m6A Regulator Information
General Information of the m6A Regulator (ID: REG00003)
| Regulator Name | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins C1/C2 (HNRNPC) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
hnRNP C1/C2; HNRPC
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | HNRNPC | ||||
| Sequence |
MASNVTNKTDPRSMNSRVFIGNLNTLVVKKSDVEAIFSKYGKIVGCSVHKGFAFVQYVNE
RNARAAVAGEDGRMIAGQVLDINLAAEPKVNRGKAGVKRSAAEMYGSVTEHPSPSPLLSS SFDLDYDFQRDYYDRMYSYPARVPPPPPIARAVVPSKRQRVSGNTSRRGKSGFNSKSGQR GSSKSGKLKGDDLQAIKKELTQIKQKVDSLLENLEKIEKEQSKQAVEMKNDKSEEEQSSS SVKKDETNVKMESEGGADDSAEEGDLLDDDDNEDRGDDQLELIKDDEKEAEEGEDDRDSA NGEDDS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | RRM HNRPC family; RALY subfamily | ||||
| Function |
Binds pre-mRNA and nucleates the assembly of 40S hnRNP particles. Interacts with poly-U tracts in the 3'-UTR or 5'-UTR of mRNA and modulates the stability and the level of translation of bound mRNA molecules . Single HNRNPC tetramers bind 230-240 nucleotides. Trimers of HNRNPC tetramers bind 700 nucleotides. May play a role in the early steps of spliceosome assembly and pre-mRNA splicing. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) has been shown to alter the local structure in mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) via a mechanism named 'm(6)A-switch', facilitating binding of HNRNPC, leading to regulation of mRNA splicing.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 3183 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Regulator Type | WRITER ERASER READER | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
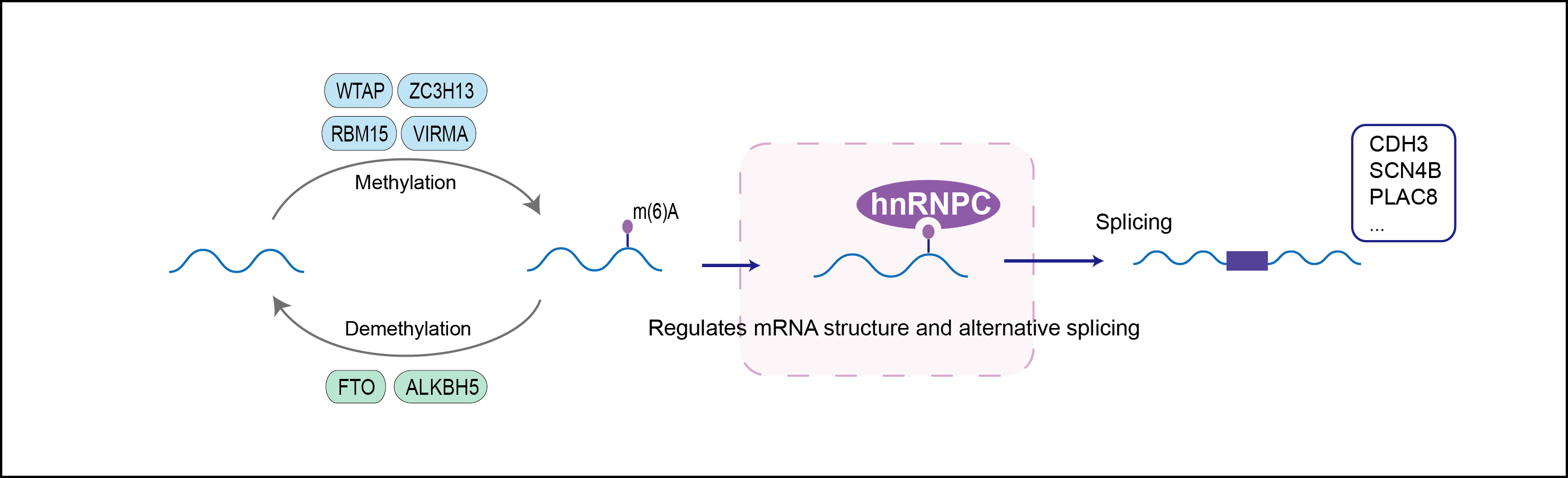
|
|||||
| Target Genes | Click to View Potential Target Genes of This Regulator | ||||
Full List of Target Gene(s) of This m6A Regulator and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
HNRNPC can regulate the m6A methylation of following target genes, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulted from the regulation of certain target gene.
Browse Target Gene related Disease
Browse Target Gene related Drug
Galectin-9 (LGALS9)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by HNRNPC | ||
| Cell Line | MG63 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: HNRNPC knockdown MG63 cells
Control: Wild type MG63 cells
|
GSE63086 | |
| Regulation |
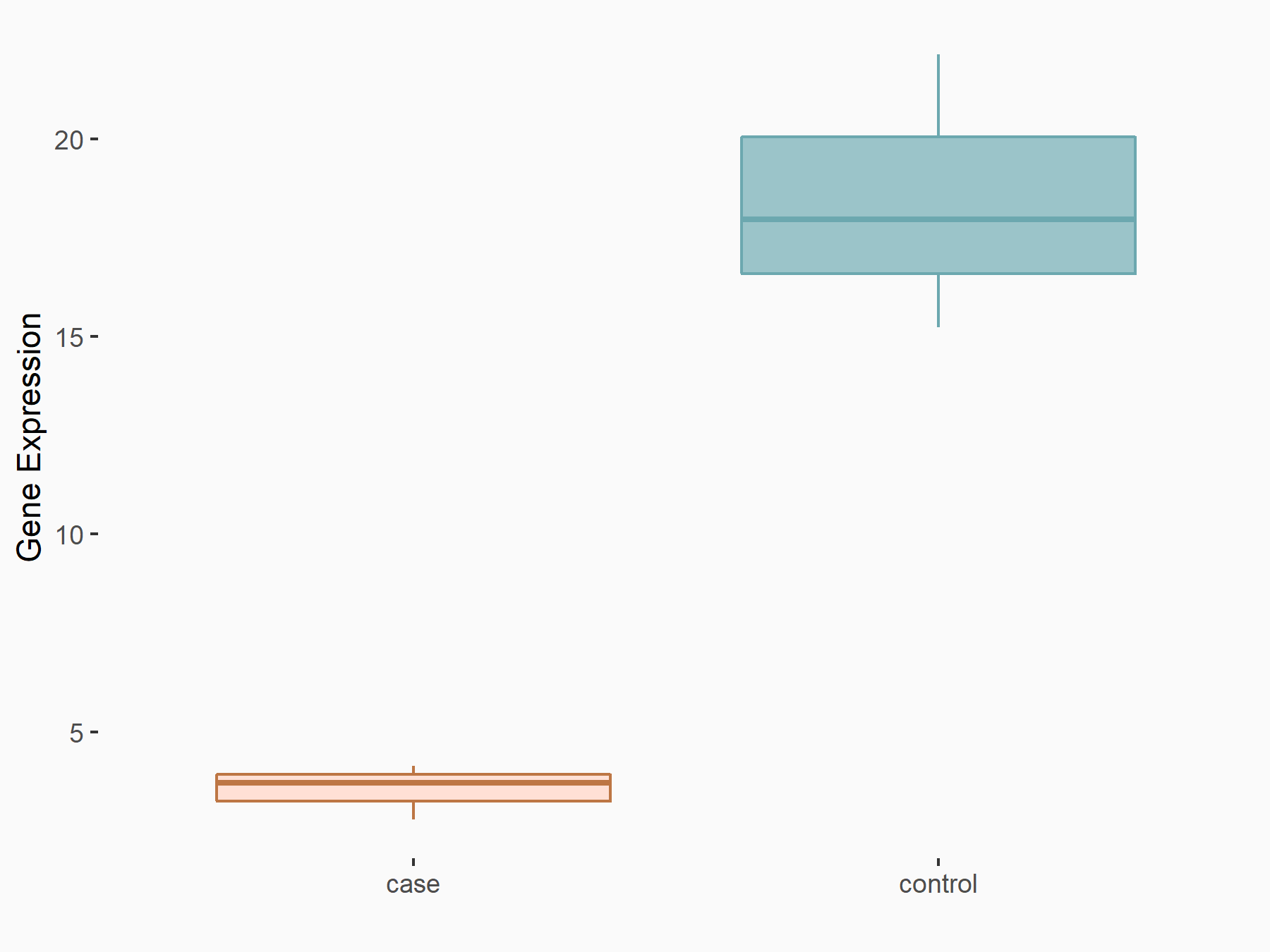 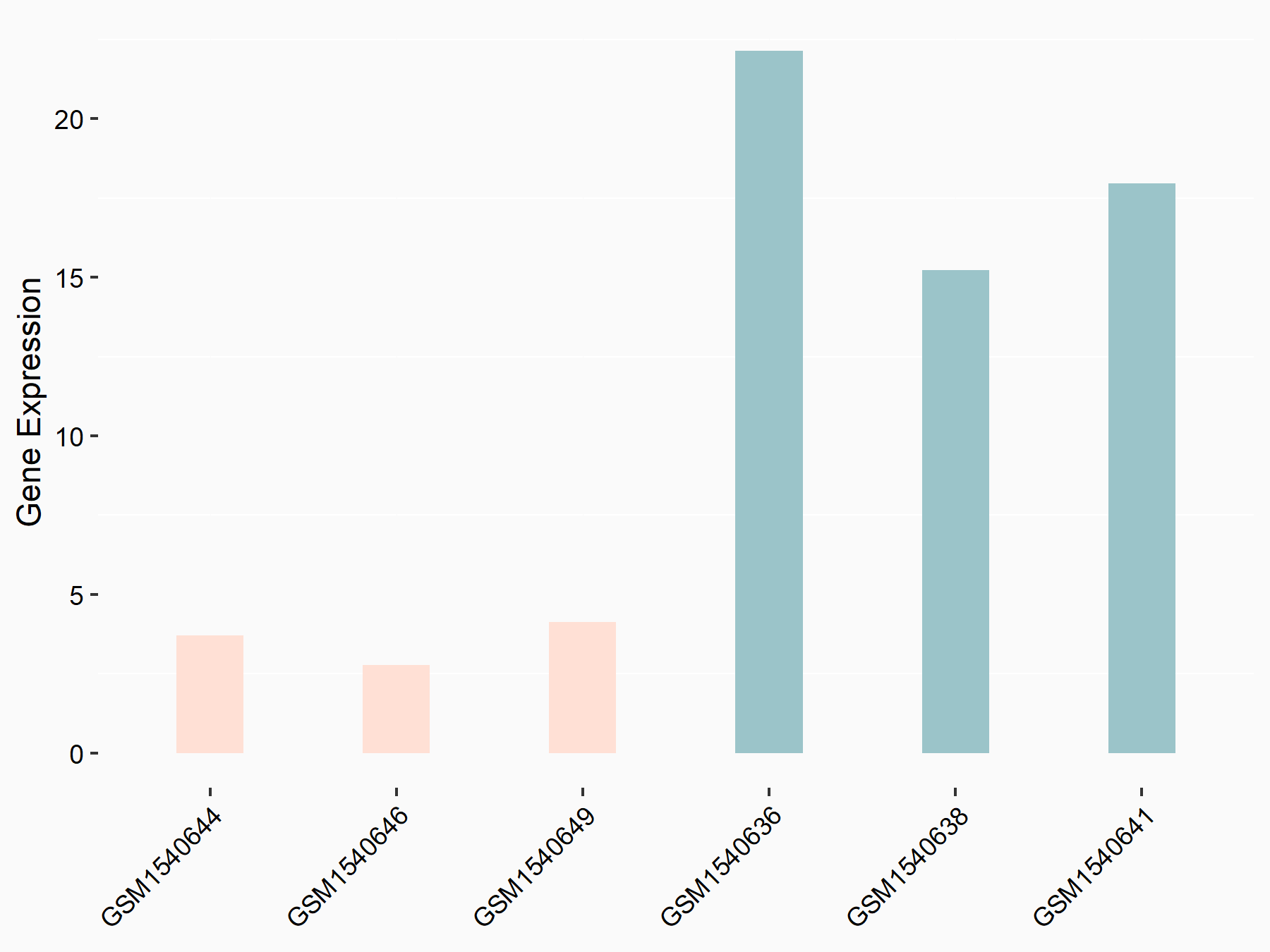 |
logFC: -2.10E+00 p-value: 1.66E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
In-vitro Model |
U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPA2B1 and HNRNPC were extensively expressed in the Glioblastoma multiforme(GBM) microenvironment. m6A regulators promoted the stemness state in GBM cancer cells. Cell communication analysis identified genes in the GALECTIN signaling network in GBM samples, and expression of these genes (Galectin-9 (LGALS9), CD44, CD45, and HAVCR2) correlated with that of m6A regulators. | |||
Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial (SOD2)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by HNRNPC | ||
| Cell Line | MG63 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: HNRNPC knockdown MG63 cells
Control: Wild type MG63 cells
|
GSE63086 | |
| Regulation |
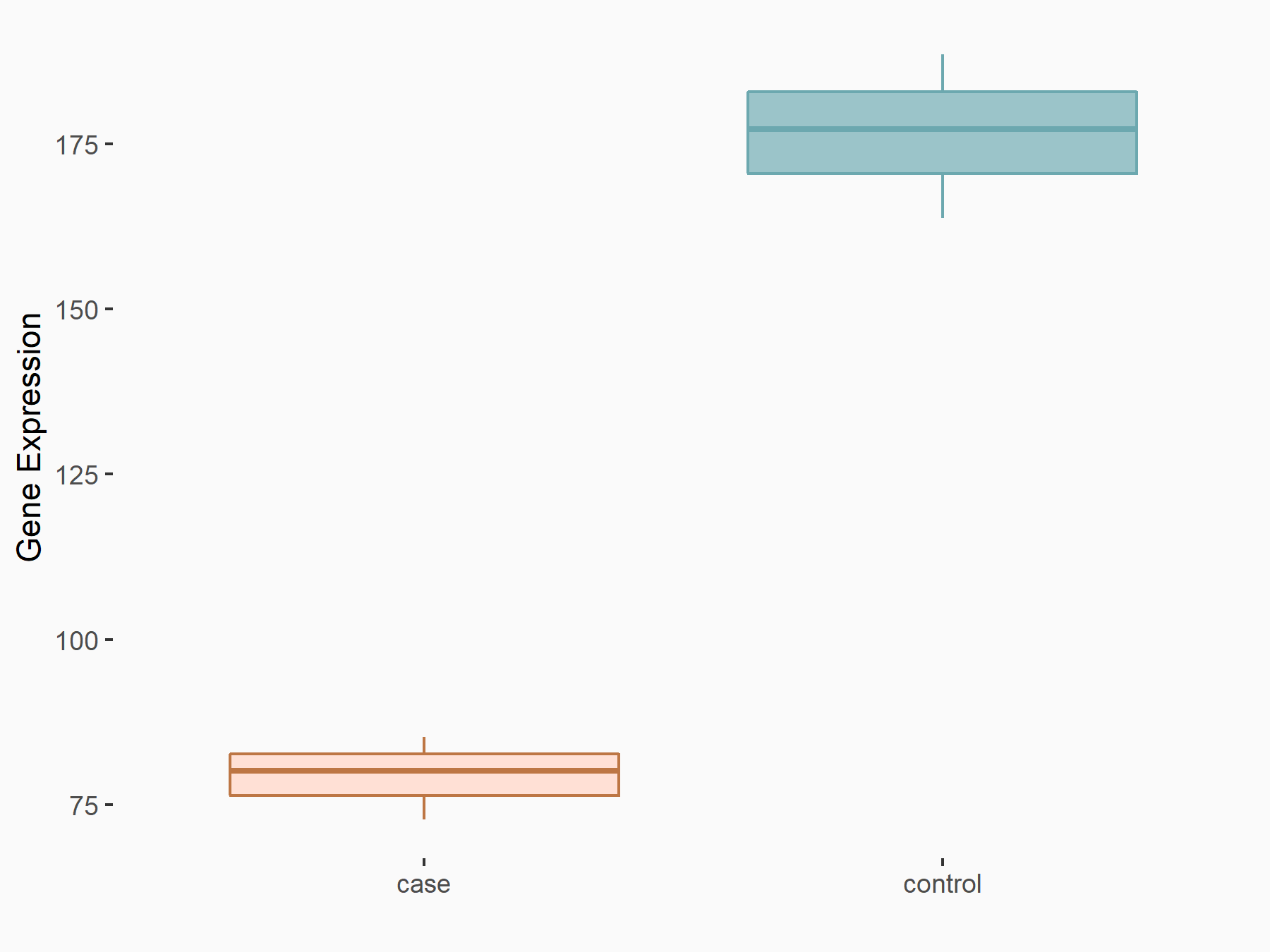 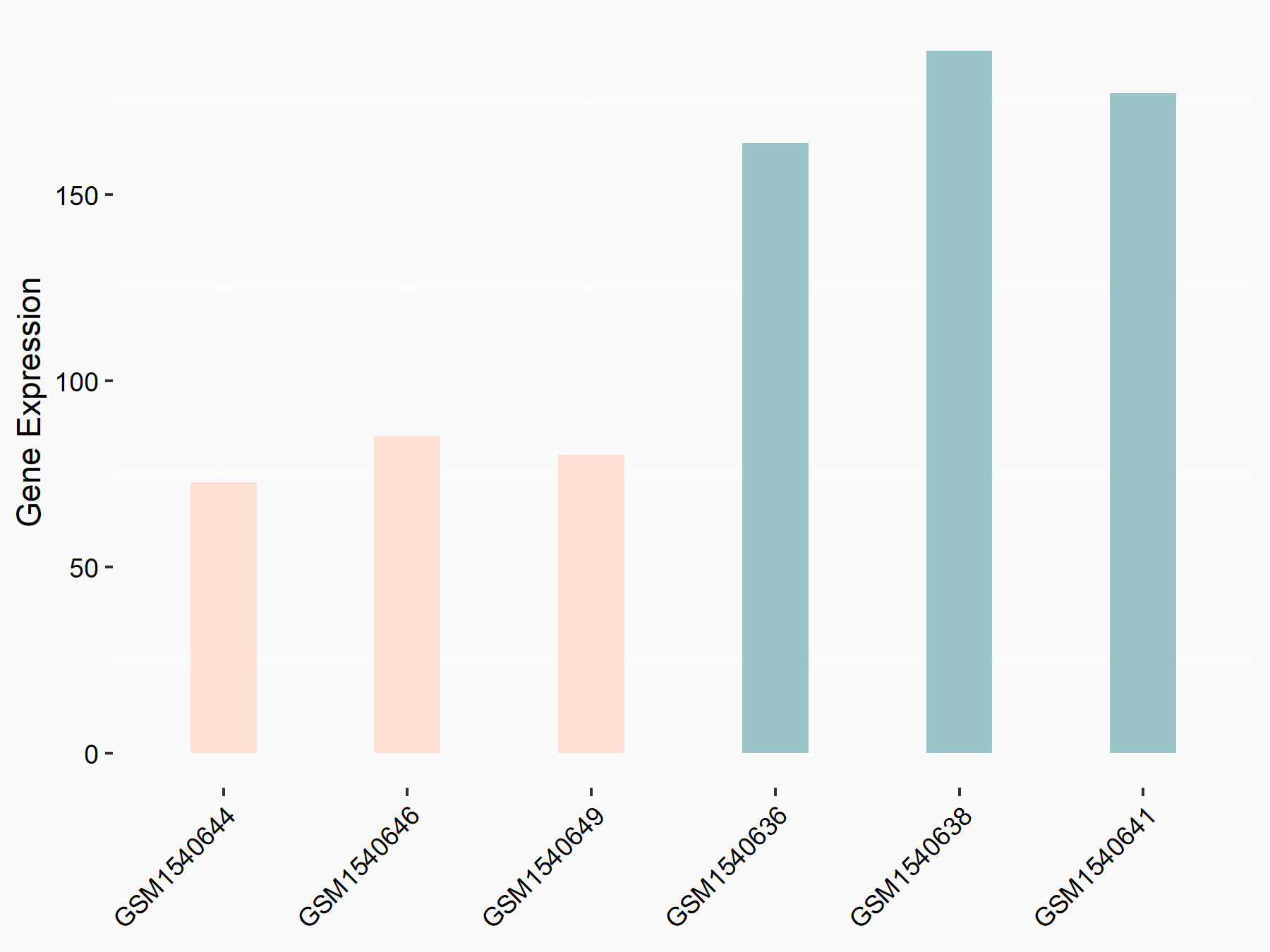 |
logFC: -1.14E+00 p-value: 6.60E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In-vitro Model |
EJ (Human bladder cancer cells) | |||
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| Response Summary | SNP rs5746136 affects m6A modification and regulate Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial (SOD2) expression by guiding the binding of hnRNPC to SOD2, which played a critical tumor suppressor role in bladder cancer cells by promoting cell apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation, migration and invasion. | |||
Adenylate kinase 4, mitochondrial (AK4)
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| UM-SCC-1 | Floor of mouth squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7707 | |
| SCC-9 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1685 | |
| NHOK (Normal oral keratinocytes) | ||||
CD44 antigen (CD44)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
In-vitro Model |
U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPA2B1 and HNRNPC were extensively expressed in the Glioblastoma multiforme(GBM) microenvironment. m6A regulators promoted the stemness state in GBM cancer cells. Cell communication analysis identified genes in the GALECTIN signaling network in GBM samples, and expression of these genes (LGALS9, CD44 antigen (CD44), CD45, and HAVCR2) correlated with that of m6A regulators. | |||
Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 (HAVCR2)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
In-vitro Model |
U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPA2B1 and HNRNPC were extensively expressed in the Glioblastoma multiforme(GBM) microenvironment. m6A regulators promoted the stemness state in GBM cancer cells. Cell communication analysis identified genes in the GALECTIN signaling network in GBM samples, and expression of these genes (LGALS9, CD44, CD45, and Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 (HAVCR2)) correlated with that of m6A regulators. | |||
Interferon beta (IFNB1)
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Immune inflammation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
PC12 | Rat adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
| Response Summary | Overexpression of HNRNPC can promote the proliferation of PC12 cells, inhibit their apoptosis, and inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors Interferon beta (IFNB1), IL-6, and TNF-Alpha, suggesting that HNRNPC can cause PD by inhibiting the proliferation of dopaminergic nerve cells, promoting their apoptosis, and causing immune inflammation. | |||
Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C (CD45)
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.00] | |||
In-vitro Model |
U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPA2B1 and HNRNPC were extensively expressed in the Glioblastoma multiforme(GBM) microenvironment. m6A regulators promoted the stemness state in GBM cancer cells. Cell communication analysis identified genes in the GALECTIN signaling network in GBM samples, and expression of these genes (LGALS9, CD44, Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C (CD45), and HAVCR2) correlated with that of m6A regulators. | |||
Transcription factor AP-2-alpha (TFAP2A)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
EO771 | Malignant neoplasms of the mouse mammary gland | Mus musculus | CVCL_GR23 |
| EMT6 | Malignant neoplasms of the mouse mammary gland | Mus musculus | CVCL_1923 | |
| 4T1.2 | Malignant neoplasms of the mouse mammary gland | Mus musculus | CVCL_GR32 | |
|
NMuMG
|
N.A. | Mus musculus | CVCL_0075 | |
microRNA 186 (MIR186)
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEEC cell line (Normal esophageal epithelial cell line) | |||
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPC, YTHDF, ZC3H13, YTHDC2, and METTL14 were dysregulated in esophageal cancer tissues. miR-186 interacted with HNRNPC and suppressed the expression of HNRNPC. Four miRNAs (microRNA 186 (MIR186), miR-320c, miR-320d, and miR-320b) were used to construct a prognostic signature, which could serve as a prognostic predictor independent from routine clinicopathological features. | |||
hsa-miR-183-3p
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| Response Summary | Rs7495 in 3'UTR of hnRNPC was associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma susceptibility in a Chinese population. The rs7495, in the hnRNPC 3'UTR, might disrupt a binding site for hsa-miR-183-3p, thus increasing the expression of hnRNPC and promoting the proliferation of PDAC cells. | |||
hsa-miR-320b
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEEC cell line (Normal esophageal epithelial cell line) | |||
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPC, YTHDF, ZC3H13, YTHDC2, and METTL14 were dysregulated in esophageal cancer tissues. miR-186 interacted with HNRNPC and suppressed the expression of HNRNPC. Four miRNAs (miR-186, miR-320c, miR-320d, and hsa-miR-320b) were used to construct a prognostic signature, which could serve as a prognostic predictor independent from routine clinicopathological features. | |||
hsa-miR-320c
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEEC cell line (Normal esophageal epithelial cell line) | |||
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPC, YTHDF, ZC3H13, YTHDC2, and METTL14 were dysregulated in esophageal cancer tissues. miR-186 interacted with HNRNPC and suppressed the expression of HNRNPC. Four miRNAs (miR-186, hsa-miR-320c, miR-320d, and miR-320b) were used to construct a prognostic signature, which could serve as a prognostic predictor independent from routine clinicopathological features. | |||
hsa-miR-320d
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEEC cell line (Normal esophageal epithelial cell line) | |||
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| TE-1 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1759 | |
| Response Summary | HNRNPC, YTHDF, ZC3H13, YTHDC2, and METTL14 were dysregulated in esophageal cancer tissues. miR-186 interacted with HNRNPC and suppressed the expression of HNRNPC. Four miRNAs (miR-186, miR-320c, hsa-miR-320d, and miR-320b) were used to construct a prognostic signature, which could serve as a prognostic predictor independent from routine clinicopathological features. | |||
Disks large-associated protein 5 (DLGAP5)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| In-vivo Model | In the xenograft tumor model in the nude mice, 5 × 106 A549 cells were mixed with 40 μg serum-EVs-oe-NC or serum-EVs-oe-HNRNPC, respectively, and then inoculated subcutaneously in the left armpit of BALB/c nude mice. / In the tumor metastasis model in nude mice, 1 × 106 A549 cells were injected into BALB/c nude mice via the tail vein. The nude mice were randomly treated with serum-EVs-oe-NC or serum-EVs-oe-HNRNPC; 20 mg EVs were injected via the tail vein once a week for 4 weeks. | |||
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
Methylosome protein WDR77 (WDR77)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
In-vitro Model |
MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| T-47D | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| HCC1937 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0290 | |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
Nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 2 (NAP1L2)
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
22Rv1 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1045 |
| HNC PC3 | Retromolar trigone squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C8XA | |
| LNCaP C4-2B | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4784 | |
| VCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2235 | |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| RWPE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3791 | |
Unspecific Target Gene
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Gemcitabine | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
In-vitro Model |
BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| HDE-CT cell line (A normal human pancreatic cell line) | ||||
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| Response Summary | Lasso regression identified a six-m6A-regulator-signature prognostic model (KIAA1429, HNRNPC, METTL3, YTHDF1, IGF2BP2, and IGF2BP3). Gene set enrichment analysis revealed m6A regulators (KIAA1429, HNRNPC, and IGF2BP2) were related to multiple biological behaviors in pancreatic cancer, including adipocytokine signaling, the well vs. poorly differentiated tumor pathway, tumor metastasis pathway, epithelial mesenchymal transition pathway, gemcitabine resistance pathway, and stemness pathway. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Response Summary | High HNRNPC expression is significantly related to poor overall survival in patients with LUAD, suggesting that HNRNPC is a cancer-promoting factor and a potential prognostic biomarker in LUAD. | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Gemcitabine
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| Pathway Response | Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| In-vitro Model | BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 |
| HDE-CT cell line (A normal human pancreatic cell line) | ||||
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| Response Summary | Lasso regression identified a six-m6A-regulator-signature prognostic model (KIAA1429, HNRNPC, METTL3, YTHDF1, IGF2BP2, and IGF2BP3). Gene set enrichment analysis revealed m6A regulators (KIAA1429, HNRNPC, and IGF2BP2) were related to multiple biological behaviors in pancreatic cancer, including adipocytokine signaling, the well vs. poorly differentiated tumor pathway, tumor metastasis pathway, epithelial mesenchymal transition pathway, gemcitabine resistance pathway, and stemness pathway. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
RNA modification
m6A Target: microRNA 21 (MIR21)
| In total 7 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00589 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | Protein sprouty homolog 2 (SPRY2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00591 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | Protein sprouty homolog 2 (SPRY2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00593 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | |
| Regulated Target | Growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m5C → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00595 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Putative methyltransferase NSUN7 (NSUN7) | |
| Regulated Target | Phosphofructokinase, muscle (PFKM) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00597 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET1 (TET1) | |
| Regulated Target | Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00599 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET2 (TET2) | |
| Regulated Target | Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00601 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET3 (TET3) | |
| Regulated Target | Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 (PTEN) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → m5C | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Target: Adenylate kinase 4, mitochondrial (AK4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05010 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 662 (LINC00662) | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | |
m6A Target: Transcription factor AP-2-alpha (TFAP2A)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05074 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-944 | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05076 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_BACH2 | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-944 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Methylosome protein WDR77 (WDR77)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05075 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-944 | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05077 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_BACH2 | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-944 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
m6A Target: Nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 2 (NAP1L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05102 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Nucleosome assembly protein 1 like 6, pseudogene (NAP1L6P) | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Prostate cancer | |
m6A Target: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05365 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1705 (LINC01705) | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-183-3p
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05469 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-183-3p | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | |
m6A Target: microRNA 186 (MIR186)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05506 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 186 (MIR186) | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-320c
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05507 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-320c | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-320d
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05508 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-320d | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
m6A Target: hsa-miR-320b
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05509 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-320b | |
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
m6A Target: microRNA 21 (MIR21)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05777 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | MicroRNA 21 (MIR21) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
Xenobiotics Compound(s) Regulating the m6A Methylation Regulator
| Compound Name | Dabigatran | Investigative |
|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Dabigatran; 211914-51-1; BIBR 953; BIBR-953; 3-[[2-[(4-carbamimidoylanilino)methyl]-1-methylbenzimidazole-5-carbonyl]-pyridin-2-ylamino]propanoic acid; CHEBI:70752; BIBR 953 (Dabigatran, Pradaxa); UNII-I0VM4M70GC; I0VM4M70GC; BIBR 953 ZW; CHEMBL48361; 3-[[2-[[(4-CARBAMIMIDOYLPHENYL)AMINO]METHYL]-1-METHYL-BENZOIMIDAZOLE-5-CARBONYL]-PYRIDIN-2-YL-AMINO]PROPANOIC ACID; N-[(2-{[(4-Carbamimidoylphenyl)amino]methyl}-1-Methyl-1h-Benzimidazol-5-Yl)carbonyl]-N-Pyridin-2-Yl-Beta-Alanine; 3-(2-(((4-carbamimidoylphenyl)amino)methyl)-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxamido)propanoic acid; C25H25N7O3; 3-[1-(2-{[(4-carbamimidoylphenyl)amino]methyl}-1-methyl-1H-1,3-benzodiazol-5-yl)-N-(pyridin-2-yl)formamido]propanoic acid; BIBR953; beta-Alanine, N-((2-(((4-(aminoiminomethyl)phenyl)amino)methyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)carbonyl)-N-2-pyridinyl-; BETA-ALANINE, N-[[2-[[[4-(AMINOIMINOMETHYL)PHENYL]AMINO]METHYL]-1-METHYL-1H-BENZIMIDAZOL-5-YL]CARBONYL]-N-2-PYRIDINYL-; Pradaxa (dabigatran); Dabigatran-[13C6]; Dabigatran-D3 solution; Dabigatran (USAN/INN); BIBR 953(Dabigatran); Epitope ID:186729; Dabigatran (BIBR-953); SCHEMBL3573; BIBR 953ZW; BIBR-953ZW; BIBR-953-ZW; Dabigatran [USAN:INN:BAN]; GTPL6380; BIBR 953,Dabigatran, Pradaxa; HSDB 8062; AOB5262; DTXSID50175419; BCP06664; ZINC1910616; BDBM50112086; BIBR 953 - Dabigatran - Pradaxa; MFCD09837830; s2196; STL450902; AKOS005266720; AM81238; CS-1399; DB14726; PB38204; SB20292; NCGC00346575-01; NCGC00346575-06; (non-labelled)Dabigatran-d4 Hydrochloride; AC-25299; AS-11488; HY-10163; BIBR 953 (Dabigatran etexilate, Pradaxa); FT-0648482; FT-0665441; 2,6-Bis[(R)-4-phenyloxazolin-2-yl]pyridine; C21556; D09707; AB01274802-01; AB01274802_02; A815190; Q419345; Q-102529; 1-Methyl-2-[(4-amidinophenyl)aminomethyl]benzimidazol-5-yl-carboxylic acid-N-(2-pyridyl)-N-(2-hydroxycarbonylethyl)amide; 1-Methyl-2-[N-(4-amidinophenyl)-aminomethyl]-benzimidazol-5-yl-carboxylic acid-N-(2-pyridyl)-N-(2-hydroxycarbonylethyl)-amide; 1-Methyl-2-[N-(4-amidinophenyl)aminomethyl]benzimidazol-5-yl-carboxylic acid-N-(2-pyridyl)-N-(2-hydroxycarbonylethyl)amide; 3-(((2-(((4-Carbamimidoylphenyl)amino)methyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)carbonyl)(pyridin-2-yl)amino)propanoic acid; 3-({2-[(4-Carbamimidoyl-phenylamino)-methyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzoimidazole-5-carbonyl}-pyridin-2-yl-amino)-propionic acid; 3-[[[2-[(4-carbamimidoylanilino)methyl]-1-methyl-5-benzimidazolyl]-oxomethyl]-(2-pyridinyl)amino]propanoic acid; 3-[[2-[[(4-carbamimidoylphenyl)amino]methyl]-1-methyl-benzimidazol-5-yl]carbonyl-pyridin-2-yl-amino]propanoic acid; 3-[[2-[[(4-carbamimidoylphenyl)amino]methyl]-1-methylbenzimidazole-5-carbonyl]-pyridin-2-ylamino]propanoic acid; b-Alanine,N-[[2-[[[4-(aminoiminomethyl)phenyl]amino]methyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl]carbonyl]-N-2-pyridinyl-; N-((2-((p-Amidinoanilino)methyl)-1-methyl-5-benzimidazolyl)carbonyl)-N-2-pyridyl-beta-alanine
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50=60000 nM
|
[14] |
| Compound Name | 3-[[2-[[4-[N'-[4-[[(3S)-4-[3-[2-[2-[3-[5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoylamino]propoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]propylamino]-4-oxo-3-[[4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)diazirin-3-yl]benzoyl]amino]butanoyl]amino]butyl]carbamimidoyl]anilino]methyl]-1-methylbenzimidazole-5-carbonyl]-pyridin-2-ylamino]propanoic acid | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL2216801
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Activity |
IC50=800 nM
|
[14] |
References