m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00746)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
PES1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | HeLa cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: METTL3 knockdown HeLa cells
Control: HeLa cells
|
GSE70061 | |
| Regulation |
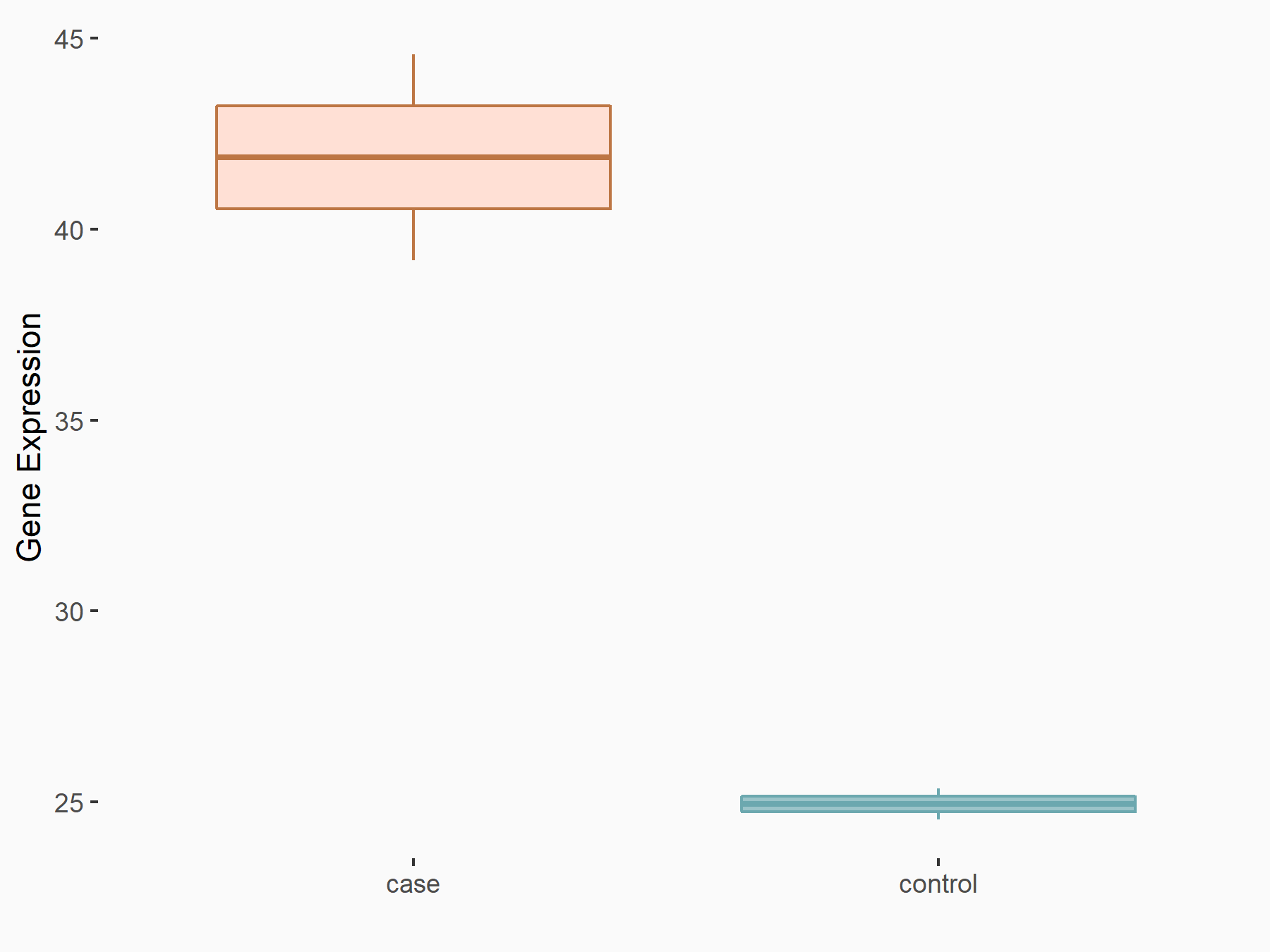 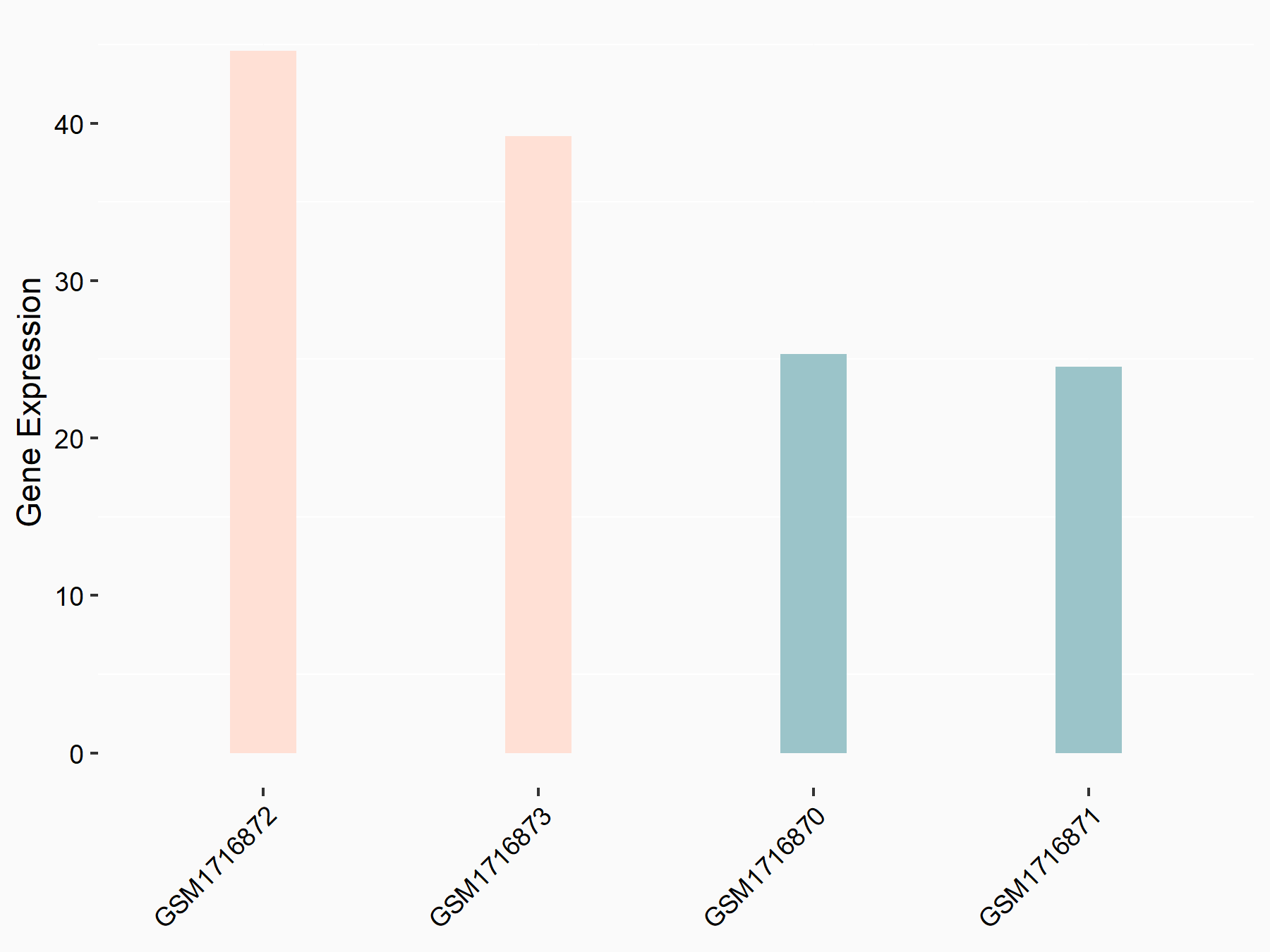 |
logFC: 7.23E-01 p-value: 7.36E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between PES1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 2.38E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase complex METTL3/METTL14 is upregulated in CML patients and that is required for proliferation of primary CML cells and CML cell lines sensitive and resistant to the TKI imatinib. METTL3 directly regulates the level of Pescadillo homolog (PES1) protein identified as an oncogene in several tumors. These results point to METTL3 as a novel relevant oncogene in CML and as a promising therapeutic target for TKI resistant CML. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2B33.2 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Decrease of S phase | |||
| In-vitro Model | U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| LAMA-84 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0388 | |
| KCL-22 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2091 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase complex METTL3/METTL14 is upregulated in CML patients and that is required for proliferation of primary CML cells and CML cell lines sensitive and resistant to the TKI imatinib. METTL3 directly regulates the level of Pescadillo homolog (PES1) protein identified as an oncogene in several tumors. These results point to METTL3 as a novel relevant oncogene in CML and as a promising therapeutic target for TKI resistant CML. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2B33.2 | ||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Decrease of S phase | |||
| In-vitro Model | U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| LAMA-84 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0388 | |
| KCL-22 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2091 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase complex METTL3/METTL14 is upregulated in CML patients and that is required for proliferation of primary CML cells and CML cell lines sensitive and resistant to the TKI imatinib. METTL3 directly regulates the level of Pescadillo homolog (PES1) protein identified as an oncogene in several tumors. These results point to METTL3 as a novel relevant oncogene in CML and as a promising therapeutic target for TKI resistant CML. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.2] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Decrease of S phase | |||
| In-vitro Model | U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| LAMA-84 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0388 | |
| KCL-22 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2091 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A methyltransferase complex METTL3/METTL14 is upregulated in CML patients and that is required for proliferation of primary CML cells and CML cell lines sensitive and resistant to the TKI imatinib. METTL3 directly regulates the level of Pescadillo homolog (PES1) protein identified as an oncogene in several tumors. These results point to METTL3 as a novel relevant oncogene in CML and as a promising therapeutic target for TKI resistant CML. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.2] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Decrease of S phase | |||
| In-vitro Model | U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| LAMA-84 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0388 | |
| KCL-22 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2091 | |
| K-562 | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0004 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00746)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: AC4SITE000060 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579345-30579346:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | TTGTCACCCTGCCAGAGAGACAGTAGATTCCCAGGGCATTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1 | ||
| Seq Type List | ac4C-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: ac4C_site_1283 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 5 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002898 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30576958-30576959:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | AGGACCTAAGTGTGATGGACCAGAGTCACTTCTCCTCCTCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30637 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002899 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579880-30579881:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GTGAACGCCAGGCTCCTTCTCCCCGTGGCAGAGTACTTCTC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000441668.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30638 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002900 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30584671-30584672:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CGGGACCTGGACGATGCCCTCTCCATGTGCTTCCTGTTTTC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30639 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002901 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30584685-30584686:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | TCATCGATGCCCTGCGGGACCTGGACGATGCCCTCTCCATG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30640 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002902 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30588058-30588059:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | TCAAAGACATCAGGTTTCTCCTCCACGAACCCATTGTCAAC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30641 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 59 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057450 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30576641-30576642:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ATTTGTTATTAAATGACTGGACTTTTGTGCCAATTGCATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; CD8T; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; iSLK; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561531 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057451 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30576707-30576708:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCCTCCCACACAGTTGGACCCGTGATTCTCAGGGTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561532 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057452 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30576756-30576757:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCCCACCCAGCCCCCTACCTACTGCCCCCATTCATCCTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561533 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057453 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30576960-30576961:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGAGGACCTAAGTGTGATGGACCAGAGTCACTTCTCCTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000441668.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561534 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057454 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30576975-30576976:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGGCAGAGGCAGGCCAGAGGACCTAAGTGTGATGGACCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561535 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057455 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30577124-30577125:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCTTCCCCCTCACAGGCCAACAAGCTGGCGGAGAAGCGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561536 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057456 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579032-30579033:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGACTGTGGAGGTCGGGAGAACCTGCCCCCATAAGCACCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; TIME; TREX; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561537 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057457 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579050-30579051:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGAAGGTCAGGAGCCAGAGGACTGTGGAGGTCGGGAGAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; iSLK; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000488719.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561538 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057458 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579260-30579261:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGAGGAGGAAGAGGACGACAACAACGAAGGTGATGGTGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000488719.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561539 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057459 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579263-30579264:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGAGGAGGAGGAAGAGGACGACAACAACGAAGGTGATGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000441668.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561540 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057460 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579299-30579300:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACATTGGCTTTCTCTAGGAAACCTGAATGAGTCAGAAGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000441668.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561541 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057461 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579319-30579320:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ATTCCCAGGGCATTCAGAGGACATTGGCTTTCTCTAGGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561542 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057462 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579346-30579347:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTTGTCACCCTGCCAGAGAGACAGTAGATTCCCAGGGCATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000441668.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561543 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057463 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579416-30579417:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CACAATTGGGACATCCCTGAACTGCCCATGGCTAAAGACGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000335214.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561544 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057464 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579426-30579427:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AAGAGAGGGCCACAATTGGGACATCCCTGAACTGCCCATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561545 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057465 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579735-30579736:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACCCAGGTGAGCGGGATGGGACTGGGCTGGCCTTGACCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561546 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057466 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579755-30579756:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGCTCTGCAGCGGGGAGAGGACCCAGGTGAGCGGGATGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; peripheral-blood; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000441668.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561547 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057467 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579841-30579842:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTGGGGTGCAGCTGCCCCCACACCTTTCACCCTTTGTGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000441668.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561548 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057468 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30579983-30579984:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGGCCCTGCGATGCAGCAGGACCCTGAGTTGCCCTCTGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000488719.1; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561549 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057469 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30580068-30580069:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCGACCGGCCTGGGCAGCAGACCTCAGTCATTGGCAGGTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; Huh7; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000488719.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561550 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057470 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30580112-30580113:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGCCACCTATGACGTCACAGACTCCCGCATCACCCATCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561551 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057471 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30580116-30580117:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTGGGGCCACCTATGACGTCACAGACTCCCGCATCACCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561552 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057472 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30580151-30580152:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGGGGAAGTGTCCTGGGACAAATCTTTGTGCATTGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561553 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057473 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30580609-30580610:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGGCCTGAAGTTCTTCCTGAACCGAGAGGTGCCCCGTGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561554 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057474 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30580645-30580646:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGAGGCGCAGGAGAAGCACAAGAAGCTTTTTGAGGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561555 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057475 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30580678-30580679:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GATGTCAGCGCAGGAGGAAGACCGCAGGAAGGAGCTGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561556 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057476 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30581098-30581099:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCCCTTCTCTCCTGTAGAAACTGGCAGCCCTCAGTGCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; MM6; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561557 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057477 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30581352-30581353:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGAGGGCACCTACGCGTTGGACTCCGAGAGTTGTATGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561558 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057478 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30581627-30581628:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCAGCACCCGACAGACGTGGACTACAGGGTCATGGCCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561559 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057479 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30581637-30581638:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTGTTCCCCAGCACCCGACAGACGTGGACTACAGGGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561560 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057480 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30584318-30584319:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GGGCTTGTGCTGCCTCCTAGACAGATATGGATGTGGAGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561561 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057481 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30584573-30584574:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CACTGTGGAGTTCATGCACTACATTATCGCTGCCCGTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561562 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057482 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30584616-30584617:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTGGCAAGTGCCACGTGCAGACCATTCAGCTGTGCCGCCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561563 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057483 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30584637-30584638:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGTTTTCCACCTTCCCGCGGACTGGCAAGTGCCACGTGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561564 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057484 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30584687-30584688:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTTCATCGATGCCCTGCGGGACCTGGACGATGCCCTCTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561565 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057485 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30585238-30585239:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCATTGGTTCTGCCAACTAGACATGTCCAAGGGATGAGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561566 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057486 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30585275-30585276:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCTCTGGCTCTTCCTGGACCCAATTCCCTGGGTCTCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561567 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057487 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30585301-30585302:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTACCAGAGGATTCCCCGAAACACATTCTGCTCTGGCTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000433575.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561568 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057488 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587146-30587147:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TTCAAGGACACAGACCAAAAACCAAGCTAGCAAATTACTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561569 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057489 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587153-30587154:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CAACTTTTTCAAGGACACAGACCAAAAACCAAGCTAGCAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561570 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057490 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587159-30587160:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGCTTGCAACTTTTTCAAGGACACAGACCAAAAACCAAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000466614.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561571 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057491 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587171-30587172:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCTGCTCAAAGAGCTTGCAACTTTTTCAAGGACACAGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561572 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057492 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587192-30587193:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CAATAGGGAATAAGACCAAGACCCTGCTCAAAGAGCTTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000466614.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561573 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057493 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587198-30587199:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGGATACAATAGGGAATAAGACCAAGACCCTGCTCAAAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000406208.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561574 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057494 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587263-30587264:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGAGCCGGGCTTTCCTCAGGACACTGCTGTTTCTTCATTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561575 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057495 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587300-30587301:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCCAACTACAAACTCGACCACATCATCAAGGAACGGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561576 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057496 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587308-30587309:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GACAATAAGCCCAACTACAAACTCGACCACATCATCAAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000335214.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561577 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057497 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587327-30587328:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CACTGTAGAGCGTTTAAAGGACAATAAGCCCAACTACAAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000466614.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561578 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057498 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30587348-30587349:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTATGGGAAGAGCGAGTGGAACACTGTAGAGCGTTTAAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000477762.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561579 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057499 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30588024-30588025:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGTCAACAAGTTCCGTGAATACAAGGTGAGGTCTGGGCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000466614.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561580 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057500 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30588050-30588051:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ATCAGGTTTCTCCTCCACGAACCCATTGTCAACAAGTTCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561581 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057501 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30588072-30588073:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AACGTTTTACCTTATCAAAGACATCAGGTTTCTCCTCCACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000354694.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561582 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057502 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30588131-30588132:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ATTTATCCCCATGAACCCAAACACAAGAAGAAGGTTAACAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402284.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561583 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057503 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30588137-30588138:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AAGGGCATTTATCCCCATGAACCCAAACACAAGAAGAAGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561584 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057504 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30589232-30589233:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CACCAACTACATCACCCGGAACAAAGCCCGGAAGAAGCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; hESC-HEK293T; MT4; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000433575.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561585 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057505 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30589244-30589245:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACGAGGCTCGGCCACCAACTACATCACCCGGAACAAAGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000433575.5; ENST00000335214.8; ENST00000406208.7; ENST00000466614.1; ENST00000405677.5; ENST00000402284.7; ENST00000354694.12; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561586 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057506 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30606845-30606846:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TAGTGCCCACCTAGCCCAGGACAAGGAGTGGAACGGGAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000492986.1; ENST00000467368.1; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561587 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057507 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30606907-30606908:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCCAGTGGTGGATTGGCAGGACCGGGTGCCTACCCGGTACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1A; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000492986.1; ENST00000402281.5; ENST00000405677.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561588 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE057508 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:30607000-30607001:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TCCTGCTTAAAGAGCCCGGGACCAGCGCAGAGGGCCTGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000492986.1; ENST00000402281.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_561593 | ||
References