m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00279)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
HSPA1A
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
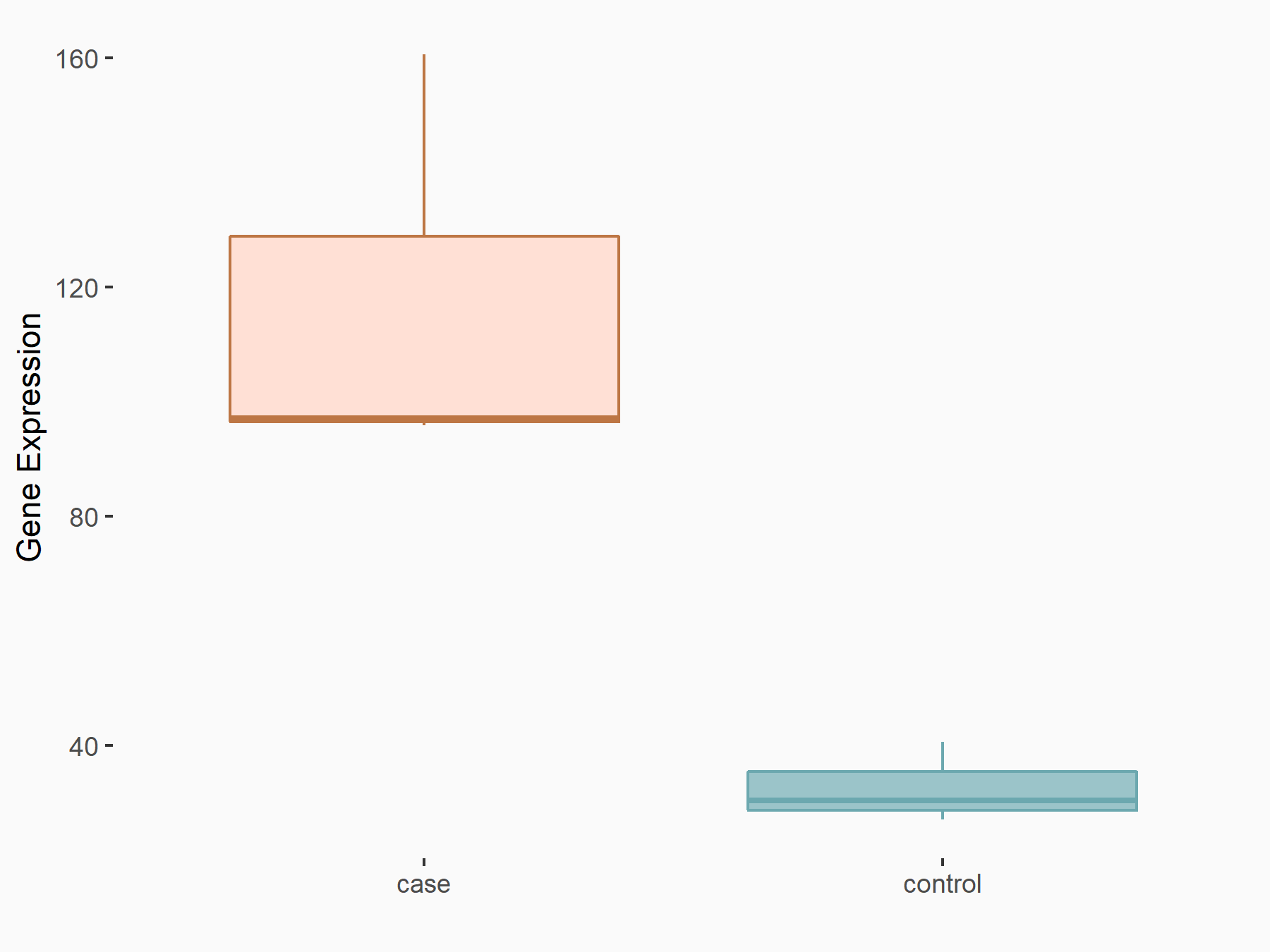  |
logFC: 1.83E+00 p-value: 7.08E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Loss of Fto also increased susceptibility of osteoblasts to genotoxic damage from metabolic stress induced by exposure to HF is also consistent with this model for FTO action. FTO functions intrinsically in osteoblasts through Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A)-NF-Kappa-B signaling to enhance the stability of mRNA of proteins that function to protect cells from genotoxic damage. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis | ICD-11: FB83.1 | ||
| In-vitro Model | 1H8 [Mouse hybridoma against human BMSC] | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_A7TU |
| In-vivo Model | FtoKO mice were backcrossed to WT C57BL/6 mice to remove Cre and bred to homozygosity. Results are reported for male mice on the same genetic background (C57BL6/J). For the diet-induced bone loss studies, mice were fed a 60% high-fat diet (D12492, Research Diets) from 6 wk of age to 24 wk. Genotyping strategies are available upon request. NBD (KKKKKKKKGGTALDWSWLQTE) with the Trp to Ala substitutions designed to render the peptide inactive underlined, was a gift from D.C.G. and dissolved in water before use. Next, 10 mg/kg NBD was intraperitoneally injected in 29-wk old FtoOc KO mice every other day for 9 d. One day after the last injection, bone was harvested for analysis of DNA damage. | |||
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
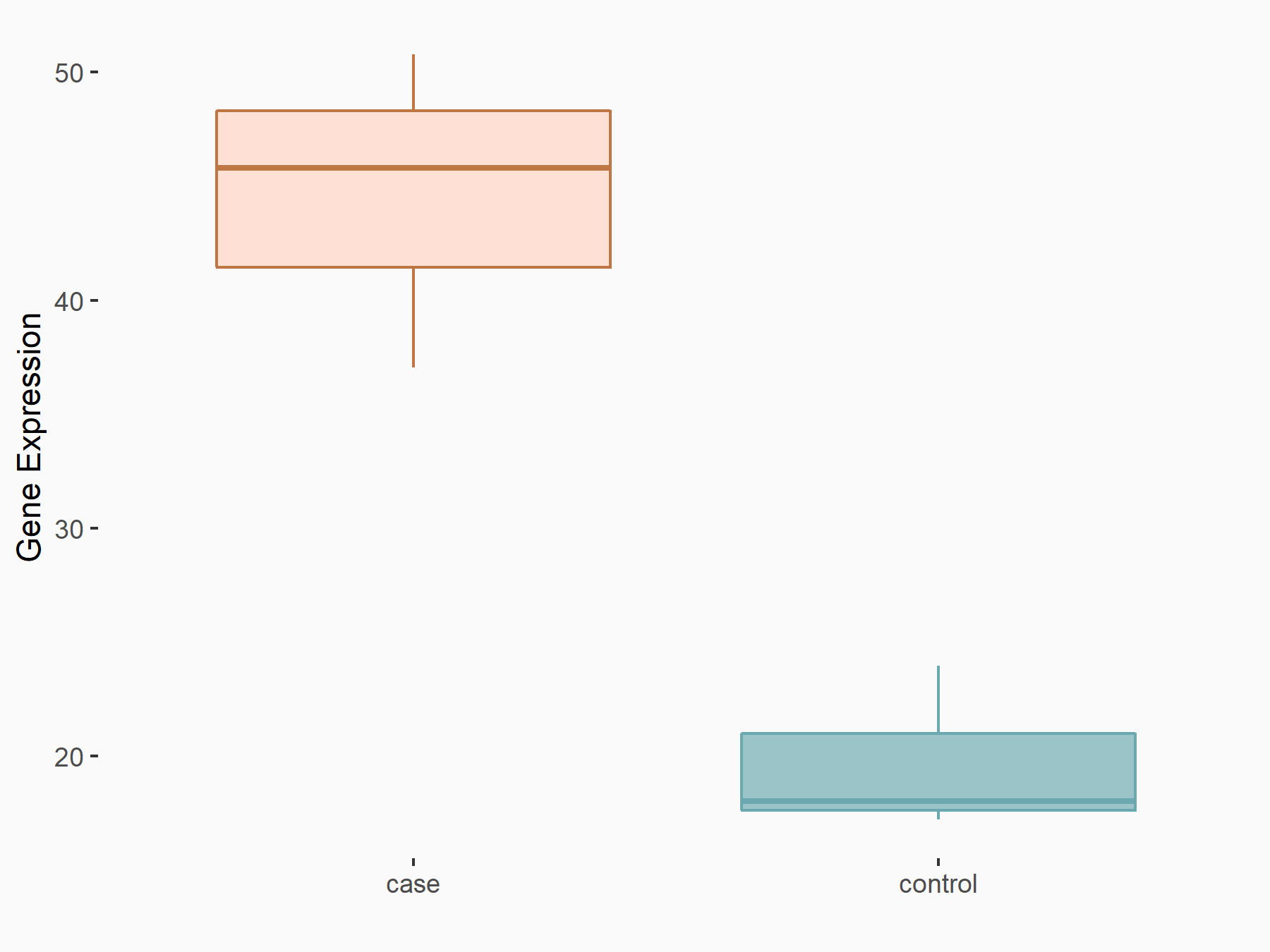  |
logFC: 1.20E+00 p-value: 8.44E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Findings show that METTL3 and METTL14 were up-regulated in preeclampsia(PE). Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A) is involved in the pathophysiology of PE as its mRNA and protein expression is regulated by m6A modification. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia | ICD-11: JA24 | ||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | ARPE-19 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 ARPE-19 cells
Control: shControl ARPE-19 cells
|
GSE202017 | |
| Regulation |
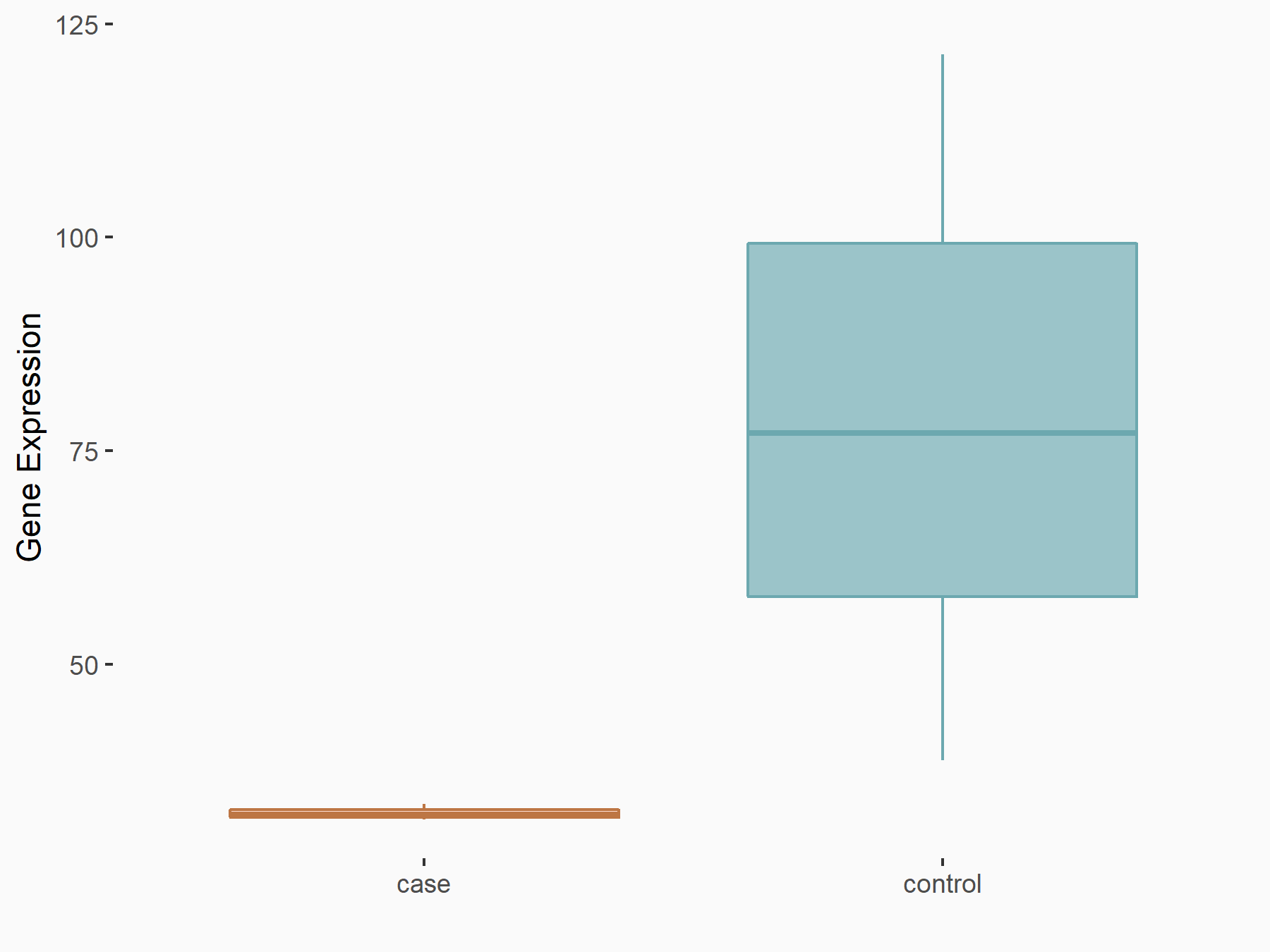  |
logFC: -1.11E+00 p-value: 1.96E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Findings show that METTL3 and METTL14 were up-regulated in preeclampsia(PE). Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A) is involved in the pathophysiology of PE as its mRNA and protein expression is regulated by m6A modification. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia | ICD-11: JA24 | ||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
YTH domain-containing protein 1 (YTHDC1) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDC1 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shYTHDC1 MOLM13 cells
Control: shControl MOLM13 cells
|
GSE178859 | |
| Regulation |
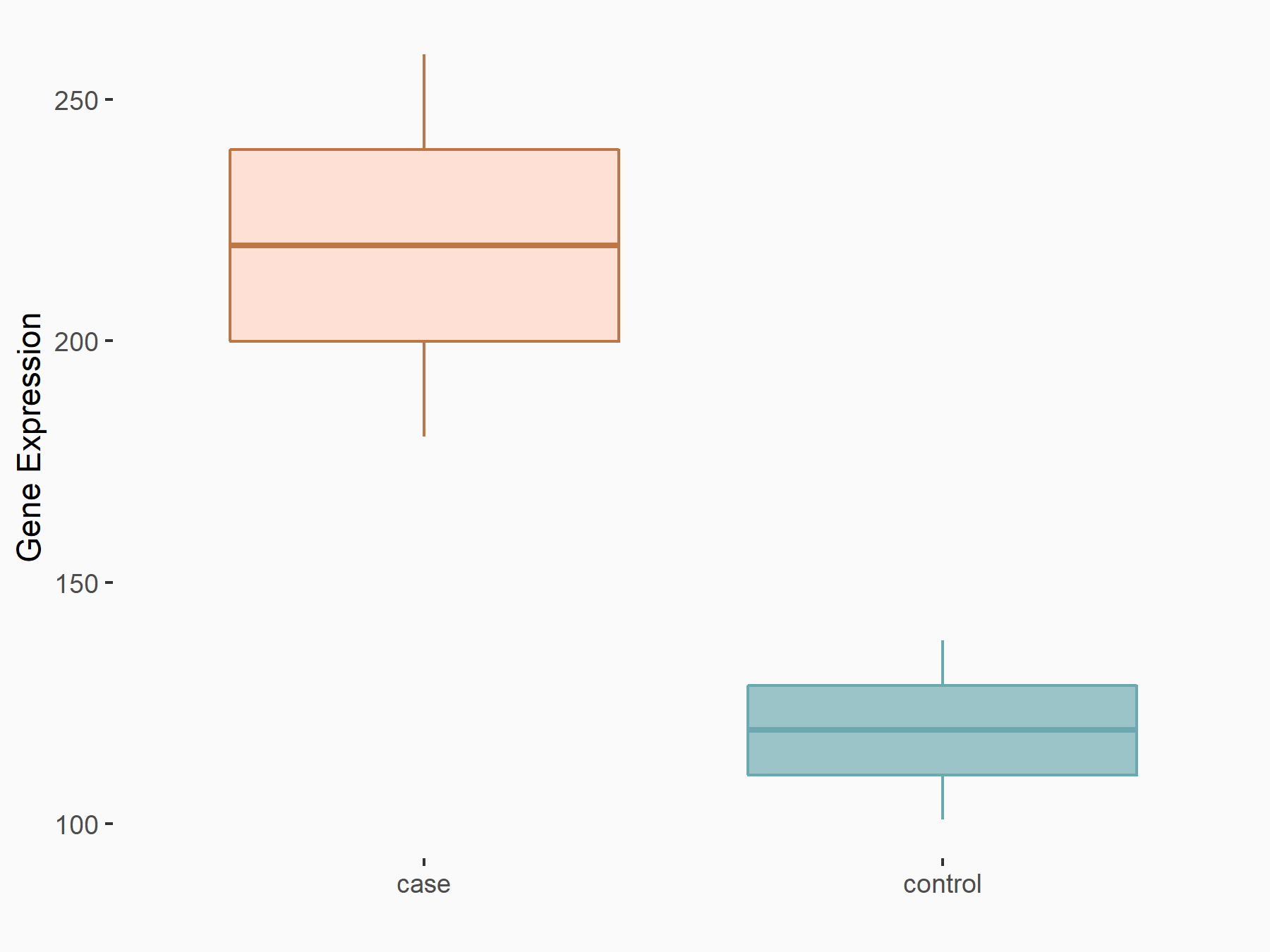  |
logFC: 8.78E-01 p-value: 3.66E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Heat directly binds to Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A), thereby targeting stress genes in a trans-acting manner. Intriguingly, Heat is heavily methylated in the form of m6A. Heat mediates these effects via the nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1, forming a transcriptional silencing complex for stress genes. Reveals a crucial role of nuclear epitranscriptome in the transcriptional regulation of heat shock response. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Effects of heat | ICD-11: NF01 | ||
| Pathway Response | RNA degradation | hsa03018 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
Low bone mass disorder [ICD-11: FB83]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Loss of Fto also increased susceptibility of osteoblasts to genotoxic damage from metabolic stress induced by exposure to HF is also consistent with this model for FTO action. FTO functions intrinsically in osteoblasts through Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A)-NF-Kappa-B signaling to enhance the stability of mRNA of proteins that function to protect cells from genotoxic damage. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | 1H8 [Mouse hybridoma against human BMSC] | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_A7TU |
| In-vivo Model | FtoKO mice were backcrossed to WT C57BL/6 mice to remove Cre and bred to homozygosity. Results are reported for male mice on the same genetic background (C57BL6/J). For the diet-induced bone loss studies, mice were fed a 60% high-fat diet (D12492, Research Diets) from 6 wk of age to 24 wk. Genotyping strategies are available upon request. NBD (KKKKKKKKGGTALDWSWLQTE) with the Trp to Ala substitutions designed to render the peptide inactive underlined, was a gift from D.C.G. and dissolved in water before use. Next, 10 mg/kg NBD was intraperitoneally injected in 29-wk old FtoOc KO mice every other day for 9 d. One day after the last injection, bone was harvested for analysis of DNA damage. | |||
Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Findings show that METTL3 and METTL14 were up-regulated in preeclampsia(PE). Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A) is involved in the pathophysiology of PE as its mRNA and protein expression is regulated by m6A modification. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Findings show that METTL3 and METTL14 were up-regulated in preeclampsia(PE). Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A) is involved in the pathophysiology of PE as its mRNA and protein expression is regulated by m6A modification. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pre-eclampsia [ICD-11: JA24] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | |||
Effects of heat [ICD-11: NF01]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Heat directly binds to Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A), thereby targeting stress genes in a trans-acting manner. Intriguingly, Heat is heavily methylated in the form of m6A. Heat mediates these effects via the nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1, forming a transcriptional silencing complex for stress genes. Reveals a crucial role of nuclear epitranscriptome in the transcriptional regulation of heat shock response. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Effects of heat [ICD-11: NF01] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing protein 1 (YTHDC1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RNA degradation | hsa03018 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| MEF (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00279)
| In total 3 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000397 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31815683-31815684:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCGTCCGGAAGGACCGAGCTCTTCTCGCGGATCCAGTGTTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_5803 | ||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000398 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31815684-31815685:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CGTCCGGAAGGACCGAGCTCTTCTCGCGGATCCAGTGTTCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_5804 | ||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000399 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817218-31817219:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGCCAACGGCATCCTGAACGTCACGGCCACGGACAAGAGCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_5805 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 63 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074433 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31815821-31815822:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCTGCGTGGGGGTGTTCCAACACGGCAAGGTGGAGATCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712321 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074434 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31815892-31815893:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAGCTACGTGGCCTTCACGGACACCGAGCGGCTCATCGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712322 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074435 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31815949-31815950:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTGGCGCTGAACCCGCAGAACACCGTGTTTGACGCGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712323 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074436 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816012-31816013:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGACCCGGTGGTGCAGTCGGACATGAAGCACTGGCCTTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712324 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074437 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816075-31816076:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCCAAGGTGCAGGTGAGCTACAAGGGGGAGACCAAGGCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712325 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074438 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816429-31816430:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTGAAGGCCACGGCCGGGGACACCCACCTGGGTGGGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712326 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074439 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816499-31816500:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTGGAGGAGTTCAAGAGAAAACACAAGAAGGACATCAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712327 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074440 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816522-31816523:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAAGAAGGACATCAGCCAGAACAAGCGAGCCGTGAGGCGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712328 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074441 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816636-31816637:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTTGAGGGCATCGACTTCTACACGTCCATCACCAGGGCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712329 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074442 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816735-31816736:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCGCGACGCCAAGCTGGACAAGGCCCAGATTCACGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712330 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074443 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816834-31816835:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTTCAACGGGCGCGACCTGAACAAGAGCATCAACCCCGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712331 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074444 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31816903-31816904:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCGGCCATCCTGATGGGGGACAAGTCCGAGAACGTGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712332 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074445 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817053-31817054:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GATCTTCACCACCTACTCCGACAACCAACCCGGGGTGCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712333 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074446 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817110-31817111:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGAGAGGGCCATGACGAAAGACAACAATCTGTTGGGGCGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712334 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074447 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817113-31817114:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGGGCCATGACGAAAGACAACAATCTGTTGGGGCGCTTCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712335 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074448 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817191-31817192:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCAGATCGAGGTGACCTTCGACATCGATGCCAACGGCATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712336 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074449 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817272-31817273:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAAGATCACCATCACCAACGACAAGGGCCGCCTGAGCAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712337 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074450 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817329-31817330:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTGCAGGAGGCGGAGAAGTACAAAGCGGAGGACGAGGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712338 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074451 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817398-31817399:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGAGTCCTACGCCTTCAACATGAAGAGCGCCGTGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712339 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074452 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817452-31817453:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGCAAGATCAGCGAGGCGGACAAGAAGAAGGTGCTGGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712340 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074453 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817470-31817471:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGACAAGAAGAAGGTGCTGGACAAGTGTCAAGAGGTCATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712341 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074454 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817536-31817537:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGAGAAGGACGAGTTTGAGCACAAGAGGAAGGAGCTGGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712342 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074455 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817582-31817583:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTAACCCCATCATCAGCGGACTGTACCAGGGTGCCGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712343 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074456 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817723-31817724:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TTTTGTTTTGGAGCTTCAAGACTTTGCATTTCCTAGTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712344 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074457 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817805-31817806:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | ATTTTTTGGTGAAGTACTGAACTTGCTTTTTTTCCGGTTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000608703.1; ENST00000375651.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712345 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074458 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817827-31817828:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTGCTTTTTTTCCGGTTTCTACATGCAGAGATGAATTTATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712346 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE074459 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817880-31817881:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GACTATTTCTTCTTTTTAATACACTTAACTCAGGCCATTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_712347 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094239 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000250.2:3149357-3149358:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCGCGACGCCAAGCTGGACAAGGCCCAGATTCACGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000430065.1; ENST00000422919.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879511 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094240 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000250.2:3149432-3149433:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGTGCAGAAGCTGCTGCAGGACTTCTTCAACGGGCGCGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000422919.1; ENST00000430065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879512 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094241 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000250.2:3149456-3149457:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTTCAACGGGCGCGACCTGAACAAGAGCATCAACCCCGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000422919.1; ENST00000430065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879513 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094242 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000250.2:3149525-3149526:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGCGGCCATCCTGATGGGGGACAAGTCCGAGAACGTGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000422919.1; ENST00000430065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879514 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094243 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000250.2:3149546-3149547:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAAGTCCGAGAACGTGCAGGACCTGCTGCTGCTGGACGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000422919.1; ENST00000430065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879515 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094244 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000250.2:3150092-3150093:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGACAAGAAGAAGGTGCTGGACAAGTGTCAAGAGGTCATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000430065.1; ENST00000422919.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879516 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094245 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000250.2:3150204-3150205:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTAACCCCATCATCAGCGGACTGTACCAGGGTGCCGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000422919.1; ENST00000430065.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879517 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094269 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000251.2:3292926-3292927:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGTTTCCGGCGTCCGGAAGGACCGAGCTCTTCTCGCGGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000449876.1; ENST00000441618.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879637 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094270 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000251.2:3293001-3293002:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCGACAGAGAGCAGGGAACCGGCATGGCCAAAGCCGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000449876.1; ENST00000441618.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879638 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094271 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000251.2:3293143-3293144:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGCTACGTGGCCTTCACGGACACCGAGCGGCTCATCGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441618.1; ENST00000449876.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879639 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094272 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000251.2:3294721-3294722:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGACAAGAAGAAGGTGCTGGACAAGTGTCAAGAGGTCATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441618.1; ENST00000449876.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879640 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094273 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000251.2:3294833-3294834:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTAACCCCATCATCAGCGGACTGTACCAGGGTGCCGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000449876.1; ENST00000441618.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879641 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094274 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000251.2:3294974-3294975:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTTGTTTTGGAGCTTCAAGACTTTGCATTTCCTAGTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441618.1; ENST00000449876.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879642 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094330 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000252.2:3063529-3063530:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCGACAGAGAGCAGGGAACCGGCATGGCCAAAGCCGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000433487.1; ENST00000452298.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879826 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094331 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000252.2:3063671-3063672:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGCTACGTGGCCTTCACGGACACCGAGCGGCTCATCGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452298.1; ENST00000433487.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879827 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094332 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000252.2:3063704-3063705:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CATCGGGGATGCGGCCAAGAACCAGGTGGCGCTGAACCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452298.1; ENST00000433487.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879828 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094333 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000252.2:3065231-3065232:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGCAAGATCAGCGAGGCGGACAAGAAGAAGGTGCTGGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000433487.1; ENST00000452298.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879829 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094335 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000252.2:3065249-3065250:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGACAAGAAGAAGGTGCTGGACAAGTGTCAAGAGGTCATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000452298.1; ENST00000433487.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879830 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094336 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000252.2:3065361-3065362:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTAACCCCATCATCAGCGGACTGTACCAGGGTGCCGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000433487.1; ENST00000452298.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_879831 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094459 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071453-3071454:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCCAAGGCTTCCCAGAGCGAACCTGTGCGGCTGCAGGCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880326 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094460 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071503-3071504:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGTTTCCGGCGTCCGGAAGGACCGAGCTCTTCTCGCGGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880327 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094461 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071578-3071579:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCGACAGAGAGCAGGGAACCGGCATGGCCAAAGCCGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880328 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094462 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071720-3071721:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGCTACGTGGCCTTCACGGACACCGAGCGGCTCATCGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880329 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094464 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071753-3071754:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CATCGGGGATGCGGCCAAGAACCAGGTGGCGCTGAACCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880330 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094465 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071768-3071769:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAAGAACCAGGTGGCGCTGAACCCGCAGAACACCGTGTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880331 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094466 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071777-3071778:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGTGGCGCTGAACCCGCAGAACACCGTGTTTGACGCGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880332 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094467 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071840-3071841:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGACCCGGTGGTGCAGTCGGACATGAAGCACTGGCCTTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GSC-11; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880333 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094468 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071879-3071880:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCAGGTGATCAACGACGGAGACAAGCCCAAGGTGCAGGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GSC-11; iSLK; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880334 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094469 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3071912-3071913:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCAGGTGAGCTACAAGGGGGACACCAAGGCATTCTACCCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GSC-11; iSLK; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880335 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094470 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3072563-3072564:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCGCGACGCCAAGCTGGACAAGGCCCAGATTCACGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880336 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094471 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3072638-3072639:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGTGCAGAAGCTGCTGCAGGACTTCTTCAACGGGCGCGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880337 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094472 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3072662-3072663:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTTCAACGGGCGCGACCTGAACAAGAGCATCAACCCCGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880338 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094473 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3073298-3073299:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGACAAGAAGAAGGTGCTGGACAAGTGTCAAGAGGTCATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880339 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094475 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3073410-3073411:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTAACCCCATCATCAGCGGACTGTACCAGGGTGCCGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880340 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094476 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3073551-3073552:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTTGTTTTGGAGCTTCAAGACTTTGCATTTCCTAGTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000383389.2; ENST00000400040.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880341 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE094477 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | GL000255.2:3073633-3073634:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATTTTTTGGTGAAGTACTGAACTTGCTTTTTTTCCGGTTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000400040.1; ENST00000383389.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_880342 | ||
N7-methylguanosine (m7G)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: m7GSITE000106 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:31817412-31817413:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTTCAACATGAAGAGCGCCGTGGAGGATGAGGGGCTCAAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | BoRed-seq&m7G-RIP-seq; m7G-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000375651.6; ENST00000608703.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m7G_site_776 | ||
References