m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00360)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
CD274
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | LX2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 LX2 cells
Control: shLuc LX2 cells
|
GSE207909 | |
| Regulation |
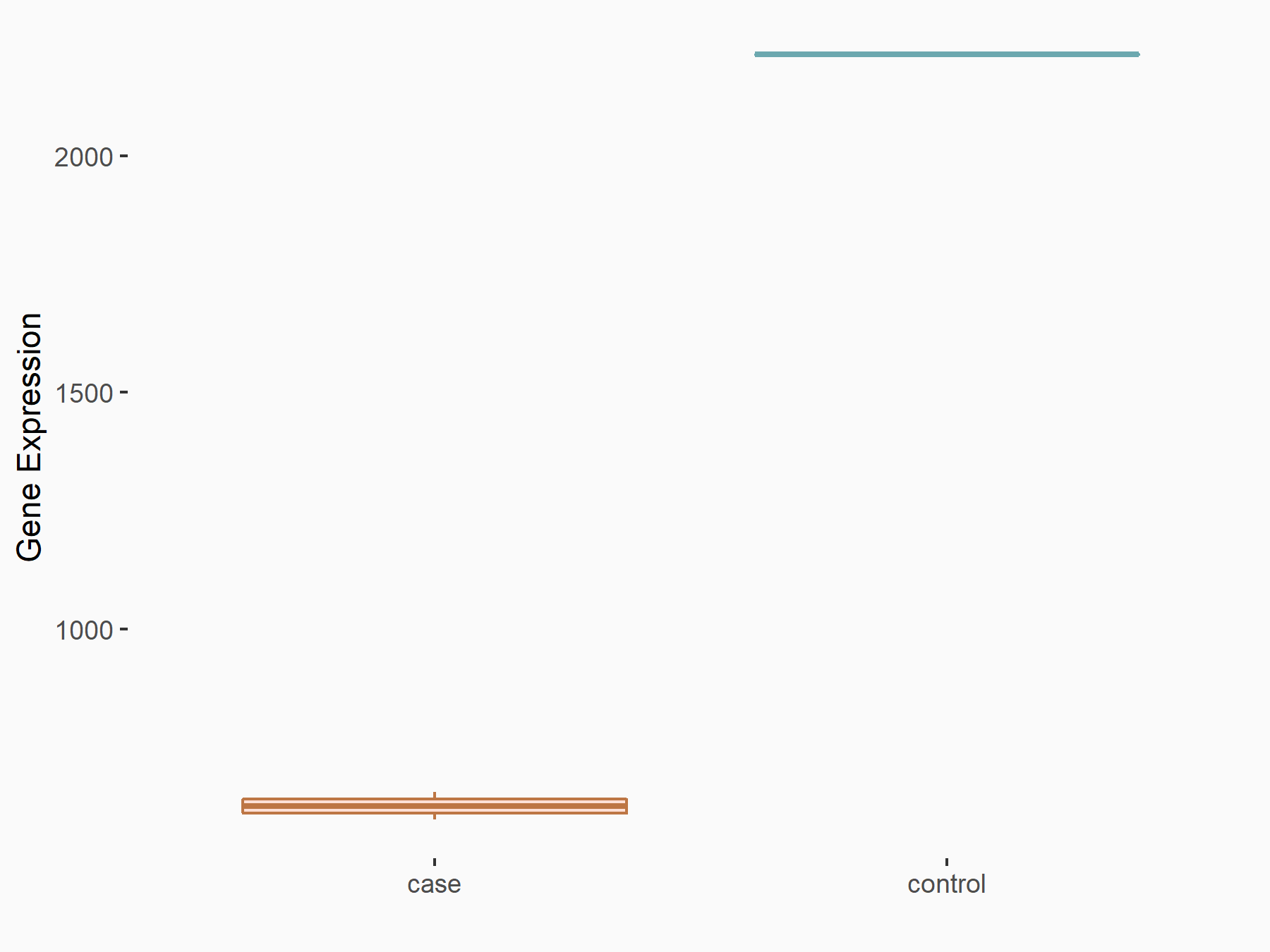 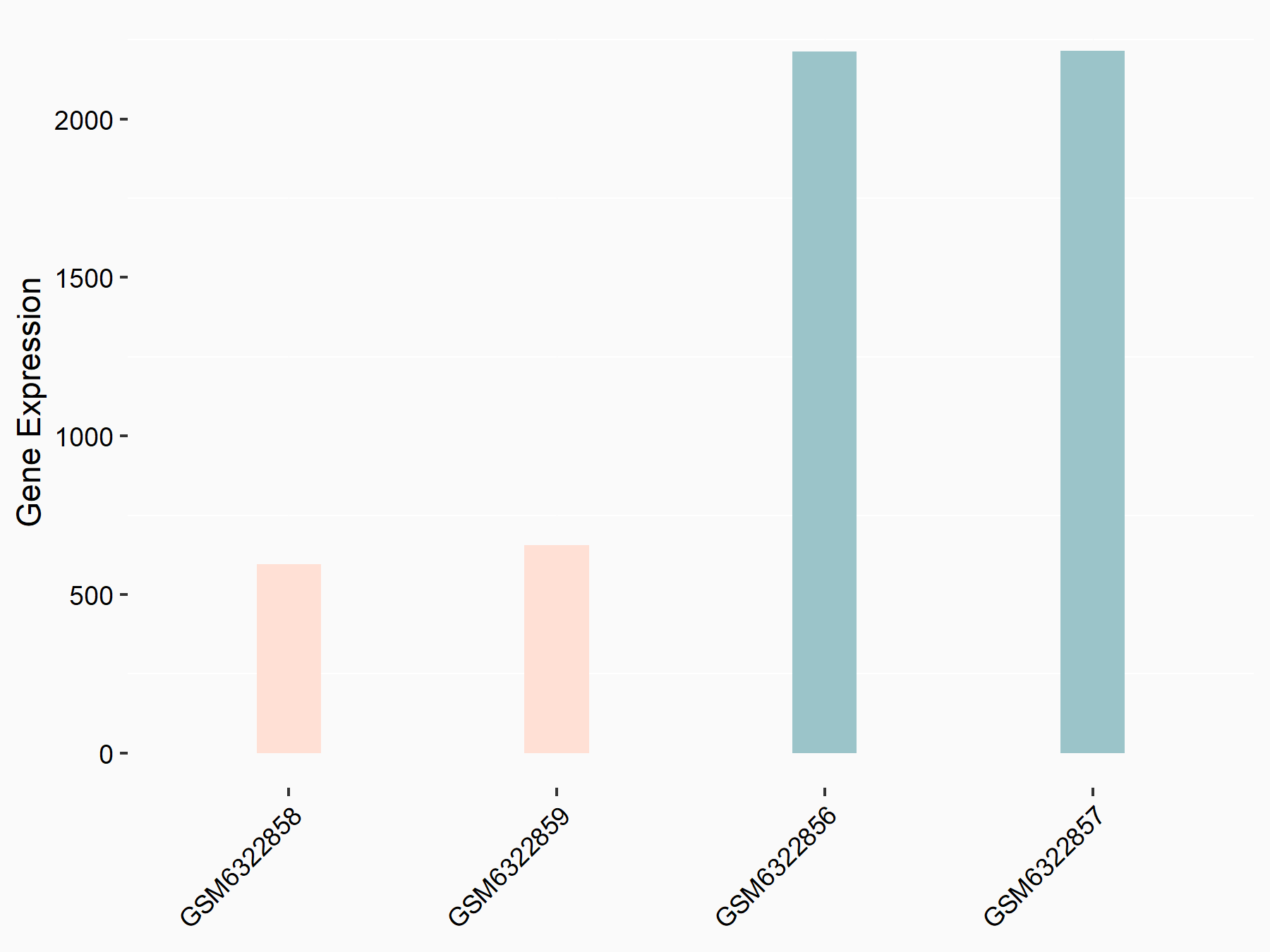 |
logFC: -1.82E+00 p-value: 4.68E-65 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
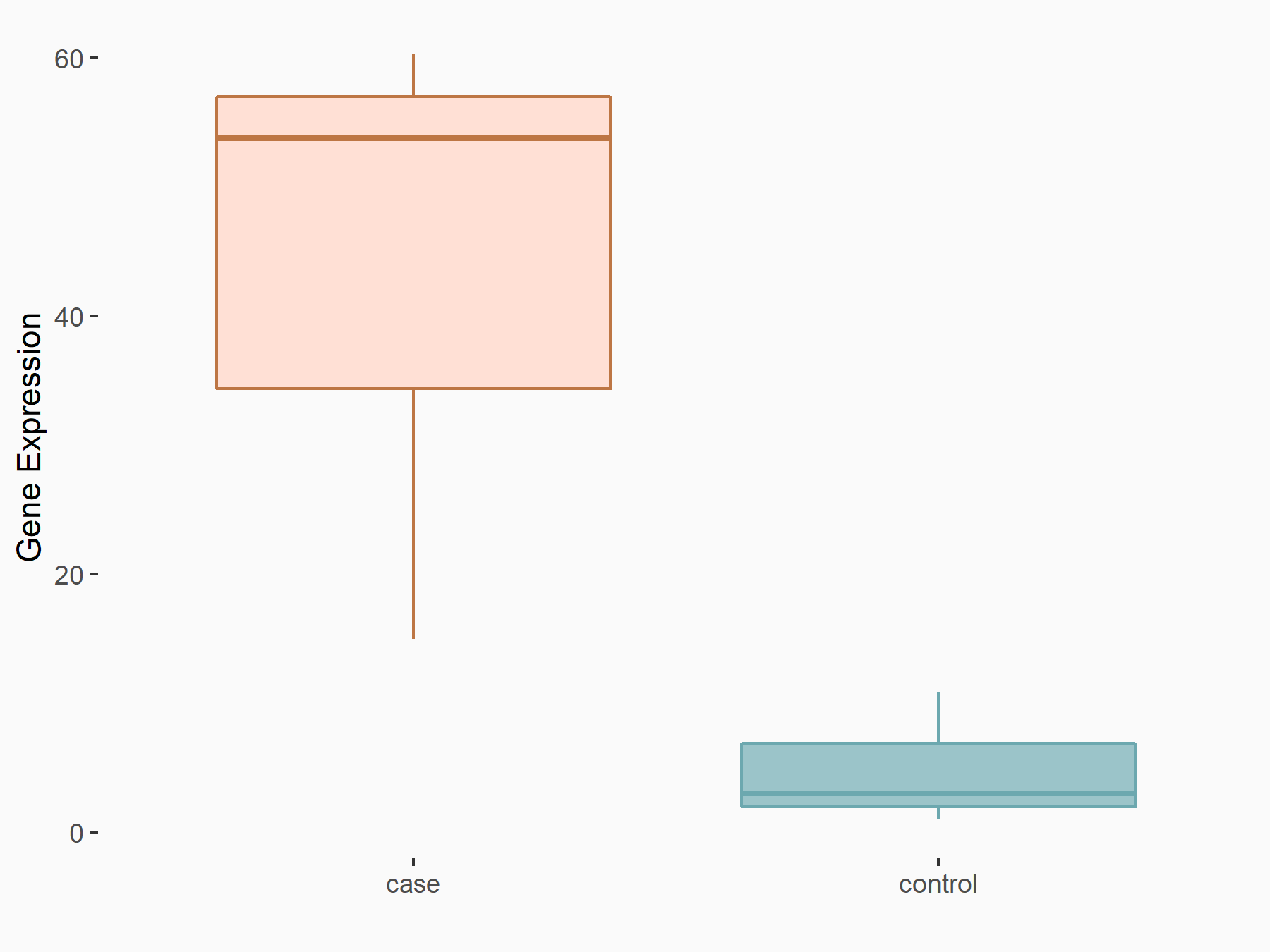
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between CD274 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 7.97E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 4 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 intensified the metastasis and proliferation of OSCC by modulating the m6A amounts of PRMT5 and Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1). | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| In-vitro Model | SCC-9 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1685 |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 | |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| In-vivo Model | Six-week-old nude mice were randomly divided into two groups (three mice per group) and cultured with continuous access to sterile food and water in pathogen-free sterile conditions. To establish the OSCC xenograft model, we subcutaneously injected 5 × 106 SCC-9 cells stably transfected with METTL3 shRNA or sh-NC vectors into nude mice. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) was a downstream target of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in breast cancer cells. METTL3-mediated PD-L1 mRNA activation was m6A-IGF2BP3-dependent. PD-L1 expression was also positively correlated with METTL3 and IGF2BP3 expression in breast cancer tissues. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Tumor immune escape | |||
| In-vitro Model | SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HCC38 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1267 | |
| 4T1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0125 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous xenograft experiments in B-NDG mice, approximately 1 × 106 MDA-MB-231 and there was subcutaneous injection of the cells that resuspended in 100 uL PBS into the left flank of the mice and were divided into 11 groups randomly (each containing 5 mice). After the treatment Atezolizumab (Selleck, Shanghai, China) or corresponding iso control antibody (Selleck, Shanghai, China) was injected intratumorally on day 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 post-MDA-MB-231 inoculations, and 5 × 106 cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells were injected in the tail vein on day 7, 14, 21. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 was essential for bladder cancer cells to resist the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells by regulating Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression. Additionally, JNK signaling contributed to tumor immune escape in a METTL3-dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| In-vitro Model | UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male C57BL/6J mice (6 weeks old) were given drinking water containing 0.05% (w/v) BBN (TCI, catalog no. B0938) for 20 weeks. After the BBN administration, mice were given normal drinking water and injected with 10% DMSO (as a control) or 20 mg/kg SP600125 (Selleck, catalog no. 129-56-6) i.p. every 3 days. After seven injections, mice were euthanized for tissue retrieval. For the bladder cancer cell-derived xenograft mouse model, male C57BL/6J mice (6 weeks old) were injected subcutaneously with 1 × 106 MB49 cells. One week after bladder cancer cell injection, 10% DMSO or 20 mg/kg SP600125 were injected i.p. every 3 days. | |||
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
 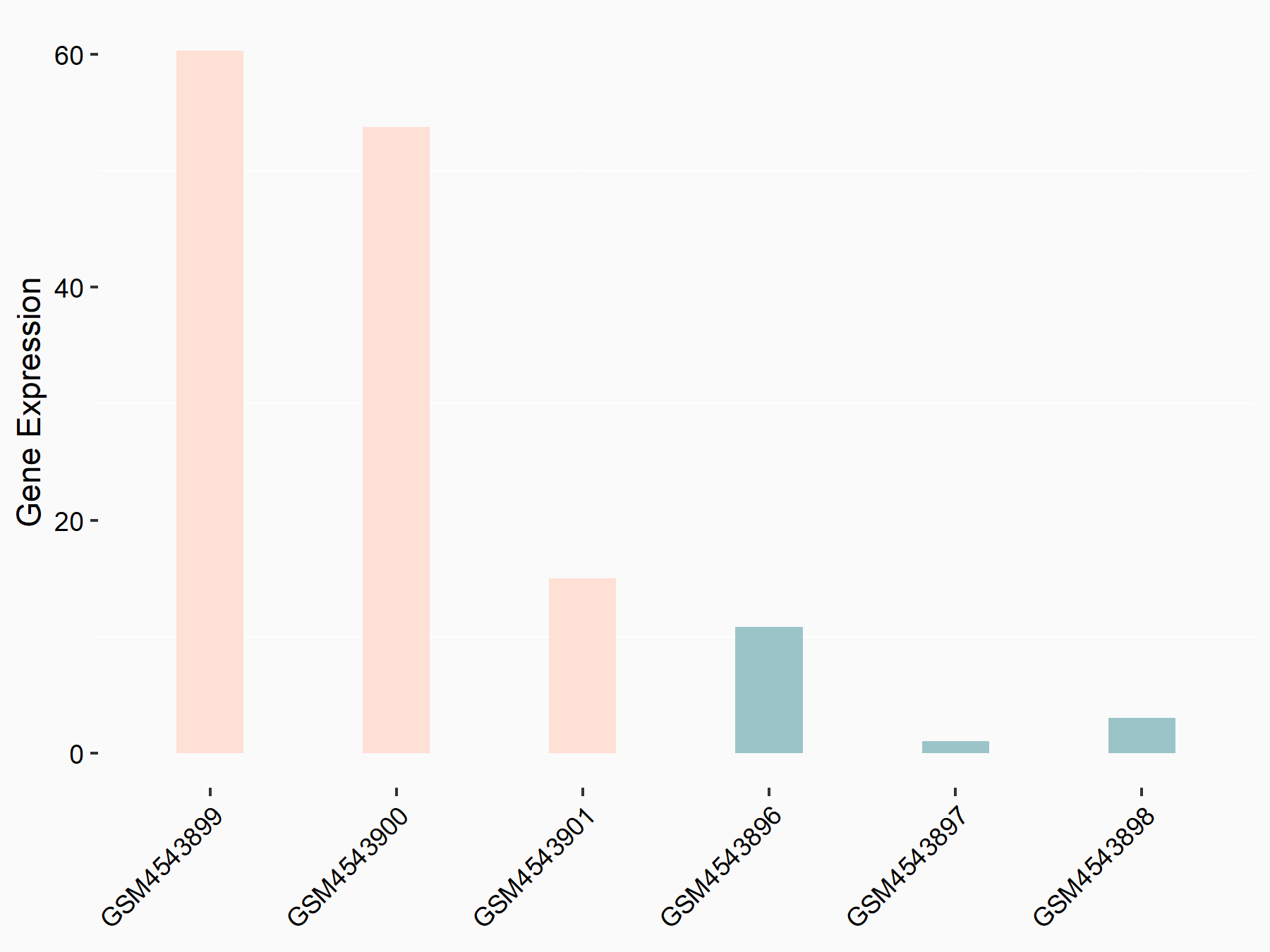 |
logFC: 3.22E+00 p-value: 3.45E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | Arecoline-induced FTO promotes the stability and expression levels of Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) transcripts through mediating m6A modification and MYC activity, respectively. PD-L1 upregulation confers superior cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to T-cell killing to OSCC cells. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | 143B cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siALKBH5 transfected 143B cells
Control: siControl 143B cells
|
GSE154528 | |
| Regulation |
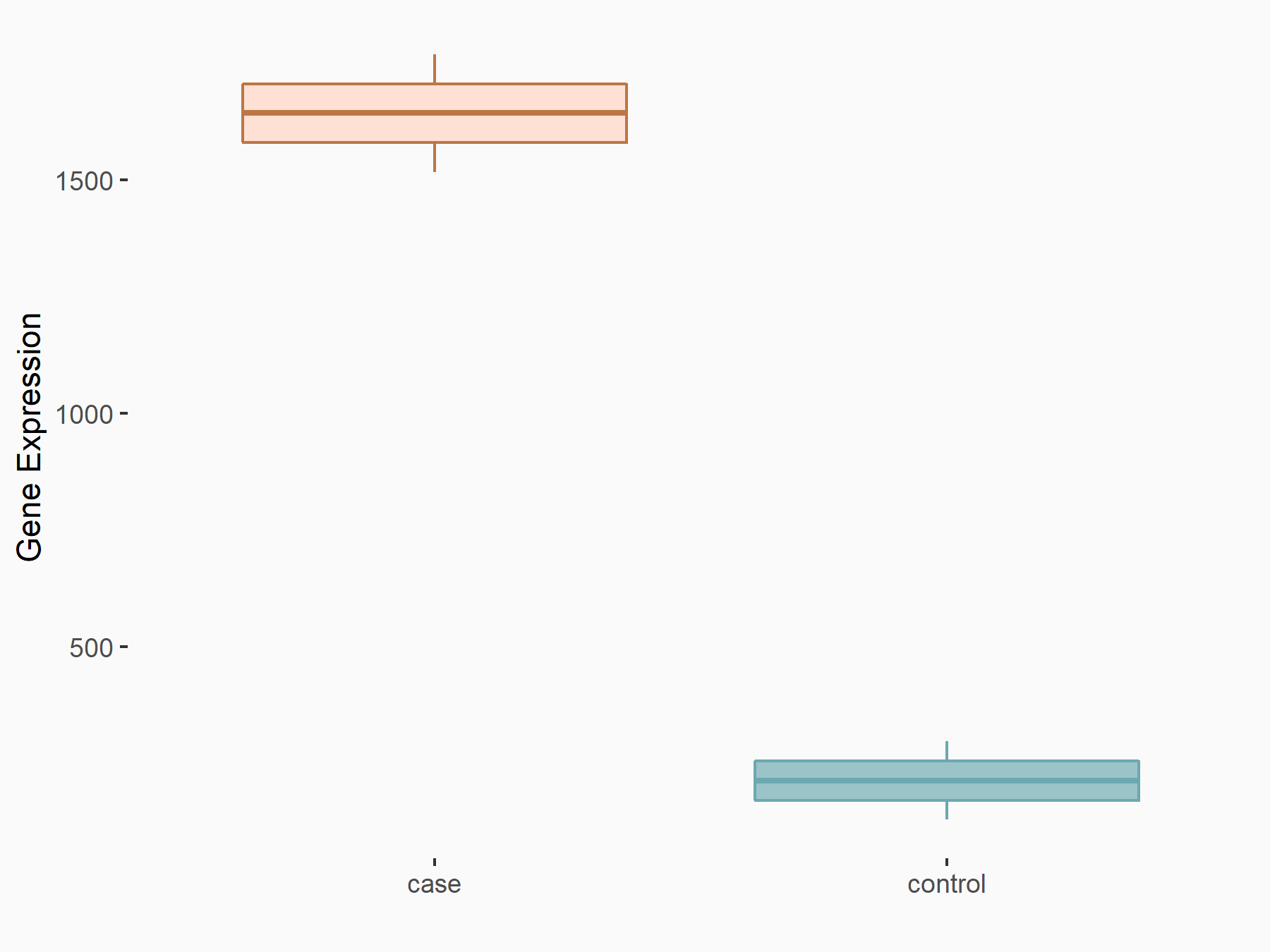  |
logFC: 2.95E+00 p-value: 3.40E-21 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 as an important m6A demethylase that orchestrates Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.10 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| In-vitro Model | TFK-1 | Cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2214 |
| RBE | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4896 | |
| LIPF178c (LIPF178c human bile duct cancer cells from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| LIPF155c (LIPF155c human bile duct cancer cells from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| LICCF (LICCF human intrahepatic bile duct cancer cell line from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| HCCC-9810 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6908 | |
| In-vivo Model | ICC tumor cells (LIPF178c-shCtrl/shALKBH5) of 5 × 106 were injected into the right flank of NCG mice. Tumor volume was calculated by the formula: volume = ab2/2 (a, the longer axis; b, the shorter axis). T-cell killing assay in vitro was conducted as previously reported (20). PBMCs from healthy donors were activated and expanded as described above. The day before tumor cell injection, PBMC (i.v. 1 × 107 cells) was adoptively transferred to NCG mice via the tail vein. At the end, the PBMC was isolated and subjected to flow cytometry for detecting T-cell percentage. | |||
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) was a downstream target of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in breast cancer cells. METTL3-mediated PD-L1 mRNA activation was m6A-IGF2BP3-dependent. PD-L1 expression was also positively correlated with METTL3 and IGF2BP3 expression in breast cancer tissues. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Tumor immune escape | |||
| In-vitro Model | SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HCC38 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1267 | |
| 4T1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0125 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous xenograft experiments in B-NDG mice, approximately 1 × 106 MDA-MB-231 and there was subcutaneous injection of the cells that resuspended in 100 uL PBS into the left flank of the mice and were divided into 11 groups randomly (each containing 5 mice). After the treatment Atezolizumab (Selleck, Shanghai, China) or corresponding iso control antibody (Selleck, Shanghai, China) was injected intratumorally on day 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 post-MDA-MB-231 inoculations, and 5 × 106 cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells were injected in the tail vein on day 7, 14, 21. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | Arecoline-induced FTO promotes the stability and expression levels of Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) transcripts through mediating m6A modification and MYC activity, respectively. PD-L1 upregulation confers superior cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to T-cell killing to OSCC cells. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 intensified the metastasis and proliferation of OSCC by modulating the m6A amounts of PRMT5 and Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1). | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| In-vitro Model | SCC-9 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1685 |
| SCC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1684 | |
| SCC-25 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1682 | |
| CAL-27 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| In-vivo Model | Six-week-old nude mice were randomly divided into two groups (three mice per group) and cultured with continuous access to sterile food and water in pathogen-free sterile conditions. To establish the OSCC xenograft model, we subcutaneously injected 5 × 106 SCC-9 cells stably transfected with METTL3 shRNA or sh-NC vectors into nude mice. | |||
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [6] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 as an important m6A demethylase that orchestrates Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.10] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| In-vitro Model | TFK-1 | Cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2214 |
| RBE | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4896 | |
| LIPF178c (LIPF178c human bile duct cancer cells from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| LIPF155c (LIPF155c human bile duct cancer cells from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| LICCF (LICCF human intrahepatic bile duct cancer cell line from China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, China)) | ||||
| HCCC-9810 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6908 | |
| In-vivo Model | ICC tumor cells (LIPF178c-shCtrl/shALKBH5) of 5 × 106 were injected into the right flank of NCG mice. Tumor volume was calculated by the formula: volume = ab2/2 (a, the longer axis; b, the shorter axis). T-cell killing assay in vitro was conducted as previously reported (20). PBMCs from healthy donors were activated and expanded as described above. The day before tumor cell injection, PBMC (i.v. 1 × 107 cells) was adoptively transferred to NCG mice via the tail vein. At the end, the PBMC was isolated and subjected to flow cytometry for detecting T-cell percentage. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | This study revealed that m6A methylation is closely related to the poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients via interference with the TIME, which suggests that m6A plays a role in optimizing individualized immunotherapy management and improving prognosis. The expression levels of METTL3, FTO and YTHDF1 in non-small cell lung cancer were changed. Patients in Cluster 1 had lower immunoscores, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, and shorter overall survival compared to patients in Cluster 2. The hallmarks of the Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (MYC) targets, E2 transcription Factor (E2F) targets were significantly enriched. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) was a downstream target of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in breast cancer cells. METTL3-mediated PD-L1 mRNA activation was m6A-IGF2BP3-dependent. PD-L1 expression was also positively correlated with METTL3 and IGF2BP3 expression in breast cancer tissues. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Tumor immune escape | |||
| In-vitro Model | SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HCC38 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1267 | |
| 4T1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0125 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous xenograft experiments in B-NDG mice, approximately 1 × 106 MDA-MB-231 and there was subcutaneous injection of the cells that resuspended in 100 uL PBS into the left flank of the mice and were divided into 11 groups randomly (each containing 5 mice). After the treatment Atezolizumab (Selleck, Shanghai, China) or corresponding iso control antibody (Selleck, Shanghai, China) was injected intratumorally on day 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 post-MDA-MB-231 inoculations, and 5 × 106 cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells were injected in the tail vein on day 7, 14, 21. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) was a downstream target of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in breast cancer cells. METTL3-mediated PD-L1 mRNA activation was m6A-IGF2BP3-dependent. PD-L1 expression was also positively correlated with METTL3 and IGF2BP3 expression in breast cancer tissues. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Tumor immune escape | |||
| In-vitro Model | SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| HCC38 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1267 | |
| 4T1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0125 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous xenograft experiments in B-NDG mice, approximately 1 × 106 MDA-MB-231 and there was subcutaneous injection of the cells that resuspended in 100 uL PBS into the left flank of the mice and were divided into 11 groups randomly (each containing 5 mice). After the treatment Atezolizumab (Selleck, Shanghai, China) or corresponding iso control antibody (Selleck, Shanghai, China) was injected intratumorally on day 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 post-MDA-MB-231 inoculations, and 5 × 106 cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells were injected in the tail vein on day 7, 14, 21. | |||
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A-related prognostic lncRNA signature serves as a crucial mediator of the immune microenvironment in bladder cancer, representing promising therapeutic targets for improving immunotherapeutic efficacy. Cluster 1 was significantly correlated with poor prognosis, advanced clinical stage, higher Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression, a higher ESTIMATEScore and immuneScore, and distinct immune cell infiltration. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
| PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 was essential for bladder cancer cells to resist the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells by regulating Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1) expression. Additionally, JNK signaling contributed to tumor immune escape in a METTL3-dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| In-vitro Model | UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 |
| T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male C57BL/6J mice (6 weeks old) were given drinking water containing 0.05% (w/v) BBN (TCI, catalog no. B0938) for 20 weeks. After the BBN administration, mice were given normal drinking water and injected with 10% DMSO (as a control) or 20 mg/kg SP600125 (Selleck, catalog no. 129-56-6) i.p. every 3 days. After seven injections, mice were euthanized for tissue retrieval. For the bladder cancer cell-derived xenograft mouse model, male C57BL/6J mice (6 weeks old) were injected subcutaneously with 1 × 106 MB49 cells. One week after bladder cancer cell injection, 10% DMSO or 20 mg/kg SP600125 were injected i.p. every 3 days. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03149 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (EHMT2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
m6A Regulator: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03479 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Regulator: Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05239 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05253 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0072309 (Circ_LIFR) | |
| Regulated Target | hsa-miR-607 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
m6A Regulator: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05923 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0058493 (Circ_RHBDD1) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00360)
| In total 20 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087596 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5457102-5457103:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | TACTGTCACGGTTCCCAAGGACCTATATGTGGTAGAGTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; fibroblasts; LCLs; Huh7; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815416 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087597 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5457163-5457164:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | TGCAAATTCCCAGTAGAAAAACAATTAGACCTGGCTGCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815417 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087598 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5457171-5457172:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGTAGAAAAACAATTAGACCTGGCTGCACTAATTGTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815418 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087599 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5457213-5457214:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | TTGGGAAATGGAGGATAAGAACATTATTCAATTTGTGCATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000498261.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815419 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087600 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5457243-5457244:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | ATTTGTGCATGGAGAGGAAGACCTGAAGGTTCAGCATAGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000381573.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815420 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087601 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5457271-5457272:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | GTTCAGCATAGTAGCTACAGACAGAGGGCCCGGCTGTTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000381573.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815421 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087602 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5457294-5457295:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | GAGGGCCCGGCTGTTGAAGGACCAGCTCTCCCTGGGAAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | GM12878; LCLs; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815422 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087603 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5462888-5462889:+ | [19] | |
| Sequence | GTGGATCCAGTCACCTCTGAACATGAACTGACATGTCAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | LCLs; CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000474218.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815423 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087604 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5462894-5462895:+ | [19] | |
| Sequence | CCAGTCACCTCTGAACATGAACTGACATGTCAGGCTGAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | LCLs; CD8T; CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000474218.1; ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000498261.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815424 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087605 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5462898-5462899:+ | [20] | |
| Sequence | TCACCTCTGAACATGAACTGACATGTCAGGCTGAGGGCTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000474218.1; ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815425 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087606 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5462940-5462941:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | CCAAGGCCGAAGTCATCTGGACAAGCAGTGACCATCAAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; LCLs; CD4T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000492923.1; ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000498261.1; ENST00000474218.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815426 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087607 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5462973-5462974:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | ATCAAGTCCTGAGTGGTAAGACCACCACCACCAATTCCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; LCLs; CD4T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000492923.1; ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000474218.1; ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000498261.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815427 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087608 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5466811-5466812:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | ATGTGGCATCCAAGATACAAACTCAAAGAAGCAAAGTGGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000498261.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815428 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087609 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5467874-5467875:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | AGACGTAATCCAGCATTGGAACTTCTGATCTTCAAGCAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; CD4T; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000381573.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815429 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087610 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5467979-5467980:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | TGGGATGCAGGCAATGTGGGACTTAAAAGGCCCAAGCACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815430 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087611 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5468008-5468009:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | GCCCAAGCACTGAAAATGGAACCTGGCGAAAGCAGAGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815431 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087612 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5468052-5468053:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | ATGAAGAAAGATGGAGTCAAACAGGGAGCCTGGAGGGAGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815432 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087613 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5468071-5468072:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | AACAGGGAGCCTGGAGGGAGACCTTGATACTTTCAAATGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000381573.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815433 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087614 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5468138-5468139:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGAAAGGATACTTCTGAACAAGGAGCCTCCAAGCAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD4T; GSC-11; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381573.8; ENST00000381577.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815434 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE087615 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:5468294-5468295:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | AGTCTCAGTGTTGGAACGGGACAGTATTTATGTATGAGTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000381577.4; ENST00000381573.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_815435 | ||
References