m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00290)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
IFNB1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
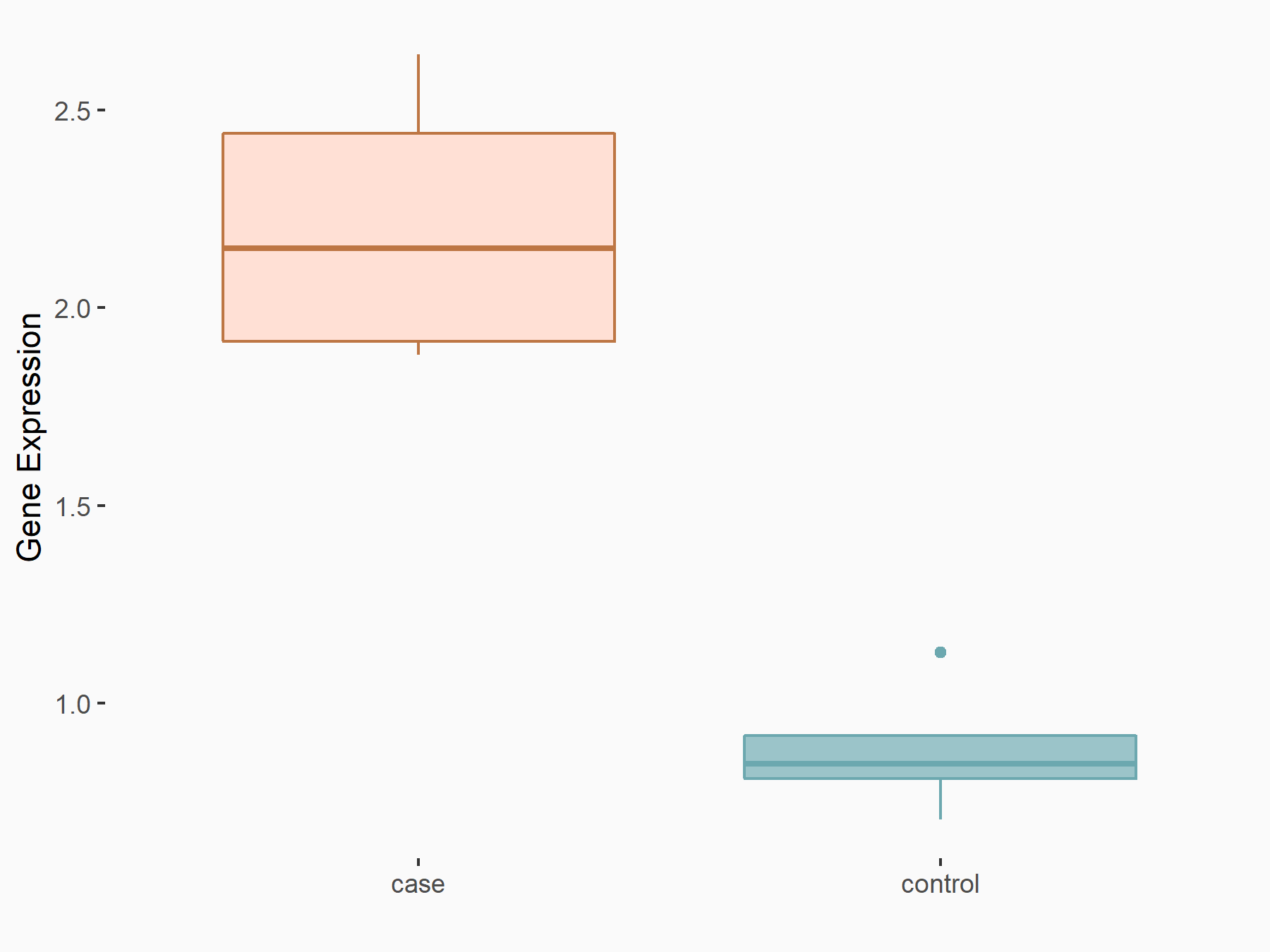  |
logFC: 7.66E-01 p-value: 2.22E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Unspecified viral infection | ICD-11: 1D9Z | ||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | Peritoneal macrophages | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: ALKBH5-/- peritoneal macrophages
Control: Wild type peritoneal macrophages
|
GSE127739 | |
| Regulation |
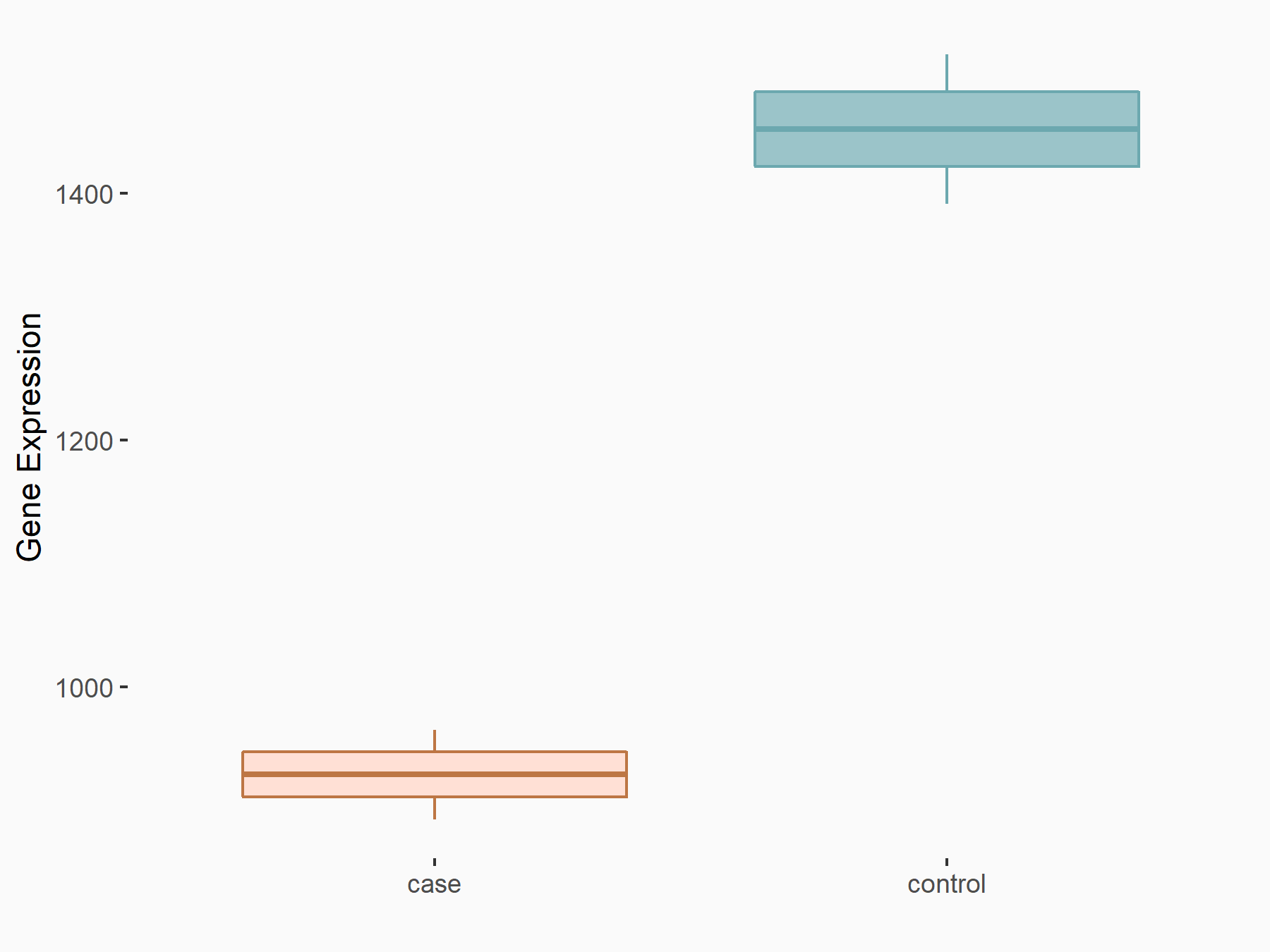  |
logFC: -6.45E-01 p-value: 8.14E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Unspecified viral infection | ICD-11: 1D9Z | ||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins C1/C2 (HNRNPC) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of HNRNPC can promote the proliferation of PC12 cells, inhibit their apoptosis, and inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors Interferon beta (IFNB1), IL-6, and TNF-Alpha, suggesting that HNRNPC can cause PD by inhibiting the proliferation of dopaminergic nerve cells, promoting their apoptosis, and causing immune inflammation. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune inflammation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | PC12 | Rat adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
Papillomaviruses [ICD-11: 1D9Z]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Unspecified viral infection [ICD-11: 1D9Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Unspecified viral infection [ICD-11: 1D9Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
Innate immunity [ICD-11: 4A00]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Innate immunity [ICD-11: 4A00] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced Interferon beta (IFNB1) mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Innate immunity [ICD-11: 4A00] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell Process | Metabolic reprogramming | |||
| Stress responses | ||||
| Aging | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BSC40 | Normal | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | CVCL_3656 |
| HCMV AD169GFP (Human cytomegalovirus) | ||||
| NHDF (Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts) | ||||
| Vero | Normal | Chlorocebus sabaeus | CVCL_0059 | |
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of HNRNPC can promote the proliferation of PC12 cells, inhibit their apoptosis, and inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors Interferon beta (IFNB1), IL-6, and TNF-Alpha, suggesting that HNRNPC can cause PD by inhibiting the proliferation of dopaminergic nerve cells, promoting their apoptosis, and causing immune inflammation. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Target Regulator | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins C1/C2 (HNRNPC) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Immune inflammation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | PC12 | Rat adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00290)
| In total 17 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087721 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077199-21077200:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AATGTACTGCATATGAAAGGACACTAGAAGATTTTGAAATT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817468 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087722 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077274-21077275:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCTGTGCCTCTGGGACTGGACAATTGCTTCAAGCATTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817469 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087723 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077279-21077280:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCCTAGCCTGTGCCTCTGGGACTGGACAATTGCTTCAAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817470 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087724 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077309-21077310:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACTTACAGGTTACCTCCGAAACTGAAGATCTCCTAGCCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817471 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087725 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077329-21077330:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AACTTTTACTTCATTAACAGACTTACAGGTTACCTCCGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817472 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087726 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077348-21077349:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CAGAGTGGAAATCCTAAGGAACTTTTACTTCATTAACAGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817473 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087727 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077376-21077377:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGTACAGTCACTGTGCCTGGACCATAGTCAGAGTGGAAATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817474 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087728 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077461-21077462:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GAAGATTTCACCAGGGGAAAACTCATGAGCAGTCTGCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817475 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087729 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077491-21077492:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AAGACAGTCCTGGAAGAAAAACTGGAGAAAGAAGATTTCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817476 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087730 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077508-21077509:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ATCAGATAAACCATCTGAAGACAGTCCTGGAAGAAAAACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817477 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087731 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077519-21077520:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TAATGTCTATCATCAGATAAACCATCTGAAGACAGTCCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817478 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087732 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077549-21077550:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GAATGAGACTATTGTTGAGAACCTCCTGGCTAATGTCTATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817479 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087733 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077562-21077563:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTAGCACTGGCTGGAATGAGACTATTGTTGAGAACCTCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817480 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087734 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077593-21077594:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AACATCTTTGCTATTTTCAGACAAGATTCATCTAGCACTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817481 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087735 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077612-21077613:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CATCTATGAGATGCTCCAGAACATCTTTGCTATTTTCAGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817482 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087736 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077696-21077697:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTGCCTCAAGGACAGGATGAACTTTGACATCCCTGAGGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817483 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087737 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:21077705-21077706:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCTTGAATACTGCCTCAAGGACAGGATGAACTTTGACATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000380232.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_817484 | ||
References