m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00364)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
PER1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | NOMO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 NOMO-1 cells
Control: shNS NOMO-1 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
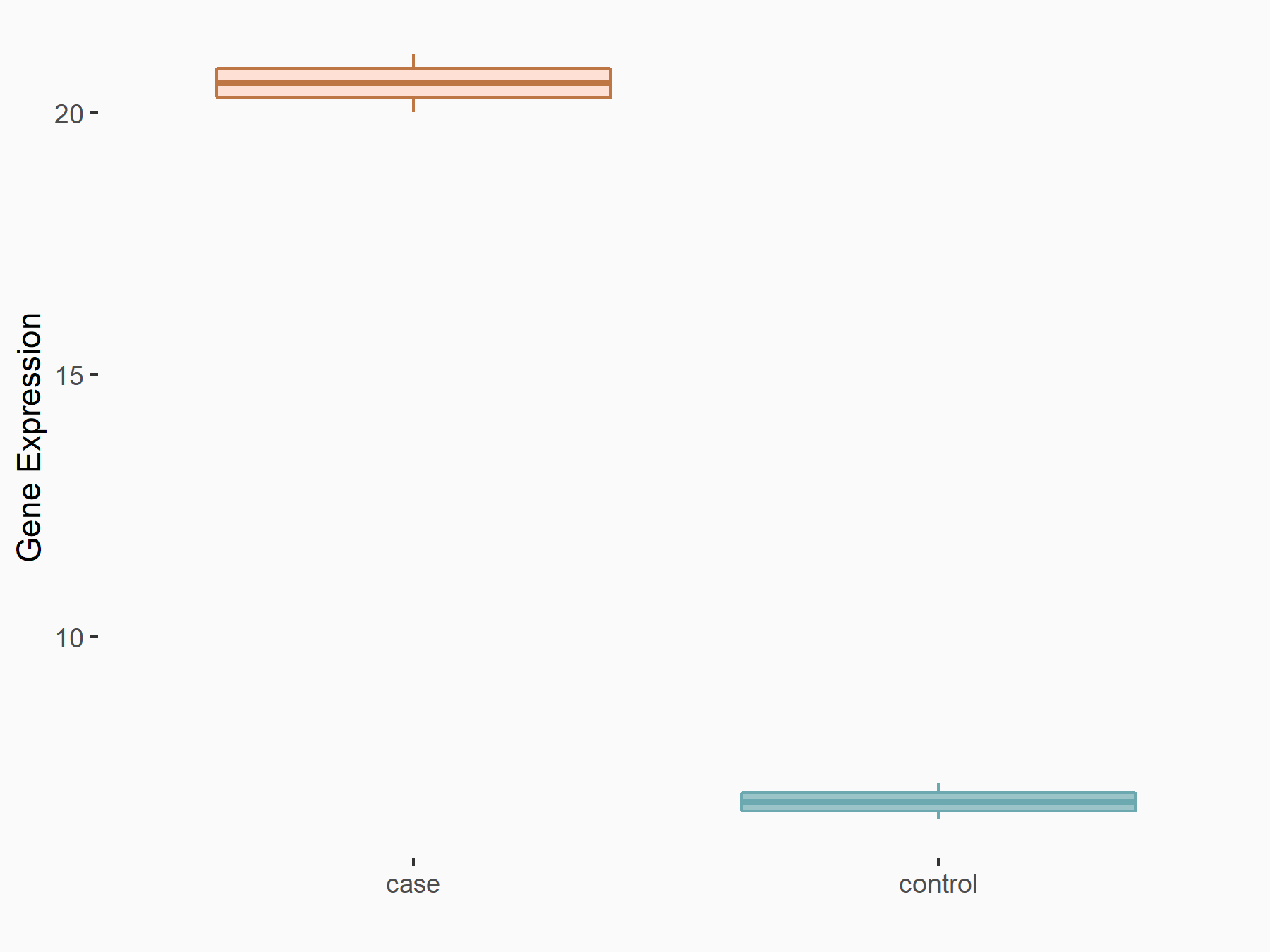  |
logFC: 1.46E+00 p-value: 8.91E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 serves as a pancreatic cancer suppressor by regulating the posttranscriptional activation of Period circadian protein homolog 1 (PER1) through m6A abolishment, which highlights a demethylation-based approach for PC diagnosis and therapy. ALKBH5 loss downregulated PER1 mRNA levels in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In-vitro Model | AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF2 | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse-cerebellum granule cell | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: YTHDF2 knockdown mouse-cerebellum granule cell
Control: Wild type mouse-cerebellum granule cell
|
GSE153688 | |
| Regulation |
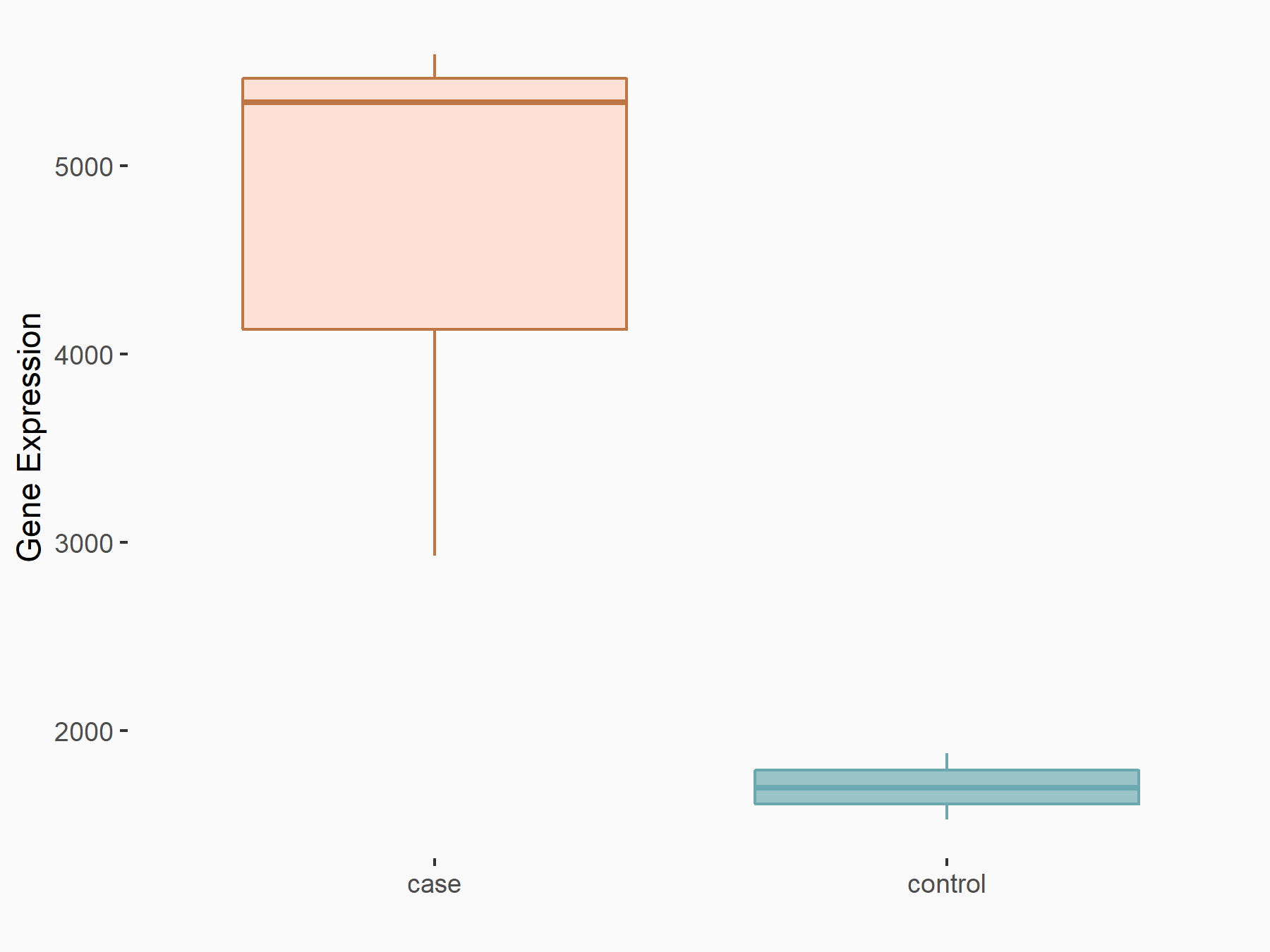  |
logFC: 1.44E+00 p-value: 9.54E-09 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 serves as a pancreatic cancer suppressor by regulating the posttranscriptional activation of Period circadian protein homolog 1 (PER1) through m6A abolishment, which highlights a demethylation-based approach for PC diagnosis and therapy. ALKBH5 loss downregulated PER1 mRNA levels in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In-vitro Model | AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 serves as a pancreatic cancer suppressor by regulating the posttranscriptional activation of Period circadian protein homolog 1 (PER1) through m6A abolishment, which highlights a demethylation-based approach for PC diagnosis and therapy. ALKBH5 loss downregulated PER1 mRNA levels in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In-vitro Model | AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 serves as a pancreatic cancer suppressor by regulating the posttranscriptional activation of Period circadian protein homolog 1 (PER1) through m6A abolishment, which highlights a demethylation-based approach for PC diagnosis and therapy. ALKBH5 loss downregulated PER1 mRNA levels in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In-vitro Model | AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03047 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Melanoma of uvea | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03048 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain (LDHB) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Melanoma of uvea | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00364)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M1ASITE000051 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8148024-8148025:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | TTCCTGCATCCTGAGGACCGACCCCTCATGCTGGCTATCCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m1A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578223.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m1A_site_424 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 82 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030217 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140489-8140490:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCTGTTACTACTTTTTTAATACAAAAAGATAAAAACGCCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347176 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030218 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140567-8140568:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGTGCTGCCCCTCAGGTGGGACCCAGGCGTTCTCAGCTGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; H1B; H1A; LCLs; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347177 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030219 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140601-8140602:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGAGTGGGGGAGGTTGGTGGACCATGGAGTCCCTGGTGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; H1B; H1A; LCLs; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347178 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030220 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140650-8140651:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCTGAGGCCCAAGCAGGACCCGGGGGTTCCAGCCCCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; H1B; H1A; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347179 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030221 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140707-8140708:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CACTTATTTATTGCGGGGAGACAGCTCTCTCTCCCACCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; H1A; H1B; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347180 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030222 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140747-8140748:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCAGCTGAGCCTGAATCTGACTCTTGAGGGTTGGGGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347181 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030223 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140807-8140808:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGAATCCTTCCCTCCCCTGGACAAAGTTGCTGACAAGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; liver; A549; HepG2; U2OS; H1B; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347182 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030224 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140873-8140874:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTTAGGGAGCAGAGAGCAGAACTCCGCAGCCCAGCCCAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347183 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030225 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140935-8140936:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTCCCACCATAGGGGGCCGGACCCCCATCACCAGCCTAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; H1A; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347184 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030226 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140968-8140969:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCTAGACCAACCAGTGGGAAACTGCCCCAGCTTCTCCCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347185 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030227 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140983-8140984:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGAACTCAGATGTGGCTAGACCAACCAGTGGGAAACTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347186 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030228 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8140999-8141000:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCTATGTCCCAATTCTCAGAACTCAGATGTGGCTAGACCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347187 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030229 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141053-8141054:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGCTAGACTCCATTCTGGGACCATCTCCAGGAGTCCATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347188 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030230 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141066-8141067:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGGAAACTGCACCAGCTAGACTCCATTCTGGGACCATCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347189 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030231 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141080-8141081:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGCCTTACCTACAGCAGGAAACTGCACCAGCTAGACTCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347190 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030232 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141146-8141147:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAAGGCTTCAAGCTCTCAGGACTTGGCTATGGAGGAGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347191 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030233 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141265-8141266:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTCTTCTCAGAGCTGGATGGACTGGGGCTGGAGCCCATGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000585284.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000583677.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347192 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030234 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141329-8141330:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCTCACCAAGGCCTGTGTGGACTGTGGGAGCAGCACCCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000583677.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000585284.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347193 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030235 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141864-8141865:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCTGAGGACCAGCGGCGGGAACTGGGTGCTGTGCACTCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000585284.1; ENST00000583677.1; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347194 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030236 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141877-8141878:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCCTCGGTTTTCTGAGGACCAGCGGCGGGAACTGGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000585284.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000583677.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347195 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030237 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141952-8141953:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAACCCCTTCTTGGGCAGGGACATGACCTCTGTGCTGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000585284.1; ENST00000583677.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347196 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030238 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8141970-8141971:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCCCAGCCTCTGCCTTCTGAACCCCTTCTTGGGCAGGGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000583677.1; ENST00000585284.1; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347197 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030239 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8142361-8142362:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGGCGGGGCTGAGCCTGGGGACCAGGTGATTAAGTACGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000585284.1; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347198 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030240 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8142744-8142745:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | AAGAGGACTCGCGCTCCGGCACAGGCTCCGCAGCCTCGGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000579098.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347199 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030241 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8142758-8142759:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CGAACTTCTGCTGCAAGAGGACTCGCGCTCCGGCACAGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000579098.1; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347200 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030242 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8142775-8142776:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGCTCCAGTGACCTGCTCGAACTTCTGCTGCAAGAGGACTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000579098.1; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347201 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030243 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8143268-8143269:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCTGCTGAGCCAGAGGCCAGACTGGTGAGCACTGACCCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579098.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347202 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030244 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8143428-8143429:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAGTCCTCCTCACCGCCCGGACTCTCCACTGTTCAACTCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347203 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030245 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8143516-8143517:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATCCTTATGGGGCACTCCAGACCCCTGCTGAAGGGCCTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; U2OS; LCLs; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347204 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030246 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8143766-8143767:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCGCCCTGCTATGTCTCACACCCCTCACCCGTGCCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347205 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030247 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8143797-8143798:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCGCTCACGCCACCACCAGAACCCTCGGGCTGAAGCGCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; U2OS; MT4; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347206 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030248 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8143841-8143842:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCGCACCCCCAAGCCGCCGACACCACTGCCGATCCAAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000578950.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347207 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030249 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144173-8144174:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATCTGTCCATGTGTCCATGGACTCACCCTGCTTCCTCCATC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000578089.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347208 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030250 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144202-8144203:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCACAGGAGTTTGGCGGACCAGAGCCATCTGTCCATGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578950.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347209 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030251 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144309-8144310:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGCAGACGCAGGACTCAGGACTGGGCTTTCCAGCCCCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; H1A; Jurkat; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347210 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030252 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144316-8144317:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCCCTGCAGGCAGACGCAGGACTCAGGACTGGGCTTTCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; H1A; Jurkat; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347211 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030253 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144423-8144424:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGTTGTCACTGATGAAGAGACATGCATAGATTCTGGGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347212 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030254 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144703-8144704:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCTCTGCCCAGTCTAGGACTGGATTGTTGGGGGGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347213 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030255 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144788-8144789:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGCAGGCTGCGTGGACTCGACAGCTCTTCCACAGCTCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347214 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030256 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144793-8144794:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GACCTGGGCAGGCTGCGTGGACTCGACAGCTCTTCCACAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347215 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030257 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144812-8144813:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTTCCTCAGCCGCTTCCGAGACCTGGGCAGGCTGCGTGGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347216 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030258 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144974-8144975:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGACATCATCATGATGGAGGACCTGCCTGGCCTAGCCCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000583559.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347217 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030259 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8144992-8144993:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCCTATCTCACTCTCCTCAGACATCATCATGATGGAGGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000578950.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347218 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030260 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8145067-8145068:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGGTTGGCTAGGCTATCAGACAGGGAGGGTGTGGTATGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000614952.1; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347219 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030261 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8145977-8145978:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CACCATCGTCCATGTGGGAGACAAGAAGCCCCCGGAGTCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000583559.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000578089.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347220 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030262 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8146380-8146381:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGGTCCAGTCTCTGTGGGGACCAAGAAAGGTAAAGATCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347221 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030263 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8146401-8146402:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTGACGACGACAGGCAGAGGACAGGTCCAGTCTCTGTGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347222 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030264 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8146605-8146606:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCAGCAGATCAACTGCCTGGACAGCATCCTCAGGTAAGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347223 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030265 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8146719-8146720:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCTTCCCTGCCAATCCCCAGACCCAGAGCTGGAGGCGGGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000585095.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347224 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030266 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8147354-8147355:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CACAGCCCCAGCCCCACGGGACTCTGTGGAGTCGGCGCCGT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000577424.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000579203.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000585095.1; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347225 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030267 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8147518-8147519:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGCCCAGCTCCCTCCCTGGACACTGATATCCAGGAGCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000577424.1; ENST00000585095.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000579203.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347226 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030268 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8147685-8147686:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGCCTTCGTGTTGGGCCGCCACAAAGTACGCACGTAAGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000578223.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000579203.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347227 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030269 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8147748-8147749:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CGGGGAGTATGTCACCATGGACACCAGCTGGGCTGGCTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000579203.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000578223.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347228 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030270 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8148004-8148005:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACCCCTCATGCTGGCTATCCACAAGAAGAGTGAGTTCCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000578223.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000579203.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347229 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030271 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8148028-8148029:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCTGTTCCTGCATCCTGAGGACCGACCCCTCATGCTGGCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578223.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347230 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030272 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8148070-8148071:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGGCTACCTGCCCCAGGACCTCCTGGGGGCCCCAGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578223.1; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347231 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030273 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8148983-8148984:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTTGGCCAGGCTGGTCTCGAACTCCTGACCTCAGGTGATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000578223.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347232 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030274 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149244-8149245:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTATCAGGTAGGTGAGGGGAACTGGAGAAGACCTCTGCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347233 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030275 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149294-8149295:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGGTTCAGGCCTCAGGGACTTTACCCAGGAGAAGTCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347234 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030276 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149385-8149386:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGAGGGGCCGGGGAACCCAGACTTTCCCTTAGTGGATTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347235 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030277 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149391-8149392:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTGCTGTGAGGGGCCGGGGAACCCAGACTTTCCCTTAGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347236 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030278 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149616-8149617:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCTGACGGGCCGAATCGTCTACATTTCGGAGCAGGCAGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000579065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347237 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030279 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149758-8149759:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTCTGAGTACACACTTCAGAACCAGGTCAGCGGCGGCCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000579065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347238 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030280 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149770-8149771:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGAGCACATCACGTCTGAGTACACACTTCAGAACCAGGTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347239 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030281 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8149818-8149819:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGGCGAGCCTTGCTCCATGGACATGTCCACCTATACCCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347240 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030282 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150018-8150019:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGGGCAAGGGCCGCTCTGGGACCCTGGCCACGCTGCAGTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; CD4T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347241 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030283 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150088-8150089:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CGGGCAAGGACTCAGAAGGAACTCATGACAGCACTTCGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000577253.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347242 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030284 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150099-8150100:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AACAGTCAGCCCGGGCAAGGACTCAGAAGGAACTCATGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347243 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030285 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150118-8150119:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGGCCCCGCAGCAGTGAACAGTCAGCCCGGGCAAGGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293; kidney; CD4T; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347244 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030286 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150242-8150243:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAGTGCCAGCTCAGAGCAGGACAACCCGTCCACCAGTGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000579065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347245 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030287 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150272-8150273:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACCCAGCAGTTCCATTGCCTACAGCCTCCTGAGTGCCAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347246 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030288 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150311-8150312:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTTGCTGTCTCCTAGCACAAACTCTCAGAGCCCATCCCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000354903.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347247 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030289 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150315-8150316:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCTGTTGCTGTCTCCTAGCACAAACTCTCAGAGCCCATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347248 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030290 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150450-8150451:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGACTCAGCCCTGCTGGAGACCACTGAGAGCAGCAAGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000584202.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347249 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030291 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150467-8150468:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTCCTCAGGCAACGGCAAGGACTCAGCCCTGCTGGAGACCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000584202.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347250 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030292 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150496-8150497:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGCGCATCTCAGCGGAGCTCACACAGCTCCTCCTCAGGCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347251 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030293 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150668-8150669:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGGGCTGATGGGGGAGGGGACCCCAGGCCTGGGGAATCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000317276.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347252 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030294 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150707-8150708:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTGTTCTCCCCATGGCCCAGACATGAGTGGCCCCCTAGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; iSLK; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000581703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347253 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030295 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150809-8150810:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAACTTCTCAACCCTCAGAGACTTAGATCTTCCACCTCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000581395.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347254 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030296 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8150827-8150828:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGGTACTGGCTGTGATCGAACTTCTCAACCCTCAGAGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000579065.1; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000498285.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000582719.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347255 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030297 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8152351-8152352:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGCGGGCAGGCGTGCGGAGGACACTCCTGCGACCAGGTAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498285.1; ENST00000581703.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000577253.5; ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000579065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347256 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030298 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8153942-8153943:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTTGGTCAGGCTGGTCTCGAACTCGCTACCTCAGGTGATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581395.5; ENST00000584202.1; ENST00000498285.1; ENST00000354903.9; ENST00000577253.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_347257 | ||
N7-methylguanosine (m7G)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: m7GSITE000039 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:8143830-8143831:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAGCCGCCGACACCACTGCCGATCCAAAGCCAAGCGCTCAC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | BoRed-seq&m7G-RIP-seq; m7G-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578950.1; ENST00000582719.5; ENST00000578089.1; ENST00000317276.9; ENST00000581082.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m7G_site_350 | ||
References