m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00438)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
USP1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
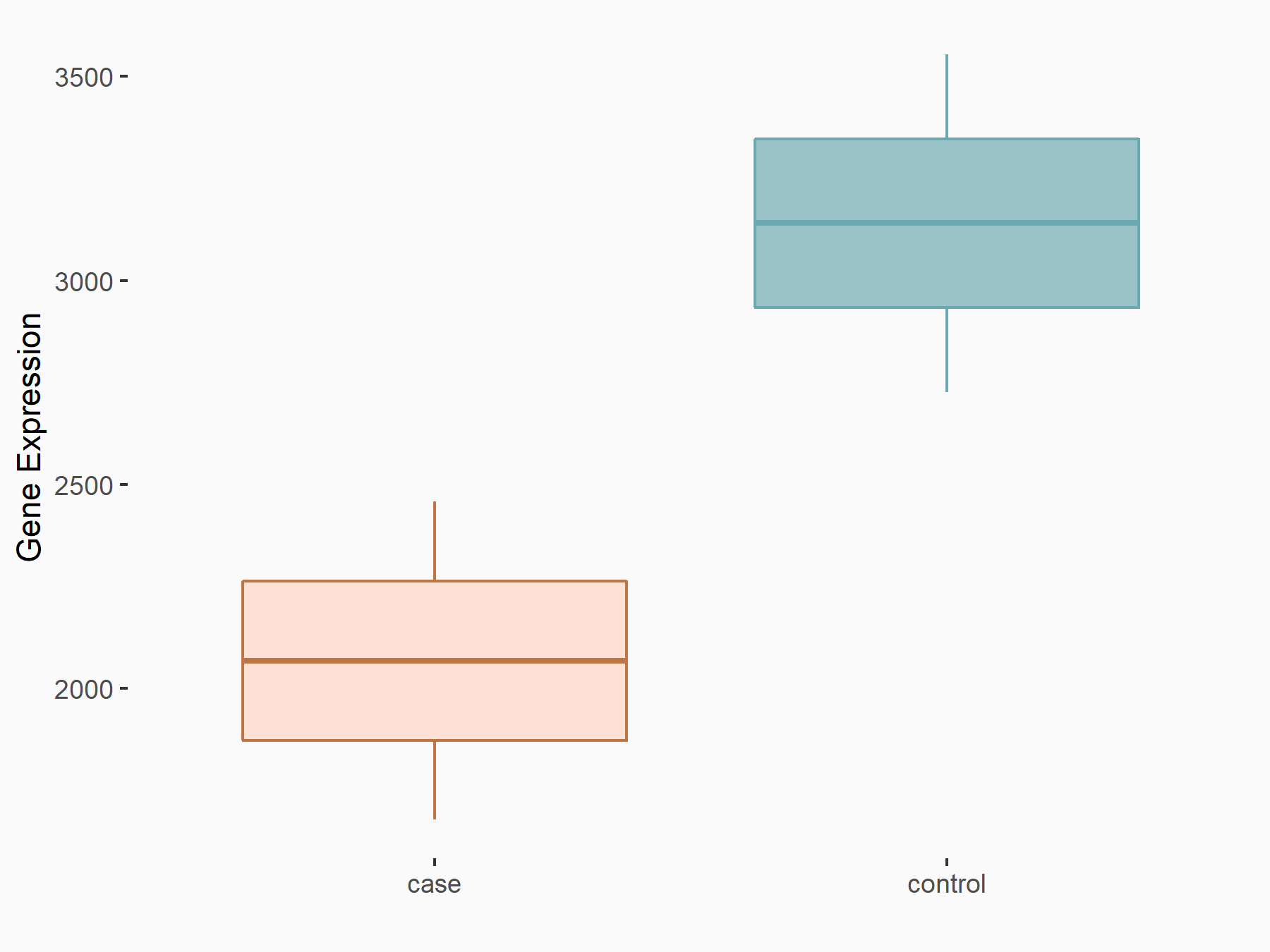  |
logFC: -6.03E-01 p-value: 1.12E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma | ICD-11: 2A90 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Dexamethasone | Approved | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma | ICD-11: 2A90 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Glucocorticoid | Investigative | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
Mature T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Dexamethasone | Approved | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Glucocorticoid | Investigative | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
Dexamethasone
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma | ICD-11: 2A90 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
Glucocorticoid
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 and Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (USP1) were upregulated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification increased USP1 and Aurora B expression. Silencing USP1 increased CEM-C1 cell sensitivity to dexamethasone, reduced cell invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and ameliorated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Mature T-cell lymphoma | ICD-11: 2A90 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | CEM/C1 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3496 |
| CCRF-CEM C7 | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6825 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Adult male C57BL/6J mice (weighting 18-25 g) were obtained from Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 1 × 107 CEM-C1 cells for tumorigenesis and randomly divided into four group: control group; control + Dex; sh-RNA + Dex; sh-USP1 + Dex. Mice treatment with Dex were intraperitoneally injected with 8 mg/kg Dex every day for 10 consecutive days after tumor growth and mice treatment with sh-RNA or sh-USP1 were injected intravenously with 2 mg/Kg sh-RNA or USP1 sh-RNA. The control group of mice were injected with the same volume of normal saline. After the treatment of each group, the mice were housed and fed in a room with an ambient temperature of 25℃, and the survival time, weight of the mice, and tumor weight were recorded. When rats were sacrificed, tissues were harvested for Western blot analysis. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00438)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008611 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449760-62449761:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | ATCTCTACAAAAAATACACAAACTAGTTTGGCGTGGTGGCG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5; rmsk_143506 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_6318 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008612 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449764-62449765:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTACAAAAAATACACAAACTAGTTTGGCGTGGTGGCGGGCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; rmsk_143506; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_6319 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 12 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002368 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437148-62437149:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGTTGCGCTCCTGGCTCTCCCGGGGCGGGCGCAGATGGGCG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000442679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2679 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002370 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437153-62437154:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CGCTCCTGGCTCTCCCGGGGCGGGCGCAGATGGGCGCCGCT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2680 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002371 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437176-62437177:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCGCAGATGGGCGCCGCTCCCGGGATGTAGTTGGTGTTGGT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2681 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002372 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439919-62439920:+ | ||
| Sequence | ACTTTCAAGAGGTAGCCCTTCAAAGAAAAACAGACTTTCCT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2682 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002373 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449783-62449784:+ | ||
| Sequence | TAGTTTGGCGTGGTGGCGGGCACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; rmsk_143506; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2683 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002374 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449785-62449786:+ | ||
| Sequence | GTTTGGCGTGGTGGCGGGCACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5; rmsk_143506 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2684 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002375 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449793-62449794:+ | ||
| Sequence | TGGTGGCGGGCACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTCAGGAGGCTGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_143506; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2685 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002376 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449794-62449795:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGTGGCGGGCACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTCAGGAGGCTGAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_143506; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2686 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002377 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449795-62449796:+ | ||
| Sequence | GTGGCGGGCACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTCAGGAGGCTGAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5; rmsk_143506 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2687 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002378 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449798-62449799:+ | ||
| Sequence | GCGGGCACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTCAGGAGGCTGAGGAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_143506; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2688 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002385 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449801-62449802:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGCACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTCAGGAGGCTGAGGAGGAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; rmsk_143506; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2689 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002386 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449803-62449804:+ | ||
| Sequence | CACTTGTGGTCCCAACTACTCAGGAGGCTGAGGAGGAGGAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; rmsk_143506; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_2690 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 125 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029128 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437088-62437089:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCGGTGGCGGAGTGCTAAAGACCCTAGCGGTTCAGGCGTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33647 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029139 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437298-62437299:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGATTTTCCTGGGGCCGGGGACCCGGCGGGCTCGGGGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33648 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029145 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437320-62437321:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCGGCGGGCTCGGGGCAGGGACTCACCTGTCGCACCCACAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33649 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029146 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437354-62437355:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCCACACTCATTCGGGTTGGACTTGCCGGCGTCACCGCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33650 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029156 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62437377-62437378:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGCCGGCGTCACCGCCGCGGACTTCGCTTTGGGCCATGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33651 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029157 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439834-62439835:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAACTTTCCTCTATAAATTAACTCTTGACACTCCTTGGGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33652 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029158 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439841-62439842:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCTATAAATTAACTCTTGACACTCCTTGGGATTTGAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33653 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029159 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439899-62439900:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATACCTAGTGAAAGTAATGGACTTTCAAGAGGTAGCCCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1A; hNPCs; A549; CD8T; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33654 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029160 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439928-62439929:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGTAGCCCTTCAAAGAAAAACAGACTTTCCTTAAAGTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33655 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029161 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439932-62439933:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGCCCTTCAAAGAAAAACAGACTTTCCTTAAAGTTTTTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; Jurkat; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33656 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029162 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439963-62439964:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGTTTTTTCAGAAAAAGGAAACTAAGAGAGCTTTGGATTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1A; hNPCs; A549; Jurkat; iSLK; MSC; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33657 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029163 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62439984-62439985:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTAAGAGAGCTTTGGATTTCACAGATTCTCAAGAAAATGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33658 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029164 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62441525-62441526:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGCACAGTCTTCACCTATAAACTGTGAGAAGAGAGAAAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33659 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029165 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62441543-62441544:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAACTGTGAGAAGAGAGAAAACTTGTTACCATTTGTGGGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000442679.5; ENST00000452143.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33660 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029166 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62441562-62441563:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AACTTGTTACCATTTGTGGGACTGAATAATCTCGGCAATAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000442679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33661 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029167 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62441581-62441582:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GACTGAATAATCTCGGCAATACTTGCTATCTTAATAGTATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33662 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029168 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62442234-62442235:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTTAAATCTGGAGTAAAGCACTTATTTAATATTATTTCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000452143.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33663 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029169 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62442294-62442295:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGATGAAGCCAATCAAAAAGACAAGGTAAGAAAAATAAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33664 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029170 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62443208-62443209:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TATGAATTGATATGCAGTTTACAGTCCTTAATCATTTCGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33665 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029171 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62443232-62443233:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCCTTAATCATTTCGGTTGAACAGCTCCAGGCTAGTTTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33666 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029172 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62443280-62443281:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCAGAGAAATATACTGATGAACTTGCCACTCAGCCAAGGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000452143.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33667 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029173 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62443309-62443310:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCCAAGGCGACTGCTTAACACACTGAGGTATAGCCTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000452143.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33668 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029174 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444740-62444741:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAAATTTTTATTTATAGGGAACTCAACCCTATGTATGAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33669 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029175 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444767-62444768:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTATGTATGAAGGATATCTACAGCATGATGCACAGGAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33670 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029176 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444808-62444809:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATTACAATGTATTTTGGGAAACATTCAAGAAACATGCCAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33671 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029177 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444819-62444820:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TTTTGGGAAACATTCAAGAAACATGCCAACTCCTAAAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33672 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029178 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444870-62444871:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAAATGTGGCAGAATTACCTACTAAGGTAGAAGAAATACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33673 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029179 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444919-62444920:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGAGGAAATGAATGGTATTAACAGCATAGAGATGGACAGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33674 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029180 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444934-62444935:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TATTAACAGCATAGAGATGGACAGTATGAGGCATTCTGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33675 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029181 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444955-62444956:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGTATGAGGCATTCTGAAGACTTTAAAGAGAAACTCCCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33676 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029182 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62444968-62444969:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCTGAAGACTTTAAAGAGAAACTCCCAAAAGGAAATGGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33677 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029183 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445000-62445001:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAATGGGAAAAGAAAAAGTGACACTGAATTTGGTAACATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33678 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029184 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445015-62445016:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AAGTGACACTGAATTTGGTAACATGAAGAAAAAAGTTAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33679 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029185 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445046-62445047:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAAGTTAAATTATCCAAGGAACACCAGTCATTGGAAGAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33680 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029186 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445066-62445067:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACACCAGTCATTGGAAGAGAACCAGAGACAAACTAGATCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33681 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029187 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445073-62445074:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCATTGGAAGAGAACCAGAGACAAACTAGATCAAAAAGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; brain; kidney; liver; A549; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33682 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029188 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445098-62445099:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTAGATCAAAAAGAAAAGCTACAAGTGATACATTAGAGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33683 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029189 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445107-62445108:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAAGAAAAGCTACAAGTGATACATTAGAGAGTCCTCCTAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33684 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029190 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445166-62445167:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCTGAAAATGAGAGTCCAAGACCCTCACAAAAGAAATCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; BGC823; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33685 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029191 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445172-62445173:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AATGAGAGTCCAAGACCCTCACAAAAGAAATCAAGAGTTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33686 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029192 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445215-62445216:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAAATTGGTTAAAGTCTGCAACTAAGCAACCCAGCATTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33687 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029193 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445263-62445264:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTGTAGTCTGGGAAAAATAACAACAAACCAAGGAGTCAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33688 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029194 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445266-62445267:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTAGTCTGGGAAAAATAACAACAAACCAAGGAGTCAAAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33689 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029195 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445270-62445271:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCTGGGAAAAATAACAACAAACCAAGGAGTCAAAGGACAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; H1299; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33690 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029196 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445286-62445287:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACAAACCAAGGAGTCAAAGGACAATCTAAAGAAAATGAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; kidney; hESC-HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; H1299; Huh7; iSLK; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33691 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029197 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445321-62445322:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGAATGTGATCCTGAAGAGGACTTGGGGAAGTGTGAAAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; H1299; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33692 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029198 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445345-62445346:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGGAAGTGTGAAAGTGATAACACAACTAATGGTTGTGGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33693 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029199 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445364-62445365:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AACACAACTAATGGTTGTGGACTTGAATCTCCAGGAAATAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; H1299; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33694 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029200 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445389-62445390:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AATCTCCAGGAAATACTGTTACACCTGTAAATGTTAATGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33695 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029201 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445415-62445416:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTAAATGTTAATGAAGTTAAACCCATAAACAAAGGTTAGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33696 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029202 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62445423-62445424:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TAATGAAGTTAAACCCATAAACAAAGGTTAGTATAATTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33697 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029203 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62447347-62447348:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATTTTCATTTTAGGTGAAGAACAAATTGGTTTTGAGCTAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; Huh7; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33698 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029204 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62447429-62447430:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCTTGGAATGTGAAAGTTTAACAGAAAGAAGAGAAGATTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33699 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029205 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62447454-62447455:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAGAAGAGAAGATTTTCAAGACATCAGTGTGCCAGTACAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hNPCs; A549; Huh7; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33700 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029206 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62447470-62447471:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAAGACATCAGTGTGCCAGTACAAGAAGATGAGCTTTCCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33701 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029207 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62448481-62448482:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TAGTTTCTCCAGAGCCAAAAACAGAAATGAAGACCCTGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hNPCs; A549; Huh7; Jurkat; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33702 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029208 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62448493-62448494:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGCCAAAAACAGAAATGAAGACCCTGAGATGGGCAATTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hNPCs; A549; Huh7; Jurkat; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33703 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029209 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62448513-62448514:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACCCTGAGATGGGCAATTTCACAATTTGCTTCAGTAGAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33704 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029210 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62448566-62448567:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGATAAATATTTCTGTGAAAACTGCCATCATTATACTGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; Huh7; Jurkat; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33705 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029211 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62448591-62448592:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CATCATTATACTGAAGCTGAACGAAGTCTTTTGTTTGACAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.925321429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33706 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029212 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62448608-62448609:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGAACGAAGTCTTTTGTTTGACAAAATGCCTGAAGTTATAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33707 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029213 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62448685-62448686:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGTAAGTATTGTAAATAAGAACTATATGAAGAAAATGAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33708 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029214 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62449929-62449930:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAAAAAAAACCCAAAACGTAACATTTTTGGTTCCGGTTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33709 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029215 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450266-62450267:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TTTGATTGTTATGGTGGTGGACTTTCCAAGATCAACACTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33710 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029216 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450280-62450281:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGGACTTTCCAAGATCAACACTCCTTTATTGACACCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33711 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029217 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450294-62450295:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGATCAACACTCCTTTATTGACACCTCTTAAATTGTCACTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33712 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029218 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450336-62450337:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGAATGGAGCACAAAGCCAACTAACGACAGCTATGGATTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33713 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029219 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450340-62450341:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATGGAGCACAAAGCCAACTAACGACAGCTATGGATTATTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.142029762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33714 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029220 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450384-62450385:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTGTGATGCATAGTGGCATTACAATTAGTAGTGGGCATTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33715 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029221 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450403-62450404:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TACAATTAGTAGTGGGCATTACACTGCTTCTGTTAAAGTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33716 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029222 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450423-62450424:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACACTGCTTCTGTTAAAGTCACTGACCTTAACAGTTTAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.469291667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33717 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029223 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450443-62450444:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACTGACCTTAACAGTTTAGAACTAGATAAAGGAAATTTTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; U2OS; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; GM12878; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33718 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029224 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450469-62450470:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAAAGGAAATTTTGTGGTTGACCAAATGTGTGAAATAGGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.839113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33719 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029225 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450497-62450498:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGTGAAATAGGTAAGCCAGAACCATTGAATGAGGAGGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33720 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029226 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450576-62450577:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAATTAGAGTTGGTGGAAATACACAGCCAAGTAAAGTTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33721 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029227 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450578-62450579:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATTAGAGTTGGTGGAAATACACAGCCAAGTAAAGTTTTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.084928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33722 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029228 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450598-62450599:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACAGCCAAGTAAAGTTTTGAACAAAAAAAATGTAGAAGCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33723 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029229 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450623-62450624:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAAAATGTAGAAGCTATTGGACTTCTTGGAGGACAAAAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33724 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029230 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450635-62450636:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCTATTGGACTTCTTGGAGGACAAAAGAGCAAAGCAGATTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33725 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029231 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450667-62450668:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGATTATGAGCTATACAACAAAGCCTCTAATCCTGATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33726 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029232 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450729-62450730:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTGAAAATAGAAATTCTGAGACTAGTGATACTACTGGGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33727 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029233 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450738-62450739:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAATTCTGAGACTAGTGATACTACTGGGACCCATGAATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33728 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029234 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450747-62450748:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGACTAGTGATACTACTGGGACCCATGAATCTGATAGAAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33729 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029235 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450766-62450767:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GACCCATGAATCTGATAGAAACAAGGAATCCAGTGACCAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33730 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029236 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450781-62450782:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAGAAACAAGGAATCCAGTGACCAAACAGGCATTAATATTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.839113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33731 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029237 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450786-62450787:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACAAGGAATCCAGTGACCAAACAGGCATTAATATTAGTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33732 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029238 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450814-62450815:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TAATATTAGTGGATTTGAGAACAAAATTTCATACGTAGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33733 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029239 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450826-62450827:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATTTGAGAACAAAATTTCATACGTAGTGCAAAGCTTAAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.084416667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33734 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029240 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450907-62450908:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAAAGTTACTGAAGAGAAGGACTTTCTGAATTCTCTTTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33735 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029241 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450933-62450934:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGAATTCTCTTTCCCCTTCTACATCTCCTACTTCTACTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; rmsk_143507; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33736 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029242 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450942-62450943:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTCCCCTTCTACATCTCCTACTTCTACTCCTTACTTGCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_143507; ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33737 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029243 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450948-62450949:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTTCTACATCTCCTACTTCTACTCCTTACTTGCTATTTTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; rmsk_143507; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33738 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029244 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62450955-62450956:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATCTCCTACTTCTACTCCTTACTTGCTATTTTATAAGAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33739 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029245 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451012-62451013:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTCCTTGTGTATATATTAAACACACCCATACAAACATTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33740 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029246 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451022-62451023:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TATATATTAAACACACCCATACAAACATTGGTAAAGTTGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33741 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029247 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451044-62451045:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAACATTGGTAAAGTTGATTACATCAAAGAATCTTTAGCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33742 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029248 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451078-62451079:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTAGCTTATCTTTTGAAGCTACTGGATATTATTGGTCTCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33743 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029249 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451131-62451132:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAAATAGTGAAATTTGAATTACTGAAAACCATGTTAATTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33744 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029250 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451138-62451139:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGAAATTTGAATTACTGAAAACCATGTTAATTTTTAGAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33745 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029251 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451156-62451157:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAACCATGTTAATTTTTAGAACTCATTTTCCTCAGTAGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33746 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029252 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451176-62451177:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACTCATTTTCCTCAGTAGAGACTAGTGATGCATTAGCTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33747 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029253 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451201-62451202:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGATGCATTAGCTTCTGGGAACAAACTTGTATCGGTTCTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33748 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029254 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451205-62451206:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCATTAGCTTCTGGGAACAAACTTGTATCGGTTCTTAATTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33749 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029255 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451237-62451238:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTTAATTAAATTATCCAAAACGGAGGCATTTAAACACTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.179660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33750 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029256 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451251-62451252:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCCAAAACGGAGGCATTTAAACACTTGGATTTACACCAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33751 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029257 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451253-62451254:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAAAACGGAGGCATTTAAACACTTGGATTTACACCAGTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.506922619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33752 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029258 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451263-62451264:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCATTTAAACACTTGGATTTACACCAGTCTTTTGTGTTTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33753 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029259 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451338-62451339:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATATTTTGGAGTAATTATCTACATGATGTTTATAGTTCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33754 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029260 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451394-62451395:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCAGAATCTCATTCAGTACATTTAGTTTTATAAGAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33755 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029261 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451447-62451448:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTTGGGCTATGTCAGAGGCACAAAGTCTAGAATGTGTGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33756 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029262 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451485-62451486:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTATTCACAATGGTGTATGTACATTTTGTGCCTTGATTCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33757 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029263 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451504-62451505:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TACATTTTGTGCCTTGATTCACTTAGAAGTGTCTCAGAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.469291667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33758 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029264 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451524-62451525:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACTTAGAAGTGTCTCAGAAAACCTGGACAGTTCGCTTCTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33759 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029265 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451530-62451531:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAGTGTCTCAGAAAACCTGGACAGTTCGCTTCTACACAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33760 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029266 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451543-62451544:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AACCTGGACAGTTCGCTTCTACACAAGAATTTTATATGTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33761 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029267 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451545-62451546:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGACAGTTCGCTTCTACACAAGAATTTTATATGTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.084928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33762 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029268 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451582-62451583:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATTTATGAAGATGATTCTGTACCCTAGTATATCTTTTTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.8355 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33763 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029269 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451608-62451609:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTATATCTTTTTGGGCATGGACTAATTTGTATCTGTTTAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33764 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029270 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451627-62451628:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GACTAATTTGTATCTGTTTAACTCATATTCTGCACGATCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33765 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029271 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451640-62451641:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGTTTAACTCATATTCTGCACGATCTGTATATAGTACATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.80452381 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33766 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029272 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451656-62451657:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGCACGATCTGTATATAGTACATCAAACTTAGAGGTGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33767 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029273 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451663-62451664:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATCTGTATATAGTACATCAAACTTAGAGGTGTGACCTTAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33768 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029274 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451701-62451702:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAATTTAACTTTTTTTAAAAACTGGGAGGTCAATAAAATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371146.5; ENST00000339950.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33769 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029275 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451760-62451761:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TATGAATATTTGAATTTTTTACTTGTATATTTTTATAAATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33770 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE029276 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:62451780-62451781:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACTTGTATATTTTTATAAATACAGCTGAGTTTTCTTAAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000339950.5; ENST00000371146.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_33771 | ||
References