m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00567)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
RIG-I
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | LX2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 LX2 cells
Control: shLuc LX2 cells
|
GSE207909 | |
| Regulation |
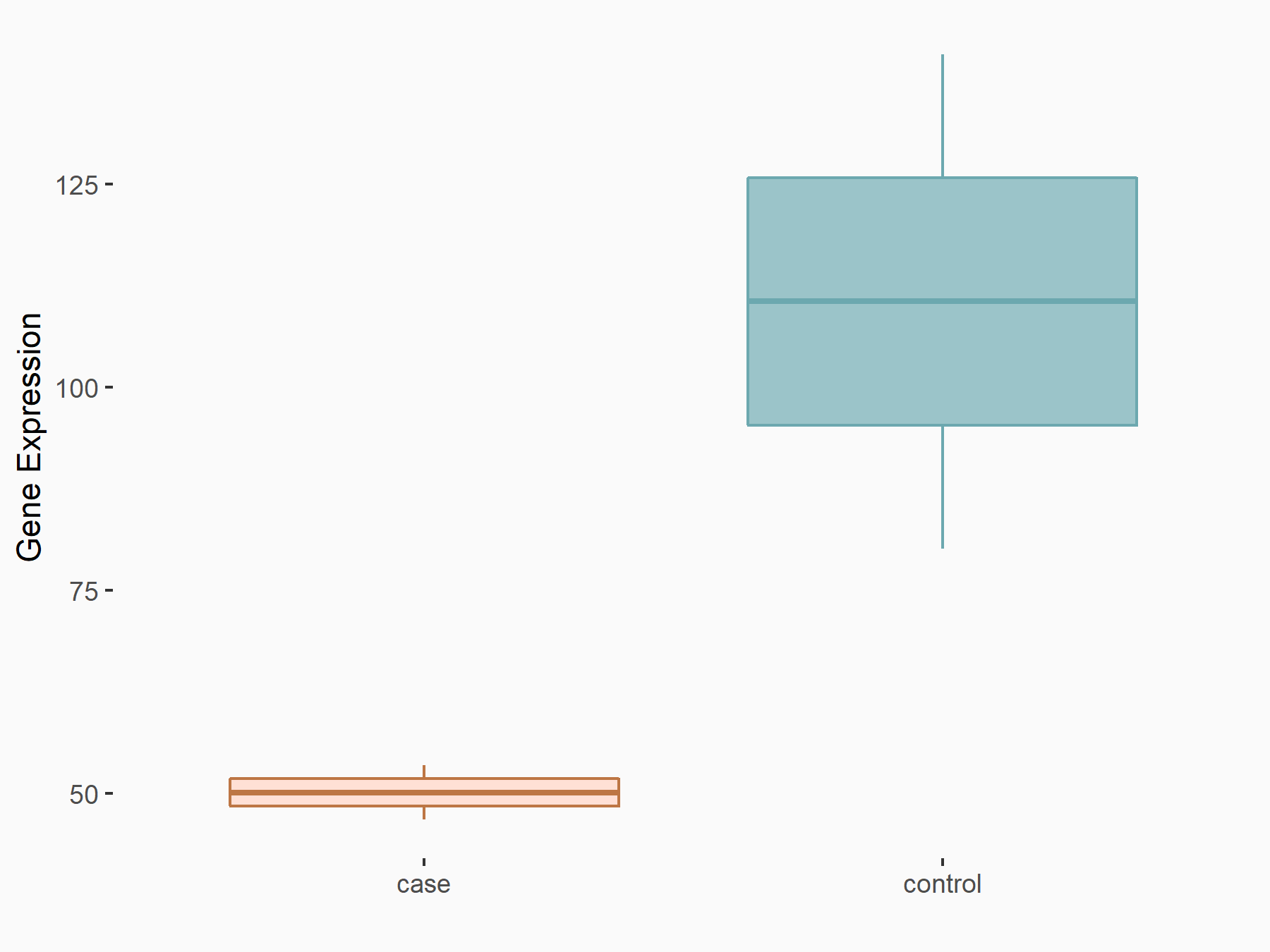  |
logFC: -1.14E+00 p-value: 3.48E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between RIG-I and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.75E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 3 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis B | ICD-11: 1E50.1 | ||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis C | ICD-11: 1E50.2 | ||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In SARS-CoV-2 infection, depletion of the host cell m6A methyltransferase METTL3 decreases m6A levels in SARS-CoV-2 and host genes, and m6A reduction in viral RNA increases RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I) binding and subsequently enhances the downstream innate immune signaling pathway and inflammatory gene expression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | COVID-19 | ICD-11: RA01 | ||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune responses | |||
| In-vitro Model | Calu-3 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0609 |
| Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 | |
| HEK293-FT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6911 | |
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
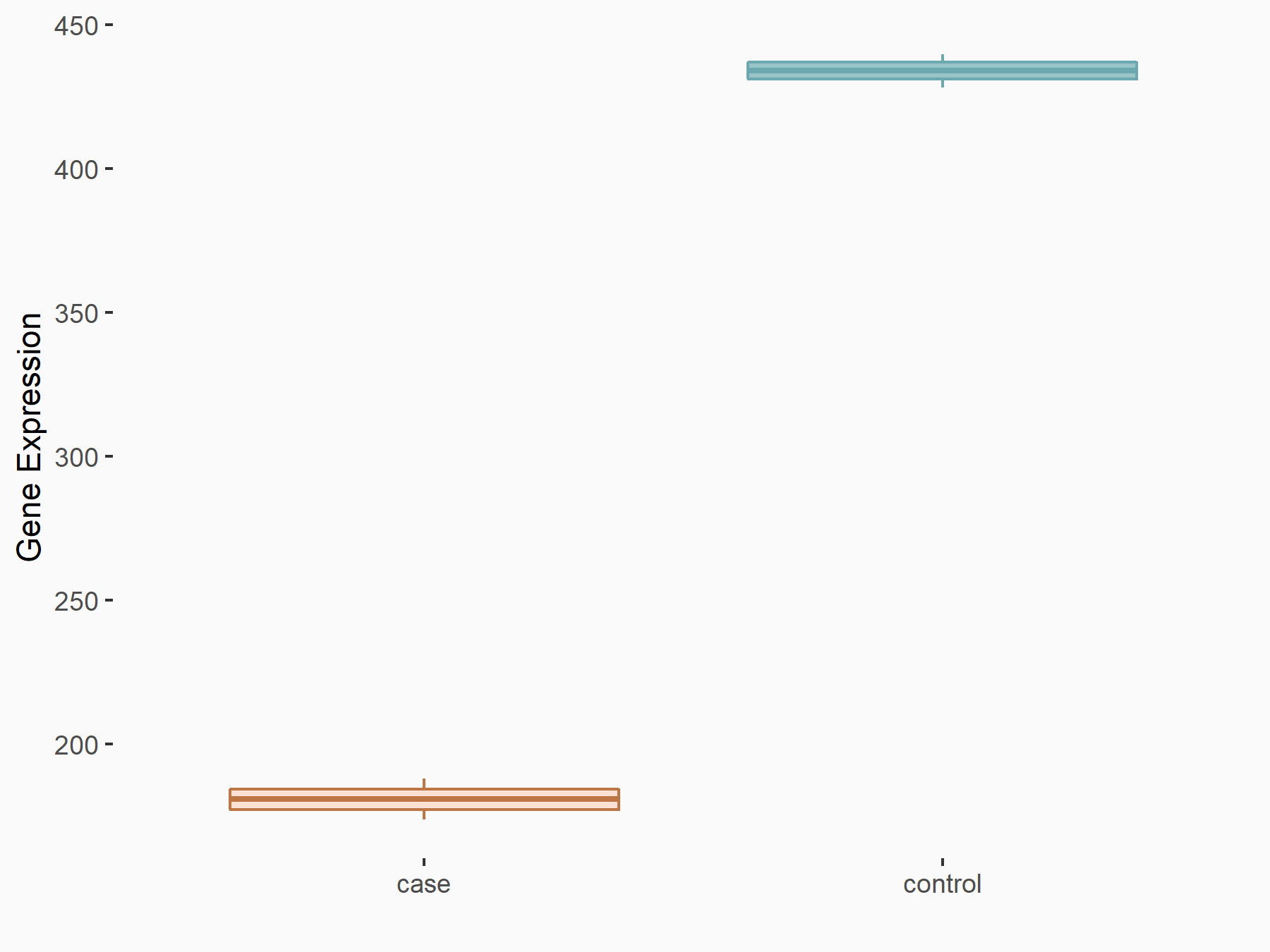  |
logFC: -1.26E+00 p-value: 3.52E-15 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis B | ICD-11: 1E50.1 | ||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis C | ICD-11: 1E50.2 | ||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | Cal27 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 Cal27 cells
Control: siScramble Cal27 cells
|
GSE185886 | |
| Regulation |
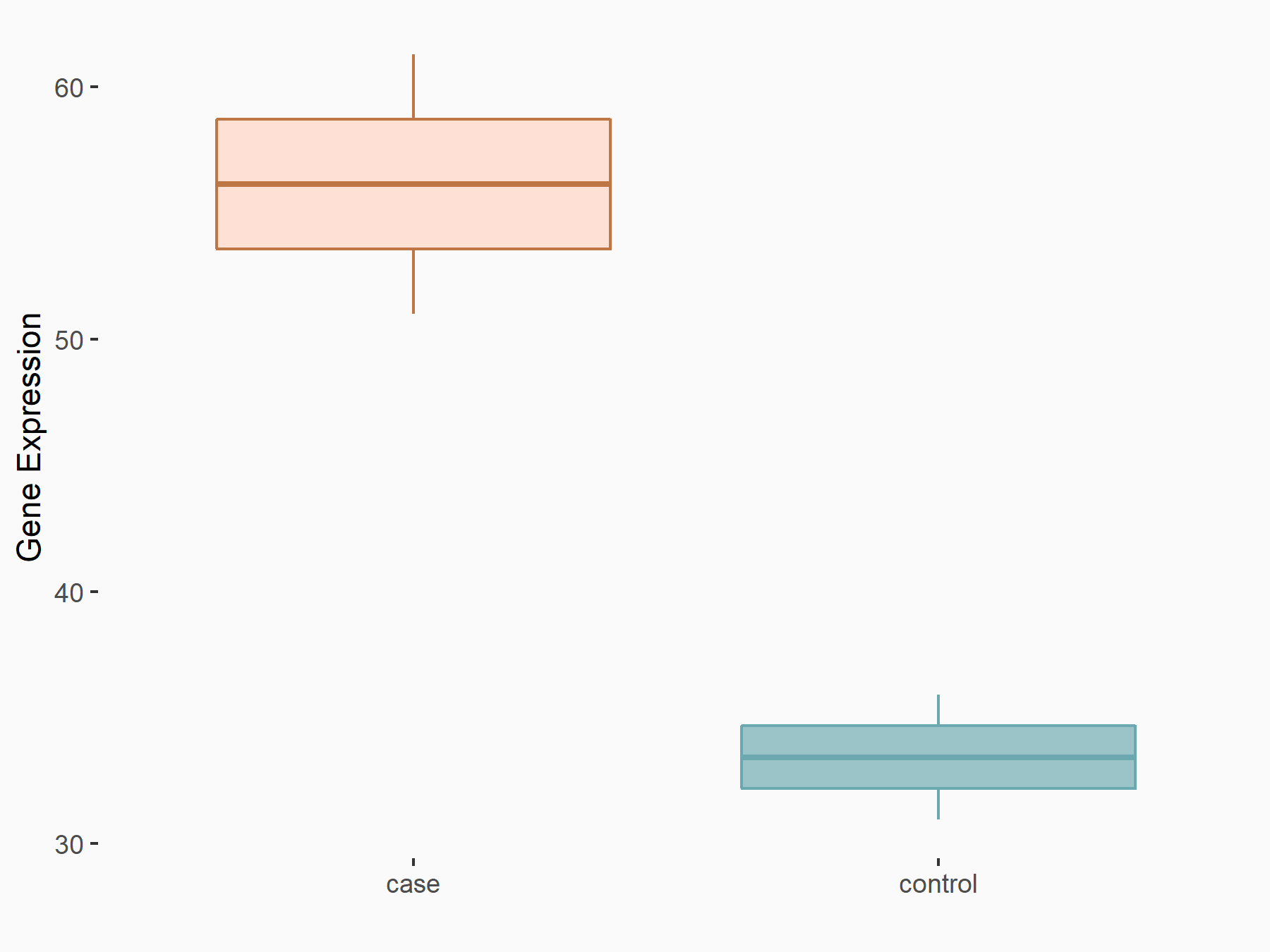 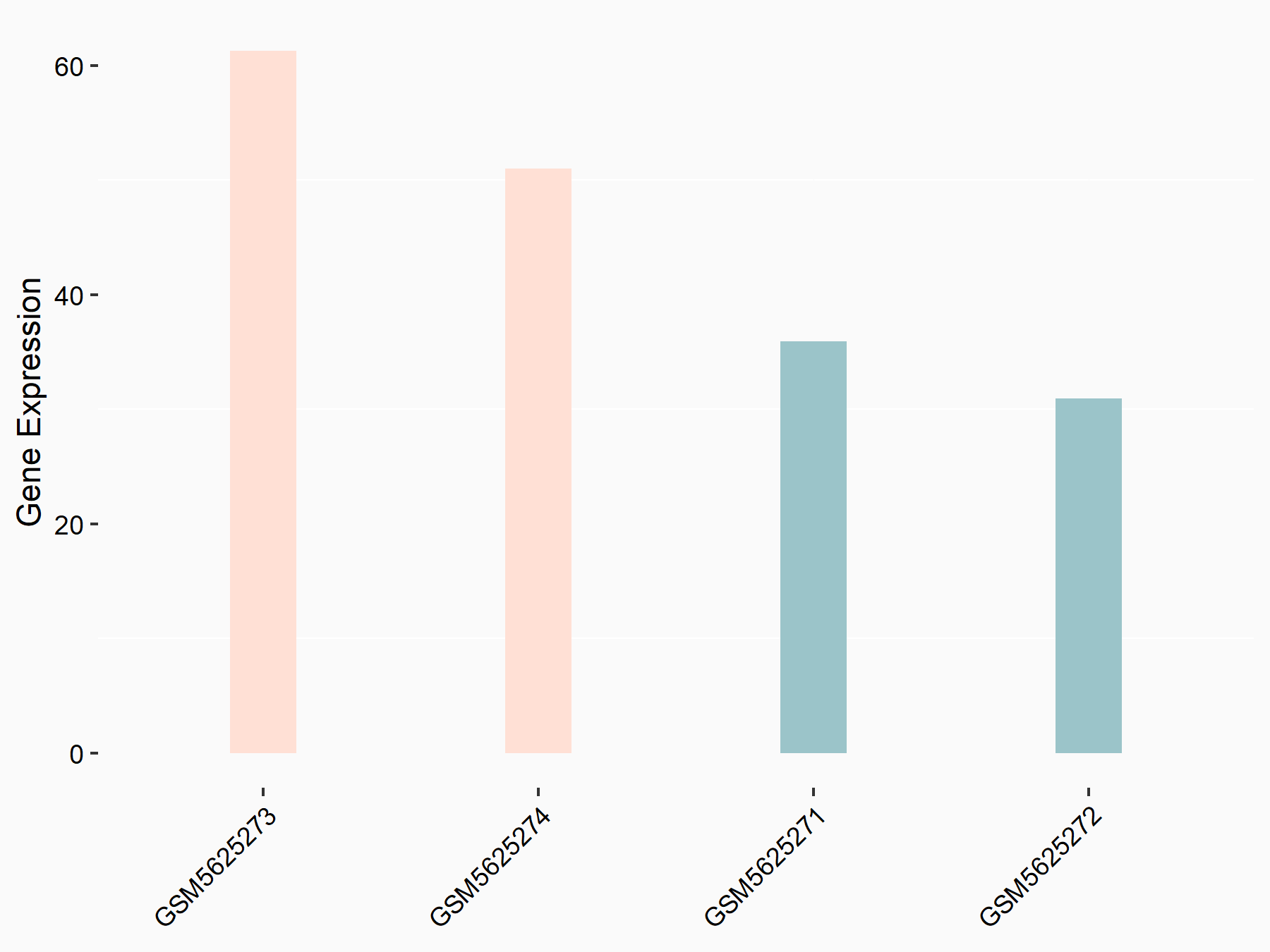 |
logFC: 7.29E-01 p-value: 2.91E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression inhibits RIG-I-mediated IFN-Alpha secretion through the IKK-Epsilon/TBK1/IRF3 pathway. Upregulation of AKLBH5 negatively correlates with RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I) and IFN-Alpha expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E | ||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| () | ||||
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 1 × 106 Cal27 cells stably transduced with lentivirus were injected into the left or right flanks of BALB/c nude mice (aged 4-6 weeks). Following stable transfection, 2 × 105 SCC7 cells were subcutaneously inoculated into C3H mice (aged 6-8 weeks). | |||
Acute viral hepatitis [ICD-11: 1E50]
| In total 4 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis B [ICD-11: 1E50.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis C [ICD-11: 1E50.2] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis B [ICD-11: 1E50.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 and METTL14 leads to an increase in viral RNA recognition by RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I), thereby stimulating type I interferon production. The obvious advantage is that m6A deficiency in HBV and HCV induces a higher IFN synthesis and in turn enhance adaptive immunity. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute hepatitis C [ICD-11: 1E50.2] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 overexpression inhibits RIG-I-mediated IFN-Alpha secretion through the IKK-Epsilon/TBK1/IRF3 pathway. Upregulation of AKLBH5 negatively correlates with RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I) and IFN-Alpha expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| In-vitro Model | CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| () | ||||
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 1 × 106 Cal27 cells stably transduced with lentivirus were injected into the left or right flanks of BALB/c nude mice (aged 4-6 weeks). Following stable transfection, 2 × 105 SCC7 cells were subcutaneously inoculated into C3H mice (aged 6-8 weeks). | |||
COVID-19 [ICD-11: RA01]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In SARS-CoV-2 infection, depletion of the host cell m6A methyltransferase METTL3 decreases m6A levels in SARS-CoV-2 and host genes, and m6A reduction in viral RNA increases RIG-I-like receptor 1 (RIG-I) binding and subsequently enhances the downstream innate immune signaling pathway and inflammatory gene expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | COVID-19 [ICD-11: RA01] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune responses | |||
| In-vitro Model | Calu-3 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0609 |
| Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0025 | |
| HEK293-FT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6911 | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00567)
| In total 13 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003113 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32455467-32455468:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTTAGTTCTCATGAGATCTGATGGTTTTATAAGTGTTTGAC | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_2734529; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134688 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003114 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456303-32456304:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTCTACAGTGGTCAGCTTTTAGTAGAGAGCATAAAAATGAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134689 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003115 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456317-32456318:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCAATGTGTATCCACTCTACAGTGGTCAGCTTTTAGTAGAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134690 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003116 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456319-32456320:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TAGCAATGTGTATCCACTCTACAGTGGTCAGCTTTTAGTAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134691 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003117 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456366-32456367:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTATGCTTACTACTAAAAGCTGTCCACTGTAGAGTTGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134693 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003118 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456369-32456370:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCATTTTTATGCTTACTACTAAAAGCTGTCCACTGTAGAGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134694 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003119 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456372-32456373:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGCCATTTTTATGCTTACTACTAAAAGCTGTCCACTGTAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134695 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003120 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456381-32456382:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAGAACATAAAGCCATTTTTATGCTTACTACTAAAAGCTGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134696 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003121 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456414-32456415:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAGCAACGTGTGGTATGGCTACACAGAGAACATGAGAACAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134697 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003122 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456450-32456451:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TATATGTAATGGTTATATGTACTCATGTTCCTGGTGTAGCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134698 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003123 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456454-32456455:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TATGTATATGTAATGGTTATATGTACTCATGTTCCTGGTGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134699 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003124 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456487-32456488:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TATGTATATGTAACTAATATACATACATACAGGTATGTATA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134700 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003125 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456489-32456490:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CATATGTATATGTAACTAATATACATACATACAGGTATGTA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_134701 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE004394 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32459401-32459402:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGAAAGTGCAAAGCCTTGGCATGTTACACAGCTGACGTAA | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_42415 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 29 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087866 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456163-32456164:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGTTGATGTTCAACACCTGGACTGAATGTCTGTTCTCAGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818395 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087867 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32456171-32456172:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TATAATGATGTTGATGTTCAACACCTGGACTGAATGTCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818396 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087868 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457065-32457066:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TAACTTTGAGTGGAGAAGAAACAAACATAGTGGGTATAATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HEK293T; HeLa; A549; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; MM6; Huh7; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818397 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087869 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457083-32457084:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCTACAGGGAATGAGTAACTTTGAGTGGAGAAGAAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818398 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087870 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457170-32457171:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | ACTGTACTCGAAGTGGAAGGACTTTCATTTTGAGAAGATAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818399 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087871 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457192-32457193:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | ATATTGCAACTGGAGTTCAGACACTGTACTCGAAGTGGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818400 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087872 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457204-32457205:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TTGTGGTGGAGGATATTGCAACTGGAGTTCAGACACTGTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818401 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087873 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457258-32457259:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GAATCCATGTGAAGTACAAGACATTTGAGATTCCAGTTATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818402 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087874 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457296-32457297:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | GATATTCTGTGCCCGACAGAACTGCAGCCATGACTGGGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; HepG2; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; CD8T; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818403 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087875 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32457364-32457365:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | AAGGAATGCTTTGTGAGTAGACCACATCCCAAGCCAAAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; HepG2; fibroblasts; A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818404 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087876 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32473017-32473018:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | CCTAAACTCAGTTTTCTAAAACCTGGCATATTGACTGGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818406 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087877 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32473032-32473033:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TGGATTGAAGGAAATCCTAAACTCAGTTTTCTAAAACCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818407 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087878 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32476999-32477000:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TAACAATTCTCTTTGTGAAAACCAGAGCACTTGTGGACGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818408 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087879 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32477023-32477024:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | AGTACCACTTAAACCCAGAGACAATAACAATTCTCTTTGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818409 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087880 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32488849-32488850:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GTTTCACTGCTTATATGTGAACATCATCTTAAAAAATTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818410 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087881 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32488875-32488876:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TGTTAAAAGGTTGTGGAAAAACCTTTGTTTCACTGCTTATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818411 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087882 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32489366-32489367:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GCCTGCTATGAAAGGAAAAAACACAATAATATGTGCTCCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818412 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087883 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32489416-32489417:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | AACTTGTACAGCCCATTTAAACCAAGAAATTACCAATTAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818413 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087884 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32489435-32489436:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TCCAGAAGTGTCTGATACAAACTTGTACAGCCCATTTAAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818414 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087885 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32492409-32492410:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | GAAAGGAACAAGTTCAGTGAACTGTGGATTGTAGAGAAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818415 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087886 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32492422-32492423:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TGCTTTGGAGAAAGAAAGGAACAAGTTCAGTGAACTGTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818416 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087887 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32492445-32492446:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | AACTGGCCCAAAACTTTGAAACTTGCTTTGGAGAAAGAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818417 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087888 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32492453-32492454:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | ACAAGGAAAACTGGCCCAAAACTTTGAAACTTGCTTTGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818418 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087889 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32492464-32492465:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TCTCAGATCAGACAAGGAAAACTGGCCCAAAACTTTGAAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818419 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087890 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32492473-32492474:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | GGAATGCCTTCTCAGATCAGACAAGGAAAACTGGCCCAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818420 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087891 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32500908-32500909:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GTATATTCAGGCTGAGAAAAACAACAAGGGCCCAATGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818421 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087892 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32526104-32526105:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TTATATCCGGAAGACCCTGGACCCTACCTACATCCTGAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; TIME; iSLK; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818422 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087893 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32526111-32526112:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TCCAGGATTATATCCGGAAGACCCTGGACCCTACCTACATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; TIME; iSLK; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379868.5; ENST00000379883.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818423 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087894 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:32526193-32526194:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGAGGCACAGCCTGCGGGGAACGTAGCTAGCTGCAAGCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.925321429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000379883.3; ENST00000379868.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_818424 | ||
References