m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00288)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
EIF4G1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
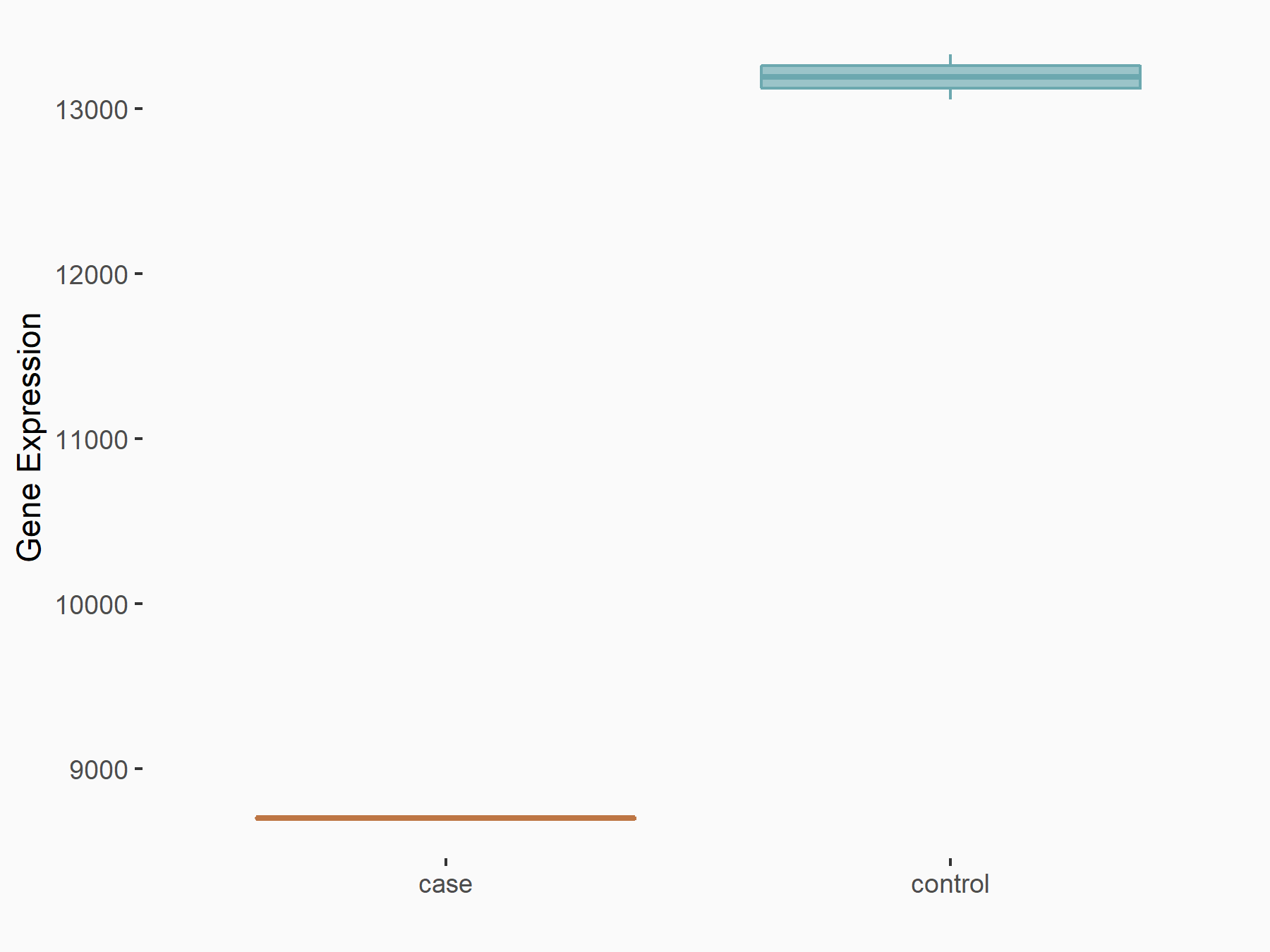 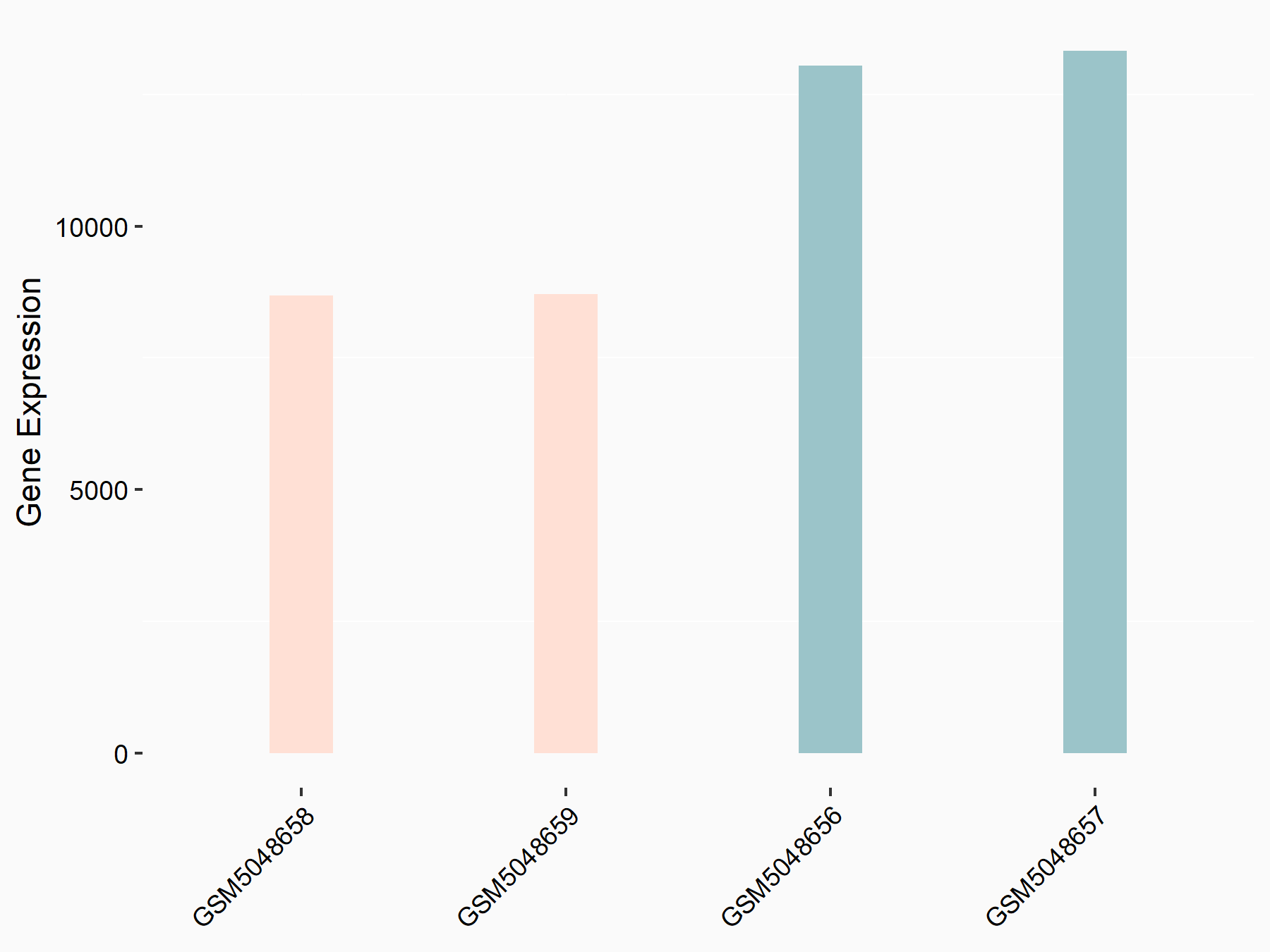 |
logFC: -6.00E-01 p-value: 2.49E-44 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The study identified the mechanism by which rapamycin affects autophagy via regulating METTL14, which provides a new idea for a potential targeted therapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma. METTL14 mediated Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) expression via m6A modification and regulated autophagy levels and biological functions in oral squamous cell carcinoma. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
| In-vitro Model | CAL-33 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1108 |
| HN-6 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8129 | |
| HSC-3 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1288 | |
| In-vivo Model | Specific pathogen-free (SPF) female NOD/SCID mice (5-6 weeks old) were randomly distributed into two groups: the OECtrl group and the OEMETTL14 groups. Phosphate buffer (200 uL) containing approximately 5 × 107 HSC3 or CAL33 cells was subcutaneously injected into the inner thigh of each mouse. The mice were euthanized two weeks after injection, and the tumour xenografts were harvested, photographed, weighed, and fixed. | |||
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
Head and neck squamous carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The study identified the mechanism by which rapamycin affects autophagy via regulating METTL14, which provides a new idea for a potential targeted therapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma. METTL14 mediated Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) expression via m6A modification and regulated autophagy levels and biological functions in oral squamous cell carcinoma. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
| In-vitro Model | CAL-33 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1108 |
| HN-6 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8129 | |
| HSC-3 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1288 | |
| In-vivo Model | Specific pathogen-free (SPF) female NOD/SCID mice (5-6 weeks old) were randomly distributed into two groups: the OECtrl group and the OEMETTL14 groups. Phosphate buffer (200 uL) containing approximately 5 × 107 HSC3 or CAL33 cells was subcutaneously injected into the inner thigh of each mouse. The mice were euthanized two weeks after injection, and the tumour xenografts were harvested, photographed, weighed, and fixed. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Rapamycin inhibited FTO activity, and directly targeted Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 (EIF4G1) transcripts and mediated their expression in an m6A-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. After FTO silencing, YTHDF2 captured eIF4G1 transcripts containing m6A, resulting in mRNA degradation and decreased expression of eIF4G1 protein, thereby promoting autophagy and reducing tumor occurrence. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00288)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000204 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184330328-184330329:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGGGAGGTTGCAGTAAGCCAAGATTGTGCCACTGCACTCCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000427845.5; rmsk_1189383; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_101615 | ||
2'-O-Methylation (2'-O-Me)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000324 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325103-184325104:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGGCAAAGACCTGGACTTTGAAAAAGCCAAGGTAGAGGTCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_5071 | ||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000323 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184324257-184324258:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGAACTTCCGAAAGCTGTTGTTGAATCGATGTCAGAAGGAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_5070 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 38 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003183 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315192-184315193:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGAAACCGGCTCCTCGACGGCCGCCGCCCGCCTGGCCTTTT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000440448.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33191 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003184 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315193-184315194:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAACCGGCTCCTCGACGGCCGCCGCCCGCCTGGCCTTTTA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33192 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003185 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315195-184315196:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AACCGGCTCCTCGACGGCCGCCGCCCGCCTGGCCTTTTAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33193 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003186 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315196-184315197:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACCGGCTCCTCGACGGCCGCCGCCCGCCTGGCCTTTTAGGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33194 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003187 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315198-184315199:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGGCTCCTCGACGGCCGCCGCCCGCCTGGCCTTTTAGGGCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000440448.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33195 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003188 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315199-184315200:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCTCCTCGACGGCCGCCGCCCGCCTGGCCTTTTAGGGCCT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33196 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003189 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315200-184315201:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCTCGACGGCCGCCGCCCGCCTGGCCTTTTAGGGCCTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33197 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003190 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315252-184315253:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCTGGCCTACACTCCTGGGCGGCGGCAGGCCTAGCTTCTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000455679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33198 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003191 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315255-184315256:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGCCTACACTCCTGGGCGGCGGCAGGCCTAGCTTCTGGCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000440448.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33199 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003192 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315258-184315259:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTACACTCCTGGGCGGCGGCAGGCCTAGCTTCTGGCCCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33200 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003193 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318484-184318485:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGGGGGGCTGAGCACGGTGGCTCACGCCTGTAGTCCCAGCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000442406.5; rmsk_1189371; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33201 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003194 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318486-184318487:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGGGGCTGAGCACGGTGGCTCACGCCTGTAGTCCCAGCACT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; rmsk_1189371; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000413967.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33202 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003195 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318488-184318489:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGGCTGAGCACGGTGGCTCACGCCTGTAGTCCCAGCACTTT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427845.5; rmsk_1189371; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33203 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003196 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318490-184318491:+ | ||
| Sequence | GCTGAGCACGGTGGCTCACGCCTGTAGTCCCAGCACTTTGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000346169.6; rmsk_1189371; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33204 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003197 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318498-184318499:+ | ||
| Sequence | CGGTGGCTCACGCCTGTAGTCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGCCAA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000424196.5; rmsk_1189371; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000350481.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33205 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003198 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318503-184318504:+ | ||
| Sequence | GCTCACGCCTGTAGTCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGCCAAGACAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; rmsk_1189371; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33206 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003199 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318955-184318956:+ | ||
| Sequence | TGGTGATGCACTCTTGTAATCCCAGCTATTCGGGAGGCTGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000382330.7; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33207 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003200 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318956-184318957:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGTGATGCACTCTTGTAATCCCAGCTATTCGGGAGGCTGAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000426123.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33208 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003201 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318957-184318958:+ | ||
| Sequence | GTGATGCACTCTTGTAATCCCAGCTATTCGGGAGGCTGAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000456033.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000440448.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33209 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003202 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318960-184318961:+ | ||
| Sequence | ATGCACTCTTGTAATCCCAGCTATTCGGGAGGCTGAGGCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000427141.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33210 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003203 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318965-184318966:+ | ||
| Sequence | CTCTTGTAATCCCAGCTATTCGGGAGGCTGAGGCAGGAGGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33211 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003204 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318972-184318973:+ | ||
| Sequence | AATCCCAGCTATTCGGGAGGCTGAGGCAGGAGGATCGCTTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000414031.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33212 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003205 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318978-184318979:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGCTATTCGGGAGGCTGAGGCAGGAGGATCGCTTGAACCCG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000456033.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33213 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003206 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318987-184318988:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGAGGCTGAGGCAGGAGGATCGCTTGAACCCGGGATGTGGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000450424.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33214 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003207 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318989-184318990:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGGCTGAGGCAGGAGGATCGCTTGAACCCGGGATGTGGAGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000421110.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33215 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003208 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318995-184318996:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGGCAGGAGGATCGCTTGAACCCGGGATGTGGAGATTGCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000411531.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33216 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003209 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318996-184318997:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGCAGGAGGATCGCTTGAACCCGGGATGTGGAGATTGCAGT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33217 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003210 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184318997-184318998:+ | ||
| Sequence | GCAGGAGGATCGCTTGAACCCGGGATGTGGAGATTGCAGTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000421110.5; rmsk_1189373; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33218 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003211 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320199-184320200:+ | ||
| Sequence | CAAGCCCTGGGCGTGGTGCCCAGAATAGGGTGCCAGAGCTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33219 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003212 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320717-184320718:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTCCACACCCACCCCTCCCCAGGTACTGTCTGCTTTTC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33220 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003213 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320718-184320719:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCTCCACACCCACCCCTCCCCAGGTACTGTCTGCTTTTCG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000413967.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33221 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003214 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320887-184320888:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGTAAAGAAGGGTTGTGGGACTCTTCAGTGCAAACTTGGTA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000441154.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33222 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003215 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322539-184322540:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAACTGGATGTTCTGTTGTTCTAGGCGAACCCGGCAGTACC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000434061.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33223 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003216 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325473-184325474:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCGTGACTGGCCCTCTGTCTCCACAGAGCAATTGGGTGCCA | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000466311.1; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000434061.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33224 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003217 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327212-184327213:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAATTTGTCTGTCTGTCTTCCAGGAGTAGCTTGAGCCGAGA | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33225 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003218 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327683-184327684:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGGCTATCATTGAGGAATATCTCCATCTCAATGACATGAAA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000482303.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33226 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003219 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327862-184327863:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCGTGCAGGAGCTGGCCTCACCCTCCTTGCTCTTCATCTTT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000482303.1; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33227 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003220 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334643-184334644:+ | ||
| Sequence | GCATCAGGGCCTTGTTTGAACAGTGGAACTTGGGAGGGTTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_33229 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 140 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063662 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184314619-184314620:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGAGCCGGAAATGGTTGTGGACTACGTCTGTGCGGCTGCGT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; H1A; HEK293T; fibroblasts; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000455679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620953 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063663 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184314657-184314658:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGTGGGGCTCGGCCGCGCGGACTGAAGGAGACTGAAGGTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; H1A; HEK293T; fibroblasts; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000426123.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620954 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063664 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184314667-184314668:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGCGCGGACTGAAGGAGACTGAAGGTAAAGCCGCCATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; H1A; HEK293T; fibroblasts; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620955 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063665 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315176-184315177:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCGACCCTCACTTGCCTGAAACCGGCTCCTCGACGGCCGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; H1A; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620956 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063666 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315331-184315332:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCCTGGGCCAGGCCCGAACCCGGTGTCCCCGGGTGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620957 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063667 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315416-184315417:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGCCTGGTGCCAGCGAGACCTGGAATTTCCGGTCTGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620958 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063668 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315505-184315506:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGGCCCTCGGATGCCCAGAACCTGTAGGCCGCACCGTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620959 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063670 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315525-184315526:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACCTGTAGGCCGCACCGTGGACTTGTTCTTAATCGAGGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620960 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063671 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315619-184315620:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTGACAGCATGTTGGTGGGGACAGGCTGTATCTTTTCTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620961 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063672 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315662-184315663:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACCCTCTTGGCATCTCTGGGACTCCGTATGGGACCCAGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427141.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620962 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063673 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315773-184315774:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCCCAACAGGTGCTGGGGGGACCCTGATGTGGCACCAAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620963 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063674 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315800-184315801:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGCACCAAATGAAATGAACAAAGCTCCACAGTCCACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620964 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063675 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315846-184315847:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCACCCGCCCCATCCCCCGGACTCCCACAGGTAATTAGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000421110.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620965 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063676 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315895-184315896:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGGGGTGGGGGTGGGGGAGACCAGGCAGTCTCCAGCCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000485712.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620966 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063677 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184315975-184315976:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCGCCTGCTGCCAAATTGAGACAGGGCCCCTGGGCTGTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620967 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063678 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184316110-184316111:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGGGCTTCCCCTCTTGCTGAACTCTGGTCTCCCCTCTTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; H1299; HEC-1-A; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000485712.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620968 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063679 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184316152-184316153:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGCGTTTCCCCCGGGGCAGACAGCGCCGGTGGTGTTCAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; MT4; A549; H1299; MM6; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620969 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063681 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184316195-184316196:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCCACAAGCGACACAAATGAACACGCCTTCTCAGCCCCGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; MT4; A549; H1299; MM6; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427141.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620970 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063682 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184317483-184317484:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGCCTCCCAGGGGGCCTACTACATCCCTGGACAGGTGAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000444134.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620971 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063683 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184317493-184317494:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGGCCTACTACATCCCTGGACAGGTGAGGCTGGGGGCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620972 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063684 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184317740-184317741:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GTTCCACATACGTTGTCCCGACACAGCAGTACCCTGTGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000455679.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620973 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063685 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184317809-184317810:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAAGCCCTACAGAATTTGGGACCTACGGTAAGCAGGGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000421110.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620974 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063686 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184319211-184319212:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCCTTTGTAAAGGGCTGGAGACAGGAACTAGACTCAAGTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000440448.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620975 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063687 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184319217-184319218:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTAAAGGGCTGGAGACAGGAACTAGACTCAAGTTAAATGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444134.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620976 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063688 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184319222-184319223:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGCTGGAGACAGGAACTAGACTCAAGTTAAATGGAACAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620977 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063689 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184319238-184319239:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTAGACTCAAGTTAAATGGAACAGGGTTGGCAGATCTCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000440448.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620978 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063690 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184319760-184319761:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCCCACCCCAGTTTTGATGAACCAGCCACCCCAGATTGCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427141.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000456033.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620979 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063692 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320360-184320361:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTGCAGCCACTGACTTGGGGACTGCTGGTGGGGTAGGGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620980 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063693 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320648-184320649:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GATCCGAATTCGAGATCCAAACCAAGGAGGAAAGGATATCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000456033.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620981 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063694 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320668-184320669:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACCAAGGAGGAAAGGATATCACAGAGGAGATCATGTCTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000456033.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620982 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063695 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320886-184320887:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TAGTAAAGAAGGGTTGTGGGACTCTTCAGTGCAAACTTGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427607.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620983 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063696 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320900-184320901:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGGACTCTTCAGTGCAAACTTGGTAACCCTTTGTGTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000421110.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620984 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063697 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184320962-184320963:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGCCTCAAGCTAATGGGGAGACGCCCCAGGTTGCTGTCATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.871321429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620985 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063698 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321402-184321403:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCACCATCCCCAGTCTTGGAACCGGGGTCTGAGCCTAATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; A549; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427607.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620986 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063699 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321446-184321447:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGTCCTCTCTATTCCTGGGGACACTATGACAACTATACAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; liver; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; H1299; Huh7; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620987 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063700 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321454-184321455:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTATTCCTGGGGACACTATGACAACTATACAAATGTCTGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000441154.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620988 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063701 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321462-184321463:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GGGGACACTATGACAACTATACAAATGTCTGTAGAAGAATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000484862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620989 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063703 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321502-184321503:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAACCCCCATCTCCCGTGAAACTGGGGAGCCATATCGCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000493299.1; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620990 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063704 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321531-184321532:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCATATCGCCTCTCTCCAGAACCCACTCCTCTCGCCGAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000484862.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620991 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063705 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321549-184321550:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAACCCACTCCTCTCGCCGAACCCATACTGGAAGTAGAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000444134.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620992 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063706 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321555-184321556:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACTCCTCTCGCCGAACCCATACTGGAAGTAGAAGTGACACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620993 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063707 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321571-184321572:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCATACTGGAAGTAGAAGTGACACTTAGCAAACCGGTTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; HEK293; kidney; hESC-HEK293T; CD8T; A549; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620994 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063708 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321582-184321583:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTAGAAGTGACACTTAGCAAACCGGTTCCAGAATCTGAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000428387.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000413967.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620995 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063709 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321644-184321645:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TCCCACCCCTTTGGCATCTCACACAGTGGAAATTCATGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000427607.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000444861.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620996 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063710 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321696-184321697:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTCCCATCTGAAGATCTGGAACCAGAGGTGGAGTCAAGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620997 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063711 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321772-184321773:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCCCTGTGCCCATTGCTCCAACTGCCCAACCTGAGGAACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620998 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063712 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321789-184321790:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCAACTGCCCAACCTGAGGAACTGCTCAACGGAGCCCCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_620999 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063714 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321797-184321798:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCAACCTGAGGAACTGCTCAACGGAGCCCCCTCGCCACCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.147845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621000 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063715 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184321824-184321825:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCCCTCGCCACCAGCTGTGGACTTAAGCCCAGTCAGTGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000457456.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621001 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063716 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322029-184322030:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGTGAGAAAGGAGGAGAGGAACTGCTCCCCCCAGAGAGTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; rmsk_1189375; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621002 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063717 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322217-184322218:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCCTGCAATGGAATCTAAGAACTAGATTAAGGACTTTTAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621003 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063718 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322427-184322428:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TAAGAAGGAGGCTGTTGGAGACCTTCTGGATGCCTTCAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; A549; H1299; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621004 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063719 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322547-184322548:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTTCTGTTGTTCTAGGCGAACCCGGCAGTACCAGAGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; A549; H1299; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621005 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063720 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322651-184322652:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTCCTGAGGAAGCAGATGAGACCTGGGACTCAAAGGAAGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1299; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000444861.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621006 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063721 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322658-184322659:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGAAGCAGATGAGACCTGGGACTCAAAGGAAGACAAAATTC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1299; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621007 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063722 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322670-184322671:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GACCTGGGACTCAAAGGAAGACAAAATTCACAATGCTGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; H1299; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621008 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063723 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322691-184322692:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAAAATTCACAATGCTGAGAACATCCAGCCCGGGGAACAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; H1299; Huh7; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621009 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063725 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322707-184322708:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGAACATCCAGCCCGGGGAACAGAAGTATGAATATAAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; liver; HepG2; H1299; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621010 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063726 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322838-184322839:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGATCAGTGGAAGCCTCTAAACCTAGAGGAGAAAAAACGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; H1299; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000350481.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621011 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063727 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322926-184322927:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CAGAAGCCAGAGGGATTGCCACATATCAGTGACGTGGTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621012 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063728 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184322949-184322950:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TATCAGTGACGTGGTGCTGGACAAGGTTAGTGGCTTCAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621013 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063729 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323091-184323092:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTCTTTGCAGGCCAATAAAACACCACTGCGGCCACTGGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621014 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063730 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323120-184323121:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGGCCACTGGATCCCACTAGACTACAAGGCATAAATTGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621015 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063731 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323123-184323124:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCACTGGATCCCACTAGACTACAAGGCATAAATTGTGGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000426123.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621016 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063732 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323146-184323147:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGGCATAAATTGTGGCCCAGACTTCACTCCATCCTTTGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621017 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063733 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323178-184323179:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTTTGCCAACCTTGGCCGGACAACCCTTAGCACCCGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621018 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063734 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323418-184323419:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCTTAGCAGGCTGGCCTGGGACCCCGGCGCTCTCAGCAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621019 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063736 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323439-184323440:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCCCGGCGCTCTCAGCAGGGACCCCGAAAAGAACCACGCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000444861.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621020 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063737 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323451-184323452:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGCAGGGACCCCGAAAAGAACCACGCAAGATCATTGCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621021 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063738 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323470-184323471:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AACCACGCAAGATCATTGCCACAGTGTTAATGACCGAAGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621022 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063739 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323496-184323497:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTAATGACCGAAGATATAAAACTGAACAAAGCAGAGAAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621023 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063740 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323501-184323502:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GACCGAAGATATAAAACTGAACAAAGCAGAGAAAGCCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621024 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063741 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323523-184323524:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AAAGCAGAGAAAGCCTGGAAACCCAGCAGCAAGCGGACGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000413967.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621025 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063742 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323539-184323540:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGAAACCCAGCAGCAAGCGGACGGCGGCTGATAAGGATCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.616982143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621026 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063743 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323587-184323588:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AAGATGCTGATGGCAGCAAAACCCAGGTACTGGCAAGTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000444861.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621027 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063744 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323814-184323815:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTGCGCTCCATCCTGAATAAACTGACACCCCAGATGTTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000413967.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621028 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063745 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323818-184323819:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCATCCTGAATAAACTGACACCCCAGATGTTCCAGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000450424.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000444861.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621029 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063747 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323870-184323871:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGTGACGCAGCTGGCCATCGACACCGAGGAACGCCTCAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621030 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063748 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184323954-184323955:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTTCTCTGTGGCCTATGCCAACATGTGCCGCTGCCTCATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000450424.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621031 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063749 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184324227-184324228:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCACTACGGAAAAGCCAACAGTGACTGTGAACTTCCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000435046.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621032 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063750 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184324240-184324241:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AAAGCCAACAGTGACTGTGAACTTCCGAAAGCTGTTGTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; BGC823; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000350481.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621033 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063751 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184324288-184324289:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCAGAAGGAGTTTGAGAAAGACAAAGATGATGATGAGGTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000421110.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621034 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063752 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184324923-184324924:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGAGCTGGAAGAGGCTCGGGACATAGCCCGGCGGCGCTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621035 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063753 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184324978-184324979:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTATTGGAGAGTTGTTCAAACTGAAGATGTTAACAGAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000444861.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621036 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063754 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325023-184325024:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATGCATGACTGTGTGGTCAAACTGCTTAAGAACCATGATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000441154.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621037 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063755 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325034-184325035:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGTCAAACTGCTTAAGAACCATGATGAAGAGTCCCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000434061.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621038 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063756 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325091-184325092:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCTCACCACCATTGGCAAAGACCTGGACTTTGAAAAAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1299 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621039 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063758 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325097-184325098:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CACCATTGGCAAAGACCTGGACTTTGAAAAAGCCAAGGTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1299 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000426123.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000413967.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621040 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063759 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325518-184325519:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGGGGATCAGGGTCCCAAGACCATTGACCAGATCCATAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7; endometrial; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000466311.1; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621041 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063760 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325556-184325557:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AAGGAGGCTGAGATGGAAGAACATCGAGAGCACATCAAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; Huh7; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000466311.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621042 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063761 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325603-184325604:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCTCATGGCCAAGGGCAGTGACAAGCGTCGGGGCGGTCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000466311.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621043 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063762 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325741-184325742:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CACGTGTCTGGGCCACTGAGACACCATGATGGAACTGAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000466311.1; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000390856.1; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621044 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063763 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325857-184325858:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTTTTTGTGTCAGGCCGTGGACTTCCCCTTGTGGATGATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; MT4; H1299; Huh7; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000466311.1; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621045 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063764 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325886-184325887:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGATGATGGTGGCTGGAACACAGTTCCCATCAGCAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; MT4; H1299; Huh7; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000466311.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621046 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063765 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184325922-184325923:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CAAAGGTAGCCGCCCCATTGACACCTCACGACTCACCAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000466311.1; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621047 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063766 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184326545-184326546:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCCTGGCTCCATCGATTCTAACAACCAGCTCTTTGCACCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000466311.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621048 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063767 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184326935-184326936:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AATCGCTTCTCAGCCCTTCAACAAGCGGTACCCACAGAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621049 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063769 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327253-184327254:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACGAGGCGAGAAAGCTGGAGACCGAGGAGACCGCCTAGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; U2OS; MT4; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621050 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063770 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327262-184327263:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAAAGCTGGAGACCGAGGAGACCGCCTAGAGCGGAGTGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; U2OS; MT4; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621051 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063771 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327292-184327293:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCGGAGTGAACGGGGAGGGGACCGTGGGGACCGGCTTGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; U2OS; MT4; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000482303.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621052 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063772 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327301-184327302:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACGGGGAGGGGACCGTGGGGACCGGCTTGATCGTGCGCGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; U2OS; MT4; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000482303.1; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000448284.1; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621053 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063773 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327321-184327322:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACCGGCTTGATCGTGCGCGGACACCTGCTACCAAGCGGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; MT4; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000482303.1; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621054 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063774 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327430-184327431:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TAGCCTCACGGAGGATCGGGACCGTGGGCGGGATGCCGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000482303.1; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621055 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063775 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327696-184327697:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GGAATATCTCCATCTCAATGACATGAAAGTAGGCAGTGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000482303.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621056 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063776 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184327788-184327789:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGTCCGGGGTCTGGGTCAGACAGTGACTGGTCTCTTCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000482303.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621057 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063777 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328197-184328198:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGTGAGGTTGGGAGTTCTAGACCAGCCTGGCCAACATGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000342981.8; rmsk_1189379; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000350481.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621058 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063778 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328220-184328221:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGCCTGGCCAACATGGTGAAACCCTGTCTCTACTAATAATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000392537.6; rmsk_1189379; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621059 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063780 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328590-184328591:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCAGAAGGAGAGTGGGGACCTGGCCTAGAATGTCTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | BGC823 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621060 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063781 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328659-184328660:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AATCTTGGAATTGGCTGAGGACATGGAAATTGACATCCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621061 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063782 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328671-184328672:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GGCTGAGGACATGGAAATTGACATCCCCCACGTGTGGCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000441154.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621062 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063783 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328702-184328703:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTGTGGCTCTACCTAGCGGAACTGGTAACACCCATTCTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000460829.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621063 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063784 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328709-184328710:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TCTACCTAGCGGAACTGGTAACACCCATTCTGCAGGAAGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621064 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063785 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328792-184328793:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGAATTCAGGGGAGGTAAAGACCAGAGGAAAGGTGGTAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621065 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063786 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328867-184328868:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GATGGAGTAGTGGTGAGAGAACTGTGGAGGCTGTCAGCATT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621066 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063787 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328915-184328916:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TCTCTTCTTGTAGGGAGATTACAAAGCCTCTGAGACCGTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621067 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063788 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184328929-184328930:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGATTACAAAGCCTCTGAGACCGTTGGGCAAAGCTGCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621068 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063789 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331338-184331339:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATTTCTACCTGAAGGCCAGGACATTGGTGCATTCGTCGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000460829.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621069 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063790 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331360-184331361:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATTGGTGCATTCGTCGCTGAACAGGTTTGGGGATGGAGTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621070 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063791 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331541-184331542:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACTCCCCTCCGAGGAGCTGAACAGGCAGCTGGAGAAGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MT4; A549; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000434061.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621071 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063792 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331758-184331759:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGAGCAGCAGATAGTATCCAACACGTTAGTTCGAGCCCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621072 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063793 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331781-184331782:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGTTAGTTCGAGCCCTCATGACGGCTGTCTGCTATTCTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.833690476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000414031.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621073 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063794 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331818-184331819:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGCAATTATTTGTAAGAGGAACCAGGGAGATGGAGGGGCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000464548.1; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621074 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063795 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331854-184331855:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGCAAGGGTGGGCCTGACAGACAAGTGGAGGGAGGTGGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000434061.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621075 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063796 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331899-184331900:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTTGGCCTCCCAGTTCTGAACCGGGGTAAGGGTATATTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000460829.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621076 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063797 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184331950-184331951:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTGTCTTCTTGTAGTTGAGACTCCCCTCCGAGTGGACGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; TIME; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621077 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063798 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184332017-184332018:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCTGCAGAAATACCTGTGTGACGAGCAGAAGGAGCTACAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.833690476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621078 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063799 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184332044-184332045:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAAGGAGCTACAGGCGCTCTACGCCCTCCAGGCCCTTGTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.05260119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000478291.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621079 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063800 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184332075-184332076:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCCCTTGTAGTGACCTTAGAACAGCCTCCCAGTAAGAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; peripheral-blood; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000422614.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000478291.1; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000435046.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621080 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063801 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334789-184334790:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGTGAAGGAGGATGCCTTCTACAGTTGGGAGAGTAGCAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621082 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063802 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334810-184334811:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGTTGGGAGAGTAGCAAGGACCCCGCTGAGCAGCAGGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; fibroblasts; GM12878; H1299; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000427845.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621083 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063803 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334897-184334898:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGAAGCAGAGGAGGAGTCTGACCACAACTGAGGGCTGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.839113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000411531.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621084 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063804 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334900-184334901:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGAGGAGGAGTCTGACCACAACTGAGGGCTGGTGGGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000411531.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000427845.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000441154.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000435046.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621085 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063805 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334926-184334927:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGGGCTGGTGGGGCCGGGGACCTGGAGCCCCATGGACACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621086 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063806 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334942-184334943:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGGACCTGGAGCCCCATGGACACACAGATGGCCCGGCTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000435046.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621087 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063807 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184334971-184334972:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGGCCCGGCTAGCCGCCTGGACTGCAGGGGGGCGGCAGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000382330.7; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000352767.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621088 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063808 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184335031-184335032:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGTAGTGTGATGTGTCTGAACTAATAAAGTGGCTGAAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000460829.5; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621089 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063809 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184335186-184335187:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGGGTGGGGAGGGGCACCAACGCCTGCCCCTGGGGTCCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.147845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000442406.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621090 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063810 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184335227-184335228:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTTATTTTCTGAAAATCACTCTCGGGACTGCCGTCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.469291667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000424196.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621091 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063811 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184335236-184335237:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TTCTGAAAATCACTCTCGGGACTGCCGTCCTCGCTGCTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000475721.5; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000434061.6; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000435046.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621092 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE063812 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr3:184335337-184335338:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACGGTGCCTGTAATTATTAAACATGAATTCAATTAAGCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000346169.6; ENST00000435046.6; ENST00000442406.5; ENST00000424196.5; ENST00000392537.6; ENST00000414031.5; ENST00000342981.8; ENST00000350481.9; ENST00000352767.7; ENST00000434061.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_621093 | ||
References