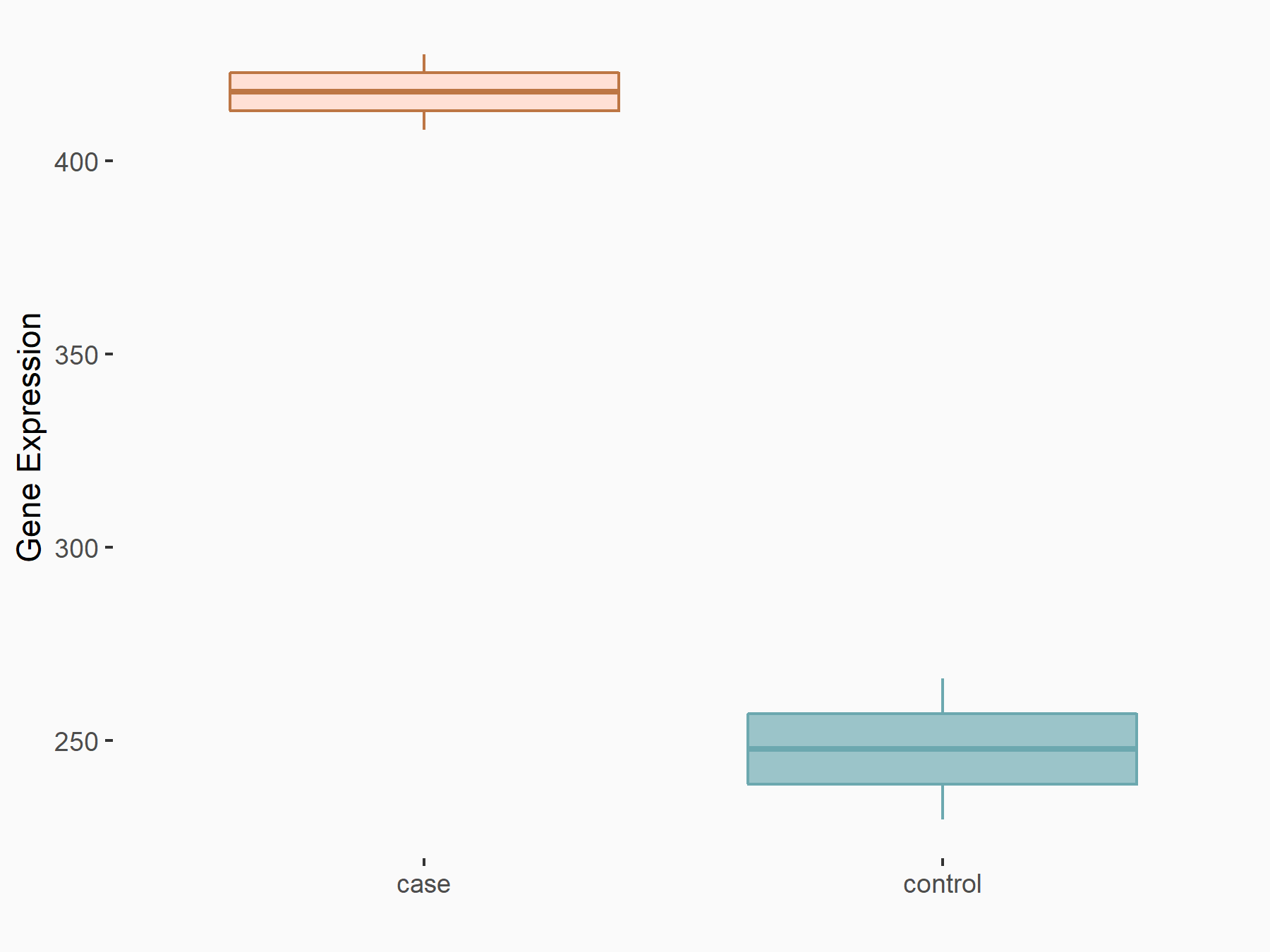 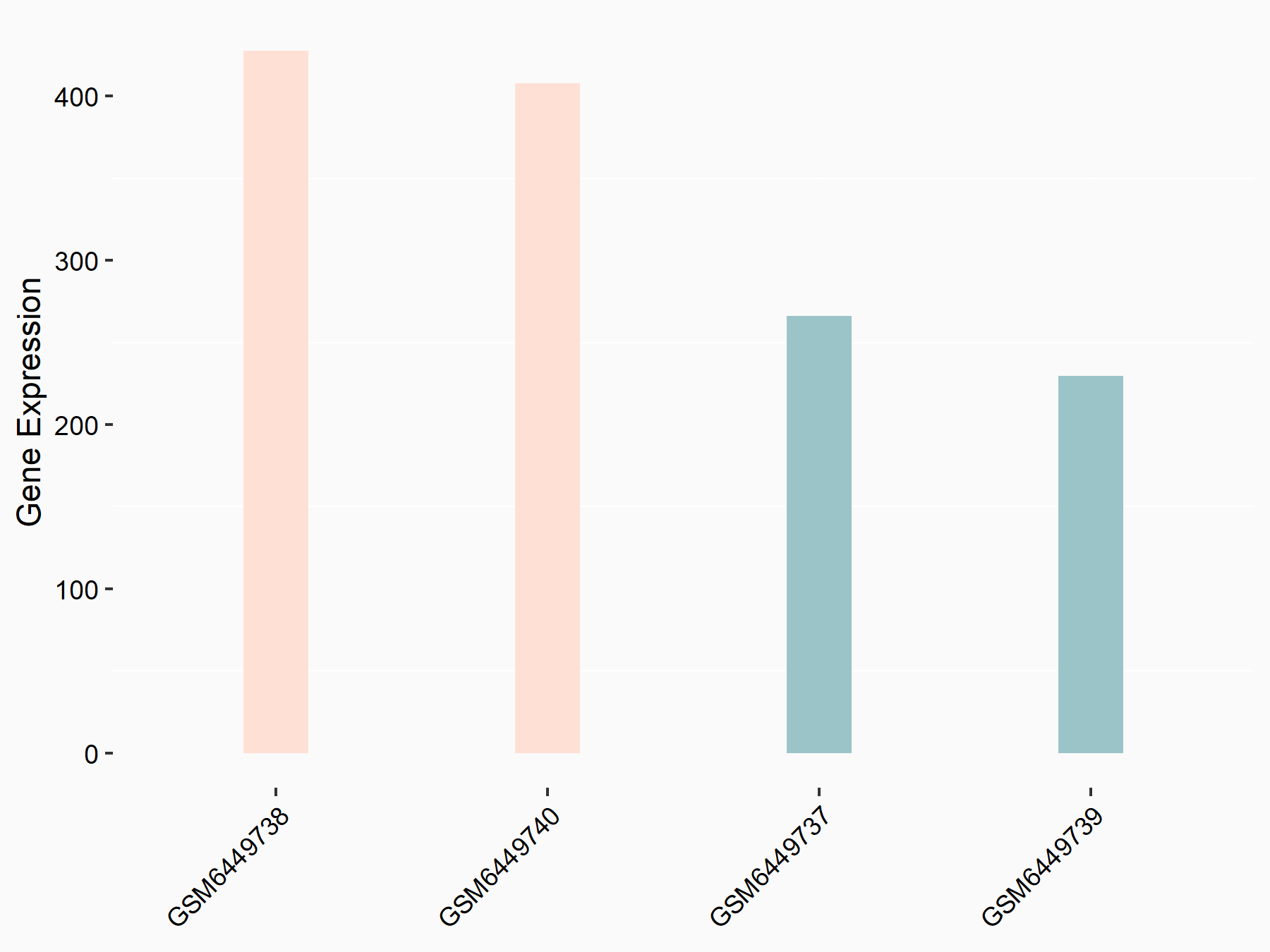 |
logFC: 7.57E-01 p-value: 2.32E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Doxil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| HCC1937 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0290 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneously transplanted tumor model, wild-type, PRMT5-overexpressing or doxorubicin-resistant MDA-MB-231 cells (5 × 106 per mouse, n = 5-7 for each group) were diluted in 100 uL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) plus 100 uL of Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and subcutaneously injected into female nude mice to investigate tumor growth. When all tumor volumes reached 100 mm3, the mice were randomly assigned and treated with the indicated drugs. In the experiment, doxorubicin was administered once a week via intravenous tail vein injection at 2 mg/kg body weight, and tadalafil was administered daily via oral gavage at 2 mg/kg body weight. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days using a digital caliper and calculated using the formula V = 1/2 × (diameter) × (smaller diameter)2. The mice were euthanized 27 days after injection. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 removed the m6A methylation of Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1) for mRNA stabilization and further enhanced DNA repair competency to decrease doxorubicin efficacy in breast cancer cells. | |||
Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
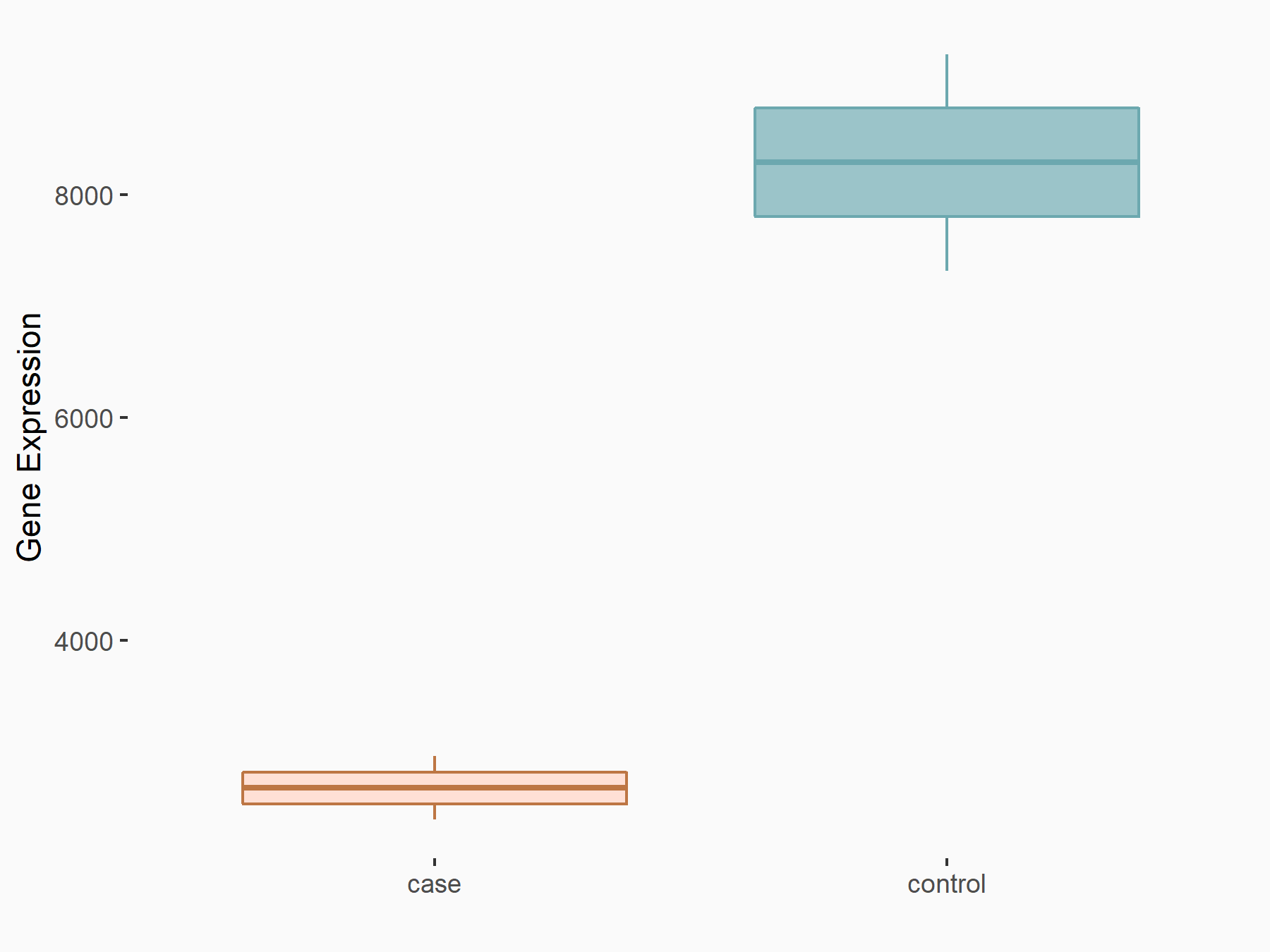 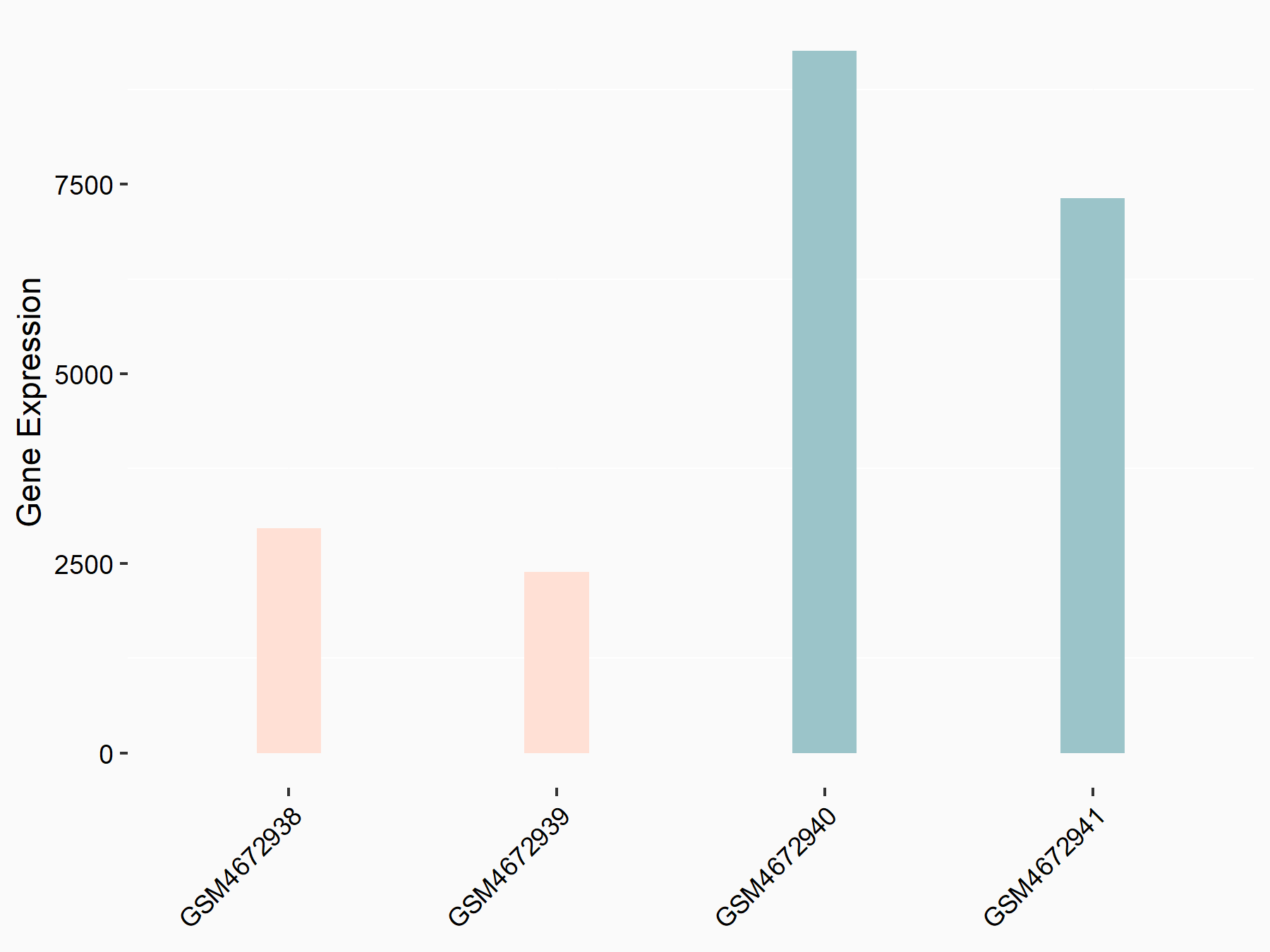 |
logFC: -1.63E+00 p-value: 8.42E-15 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Spina bifida [ICD-11: LA02]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neural tube defect [ICD-11: LA02.Z] | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
HT22 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were maintained on a 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m.). On day 7.5 of pregnancy (E7.5), ethionine (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was intraperitoneally injected only once at a dose of 500 mg/kg to establish the NTDs embryo model. And SAM (MedChemExpress, USA) was intraperitoneally injected only once at a dose of 30 mg/kg. The same dose was intraperitoneally injected to the pregnant mice for control group. | |||
| Response Summary | SAM not only played a compensatory role, but also led to m6A modification changes in neural tube development and regulation. Ethionine affected m6A modification by reducing SAM metabolism. METTL3 is enriched in HT-22 cells, and METTL3 knockdown reduces cell proliferation and increases apoptosis through suppressing Wnt/Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1/Beta-catenin) signaling pathway. Overexpression of ALKBH5 can only inhibit cell proliferation, but cannot promote cell apoptosis. | |||
CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
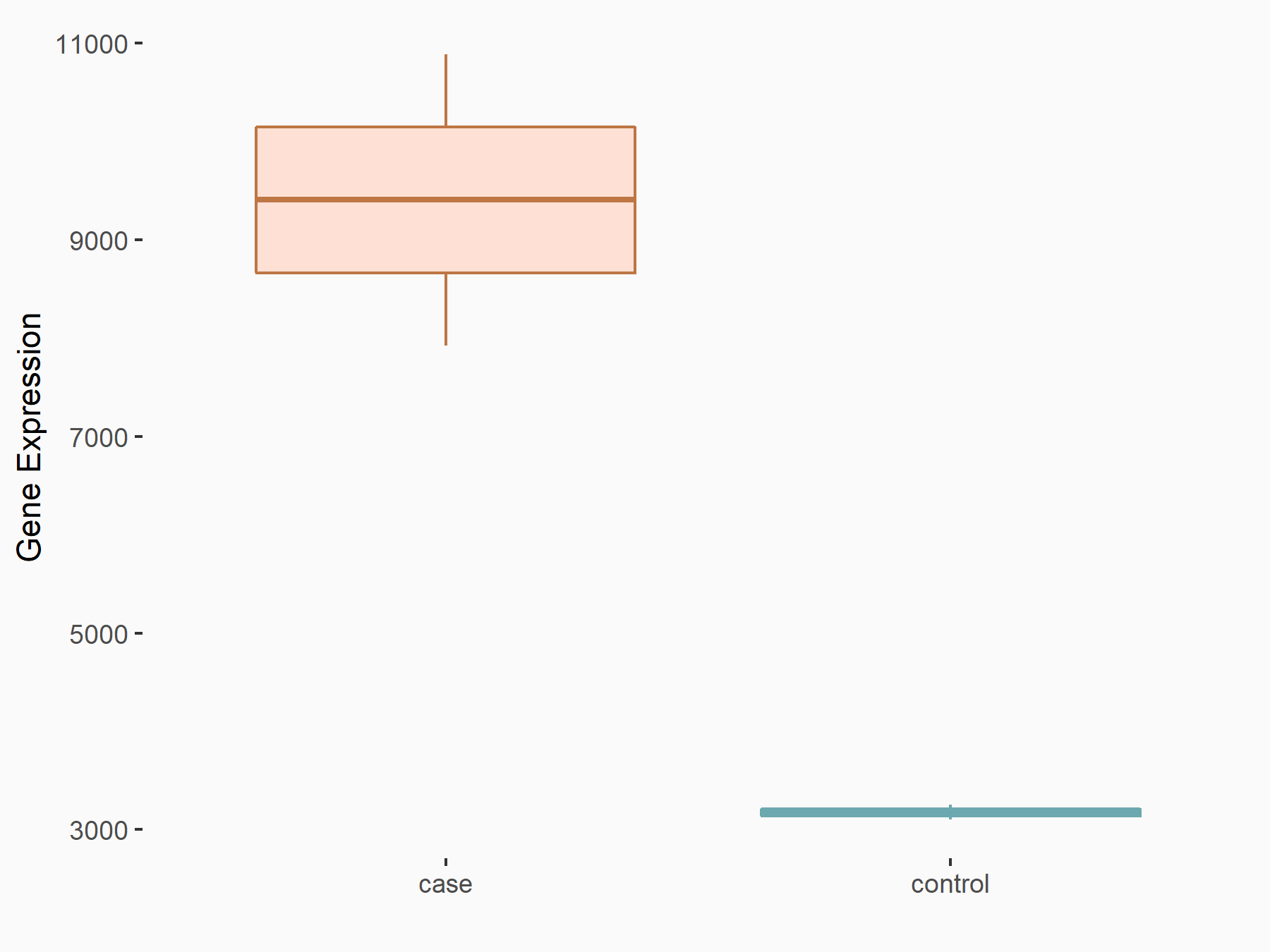 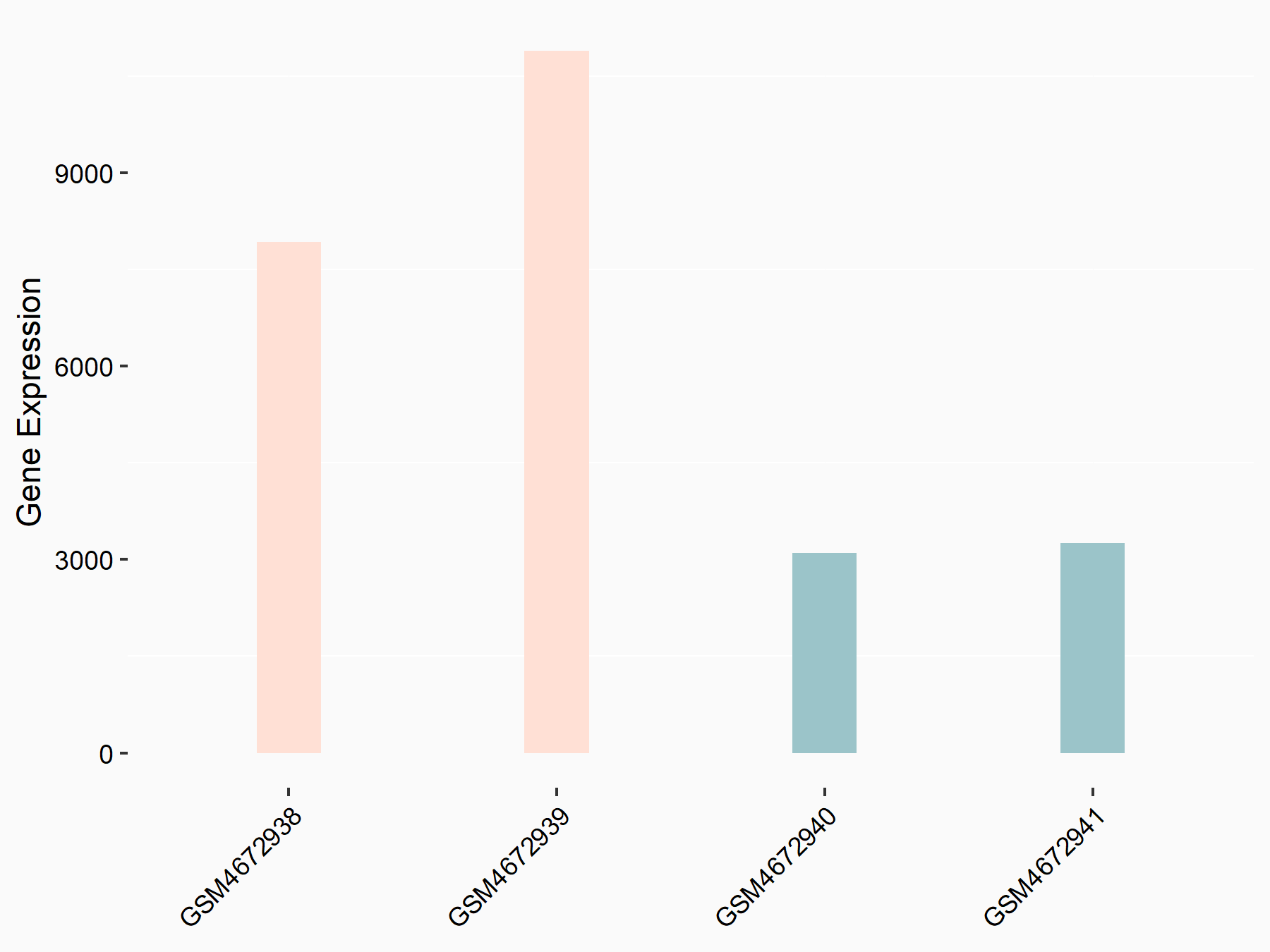 |
logFC: 1.57E+00 p-value: 8.38E-14 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| RWPE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3791 | |
| NSTC2 (Nickel-induced transformation of human cells) | ||||
| MC-SV-HUC T-2 | Ureteral tumor cell | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6418 | |
| 16HBE14o- | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0112 | |
| In-vivo Model | To test for malignant transformation, 1×107 cells were inoculated subcutaneously in the dorsal thoracic midline of ten NOD/SCID mice (Weitong Lihua Experimental Animal Technology Co. Ltd). Tumor formation and growth were assessed every 3 days. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase METTL3 and demethylases ALKBH5 mediate the m6A modification in 3'-UTR of CDCP1 mRNA. METTL3 and CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) are upregulated in the bladder cancer patient samples and the expression of METTL3 and CDCP1 is correlated with the progression status of the bladder cancers. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | CAG cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 CAG cells
Control: shNC CAG cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
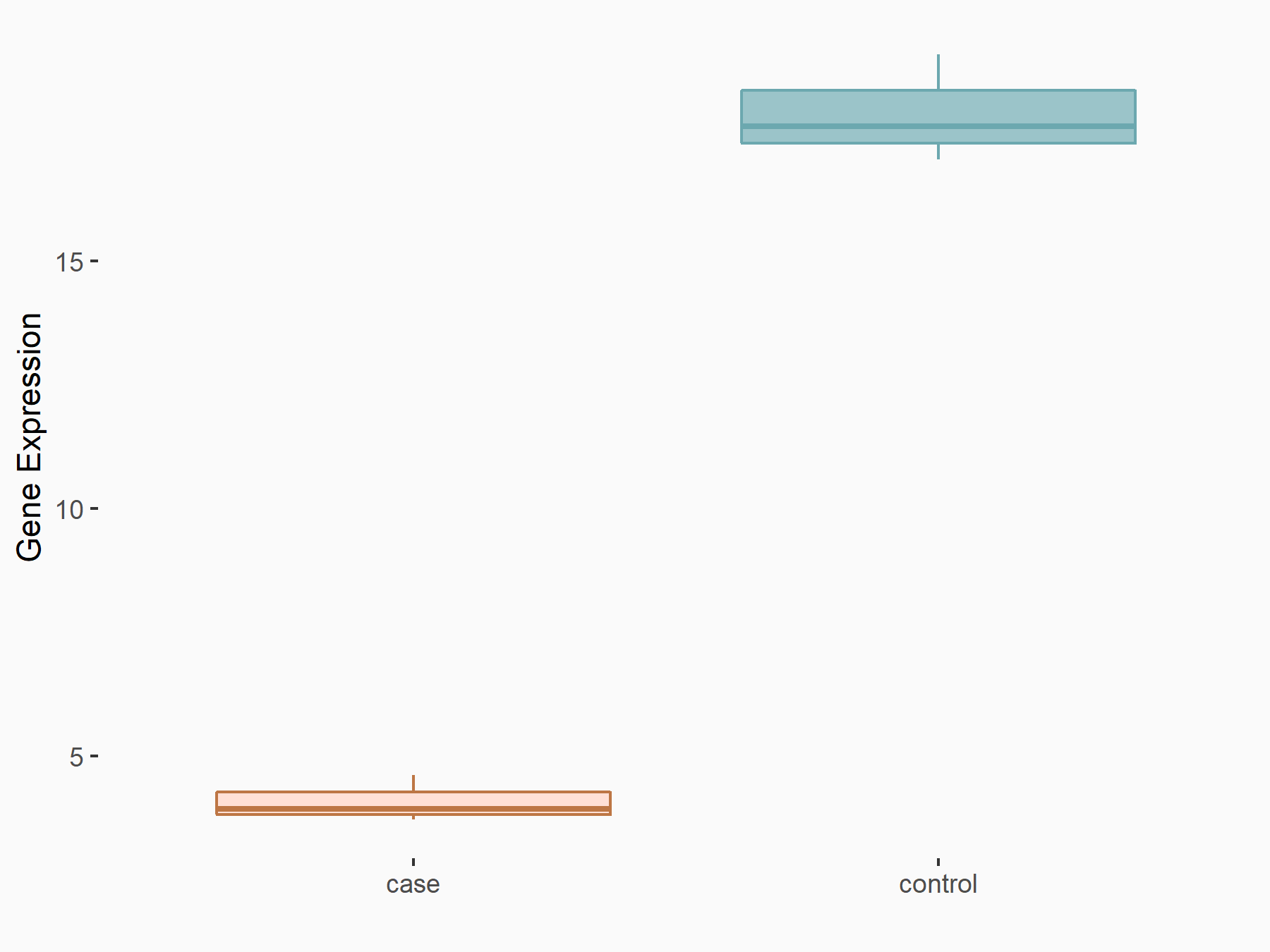 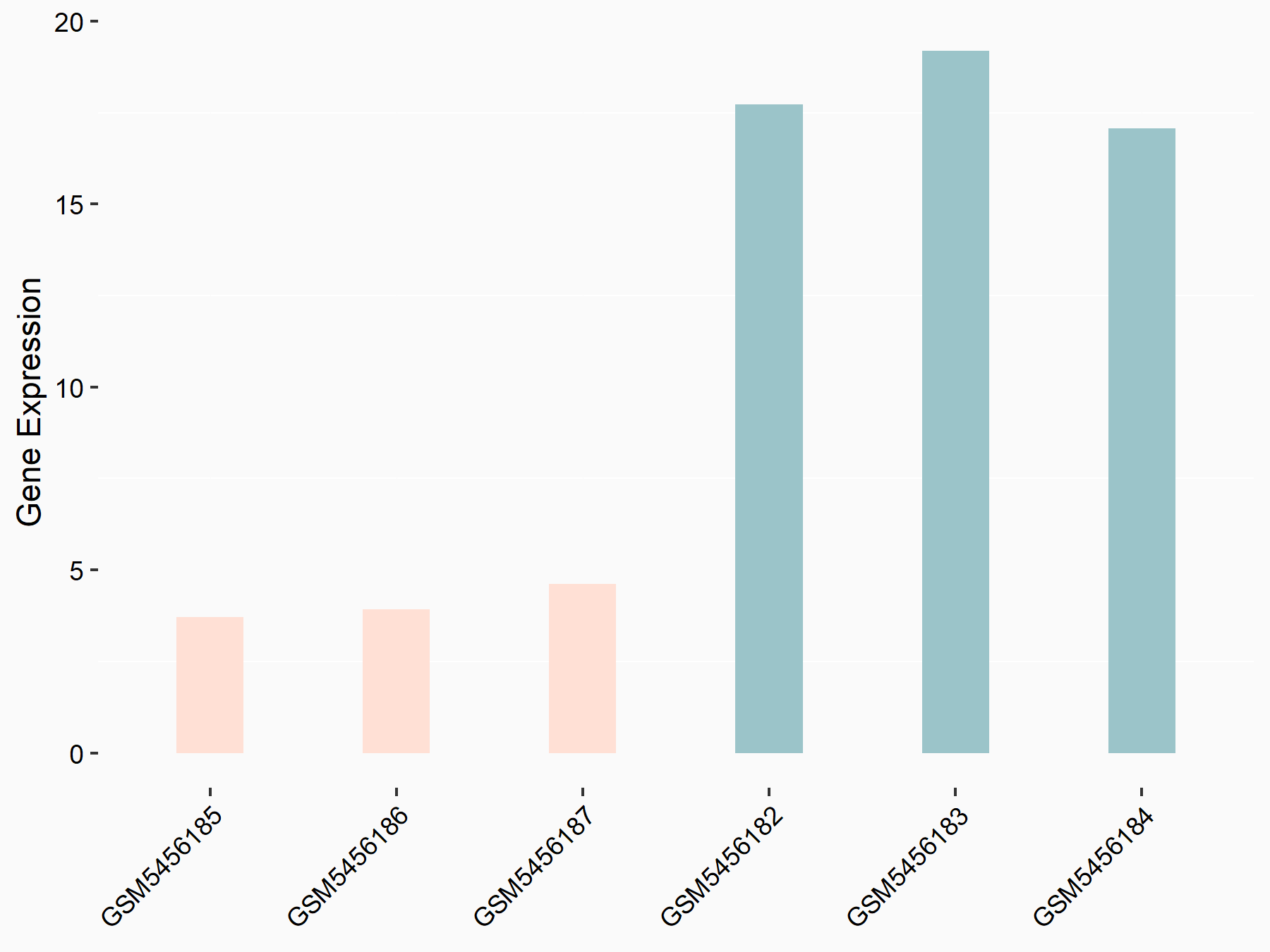 |
logFC: -1.90E+00 p-value: 1.35E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
OE21 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2661 |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| TE-5 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1764 | |
| TE-9 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1767 | |
| In-vivo Model | The OE21 cells were stably transfected with sh-ALKBH5 (#1), sh-ALKBH5 (#2) or sh-scramble as negative control and injected (2 × 106 cells/mouse in 100 uL volume) subcutaneously into the back of male athymic BALB/c nude mice (6 weeks old, Japan SLC). | |||
| Response Summary | Expression of CDKN1A (p21) was significantly up-regulated in ALKBH5-depleted cells, and m6 A modification and stability of Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A) mRNA were increased by ALKBH5 knockdown. Identify ALKBH5 as the first m6 A demethylase that accelerates cell cycle progression and promotes cell proliferation of ESCC cells, which is associated with poor prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Arrest cell cycle at G1 phase | |||
In-vitro Model |
NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 |
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H2087 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1524 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| ABC-1 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1066 | |
| NCI-H358 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1559 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | |
| PC-3 [Human lung carcinoma] | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S982 | |
| PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | |
| RERF-LC-MS | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1655 | |
| HLC-1 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5529 | |
| LC-2/ad | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1373 | |
| Response Summary | The expression of Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A) or TIMP3 was increased by ALKBH5 knockdown. In conclusions, the ALKBH5-IGF2BPs axis promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity, which in turn causes the unfavorable prognosis of NSCLC. | |||
DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
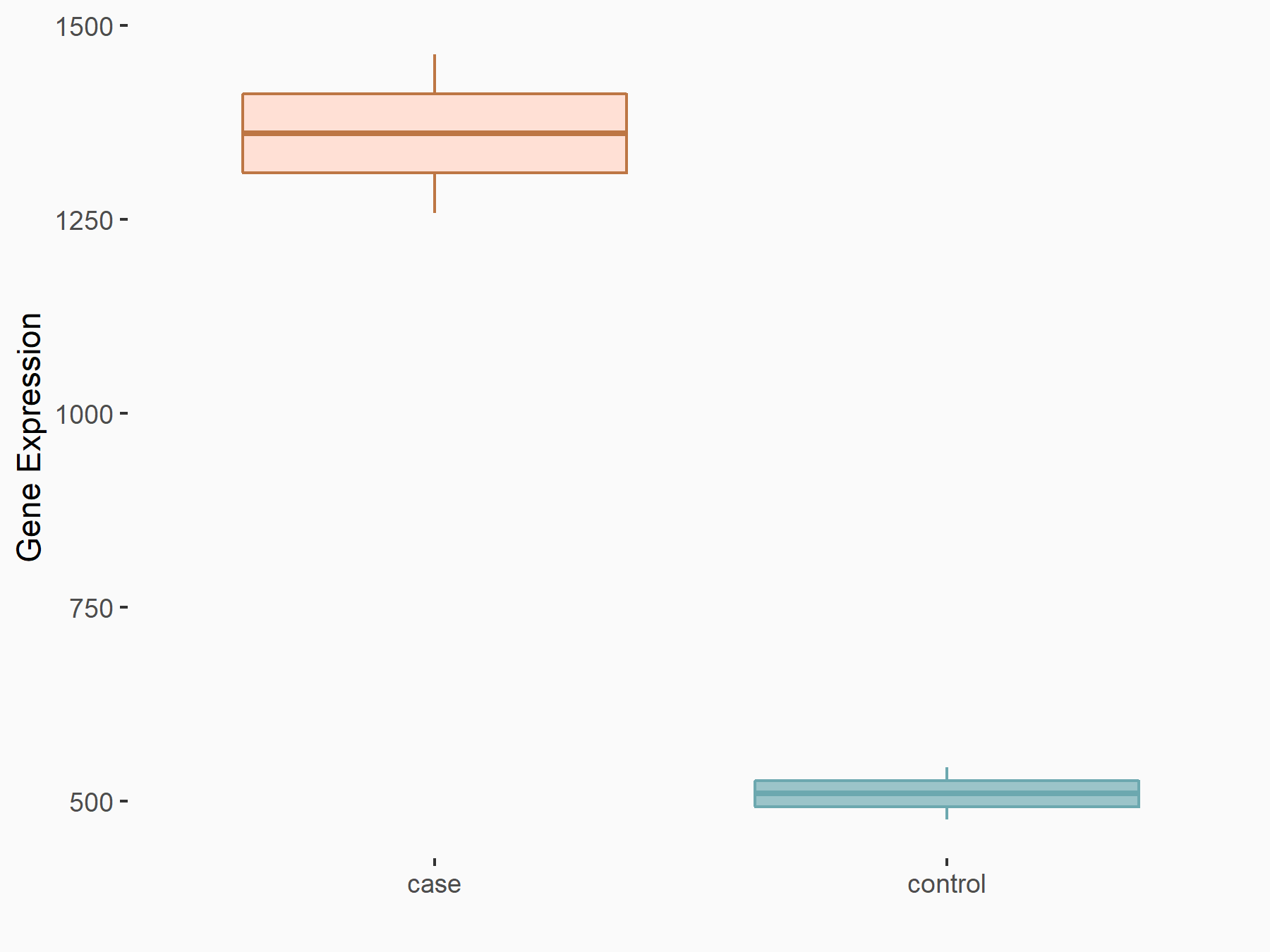 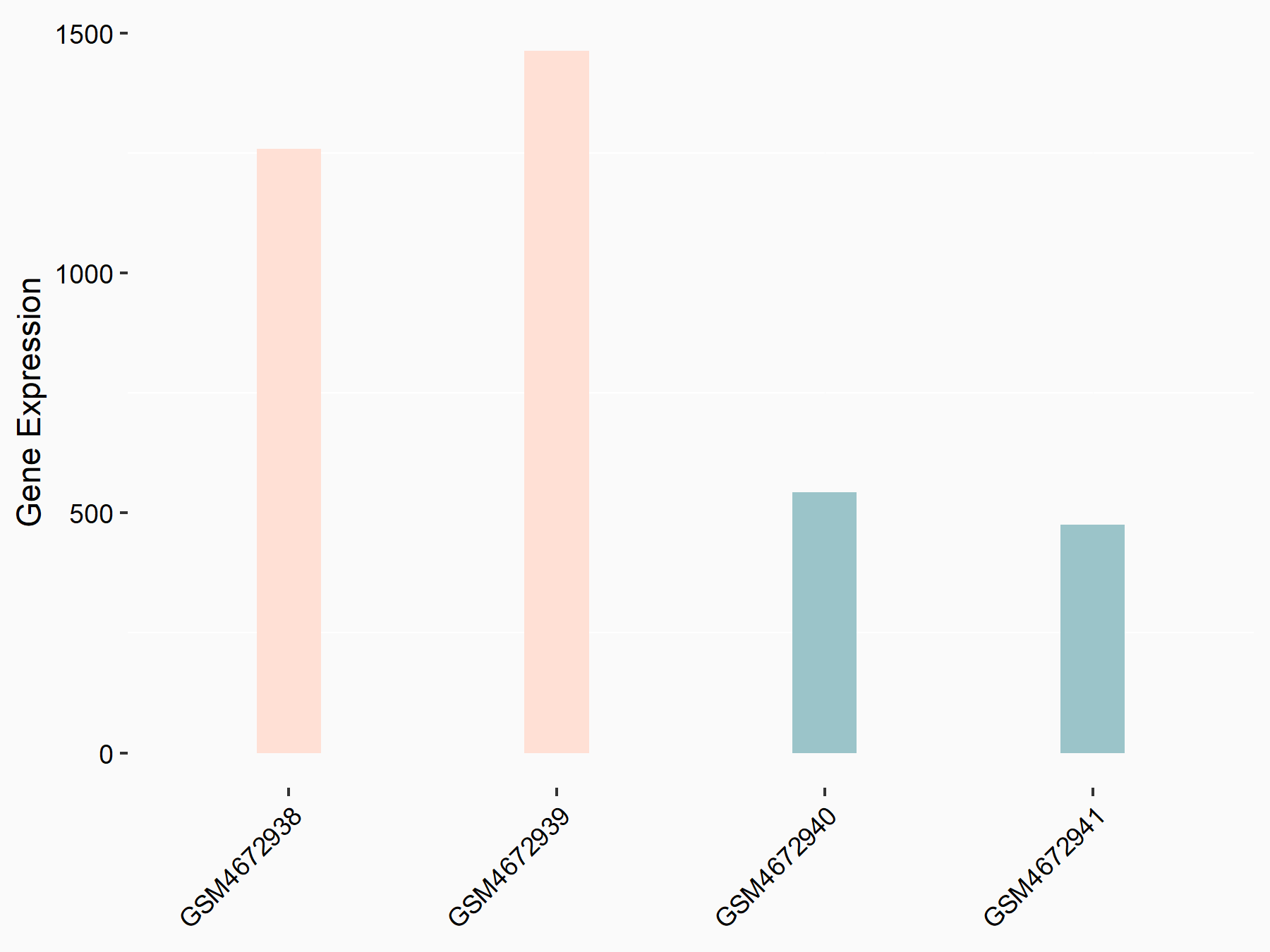 |
logFC: 1.42E+00 p-value: 9.24E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Nucleus pulposus cell (The NP tissues were cut into pieces after collection during surgery) | |||
| Response Summary | Theses findings reveal an epigenetic interplay mechanism in NPC senescence and IVD degeneration, presenting a critical pro-senescence role of ALKBH5 and m6A hypomethylation, highlighting the therapeutic potential of targeting the m6A/DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B)/E4F1 axis for treating IVD degeneration. | |||
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase BRE1B (RNF40)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
 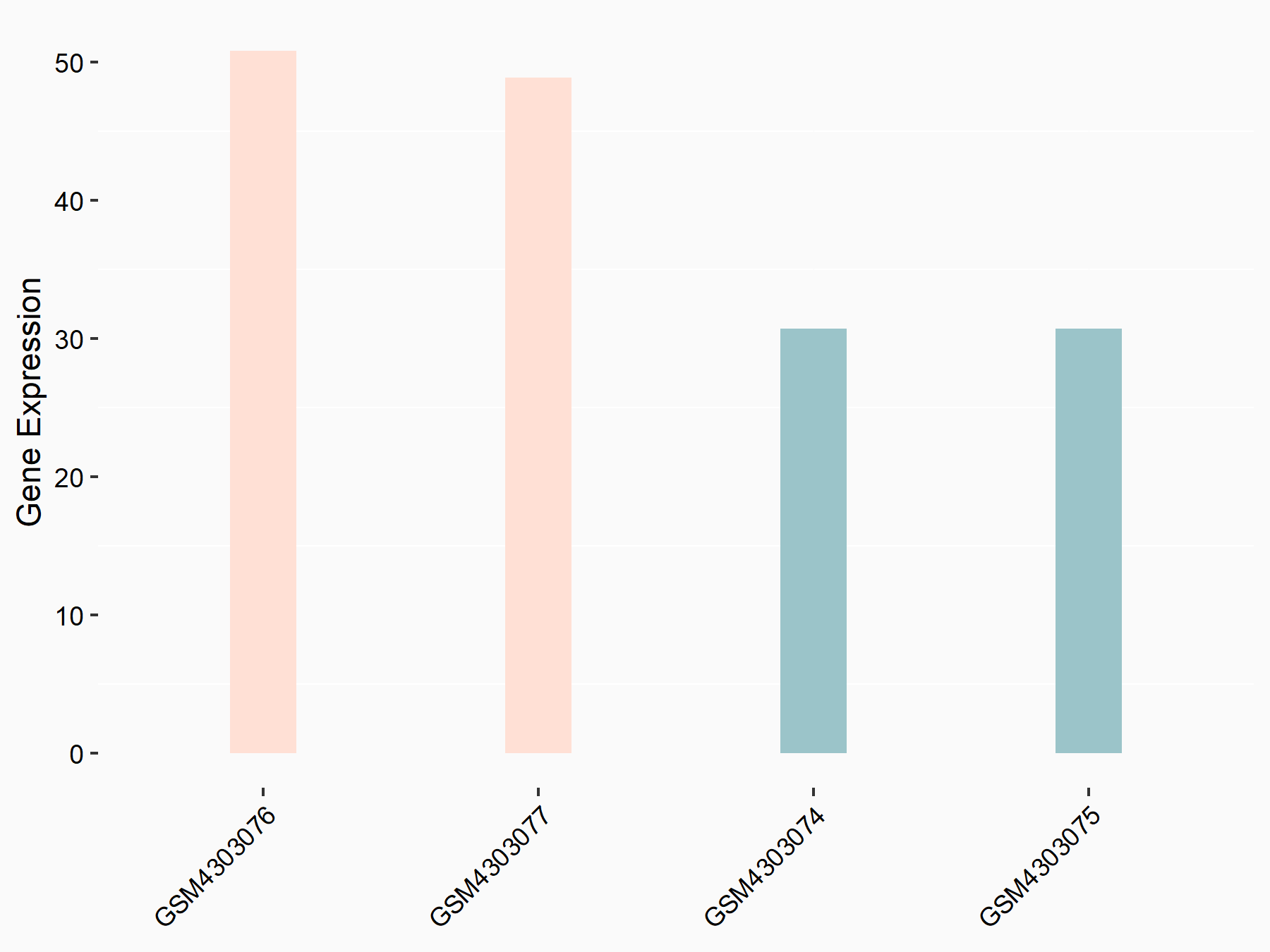 |
logFC: 6.81E-01 p-value: 5.37E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasome pathway degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| SaOS-2 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0548 | |
| OS-17 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9992 | |
| IMR-90 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0347 | |
| hFOB 1.19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3708 | |
| 143B | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 | |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor xenograft studies, 143B cells stably expressing scrambled shRNA or ALKBH5 shRNA (1 × 106) were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of 4-week-old athymic nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In osteosarcoma, ALKBH5 mediates its protumorigenic function by regulating m6A levels of histone deubiquitinase USP22 and the ubiquitin ligase E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase BRE1B (RNF40). | |||
eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4EBP1/EIF4EBP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
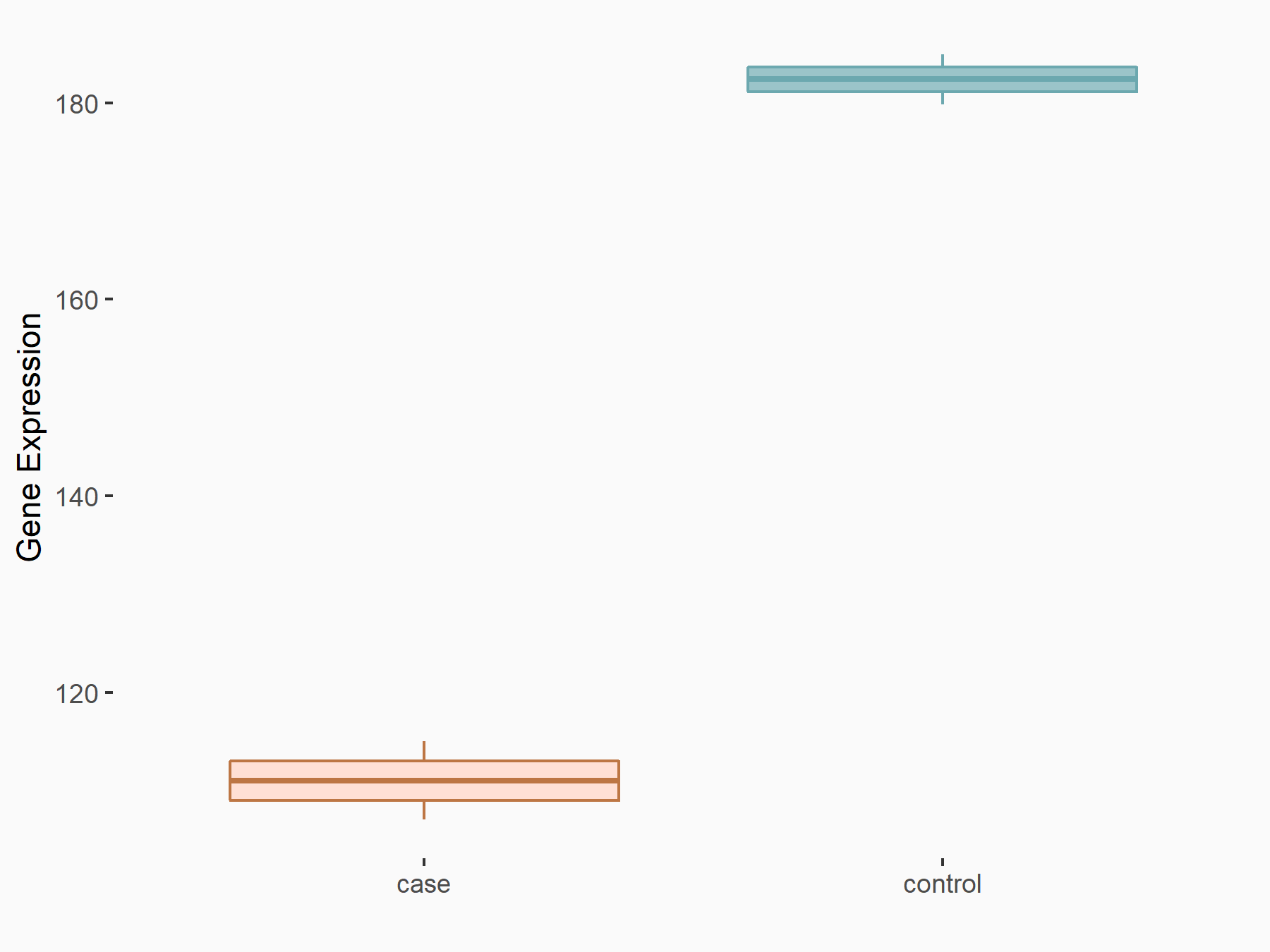 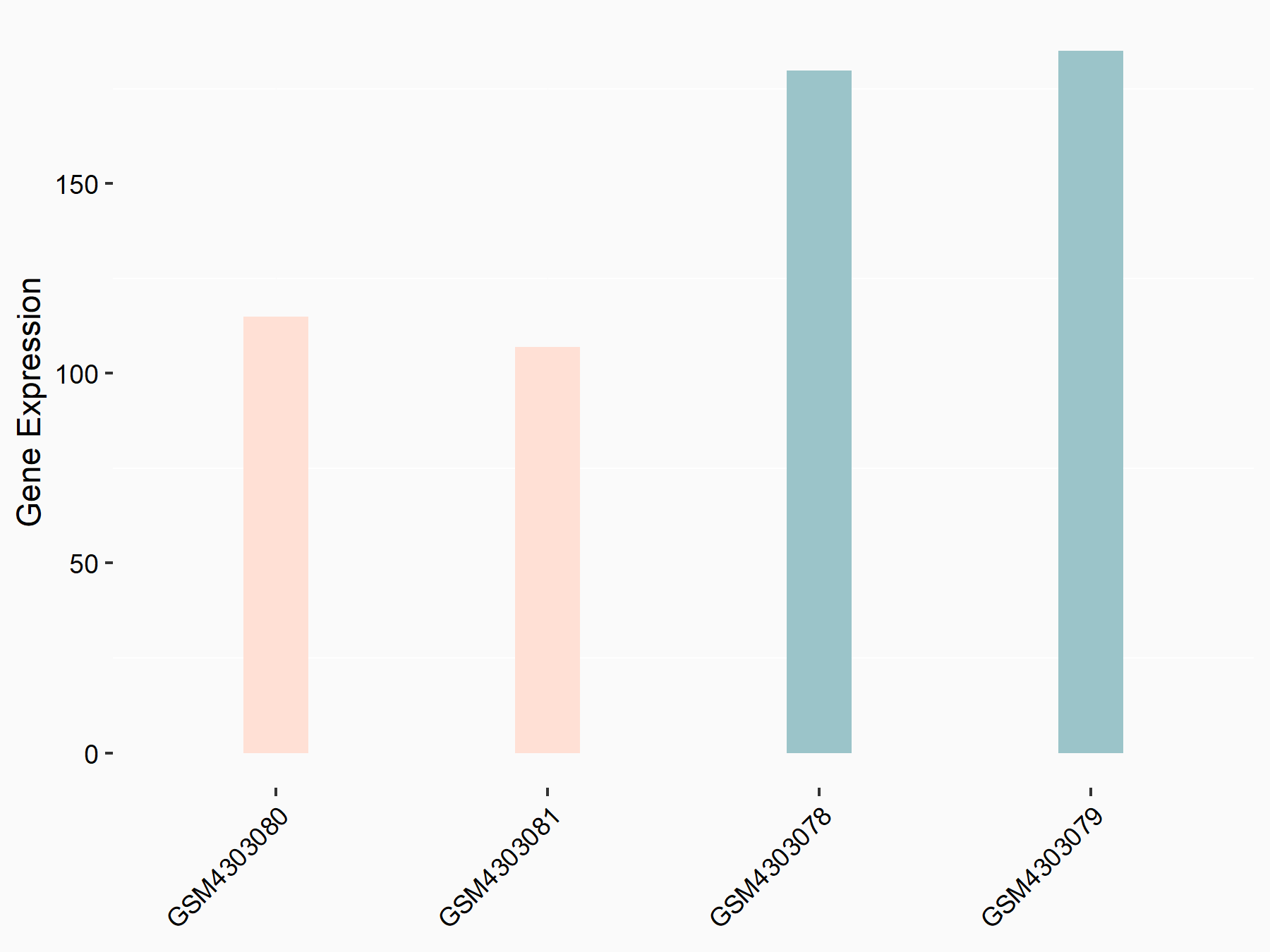 |
logFC: -7.12E-01 p-value: 2.44E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | HL-60 cells (1 × 107) suspended in 0.1 ml PBS containing 50% Matrigel were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of the mice. When tumor sizes reached 200 mm3, the mice were randomly distributed into four groups with the indicated dosages of saline, cytarabine and BP alone or in combination. For BP injections, the solution was delivered intraperitoneally at 106 ug/kg body weight for the first 8 consecutive days. For cytarabine injections, the solution was delivered intraperitoneally at 100 mg/kg body weight three times (once every three days). The combination group was administered intraperitoneally three times (once every three days) with the same dosages as described above. The control group was treated with an equivalent amount of saline. | |||
| Response Summary | Bioactive peptides can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation by downregulating ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation of eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4EBP1/EIF4EBP1) and MLST8 mRNAs, which have potential to prevent and treat this disease. | |||
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
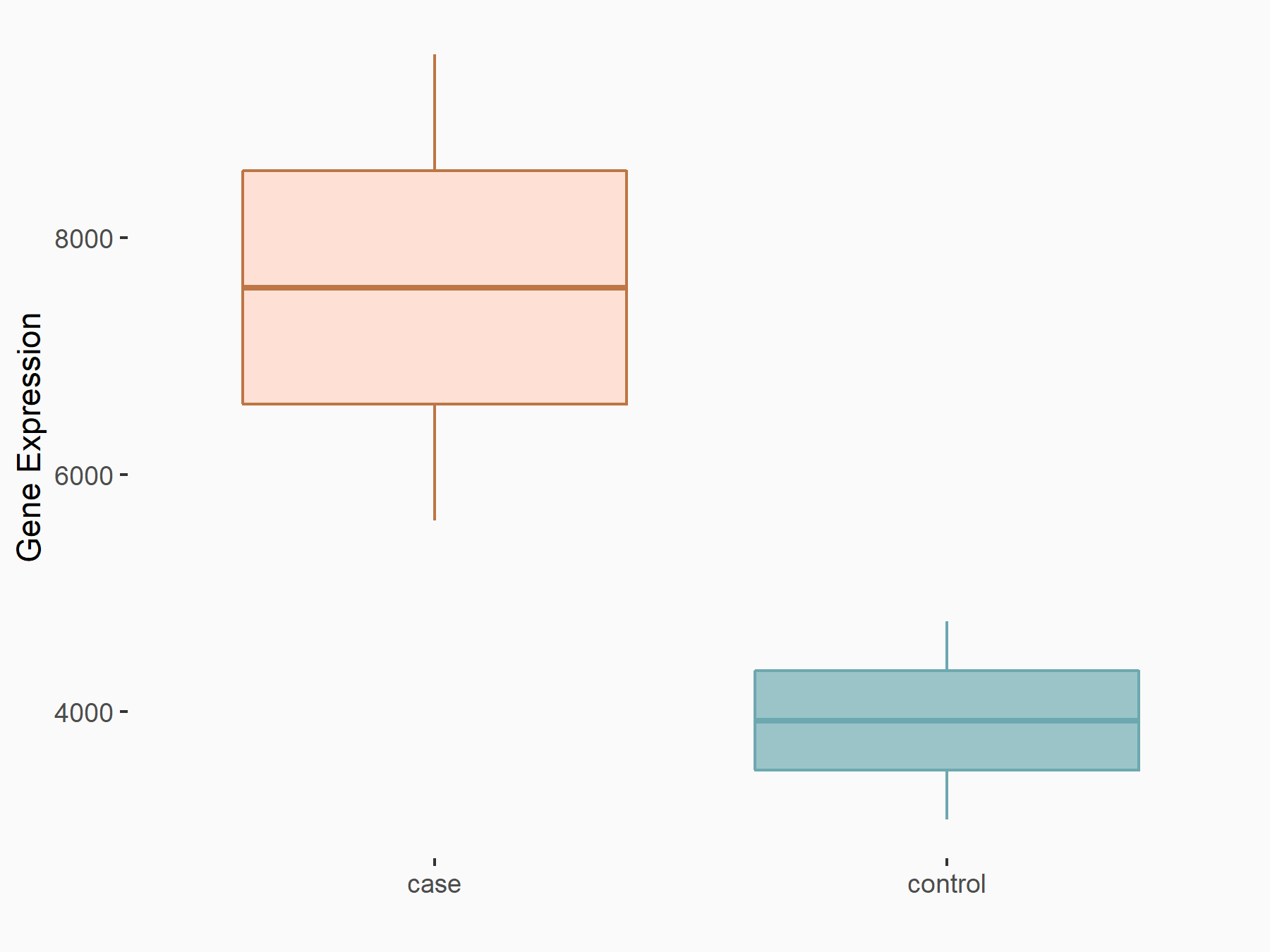  |
logFC: 9.50E-01 p-value: 4.65E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
In-vitro Model |
A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| CoC1 | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6891 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | SKOV3 or A2780 cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral vectors and injected (5 × 106 cells/mouse in 200 uL volume) subcutaneously into the left armpit of 6-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 21 days, the animals were sacrificed to confirm the presence of tumors and weigh the established tumors. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is a tumor-promoting gene in epithelial ovarian cancer, which is involved in the mTOR pathway and BCL-2-Beclin1 complex. ALKBH5 activated Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-PIK3CA-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. | |||
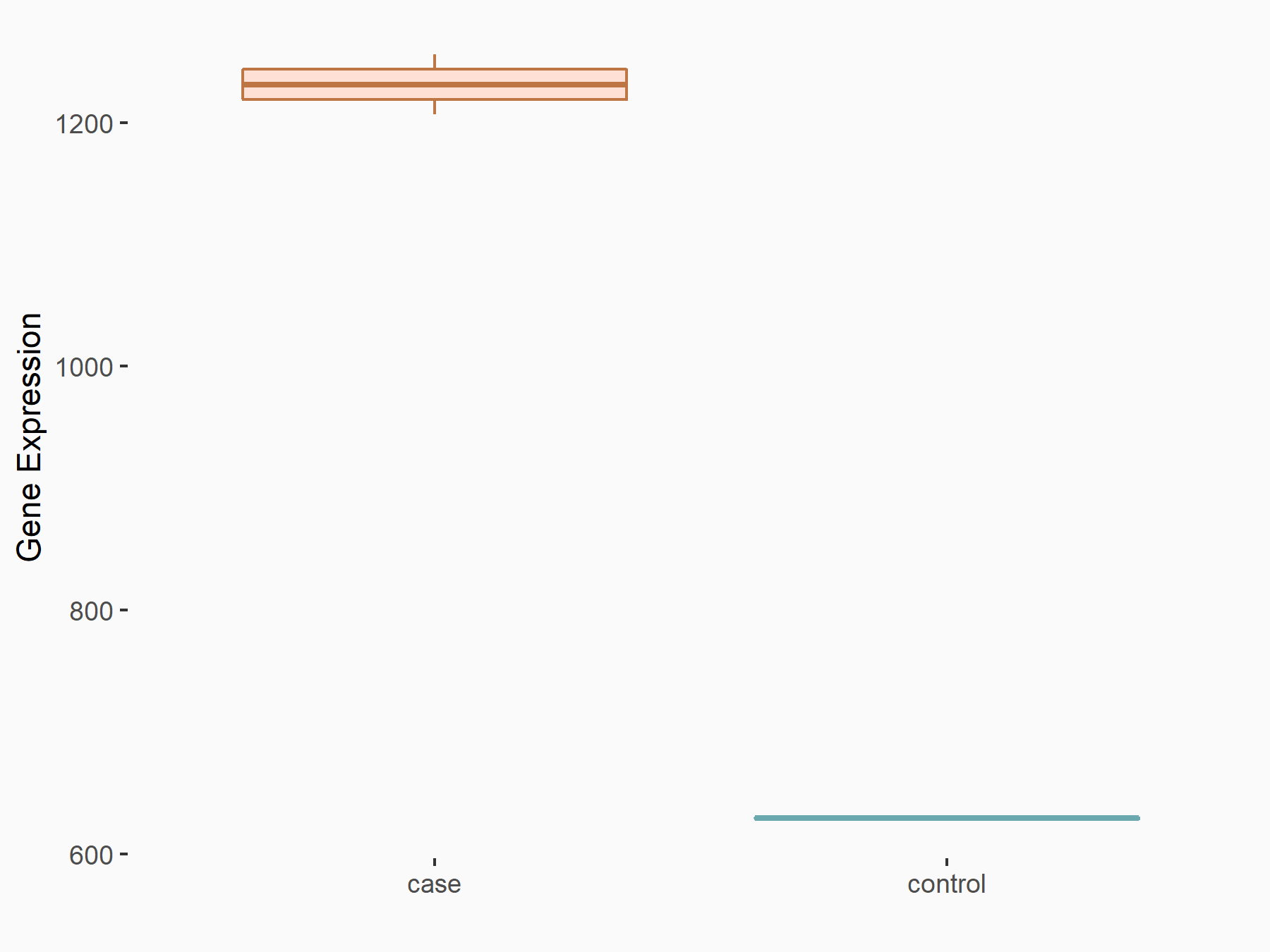
F-box/LRR-repeat protein 5 (FBXL5)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | human pluripotent stem cells | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: hILO ALKBH5knockout cells
Control: hILO wild type cells
|
GSE163945 | |
| Regulation |
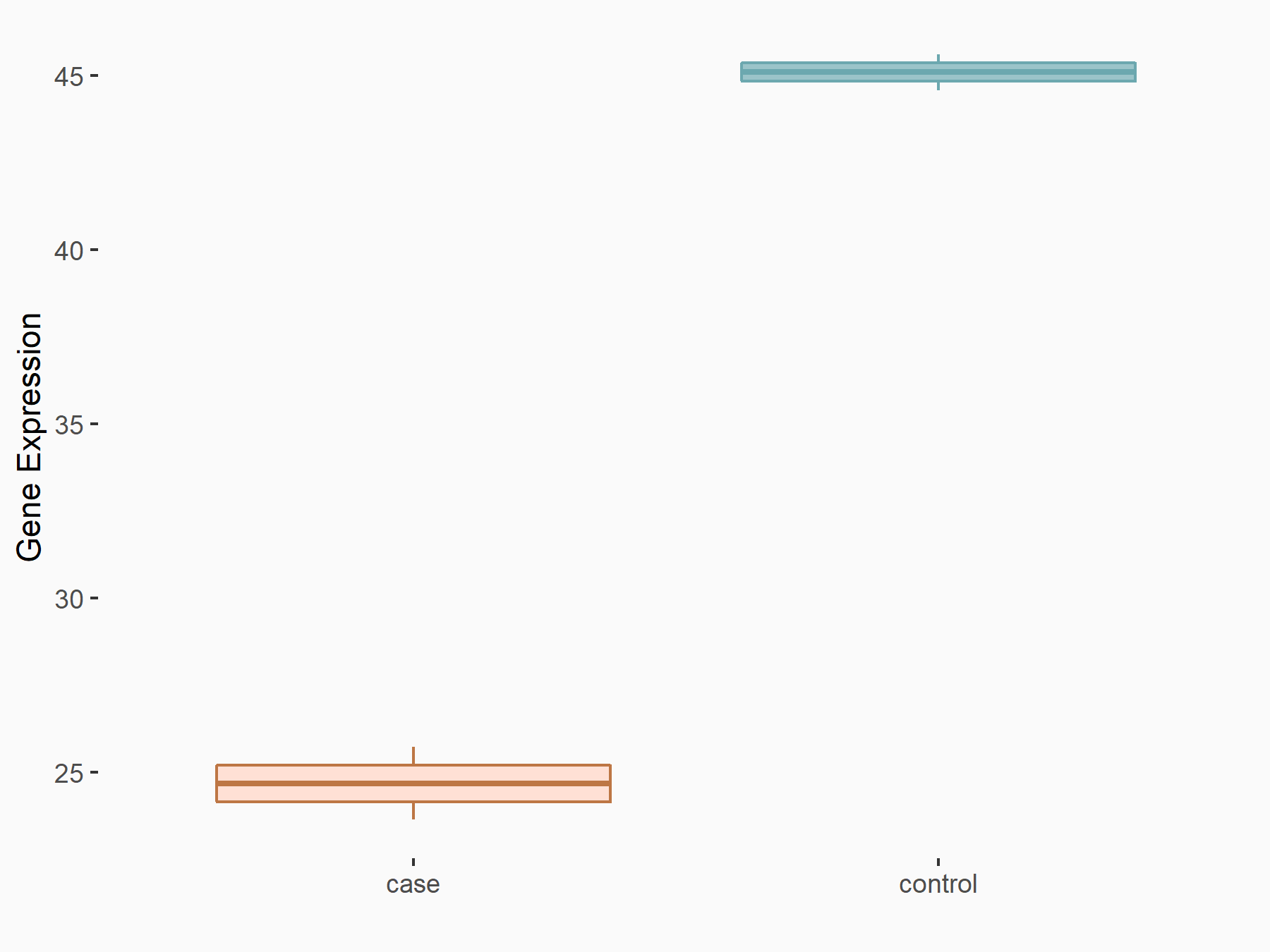  |
logFC: -8.45E-01 p-value: 2.55E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Adherens junction | hsa04520 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression incurred a significant reduction in iron-regulatory protein IRP2 and the modulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) SNAI1. Owing to F-box/LRR-repeat protein 5 (FBXL5)-mediated degradation, ALKBH5 overexpression incurred a significant reduction in iron-regulatory protein IRP2 and the modulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) SNAI1. ALKBH5 in protecting against PDAC through modulating regulators of iron metabolism and underscore the multifaceted role of m6A in pancreatic cancer. | |||
Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
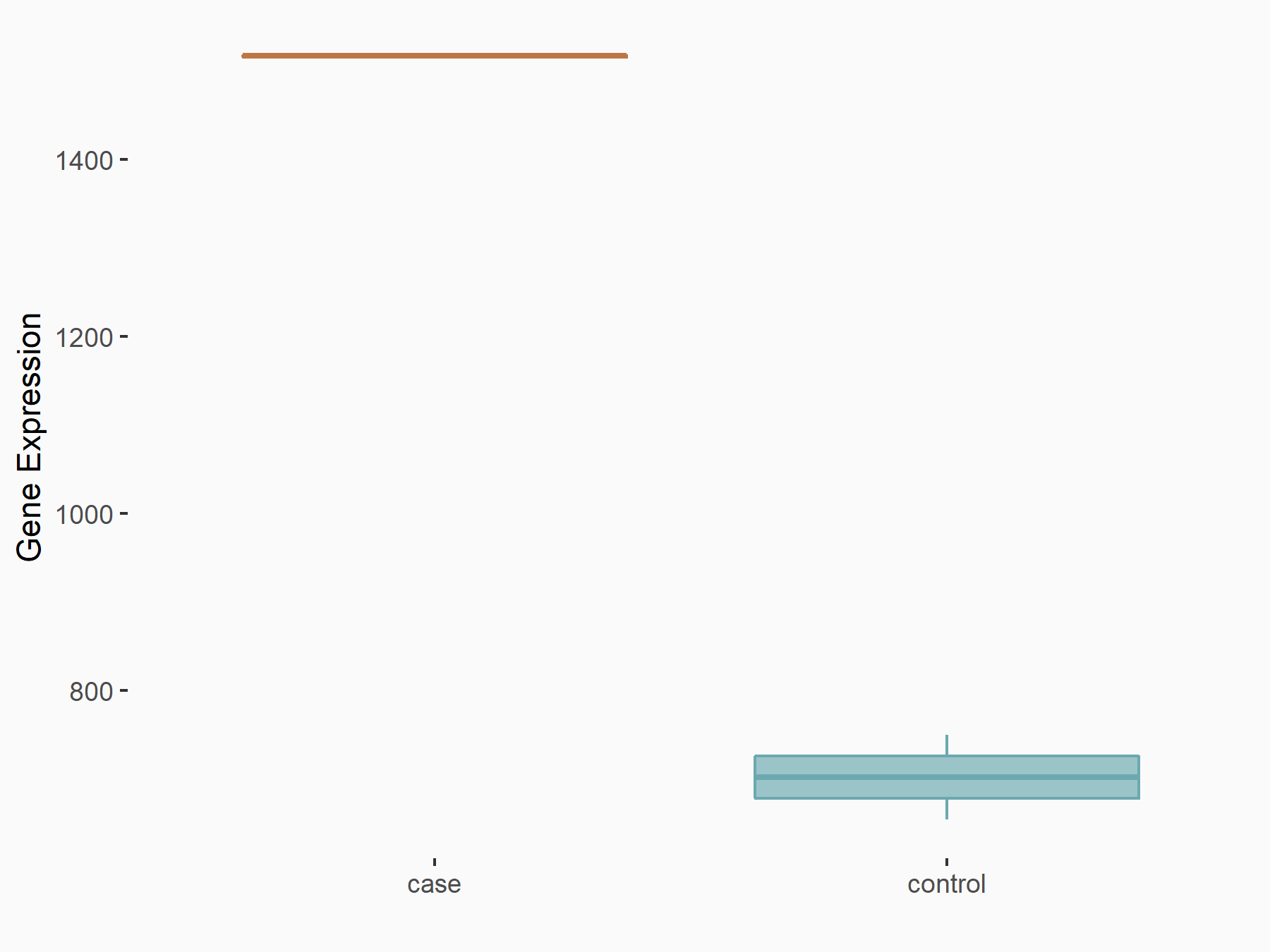 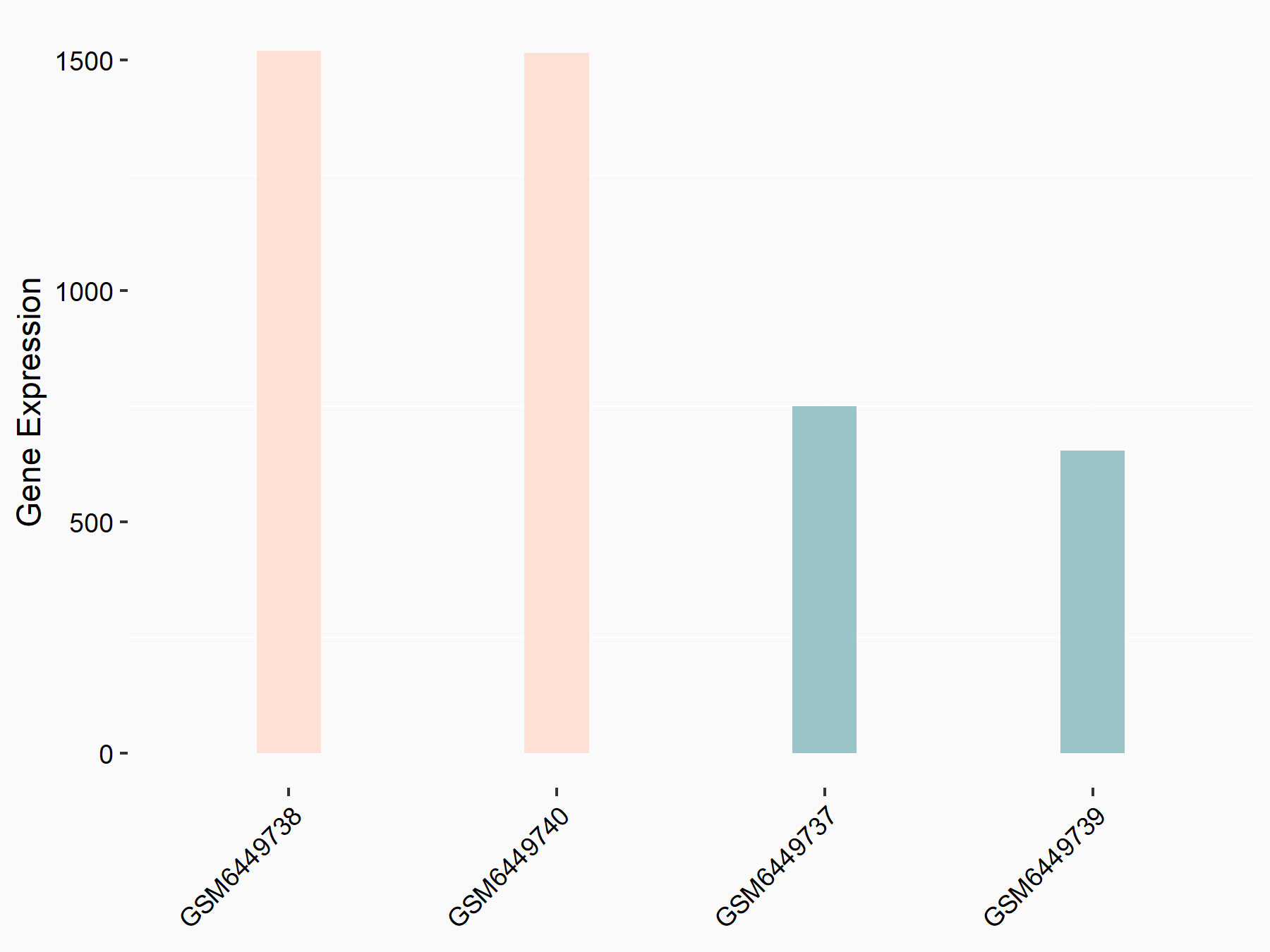 |
logFC: 1.11E+00 p-value: 1.78E-33 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [14] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Glioma | hsa05214 | ||
| Cell Process | Cells proliferation | |||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells (hsa04550) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 |
| Hs 683 | Oligodendroglioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0844 | |
| SW1783 | Anaplastic astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1722 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the animal survival analysis, mice were intracranially injected with 10,000 GSCs and maintained until moribund or 80 days after injection. For the rescue studies, GSCs with ALKBH5 or FOXM1-AS shRNAs were co-transfected with a FOXM1, ALKBH5 wild-type or mutant expression construct. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and FOXM1-AS disrupted GSC tumorigenesis through the Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) axis. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [15] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and invasion | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H522 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1567 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1 × 107 A549 cells were subcutaneously implanted into 4-week-old NOD/SCID mice. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A demethylase ALKBH5 affects the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells under IH by downregulating m6A modification on Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) mRNA and by promoting FOXM1 expression.high FOXM1 expression was associated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis. | |||
Melanoma of uvea [ICD-11: 2D0Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [16] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma of uvea [ICD-11: 2D0Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
ARPE-19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0145 |
| C918 | Uveal melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8471 | |
| MuM-2B | Uveal melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3447 | |
| In-vivo Model | The in vivo experiment method for transplantation of tumors was subcutaneous injection of 1 × 107 ALKBH5-stable knockdown C918 cells into BALB/c nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | AKLBH5-induced m6A demethylation of Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) mRNA promotes uveal melanoma progression. | |||
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis [ICD-11: CB03]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pulmonary Fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03.4] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
NIH 3T3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0594 |
| MRC-5 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0440 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the mouse model of miR-320a-3p overexpression, a total of 24 male C57BL/6 mice were divided randomly into four groups (n = 6 in each group): saline, silica, silica plus AAV9-miR-NC, and silica plus AAV9-miR-320a-3p. The mice in the silica plus AAV9-miR-NC/AAV9-miR-320a-3p groups were anesthetized using the same method, then administered intratracheally 50 uL AAV9-miR-NC/AAV9-miR-320a-3p per mouse at a titer of 8 × 1012 v. g./ml. Three weeks later, these mice were treated in the same way using anesthesia, saline, and silica as mentioned above. Subsequently, after 4 weeks, the mice were sacrificed, and the lungs were isolated and frozen at -80 ℃ for further study. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 promotes silica-induced lung fibrosis via the miR-320a-3p/FOXM1 axis or targeting Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) directly. | |||
Certain specified disorders of cornea [ICD-11: 9A78]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Certain specified disorders of cornea [ICD-11: 9A78.0] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-CS
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0F27 |
| In-vivo Model | General anesthesia in mice was induced by intraperitoneal injection of a 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution at 40 mg/kg. Excessive whiskers were trimmed, and topical anesthesia was performed using 0.5% proparacaine hydrochloride (Alcon, Geneva, Switzerland). A circular filter paper (2.0 mm × 2.0 mm) soaked with NaOH (1 mol/L) was attached to the central cornea of the right eye for 40 seconds to induce an alkali injury. Afterward, the paper was quickly removed, and the conjunctival sac was washed entirely with 0.9% sterile saline solution for one minute. Mice were then treated with ofloxacin eye drops twice daily for three days to prevent infection. Mice were randomly selected for three, seven, and 14 days or seven days after modeling, and their right corneas were harvested for subsequent experiments. | |||
Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
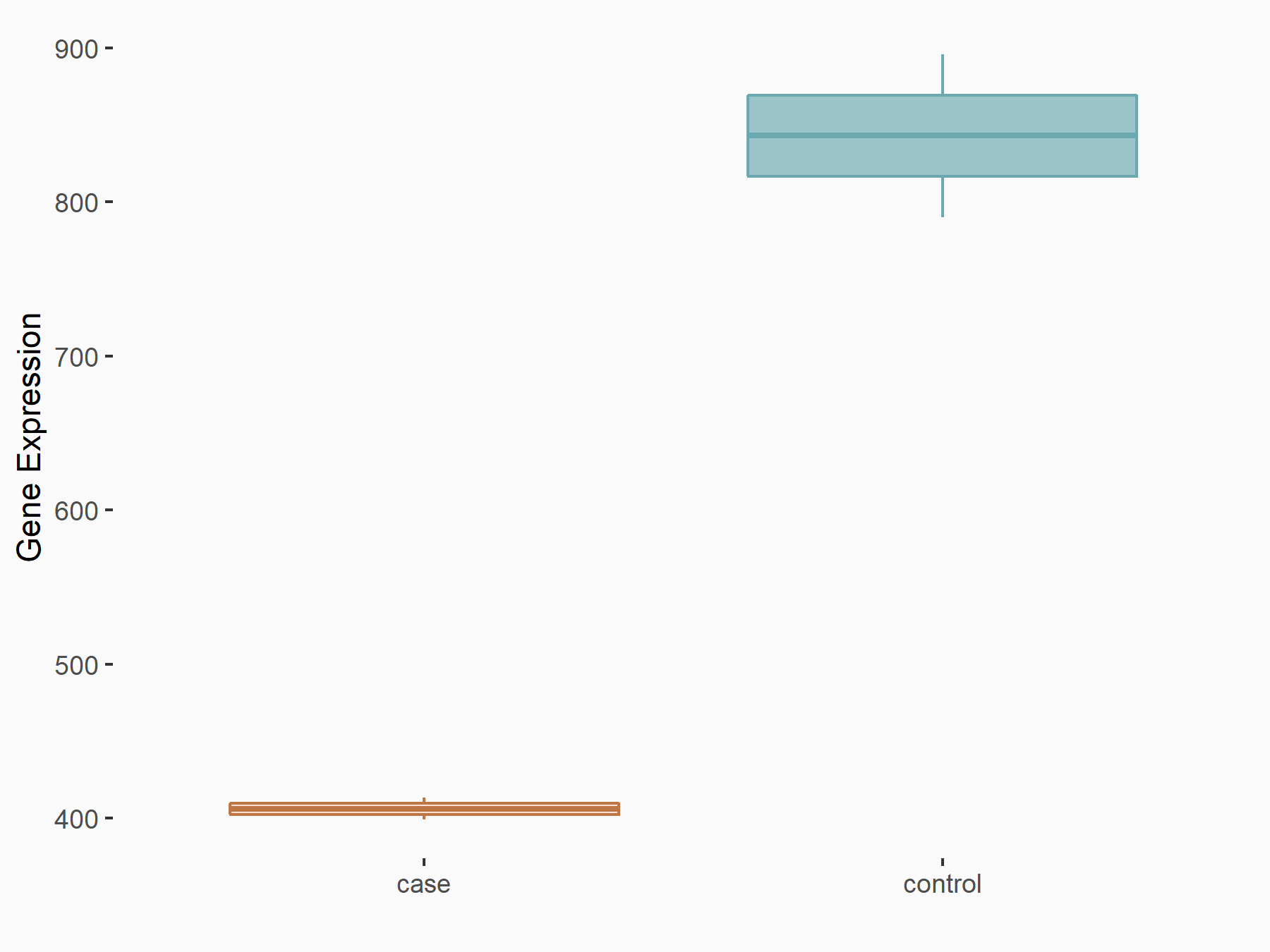 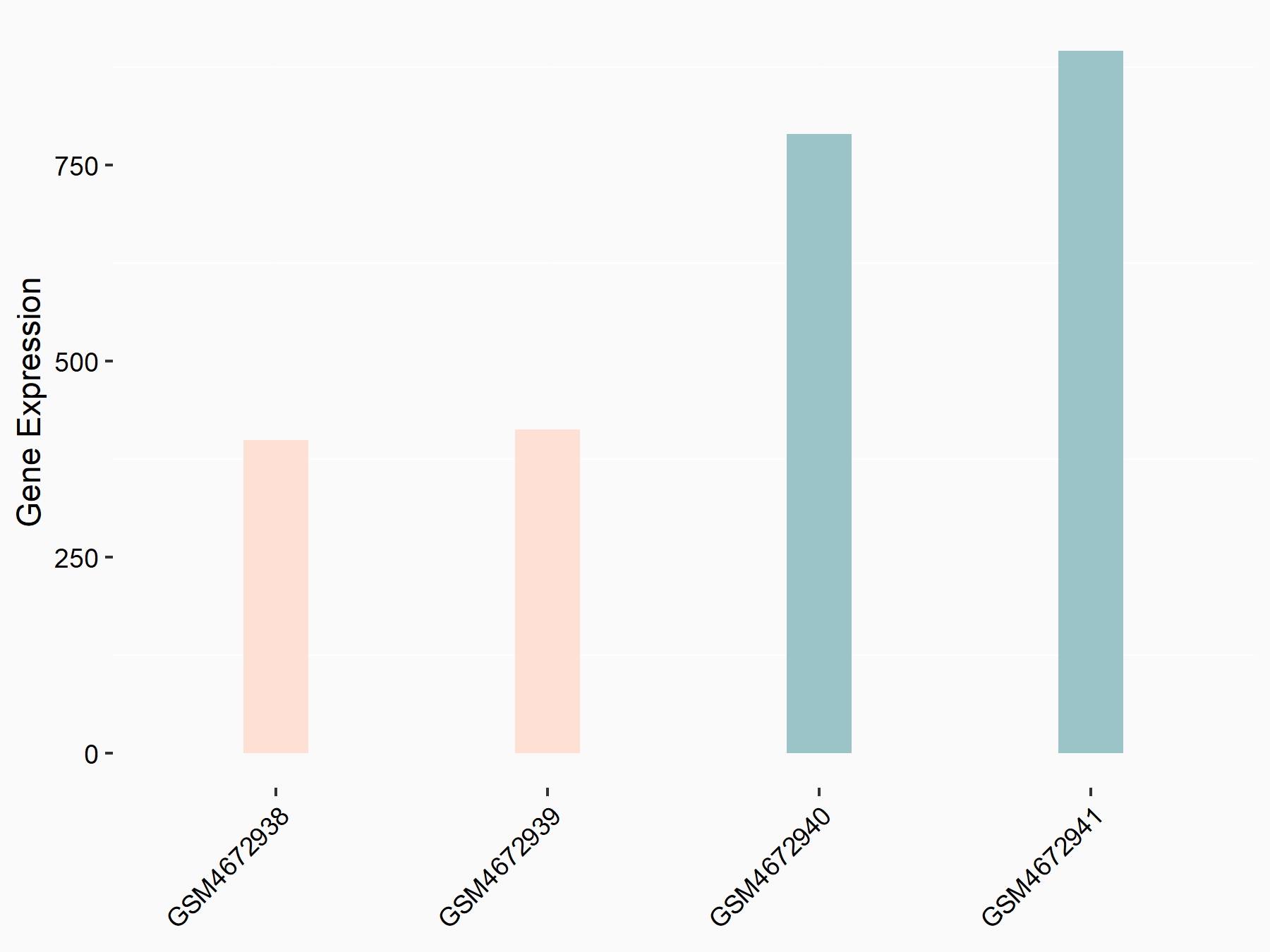 |
logFC: -1.05E+00 p-value: 3.53E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | ||
In-vitro Model |
Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 plays an antitumor role in colorectal cancer by modulating the Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)/miR-21/SPRY2 axis, which not only suggests a regulatory effect between ALKBH5 and FOXO3, but also provides a new therapeutic direction for colorectal cancer. | |||
Cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43.7] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
Neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (Primary myocyte cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | The model mice were intraperitoneally injected with streptozotocin (STZ; Sigma-Aldrich Corp., USA). The dose of STZ was 50 mg/kg for 5 days. 7 days after the last injection, blood glucose concentrations were recorded. Mouse models of diabetes were considered established when fasting blood glucose concentrations reached >11.1 mmol/L, and body weight was measured. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 was upregulated in the cardiomyocytes of diabetic cardiomyopathy mice and posttranscriptionally activated Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3) by m6A demethylation in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner.This work reveals the key function of the ALKBH5-FOXO3-CDR1as/Hippo signaling pathway in DCM and provides insight into the critical roles of m6A methylation in DCM. | |||
High mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
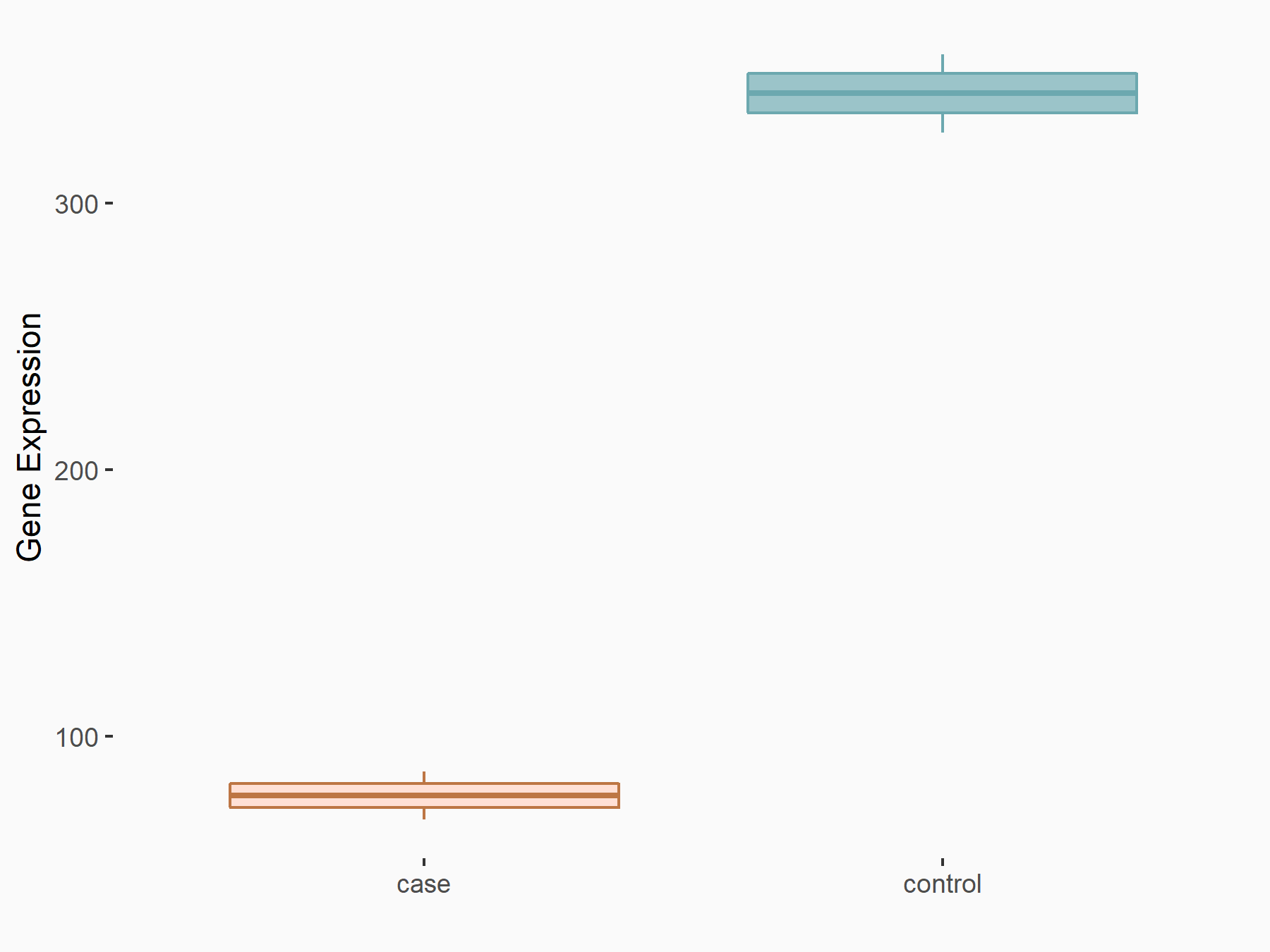  |
logFC: -2.13E+00 p-value: 2.89E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Immune Response | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5-dependent High mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) expression mediates STING-interferon regulatory factor 3 innate immune response in radiation-induced liver diseases. | |||
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
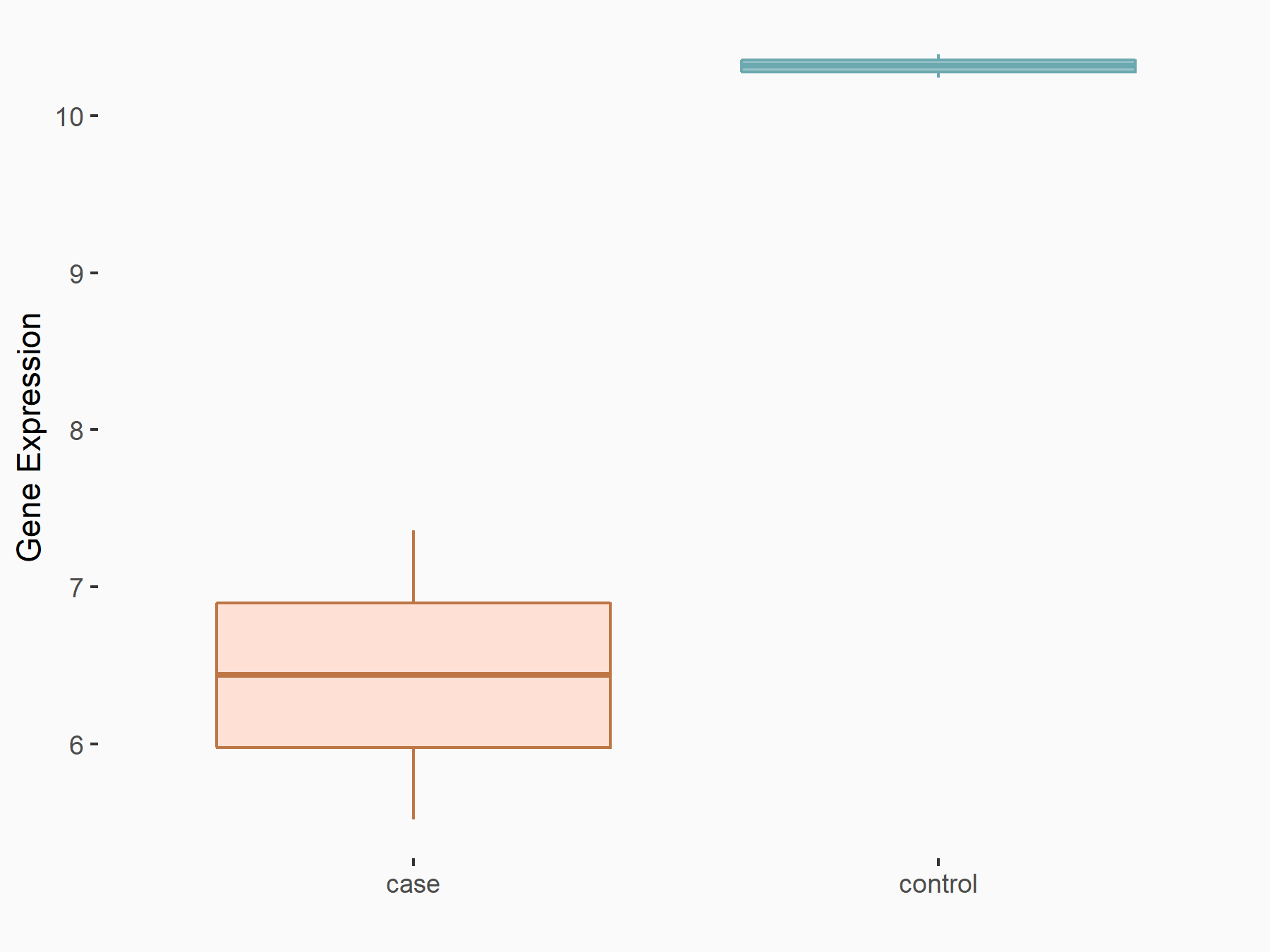  |
logFC: -6.16E-01 p-value: 4.93E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
T HESCs | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C464 |
| RL95-2 | Endometrial adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0505 | |
| HEC-1-A | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0293 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 promoted proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer via erasing Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) m6A-modifications. | |||
Interferon beta (IFNB1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | Peritoneal macrophages | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: ALKBH5-/- peritoneal macrophages
Control: Wild type peritoneal macrophages
|
GSE127739 | |
| Regulation |
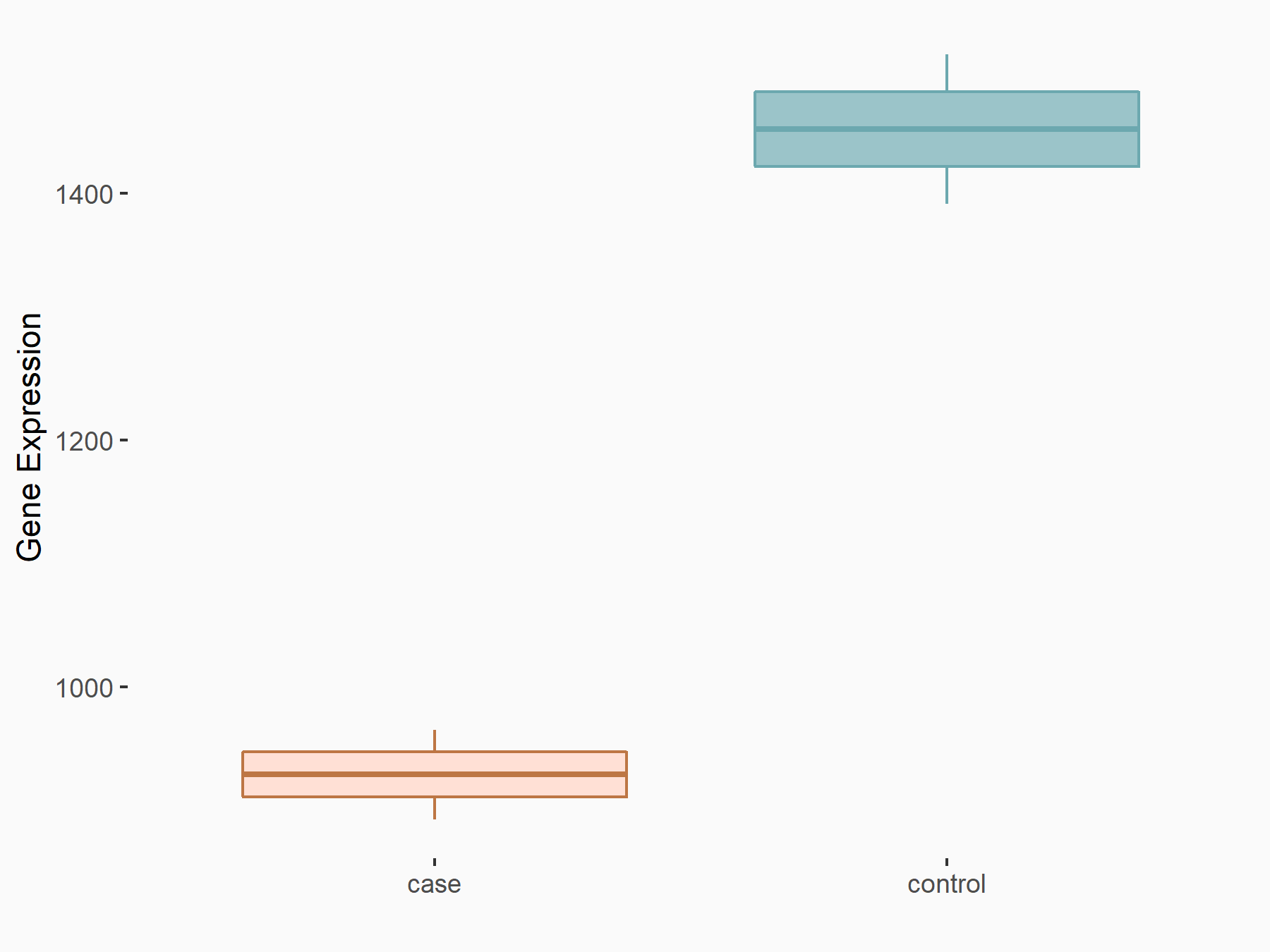  |
logFC: -6.45E-01 p-value: 8.14E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Papillomaviruses [ICD-11: 1D9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Unspecified viral infection [ICD-11: 1D9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
Innate immunity [ICD-11: 4A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Innate immunity [ICD-11: 4A00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 1 (LYPD1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
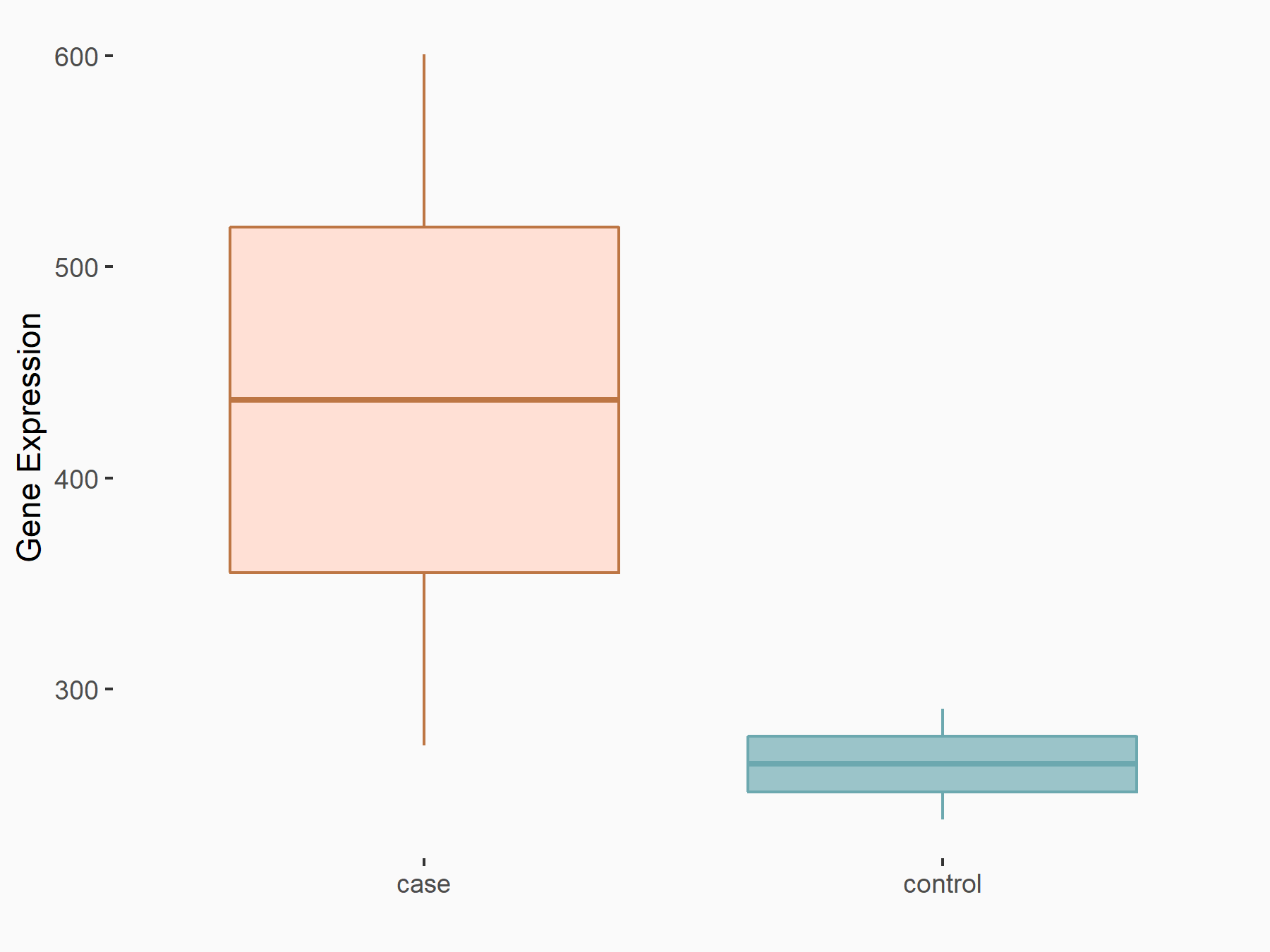  |
logFC: 7.22E-01 p-value: 3.53E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [23] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| BEL-7402 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5492 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 suppressed the proliferation and invasion capabilities of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation led to a post-transcriptional inhibition of Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 1 (LYPD1). | |||
Metalloproteinase inhibitor 3 (TIMP3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
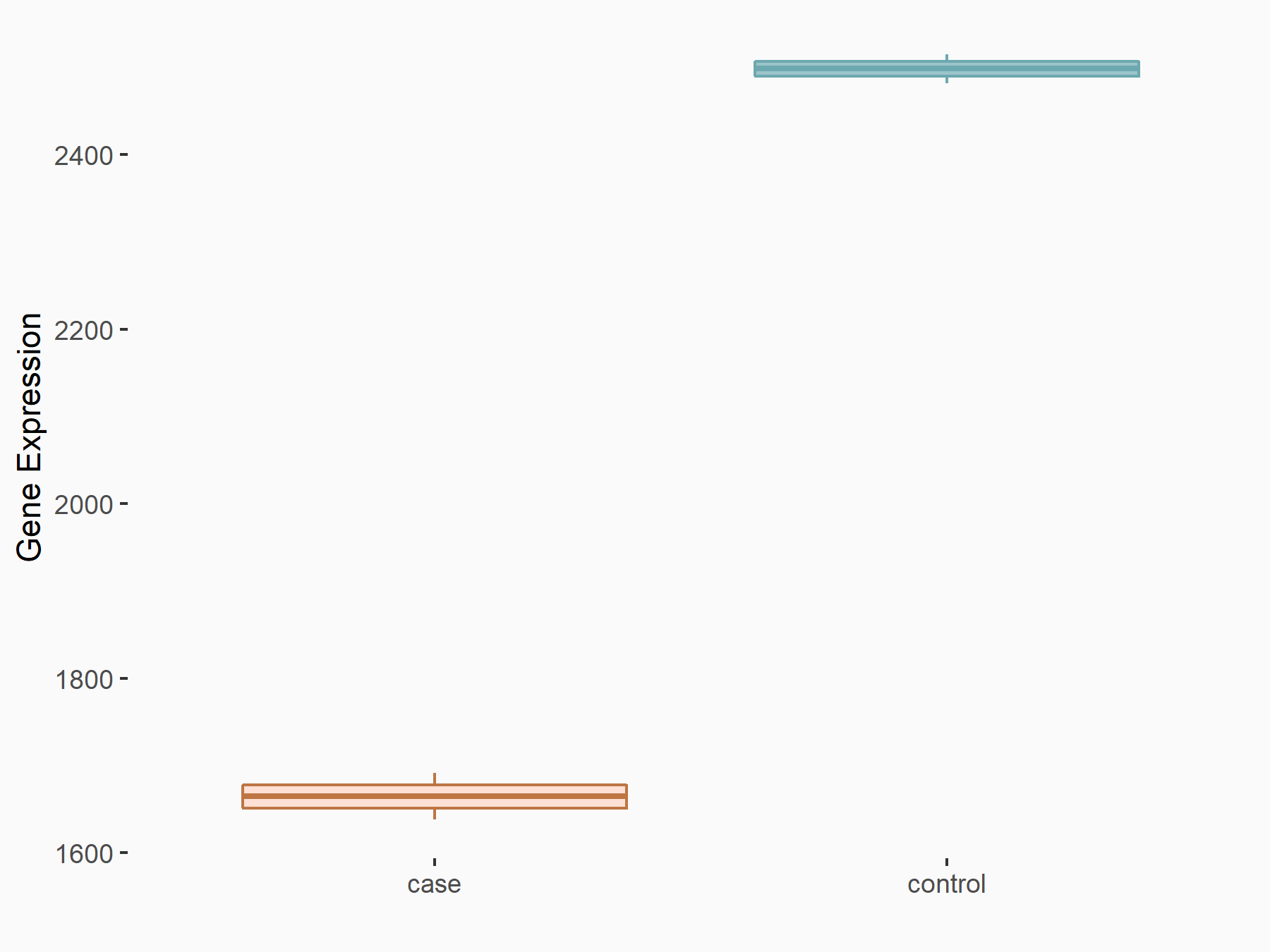  |
logFC: -5.86E-01 p-value: 2.60E-20 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [24] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| NHBE (Normal bronchial epithelial cells) | ||||
| SK-MES-1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0630 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 A549 cells stably transfected with shRNA-ALKBH5 were injected into the flank of male athymic BALB/c nude mice (4-5 weeks old, 10 mice). | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 repress Metalloproteinase inhibitor 3 (TIMP3) transcript stability, thereby inhibiting TIMP3 translational production.the present research confirmed the ALKBH5/TIMP3 pathway in the non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC) oncogenesis progress, providing a novel insight for the epitranscriptome and potential therapeutic target for NSCLC. | |||
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
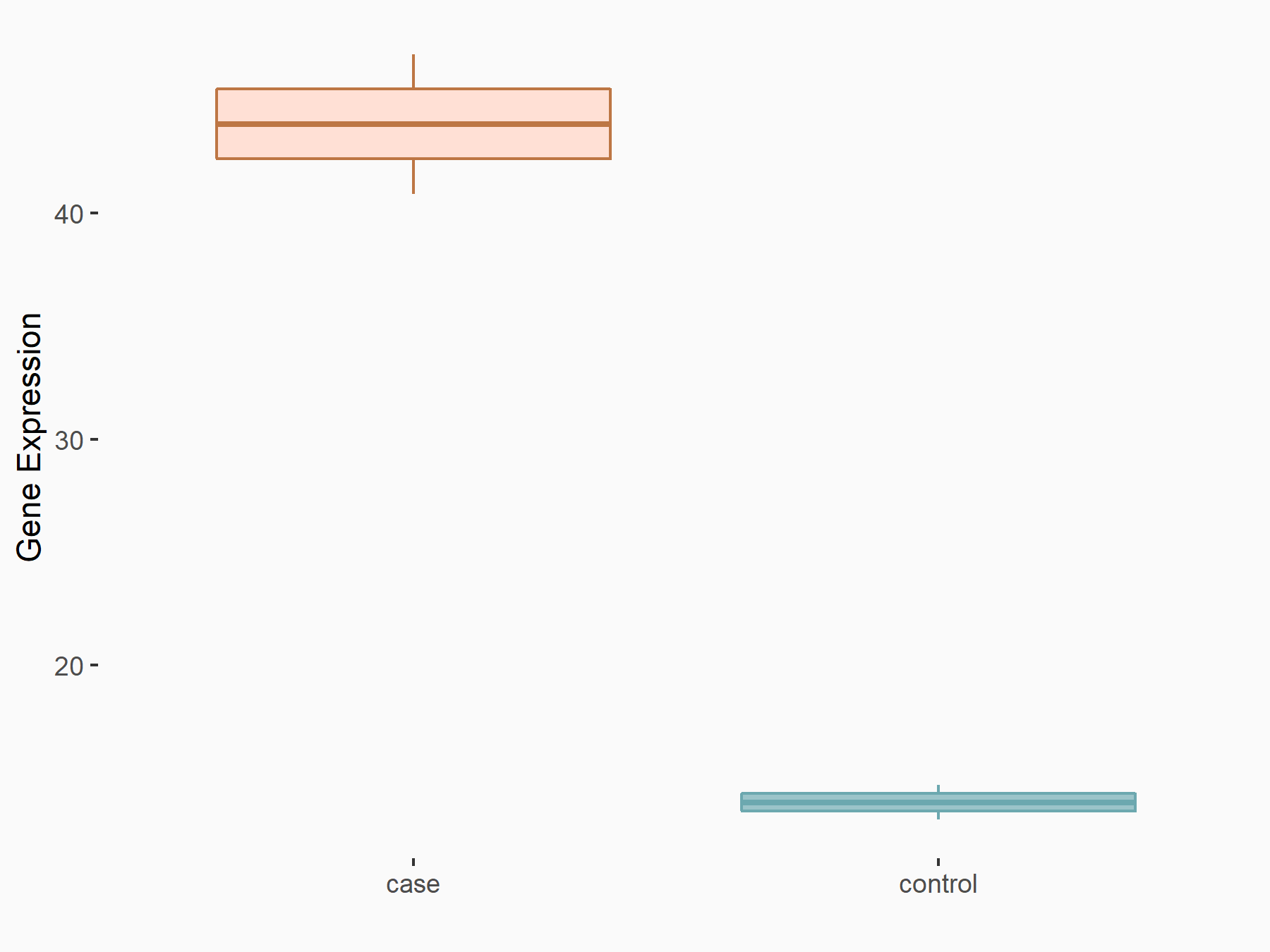  |
logFC: 1.59E+00 p-value: 2.50E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were divided into control group and ALKBH5-overexpressing group (9 mice per group). ALKBH5-overexpressing and control A549 cells (3 × 106 cells/mouse) in 200 uL PBS were intravenously (i.v.) injected into the lateral tail vein of mice. At every 5th day post-inoculation, TGF-Beta-1 (4 ug/kg body weight) was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected to promote tumor cell metastasis. Eight weeks later, the mice were euthanized, and then their lungs and livers were taken out and fixed in Bouin's solution (Sigma Aldrich, HT101128) or 4% Paraformaldehyde (Beyotime, p0099, Shanghai, China) for macroscopically metastatic nodule analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 weakens YTHDF1/3-mediated TGF-Beta-R2 and Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) mRNA stabilization, and abolishes YTHDF2-mediated SMAD6 mRNA degradation, supporting the notion that ALKBH5 inhibits TGF-Beta-induced EMT and invasion of NSCLC cells via YTHD1/2/3-mediated mechanism. | |||
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 6 (SMAD6)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | THP1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: ALKBH5 knockdown THP1 cells
Control: Wild type THP1 cells
|
GSE128574 | |
| Regulation |
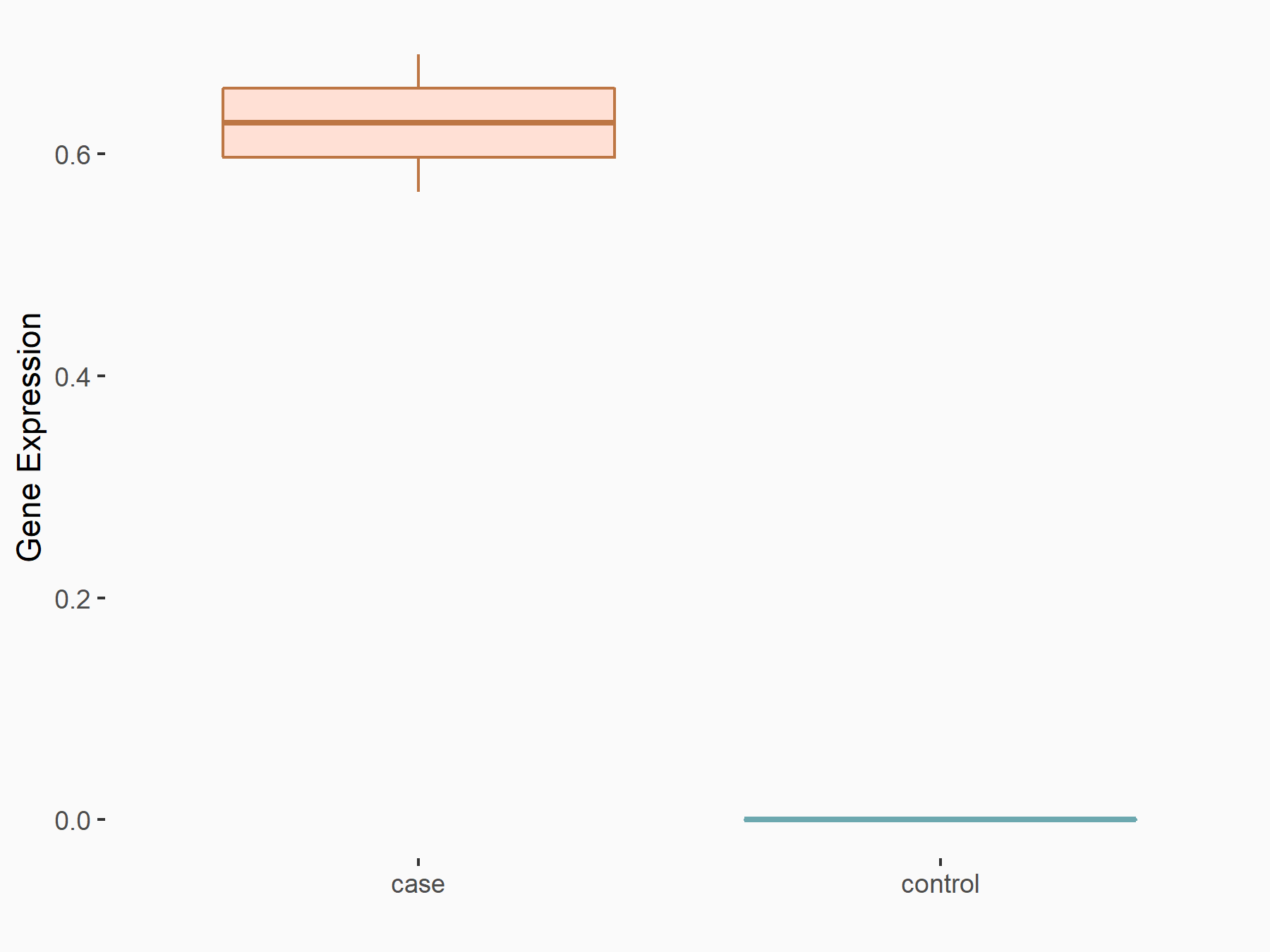  |
logFC: 7.02E-01 p-value: 2.75E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were divided into control group and ALKBH5-overexpressing group (9 mice per group). ALKBH5-overexpressing and control A549 cells (3 × 106 cells/mouse) in 200 uL PBS were intravenously (i.v.) injected into the lateral tail vein of mice. At every 5th day post-inoculation, TGF-Beta-1 (4 ug/kg body weight) was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected to promote tumor cell metastasis. Eight weeks later, the mice were euthanized, and then their lungs and livers were taken out and fixed in Bouin's solution (Sigma Aldrich, HT101128) or 4% Paraformaldehyde (Beyotime, p0099, Shanghai, China) for macroscopically metastatic nodule analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 weakens YTHDF1/3-mediated TGF-Beta-R2 and SMAD3 mRNA stabilization, and abolishes YTHDF2-mediated Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 6 (SMAD6) mRNA degradation, supporting the notion that ALKBH5 inhibits TGF-Beta-induced EMT and invasion of NSCLC cells via YTHD1/2/3-mediated mechanism. | |||
Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
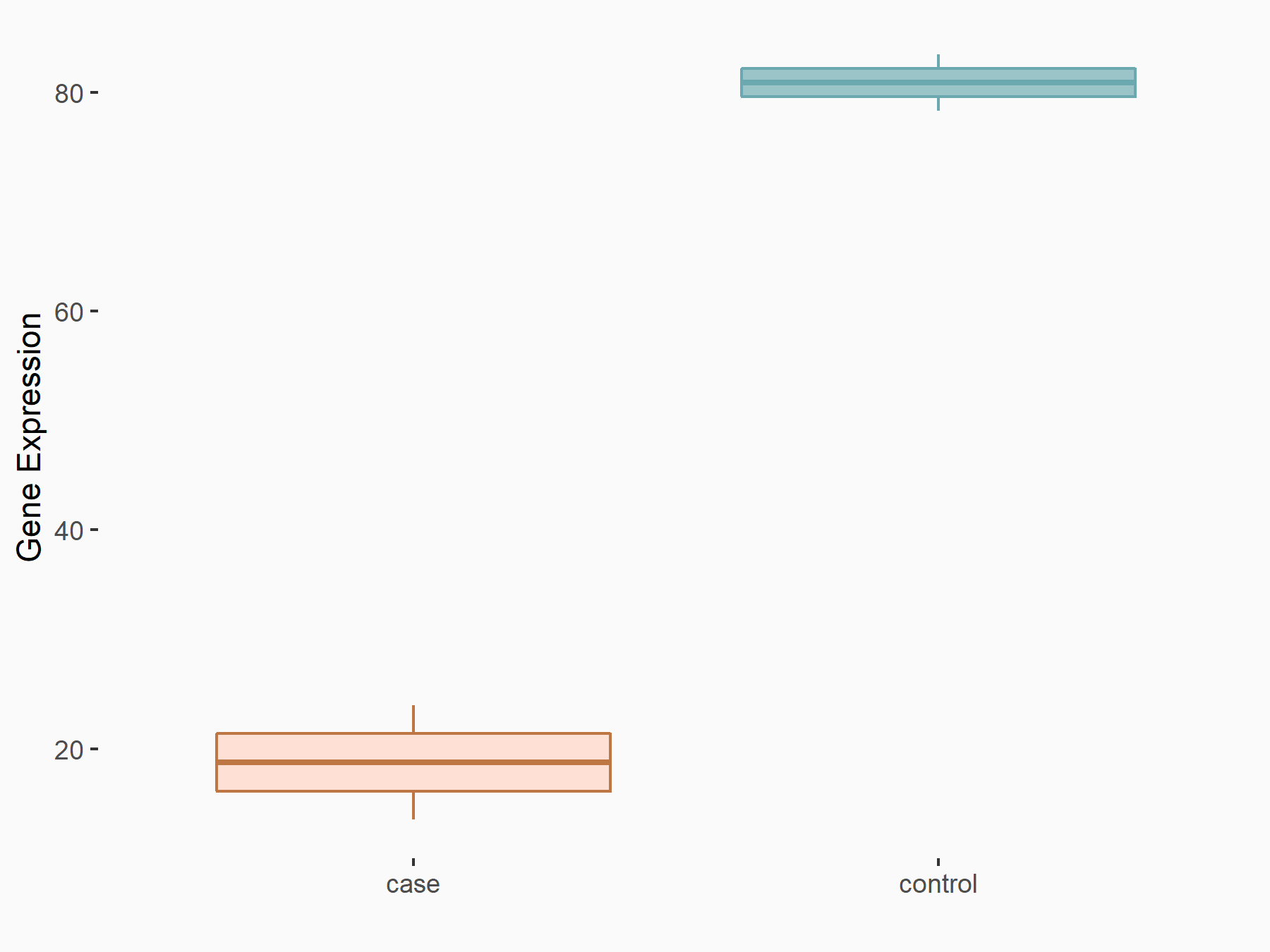  |
logFC: -2.10E+00 p-value: 1.89E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [26] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation enhanced the stability of KCNK15-AS1. In pancreatic cancer, KCNK15-AS1 bound to KCNK15 to inhibit its translation, and interacted with MDM2 to induce REST ubiquitination, which eventually facilitated Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN) transcription to inactivate AKT pathway. | |||
Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88 (MYD88)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
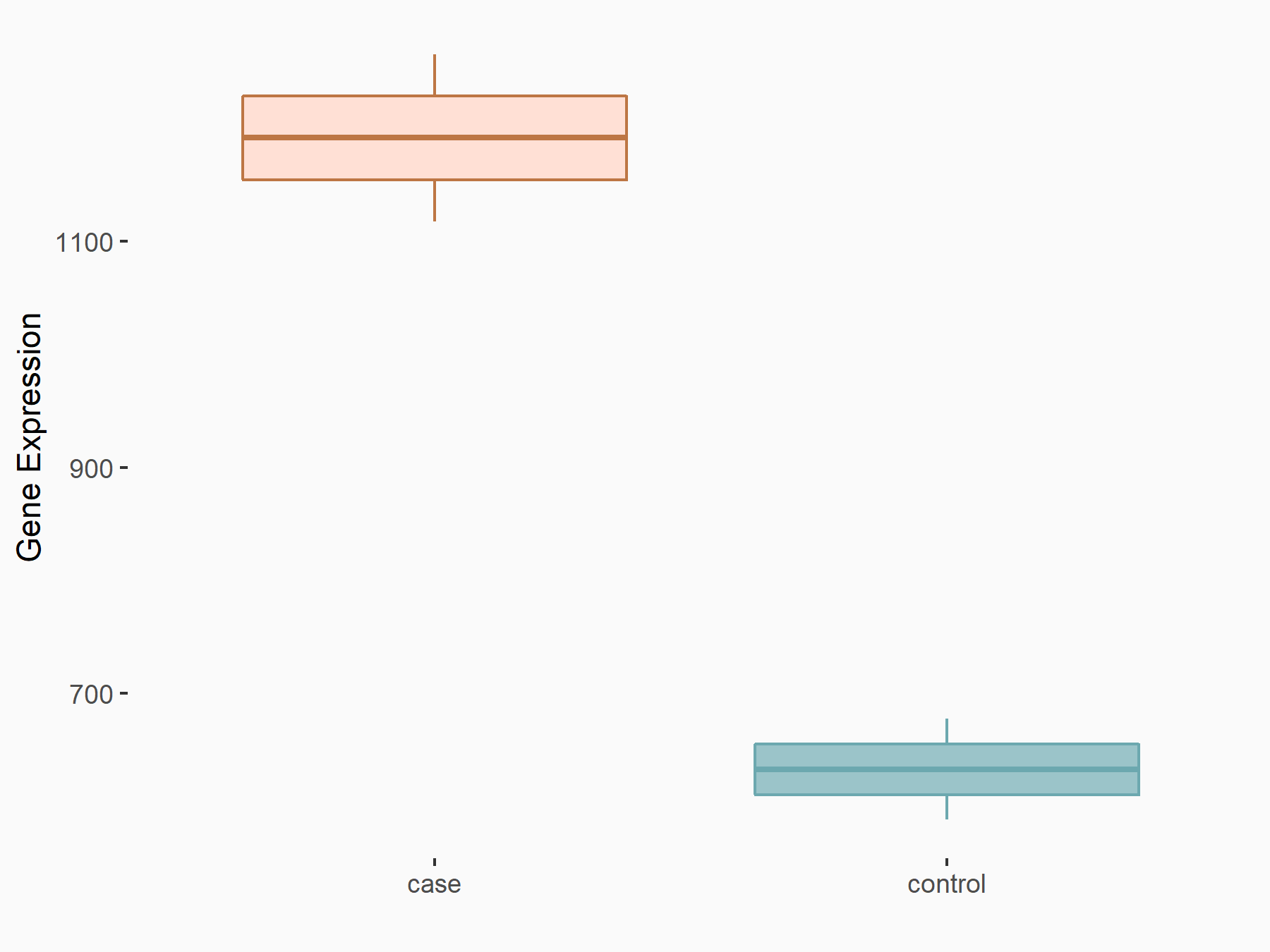  |
logFC: 9.11E-01 p-value: 2.76E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Skeletal anomaly [ICD-11: LD24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [27] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Skeletal anomaly [ICD-11: LD24] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | ||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
In-vitro Model |
Mesenchymal stem cell line (NP tissues were used to isolate NP cells) | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 positively regulates expression of Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88 (MYD88), a critical upstream regulator of NF-Kappa-B signaling, by facilitating m6A methylation modification to MYD88-RNA, subsequently inducing the activation of NF-Kappa-B which is widely regarded as a repressor of osteogenesis and therefore suppressing osteogenic progression. The METTL3-mediated m6A methylation is found to be dynamically reversed by the demethylase ALKBH5. | |||
Myt1 kinase (PKMYT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
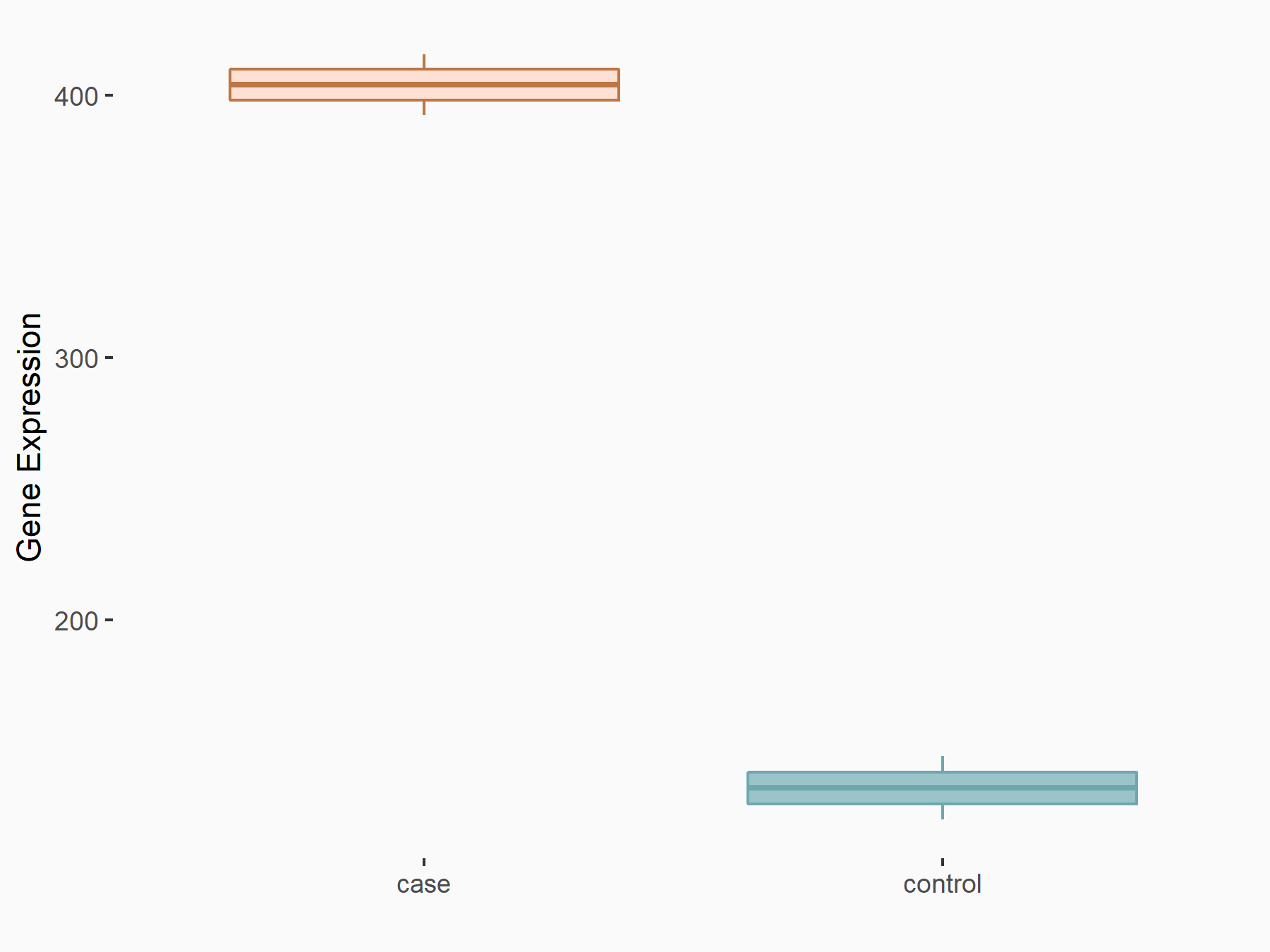  |
logFC: 1.57E+00 p-value: 1.28E-17 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [28] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
In-vitro Model |
SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | |
| In-vivo Model | After randomly assignment and anesthetization, nude mice were injected with 5 × 106 cells suspended in 100 uL PBS into the tail vein (n = 5 per group). | |||
| Response Summary | Myt1 kinase (PKMYT1), as a downstream target of ALKBH5, promoted invasion and migration in GC. Moreover IGF2BP3 helped stabilize the mRNA stability of PKMYT1 via its m6A modification site. | |||
Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 1 (PRRX1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
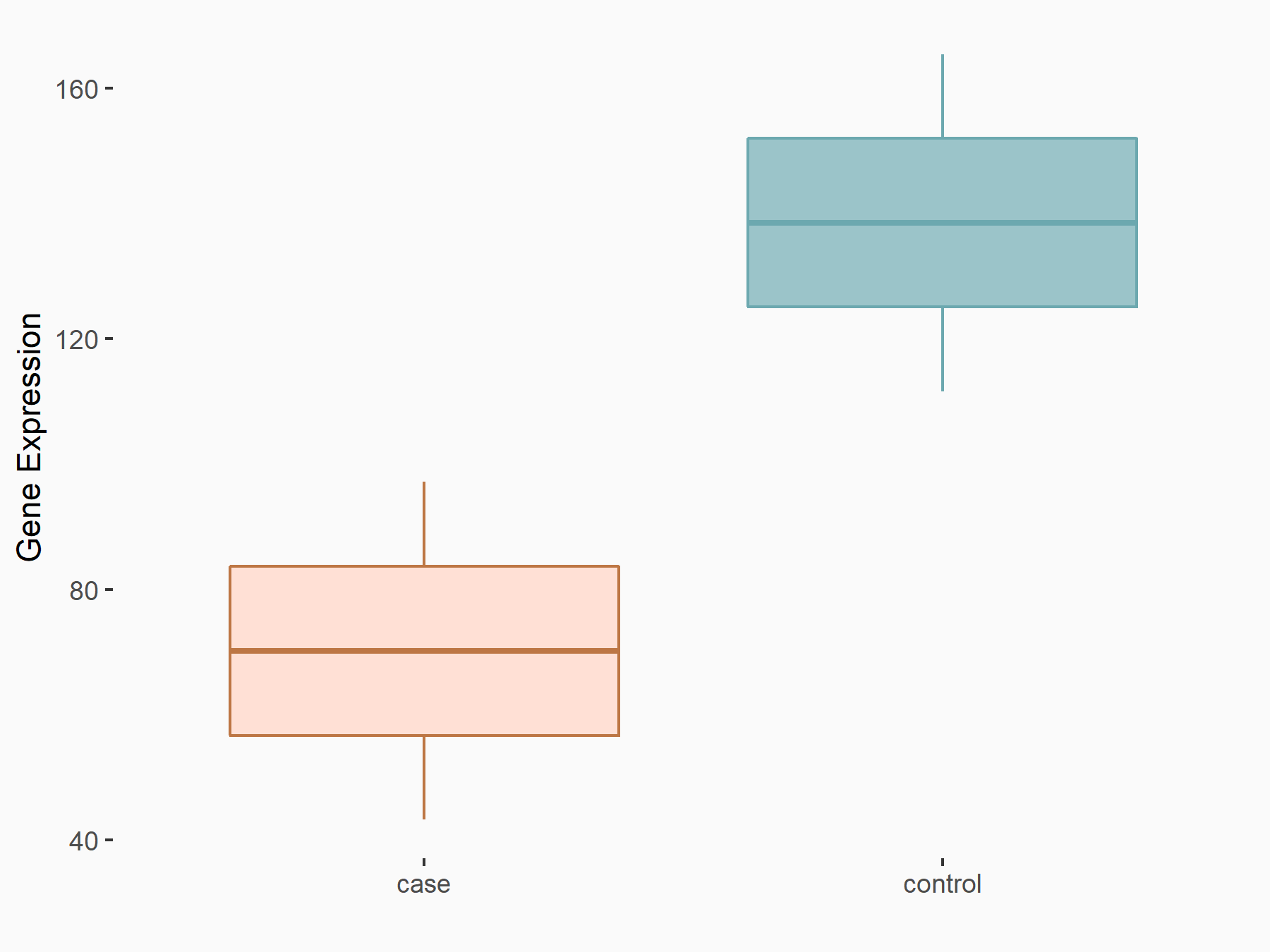 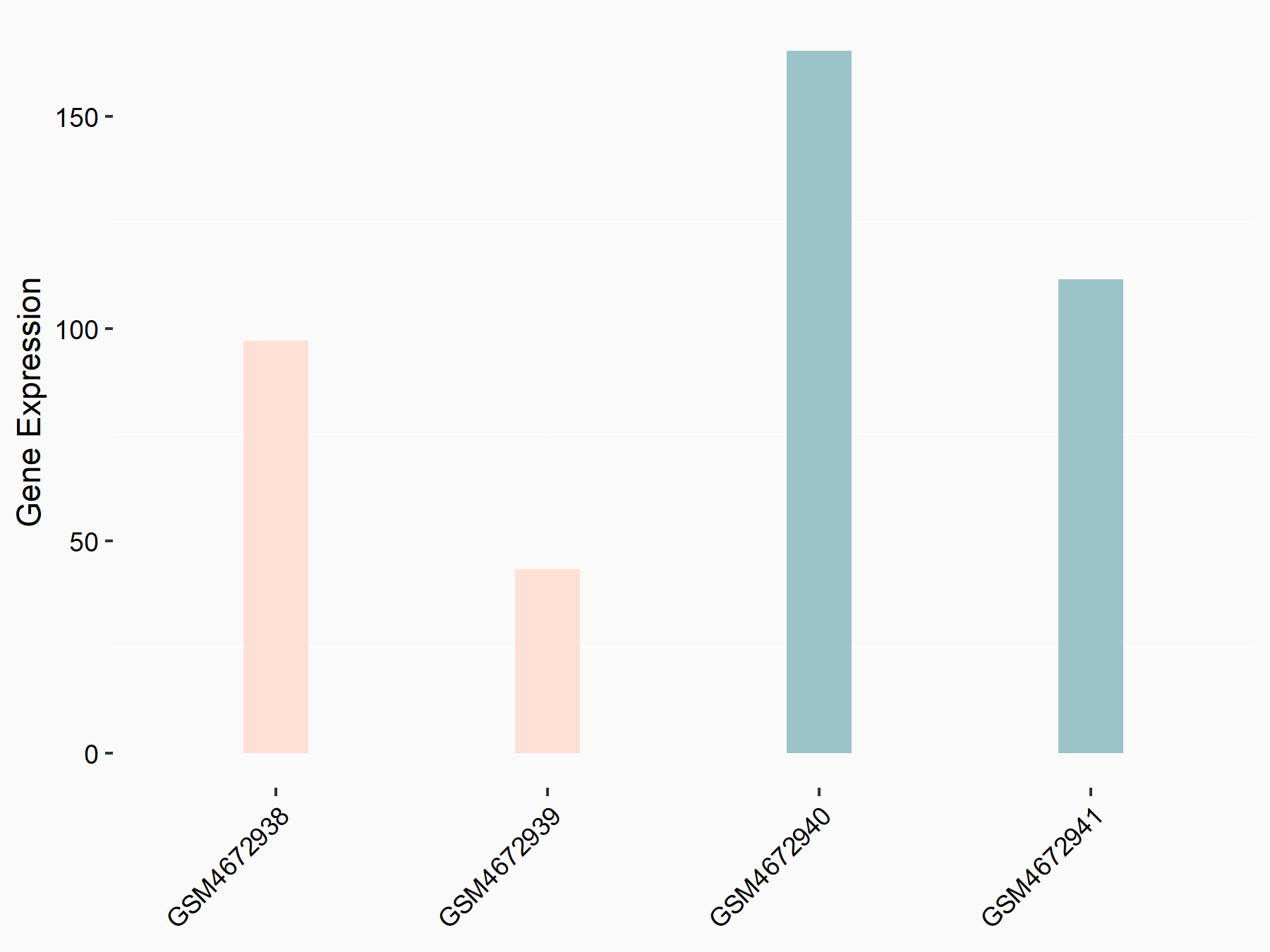 |
logFC: -9.92E-01 p-value: 2.75E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
In-vitro Model |
PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | Cells at 1 × 106 were subcutaneously injected into the mice similarly to nude mice. Twenty-eight days later, grafted tumors were collected and morphologically analyzed. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of p53 or inhibition of p53's transcriptional activity by addition of its specific inhibitor PFT-Alpha decreased expression of ALKBH5 and Cancer stem cells' malignancies, the pivotal role of ALKBH5 in Cancer stem cells derived from nonsmall-cell lung cancer and highlight the regulatory function of the p53/ALKBH5 axis in modulating CSC progression. p53 transcriptionally regulates Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 1 (PRRX1), which is consistent with our previous report. | |||
Period circadian protein homolog 1 (PER1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
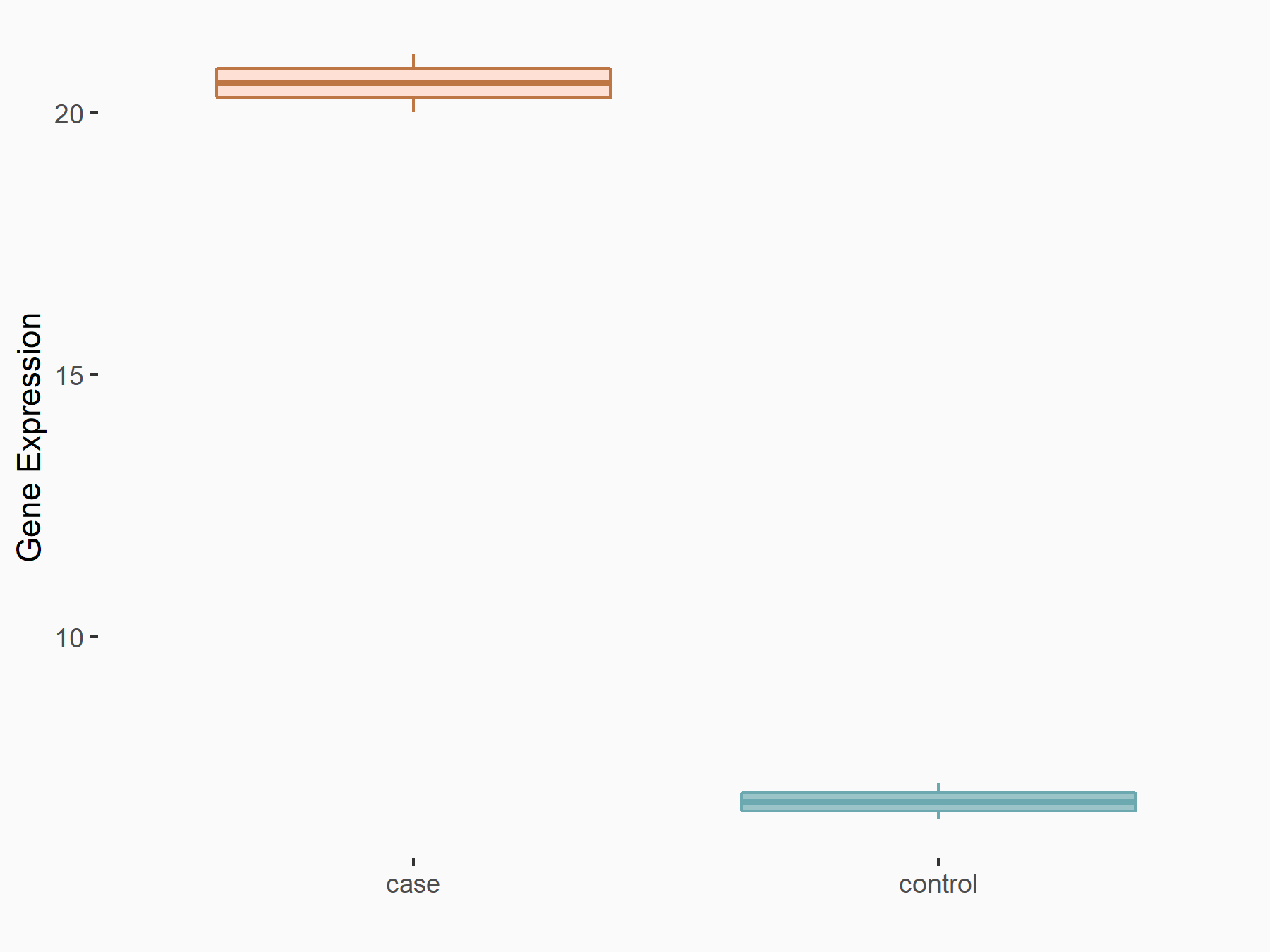 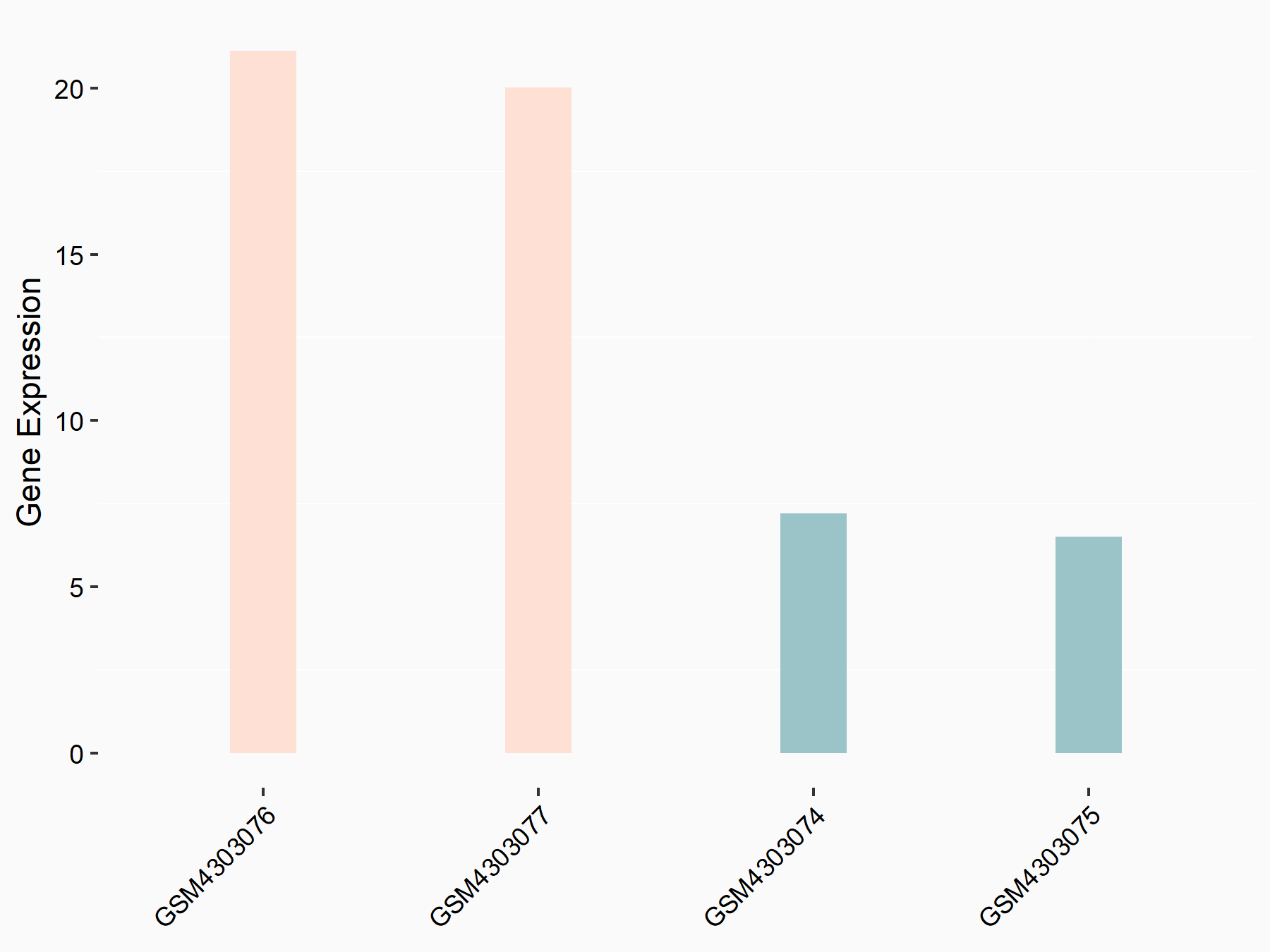 |
logFC: 1.46E+00 p-value: 8.91E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [30] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 serves as a pancreatic cancer suppressor by regulating the posttranscriptional activation of Period circadian protein homolog 1 (PER1) through m6A abolishment, which highlights a demethylation-based approach for PC diagnosis and therapy. ALKBH5 loss downregulated PER1 mRNA levels in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. | |||
PI3-kinase subunit alpha (PI3k/PIK3CA)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
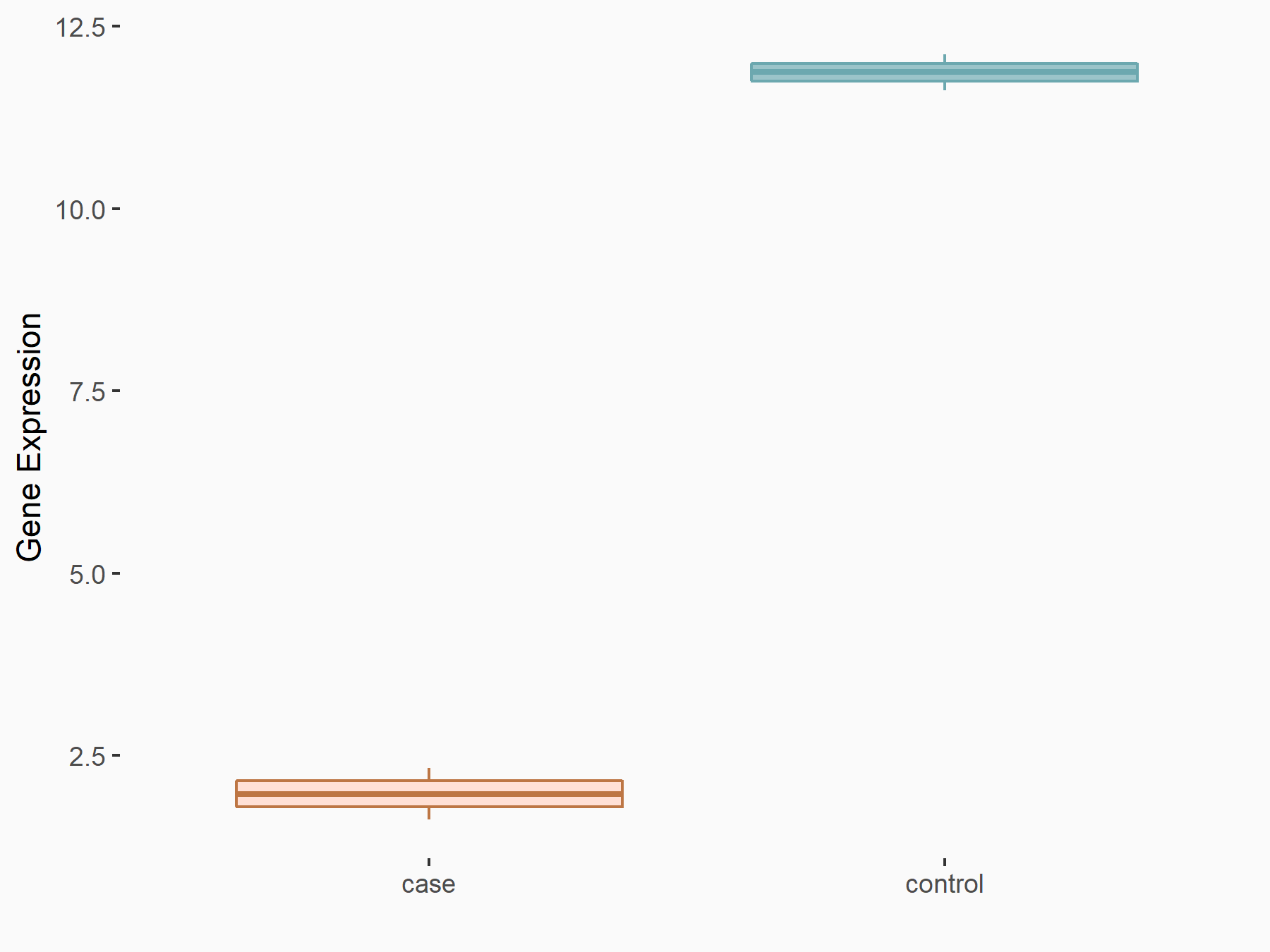  |
logFC: -2.12E+00 p-value: 2.82E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
In-vitro Model |
A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| CoC1 | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6891 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | SKOV3 or A2780 cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral vectors and injected (5 × 106 cells/mouse in 200 uL volume) subcutaneously into the left armpit of 6-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 21 days, the animals were sacrificed to confirm the presence of tumors and weigh the established tumors. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is a tumor-promoting gene in epithelial ovarian cancer, which is involved in the mTOR pathway and BCL-2-Beclin1 complex. ALKBH5 activated EGFR-PI3-kinase subunit alpha (PI3k/PIK3CA)-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. | |||
Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
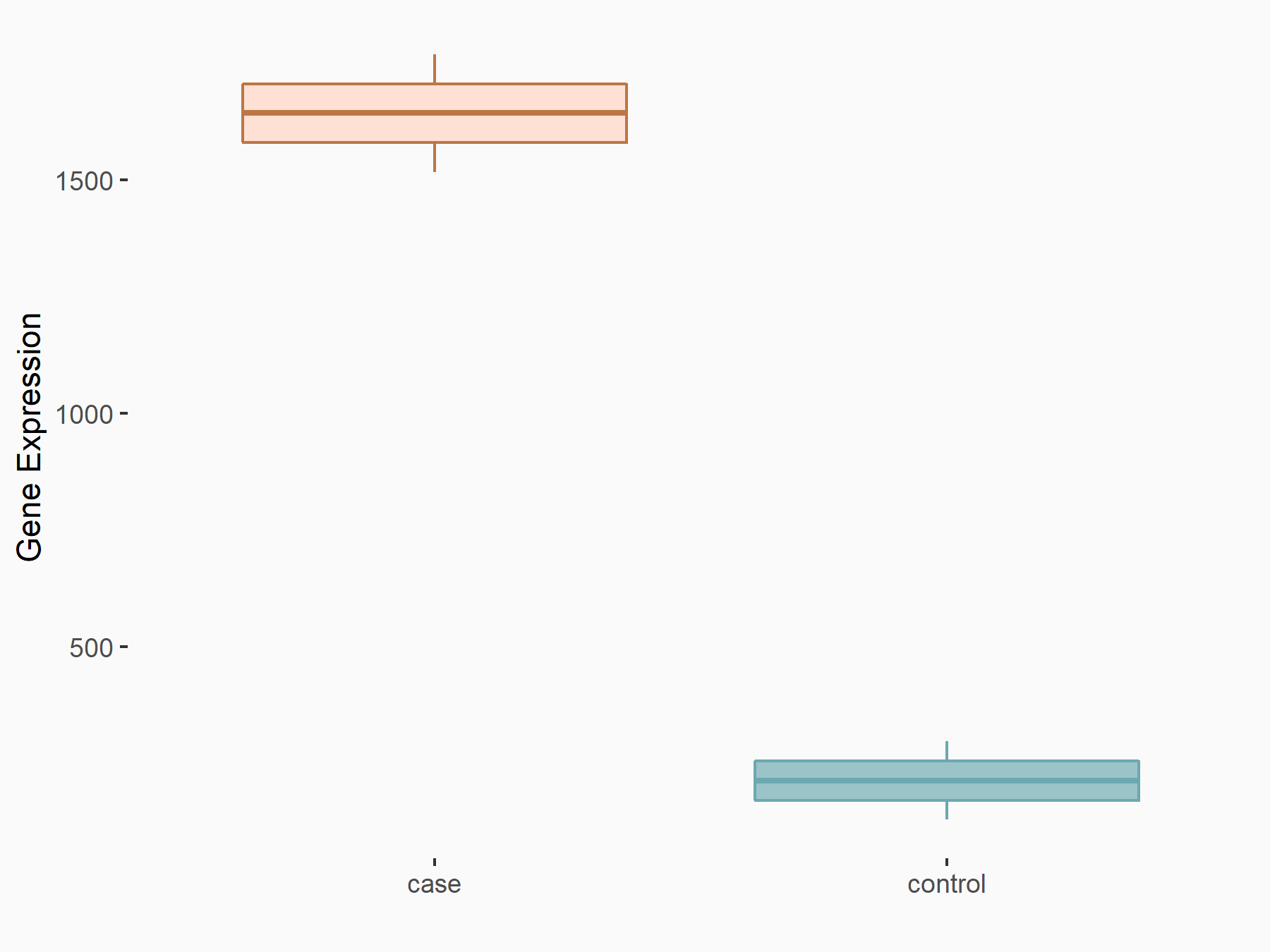  |
logFC: 2.95E+00 p-value: 3.40E-21 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [31] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
In-vitro Model |
TFK-1 | Cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2214 |
| RBE | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4896 | |
| LIPF178c (LIPF178c human bile duct cancer cells from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| LIPF155c (LIPF155c human bile duct cancer cells from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| LICCF (LICCF human intrahepatic bile duct cancer cell line from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| HCCC-9810 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6908 | |
| In-vivo Model | ICC tumor cells (LIPF178c-shCtrl/shALKBH5) of 5 × 106 were injected into the right flank of NCG mice. Tumor volume was calculated by the formula: volume = ab2/2 (a, the longer axis; b, the shorter axis). T-cell killing assay in vitro was conducted as previously reported (20). PBMCs from healthy donors were activated and expanded as described above. The day before tumor cell injection, PBMC (i.v. 1 × 107 cells) was adoptively transferred to NCG mice via the tail vein. At the end, the PBMC was isolated and subjected to flow cytometry for detecting T-cell percentage. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 as an important m6A demethylase that orchestrates Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). | |||
Protein patched homolog 1 (PTCH1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
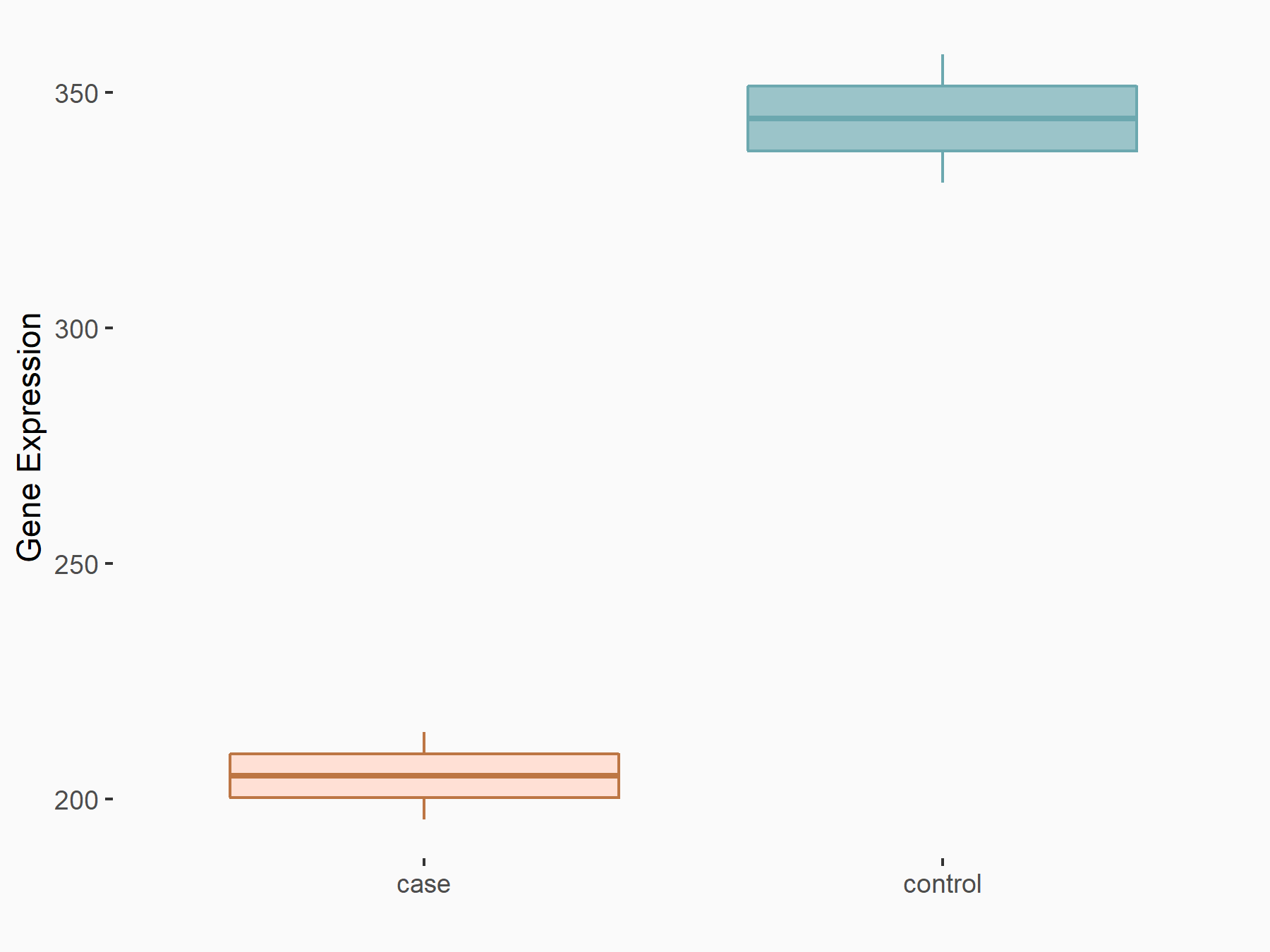  |
logFC: -7.48E-01 p-value: 6.04E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis [ICD-11: DB93]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [32] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatic fibrosis [ICD-11: DB93.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hedgehog signaling pathway | hsa04340 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HSCs (Hepatic stellate cells(HSCs) were purchased from American Type Culture Collections (Manassas, VA)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | Liver fibrosis mice model was induced by intraperitoneal CCl4 injection for 12 weeks. The dose regimen for CCl4 in mice is 1 ml kg-1, diluted to 50% with olive oil twice per week for 12 weeks. Until 11 weeks, mice with liver-specific disruption of ALKBH5 were given hydrodynamic tail-vein injections of LV5-ALKBH5. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 mediated Protein patched homolog 1 (PTCH1) activation via a m6A-dependent manner,ALKBH5 ameliorated liver fibrosis and suppressed HSCs activation via triggering PTCH1 activation in a m6A dependent manner. | |||
Protein phosphatase 1A (PPM1A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
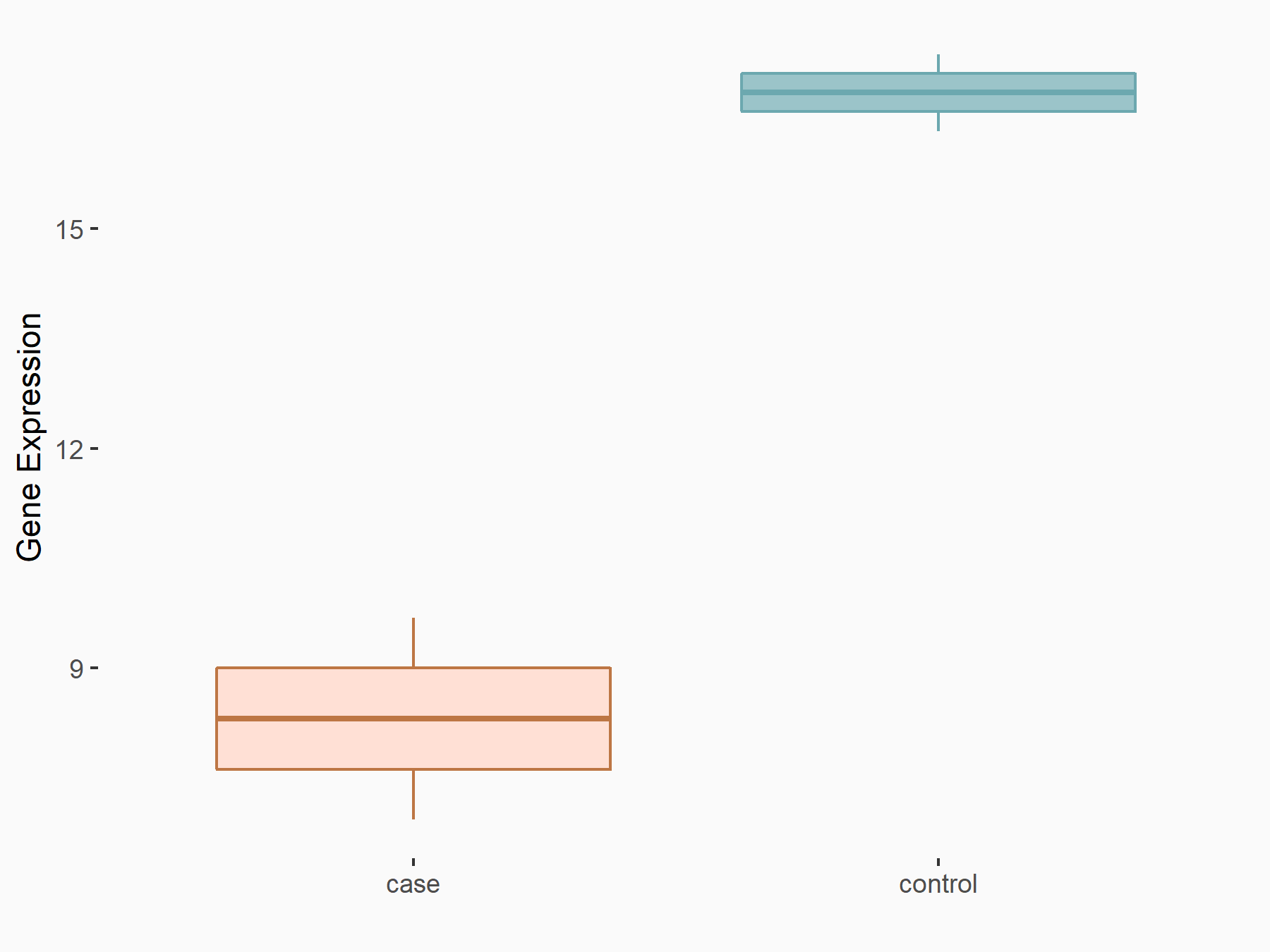  |
logFC: -9.55E-01 p-value: 2.96E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [33] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Azoospermia [ICD-11: GB04.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| In-vivo Model | Male SPF BALB/c mice (qls02-0202) were purchased from Qinglongshan animal breeding farm. Mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation and testes were obtained for following histopathological analyses. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification promoted translation of Protein phosphatase 1A (PPM1A) (protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform), a negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, but decreased expression of CAMKK2 (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta), a positive AMPK regulator, by reducing its RNA stability. Similar regulation of METTL14, ALKBH5, and m6A was also observed in LCs upon treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin (HsCG). Knock down of YTHDF1 failed to change the expression of CAMKK2 Providing insight into novel therapeutic strategies by exploiting m6A RNA methylation as targets for treating azoospermatism and oligospermatism patients with reduction in serum testosterone. | |||
Protein salvador homolog 1 (SAV1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
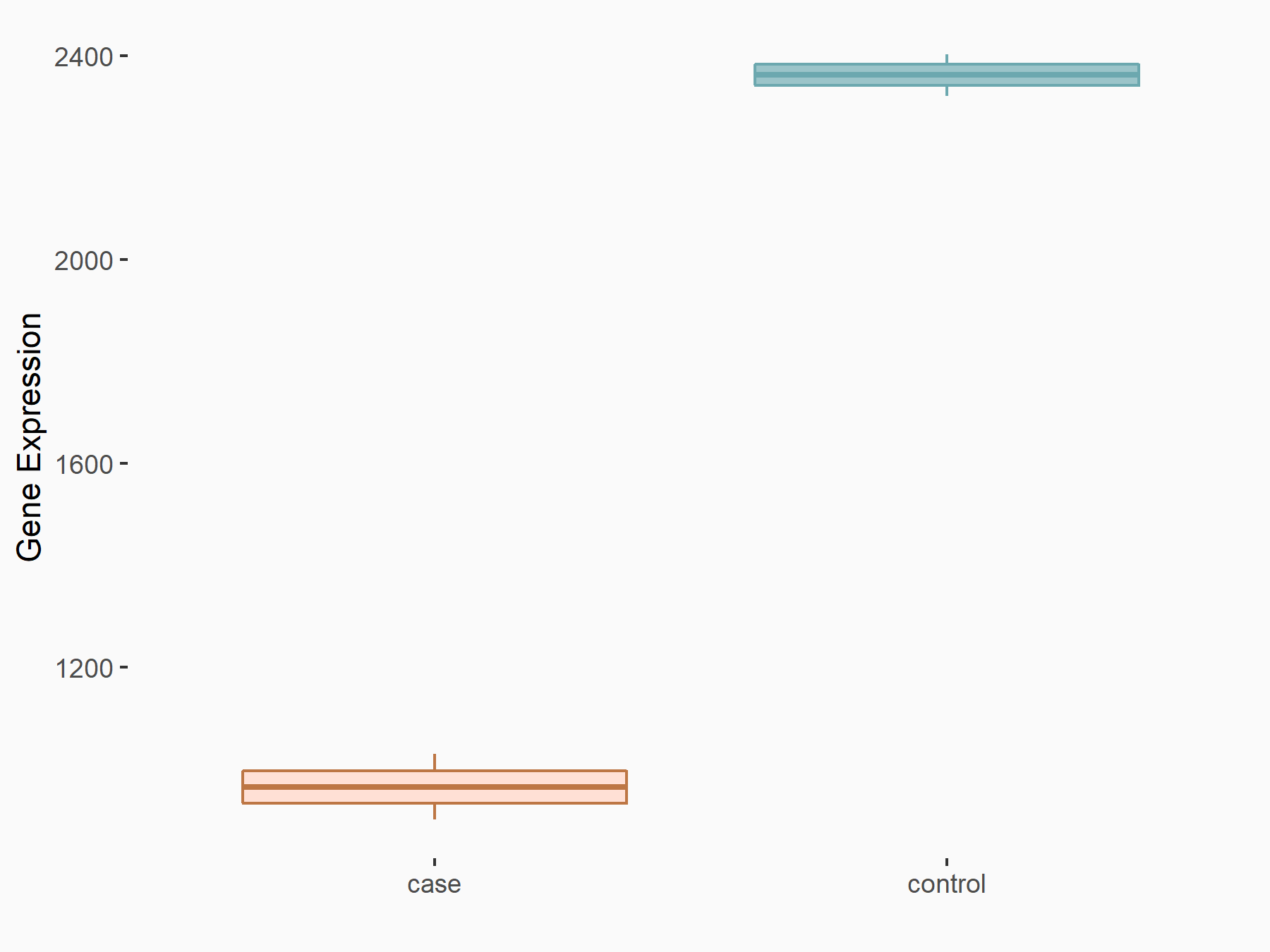  |
logFC: -1.29E+00 p-value: 1.15E-10 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [34] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
U266 (Human multiple myeloma cells) | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0014 | |
| NCI-H929 | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1600 | |
| ARH-77 | Human leukemia tumor | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1072 | |
| Response Summary | Inhibiting ALKBH5 in Multiple Myeloma cells increased Protein salvador homolog 1 (SAV1) m6A levels, decreased SAV1 mRNA stability and expression, suppressed the stem cell related HIPPO-pathway signalling and ultimately activates the downstream effector YAP, exerting an anti-myeloma effect. | |||
Protein sprouty homolog 2 (SPRY2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
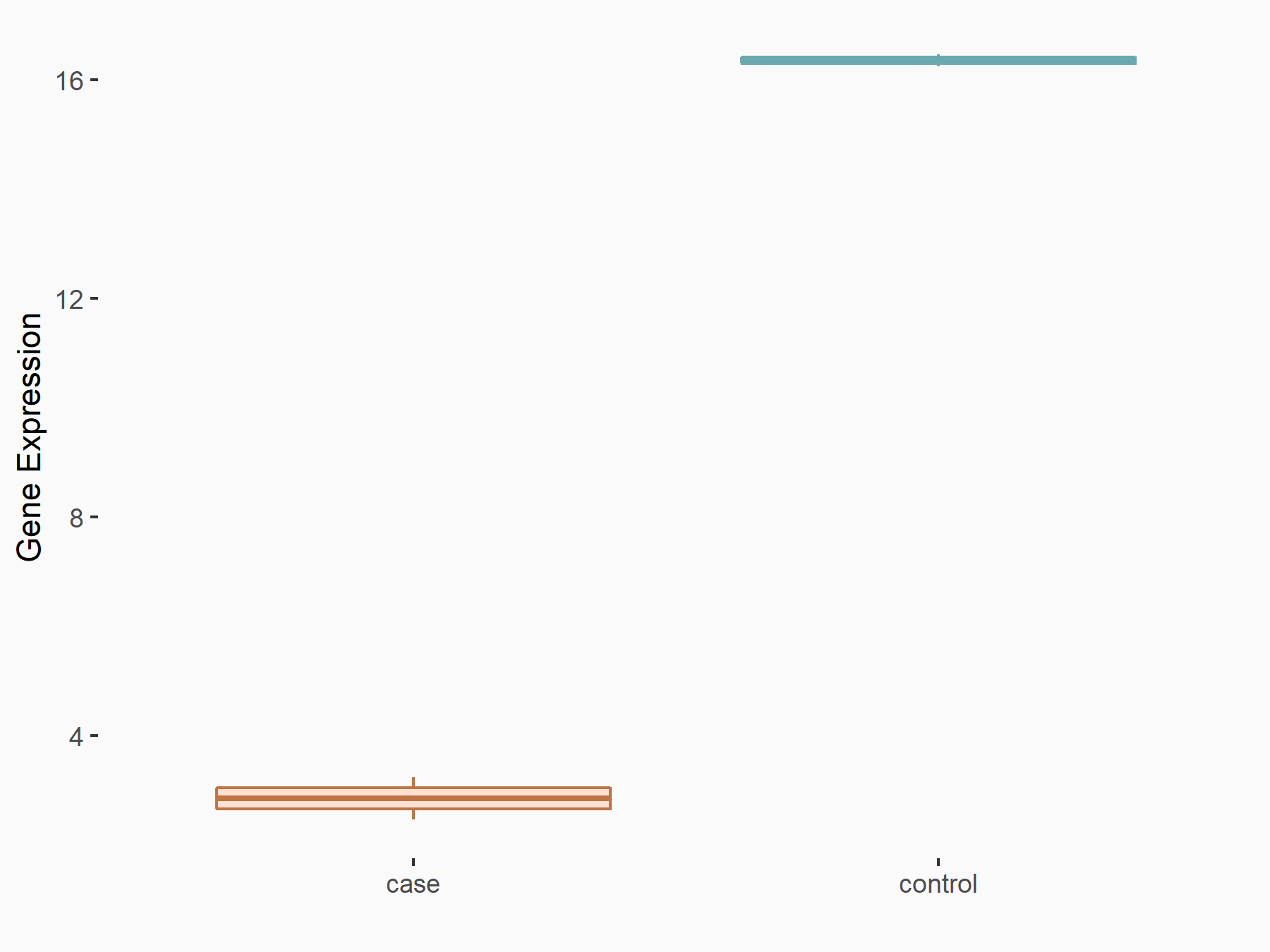  |
logFC: -2.18E+00 p-value: 1.77E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | ||
In-vitro Model |
Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 plays an antitumor role in colorectal cancer by modulating the FOXO3/miR-21/Protein sprouty homolog 2 (SPRY2) axis, which not only suggests a regulatory effect between ALKBH5 and FOXO3, but also provides a new therapeutic direction for colorectal cancer. | |||
Protein Wnt-5a (WNT5A)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | CAG cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 CAG cells
Control: shNC CAG cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
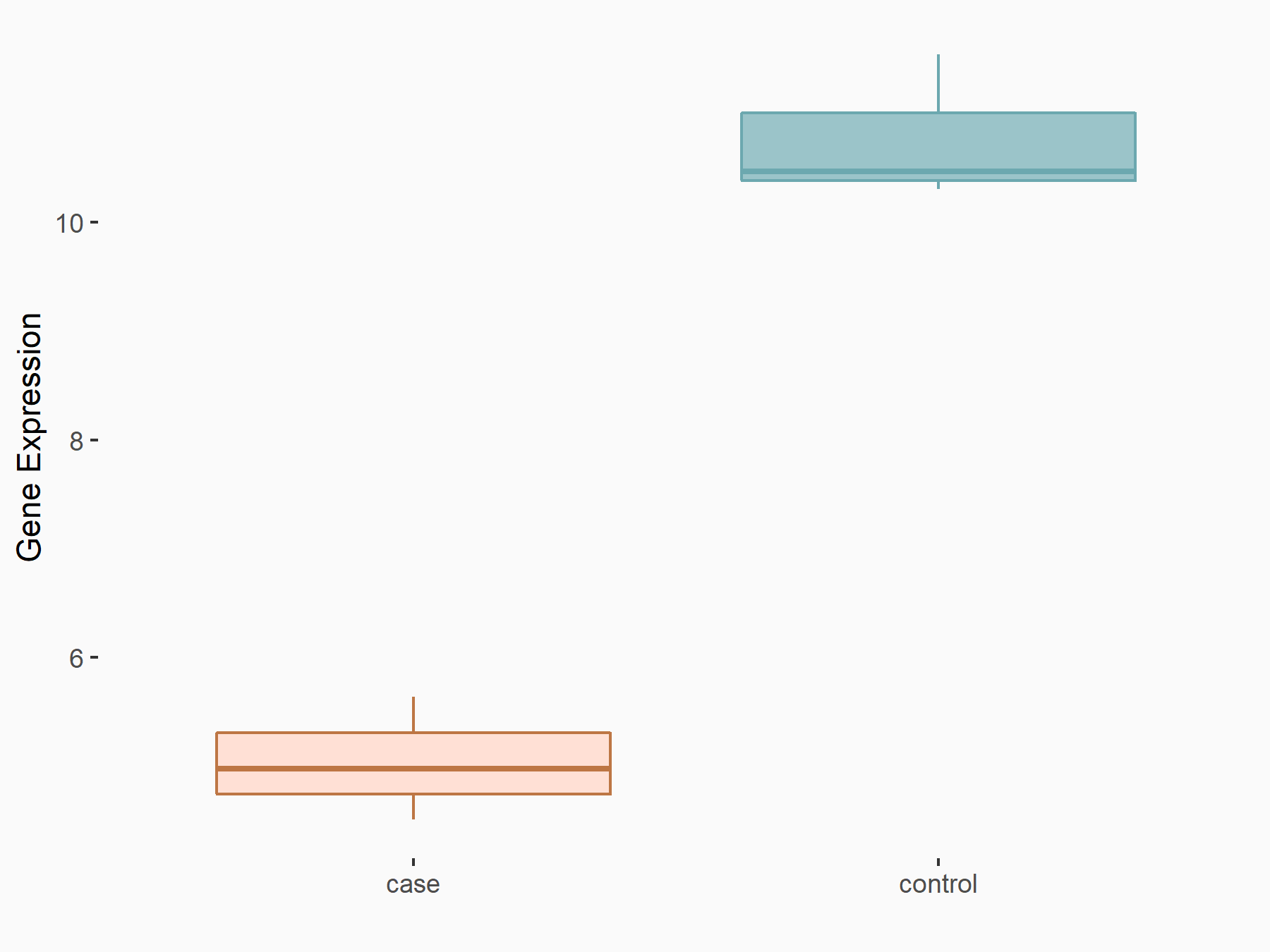 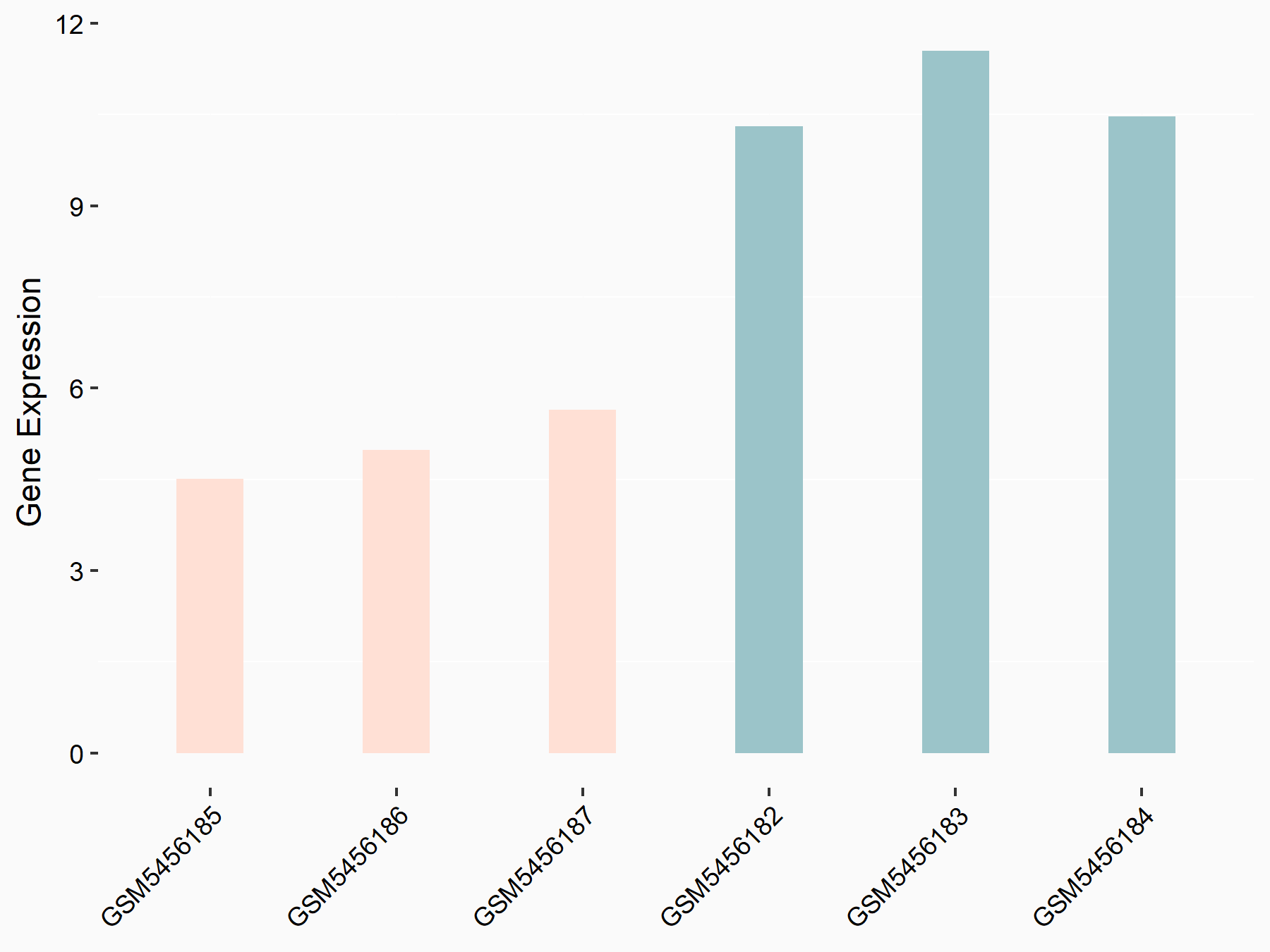 |
logFC: -9.66E-01 p-value: 2.63E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [35] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
CMECs (Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells ) | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is a negative regulator of post-ischemic angiogenesis via post-transcriptional modulation and destabilization of Protein Wnt-5a (WNT5A) mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
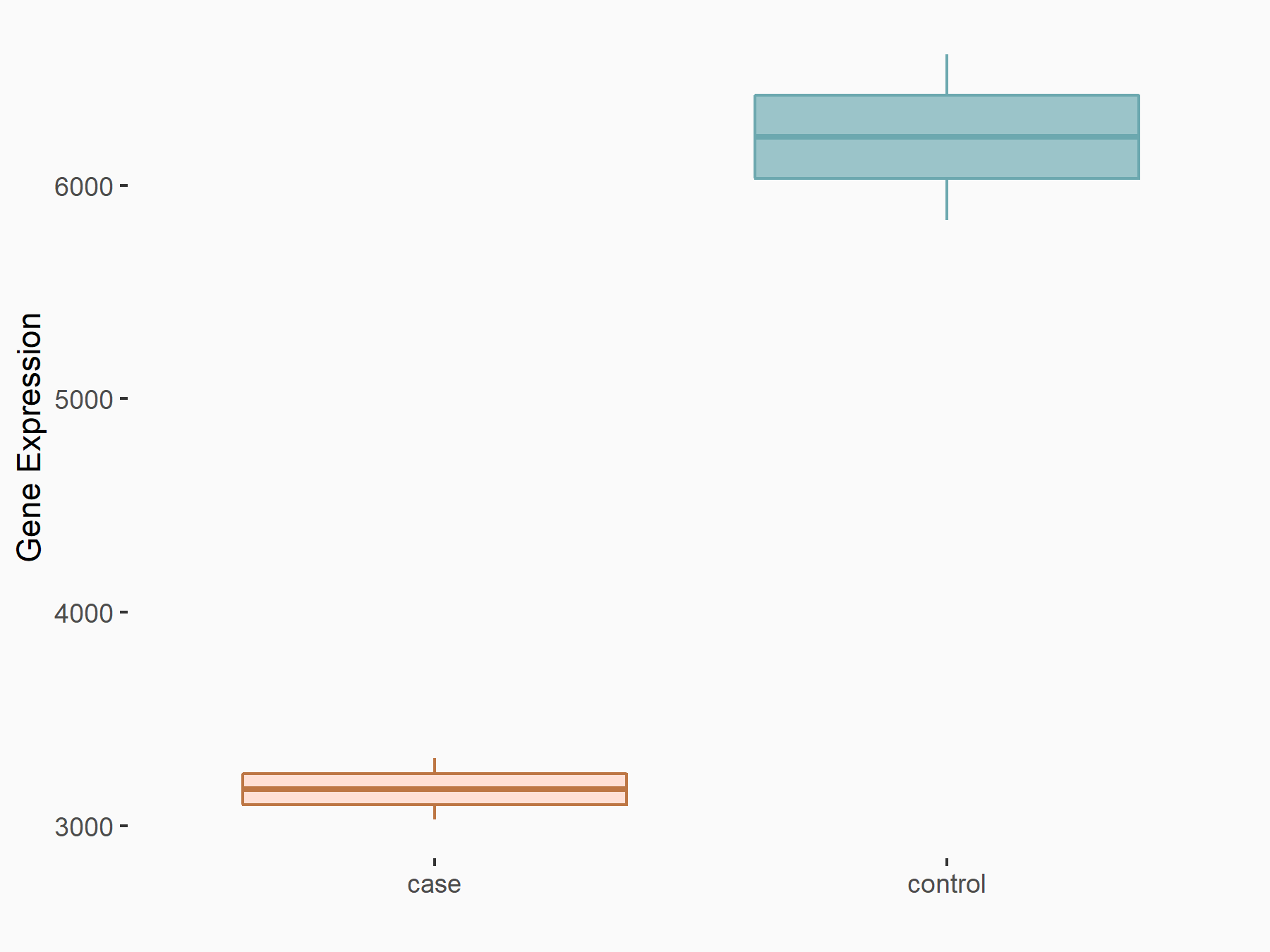 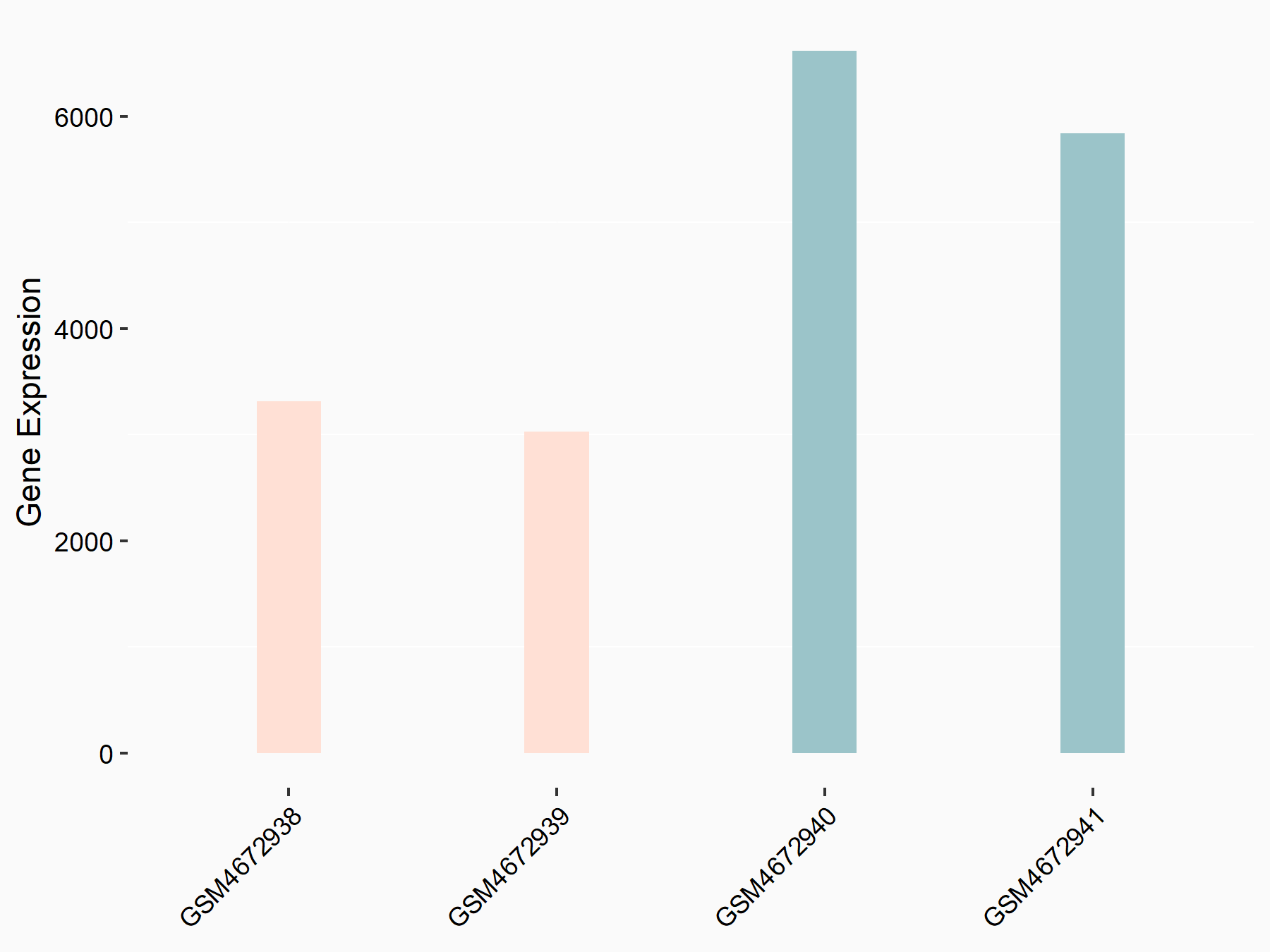 |
logFC: -9.73E-01 p-value: 3.10E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [26] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation enhanced the stability of KCNK15-AS1. In pancreatic cancer, KCNK15-AS1 bound to KCNK15 to inhibit its translation, and interacted with MDM2 to induce REST ubiquitination, which eventually facilitated PTEN transcription to inactivate RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) pathway. | |||
Ossification of spinal ligaments [ICD-11: FA83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ossification of spinal ligaments [ICD-11: FA83] | |||
| Responsed Drug | MK22606 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Ossification | |||
In-vitro Model |
Ligamentum flavum cells (Ligamentum flavum cells) | |||
| Response Summary | The overexpression of ALKBH5 led to the activation of RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1), and BMP2 was regulated by ALKBH5 through the AKT signaling pathway. ALKBH5 promoted the osteogenesis of the ligamentum flavum cells through BMP2 demethylation and AKT activation. MK22606 is an AKT inhibitor. Moreover, when ALKBH5 was knocked down in the ligamentum flavum cells, p-AKT was inhibited when compared with that in the overexpressed ALKBH5 and control groups. | |||
RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | Cal27 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 Cal27 cells
Control: siScramble Cal27 cells
|
GSE185886 | |
| Regulation |
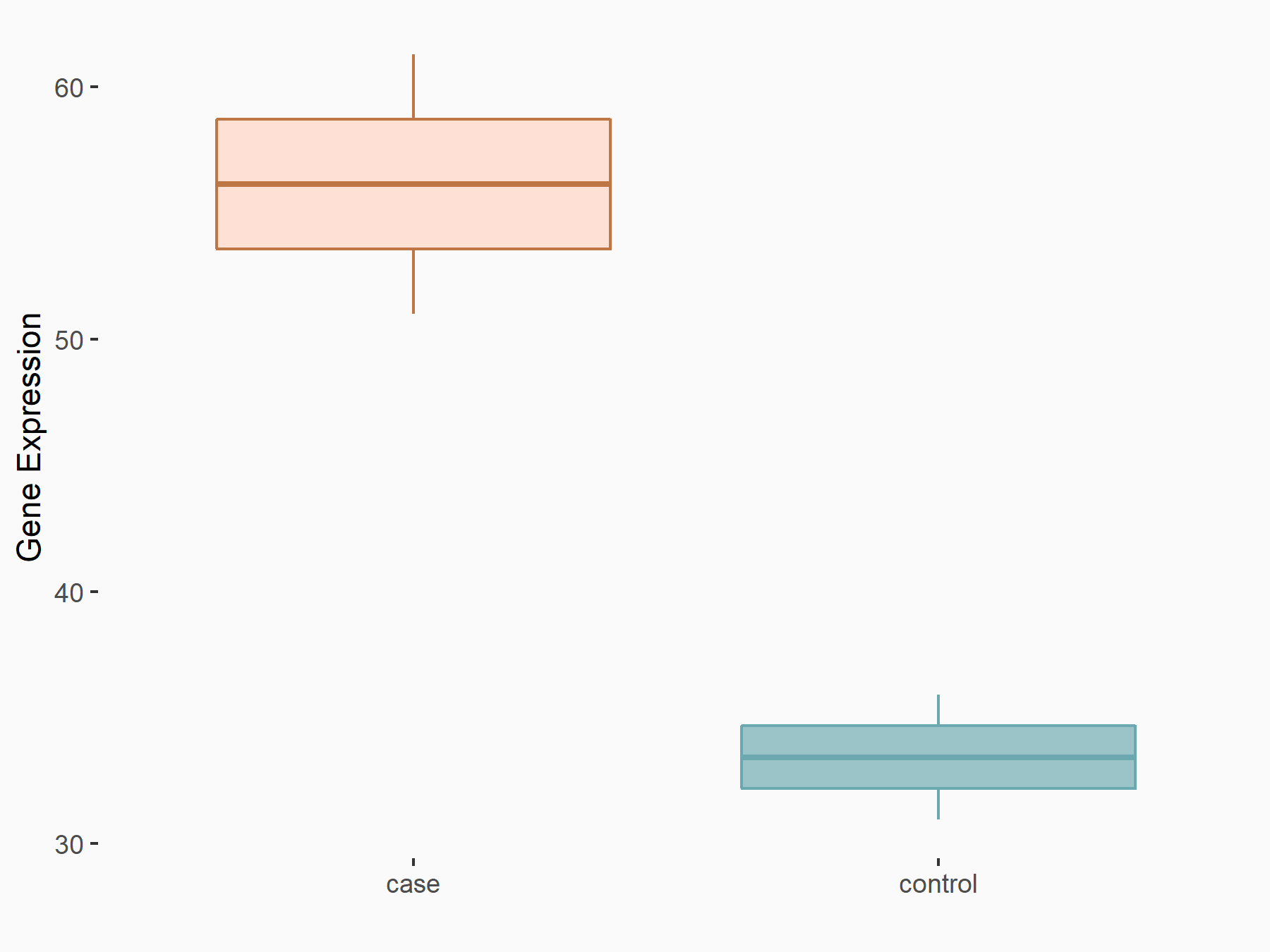 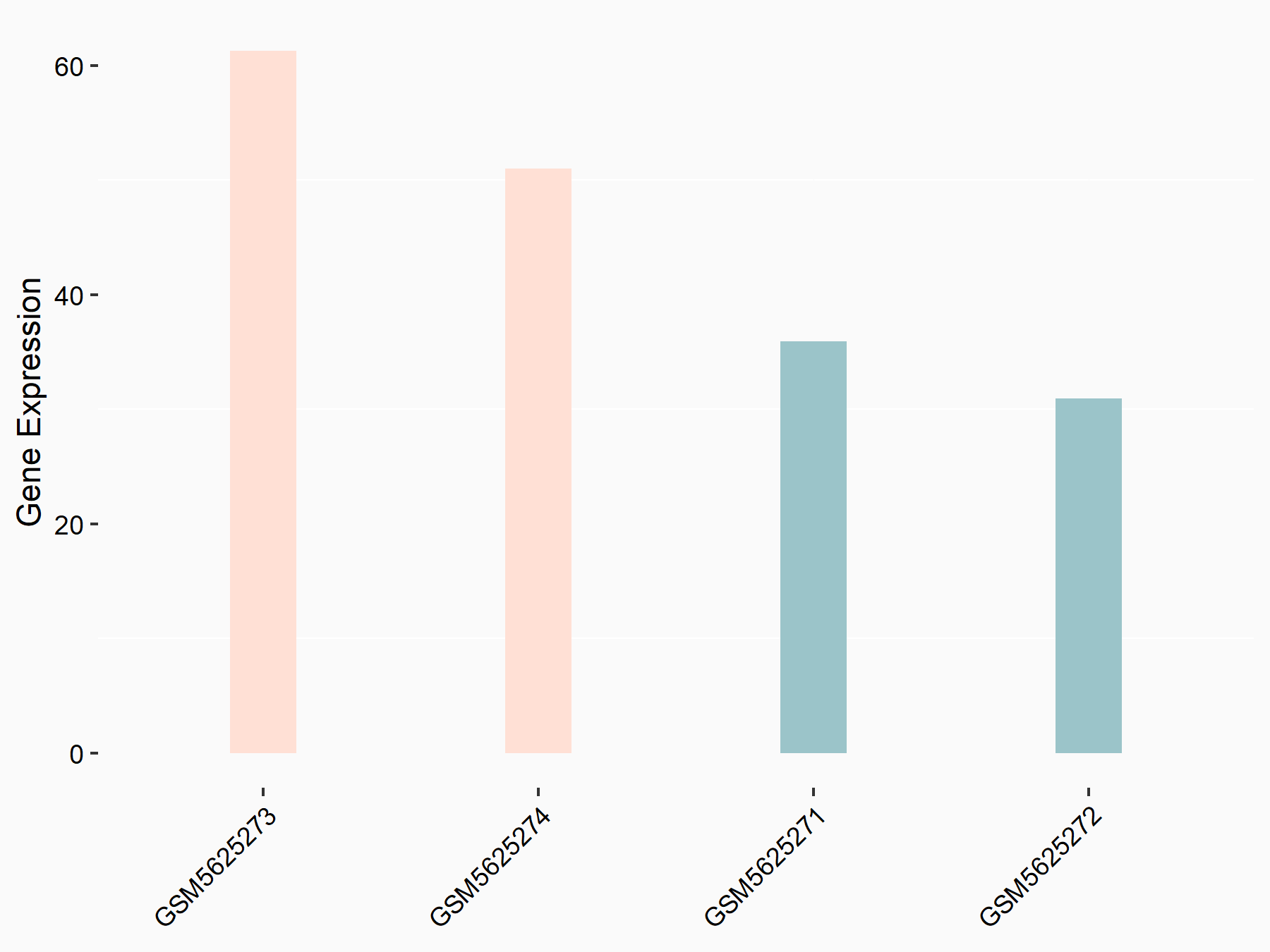 |
logFC: 7.29E-01 p-value: 2.91E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [36] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
In-vitro Model |
CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| () | ||||
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 1 × 106 Cal27 cells stably transduced with lentivirus were injected into the left or right flanks of BALB/c nude mice (aged 4-6 weeks). Following stable transfection, 2 × 105 SCC7 cells were subcutaneously inoculated into C3H mice (aged 6-8 weeks). | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression inhibits RIG-I-mediated IFN-Alpha secretion through the IKK-Epsilon/TBK1/IRF3 pathway. Upregulation of AKLBH5 negatively correlates with RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I) and IFN-Alpha expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients. | |||
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | CAG cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 CAG cells
Control: shNC CAG cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
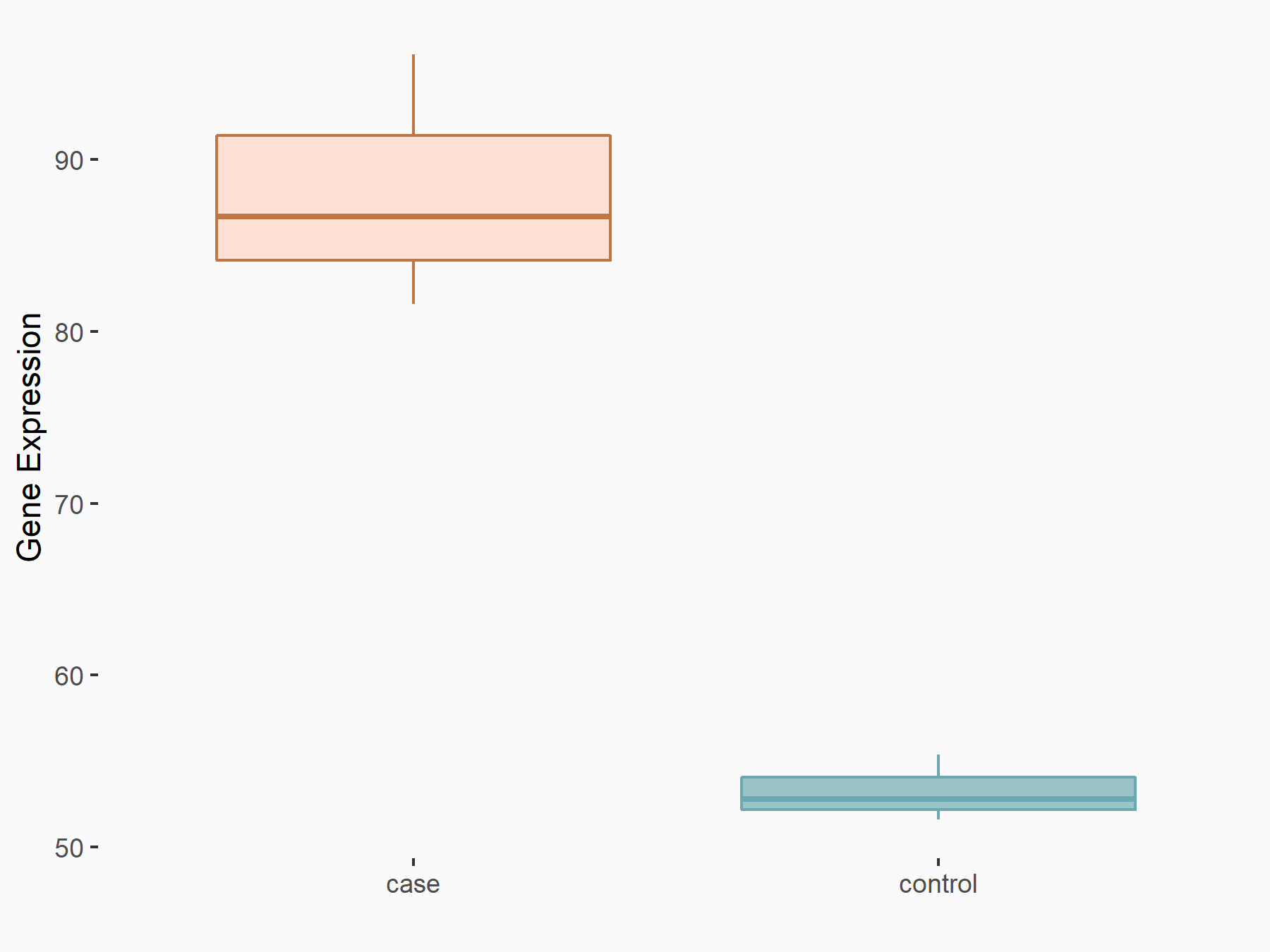 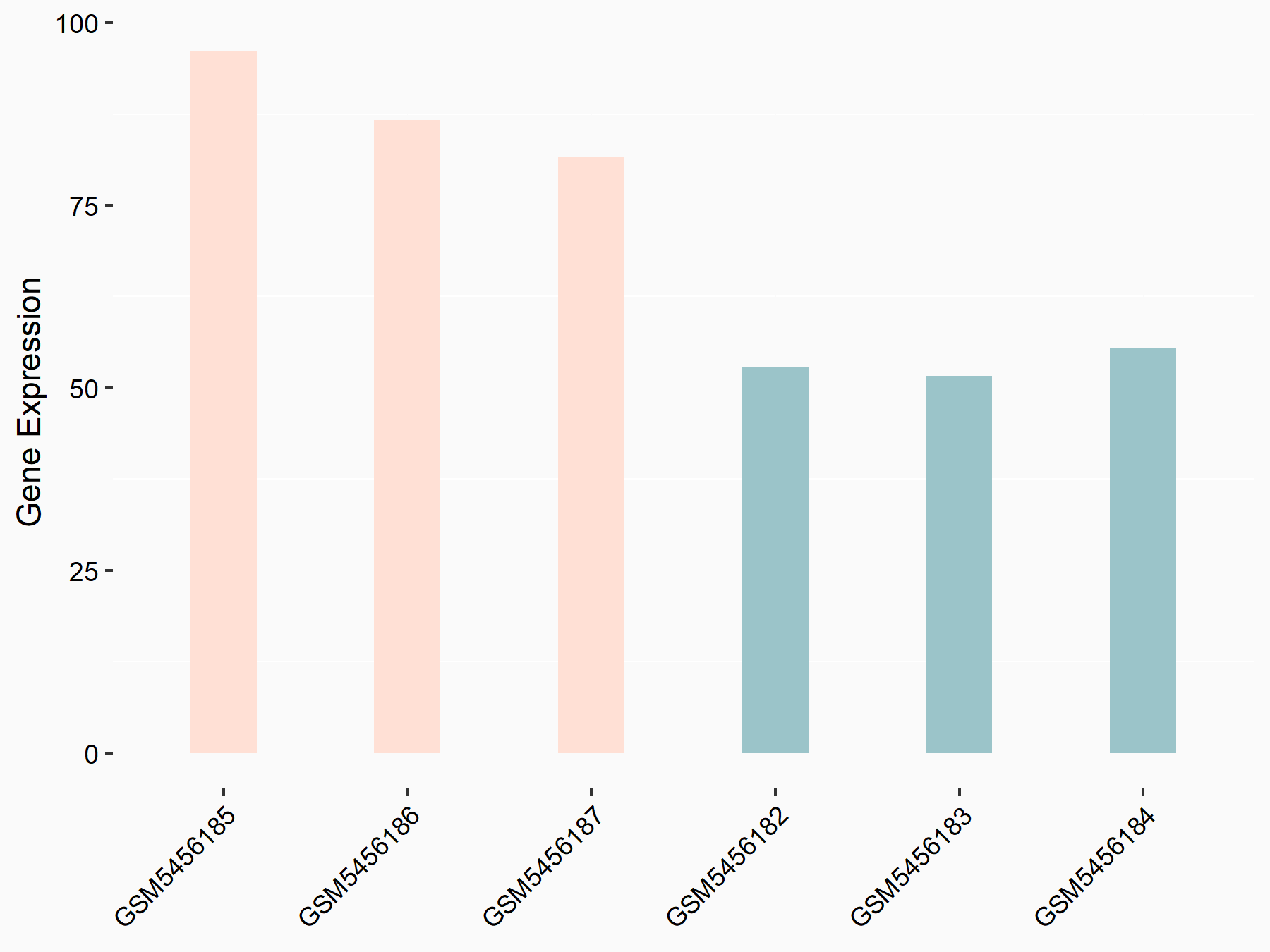 |
logFC: 7.14E-01 p-value: 3.96E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system [ICD-11: FC0Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [37] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the musculoskeletal system [ICD-11: FC0Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mRNA surveillance pathway | hsa03015 | ||
| RNA degradation | hsa03018 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 promotes osteogenesis through modulating Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) mRNA stability. | |||
Scavenger receptor class F member 1 (SCARF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
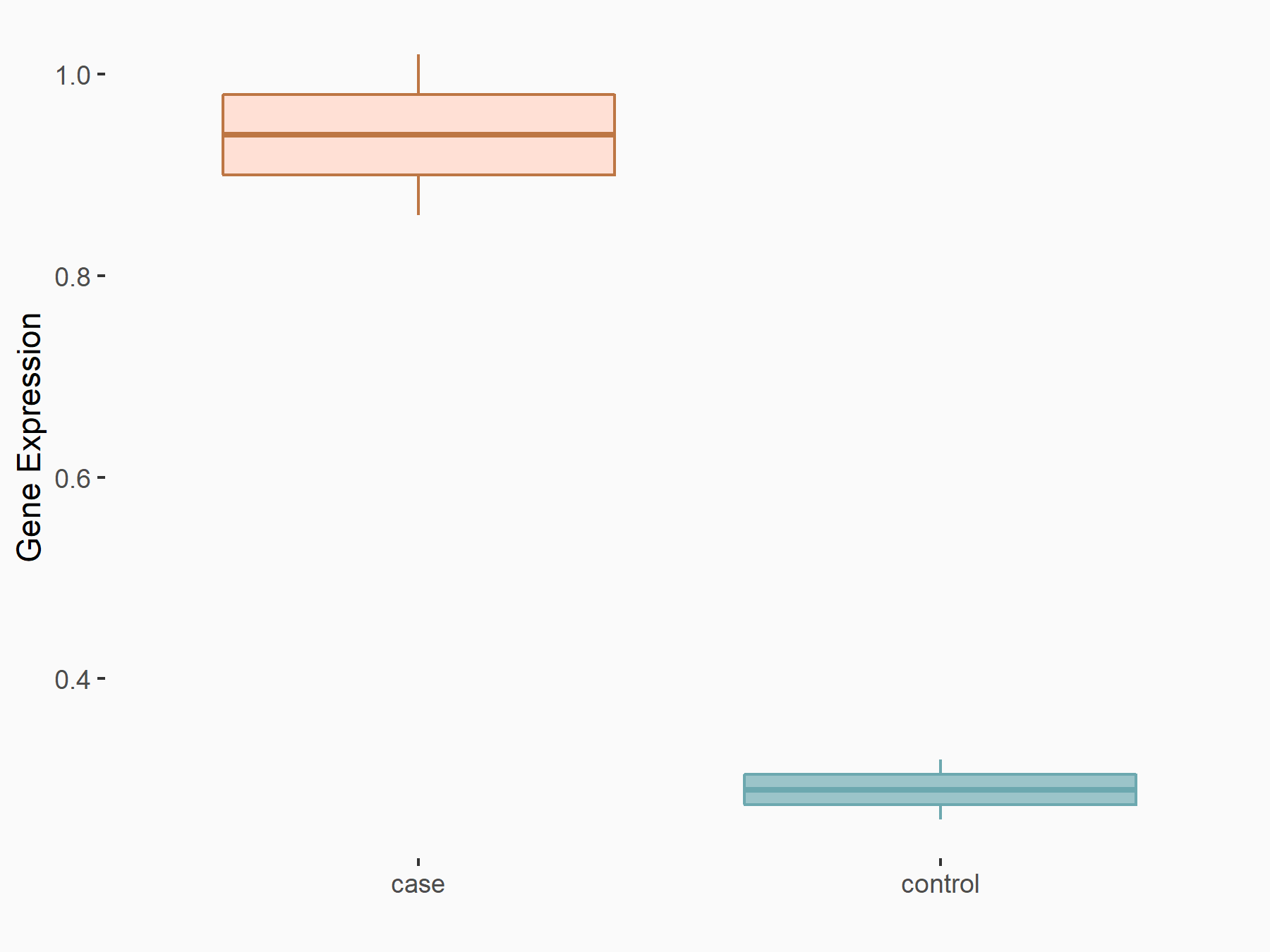 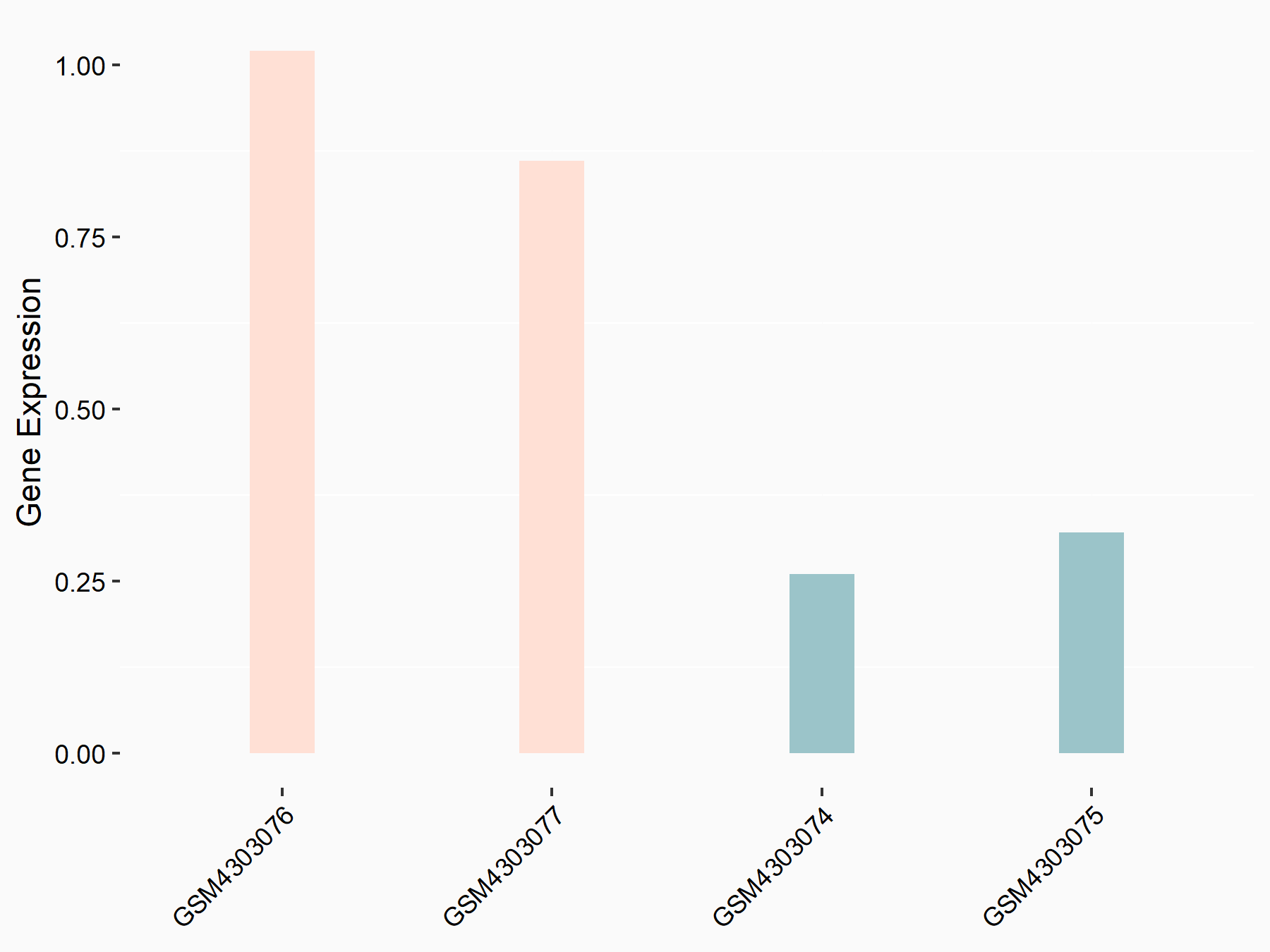 |
logFC: 5.88E-01 p-value: 6.33E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [38] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Cell Process | Lysosomal escape | |||
| In-vivo Model | Wild-type C57 (female, 12-16 weeks old), ALKBH5 /- mice (female and male, 12-16 weeks old), and SPF-grade SD rats (female, 180-230 g) were used to establish the AMI model.Sodium pentobarbital diluted to 10 mg/mL was used to anesthetize the mice or rat at the dose of 50 mg/kg through an intraperitoneal injection. By using a small animal ventilator with endotracheal intubation, thoracotomy was performed at the left fourth intercostal region. The heart was exposed, and the left anterior descending coronary artery (LCA) was occluded through a 6-0 silk suture that was placed 2-3 mm distal to the origin of the LCA with a slipknot. The apical region turned white, and ST segment elevation and T wave inversion of ECG showed that the AMI model was successfully established. Forty-five minutes after ischemia, the slipknot was released, and the ischemic region was reperfused. PBS (0.2 ml), HSSS (23.5 mg/kg, 0.2 ml), IOX1 (10 mg/kg, 0.2 ml), and HSSS-I (33.5 mg/kg, containing 10 mg/kg IOX1, 0.2 ml) were administered through caudal vein injection for 14 days at the frequency of one time per day. | |||
| Response Summary | IOX1, which is an inhibitor of ALKBH5, was loaded on HSSS to form HSSS-I, which could effectively ameliorate cardiac dysfunction in acute myocardial infarction. The surface-modified bioengineered ferritin nanocage targeted the dying cells in the infarct area under the guidance of Scavenger receptor class F member 1 (SCARF1). These cells were then phagocytosed through recognition of their TfR1 receptor. | |||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase LATS2 (LATS2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | CAG cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 CAG cells
Control: shNC CAG cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
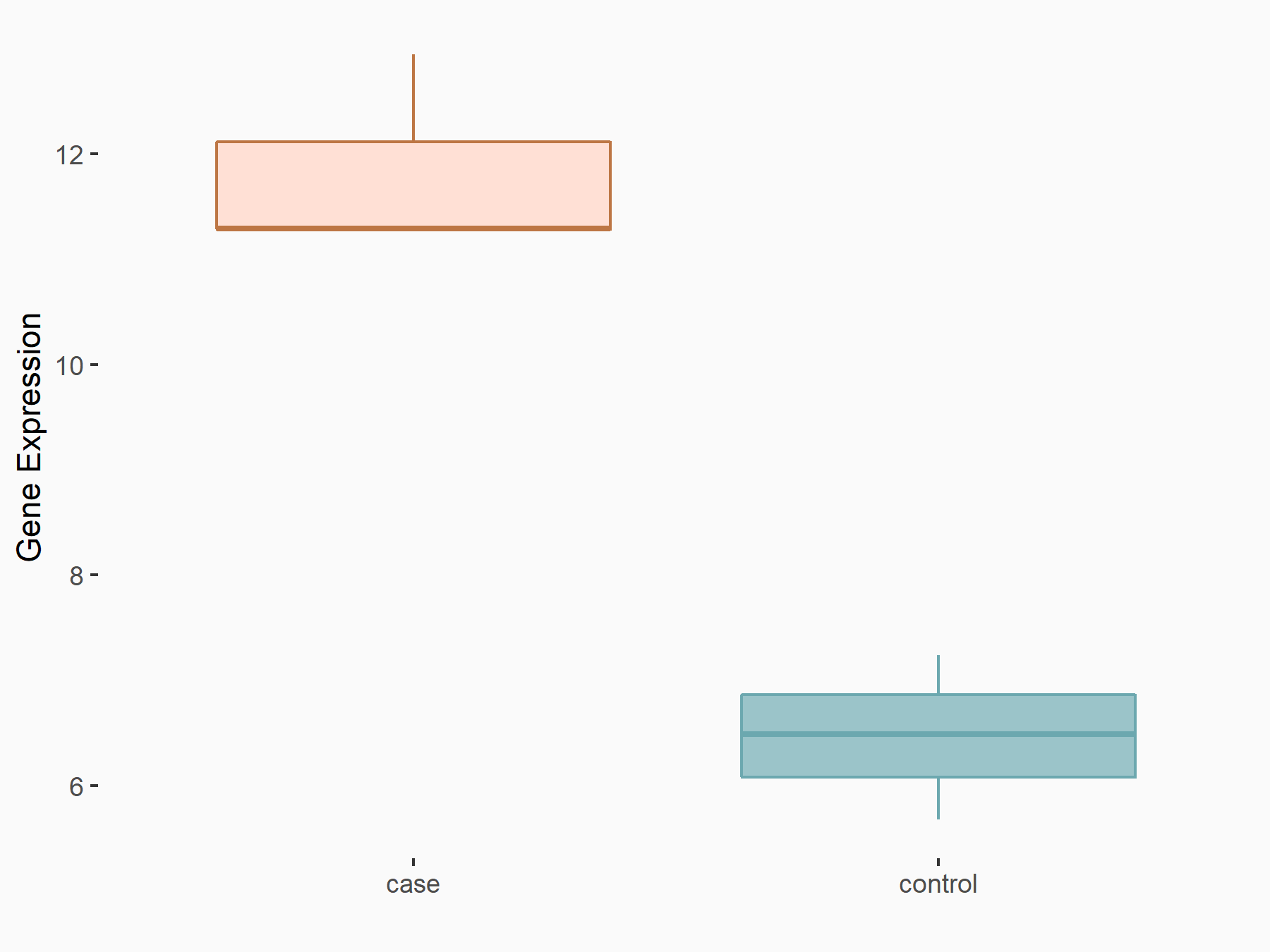 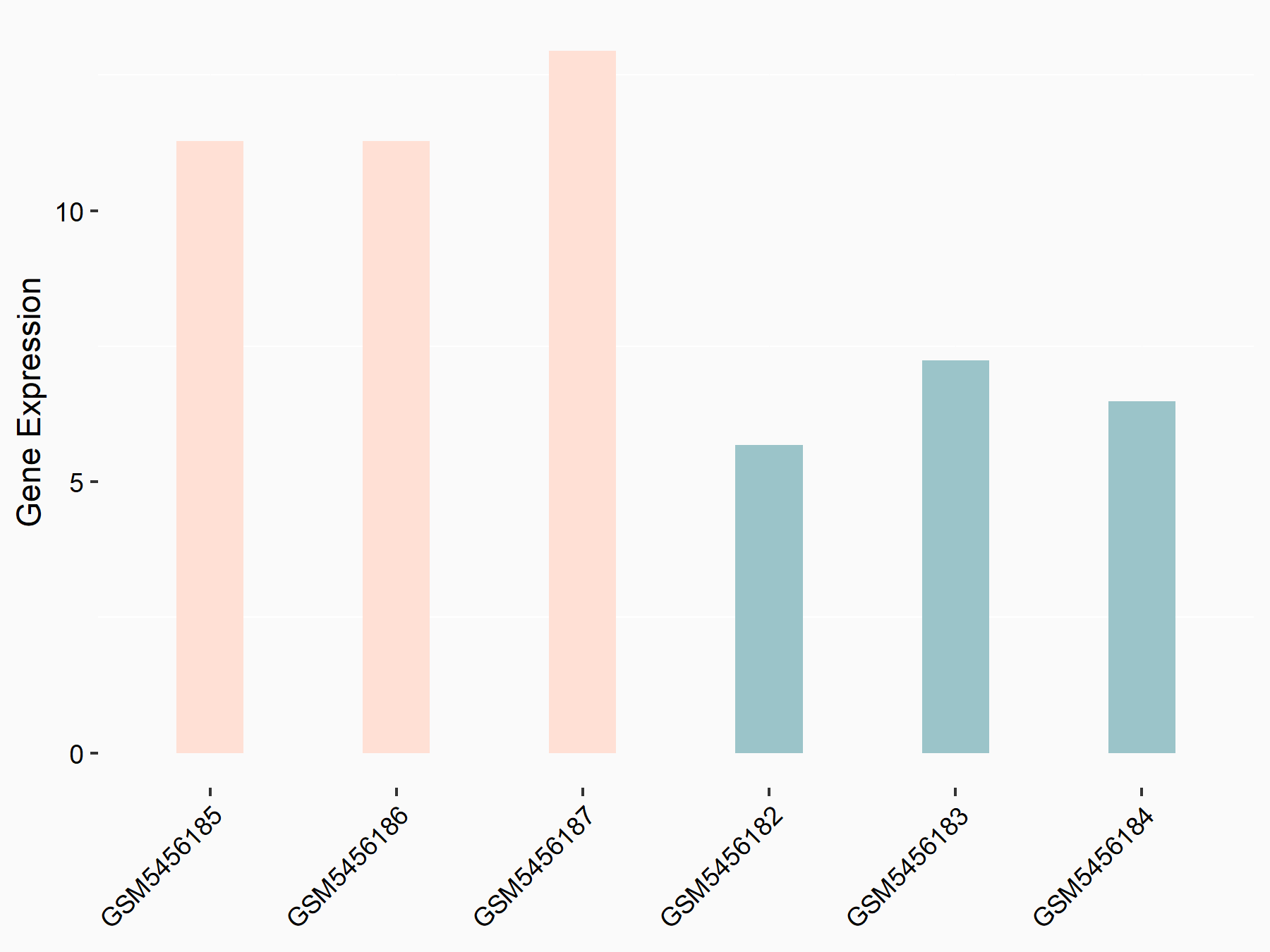 |
logFC: 7.85E-01 p-value: 1.18E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [39] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell EMT | ||||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the experiments, mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into indicated groups (five mice per group). To assess the in vivo effects of cycloleucine, the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter from mice and then these xenografted mice were feed with Vehicle or cycloleucine (25 mg/kg twice weekly) and tumor volume were measured every 3 day. Tumor volume was estimated as 0.5 × a2 × b (where a and b represent a tumors short and long diameter, respectively). Mice were euthanized after 7 weeks and the tumors were measured a final time. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing YTHDFs-mediated YAP expression and inhibiting miR-107/Serine/threonine-protein kinase LATS2 (LATS2)-mediated YAP activity in non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11 (STK11/LKB1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
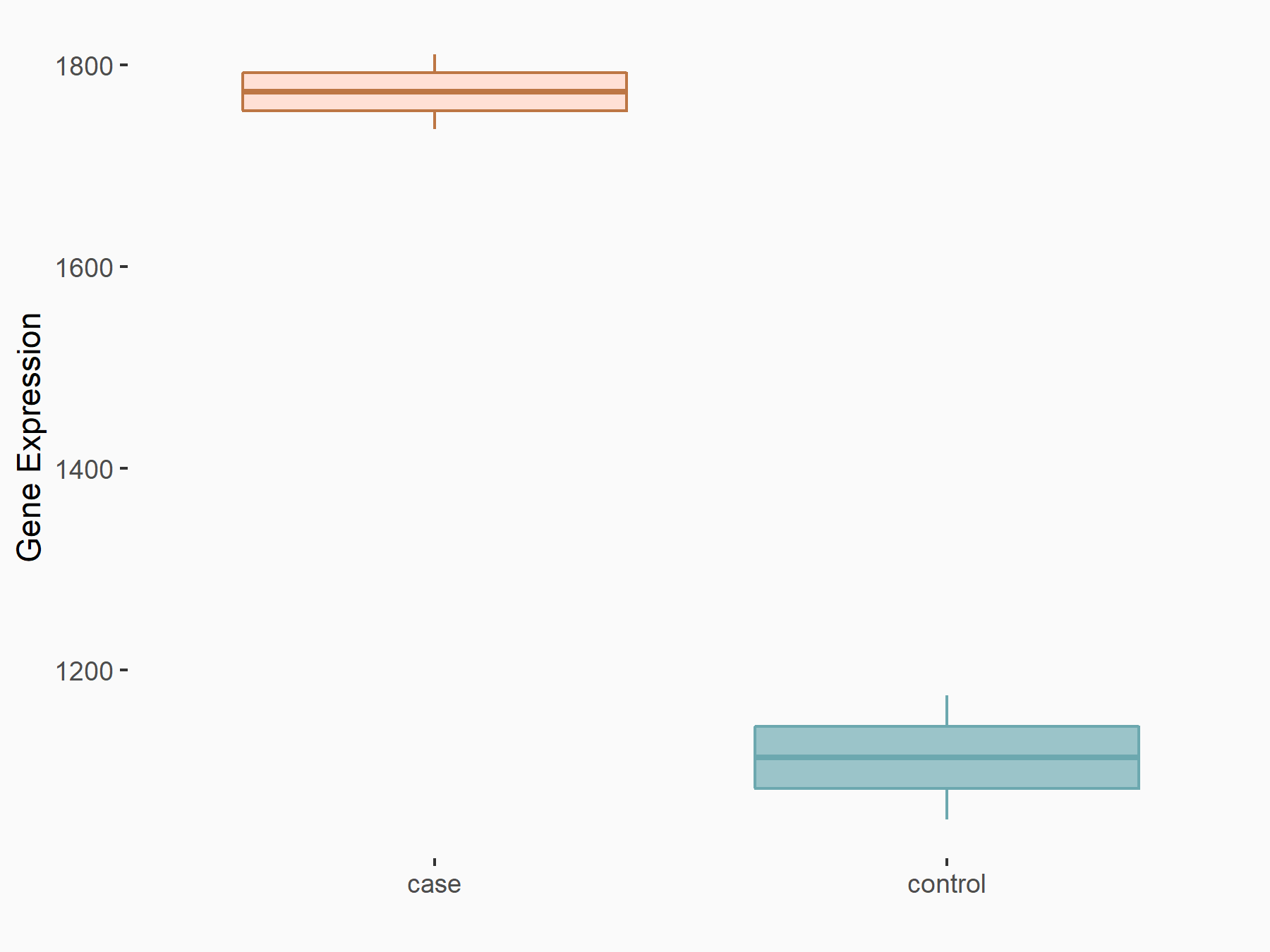  |
logFC: 6.73E-01 p-value: 8.05E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [40] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| MRC-9 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2629 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| H1795 (Lung cancer H1795 cell lines were purchased from ATCC, USA) | ||||
| NCI-H1792 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1495 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1490 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 gain- or loss-of function could effectively reverse Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11 (STK11/LKB1) regulated cell proliferation, colony formation, and migration of KRAS-mutated lung cancer cells. | |||
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
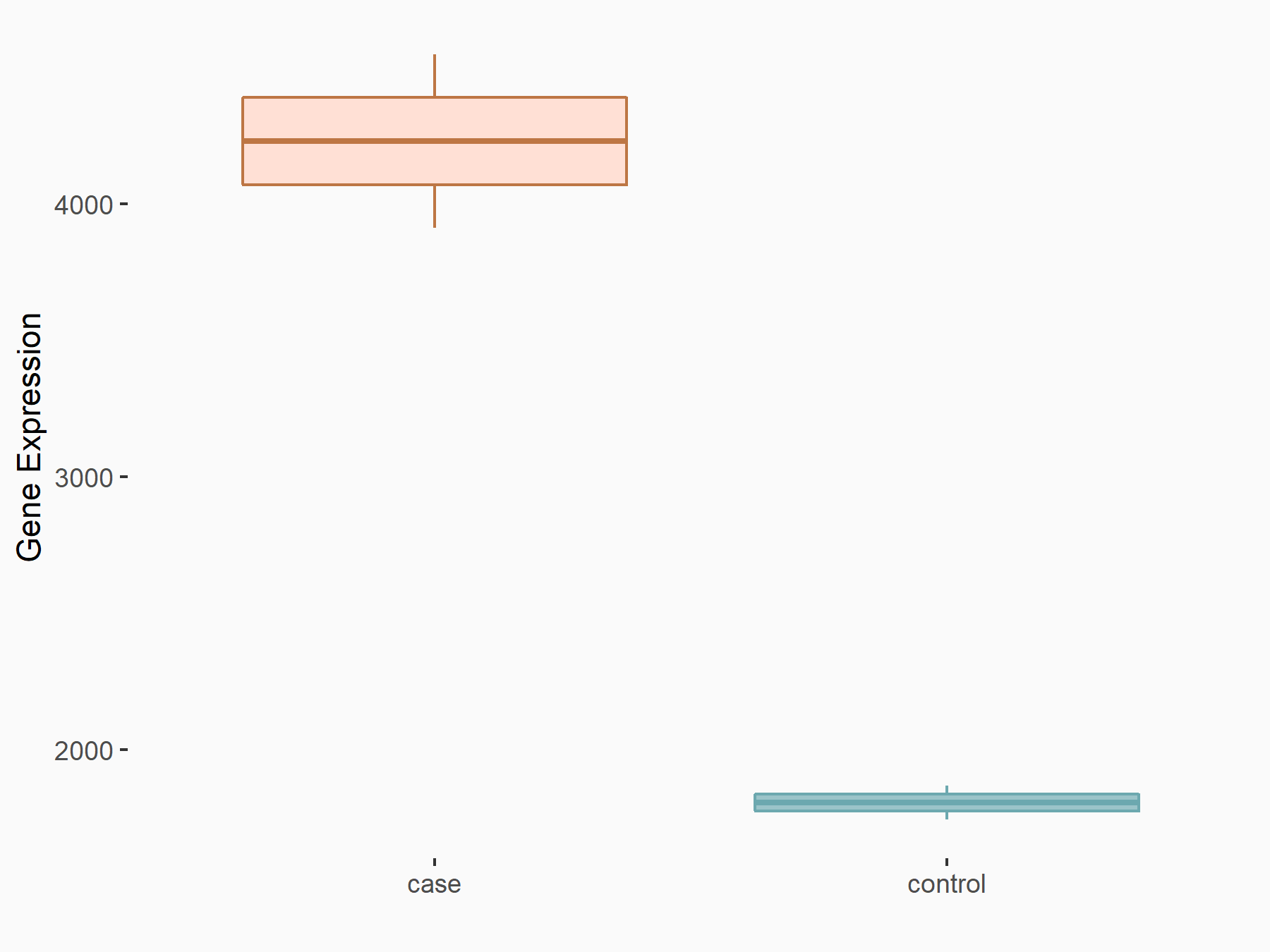  |
logFC: 1.23E+00 p-value: 2.84E-10 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [41] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
In-vitro Model |
U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| OS3 [Human osteosarcoma] | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_F866 | |
| OS2 [Human osteosarcoma] | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_F865 | |
| OS1 [Human osteosarcoma] | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_F864 | |
| KHOS/NP | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2546 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 inactivated Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway by increasing SOCS3 expression via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Reducing m6A mRNA levels in human osteosarcoma cells through ALKBH5 up-regulation lead to cell proliferation inhibition, cell apoptosis and cycle arrest. | |||
Sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
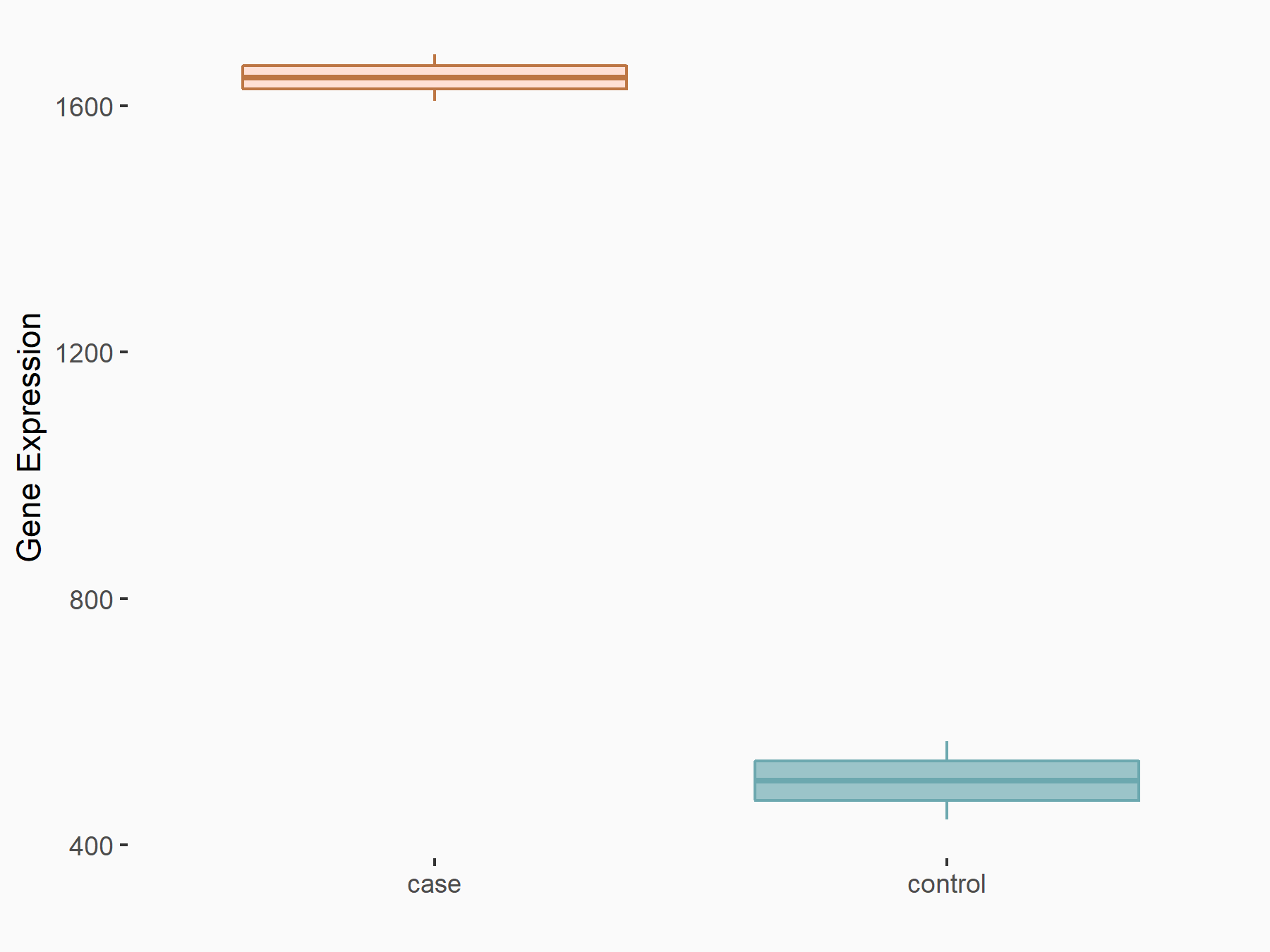  |
logFC: 1.71E+00 p-value: 1.04E-14 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [42] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| HMVE (human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVE) were obtained from ATCC (ATCC-CRL1730)) | ||||
| Response Summary | The study aimed to find the role of m6A RNA demethylase alkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) in ECs angiogenesis during ischemic injury. ALKBH5 helps in the maintenance of angiogenesis in endothelial cells following acute ischemic stress via reduced SPHK1 m6A methylation and downstream eNOS-AKT signaling. | |||
Stimulator of interferon genes protein (STING1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | CAG cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 CAG cells
Control: shNC CAG cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
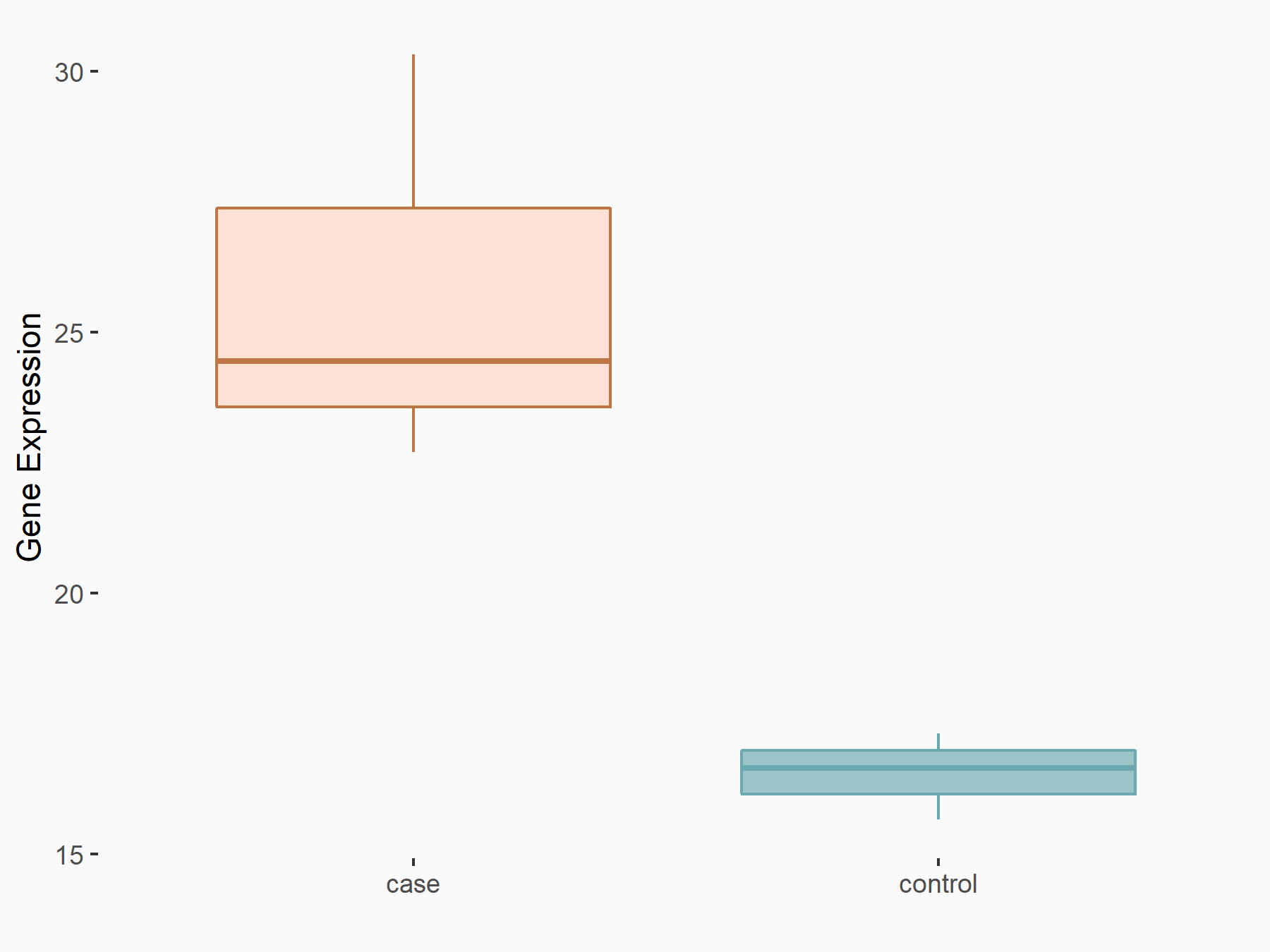  |
logFC: 6.04E-01 p-value: 6.54E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Immune Response | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5-dependent HMGB1 expression mediates Stimulator of interferon genes protein (STING1)-interferon regulatory factor 3 innate immune response in radiation-induced liver diseases. | |||
SUMO specific peptidase 1 (SENP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
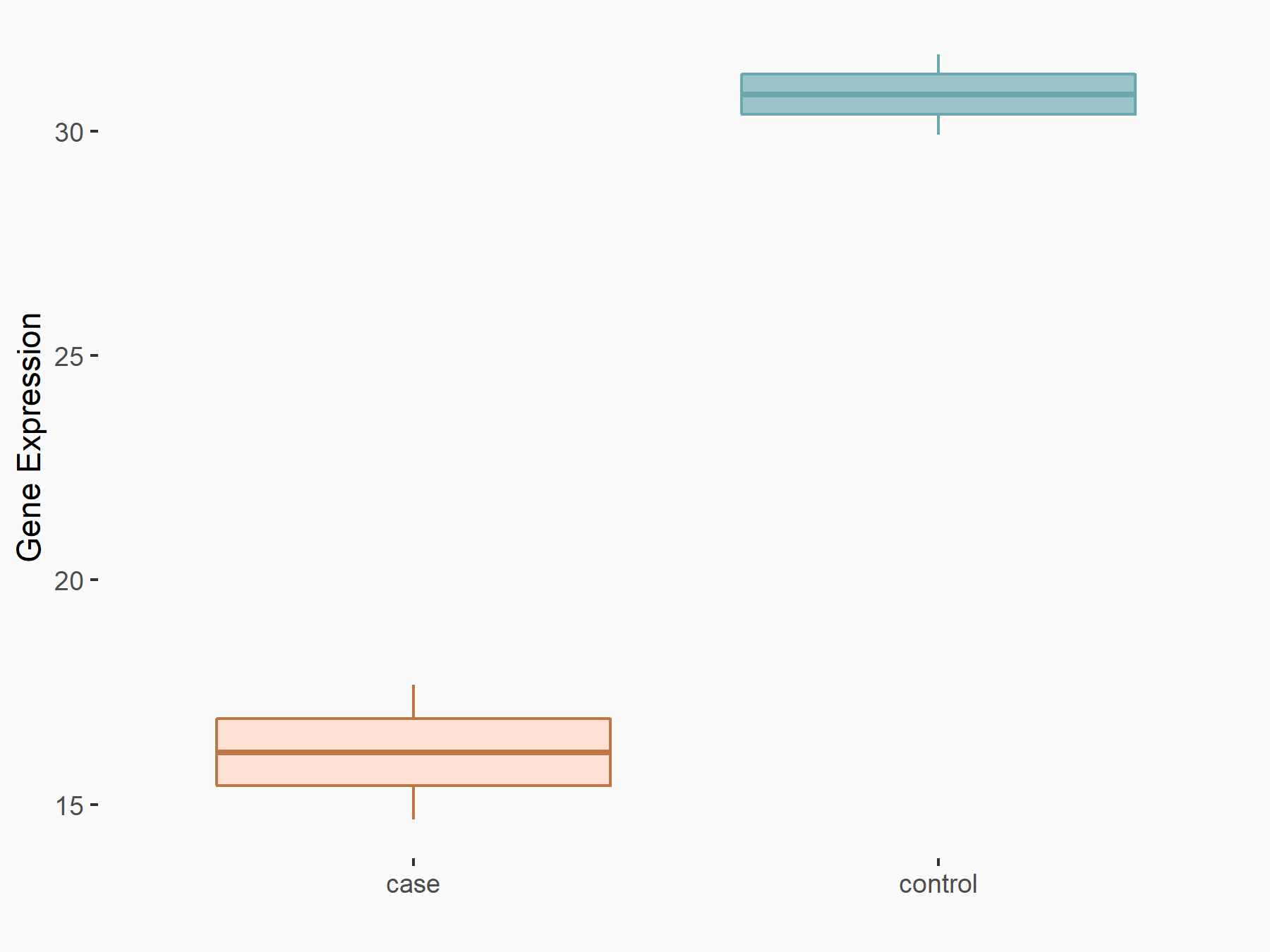  |
logFC: -8.95E-01 p-value: 1.12E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [43] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | |||
| Cell Process | Oxygen species(ROS)-induced stress | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | For the ROS-induced DNA damage analysis, the indicated cell lines were treated with or without 100 uM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), or 80 uM Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) for 6 hours. For the in vivo ROS study, DMSO and 5 mg/kg CCCP was intraperitoneally injected in to three pairs of mice. | |||
| Response Summary | ROS promotes ALKBH5 SUMOylation through activating ERK/EPHB2/JNK signaling, leading to inhibition of ALKBH5 m6A demethylase activity by blocking substrate accessibility. Post-translational modification of ALKBH5 regulates ROS-induced DNA damage response. ROS specifically promotes ALKBH5 but not FTO, METTL3 and METTL14 SUMOylation by enhancing the interaction of ALKBH5 and UBC9 and inhibiting the association between ALKBH5 and SUMO specific peptidase 1 (SENP1). | |||
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | RPMI-8226 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 RPMI8226 cells
Control: shNC RPMI8226 cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
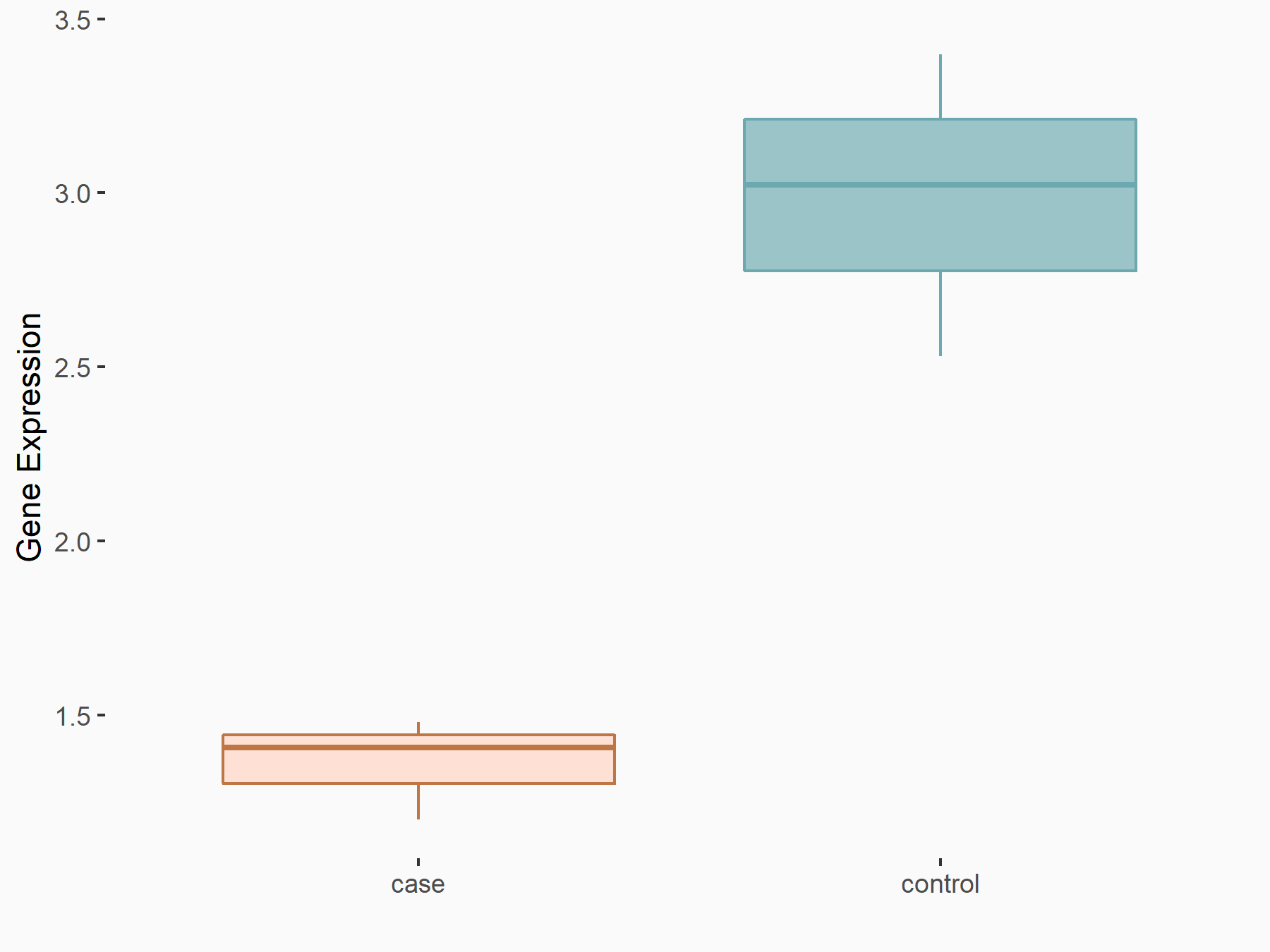  |
logFC: -7.50E-01 p-value: 1.38E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [41] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
In-vitro Model |
U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| OS3 [Human osteosarcoma] | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_F866 | |
| OS2 [Human osteosarcoma] | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_F865 | |
| OS1 [Human osteosarcoma] | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_F864 | |
| KHOS/NP | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2546 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 inactivated STAT3 pathway by increasing Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) expression via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Reducing m6A mRNA levels in human osteosarcoma cells through ALKBH5 up-regulation lead to cell proliferation inhibition, cell apoptosis and cycle arrest. | |||
Target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8 (MLST8)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
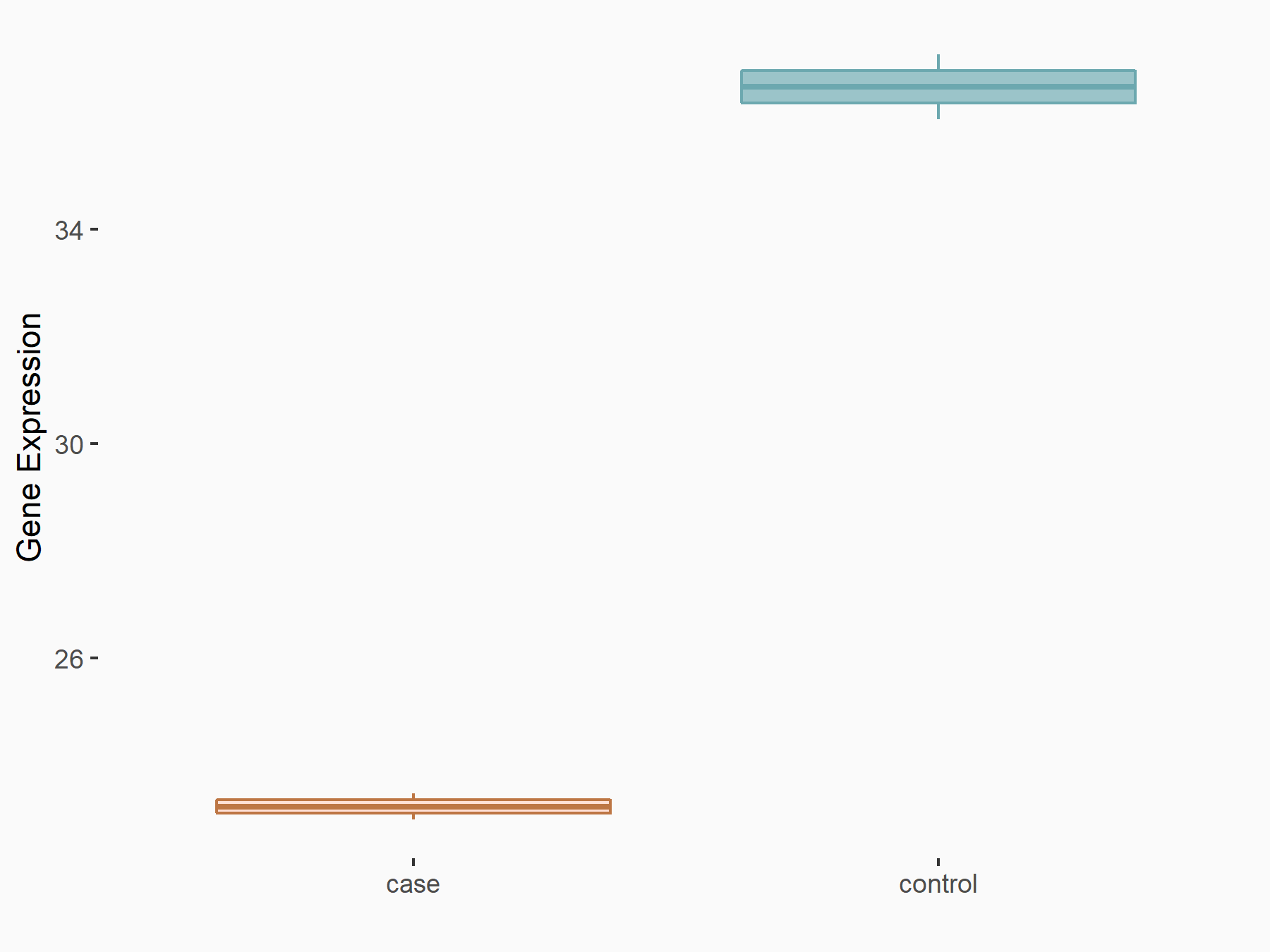  |
logFC: -6.36E-01 p-value: 6.23E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | HL-60 cells (1 × 107) suspended in 0.1 ml PBS containing 50% Matrigel were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of the mice. When tumor sizes reached 200 mm3, the mice were randomly distributed into four groups with the indicated dosages of saline, cytarabine and BP alone or in combination. For BP injections, the solution was delivered intraperitoneally at 106 ug/kg body weight for the first 8 consecutive days. For cytarabine injections, the solution was delivered intraperitoneally at 100 mg/kg body weight three times (once every three days). The combination group was administered intraperitoneally three times (once every three days) with the same dosages as described above. The control group was treated with an equivalent amount of saline. | |||
| Response Summary | Bioactive peptides can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation by downregulating ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation of EIF4EBP1 and Target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8 (MLST8) mRNAs, which have potential to prevent and treat this disease. | |||
TGF-beta receptor type-2 (TGF-Beta-R2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
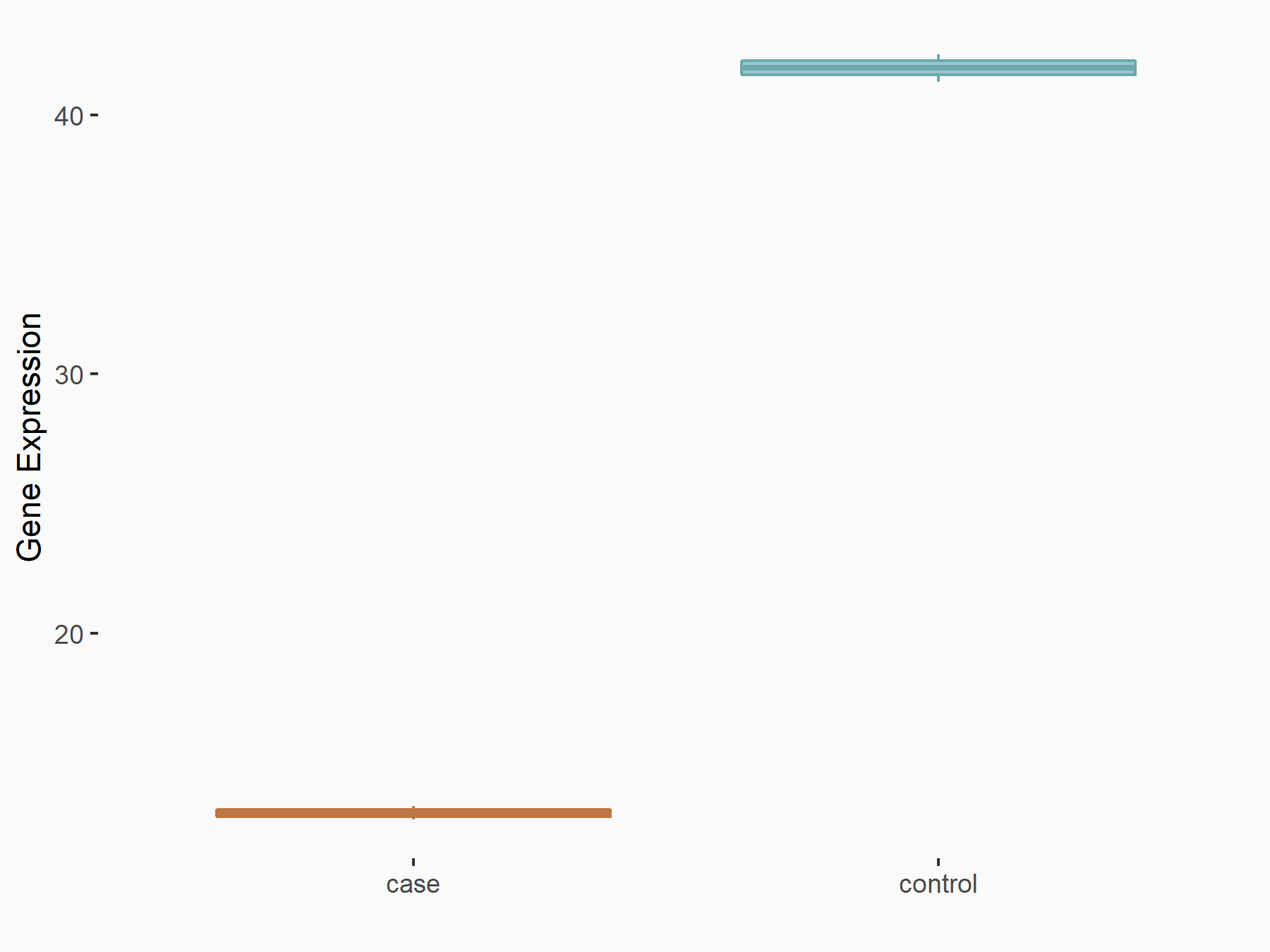  |
logFC: -1.61E+00 p-value: 9.99E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were divided into control group and ALKBH5-overexpressing group (9 mice per group). ALKBH5-overexpressing and control A549 cells (3 × 106 cells/mouse) in 200 uL PBS were intravenously (i.v.) injected into the lateral tail vein of mice. At every 5th day post-inoculation, TGF-Beta-1 (4 ug/kg body weight) was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected to promote tumor cell metastasis. Eight weeks later, the mice were euthanized, and then their lungs and livers were taken out and fixed in Bouin's solution (Sigma Aldrich, HT101128) or 4% Paraformaldehyde (Beyotime, p0099, Shanghai, China) for macroscopically metastatic nodule analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 weakens YTHDF1/3-mediated TGF-beta receptor type-2 (TGF-Beta-R2) and SMAD3 mRNA stabilization, and abolishes YTHDF2-mediated SMAD6 mRNA degradation, supporting the notion that ALKBH5 inhibits TGF-Beta-induced EMT and invasion of NSCLC cells via YTHD1/2/3-mediated mechanism. | |||
TNF alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
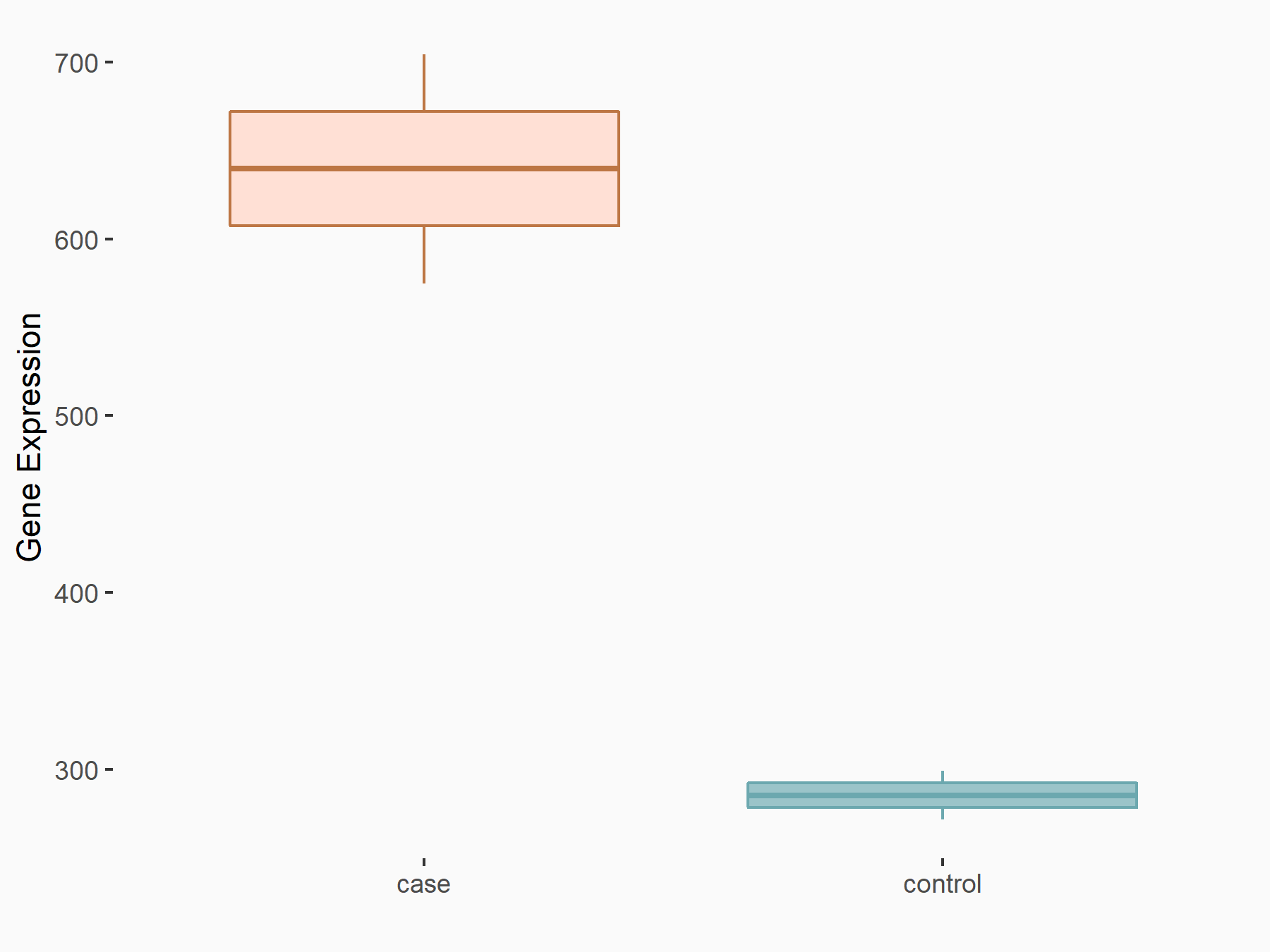  |
logFC: 1.17E+00 p-value: 2.43E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Retinopathy [ICD-11: 9B71]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [44] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic retinopathy [ICD-11: 9B71.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BV-2 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0182 |
| In-vivo Model | The male Sprague-Dawley rats (8 weeks old, 200-220 g) were purchased from the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University. Streptozotocin (Sigma, USA) was given by intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 60 mg/Kg to induce diabetics rats, while the control rats were given by empty citrate buffer. One week after induction, those rats with blood glucose levels > 16.7 mmol/L for three times were considered as successful inducted diabetes. All the rats did not receive insulin during the experiments.In the intraocular injection experiments, rats confirmed as the DM model (blood glucose levels > 16.7 mmol/L for three times) were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/Kg). A total of 10 ul DMEM with 1*109 TU lentiviruses (A20-overexpression, OE-A20 group) or the same volume of DMEM with control lentiviruses (OE-NC group) was injected into the vitreous cavity using a 33-gauge needle. This treatment was performed one time per month, and the rats were sacrificed for further experiments at the 3 months. | |||
| Response Summary | Lower expression TNF alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) resulted in the enhanced M1 polarization of retinal microglia in diabetic retinopathy, which was caused by ALKBH5 mediated m6A modification. | |||
TNF receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | RPMI-8226 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 RPMI8226 cells
Control: shNC RPMI8226 cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
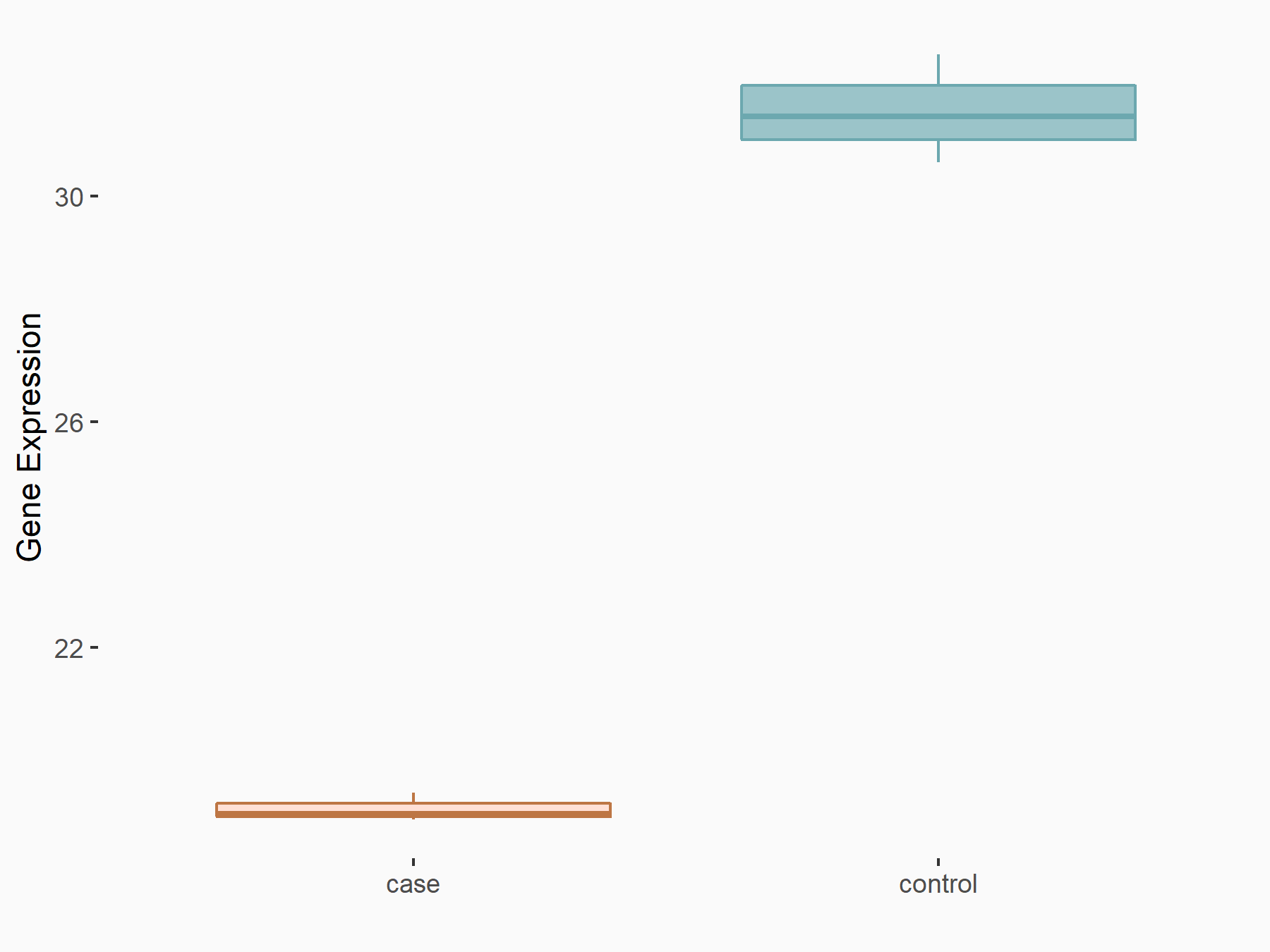  |
logFC: -6.91E-01 p-value: 6.11E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [45] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| RNA stability | ||||
In-vitro Model |
CAG | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_D569 |
| RPMI-8226 | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0014 | |
| U266 (Human multiple myeloma cells) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | 5 × 105 selected cells were injected via the tail vein into 4- to 5-week-old NCG mice. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 promoted multiple myeloma cell growth and survival through TNF receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1)-mediated activation of NF-Kappa-B and MAPK signaling pathways. | |||
TNF receptor-associated factor 4 (TRAF4)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
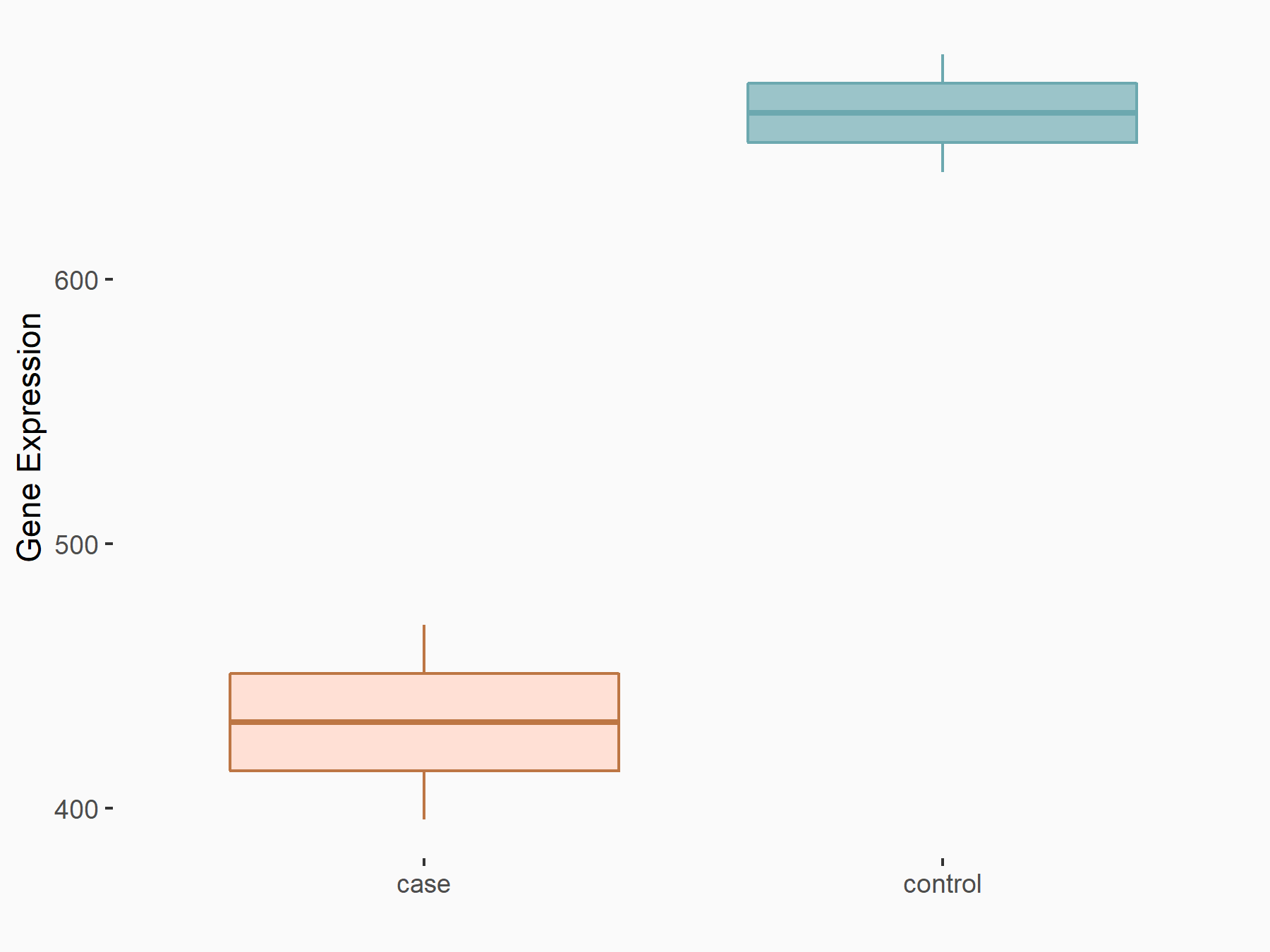  |
logFC: -6.18E-01 p-value: 8.54E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [46] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120), Proteasome | ||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SVF (Stromal vascular cell fraction (SVF) was isolated from minced inguinal adipose tissue of male C57BL/6J mice (3-4 weeks old)) | |||
| 3T3-L1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0123 | |
| In-vivo Model | Before the tests, animals were fasted for 8 h. l glucose tolerance test (GTT) was conducted during week 11 on the diet. The mice were challenged with 2 g/kg body weight d-glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). Insulin tolerance test (ITT) was conducted during week 12 on the diet. For insulin tolerance test, mice were injected intraperitoneally with 0.75 U/kg body weight insulin (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). For both tests, blood samples were taken from the tail vein and glucose levels were measured at indicated time points after administration using an AlphaTRAK glucometer. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-dependent TNF receptor-associated factor 4 (TRAF4) expression upregulation by ALKBH5 and YTHDF1 contributes to curcumin-induced obesity prevention. | |||
Transcription factor E4F1 (E4F1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
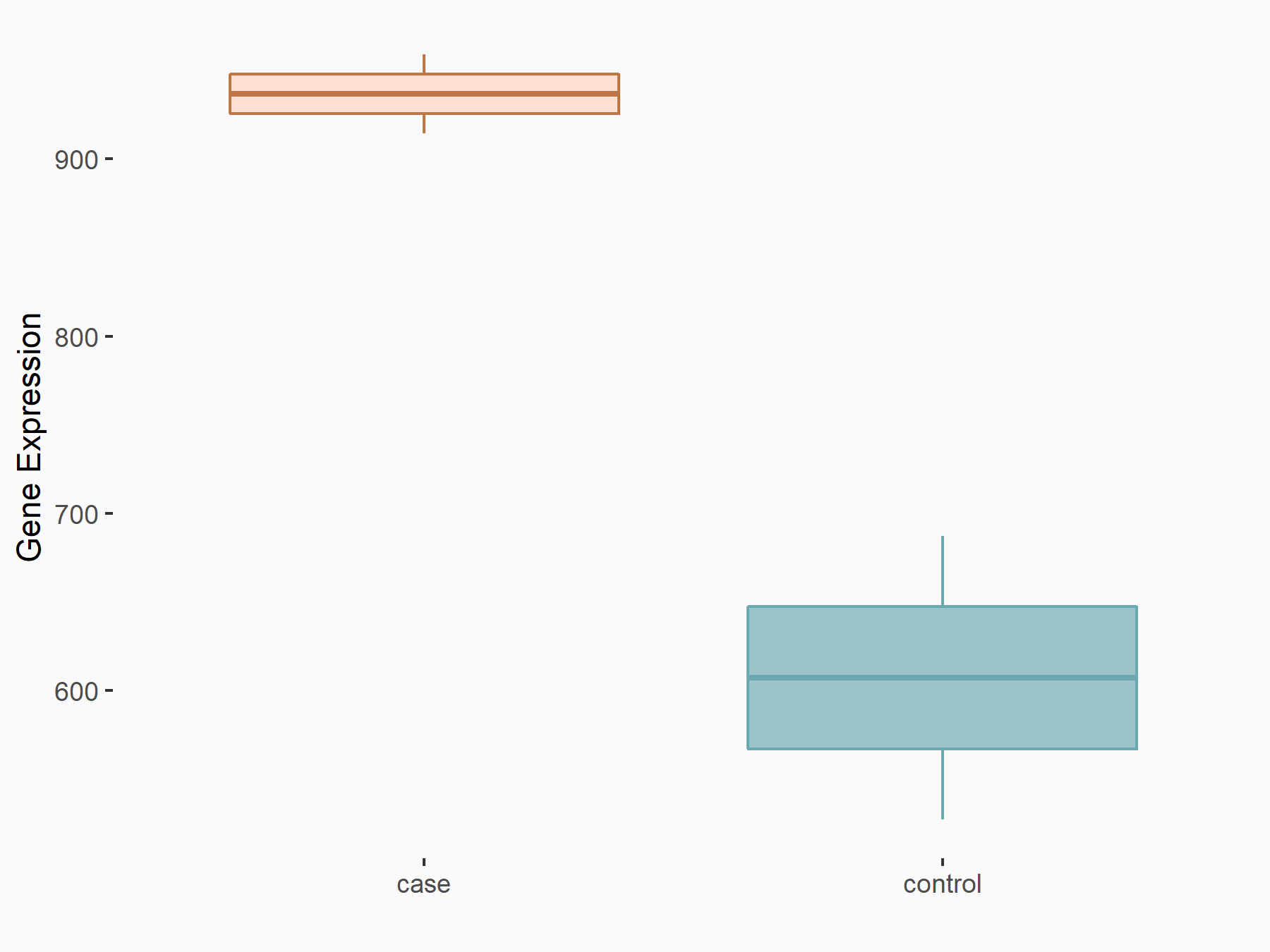  |
logFC: 6.27E-01 p-value: 6.56E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Nucleus pulposus cell (The NP tissues were cut into pieces after collection during surgery) | |||
| Response Summary | Theses findings reveal an epigenetic interplay mechanism in NPC senescence and IVD degeneration, presenting a critical pro-senescence role of ALKBH5 and m6A hypomethylation, highlighting the therapeutic potential of targeting the m6A/DNMT3B/Transcription factor E4F1 (E4F1) axis for treating IVD degeneration. | |||
Transcription factor EB (TFEB)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | THP1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: ALKBH5 knockdown THP1 cells
Control: Wild type THP1 cells
|
GSE128574 | |
| Regulation |
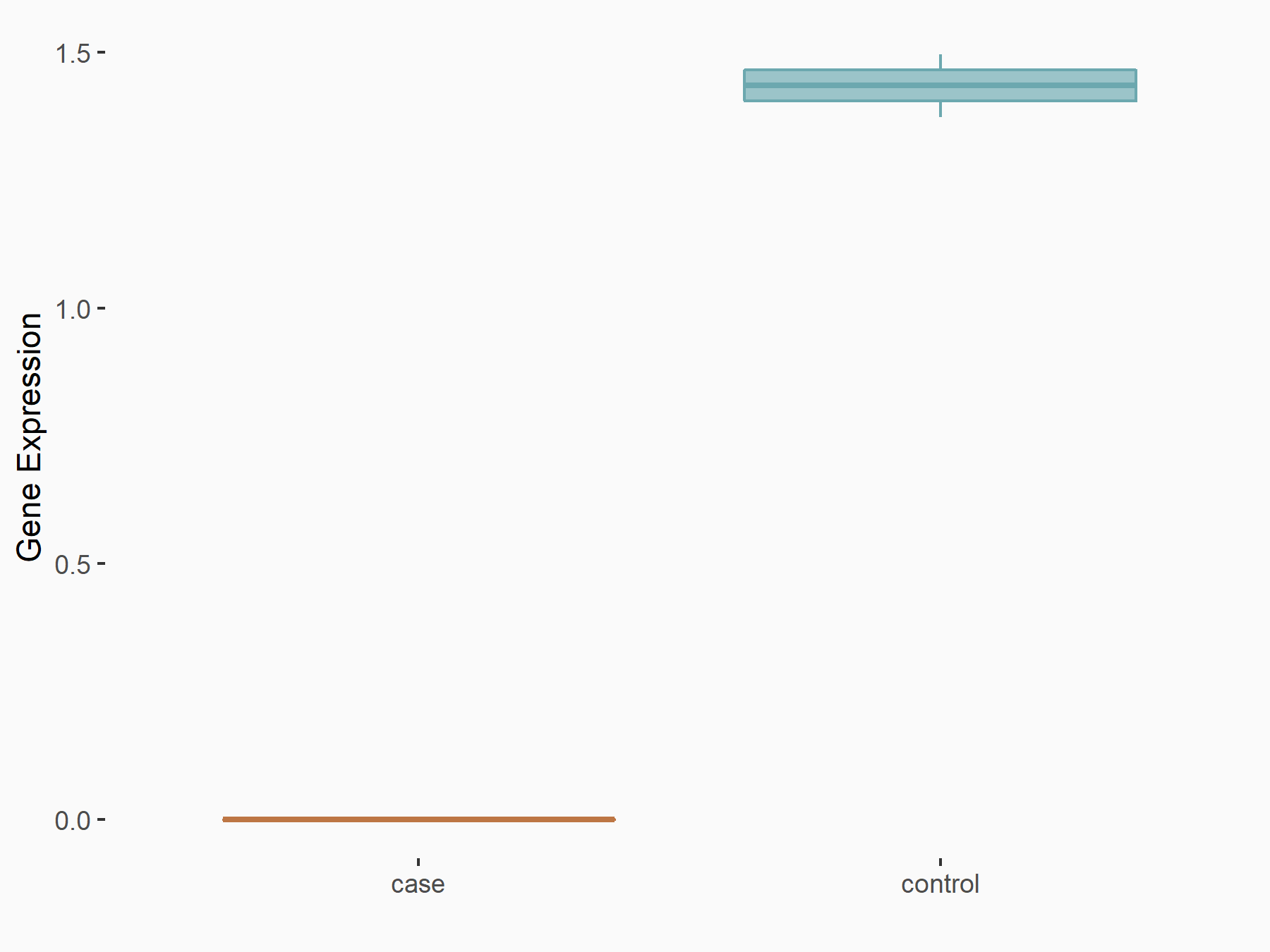  |
logFC: -1.28E+00 p-value: 2.60E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [47] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210) | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
H9c2(2-1) | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0286 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | To cause I/R injury, mice were subjected to 30 min of LAD ischemia followed by 60 min of reperfusion. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 methylates Transcription factor EB (TFEB), a master regulator of lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy genes, at two m6A residues in the 3'-UTR, which promotes the association of the RNA-binding protein HNRNPD with TFEB pre-mRNA and subsequently decreases the expression levels of TFEB. METTL3-ALKBH5 and autophagy, providing insight into the functional importance of the reversible mRNA m6A methylation and its modulators in ischemic heart disease. | |||
Transcription factor SOX-2 (SOX2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | human pluripotent stem cells | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: hILO ALKBH5knockout cells
Control: hILO wild type cells
|
GSE163945 | |
| Regulation |
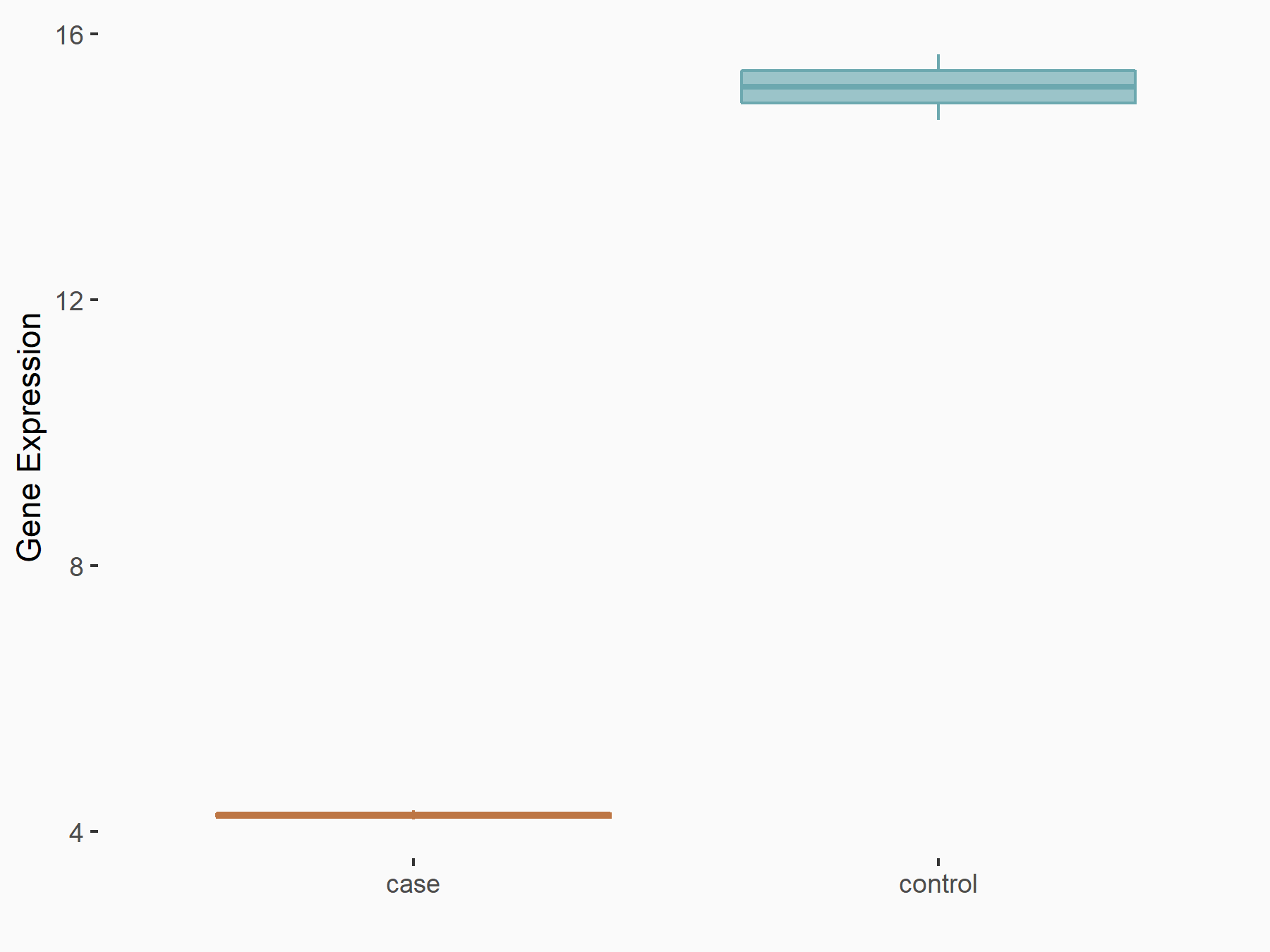  |
logFC: -1.63E+00 p-value: 3.34E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [48] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | |||
In-vitro Model |
EC cell line (Primary EC cells) | |||
| HEC-1-A | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0293 | |
| Ishikawa | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 | |
| RL95-2 | Endometrial adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0505 | |
| In-vivo Model | A method of randomisation was used to determine the experimental groups. In total, 78 female BALB/c nu/nu mice (4-6-week-old) were selected at random and were divided into different groups. A total of 5 × 106 ISK cells or 1 × 104 ECSCisk were suspended in 100 uL of PBS and then were injected into the mice. After 2 weeks, the presence of tumours was examined. ISK cells (5 × 106, 5 × 105, 5 × 104, 1 × 104, or 1 × 103) and ECSCisk (1 × 104, 1 × 103, 1 × 102, 10, or 1) were injected and analysed for their abilities to form xenograft tumours. After 4 weeks, subsequent experiments were performed. | |||
| Response Summary | HIF-dependent ALKBH5 expression increases in hypoxic TMEs, resulting in the demethylation of Transcription factor SOX-2 (SOX2) mRNA and the maintenance of the Endometrial cancer stem cells phenotype; these data indicate that ECSCs maintain their stemness by activating the HIF/ALKBH5/SOX2 axis under hypoxic conditions. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [40] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MRC-9 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2629 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1490 | |
| H1795 (Lung cancer H1795 cell lines were purchased from ATCC, USA) | ||||
| NCI-H1792 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1495 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
Diabetic foot ulcers [ICD-11: BD54]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [96] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic foot ulcers [ICD-11: BD54] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
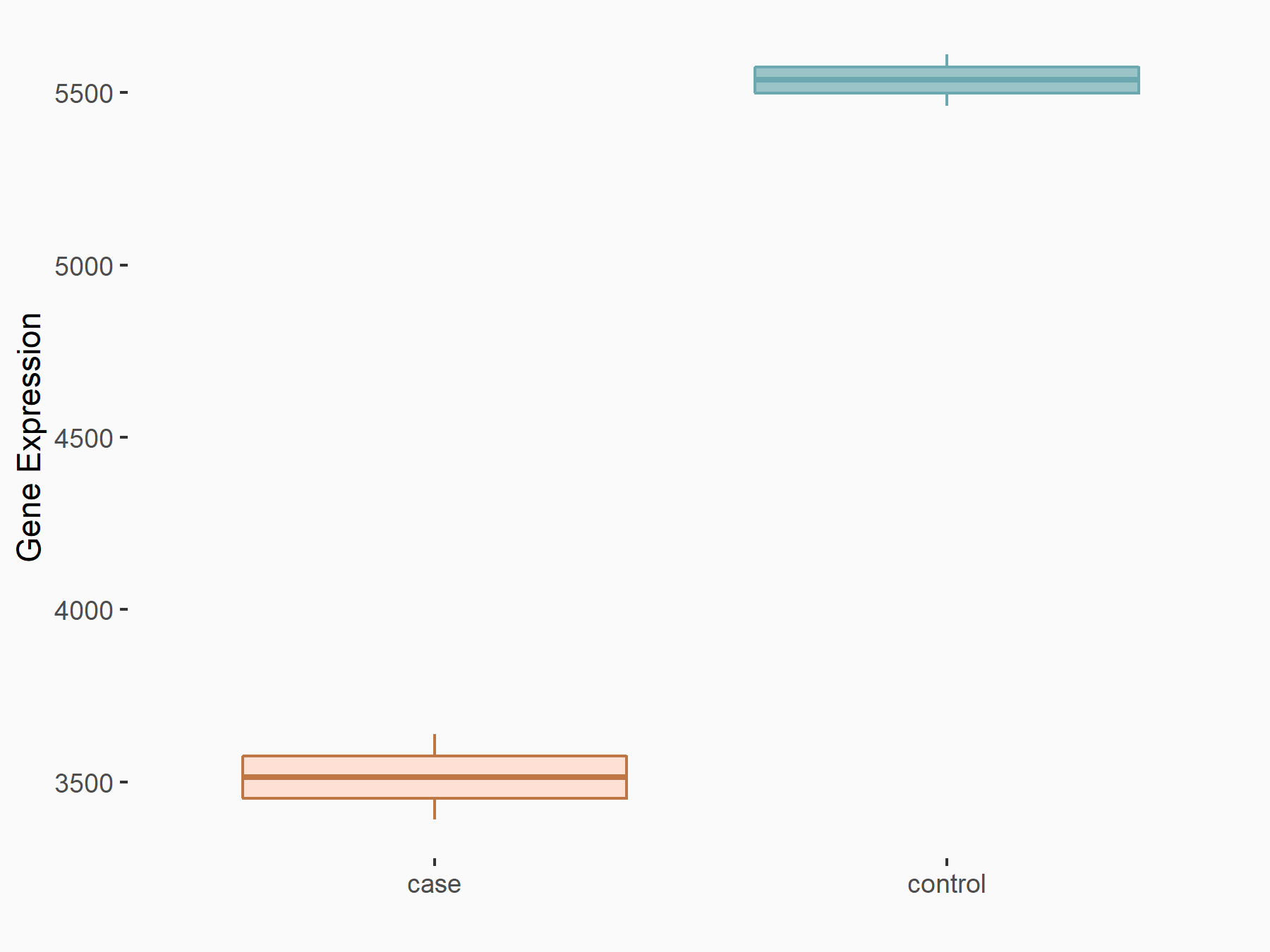  |
logFC: -6.56E-01 p-value: 3.77E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [49] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of pre-miR-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [39] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell EMT | ||||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the experiments, mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into indicated groups (five mice per group). To assess the in vivo effects of cycloleucine, the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter from mice and then these xenografted mice were feed with Vehicle or cycloleucine (25 mg/kg twice weekly) and tumor volume were measured every 3 day. Tumor volume was estimated as 0.5 × a2 × b (where a and b represent a tumors short and long diameter, respectively). Mice were euthanized after 7 weeks and the tumors were measured a final time. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing YTHDFs-mediated Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) expression and inhibiting miR-107/LATS2-mediated YAP activity in non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [50] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Cas9 and sgRNA were microinjected into the fertilized eggs of C57BL/6J mice, which were then transplanted to obtain positive F0 mice. The statuses of F0 mice were confirmed by PCR and sequencing. Next, positive F0 mice were mated with C57BL/6J mice to yield stable F1 generation mice. F1 and F2 transgenic mice were used in this study. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation improved the mRNA stability of YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA-binding protein 1 (YTHDF1), thereby increasing its expression, which consequently promoted the translation of Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1).This finding suggests a novel potential therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction cardiac regeneration. | |||
Menopausal disorder [ICD-11: GA30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [97] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Premature ovarian failure [ICD-11: GA30.6] | |||
| Responsed Drug | 4-Vinylcyclohexene diepoxide | Investigative | ||
In-vitro Model |
COV434 | Ovarian small cell carcinoma, hypercalcemic type | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2010 |
Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | Neutrophils | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: Alkbh5-/- neutrophils
Control: Wild type neutrophils
|
GSE198316 | |
| Regulation |
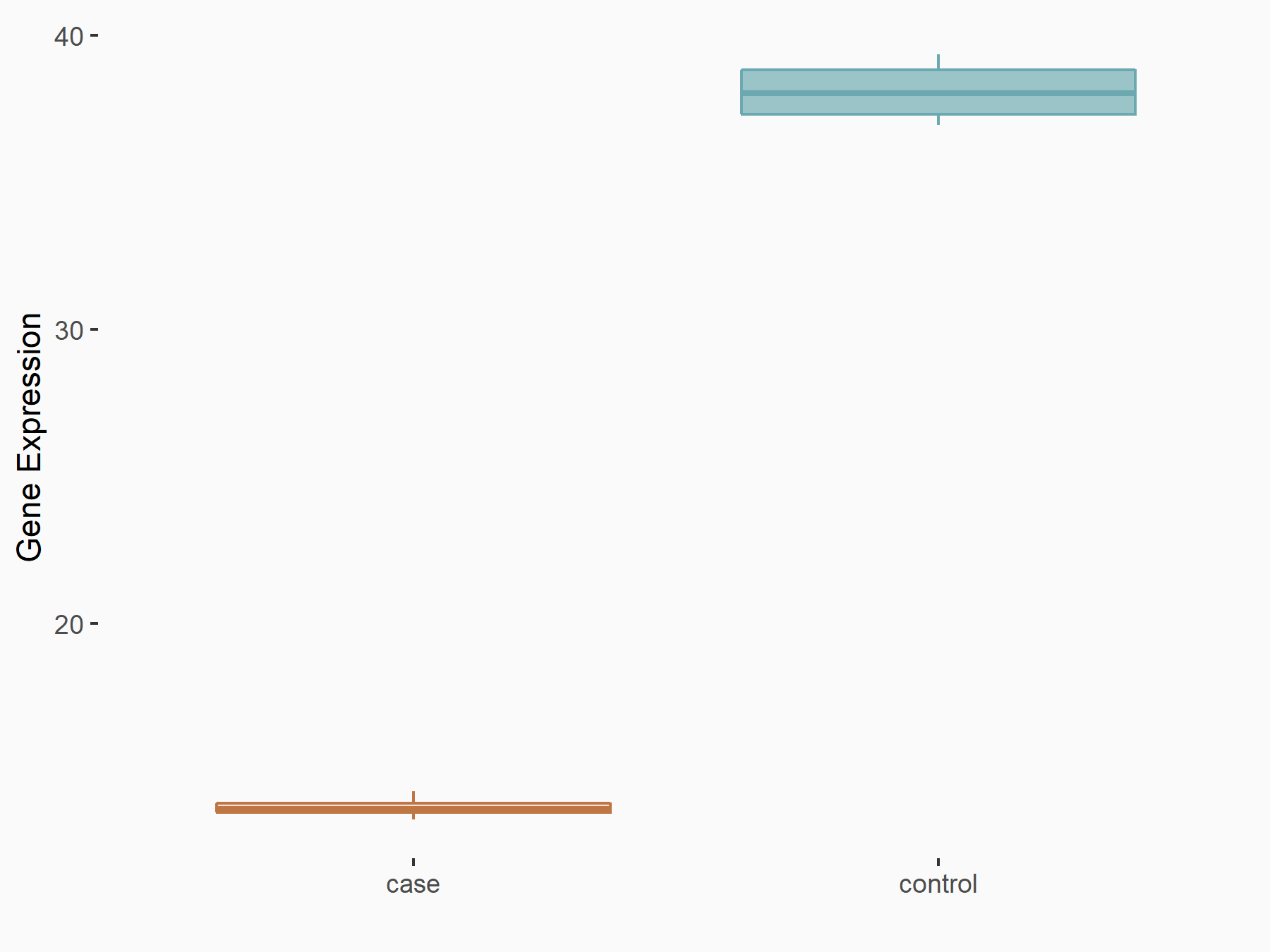  |
logFC: -1.41E+00 p-value: 1.41E-09 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [38] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Cell Process | Lysosomal escape | |||
| In-vivo Model | Wild-type C57 (female, 12-16 weeks old), ALKBH5 /- mice (female and male, 12-16 weeks old), and SPF-grade SD rats (female, 180-230 g) were used to establish the AMI model.Sodium pentobarbital diluted to 10 mg/mL was used to anesthetize the mice or rat at the dose of 50 mg/kg through an intraperitoneal injection. By using a small animal ventilator with endotracheal intubation, thoracotomy was performed at the left fourth intercostal region. The heart was exposed, and the left anterior descending coronary artery (LCA) was occluded through a 6-0 silk suture that was placed 2-3 mm distal to the origin of the LCA with a slipknot. The apical region turned white, and ST segment elevation and T wave inversion of ECG showed that the AMI model was successfully established. Forty-five minutes after ischemia, the slipknot was released, and the ischemic region was reperfused. PBS (0.2 ml), HSSS (23.5 mg/kg, 0.2 ml), IOX1 (10 mg/kg, 0.2 ml), and HSSS-I (33.5 mg/kg, containing 10 mg/kg IOX1, 0.2 ml) were administered through caudal vein injection for 14 days at the frequency of one time per day. | |||
| Response Summary | IOX1, which is an inhibitor of ALKBH5, was loaded on HSSS to form HSSS-I, which could effectively ameliorate cardiac dysfunction in acute myocardial infarction. The surface-modified bioengineered ferritin nanocage targeted the dying cells in the infarct area under the guidance of Scarf1. These cells were then phagocytosed through recognition of their Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC) receptor. | |||
Transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 3 (TACC3)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
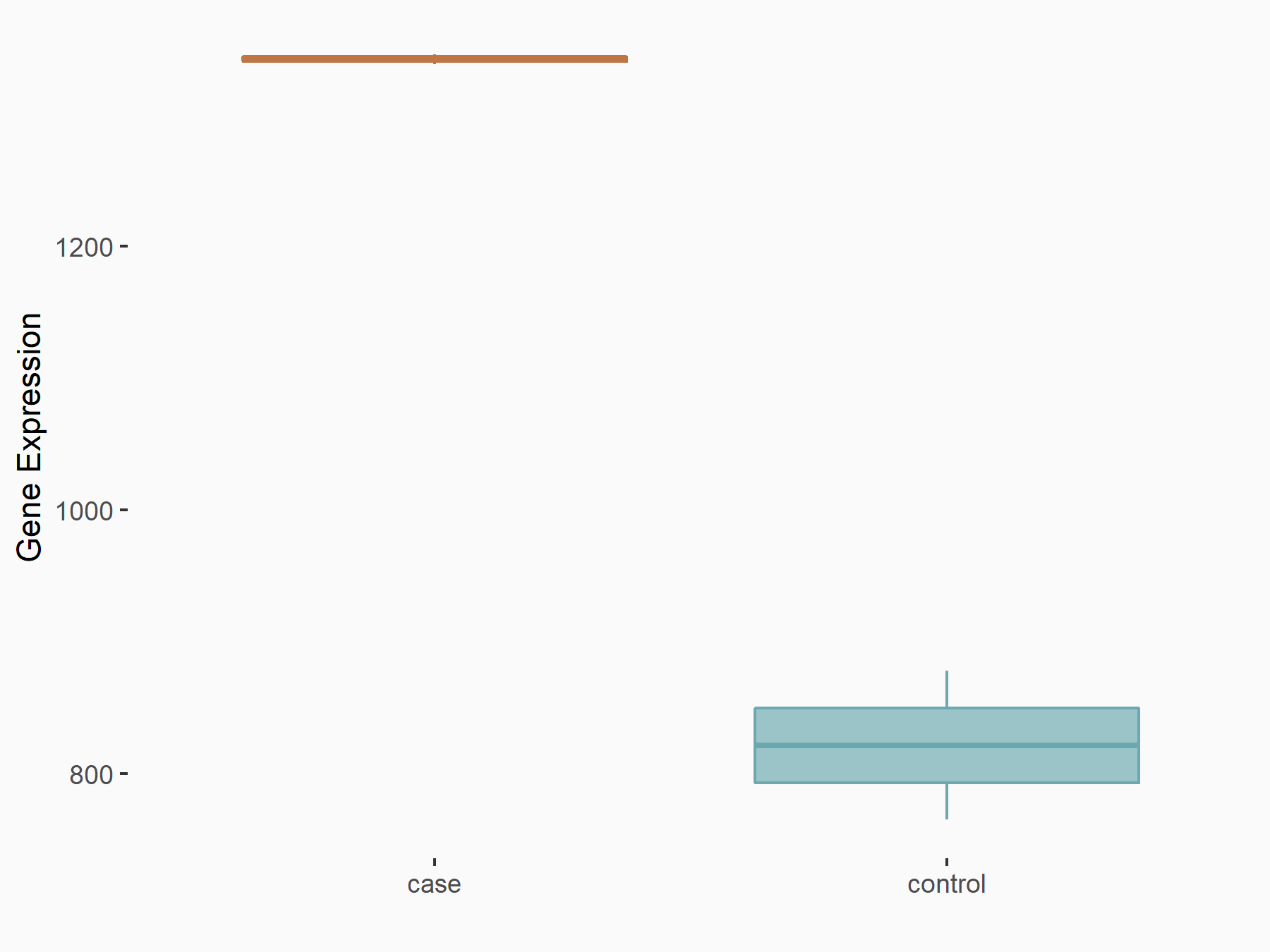  |
logFC: 7.07E-01 p-value: 2.85E-14 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [51] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | ||
| Cell Process | Self-renewal | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| Mono-Mac-6 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1426 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | GRNA and Cas9 mRNA were mixed at concentration of 50 and 100 ng/ul, respectively, and injected to the cytoplasm of one-cell-stage embryos of C57BL/6 genetic background. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 exerts tumor-promoting effects in acute myeloid leukemia by post-transcriptional regulation of its critical targets such as Transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 3 (TACC3), a prognosis-associated oncogene in various cancers. | |||
Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 (JAK2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
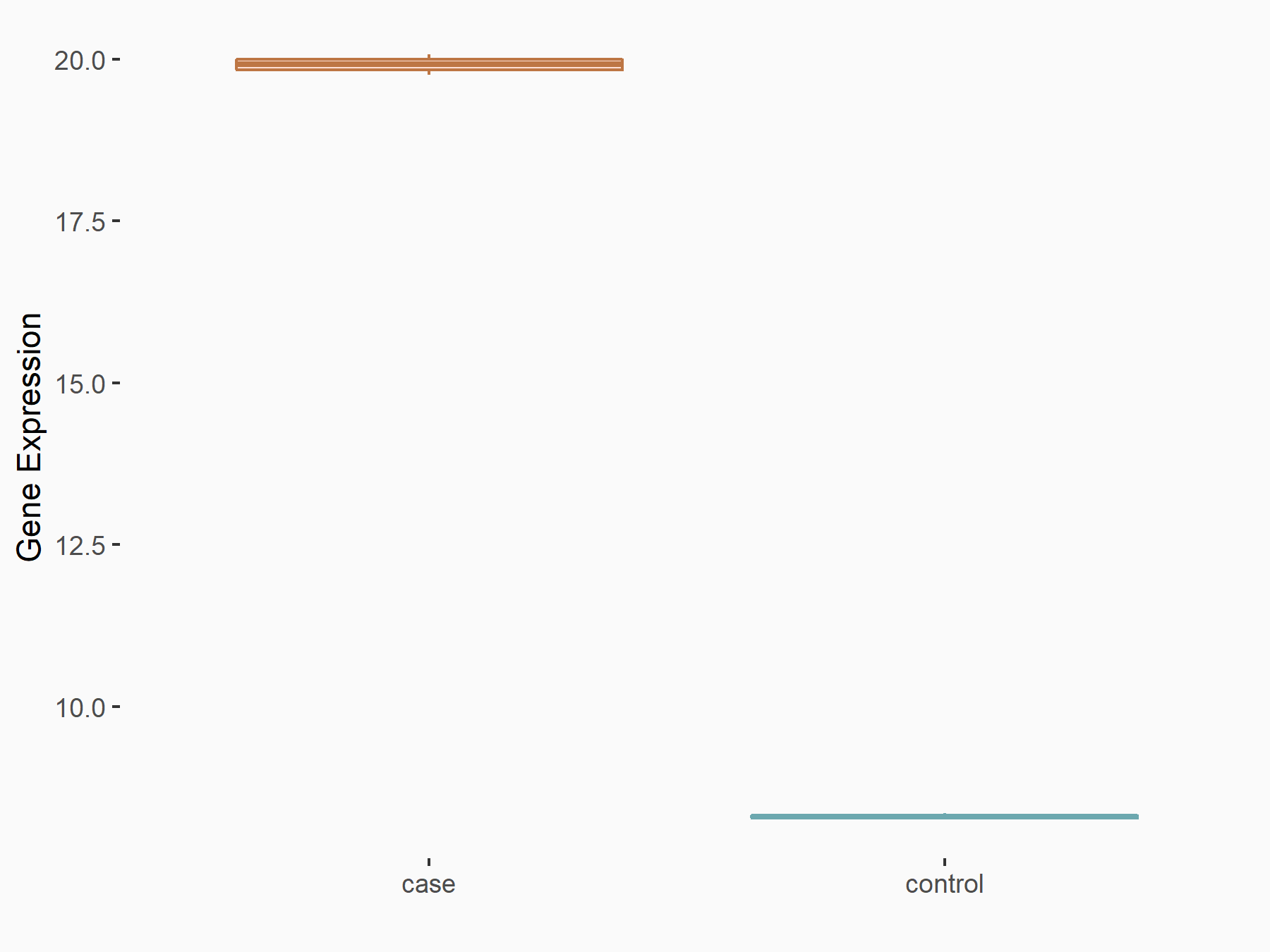  |
logFC: 1.17E+00 p-value: 2.74E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [52] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HO8910-DDP (HO8910 underwent continuous stepwise exposure to increasing concentrations of cisplatin to create the cisplatin-resistant cell lines HO8910-DDP) | |||
| HO-8910 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6868 | |
| A2780-DDP (A2780 underwent continuous stepwise exposure to increasing concentrations of cisplatin to create the cisplatin-resistant cell line) | ||||
| A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 | |
| In-vivo Model | About 5× 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the axilla of the female athymic BALB/C nude mice (4 week-old, 18-20 g). When the average tumor size reached approximately 100mm3 (after 1 week), mice were then randomized into two groups and treated with cisplatin (5 mg/kg) or normal saline (NS) weekly. | |||
| Response Summary | The ALKBH5-HOXA10 loop jointly activates the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway by mediating Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 (JAK2) m6A demethylation, promoting epithelial ovarian cancer resistance to cisplatin. | |||
Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO (AXL)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
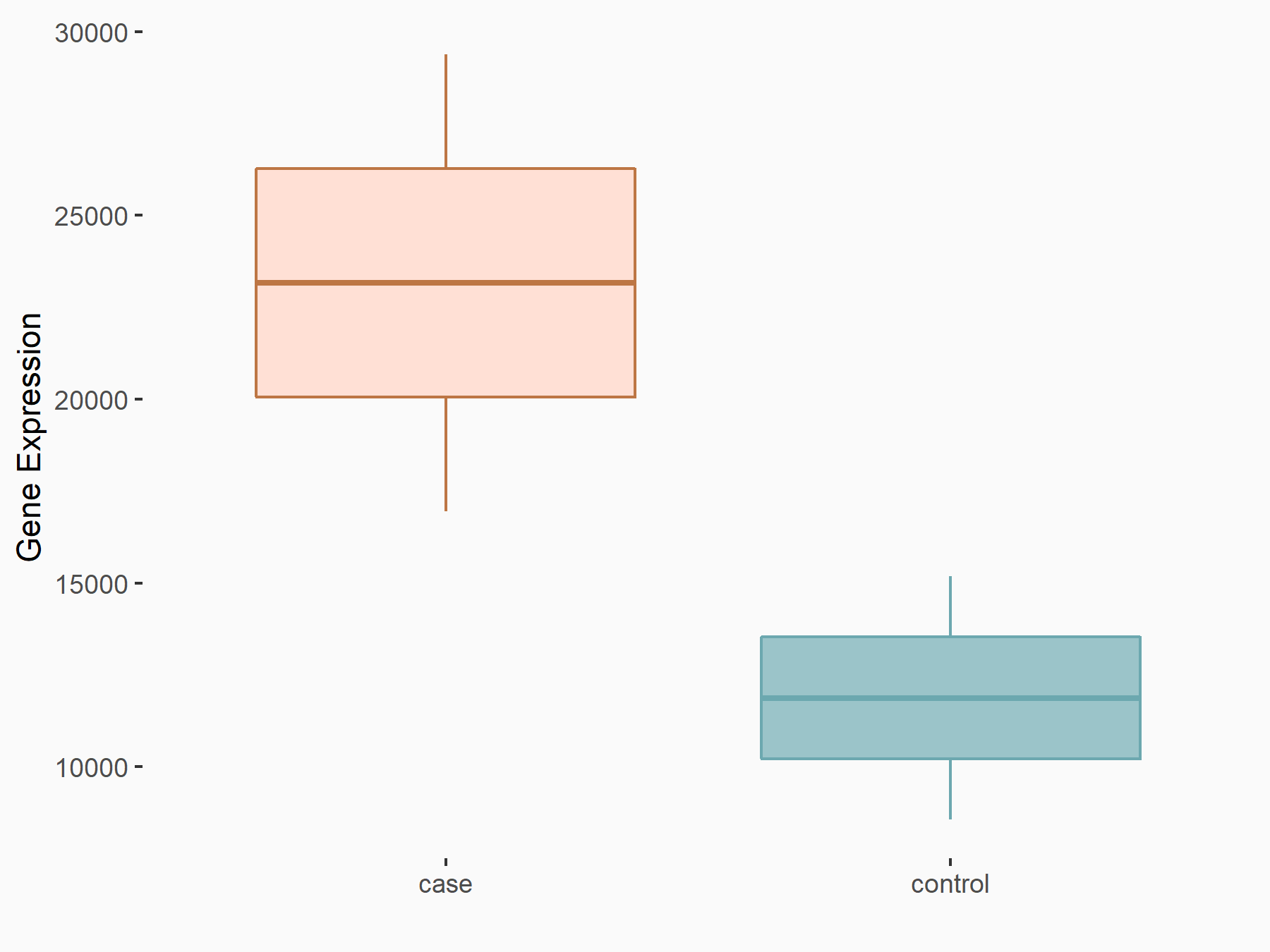  |
logFC: 9.65E-01 p-value: 8.11E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [53] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| In-vivo Model | Congenic recipient mice (CD45.2) at 8-10 weeks old were used for AML transplantation, and CD45.1 recipients at 8-10 weeks old were used for normal hematopoietic transplantation assays. | |||
| Response Summary | Expression of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 is regulated by chromatin state alteration during leukemogenesis of human acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and ALKBH5 is required for maintaining leukemia stem cell (LSC) function but is dispensable for normal hematopoiesis. ALKBH5 affects mRNA stability of receptor tyrosine kinase Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO (AXL) in an m6A-dependent way. | |||
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [99] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Chlorogenic acid | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
AML12 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0140 |
| THLE-2 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3803 | |
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
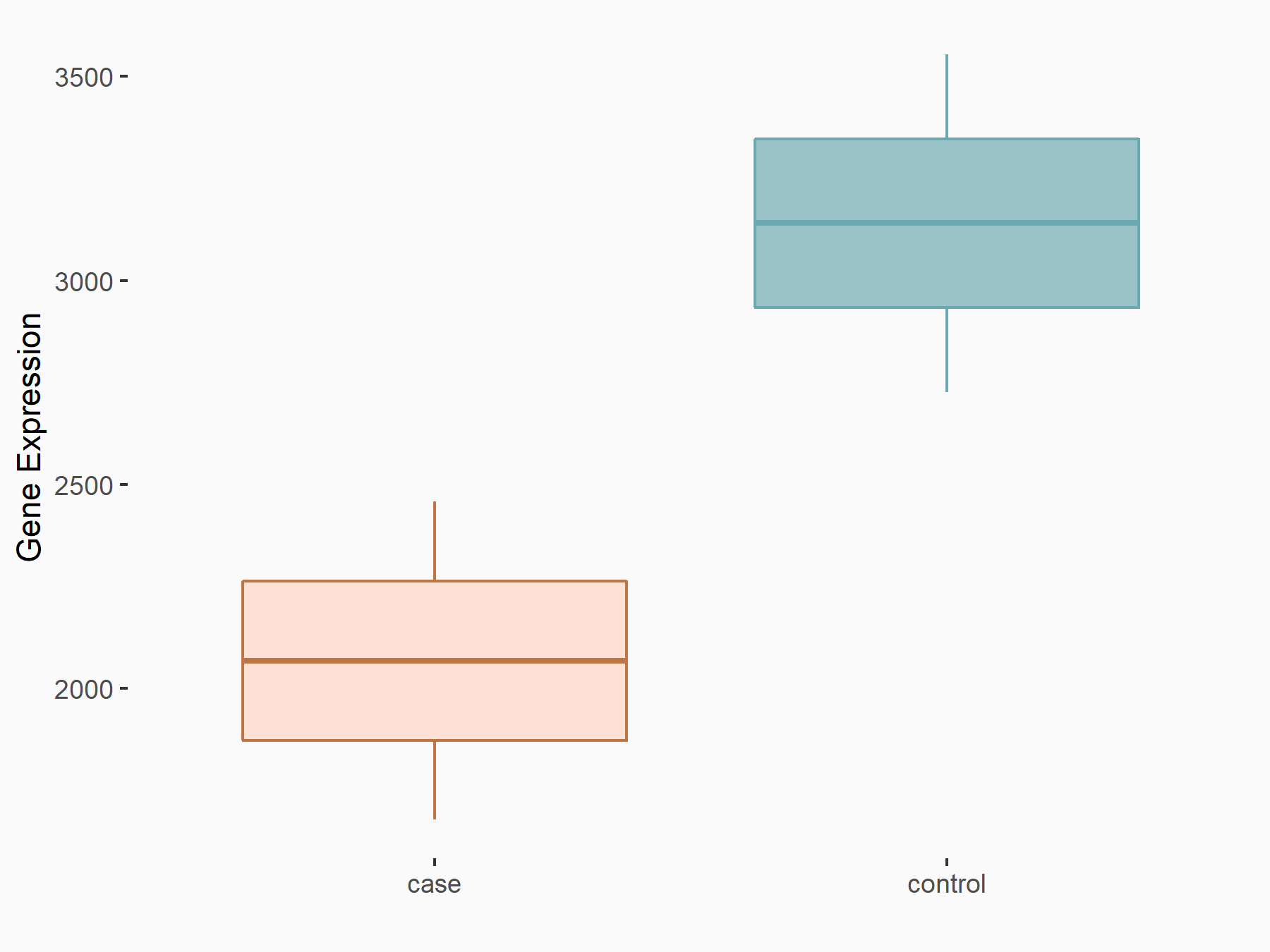  |
logFC: -6.03E-01 p-value: 1.12E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Mature T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Dexamethasone | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Glucocorticoid | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 22 (USP22)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
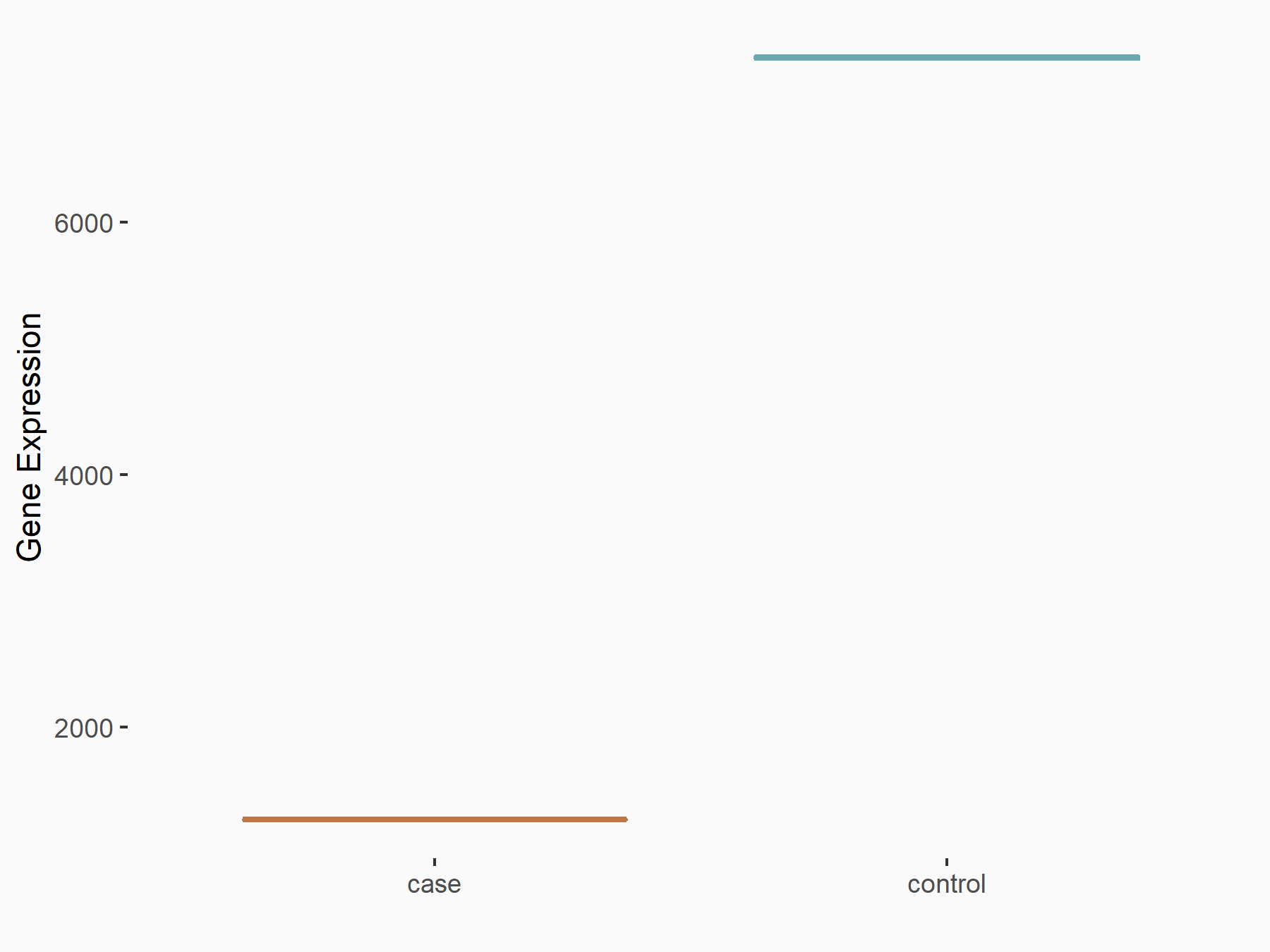 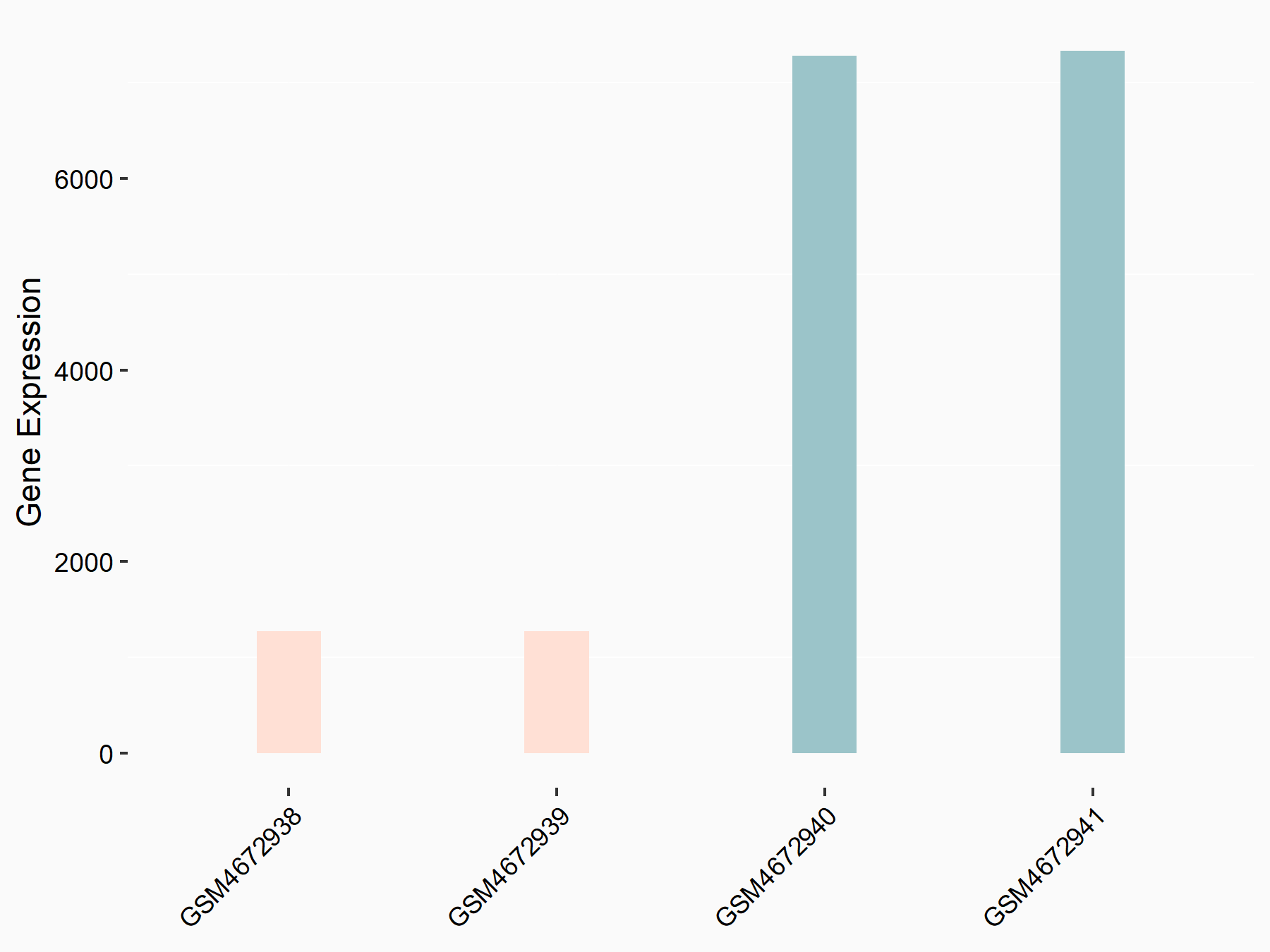 |
logFC: -2.53E+00 p-value: 1.55E-42 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Proteasome pathway degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| SaOS-2 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0548 | |
| OS-17 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9992 | |
| IMR-90 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0347 | |
| hFOB 1.19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3708 | |
| 143B | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 | |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor xenograft studies, 143B cells stably expressing scrambled shRNA or ALKBH5 shRNA (1 × 106) were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of 4-week-old athymic nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In osteosarcoma, ALKBH5 mediates its protumorigenic function by regulating m6A levels of histone deubiquitinase Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 22 (USP22) and the ubiquitin ligase RNF40. | |||
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C (UBE2C)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
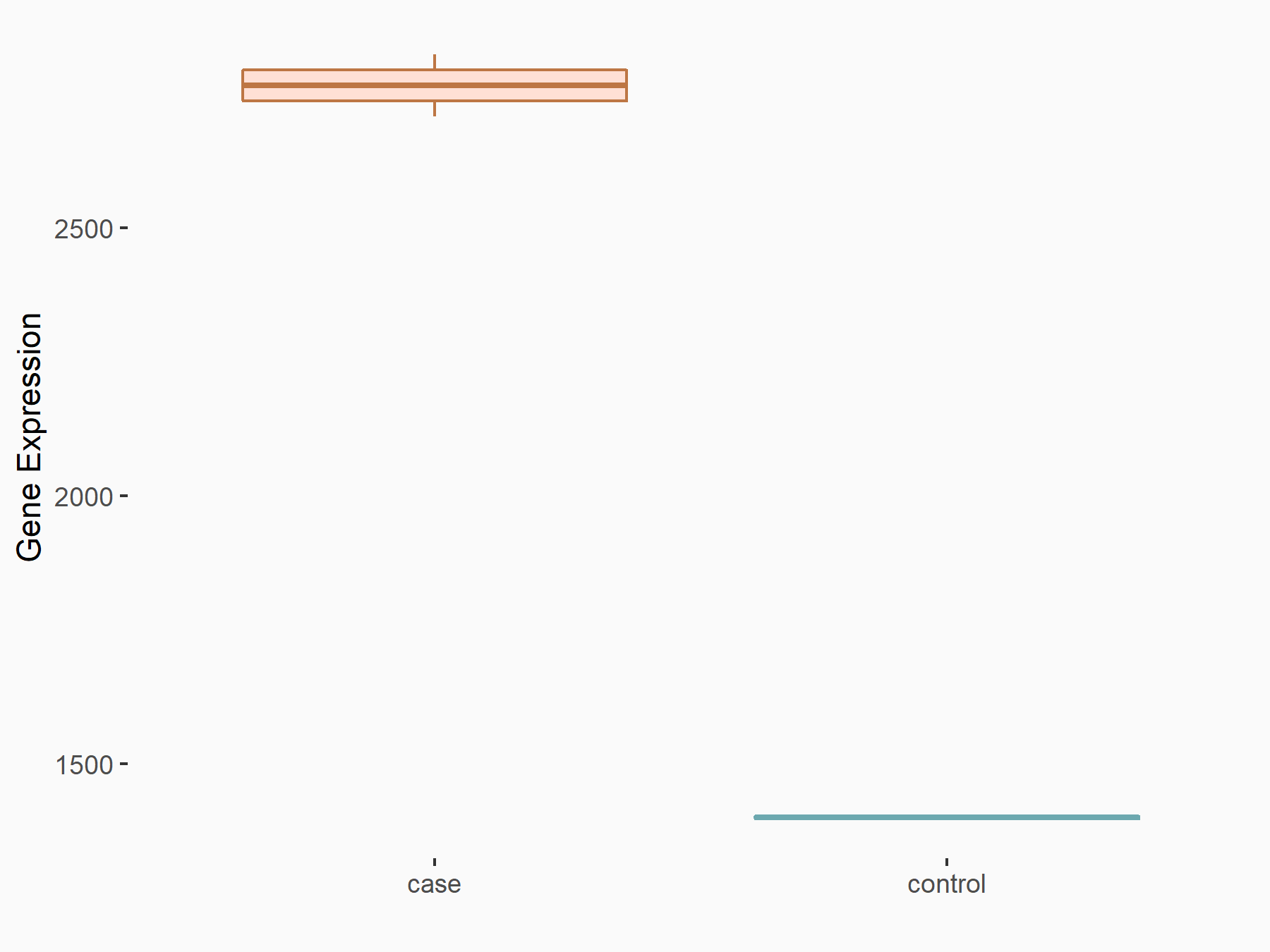 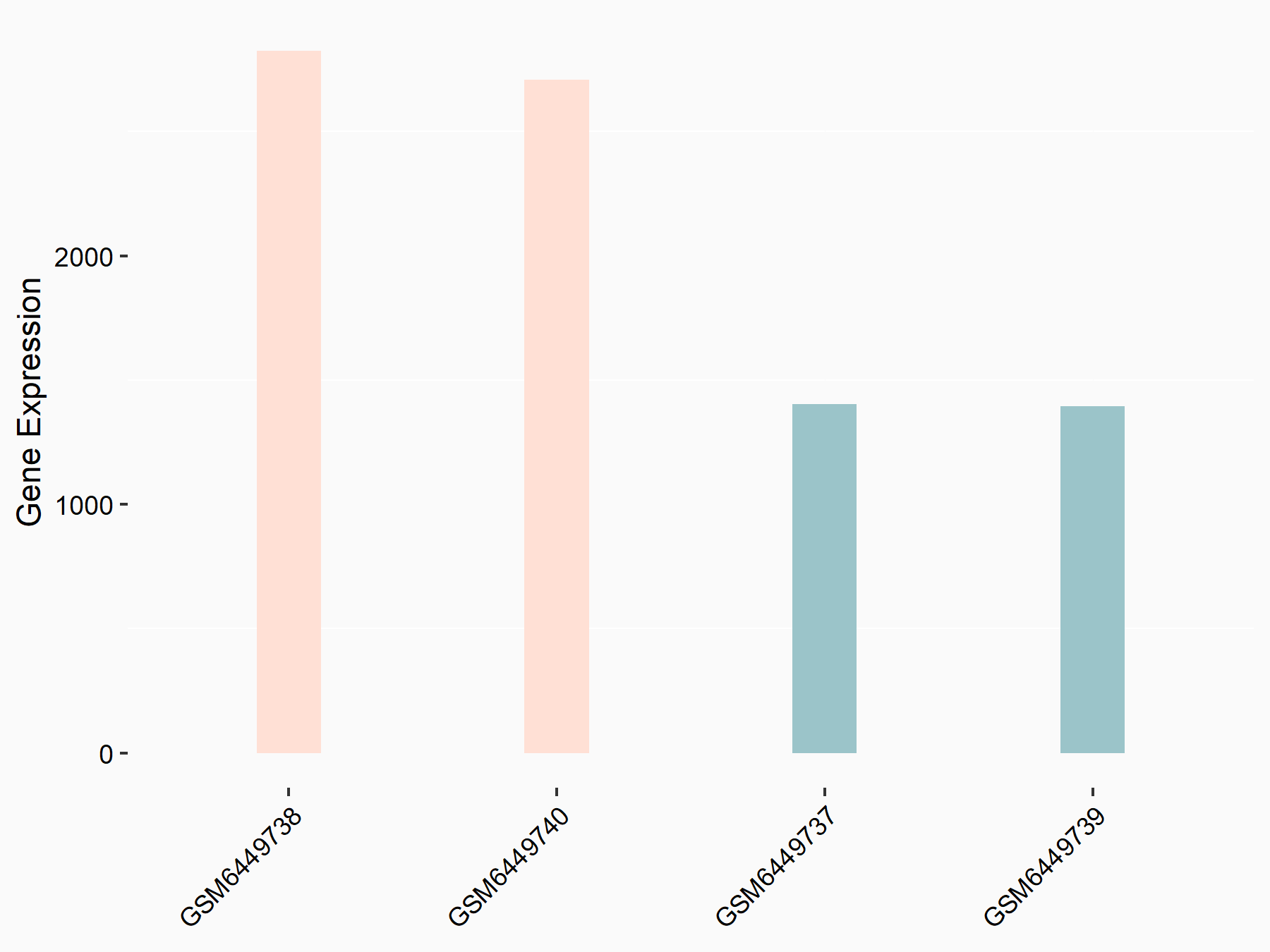 |
logFC: 9.83E-01 p-value: 3.48E-52 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [55] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion | |||
| Ubiquitination degradation | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
In-vitro Model |
PLA-801D | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7110 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| HBEC (Human lung cancer cell) | ||||
| PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | |
| Response Summary | Deregulated Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C (UBE2C)-autophagy repression axis drives NSCLC progression which renders varieties of potential molecular targets in cancer therapy of NSCLC. UBE2C is repressed post-transcriptionally via tumor suppressor miR-381 and epitranscriptionally stabilized with maintenance of lower m6A level within its mature RNAs due to the upregulation of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 in NSCLC. | |||
Zinc finger protein SNAI1 (SNAI1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | CAG cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 CAG cells
Control: shNC CAG cells
|
GSE180214 | |
| Regulation |
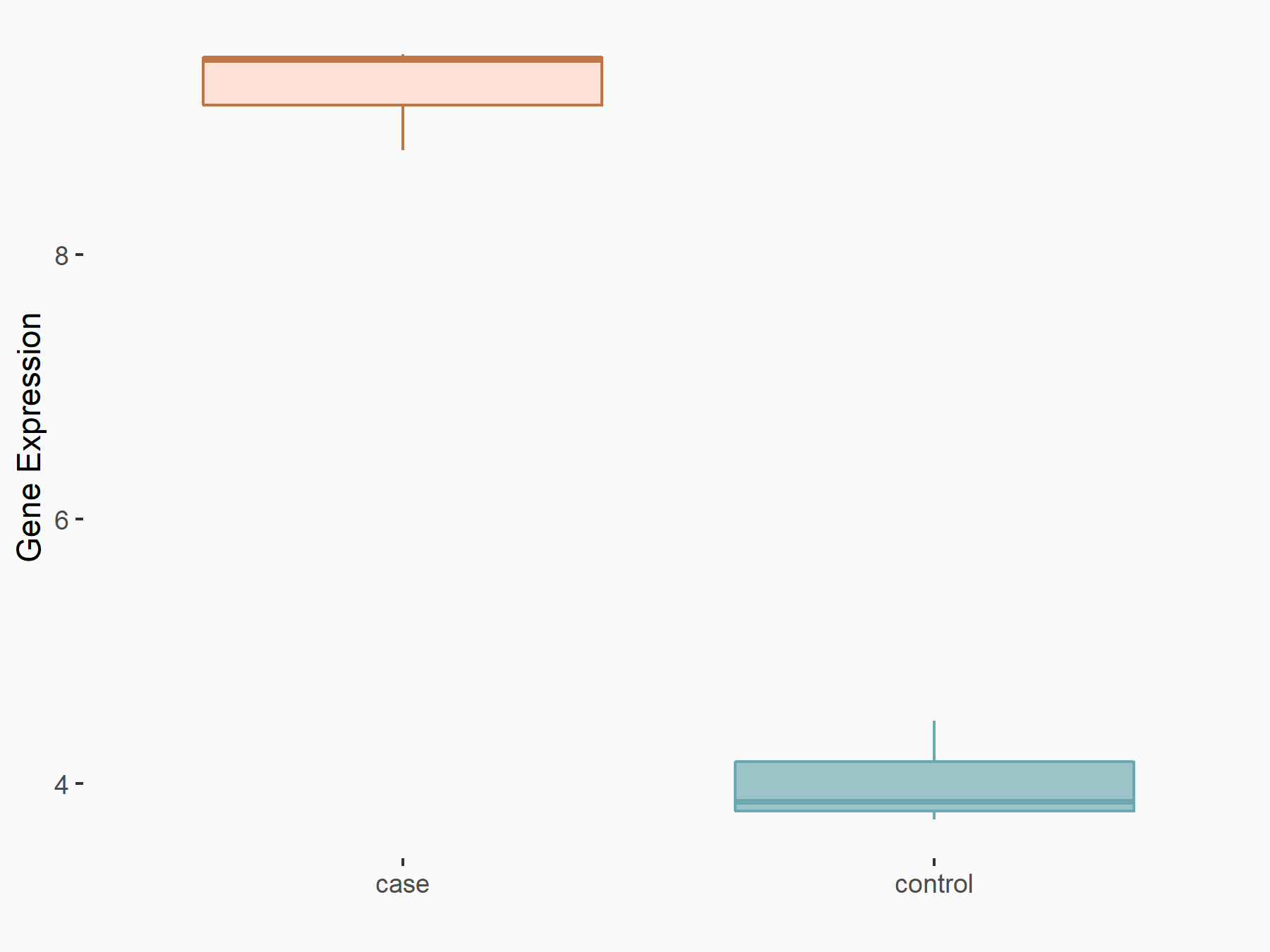 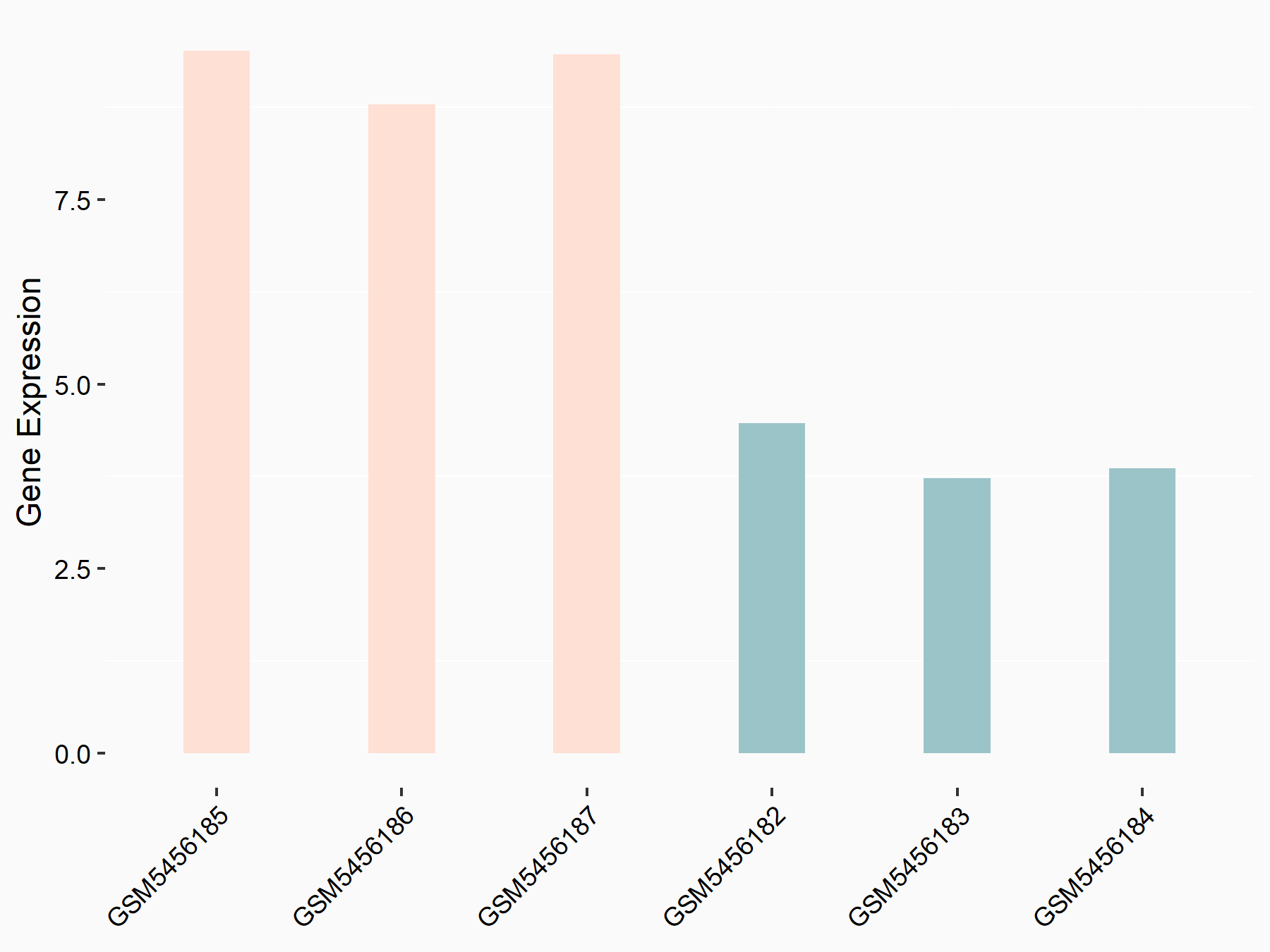 |
logFC: 1.03E+00 p-value: 7.72E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Adherens junction | hsa04520 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression incurred a significant reduction in iron-regulatory protein IRP2 and the modulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) Zinc finger protein SNAI1 (SNAI1). Owing to FBXL5-mediated degradation, ALKBH5 overexpression incurred a significant reduction in iron-regulatory protein IRP2 and the modulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) SNAI1. ALKBH5 in protecting against PDAC through modulating regulators of iron metabolism and underscore the multifaceted role of m6A in pancreatic cancer. | |||
Hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis [ICD-11: DB93]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [102] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis [ICD-11: DB93] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
 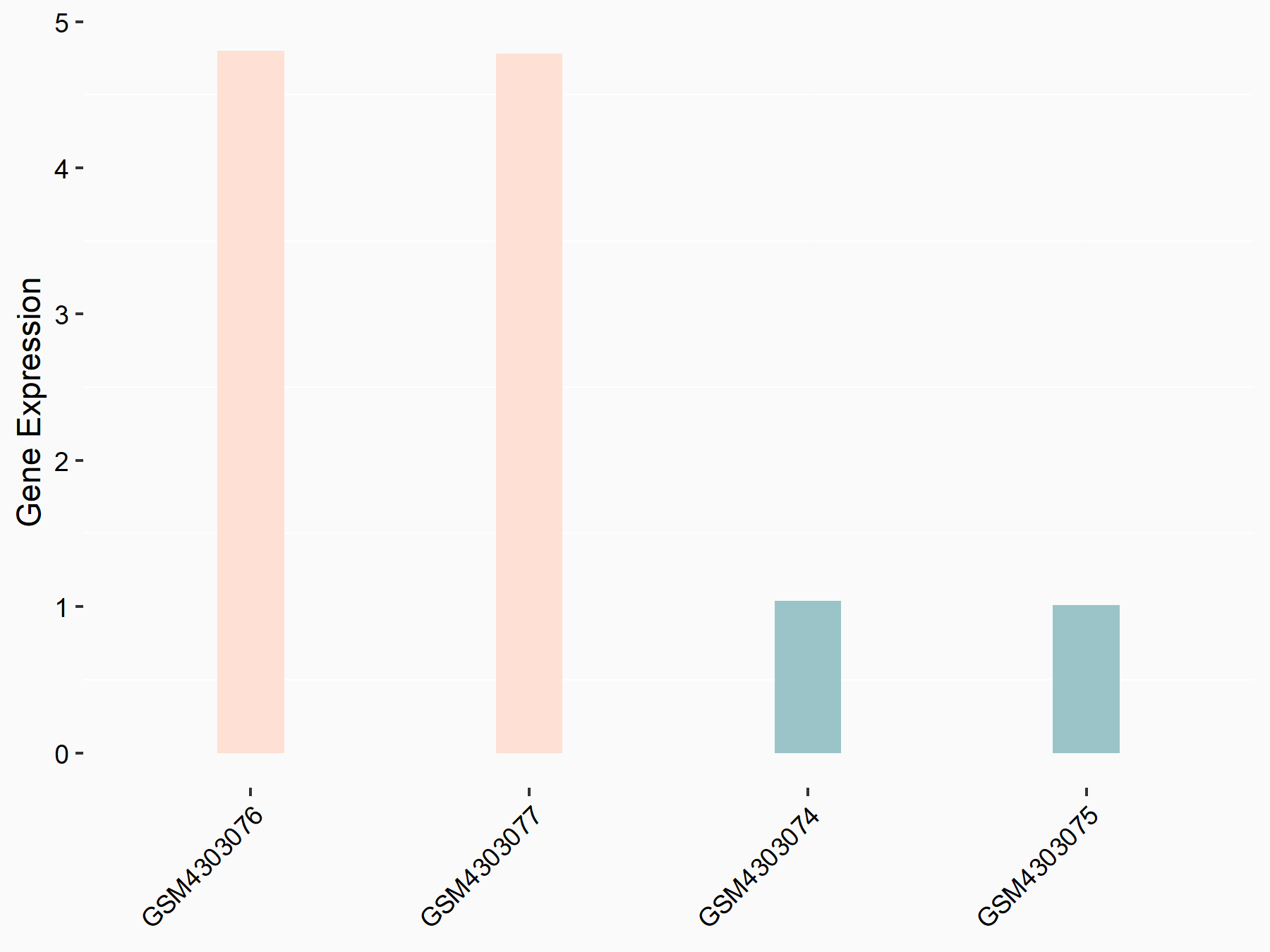 |
logFC: 1.52E+00 p-value: 9.12E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [56] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
AMC-HN-8 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5966 |
| HOK | Normal | Hexagrammos otakii | CVCL_YE19 | |
| Tu 212 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4915 | |
| In-vivo Model | 1 × 106 (100 ul) cells of infected and uninfected by lentiviral were, respectively, injected subcutaneously into nude mice which divided randomly into scramble group and shKCNQ1OT1-1 group. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 mediates KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) expression via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner and KCNQ1OT1 could directly bind to HOXA9 to further regulate the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells. | |||
Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
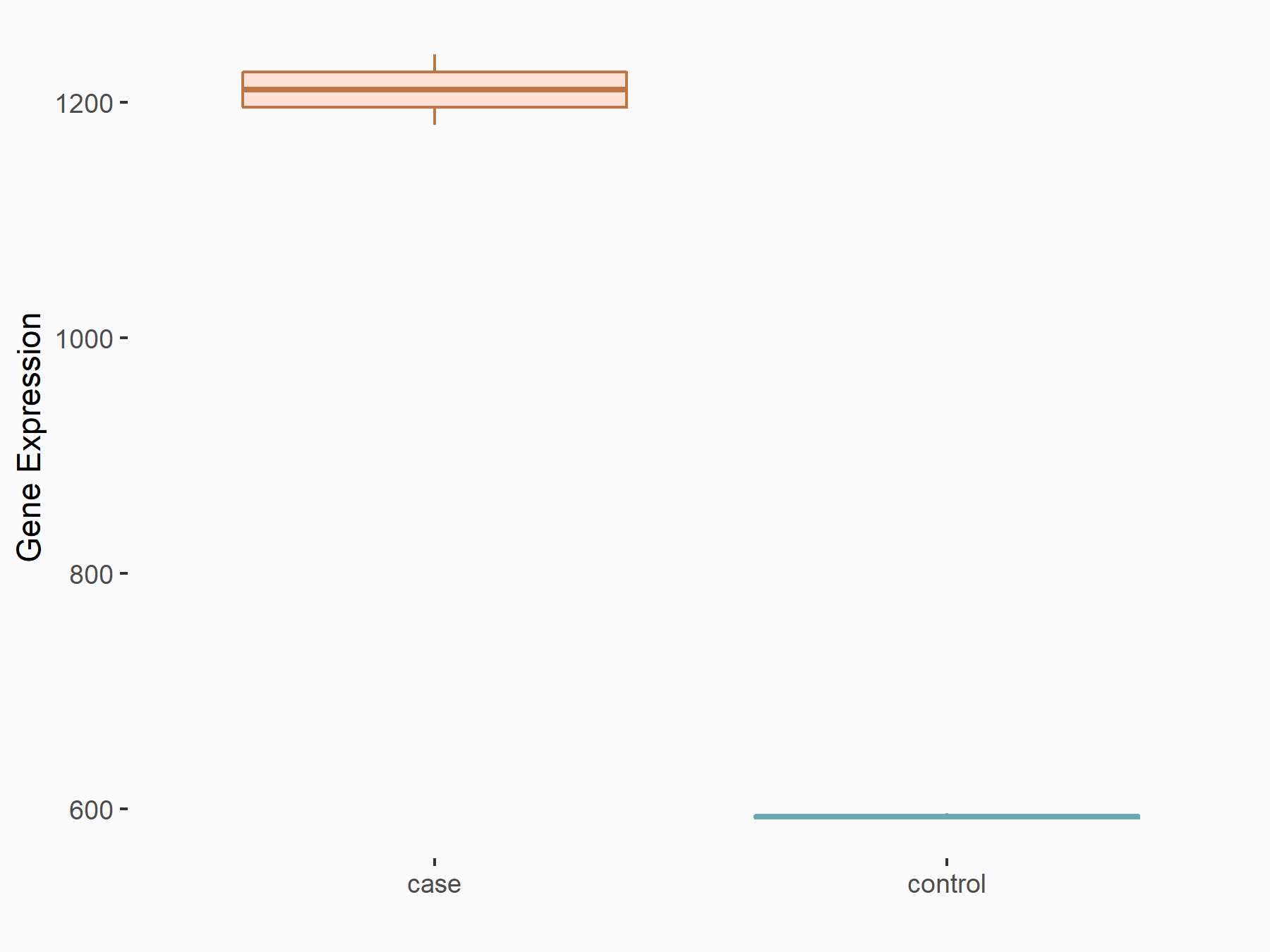  |
logFC: 1.03E+00 p-value: 3.88E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Urinary/pelvic organs injury [ICD-11: NB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [57] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of kidney [ICD-11: NB92.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HK2 | Normal | Acipenser baerii | CVCL_YE28 |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 could up-regulate Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) expression by demethylation. Furthermore, dexmedetomidine inhibited the expression of ALKBH5 in LPS-treated HK-2 cells. Dexmedetomidine suppressed the biological behavior of HK-2 cells treated with LPS by inhibiting the expression of ALKBH5 in vitro, which provides potential targets for the prevention and treatment of sepsis-induced kidney injury. Dexmedetomidine suppressed the biological behavior of HK-2 cells treated with LPS by inhibiting the expression of ALKBH5 in vitro, which provides potential targets for the prevention and treatment of sepsis-induced kidney injury. | |||
Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
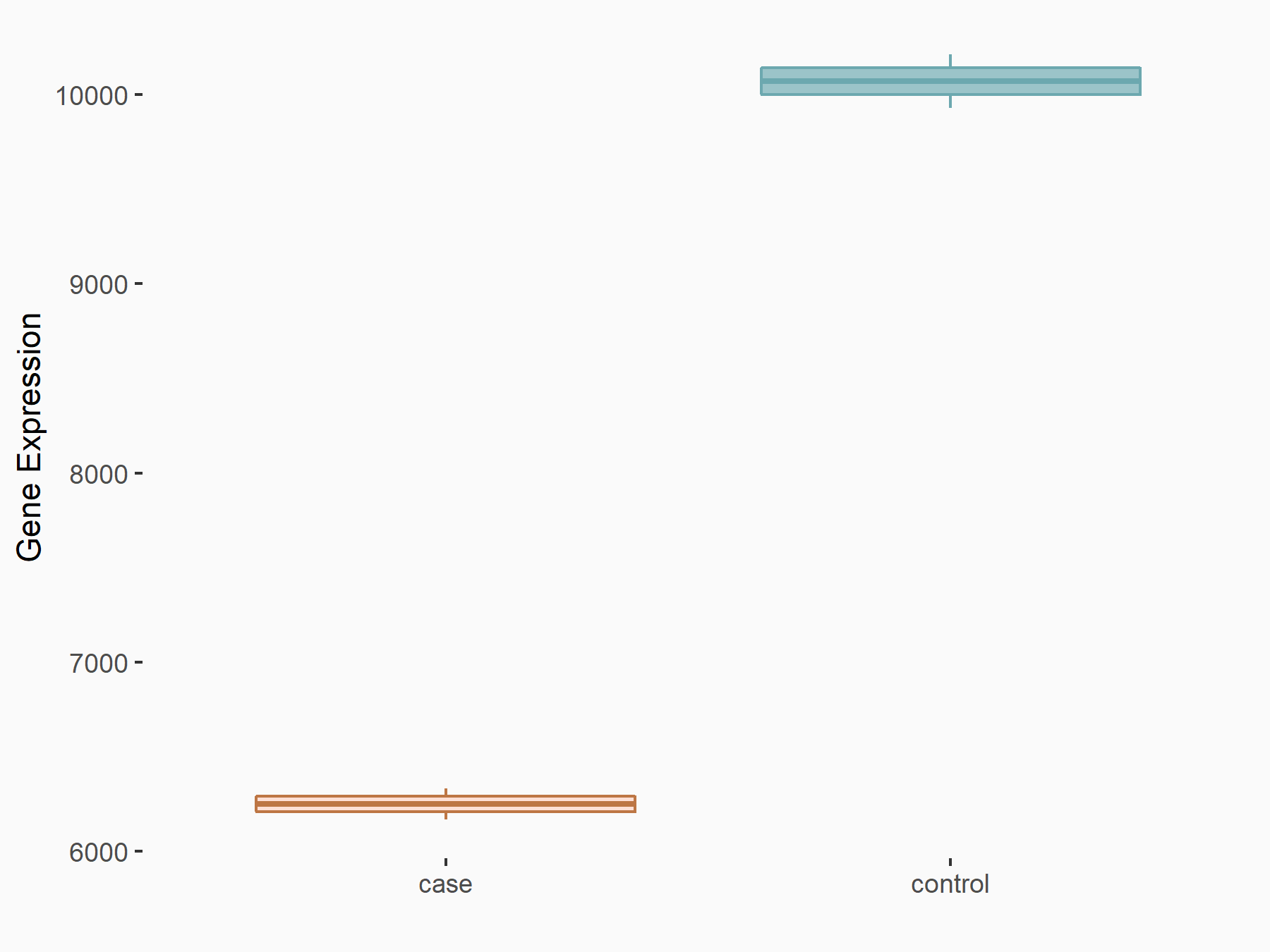  |
logFC: -6.88E-01 p-value: 8.40E-87 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [58] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | hsa05202 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune | |||
In-vitro Model |
GL261 | Mouse glioblastoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_Y003 |
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Male C57BL/6 mice (4-6 weeks old) were used in all tumor allografting experiments and transplanted with GL261-luc cells (1×105) into the frontal lobes of brains. | |||
| Response Summary | Hypoxia-induced ALKBH5 erased m6A deposition from the lncRNA NEAT1, stabilizing the transcript and facilitating Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)-mediated paraspeckle assembly. Ectopic expression of CXCL8 in ALKBH5-deficient glioblastoma multiforme cells partially restored TAM recruitment and tumor progression. | |||
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [59] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 promotes Gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by demethylating the lncRNA Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1). | |||
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [60] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and migration | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 |
| HIEC (Normal intestinal epithelial cells) | ||||
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | To establish xenograft model, RKO cells (1 × 107) tansduced with si-control (si-NC) or si-ALKBH5 or si-ALKBH5+NEAT1 were injected subcutaneously into the right flank of the nude mice (n = 6 each group) every 5 days for 4 times. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 knockdown suppressed malignant behavior of colon cancer partially through Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) by demethylation in vitro and vivo, suggesting that ALKBH5-NEAT1 axis is a potential therapeutic target for colon cancer treatment. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [61] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and migration | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 |
| L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 could up-regulate Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) expression by inhibiting m6A enrichment. ALKBH5-induced NEAT1 promoted cell proliferation and migration of HCC by sponging miR-214 in vitro, which provided a potential therapeutic target for HCC. | |||
Infantile hemangioma [ICD-11: 2E81]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [62] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Infantile hemangioma [ICD-11: 2E+81] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
XPTS-1 | Infantile hemangioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_9U60 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 knockdown suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion of infantile hemangioma cells, while promoting cell apoptosis. ALKBH5 promoted lncRNA Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) expression by reducing the m6A modification of lncRNA NEAT1. | |||
Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
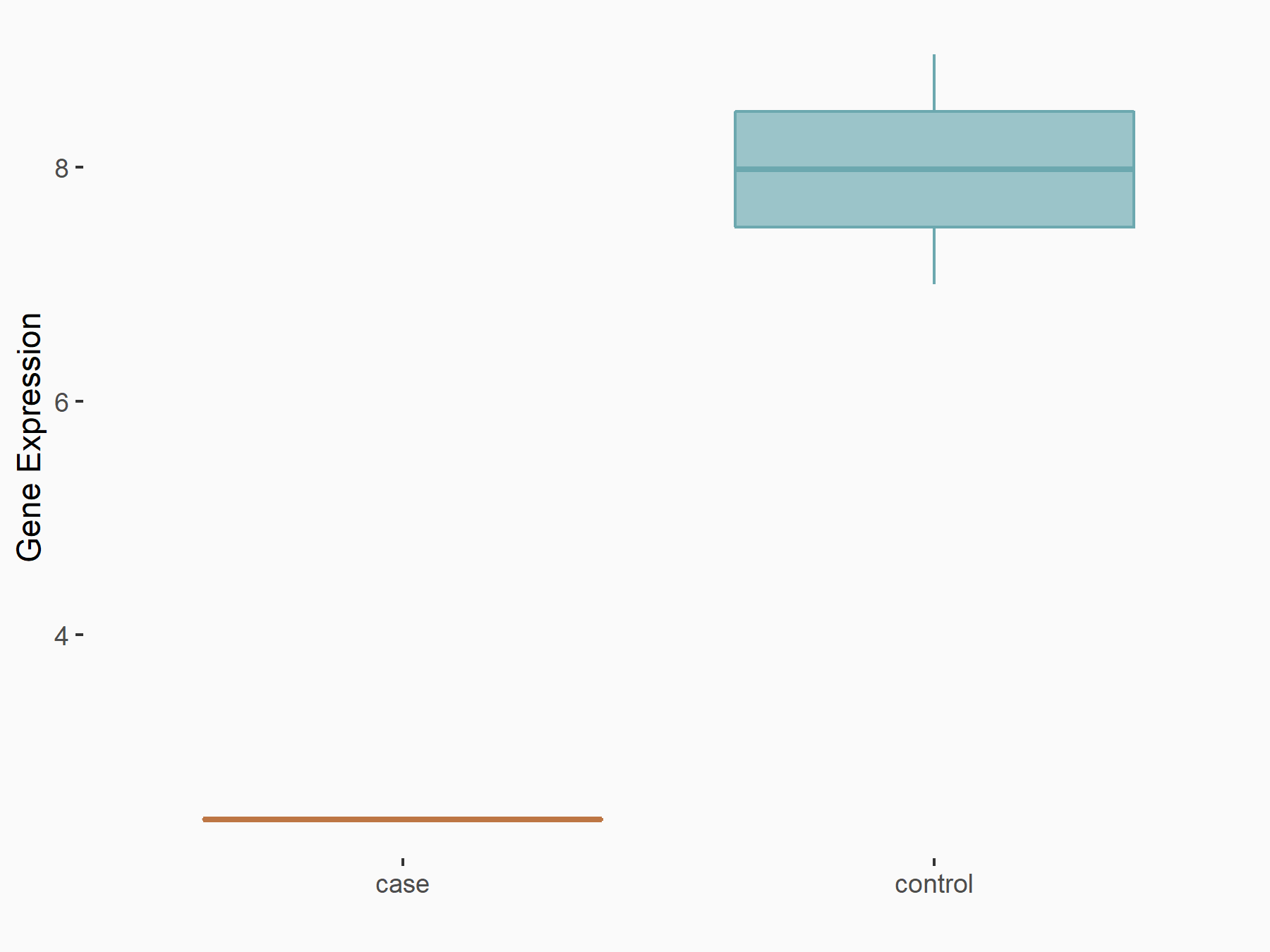 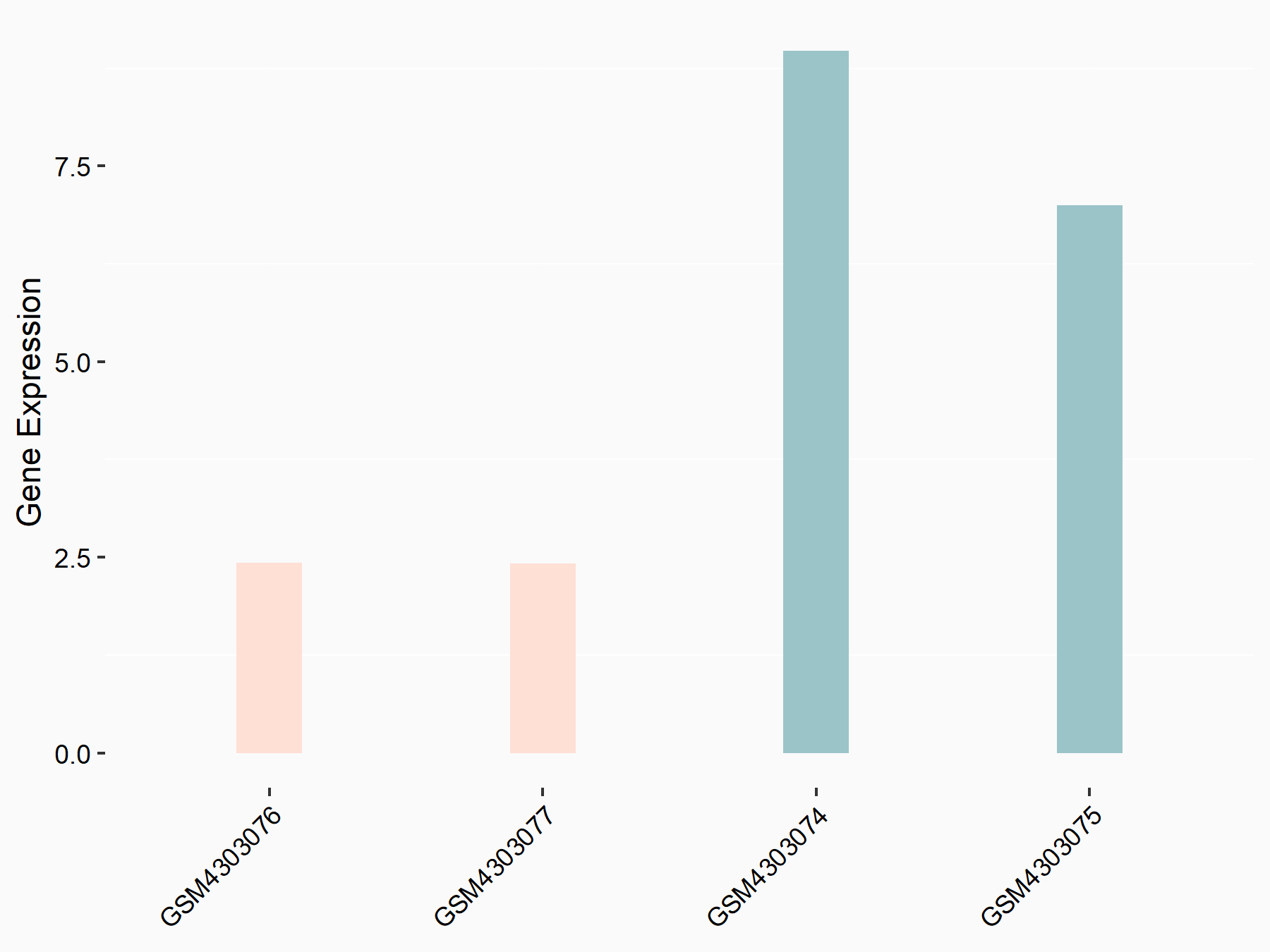 |
logFC: -1.38E+00 p-value: 6.15E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [63] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
143B | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 |
| HOS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0312 | |
| SaOS-LM7 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0515 | |
| MG-63 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 | |
| NHOst (Normal human osteoblast cells) | ||||
| SaOS-2 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0548 | |
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 | |
| In-vivo Model | Indicated stable 143B cells were subcutaneously injected into nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 decreased the m6A modification of Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1), thus inhibiting the binding of reader protein YTHDF2 in PVT1. ALKBH5-mediated PVT1 upregulation promoted the osteosarcoma cell proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. | |||
RMRP
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
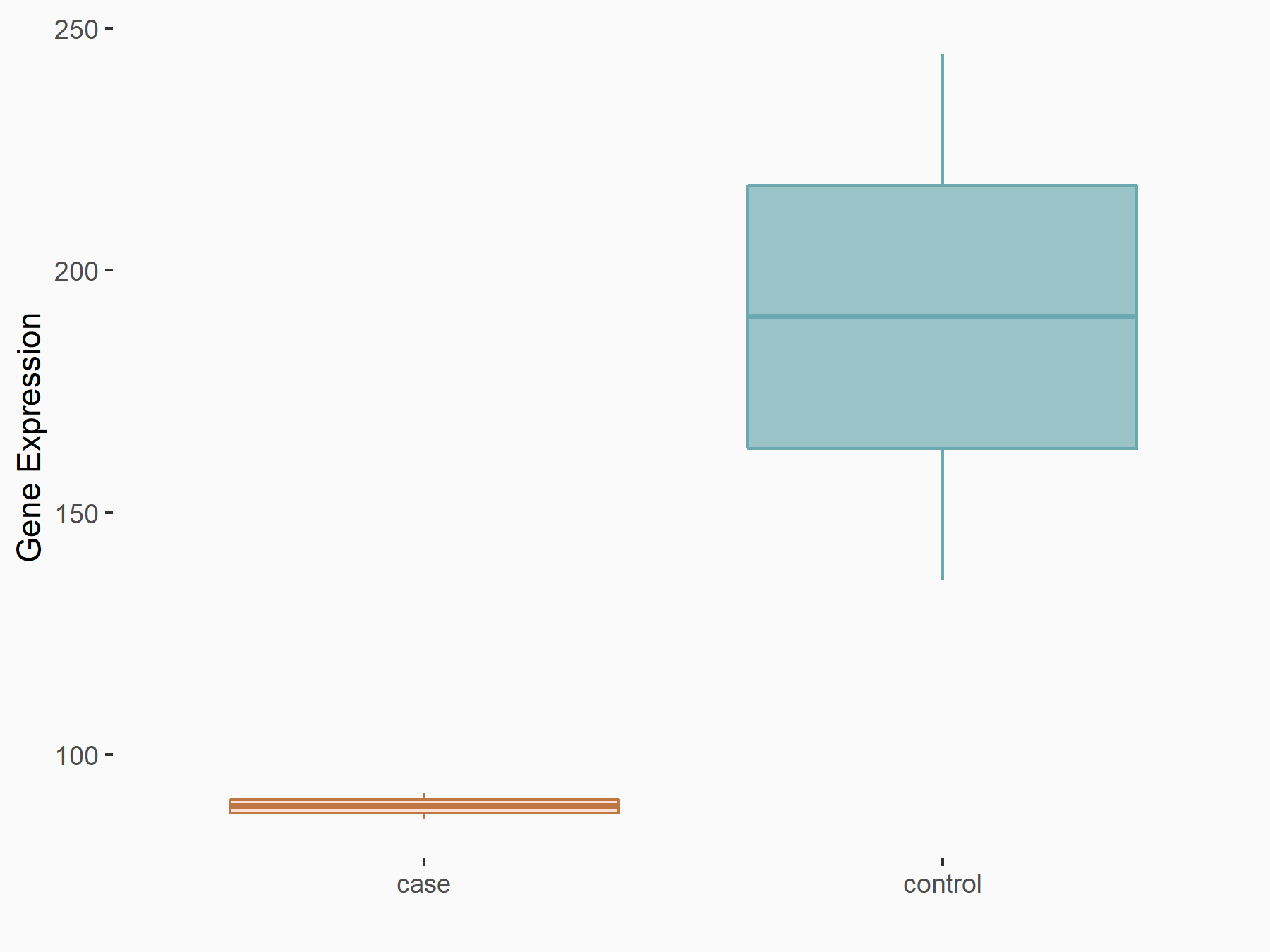 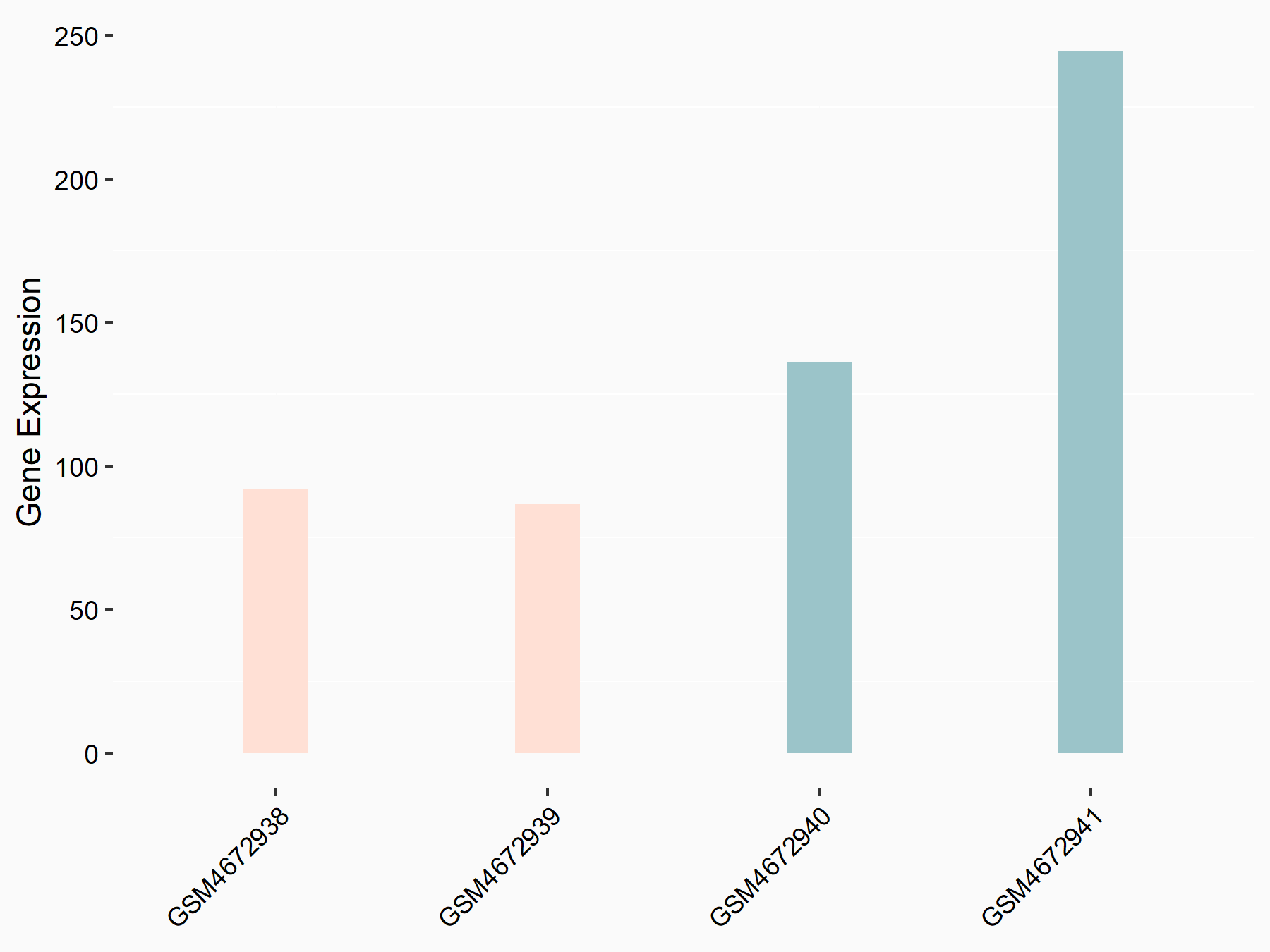 |
logFC: -1.09E+00 p-value: 4.52E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [64] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| XWLC-05 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_IQ71 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were maintained in cages under standard environmental conditions (temperature 25 ± 2 ℃, humidity 55 ± 5% and 12-h light/12-h dark cycle) and given free access to food and tap water. All mice were randomly divided into three groups with 6 in each group. To establish xenograft model, A549 cells (1 × 107) transfected with si-control (si-NC), si-ALKBH5 or si-ALKBH5 + RMRP were injected subcutaneously into a single side of the armpit of each mouse. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 knockdown, was able to inhibit malignant behavior of lung adenocarcinoma by regulating RMRP expression via demethylation. RMRP and ALKBH5 therefore represent promising therapeutic targets for lung adenocarcinoma. | |||
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [107] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| HO-8910 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6868 | |
| OVCAR-8 | High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1629 | |
| In-vivo Model | Stable cell clones, at a density of 5000 cells, were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of six-week-old male nude (nu/nu) mice (SLAC, Shanghai, China). These clones were infected with SKOV3-Nc and SKOV3-shALKBH5 in 100 uL of sterilized phosphate-buffered saline. Mice were allowed to recover for six weeks before reinjection. In each group, the tumor weights of six mice were measured and recorded. All mice were euthanized within six weeks post-surgery, following the removal of their tumors. Tumor sizes were measured using Vernier calipers, with the volume calculated as 1/2 length × width^2. | |||
72 kDa type IV collagenase (MMP2)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [65] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [66] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010) | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
In-vitro Model |
UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| 253J | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7935 | |
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
| Response Summary | Knockdown of ALKBH5 promoted bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and decreased cisplatin chemosensitivity, ALKBH5 inhibited the progression and sensitized bladder cancer cells to cisplatin through a Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2)-mediated glycolysis pathway in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [67] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HIEC-6 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6C21 |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| In-vivo Model | Colorectal cancer cells were seeded in culture plates for 24 h prior to cotransfection with GFP-CARMN, and a vector using Lipofectamine 2000. After 48 h, RNA immunoprecipitation was performed using/Colorectal cancer cells were plated in 24-well plates and incubated for 24 h before cotransfection with the luciferase reporter vector, and the Renilla vector. antibodies against FTO, METTL3 and ALKBH5 from the EZ-Magna RIP-Kit (Millipore). | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [68] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Response Summary | Deletion of METTL16 or ALKBH5 predicted poor OS and DFS of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. And this study found significant associations between the genetic alterations and clinicopathological features as well as Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) alteration. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [29] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
In-vitro Model |
PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | Cells at 1 × 106 were subcutaneously injected into the mice similarly to nude mice. Twenty-eight days later, grafted tumors were collected and morphologically analyzed. | |||
| Response Summary | Knockdown of Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) or inhibition of p53's transcriptional activity by addition of its specific inhibitor PFT-Alpha decreased expression of ALKBH5 and Cancer stem cells' malignancies, the pivotal role of ALKBH5 in Cancer stem cells derived from nonsmall-cell lung cancer and highlight the regulatory function of the p53/ALKBH5 axis in modulating CSC progression. p53 transcriptionally regulates PRRX1, which is consistent with our previous report. | |||
Female reproductive system disorders [ICD-11: SC4Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [69] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Female reproductive system disorders [ICD-11: SC4Y] | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| In-vivo Model | Neo-resistant recombinant ESCs were analyzed for correct 3' and 5' targeting through hybridization by standard protocols, and we identified seven correctly targeted clones. Following ESC cell injection, several high-percentage chimera males were born. These were bred with Cre-expressing mice, and Cre-mediated excision of Alkbh5 exon 1 was tested in 26 agouti F1 pups. Two animals tested positive for the excised allele. These two mice, heterozygous for the constitutive allele (Alkbh5+/-), were analyzed by Southern blot analysis and used for further breeding to generate Alkbh5-/- mice. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 as another mammalian demethylase that oxidatively reverses m(6)A in mRNA in vitro and in vivo. Alkbh5-deficient male mice have increased m(6)A in mRNA and are characterized by impaired fertility resulting from apoptosis that affects meiotic metaphase-stage spermatocytes. Identified in mouse testes 1,551 differentially expressed genes that cover broad functional categories and include spermatogenesis-related mRNAs involved in the Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) functional interaction network. | |||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [70] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 | |
| HIEC-6 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6C21 | |
| In-vivo Model | 3 × 106 CRC cells were inoculated subcutaneously into the right hind leg of BALB/c nude mice. There were 12 nude mice per group. The tumor volume was observed and calculated every 5 days according to the formula: tumor volume = (length × width2)/2. After 30 days, nude mice were euthanatized through intraperitoneal injection of excessive pentobarbital (> 100 mg/kg). | |||
Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1)
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [71] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | An anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT)-induced OA model was constructed in mice. Briefly, 10-week-old male C57BL/6 mice were anesthetized, and the skin was prepared. The knee joint capsule was opened, and the ACL was carefully transected with microsurgical scissors under a microscope. For the sham operation, the right knee joints were exposed, but the ligament was not transected. At 1 week, 3 weeks, 5 weeks and 7 weeks after the operation, 10 μl of DMEM containing 1 * 10^5 control MSCs or ALKBH5-overexpressing MSCs was injected into the knee joint with an insulin syringe (BD Bioscience, 324702), with 10 μl of DMEM as a control. | |||
DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein (DDIT4)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [72] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HOK | Normal | Hexagrammos otakii | CVCL_YE19 |
| In-vivo Model | Briefly, two million UM-SCC-1 cells stably expressing shRNA scramble or shRNAs against RBM33 and ALKBH5 were subcutaneously injected into two flanks of each NSGS mice. Tumor volume and mice weight measurements were taken every 4 days and 7 days respectively. For the in vivo ALKBH5 inhibition assay, the HNSCC PDX tumors TM01145 and TM01420 were purchased from Jackson Laboratory. 15 mg/kg 2,4-PDCA was given i.p. every four days when tumor volume reaches ~100 mm3. And, tumor volume was calculated according to the formula: [D×(d2)] /2 where D represents the large diameter of the tumor and d represents the small diameter of the tumor. Animals were individually monitored throughout the experiment. | |||
ELAV-like protein 1 (HuR/ELAVL1)
Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [73] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor xenograft studies, MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with scrambled-siRNA or METTL14-siRNA or ALKBH5-siRNA (2 × 106) were mixed with Matrigel and injected subcutaneously in the flank of 6-week-old female athymic nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL14 and ALKBH5 determine the m6A status of target genes by controlling each other's expression and by inhibiting m6A reader YTHDF3 (YTH N 6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 3), which blocks RNA demethylase activity. ALKBH5/METTL14 constitute a positive feedback loop with RNA stability factor ELAV-like protein 1 (HuR/ELAVL1) to regulate the stability of target transcripts. This study unveils a previously undefined role for m6A in cancer and shows that the collaboration among writers-erasers-readers sets up the m6A threshold to ensure the stability of progrowth/proliferation-specific genes, and protumorigenic stimulus. | |||
Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1)
Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [75] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C6Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Doxil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| In-vivo Model | 6-week old immunodeficient mice (Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center, Guangzhou, China) were selected for generating a subcutaneous xenograft model. MDA-MB-231/DOX cells were implanted subcutaneously into the immunodeficient mice. 7 days later, mice were randomly divided into 4 groups, administrated with vehicle control, FOXO1 inhibitor AS1842856 (20 mg/kg/day, i. p.), Doxorubicin (5 mg/kg/day, i. p.), and AS1842856 combined with Doxorubicin, respectively. Tumor formation was examined every 4 days. | |||
Frizzled-10 (FZD10)
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [76] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | PARPi | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
UWB1.289 | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B079 |
| PEO1 | Ovarian cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2686 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 107 PARP inhibitor resistant PEO1 cells were suspended in 200 uL PBS : Matrigel (1:1) unilaterally injected subcutaneously into the right dorsal flank of 6-8 week-old female immunocompromised non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD/SCID) gamma (NSG) mice. When the average tumor size reached ~100 mm3, the mice were then randomized into four groups and treated with vehicle control, Olaparib (50 mg/kg), XAV939 (5 mg/kg) or a combination daily for 18 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Downregulation of m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 was sufficient to increase Frizzled-10 (FZD10) mRNA m6A modification and reduce PARPi sensitivity, the finding elucidates a novel regulatory mechanism of PARPi resistance in EOC by showing that m6A modification of FZD10 mRNA contributes to PARPi resistance in BRCA-deficient EOC cells via upregulation of Wnt/Bete-catenin pathway. | |||
Hexokinase-2 (HK2)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [77] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the mouse xenograft model, 2 × 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank regions of female BALB/c nude mice (4-5 weeks). | |||
Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [78] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Motor neuron disease [ICD-11: 8B60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [79] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Progressive muscular atrophy [ICD-11: 8B60.3] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | ||
| In-vivo Model | Mice bearing the Alkbh5-floxed allele (Alkbh5 fl/fl , Cyagen) were crossed with transgenic mice expressing Cre recombinase under the control of the Myl1 promoter (Myl1-Cre; Stock No: 024713, The Jackson Laboratory) to generate muscle-specific Alkbh5 knockout mice (Myl1-Cre;Alkbh5 fl/fl ). Littermate Alkbh5fl/fl mice were used as controls. Genotyping by tail DNA and PCR were performed at 4 weeks of age. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 demethylates and stabilizes Hdac4 mRNA. Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) interacts with and deacetylates FoxO3, resulting in a significant increase in FoxO3 expression. These results suggest that ALKBH5 is a potential therapeutic target for neurogenic muscle atrophy. | |||
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2)
Endometriosis [ICD-11: GA10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [80] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometriosis [ICD-11: GA10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Homeobox protein NANOG (NANOG)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [81] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Temozolomide | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | U251/TR cells (2 × 106 per mouse) with stable transfection of sh-circ_0072083 or sh-NC were subcutaneously injected into mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In glioma, hsa_circ_0072083 could regulate Homeobox protein NANOG (NANOG) and ALKBH5 via targeting miR-1252-5p to control temozolomide resistance. circ_0072083 silence reduced NANOG expression via blocking ALKBH5-mediated demethylation. | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [82] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | ||
| Cell Process | Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells (hsa04550) | |||
In-vitro Model |
BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 |
| HCC1954 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1259 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MDA-MB-435 | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0417 | |
| SUM-149 (Human breast cancer cell SUM149) | ||||
| SUM-159 (A mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cell line) | ||||
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75.1 A3 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_YX82 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 1,000 breast cancer cells were injected into the mammary fat pad of 6-8-wk-old female NSG mice in a 1:1 suspension of Matrigel (BD Biosciences) in PBS solution. At 10 wk after injection, mice were examined for the presence of tumors, which were harvested for analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | Homeobox protein NANOG (NANOG) activity does not merely compensate for reduced O2 levels but significantly increases ALKBH5, JMJD2C, and TET1 activity in hypoxic breast cancer cells, leading to transcriptional and posttranscriptional changes in gene expression that promote the specification and/or maintenance of BCSCs. ALKBH5 overexpression decreased Homeobox protein NANOG (NANOG) mRNA methylation, increased NANOG levels, and increased the percentage of BCSCs,. | |||
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [84] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEY | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0297 |
| HO-8910 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6868 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | Female athymic BALB/c nude mice (4-week-old) were provided (SLAC Laboratory Animal Co. Ltd.). The animals were raised in a pathogen-free animal laboratory and randomly divided into the control or experimental group (six mice in each group). | |||
| Response Summary | Homeobox protein NANOG (NANOG) served as a target in ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification in ovarian cancer. | |||
Integrin alpha-6 (ITGA6)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [85] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell adhesion | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 1 × 107 cells were subcutaneously implanted into 5-week-old BALB/cJNju-Foxn1nu/Nju nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A writer METTL3 and eraser ALKBH5 altered cell adhesion by regulating Integrin alpha-6 (ITGA6) expression in bladder cancer cells. m6A is highly enriched within the ITGA6 transcripts, and increased m6A methylations of the ITGA6 mRNA 3'UTR promotes the translation of ITGA6 mRNA via binding of the m6A readers YTHDF1 and YTHDF3. Inhibition of ITGA6 results in decreased growth and progression of bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. | |||
Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1)
Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour [ICD-11: 2B5D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [87] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HO-8910 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6868 |
| A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 | |
| In-vivo Model | We injected 8 × 105 HO8910 cells into the footpads of mice. The mice were randomized two weeks after tumor cell injection to receive either an ITGB1 blocking antibody (Santa, CA, USA) or an IgG isotype antibody twice per week for four weeks 22,23. Y15 (30 mg/kg) against p-FAK (Tyr397) and PBS as a control were intraperitoneally injected twice per week for four weeks in the FAK-treatment assays. The main tumors and popliteal LNs were harvested and fixed in paraformaldehyde after six weeks of tumor cell inoculation. LN volumes were calculated as follows: LN volume (mm3) = (length [mm]) × (width [mm])2 × 0.52. The formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples were analysed using immunohistochemistry and haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. | |||
Iron-responsive element-binding protein 2 (IRP2)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Adherens junction | hsa04520 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression incurred a significant reduction in iron-regulatory protein Iron-responsive element-binding protein 2 (IRP2) and the modulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) SNAI1. Owing to FBXL5-mediated degradation, ALKBH5 overexpression incurred a significant reduction in iron-regulatory protein IRP2 and the modulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) SNAI1. ALKBH5 in protecting against PDAC through modulating regulators of iron metabolism and underscore the multifaceted role of m6A in pancreatic cancer. | |||
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [65] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK/ERK2/MAPK1)
BackgroundAllergic rhinitis [ICD-11: CA08]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [88] | |||
| Responsed Disease | BackgroundAllergic rhinitis [ICD-11: CA08.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 (SMAD7)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [40] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MRC-9 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2629 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1490 | |
| H1795 (Lung cancer H1795 cell lines were purchased from ATCC, USA) | ||||
| NCI-H1792 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1495 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [89] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 |
| Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 | |
| KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 | |
| TE-10 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1760 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were acclimatized and fed for one week. Then, they were randomly divided into two groups: sh-NC group and sh-SHMT2 group. Cells transfected with sh-NC or sh-SHMT2 were subsequently cultured routinely. Next, cells with logarithmic growth phase (1 ×106) were taken and injected to the right axilla of nude mice. After subcutaneous inoculation, the mice were observed for their mental status, activity, and tumor formation. The tumor volume was monitored every 4 days, and the mice were euthanized after 28 days. Tumor tissues were separated and weighed from nude mice. A portion of the dissected tumor tissue was fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin blocks and sectioned. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [40] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MRC-9 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2629 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1490 | |
| H1795 (Lung cancer H1795 cell lines were purchased from ATCC, USA) | ||||
| NCI-H1792 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1495 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3)
Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [90] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
Injury of heart [ICD-11: NB31]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [91] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Myocardial injury [ICD-11: NB31.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Male C57BL/6 mice (25-30 g) were obtained from Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China) and were provided adaptive feeding for a week at the suitable temperature and humidity. All animals were housed in micro-isolator cages with free access to food and water according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The myocardial I/R operation were followed by previous research (Song et al., 2015). The mice were randomly divided into myocardial I/R group (n = 10) and sham group (n = 10). Mice were anesthetized (50 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium, intraperitoneal injection) before assays. The supine of mice were fixed on the operating table connected with the standard lead II electrocardiogram. The left thorax was cut to expose the heart and the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery was ligated by 7/0 sterile suture. Myocardial ischemia was induced by LAD ligation for 30 min followed by 120 min of reperfusion. Sham group mice underwent the same surgical procedures without LAD coronary artery ligation. After assay, the surviving animals were transferred to institution's animal department for euthanizing mice. | |||
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG)
Preeclampsia [ICD-11: JA23]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [92] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Preeclampsia [ICD-11: JA23] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Retinoic acid-induced protein 1 (RAI1)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [93] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 demethylated pri-miR-194-2 and inhibited miR-194-2 biogenesis through an m6A/DGCR8-dependent manner. ALKBH5/miR-194-2/Retinoic acid-induced protein 1 (RAI1) axis was also validated in clinical samples. This study revealed ALKBH5 in miRNAs biogenesis and provide novel insight for developing treatment strategies in esophageal cancer. | |||
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A (STAT5A)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [94] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HT22 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 |
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [95] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1490 | |
| In-vivo Model | A549 cells (5 × 106) were subcutaneously transplanted into nude mice. Tumor size was assessed every 7 days. EVs (10 μg) were injected subcutaneously into mice every 3 days. The mice were sacrificed, tumors were removed, and their weights were recorded in the fourth week. In addition, the nude mice were injected with A549 cells (2 × 106) through the tail vein, and EVs (10 μg) were injected into mice via the tail vein every 3 days. The bilateral lung tissues were resected and stained with hematoxylin-eosin. | |||
Transcriptional repressor protein YY1 (YY1)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [98] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 | |
| BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five-week-old male BALB/c nude mice were used for tumor growth studies in vivo. Briefly, AGS cells were subcutaneously injected into the dorsal side of mice blindly and randomly (n = 5 per group). | |||
Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 I (UBE2I/UBC9)
Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [43] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the circulatory system [ICD-11: BE2Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||
| Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species | hsa05208 | |||
| Cell Process | Oxygen species(ROS)-induced stress | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| In-vivo Model | For the ROS-induced DNA damage analysis, the indicated cell lines were treated with or without 100 uM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), or 80 uM Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) for 6 hours. For the in vivo ROS study, DMSO and 5 mg/kg CCCP was intraperitoneally injected in to three pairs of mice. | |||
| Response Summary | ROS promotes ALKBH5 SUMOylation through activating ERK/EPHB2/JNK signaling, leading to inhibition of ALKBH5 m6A demethylase activity by blocking substrate accessibility. Post-translational modification of ALKBH5 regulates ROS-induced DNA damage response. ROS specifically promotes ALKBH5 but not FTO, METTL3 and METTL14 SUMOylation by enhancing the interaction of ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 I (UBE2I/UBC9) and inhibiting the association between ALKBH5 and SENP1. | |||
Ubiquitin-like protein ATG12 (ATG12)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [100] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92.Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA)
Certain specified disorders of cornea [ICD-11: 9A78]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Certain specified disorders of cornea [ICD-11: 9A78.0] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-CS
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0F27 |
| In-vivo Model | General anesthesia in mice was induced by intraperitoneal injection of a 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution at 40 mg/kg. Excessive whiskers were trimmed, and topical anesthesia was performed using 0.5% proparacaine hydrochloride (Alcon, Geneva, Switzerland). A circular filter paper (2.0 mm × 2.0 mm) soaked with NaOH (1 mol/L) was attached to the central cornea of the right eye for 40 seconds to induce an alkali injury. Afterward, the paper was quickly removed, and the conjunctival sac was washed entirely with 0.9% sterile saline solution for one minute. Mice were then treated with ofloxacin eye drops twice daily for three days to prevent infection. Mice were randomly selected for three, seven, and 14 days or seven days after modeling, and their right corneas were harvested for subsequent experiments. | |||
Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [101] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gemcitabine | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| Capan-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0237 | |
| Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression sensitizes Pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine treatment, and it represses PDAC tumorigenesis by reducing m6A levels of Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1) and hindering activation of Wnt signaling. | |||
Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [103] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and metastasis | |||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| Normal cervical epithelium cell line (HCvEpC) (Isolated from cervical tissue) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | 200 uL PBS containing 1×107 cells of stable cells were subcutaneously injected into male BALB/c athymic nude mice (6-week old, 18-20 g). | |||
| Response Summary | The GAS5-AS1 expression in cervical cancer tissues was markedly decreased when compared with that in the adjacent normal tissues. GAS5-AS1 interacted with the tumor suppressor Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5), and increased its stability by interacting with RNA demethylase ALKBH5 and decreasing GAS5 N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification. m6A-mediated GAS5 RNA degradation relied on the m6A reader protein YTHDF2-dependent pathway. | |||
H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [104] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
H9c2(2-1) | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0286 |
| HEK293-A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6910 | |
KCNK15 and WISP2 antisense RNA 1 (KCNK15-AS1)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [105] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| Cell migration and invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 inhibits pancreatic cancer motility by demethylating lncRNA KCNK15 and WISP2 antisense RNA 1 (KCNK15-AS1). | |||
Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2598 (LINC02598/RP11)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [106] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of METTL3 upregulates Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2598 (LINC02598/RP11) expression in colorectal cancer cells. Overexpression of ALKBH5 downregulates RP11 expression. | |||
Small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 (SNHG3)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [108] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
microRNA 107 (MIR107)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [39] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell EMT | ||||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| Calu-6 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0236 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the experiments, mice were injected with 5 × 106 lung cancer cells with stably expression of relevant plasmids and randomly divided into indicated groups (five mice per group). To assess the in vivo effects of cycloleucine, the xenografted tumors had reached approximately 5 mm in diameter from mice and then these xenografted mice were feed with Vehicle or cycloleucine (25 mg/kg twice weekly) and tumor volume were measured every 3 day. Tumor volume was estimated as 0.5 × a2 × b (where a and b represent a tumors short and long diameter, respectively). Mice were euthanized after 7 weeks and the tumors were measured a final time. | |||
| Response Summary | m6A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing YTHDFs-mediated YAP expression and inhibiting microRNA 107 (MIR107)/LATS2-mediated YAP activity in non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
microRNA 21 (MIR21)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Pathway Response | FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | ||
In-vitro Model |
Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 plays an antitumor role in colorectal cancer by modulating the FOXO3/microRNA 21 (MIR21)/SPRY2 axis, which not only suggests a regulatory effect between ALKBH5 and FOXO3, but also provides a new therapeutic direction for colorectal cancer. | |||
microRNA 7-1 (MIR7-1)
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
In-vitro Model |
A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| CoC1 | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6891 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| In-vivo Model | SKOV3 or A2780 cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral vectors and injected (5 × 106 cells/mouse in 200 uL volume) subcutaneously into the left armpit of 6-week-old BALB/c nude mice. After 21 days, the animals were sacrificed to confirm the presence of tumors and weigh the established tumors. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is a tumor-promoting gene in epithelial ovarian cancer, which is involved in the mTOR pathway and microRNA 7-1 (MIR7-1)-Beclin1 complex. ALKBH5 activated EGFR-PIK3CA-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through microRNA 7-1 (MIR7-1) and BCL-2. | |||
miR-194-2
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [93] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 demethylated pri-miR-194-2 and inhibited miR-194-2 biogenesis through an m6A/DGCR8-dependent manner. ALKBH5/miR-194-2/RAI1 axis was also validated in clinical samples. This study revealed ALKBH5 in miRNAs biogenesis and provide novel insight for developing treatment strategies in esophageal cancer. | |||
hsa-miR-143-3p
Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [109] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Aortic aneurysm or dissection [ICD-11: BD50] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RNA degradation | hsa03018 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
In-vitro Model |
IM-HAEC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B5WL |
| In-vivo Model | Osmotic mini-pumps containing AngII (1 ug/kg/min, Enzo Bioche) were implanted in 7-week-old male mice. To interfere with the expression of KIAA1429, ALKBH5, or DDX6 in vivo, adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV9) vectors carrying a variety of overexpression plasmids or interfering RNA were randomly injected through the tail vein to C57BL/6N mice. | |||
| Response Summary | KIAA1429 is downregulated while ALKBH5 is upregulated in aortic tissues from aortic dissection patients. KIAA1429/ALKBH5-mediated m6A modifications can regulate the processing of hsa-miR-143-3p through interacting with the microprocessor protein DGCR8. KIAA1429 and ALKBH5 can oppositely regulate HASMC proliferation, HAEC apoptosis, and AD progression in AngII-infused mice via the miR-143-3p/DDX6 pathway. | |||
hsa-mir-181b-1
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [49] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell growth | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 |
| In-vivo Model | Three-week-old BABL/c female nude mice were randomized into three groups. 5 × 106 143B cells were subcutaneously injected in mice, and the tumor volume was assessed every 2 weeks. Eight weeks after injection, the animals were killed. The xenograft tumors were harvested and the tumor volumes were calculated by the standard formula: length × width2/2. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 is an anti-tumor factor or a pro-apoptotic factor, acting at least partially by suppressing YAP expression through dual mechanisms with direct m6A methylation of YAP and indirect downregulation of YAP level due to methylation of hsa-mir-181b-1. Further results revealed that m6A methylated pre-miR-181b-1 was subsequently recognized by m6A-binding protein YTHDF2 to mediate RNA degradation. However, methylated YAP transcripts were recognized by YTHDF1 to promote its translation. ALKBH5 overexpression was considered a new approach of replacement therapy for osteosarcoma treatment. | |||
hsa-miR-21-5p
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [110] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| HEK293-A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6910 | |
| Response Summary | In non-small cell lung cancer, m6A marks in mature hsa-miR-21-5p could directly affect its silencing potency towards target genes, which finally impaired its promotion to proliferation and motility. Depletion of the demethylase ALKBH5 altered the m6A abundance of miR-21-5p, thereby changing the expression levels of its target gene. | |||
hsa-miR-320a-3p
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis [ICD-11: CB03]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pulmonary Fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03.4] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
NIH 3T3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0594 |
| MRC-5 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0440 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the mouse model of miR-320a-3p overexpression, a total of 24 male C57BL/6 mice were divided randomly into four groups (n = 6 in each group): saline, silica, silica plus AAV9-miR-NC, and silica plus AAV9-miR-320a-3p. The mice in the silica plus AAV9-miR-NC/AAV9-miR-320a-3p groups were anesthetized using the same method, then administered intratracheally 50 uL AAV9-miR-NC/AAV9-miR-320a-3p per mouse at a titer of 8 × 1012 v. g./ml. Three weeks later, these mice were treated in the same way using anesthesia, saline, and silica as mentioned above. Subsequently, after 4 weeks, the mice were sacrificed, and the lungs were isolated and frozen at -80 ℃ for further study. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 promotes silica-induced lung fibrosis via the hsa-miR-320a-3p/FOXM1 axis or targeting FOXM1 directly. | |||
hsa_circ_0008542 (Circ_PHF12)
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system [ICD-11: FC0Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [111] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diseases of the musculoskeletal system [ICD-11: FC0Z] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
| MC3T3-E1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0409 | |
| In-vivo Model | Circ_0008542, where rats were injected with exosomes containing circ_0008542 into the tail vein for 8 weeks. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 acts on the m6A functional site of 1956 bp in hsa_circ_0008542. RNA demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits the binding of circ_0008542 with miRNA-185-5p to correct the bone resorption process. | |||
5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3A (HTR3A)
Pain disorders [ICD-11: 8E43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [112] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuropathic pain [ICD-11: 8E43.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Adipogenesis regulatory factor (ADIRF)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [113] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| H157 | Buccal mucosa squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2458 | |
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
Alpha-actinin-4 (ACTN4)
SARS-CoV-2 [ICD-11: XN109]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [114] | |||
| Responsed Disease | SARS-CoV-2 [ICD-11: XN109] | |||
In-vitro Model |
A549-ACE2 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C0Q5 |
| A549-ACE2 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C0Q5 | |
|
Vero C1008
|
N.A. | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0574 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
Atrial natriuretic peptide-converting enzyme (CORIN)
Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [115] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
BET1-like protein (BET1L)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [116] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous xenotransplantation, 3- to 4-week-old male BALB/c nude mice were randomly divided into groups (8 mice per group) and injected in the back flank with 100 μL of 1.0 × 107 suspended cells. | |||
C-C motif chemokine 28 (CCL28)
Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [117] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke [ICD-11: 8B11] | |||
| Responsed Drug | IOX1 | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mice (6-8 weeks, male) were subjected to unilateral renal pedicle clamping for 45 min. The animals were kept on a warm pad to maintain the constant body temperature (37 °C). Then the clamps were released for reperfusion. A sham operation was performed in a similar manner, except for clamping of the renal pedicles. Different groups of animals were euthanasia under isoflurane at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 120 h, and 4 weeks after ischemia. For CCL28 treatment, recombinant mouse CCL28 (50 μg/kg) were administrated through tail vein injection before surgery. For anti-CD25 treatment, PC61 mAb (10 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally 3 days prior to ischemia. For CCL28 antibody treatment, CCL28 antibody (100 μg/per mouse) were administrated through tail vein injection 2 h before surgery. For IOX1 (Selleck, USA) treatment, IOX1 (10 mg/kg) were administrated through tail vein injection before surgery. When determining the dosage of IOX1 in treating the IRI mice, we set a concentration gradient of 0 mg/kg, 2 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg to detect the most appropriate concentration of IOX1. | |||
CALML3 antisense RNA 1 (CALML3-AS1)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [118] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Cell division cycle-associated protein 4 (CDCA4)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [119] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H157 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0463 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| Calu-3 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0609 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the action of CDCA4, mice were set into Control, sh-NC, sh-CDCA4 groups, 6 mice/group. For the action of ALKBH5 in CDCA4, mice were set into oe-NC, oe-CDCA4, oe-CDCA4 + sh-NC, oe-CDCA4 + sh-ALKBH5 groups, 6 mice/group. In brief, 1 × 106/100 μL LLC cells were injected subcutaneously into the right flank of mice to establish a tumor model. LLC cells stably transfected with oe-NC, oe-CDCA4, oe-CDCA4 + sh-NC and oe-CDCA4 + sh-ALKBH5 were injected into each group of mice . | |||
Circ_AFF2
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [120] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0320 | |
| LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0399 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| NCM460 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0460 | |
Circ_PUM1
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [121] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-N-SH | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0531 |
| SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| SK-N-AS | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1700 | |
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (CDKN1C)
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [122] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1)
Pulmonary hypertension [ICD-11: BB01]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [123] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pulmonary arterial hypertension [ICD-11: BB01.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | The 8-week-old male Alkbh5 KI or Alkbh5 KO mice and their littermate WT mice were randomly exposed to either 21% oxygen (normoxia) or 10% oxygen (hypoxia) condition in a ventilated anoxic chamber (TOW-INT TECH Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China) for 4 weeks. The anoxic chamber was opened 2 times a week for 10 min each time for cheaning and refilling standard mouse chow and water. After 4 weeks of hypoxia period, the mice were anesthetized, hemodynamics were evaluated, followed by rapid removal of the heart and lungs at the end of the assessment. | |||
Diacylglycerol kinase eta (DGKH)
Secondary neurocognitive syndrome [ICD-11: 6E67]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [124] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Secondary neurocognitive syndrome [ICD-11: 6E67] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 1 (DUSP1)
Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1C41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [125] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1C41] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase DTX4 (DTX4)
Epstein Barr virus [ICD-11: XN0R2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [126] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Epstein Barr virus [ICD-11: XN0R2] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BJAB | Burkitt lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5711 |
| BL-41/95 | Burkitt lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C5V2 | |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase pellino homolog 2 (PELI2)
Unspecific body region injury [ICD-11: ND56]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [127] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cutaneous wound [ICD-11: ND56.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HaCaT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0038 |
Fatty acid-binding protein 5 (FABP5)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [128] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms [ICD-11: 2C10.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
QGP-1 | Pancreatic somatostatinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3143 |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor xenograft models, QGP-1cells (5 × 106) with ALKBH5 over-expression, ALKBH5 over-expression with FABP5 knockdown, and negative control were subcutaneously injected into the right axilla of female BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks). After 4 weeks, the mice were sacrificed via a form of euthanasia. | |||
Fatty-acid amide hydrolase 1 (FAAH)
Single episode depressive disorder, severe, without psychotic symptoms [ICD-11: 6A70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [129] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Major depressive disorder [ICD-11: 6A70.3] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [130] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Glutamate--cysteine ligase regulatory subunit (GCLM)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [131] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| ENSA (A human embryonic stem derived neural progenitor cell) | ||||
| NSC11 (Pluripotent derived neural progenitor cell) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Intracranial xenografts were generated by implanting 20,000 patient derived GSCs into the right cerebral cortex of mice at a depth of 3.5 mm. Housing conditions and animal status were supervised by a veterinarian. Euthanasia was taken until neurologic symptoms included hunched posture, gait changes, or lethargy were observed, at which point they were sacrificed. Brains were harvested and frozen at -80 °C with O.C.T. compound (4583, Tissue-Tek) directly or fixed in 4 % formaldehyde for 48 hours then stored in 70 % ethanol, and sectioned. | |||
Glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 (CHAC1)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [132] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| MKN1 | Gastric adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1415 | |
| MKN28 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1416 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
HBV encodes X protein (HBX)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [133] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Heparan Sulfate-Glucosamine 3-Sulfotransferase 3B1 Intronic Transcript 1 (HS3ST3B1-IT1)
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [134] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | 8-week-old male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into three groups: Ctrl+AAV-NC group (n=7), MIA+AAV-NC group (n=7), and MIA+ AAV-IT1 group (n=7). For the induction of OA, mice were given an intra-articular injection of MIA (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) in the knee. Control mice were given normal saline in the same volume. One week later, 20 μL of AAV-HS3ST3B1-IT1 or AAV-NC (GeneChem, Shanghai, China) were injected into the knee joints of mice. Treatments were administered once per week for 3 consecutive weeks. Six weeks later, the mice were euthanized, and the knee joints were collected and store at -80°C. | |||
Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A (KAT2A)
Cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [135] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43.7] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
hsa-miR-193a-3p
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [136] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 |
| Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 | |
| In-vivo Model | Stable cells were selected with 2 μg/ml puromycin for two weeks. Male athymic BALB/c nude mice (4-5 weeks old) were used. Subcutaneous tumor growth assays were used for growth assay. A total of 5 × 106 cells was subcutaneously injected into the nude mice (n = 3). The tumor volume was measured. The mice were sacrificed 4 weeks after injection. The tumor tissues were isolated and weighed. A tail vein injection model was used for metastasis assays. A total of 5 × 105 cells were injected into tail vein of nude mice (n = 3). | |||
hsa-miR-506-3p
Papillary Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: XH1ND9]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [137] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: XH1ND9] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| IHH-4 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2960 | |
| HTh83 | Thyroid gland anaplastic carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0046 | |
| KTC-1 | Thyroid carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6300 | |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
hsa_circ_0000417 (circ_CPSF6)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [138] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 | |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| B76.1/Huh7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U443 | |
| SNU-449 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0454 | |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
| L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| In-vivo Model | HCC cells stably transfected with empty vector or circCPSF6 were subject to construct animal models, followed by the regular treatment of verteporfin, an inhibitor of YAP signaling. | |||
| Response Summary | CircCPSF6 was dominated by ALKBH5-mediated demethylation, followed by the recognization and destabilization by YTHDF2. Meanwhile, circCPSF6 was upregulated in HCC specimens, and elevated hsa_circ_0000417 (circCPSF6) expression served as an independent prognostic factor for worse survival of patients with HCC. | |||
Inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPA)
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [140] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 |
| In-vivo Model | Leukemic BM cells (RFP+) isolated from primary RUNX1-RUNX1T1 and KITN822K leukemia mice were transduced with shNC or shAlkbh5 and 1 × 106 transduced cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated 6- to 8-week-old BALB/c recipient mice. The xenograft mouse model was established by injecting 1 × 106 Kasumi-1 cells expressing shNC or shALKBH5 into NOD scid gamma (NSG) mice via tail vein. For the human AML PDX models, 1 × 106 t (8;21) AML patient-derived bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMNCs) expressing shNC or shALKBH5 were transplanted into NSG recipient mice intravenously. | |||
Interleukin-17A (IL17A)
Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [141] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
JmjC domain-containing protein 8 (JMJD8)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [142] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
LOC4191
E. coli [ICD-11: XN6P4]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [143] | |||
| Responsed Disease | E. coli [ICD-11: XN6P4] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MAC-T
|
N.A. | Bos taurus | CVCL_U226 |
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 115 (LINC00115)
Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [144] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C6Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Acetaminophen | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (CD58)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [145] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-3, mitochondrial (SIRT3)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [146] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 | |
| Ect1/E6E7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3679 | |
| In-vivo Model | The animals were maintained in pathogen-free conditions at 21°C ± 2°C and 55% ± 5% humidity with free access to food and water. Mice were randomly divided into three groups (n = 8 per group) and received a subcutaneous injection of 2 × 106 stably transfected SiHa cells containing the indicated lentivirus (empty, Lv-ALKBH5, Lv-ALKBH5 + Lv-ACC1) diluted in PBS in the left flank. The mice were sacrificed when tumours were apparent on day 30. Tumour volume was recorded 7, 14, 21 and 28 days after injection with a Vernier calliper. After euthanasia, xenografts were excised from mice and weighed. | |||
Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 (TYK2)
Epstein Barr virus [ICD-11: XN0R2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [126] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Epstein Barr virus [ICD-11: XN0R2] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BJAB | Burkitt lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5711 |
| BL-41/95 | Burkitt lymphoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C5V2 | |
Osteopontin (SPP1)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [147] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Carboplatin | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
SK-N-SH | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0531 |
| SK-N-BE(2) | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0528 | |
| SK-N-BE(2)-C | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0529 | |
| SK-N-AS | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1700 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [147] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Etoposide | Approved | ||
In-vitro Model |
SK-N-SH | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0531 |
| SK-N-BE(2) | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0528 | |
| SK-N-BE(2)-C | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0529 | |
| SK-N-AS | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1700 | |
Placenta-specific gene 8 protein (PLAC8)
Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [148] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HTR-8/SVneo | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7162 |
Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM1)
Certain specified disorders of cornea [ICD-11: 9A78]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [74] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Certain specified disorders of cornea [ICD-11: 9A78.0] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HUVEC-CS
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0F27 |
| In-vivo Model | General anesthesia in mice was induced by intraperitoneal injection of a 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution at 40 mg/kg. Excessive whiskers were trimmed, and topical anesthesia was performed using 0.5% proparacaine hydrochloride (Alcon, Geneva, Switzerland). A circular filter paper (2.0 mm × 2.0 mm) soaked with NaOH (1 mol/L) was attached to the central cornea of the right eye for 40 seconds to induce an alkali injury. Afterward, the paper was quickly removed, and the conjunctival sac was washed entirely with 0.9% sterile saline solution for one minute. Mice were then treated with ofloxacin eye drops twice daily for three days to prevent infection. Mice were randomly selected for three, seven, and 14 days or seven days after modeling, and their right corneas were harvested for subsequent experiments. | |||
Polyamine-transporting ATPase 13A3 (ATP13A3)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [149] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCoEpiC (Healthy colon epithelial HCoEpiC cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | The nude mice were randomly assigned to two groups consisting of six mice each. We injected transformed cells (P0 and P40) into the flank of each mouse in 0.1 mL of sterile PBS to form xenograft tumors. The tumor volume was measured every 2 or 3 days (volume = length × width2 × 1/2). The tumors were resected, imaged, and weighed after the mice were sacrificed. One piece of each tumor tissue was fixed in 4% (v/v) paraformaldehyde for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining, and the remaining tissue was stored at -80 °C. | |||
Procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 2 (PLOD2)
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [150] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
GC-2spd(ts)
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_6633 |
| In-vivo Model | 20 adult male Wistar rats (180-200 g) were purchased from the Guangdong Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention. A 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle was maintained for the animals and they were fed standard food pellets and water as needed. | |||
Progestin and adipoQ receptor family member 4 (PAQR4)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [151] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
In-vitro Model |
LM3 | Malignant neoplasms | Mus musculus | CVCL_D269 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HLF | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2947 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous xenograft model, 1 × 106 tumor cells were resuspended in 100 μL of DMEM and then injected into the axilla of each mouse (n = 5 mice per group). The mice were sacrificed after 2 weeks, the tumor weight was recorded, and the tumor volume was calculated according to the following equation: volume = 1/2*(length × width2). After the experiment, the specimens were fixed with 4% formaldehyde. For the intrahepatic tumor implantation model, 1 × 106 tumor cells were resuspended in 100 μL of DMEM and then inoculated under the capsule of the right lobe of the liver (n = 5 mice per group). The mice were sacrificed after 4 weeks, and the tumors were removed and subjected to HE staining. | |||
Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 6 (PRMT6)
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [152] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
LNCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0395 |
| HNC PC3 | Retromolar trigone squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C8XA | |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| 22Rv1 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1045 | |
Protein E6 (E6)
Malignant neoplasms of tonsil [ICD-11: 2B69]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [153] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant neoplasms of tonsil [ICD-11: 2B69] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
WSU-HN26 | Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5523 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| C33A2 (The C33A2 cell line originates from C33A and has the subgenomic HPV16 plasmid pBELsLuc stably integrated into the genome) | ||||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of the ALKBH5 promoted production of intron retention on the human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) Protein E6 (E6) mRNAs thereby promoting E6 mRNA production. METLL3 induced production of intron-containing HPV16 E1 mRNAs over spliced E2 mRNAs and altered HPV16 L1 mRNA splicing in a manner opposite to ALKBH5. Overexpression of YTHDC1, enhanced retention of the E6-encoding intron and promoted E6 mRNA production. HPV16 mRNAs are m6A-methylated in tonsillar cancer cells. | |||
Protein flightless-1 homolog (FLII)
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [154] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
RWPE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3791 |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor growth measurement, 5 × 106 stably transfected 22RV1 cells were subcutaneously injected into mice at the flank site. Then, the volume (V) of xenograft tumors was examined once per week as follows: V = length × width2/2. After 4 weeks, the mice were euthanized via intraperitoneal injection of 150 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium, and the tumors were taken out and weighed, and collected for immunohistochemistry (IHC) to examine the expression of the proliferation marker Ki67 (1:200, ab16667, Abcam) in xenograft tumors. For tumor metastasis measurement, 5 × 106 stably transfected 22RV1 cells were injected into mice through tail vein. | |||
Pseudorabies Virus (PRV)
Rabies [ICD-11: 1C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [155] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rabies [ICD-11: 1C82] | |||
| Responsed Drug | 3-deazidenosine | Investigative | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
PK-15
|
N.A. | Sus scrofa | CVCL_2160 |
Putative E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR7 (UBR7)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [156] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
RAS protein activator like-3 (RASAL3)
DOX-induced cardiotoxicity [ICD-11: BA00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [157] | |||
| Responsed Disease | DOX-induced cardiotoxicity [ICD-11: BA00.Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Doxil | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Ras-related protein Rab-5A (RAB5A)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [158] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Briefly, 4 × 106 transfected HCT116 cells or 8 × 106 transfected SW480 cells in 0.1 mL PBS were injected into mice subcutaneously, and these mice were randomly divided into the experimental and control group. | |||
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 (ERBB4)
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [159] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Col1alpha2creER mice were crossed with ALKBH5flox/flox mice (Cyagen, China) to generate mice heterozygous for both alleles. Then ALKBH5flox/flox mice and heterozygous mice from the first cross produced ALKBH5flox/floxCol1alpha2creER mice, which were used in experiments. The 6-week-old ALKBH5flox/floxCol1alpha2creER mice were administration intraperitoneal injection of the tamoxifen suspension (30 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich) for 7 days. The ALKBH5flox/flox mice and Col1alpha2creER mice as control were injected in in the same manner. | |||
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor TIAM1 (TIAM1)
Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [160] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 |
| IHH-4 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2960 | |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| In-vivo Model | Seven-week nude mice (male) were obtained from Hunan SJA Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd (Hunan, Changsha) and housed under artificial light for 12 h during the day followed by 12-h dark period at night with free access to food and water. Animal procedures complied with the guidelines of the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. Stable ALKBH5-overexpressed BCPAP cells were injected subcutaneously into the left flank of nude mice. After 5 weeks of inoculation, tumors were removed and weighted, and tumor size was measured every week. Xenograft tumors were lysed in RIPA buffer and the subjected for qRT-PCR and western blot detection of ALKBH5, TIAM1, Nrf2, and HO-1 as mentioned above. | |||
RNA component of 7SK nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RN7SK)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [161] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H23 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1547 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H2009 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1514 | |
| MRC-5 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0440 | |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 (PAK5)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [162] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
| In-vivo Model | Tumor xenograft models were established, with each group consisting of 5 mice (n = 5 per group), including ALKBH5, ALKBH5/shPAK5, NC, shCon, shPAK5, shALKBH5, and shALKBH5. Subcutaneous injections of stably transfected HeLa cells (2.0 × 106 cells) were administered into the armpit region of the nude mice. The tumor volume was regularly monitored using the formula: volume = 0.5 × length × width2. After 5 weeks, the mice were euthanized and the weight of tumor was measured. In the lung metastasis models, which were conducted in nude mice, the groups consisted of 5 mice per group, similar to the tumor xenograft models. In these models, HeLa cells (2.0 × 106) that had been stably transfected were injected into the mice through the tail vein. After 5 weeks, the mice were euthanized. The lung tissues were excised, photographed, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for H&E staining. | |||
SLAM family member 7 (SLAMF7)
Silicosis [ICD-11: CA60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [163] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Silicosis [ICD-11: CA60.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male C57BL/6 mice (6-8 weeks, 20-22 g) were supplied by Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention (Wuhan, China) and housed in the observation room. The mice were fed and kept under strict conditions of 22-26 °C, a standard 12 h light/dark cycle and 50 ± 5% relative humidity for 7 days to adapt to the conditions. Before the interventions, the mice were anesthetized with Chloral hydrate and divided into two groups at three time points: control mice were intratracheally instilled with 50 μL of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and the silica-exposed group contained 50 μL of 50 mg/mL (2.5 mg) silica particles. Then, the mice were sacrificed by anesthesia on 7, 28 and 84 days after silica treatment, and the lung tissues and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were harvested for further study. | |||
small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15)
Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [164] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.1] | |||
In-vitro Model |
RPMI-8226 | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0014 |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 1 × 107 cotransfected RPMI8226 MM cells, control RPMI8226 MM cells (shNC + LV-NC), ALKBH5-depleted RPMI8226 MM cells (shALKBH5 + LV-NC), or ALKBH5-depleted-SNHG15-overexpressed RPMI8226 MM cells (shALKBH5 + LV-SNHG15), were subcutaneously injected into the right flanks of the 4-wk-old male NOD/SCID mice (n = 6 for each group) to establish a human MM-xenografted model. Tumor growth was monitored every 3 days. The mice were euthanized after 4 wk, and tumors were measured (Tumor volume = 3.14/6 × length × width2) and harvested. | |||
Splicing factor 3B subunit 1 (SF3B1)
Leukemogenesis [ICD-11: 2A82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [165] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukemogenesis [ICD-11: 2A82] | |||
Suppressor of tumorigenicity 14 protein (ST14)
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [159] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Col1alpha2creER mice were crossed with ALKBH5flox/flox mice (Cyagen, China) to generate mice heterozygous for both alleles. Then ALKBH5flox/flox mice and heterozygous mice from the first cross produced ALKBH5flox/floxCol1alpha2creER mice, which were used in experiments. The 6-week-old ALKBH5flox/floxCol1alpha2creER mice were administration intraperitoneal injection of the tamoxifen suspension (30 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich) for 7 days. The ALKBH5flox/flox mice and Col1alpha2creER mice as control were injected in in the same manner. | |||
SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 (SMARCA5)
Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [167] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71] | |||
Taurine up-regulated 1 protein (TUG1)
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [168] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2)
Hypopharyngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2B6D]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [169] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6D.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
FaDu | Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1218 |
| Detroit 562 | Pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1171 | |
| In-vivo Model | HPSCC FaDu or Detroit 562 cells (1 × 106 cells) expressing vector control and construct lentiviruses were subcutaneously injected into the right flanks of 4-week-old male nude mice. Tumor diameters and body weight were recorded every 3 days for 1-6 weeks. Detroit 562 and FaDu cells (1 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into the right flanks of 4-week-old male nude mice. | |||
Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 (JAK1)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [170] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BGC-823 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 |
| In-vivo Model | BGC-823 (3 × 106) cells that stably expressed or silenced ALKBH5 and LINC00659 and their paired control cells were injected into the left side of each mouse. For cell metastasis experiments in vivo, BGC-823 (3 × 106) cells that stably overexpressed or silenced ALKBH5 and LINC00659 and their paired control cells were injected through tail vein. | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Viral infections [ICD-11: 1D9Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [171] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Viral infections [ICD-11: 1D9Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Response Summary | m6A is the most abundant internal modification described in eukaryotic mRNA and several viral RNA including human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) infection. METTL3/METTL14 m6A writer complex plays a negative role in HRSV infections protein synthesis and viral titers, while m6A erasers FTO and ALKBH5 had the opposite effect. | |||
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [172] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
| Pathway Response | DNA replication | hsa03030 | ||
| Cell Process | Homologous recombination | |||
In-vitro Model |
GBMSCs (Glioblastoma stem cells) | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 contributes to the aggressiveness of GBM by favoring the invasion of GBMSCs. | |||
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [174] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Summary | In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients, a majority of highly expressed m6A regulatory genes is associated with poor OS, in particular ALKBH5, whereas YTHDC2 was associated with better prognosis. | |||
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [175] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and invasion | |||
In-vitro Model |
KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1348 |
| Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6898 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 as a demethylase was lowly expressed in cancer progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and acts as a crucial component in ESCC progression. | |||
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [177] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Pathway Response | Proteoglycans in cancer | hsa05205 | ||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| MKN45 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 2×106 tumor cells were suspended in 200 uL of PBS and injected the right flank of nude mice. The tumor sizes were measured weekly as soon as the tumors were measurable, and the tumor volumes were calculated using the following formula: volume (mm3) = width2 (mm2) × length (mm)/2. After 4 weeks, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumors were harvested. | |||
| Response Summary | NcRNA, lncNRON, exhibits oncogenic roles in the progression of gastric cancer. NRON, as a possible additional regulatory subunit of the m6A eraser, strengthens the m6A recognition of RNAs by m6A eraser ALKBH5 to enhance Nanog mRNA stability and expression. | |||
Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [178] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| HCT 8 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2478 | |
| RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the animal studies, 6-week-old male athymic BALB/c nude mice were implanted with modified ALKBH5 expressing Hct116 or RKO cells (105/ml, 200 ml) via lateral tail vein injection. All the mice were killed after 6 weeks, and the lungs were subjected to H&E staining. | |||
| Response Summary | The tumor repressive role of ALKBH5 in colon cancer. ALKBH5 was downregulated in human colon cancer tissues, where its decreased expression significantly correlated with distant metastasis and American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage. | |||
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [179] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Pathway Response | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||
| Cell Process | Ubiquitination degradation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCCLM3 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6832 |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| THLE-2 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3803 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 5×106 control and CASC11 overexpressing Huh7 cells were suspended in the 100 uL serum-free DMEM medium and then injected subcutaneously. For the metastatic model, 1×105 control and CASC11 overexpressing Huh7 cells were suspended in the 50 uL serum-free DMEM medium, followed by being injected into the tail vein of nude mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In hepatocellular carcinoma, CASC11 decreased UBE2T N6-methyladenosine (m6A) level via recruiting ALKBH5. CASC11 inhibited the association between UBE2T mRNA and m6A reader protein YTHDF2. | |||
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [180] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Response Summary | The m6A-demethylases ALKBH5 and FTO are dysregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and could be used as prognostic biomarkers. ALKBH5 mRNA, as well as ALKBH5 and FTO protein expressions, was significantly downregulated in ccRCC compared to normal tissue and most of the other studied tumour entities. | |||
Lupus erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [181] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lupus erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40] | |||
In-vitro Model |
PBMCs (Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are isolated from peripheral blood and identified as any blood cell with a round nucleus) | |||
| Response Summary | Functionally, the overexpression of ALKBH5 promoted apoptosis and inhibited the proliferation of T cells. ALKBH5 expression is downregulated in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and could affect the apoptosis and proliferation of T cells. | |||
Presbycusis [ICD-11: AB54]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [183] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Presbycusis [ICD-11: AB54] | |||
Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [184] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemic heart disease [ICD-11: BA40-BA6Z] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HL-1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0303 |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 18 mice were randomly divided into 2 groups, a sham group (n=9), and a MIRI group (n=9). Operators were blinded to the allocation. The MIRI mice were established by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery. After peritoneal anesthesia with 1% pentobarbital sodium, surgical incisions were made between the third and fourth sternal intercostals to expose the heart. The left anterior descending coronary artery was identified under the microscope, and the left atrial appendage was ligated at the 1 cm lower margin with a suture needle to induce ischemia for 30 minutes. Then, the slip knot was unwound for 24 h of reperfusion. The sham group was not ligated. No unexpected adverse events were observed and animals were not excluded. Myocardium and peripheral blood were collected after the mice were sacrificed at 24 h reperfusion. Each group was analyzed in at least 3 independent experiments, which made the group size of each experiment 3. | |||
| Response Summary | The downregulated ALKBH5 contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury(MIRI) process by increasing the m6A modification of Trio mRNA and downregulating Trio. | |||
Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [185] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z] | |||
| Pathway Response | PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | ||
| Cell Process | Fatty degeneration | |||
| In-vivo Model | A total of 24 male mice were randomly allocated to LFD (low-fat diet), LFDR (low-fat diet + resveratrol), HFD (high-fat diet), and HFDR (high-fat diet + resveratrol) groups for 12 weeks (n = 6/group). | |||
| Response Summary | The beneficial effect of resveratrol on lipid metabolism disorder under HFD is due to a decrease of m6A RNA methylation and an increase of PPARalpha mRNA, providing mechanistic insights into the function of resveratrol in alleviating the disturbance of lipid metabolism in mice. The resveratrol in HFD increased the transcript levels of methyltransferase like 3 (METTL3), alkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5), fat mass and obesity associated protein (FTO), and YTH domain family 2 (YTHDF2), whereas it decreased the level of YTH domain family 3 (YTHDF3) and m6A abundance in mice liver. | |||
Menopausal disorder [ICD-11: GA30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [186] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Premature ovarian failure [ICD-11: GA30.6] | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
Hgc (Primary human ovarian granulosa cells) | |||
| In-vivo Model | To build the mouse model for POI, cyclophosphamide (CTX) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) was used a high-dose treatment (120 mg/kg, 2 weeks). | |||
| Response Summary | The decreased mRNA and protein expression levels of FTO are responsible for the increase in m6A in POI, which can further increase the risk of complications of POI. FACS was used to measure the levels of proliferation and apoptosis, and siRNA was used to establish FTO and ALKBH5 knockdown cell lines. The m6A content in the RNA from POI patients and POI mice was significantly higher than control groups and that POI was characterized by the content of m6A. | |||
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [187] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
GC-1 spg | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_8872 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mouse GC-1 spg cells were treated with the ester form of meclofenamic acid (MA2) to inhibit the demethylase activity of FTO. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, METTL14, ALKBH5 and YTHDC2 are involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis. MA2 affected CDKs expression through the m6A-dependent mRNA degradation pathway, and thus repressed spermatogonial proliferation. Additionally, mutation of the predicted m6A sites in the Cdk2-3'UTR could mitigated the degradation of CDK2 mRNA after MA2 treatment. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [188] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Arrest of spermatogenesis [ICD-11: GB04.Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| Response Summary | A knockout of the Alkbh5 gene in mice resulted in impaired male fertility due to compromised spermatogenesis. | |||
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
 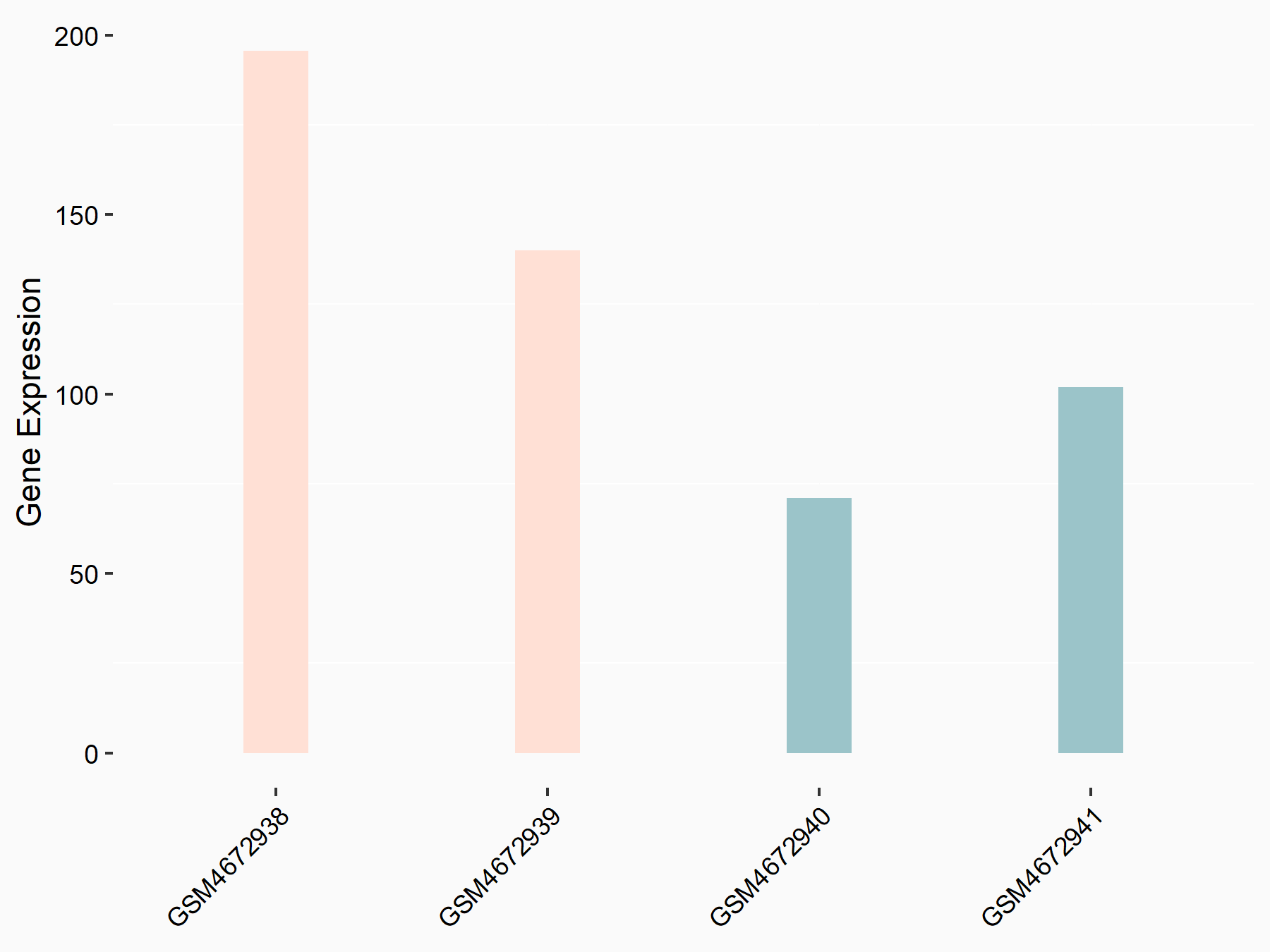 |
logFC: 9.58E-01 p-value: 1.09E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
MK22606
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ossification of spinal ligaments | ICD-11: FA83 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Ossification | |||
| In-vitro Model | Ligamentum flavum cells (Ligamentum flavum cells) | |||
| Response Summary | The overexpression of ALKBH5 led to the activation of p-AKT, and Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) was regulated by ALKBH5 through the AKT signaling pathway. ALKBH5 promoted the osteogenesis of the ligamentum flavum cells through BMP2 demethylation and AKT activation. MK22606 is an AKT inhibitor. Moreover, when ALKBH5 was knocked down in the ligamentum flavum cells, p-AKT was inhibited when compared with that in the overexpressed ALKBH5 and control groups. | |||
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | HaCAT cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 HaCAT cells
Control: siControl HaCAT cells
|
GSE211076 | |
| Regulation |
 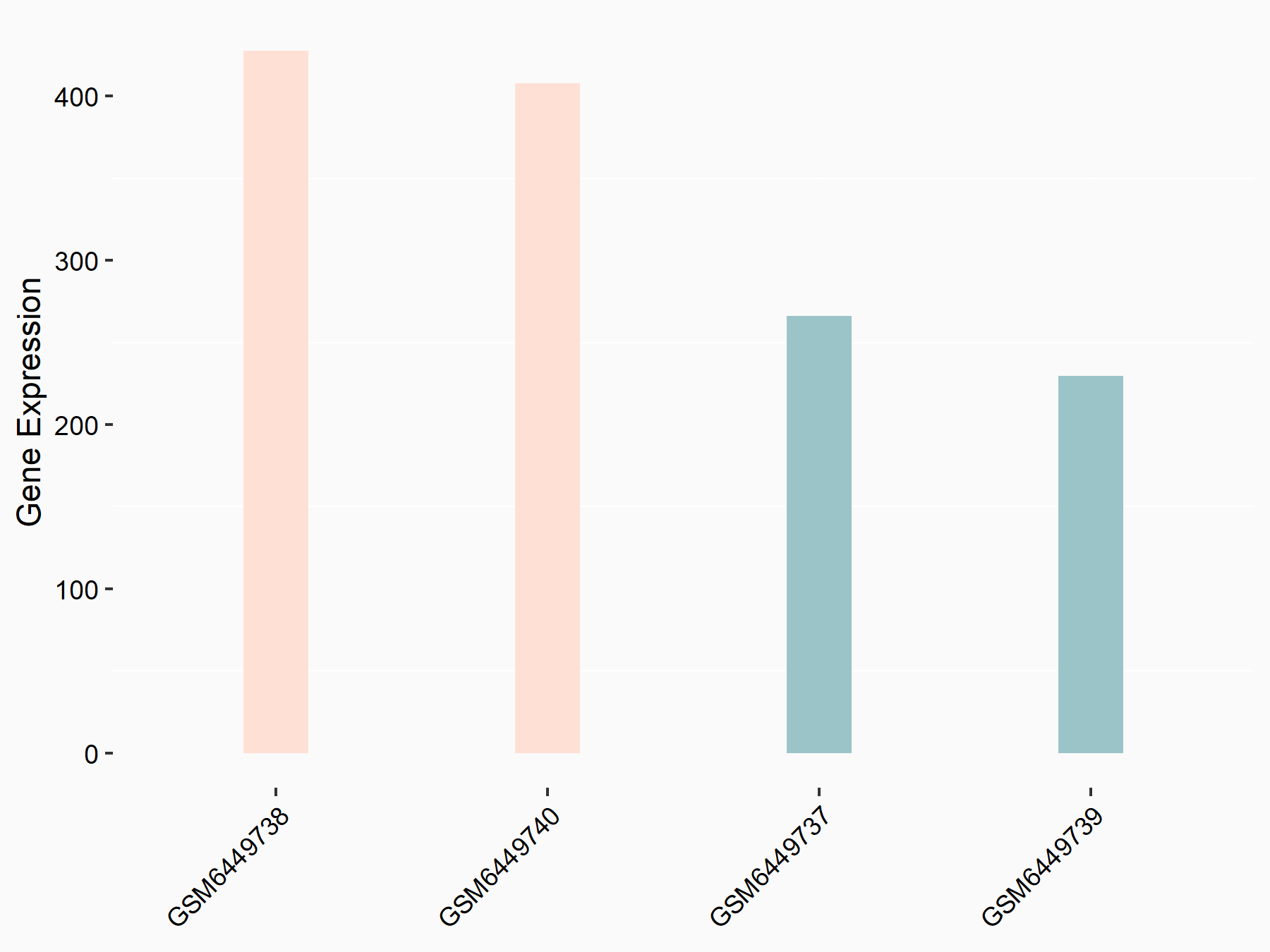 |
logFC: 7.57E-01 p-value: 2.32E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Doxil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| HCC1937 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0290 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneously transplanted tumor model, wild-type, PRMT5-overexpressing or doxorubicin-resistant MDA-MB-231 cells (5 × 106 per mouse, n = 5-7 for each group) were diluted in 100 uL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) plus 100 uL of Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and subcutaneously injected into female nude mice to investigate tumor growth. When all tumor volumes reached 100 mm3, the mice were randomly assigned and treated with the indicated drugs. In the experiment, doxorubicin was administered once a week via intravenous tail vein injection at 2 mg/kg body weight, and tadalafil was administered daily via oral gavage at 2 mg/kg body weight. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days using a digital caliper and calculated using the formula V = 1/2 × (diameter) × (smaller diameter)2. The mice were euthanized 27 days after injection. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 removed the m6A methylation of Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1) for mRNA stabilization and further enhanced DNA repair competency to decrease doxorubicin efficacy in breast cancer cells. | |||
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
 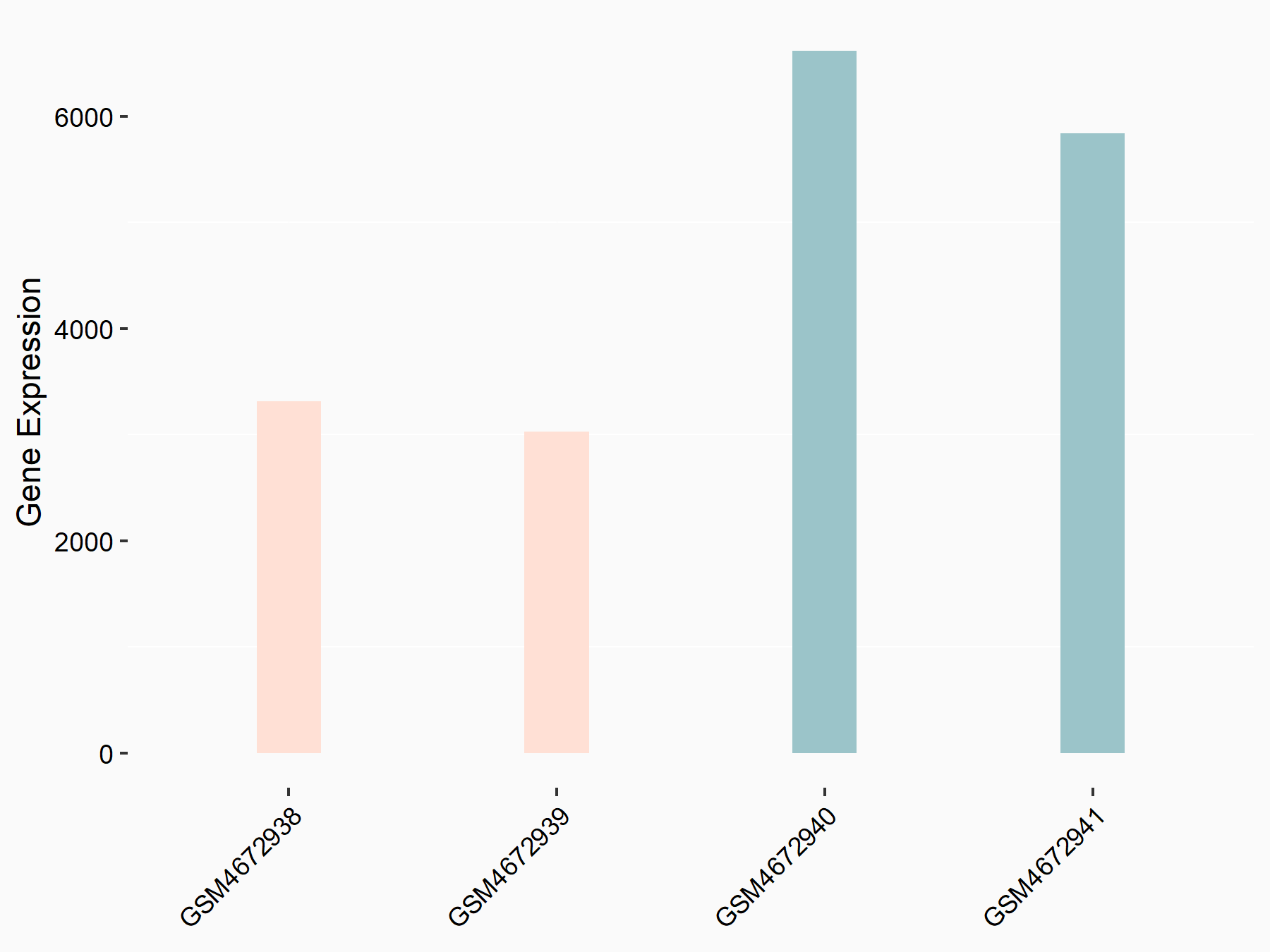 |
logFC: -9.73E-01 p-value: 3.10E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
MK22606
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ossification of spinal ligaments | ICD-11: FA83 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
| Cell Process | Ossification | |||
| In-vitro Model | Ligamentum flavum cells (Ligamentum flavum cells) | |||
| Response Summary | The overexpression of ALKBH5 led to the activation of RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1), and BMP2 was regulated by ALKBH5 through the AKT signaling pathway. ALKBH5 promoted the osteogenesis of the ligamentum flavum cells through BMP2 demethylation and AKT activation. MK22606 is an AKT inhibitor. Moreover, when ALKBH5 was knocked down in the ligamentum flavum cells, p-AKT was inhibited when compared with that in the overexpressed ALKBH5 and control groups. | |||
Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 (JAK2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
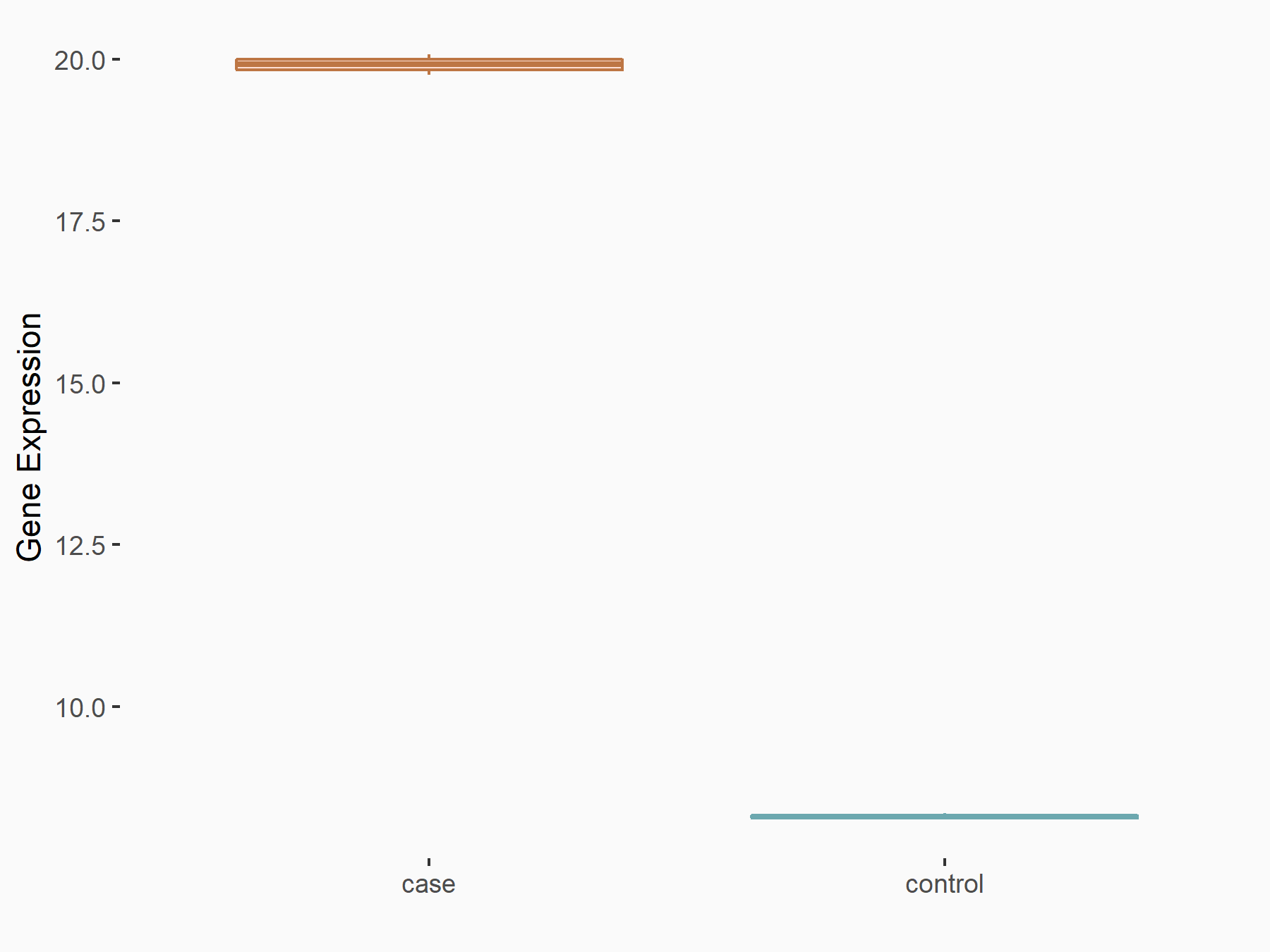  |
logFC: 1.17E+00 p-value: 2.74E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [52] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary | ICD-11: 2B5D.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HO8910-DDP (HO8910 underwent continuous stepwise exposure to increasing concentrations of cisplatin to create the cisplatin-resistant cell lines HO8910-DDP) | |||
| HO-8910 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6868 | |
| A2780-DDP (A2780 underwent continuous stepwise exposure to increasing concentrations of cisplatin to create the cisplatin-resistant cell line) | ||||
| A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 | |
| In-vivo Model | About 5× 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the axilla of the female athymic BALB/C nude mice (4 week-old, 18-20 g). When the average tumor size reached approximately 100mm3 (after 1 week), mice were then randomized into two groups and treated with cisplatin (5 mg/kg) or normal saline (NS) weekly. | |||
| Response Summary | The ALKBH5-HOXA10 loop jointly activates the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway by mediating Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 (JAK2) m6A demethylation, promoting epithelial ovarian cancer resistance to cisplatin. | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
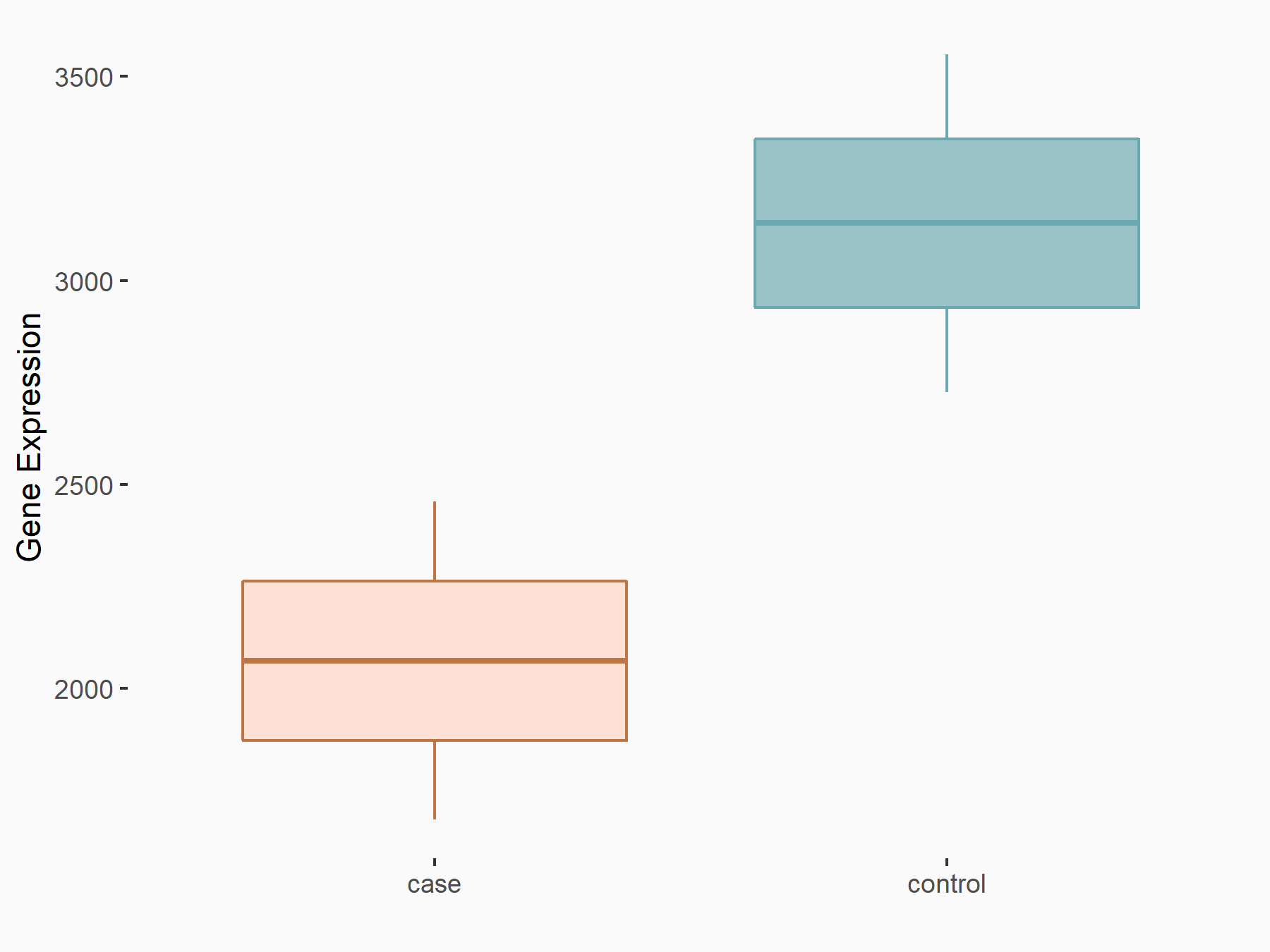  |
logFC: -6.03E-01 p-value: 1.12E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Dexamethasone
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma | ICD-11: 2A90 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
Glucocorticoid
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [54] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma | ICD-11: 2A90 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2)
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [66] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010) | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
| In-vitro Model | UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| 253J | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7935 | |
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
| Response Summary | Knockdown of ALKBH5 promoted bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and decreased cisplatin chemosensitivity, ALKBH5 inhibited the progression and sensitized bladder cancer cells to cisplatin through a Casein kinase II subunit alpha' (CSNK2A2)-mediated glycolysis pathway in an m6A-dependent manner. | |||
Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1)
Doxil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [75] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C6Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| In-vivo Model | 6-week old immunodeficient mice (Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center, Guangzhou, China) were selected for generating a subcutaneous xenograft model. MDA-MB-231/DOX cells were implanted subcutaneously into the immunodeficient mice. 7 days later, mice were randomly divided into 4 groups, administrated with vehicle control, FOXO1 inhibitor AS1842856 (20 mg/kg/day, i. p.), Doxorubicin (5 mg/kg/day, i. p.), and AS1842856 combined with Doxorubicin, respectively. Tumor formation was examined every 4 days. | |||
Frizzled-10 (FZD10)
PARPi
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [76] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Malignant mixed epithelial mesenchymal tumour of ovary | ICD-11: 2B5D.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| In-vitro Model | UWB1.289 | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B079 |
| PEO1 | Ovarian cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2686 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 107 PARP inhibitor resistant PEO1 cells were suspended in 200 uL PBS : Matrigel (1:1) unilaterally injected subcutaneously into the right dorsal flank of 6-8 week-old female immunocompromised non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD/SCID) gamma (NSG) mice. When the average tumor size reached ~100 mm3, the mice were then randomized into four groups and treated with vehicle control, Olaparib (50 mg/kg), XAV939 (5 mg/kg) or a combination daily for 18 days. | |||
| Response Summary | Downregulation of m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 was sufficient to increase Frizzled-10 (FZD10) mRNA m6A modification and reduce PARPi sensitivity, the finding elucidates a novel regulatory mechanism of PARPi resistance in EOC by showing that m6A modification of FZD10 mRNA contributes to PARPi resistance in BRCA-deficient EOC cells via upregulation of Wnt/Bete-catenin pathway. | |||
Homeobox protein NANOG (NANOG)
Temozolomide
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [81] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cellular Processes | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| U251 (Fibroblasts or fibroblast like cells) | ||||
| U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | U251/TR cells (2 × 106 per mouse) with stable transfection of sh-circ_0072083 or sh-NC were subcutaneously injected into mice. | |||
| Response Summary | In glioma, hsa_circ_0072083 could regulate Homeobox protein NANOG (NANOG) and ALKBH5 via targeting miR-1252-5p to control temozolomide resistance. circ_0072083 silence reduced NANOG expression via blocking ALKBH5-mediated demethylation. | |||
Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1)
4-Vinylcyclohexene diepoxide
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [97] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Premature ovarian failure | ICD-11: GA30.6 | ||
| In-vitro Model | COV434 | Ovarian small cell carcinoma, hypercalcemic type | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2010 |
Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO (AXL)
Chlorogenic acid
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [99] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | ICD-11: DB92 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | AML12 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0140 |
| THLE-2 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3803 | |
Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1)
Gemcitabine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [101] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| In-vitro Model | AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| Capan-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0237 | |
| Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression sensitizes Pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine treatment, and it represses PDAC tumorigenesis by reducing m6A levels of Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1) and hindering activation of Wnt signaling. | |||
C-C motif chemokine 28 (CCL28)
IOX1
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [117] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute ischemic stroke | ICD-11: 8B11 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mice (6-8 weeks, male) were subjected to unilateral renal pedicle clamping for 45 min. The animals were kept on a warm pad to maintain the constant body temperature (37 °C). Then the clamps were released for reperfusion. A sham operation was performed in a similar manner, except for clamping of the renal pedicles. Different groups of animals were euthanasia under isoflurane at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 120 h, and 4 weeks after ischemia. For CCL28 treatment, recombinant mouse CCL28 (50 μg/kg) were administrated through tail vein injection before surgery. For anti-CD25 treatment, PC61 mAb (10 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally 3 days prior to ischemia. For CCL28 antibody treatment, CCL28 antibody (100 μg/per mouse) were administrated through tail vein injection 2 h before surgery. For IOX1 (Selleck, USA) treatment, IOX1 (10 mg/kg) were administrated through tail vein injection before surgery. When determining the dosage of IOX1 in treating the IRI mice, we set a concentration gradient of 0 mg/kg, 2 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg to detect the most appropriate concentration of IOX1. | |||
Glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 (CHAC1)
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [132] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| MKN1 | Gastric adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1415 | |
| MKN28 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1416 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
hsa_circ_0003552 (Circ_MOCOS)
Benzo[a]pyrene
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [139] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 115 (LINC00115)
Acetaminophen
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [144] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C6Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Osteopontin (SPP1)
Carboplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [147] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuroblastoma | ICD-11: 2A00.11 | ||
| In-vitro Model | SK-N-SH | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0531 |
| SK-N-BE(2) | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0528 | |
| SK-N-BE(2)-C | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0529 | |
| SK-N-AS | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1700 | |
Etoposide
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [147] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Neuroblastoma | ICD-11: 2A00.11 | ||
| In-vitro Model | SK-N-SH | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0531 |
| SK-N-BE(2) | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0528 | |
| SK-N-BE(2)-C | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0529 | |
| SK-N-AS | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1700 | |
Pseudorabies Virus (PRV)
3-deazidenosine
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [155] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rabies | ICD-11: 1C82 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model |
PK-15
|
N.A. | Sus scrofa | CVCL_2160 |
RAS protein activator like-3 (RASAL3)
Doxil
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [157] | |||
| Responsed Disease | DOX-induced cardiotoxicity | ICD-11: BA00.Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Ethyl ester form of meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [187] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility | ICD-11: GB04 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell cycle | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In-vitro Model | GC-1 spg | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_8872 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Mouse GC-1 spg cells were treated with the ester form of meclofenamic acid (MA2) to inhibit the demethylase activity of FTO. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3, METTL14, ALKBH5 and YTHDC2 are involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis. MA2 affected CDKs expression through the m6A-dependent mRNA degradation pathway, and thus repressed spermatogonial proliferation. Additionally, mutation of the predicted m6A sites in the Cdk2-3'UTR could mitigated the degradation of CDK2 mRNA after MA2 treatment. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
RNA modification
m6A Target: Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00415 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00416 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00449 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 214 (MIR214) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00513 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-mir-18a | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00417 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00418 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00463 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 149 (MIR149) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00464 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyltransferase-like protein 1 (METTL1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 149 (MIR149) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m7G → m6A | |
m6A Target: Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00434 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methyltransferase-like protein 1 (METTL1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 125a (MIR125A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m7G | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00439 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 214 (MIR214) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00473 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 181a-1 (MIR181A1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00475 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 155 (MIR155) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
m6A Target: Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00450 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 214 (MIR214) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00522 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 221 (MIR221) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00557 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00535 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 26a-1 (MIR26A1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
m6A Target: pri-miR-143
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00568 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00571 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m6Am | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00574 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00577 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit DKC1 (DKC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Pseudouridine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00580 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA cytosine C(5)-methyltransferase NSUN2 (NSUN2) | |
| Regulated Target | H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
m6A Target: hsa-mir-181b-1
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00678 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6Am → m6A | |
DNA modification
m6A Target: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02025 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Transcription factor E4F1 (E4F1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
| Disease | Intervertebral disc degeneration | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor SOX-2 (SOX2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02034 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 (SMAD7)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02035 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02036 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Ubiquitin-like protein ATG12 (ATG12)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02110 | ||
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02134 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11 (STK11/LKB1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02135 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO (AXL)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02276 | ||
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | |
| Drug | Chlorogenic acid (CGA) | |
Histone modification
m6A Target: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03005 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4A (KDM4A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Intervertebral disc degeneration | |
m6A Target: Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO (AXL)
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03020 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03021 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03022 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2C (KMT2C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03023 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4B (KDM4B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03024 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Probable JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2C (JMJD1C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
m6A Target: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 22 (USP22)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03040 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 22 (USP22) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H2A lysine 119 ubiquitination (H2AK119ub) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Osteosarcoma | |
m6A Target: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase BRE1B (RNF40)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03041 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase BRE1B (RNF40) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H2A lysine 119 ubiquitination (H2AK119ub) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Osteosarcoma | |
m6A Target: small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03066 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2 (SETD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 36 trimethylation (H3K36me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03081 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Endometriosis | |
m6A Target: Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03084 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03189 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) | |
| Regulated Target | Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Progressive muscular atrophy | |
m6A Target: Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A (KAT2A)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03088 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A (KAT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03090 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A (KAT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9Ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05844 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A (KAT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05846 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A (KAT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Diabetic cardiomyopathy | |
m6A Target: Putative E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR7 (UBR7)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03092 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Putative E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR7 (UBR7) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H2B lysine 120 ubiquitination (H2BK120ub) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: JmjC domain-containing protein 8 (JMJD8)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03100 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03462 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 115 (LINC00115)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03104 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETDB1 (SETDB1) | |
| Regulated Target | Polo like kinase 3 (PLK3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | |
| Drug | Acetaminophen | |
m6A Target: Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 (PAK5)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03117 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03119 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (AIFM2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03125 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Vorinostat | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06043 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Trichostatin A | |
m6A Target: 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3A (HTR3A)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03129 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 11 (HDAC11) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Neuropathic pain | |
m6A Target: Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (CD58)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03131 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06019 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03154 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
m6A Target: Zinc finger protein SNAI1 (SNAI1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03159 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis | |
m6A Target: HBV encodes X protein (HBX)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03201 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Taurine up-regulated 1 protein (TUG1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03202 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (EHMT2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Drug | Adriamycin | |
m6A Target: Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03235 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 (RBBP5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03236 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 (RBBP5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
m6A Target: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03237 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 3B (KDM3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Preeclampsia | |
m6A Target: Transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 3 (TACC3)
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03256 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03260 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03264 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2C (KMT2C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03268 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4B (KDM4B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03272 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Probable JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2C (JMJD1C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
m6A Target: eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4EBP1/EIF4EBP1)
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03257 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03261 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03265 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2C (KMT2C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03269 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4B (KDM4B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03273 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Probable JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2C (JMJD1C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
m6A Target: Target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8 (MLST8)
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03258 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03262 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03266 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2C (KMT2C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03270 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4B (KDM4B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03274 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Probable JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2C (JMJD1C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
m6A Target: Inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPA)
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03259 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03263 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03267 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2C (KMT2C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03271 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 4B (KDM4B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03275 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Probable JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2C (JMJD1C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | |
m6A Target: Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03355 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03451 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03469 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03535 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06020 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Prp31 (PRPF31/RP11)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03356 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03452 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: microRNA 21 (MIR21)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03357 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03453 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03358 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03454 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Protein sprouty homolog 2 (SPRY2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03359 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03455 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03360 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03456 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Polyamine-transporting ATPase 13A3 (ATP13A3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03361 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03457 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Circ_AFF2
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03362 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03458 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Ras-related protein Rab-5A (RAB5A)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03363 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03459 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Hexokinase-2 (HK2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03364 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03460 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: BET1-like protein (BET1L)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03365 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03461 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03366 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03463 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03533 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03370 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETDB1 (SETDB1) | |
| Regulated Target | Polo like kinase 3 (PLK3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer | |
| Drug | Doxil | |
m6A Target: Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03403 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03406 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-3, mitochondrial (SIRT3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03404 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03407 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: Myt1 kinase (PKMYT1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03470 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06021 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Transcriptional repressor protein YY1 (YY1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03471 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06022 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: Glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 (CHAC1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03472 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Drug | cisplatin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06023 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Drug | cisplatin | |
m6A Target: hsa_circ_0000417 (circ_CPSF6)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03532 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 1 (LYPD1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03534 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Progestin and adipoQ receptor family member 4 (PAQR4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03536 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05956 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) | |
| Regulated Target | Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase alkB homolog 7, mitochondrial (ALKBH7) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Doxorubicin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05957 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) | |
| Regulated Target | Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase alkB homolog 7, mitochondrial (ALKBH7) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Drug | Tadalafil | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Target: Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05049 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | GAS5 antisense RNA 1 (GAS5-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05399 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5) | |
| Regulated Target | GAS5 antisense RNA 1 (GAS5-AS1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05056 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | FOXM1 Antisense RNA (FOXM1-AS) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Brain cancer | |
m6A Target: Fatty-acid amide hydrolase 1 (FAAH)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05059 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_STAG1 | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Major depressive disorder | |
m6A Target: Lnc-AK311120
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05062 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lnc-AK311120 | |
| Regulated Target | YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein C2 (YTHDC2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor SOX-2 (SOX2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05097 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 155 (MIR155) | |
| Regulated Target | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Diabetic foot ulcers | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05886 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | SOX2 overlapping transcript (SOX2OT) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Glioblastoma | |
| Drug | Temozolomide | |
m6A Target: H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05105 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-124-3p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Acute ischemic stroke | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-193a-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05110 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-193a-3p | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
m6A Target: NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05154 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-193a-3p | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Injury of heart | |
| Drug | Suxiao Jiuxin Pill | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-506-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05207 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_NRCAM | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Papillary Thyroid Cancer | |
m6A Target: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 (JAK1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05208 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 659 (LINC00659) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: 72 kDa type IV collagenase (MMP2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05231 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-141-3p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05232 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-141-3p | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05233 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-141-3p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05234 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-141-3p | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Target: KCNK15 and WISP2 antisense RNA 1 (KCNK15-AS1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05376 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | KCNK15 and WISP2 antisense RNA 1 (KCNK15-AS1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05543 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | KCNK15 and WISP2 antisense RNA 1 (KCNK15-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Potassium two pore domain channel subfamily K member 15 (KCNK15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
m6A Target: microRNA 7-1 (MIR7-1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05378 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 7-1 (MIR7-1) | |
| Regulated Target | Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
m6A Target: Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)
| In total 5 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05395 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05444 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05528 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Brain cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05621 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 378b (MIR378B) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Infantile hemangioma | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05639 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 214 (MIR214) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05417 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Osteosarcoma | |
m6A Target: microRNA 107 (MIR107)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05419 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 107 (MIR107) | |
| Regulated Target | Serine/threonine-protein kinase LATS2 (LATS2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2598 (LINC02598/RP11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05460 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2598 (LINC02598/RP11) | |
| Regulated Target | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SIAH1 (SIAH1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-mir-181b-1
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05466 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-mir-181b-1 | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional coactivator YAP1 (YAP1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Osteosarcoma | |
m6A Target: RMRP
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05493 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RMRP | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05677 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RMRP | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-21-5p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05511 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-21-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-143-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05513 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | pri-miR-143 | |
| Regulated Target | DEAD-box helicase 6 (DDX6) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Aortic aneurysm or dissection | |
m6A Target: microRNA 21 (MIR21)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05538 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Regulated Target | Protein sprouty homolog 2 (SPRY2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05542 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Homeobox A9 (HOXA9) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Laryngeal cancer | |
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05552 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Injury of kidney | |
| Drug | Dexmedetomidine* | |
m6A Target: hsa_circ_0000417 (circ_CPSF6)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05559 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0000417 (Circ_CPSF6) | |
| Regulated Target | Poly(rC)-binding protein 2 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa_circ_0008542 (Circ_PHF12)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05570 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0008542 (Circ_PHF12) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-185-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Diseases of the musculoskeletal system | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-320a-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05616 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-320a-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pulmonary Fibrosis | |
m6A Target: miR-194-2
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05622 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MiR-194-2 | |
| Regulated Target | Retinoic acid-induced protein 1 (RAI1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| Drug | Verteporfin | |
m6A Target: RNA component of 7SK nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RN7SK)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05649 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA component of 7SK nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RN7SK) | |
| Regulated Target | The positive transcription elongation factor b complex (P-TEFb) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa_circ_0003552 (Circ_MOCOS)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05664 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0003552 (Circ_MOCOS) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Drug | Benzo[a]pyrene | |
m6A Target: Circ_AFF2
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05684 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_AFF2 | |
| Regulated Target | Cullin associated and neddylation dissociated 1 (CAND1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Target: small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05733 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2 (SETD2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
m6A Target: Heparan Sulfate-Glucosamine 3-Sulfotransferase 3B1 Intronic Transcript 1 (HS3ST3B1-IT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05742 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Heparan Sulfate-Glucosamine 3-Sulfotransferase 3B1 Intronic Transcript 1 (HS3ST3B1-IT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Heparan sulfate-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 3B1 (HS3ST3B1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Osteoarthritis | |
m6A Target: CALML3 antisense RNA 1 (CALML3-AS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05758 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CALML3 antisense RNA 1 (CALML3-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Target: Circ_PUM1
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05771 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_PUM1 | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-423-5p | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Neuroblastoma | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05894 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-423-5p | |
| Regulated Target | Proliferation-associated protein 2G4 (PA2G4) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Neuroblastoma | |
m6A Target: Small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 (SNHG3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05821 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 (SNHG3) | |
| Regulated Target | ELAV-like protein 1 (HuR/ELAVL1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Acute ischemic stroke | |
Xenobiotics Compound(s) Regulating the m6A Methylation Regulator
| Compound Name | MPV 1440 | Approved |
|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Dexmedetomidina; Dexmedetomidinum; MPV 1440; MPV-1440; Precedex (TN); Dexmedetomidine (USAN/INN); (+)-4-((S)-alpha,2,3-Trimethylbenzyl)imidazole; 4-[(1S)-1-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)ethyl]-1H-imidazole; 5-[(1S)-1-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)ethyl]-1H-imidazole
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
ALKBH5 could up-regulateMALAT1 expression by demethylation. Furthermore, dexmedetomidine inhibited the expression of ALKBH5 in LPS-treated HK-2 cells. Dexmedetomidine suppressed the biological behavior of HK-2 cells treated with LPS by inhibiting the expression of ALKBH5 in vitro, which provides potential targets for the prevention and treatment of sepsis-induced kidney injury. Dexmedetomidine suppressed the biological behavior of HK-2 cells treated with LPS by inhibiting the expression of ALKBH5 in vitro, which provides potential targets for the prevention and treatment ofsepsis-induced kidney injury.
|
[57] |
| Compound Name | Citric acid | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
citric acid; 77-92-9; 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid; Citric acid, anhydrous; Anhydrous citric acid; Citro; Aciletten; Citretten; Chemfill; Hydrocerol A; 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-; 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid; Citric acid anhydrous; Kyselina citronova; 2-Hydroxytricarballylic acid; Caswell No. 221C; F 0001 (polycarboxylic acid); 3-Carboxy-3-hydroxypentane-1,5-dioic acid; 2-Hydroxypropanetricarboxylic acid; FEMA No. 2306; FEMA Number 2306; K-Lyte; Kyselina citronova [Czech]; K-Lyte DS; CCRIS 3292; HSDB 911; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 021801; Uro-trainer; AI3-06286; UNII-XF417D3PSL; Suby G; NSC 30279; NSC 626579; BRN 0782061; Citric acid,anhydrous; MFCD00011669; CHEMBL1261; XF417D3PSL; Kyselina 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propantrikarbonova [Czech]; Kyselina 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propantrikarbonova; CHEBI:30769; .beta.-Hydroxytricarballylic acid; citr; NSC30279; NSC-30279; NSC626579; NSC-626579; Citric acid, 99%; NCGC00090954-03; E330; DSSTox_CID_332; E 330; beta-Hydroxytricarballylic acid; CITRATE ANION; DSSTox_RID_75520; DSSTox_GSID_20332; 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, homopolymer; Citric acid [USAN:JAN]; CAS-77-92-9; 141633-96-7; 1,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-; NSC-112226; EINECS 201-069-1; Citraclean; Citronensaeure; Acidum citricum; citric-acid; Citricum acidum; Citric acid bp; Anhydrous citrate; 2fwp; 4aci; 4nrm; H3cit; Citric acid, anhydrous [USP:JAN]; Citric acid,hydrous; Citric Acid,(S); Citric acid, hydrous; Citric acid (8CI); K-Lyte (Salt/Mix); 1i2s; 1o4l; 1rq2; 1y4a; 2bo4; 2c4v; 2fw6; 4to8; Citraclean (Salt/Mix); Citric acid-[13C6]; Citric Acid (Anhydrous); 10402-15-0; Spectrum3_001850; WLN: QV1XQVQ1VQ; beta-Hydroxytricarballylate; cid_311; K-Lyte/Cl (Salt/Mix); K-Lyte DS (Salt/Mix); Acidum citricum monohydrate; bmse000076; HOC(CH2COOH)2COOH; EC 201-069-1; NCIStruc1_000057; NCIStruc2_000099; NCIOpen2_004062; NCIOpen2_004502; Oprea1_502996; BSPBio_003240; Citric acid anhydrous (JAN); 4-03-00-01272 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); Citric Acid, anhydrous, USP; MLS001066346; citric acid (Fragrance Grade); Citric acid, anhydrous (USP); Anhydrous citric acid (JP17); GTPL2478; INS NO.330; Citric Acid (Industrial Grade); Citric acid, analytical standard; DTXSID3020332; BDBM14672; Citric acid, p.a., 99.5%; KBio3_002740; INS-330; 4o61; Citric acid 5% solution in water; Citric acid, Electrophoresis Grade; HMS1787N01; HMS2268B04; Pharmakon1600-01300013; ZINC895081; Citric acid 10% solution in water; HY-N1428; STR12052; 1,2,3-Tricarboxy-2-hydroxypropane; Tox21_113436; Tox21_202405; Tox21_300124; BBL002530; NSC759606; s5761; STK286098; AKOS000119911; Citric acid, LR, anhydrous, >=99%; 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate; CS-6965; DB04272; MCULE-7981253226; NSC-759606; 3-Carboxy-3-hydroxypentane-1,5-dioate; Citric acid, >=99.5%, FCC, FG; Citric acid, ACS reagent, >=99.5%; Citric Acid, anhydrous powder, A.C.S.; 2-Hydroxy-1,3-propanetricarboxylic acid; NCGC00090954-01; NCGC00090954-02; NCGC00090954-04; NCGC00090954-05; NCGC00254055-01; NCGC00259954-01; BP-31028; Citric Acid, anhydrous granular, A.C.S.; NCI60_022579; SMR000471840; 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxyic acid; Citric acid 50% solution in water (w/w); SBI-0206765.P001; Citric acid, SAJ first grade, >=99.5%; 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propane tricarboxylic acid; 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanenetricarboxylic acid; B7297; C1949; Citric Acid, Aqueous Solution (Food Grade); Citric acid, Vetec(TM) reagent grade, 99%; E-330; FT-0623957; FT-0665073; FT-0728530; C00158; D00037; AE-562/40806920; Citric acid, BioUltra, anhydrous, >=99.5% (T); Q159683; J-520099; 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy- (9CI); Z56754862; Citric acid (monohydrate): H2O = 1 g : 1 ml solution; Citric acid, certified reference material, TraceCERT(R); Citric acid, meets USP testing specifications, anhydrous; F2191-0222; 8F5D336A-442D-434A-9FB0-E400FF74E343; Citrate standard for IC, 1000 mg/L, analytical standard; 1,2,3-PROPANETRICARBOXYLIC ACID,2-HYDROXY (CITRIC ACID); Citric acid, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; Citric acid, anhydrous, cell culture tested, plant cell culture tested; Citric acid, anhydrous, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Citric acid, anhydrous, free-flowing, Redi-Dri(TM), ACS reagent, >=99.5%; Citric acid, Anhydrous, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; Citric acid, meets analytical specification of Ph. Eur., BP, USP, E330, anhydrous, 99.5-100.5% (based on anhydrous substance)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50 = 488000 nM
|
[190] |
| Compound Name | IOX1 | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
5852-78-8; 8-Hydroxyquinoline-5-Carboxylic Acid; 8-Hydroxy-5-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 5-Carboxy-8-hydroxyquinoline; IOX 1; UNII-JM015YQC1C; IOX-1; 5-carboxy-8HQ; 5-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-hydroxy-; JM015YQC1C; CHEMBL1230640; 4bio; 4jht; 8XQ; 4ie4; AC1LA0UV; MLS002729056; GTPL8230; SCHEMBL6068195; KS-00000PPH; CHEBI:93239; CTK1E0142; DTXSID20207236; AOB6499; JGRPKOGHYBAVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N; MolPort-006-673-354; HMS3653E21; ZINC5933707; BCP16996; s7234; BDBM50396018; 2184AH; IOX1, > AKOS016371793
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
IOX1, which is an inhibitor of ALKBH5, was loaded on HSSS to form HSSS-I, which could effectively ameliorate cardiac dysfunction inacute myocardial infarction. The surface-modified bioengineered ferritin nanocage targeted the dying cells in the infarct area under the guidance ofScarf1. These cells were then phagocytosed through recognition of their TfR1 receptor.
|
[38] |
References