m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00309)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
CAMKK2
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Neural progenitor cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout NPCs
Control: Wild type NPCs
|
GSE158985 | |
| Regulation |
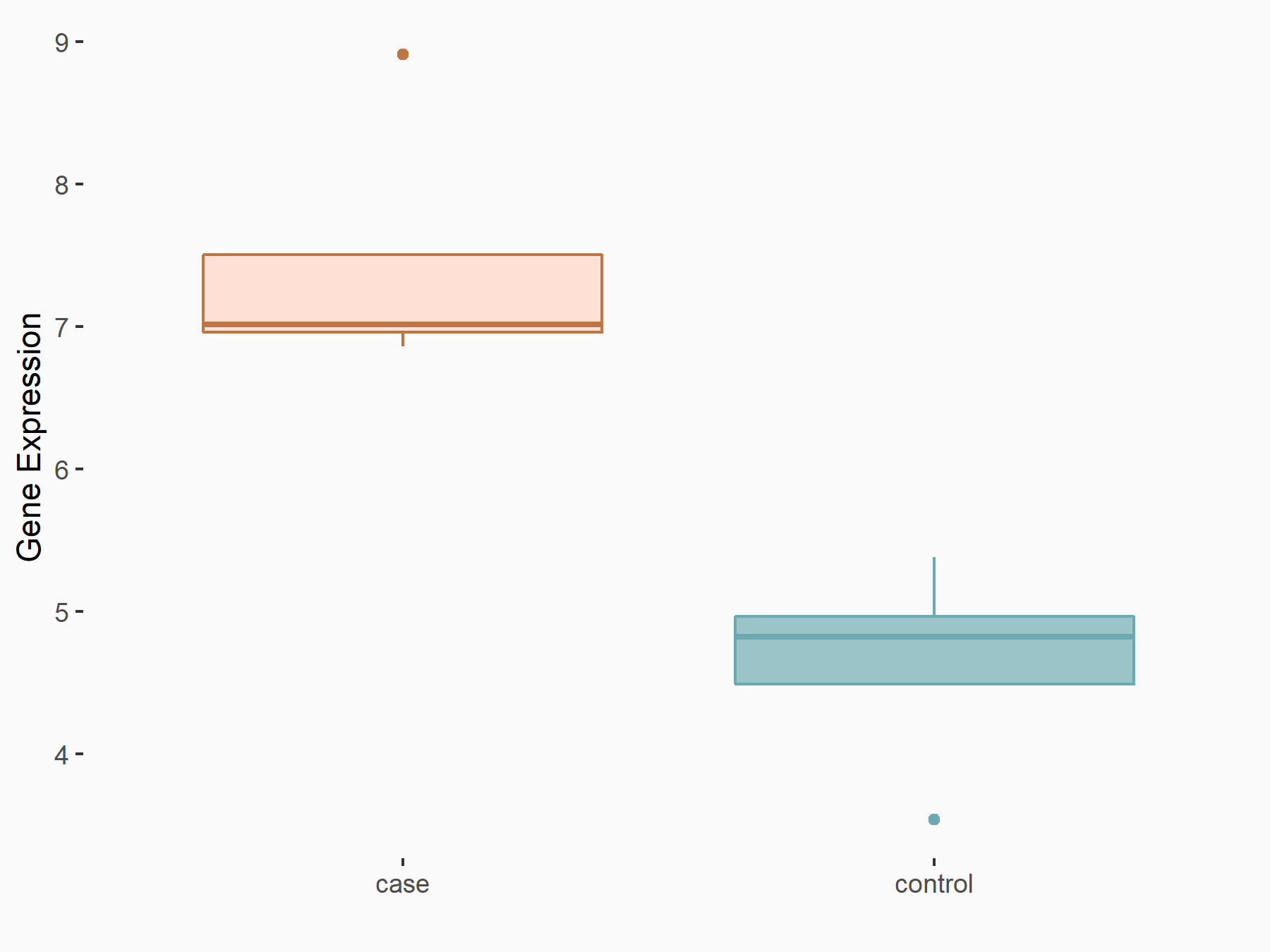 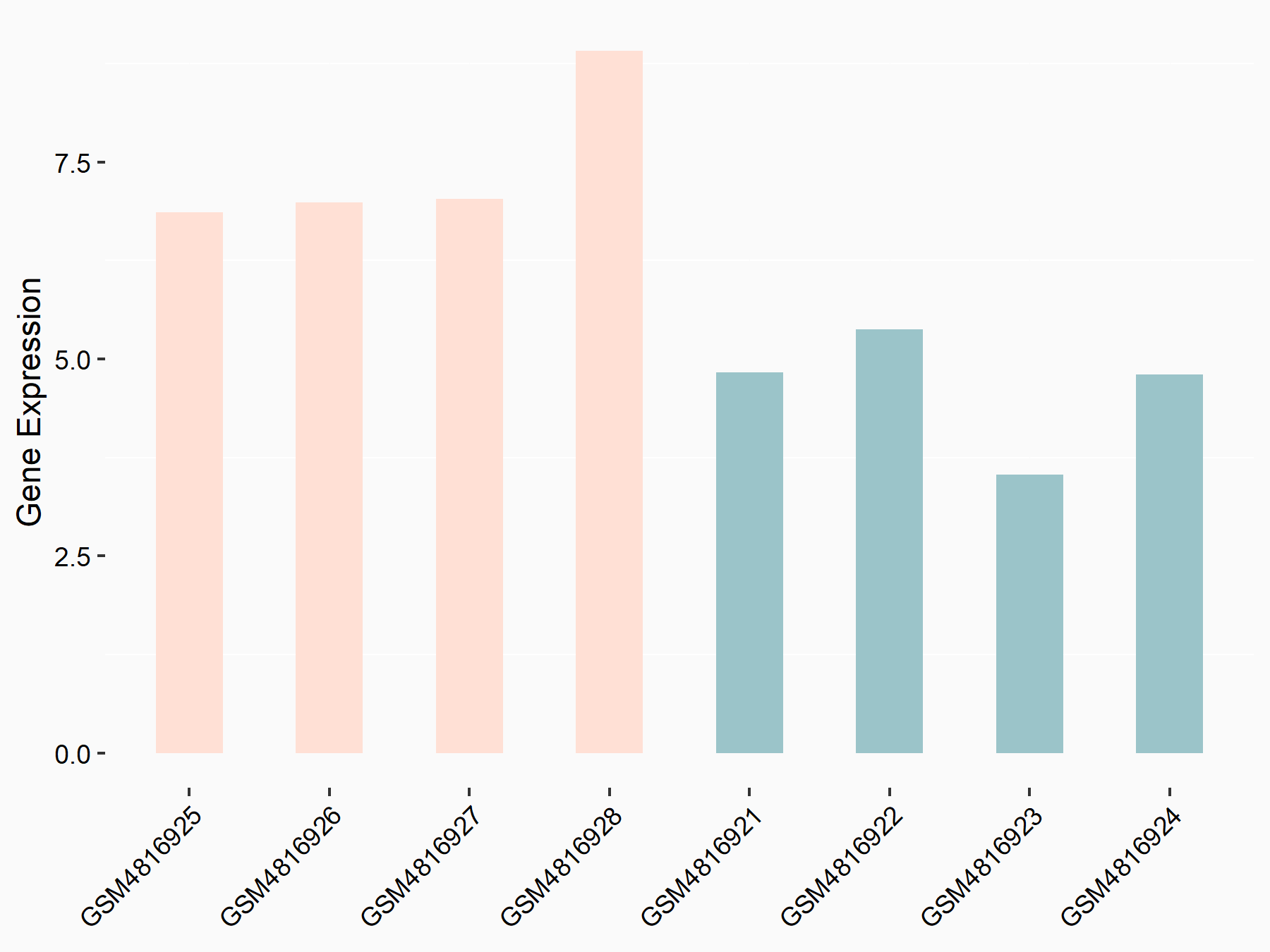 |
logFC: 5.88E-01 p-value: 3.22E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification promoted translation of PPM1A (protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform), a negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, but decreased expression of Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CAMKK2) (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta), a positive AMPK regulator, by reducing its RNA stability. Similar regulation of METTL14, ALKBH5, and m6A was also observed in LCs upon treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin (HsCG). Knock down of YTHDF1 failed to change the expression of CAMKK2 Providing insight into novel therapeutic strategies by exploiting m6A RNA methylation as targets for treating azoospermatism and oligospermatism patients with reduction in serum testosterone. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Azoospermia | ICD-11: GB04.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| In-vivo Model | Male SPF BALB/c mice (qls02-0202) were purchased from Qinglongshan animal breeding farm. Mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation and testes were obtained for following histopathological analyses. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification promoted translation of PPM1A (protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform), a negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, but decreased expression of Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CAMKK2) (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta), a positive AMPK regulator, by reducing its RNA stability. Similar regulation of METTL14, ALKBH5, and m6A was also observed in LCs upon treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin (HsCG). Knock down of YTHDF1 failed to change the expression of CAMKK2 Providing insight into novel therapeutic strategies by exploiting m6A RNA methylation as targets for treating azoospermatism and oligospermatism patients with reduction in serum testosterone. knock down of YTHDF2 increased expression of Camkk2 at both mRNA and protein levels to a similar extent as knock down of METTL14 in both TM3 cells and primary LCs. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Azoospermia | ICD-11: GB04.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| In-vivo Model | Male SPF BALB/c mice (qls02-0202) were purchased from Qinglongshan animal breeding farm. Mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation and testes were obtained for following histopathological analyses. | |||
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification promoted translation of PPM1A (protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform), a negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, but decreased expression of Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CAMKK2) (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta), a positive AMPK regulator, by reducing its RNA stability. Similar regulation of METTL14, ALKBH5, and m6A was also observed in LCs upon treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin (HsCG). Knock down of YTHDF1 failed to change the expression of CAMKK2 Providing insight into novel therapeutic strategies by exploiting m6A RNA methylation as targets for treating azoospermatism and oligospermatism patients with reduction in serum testosterone. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Azoospermia [ICD-11: GB04.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| In-vivo Model | Male SPF BALB/c mice (qls02-0202) were purchased from Qinglongshan animal breeding farm. Mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation and testes were obtained for following histopathological analyses. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | m6A modification promoted translation of PPM1A (protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform), a negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, but decreased expression of Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CAMKK2) (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta), a positive AMPK regulator, by reducing its RNA stability. Similar regulation of METTL14, ALKBH5, and m6A was also observed in LCs upon treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin (HsCG). Knock down of YTHDF1 failed to change the expression of CAMKK2 Providing insight into novel therapeutic strategies by exploiting m6A RNA methylation as targets for treating azoospermatism and oligospermatism patients with reduction in serum testosterone. knock down of YTHDF2 increased expression of Camkk2 at both mRNA and protein levels to a similar extent as knock down of METTL14 in both TM3 cells and primary LCs. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Azoospermia [ICD-11: GB04.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | TM3 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_4326 |
| In-vivo Model | Male SPF BALB/c mice (qls02-0202) were purchased from Qinglongshan animal breeding farm. Mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation and testes were obtained for following histopathological analyses. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00309)
| In total 4 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005925 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121245896-121245897:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | TCATGTTCCATTGCACAGACAGACCGCTTTGAGTTTATCTT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_32917 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005926 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121253376-121253377:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | TCGCTGACTTTGGTGTGAGCAATGAATTCAAGGGCAGTGAC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_32918 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005927 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121272987-121272988:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | TCCCCAGAGCCTAGCACAGTACCTGGTGCATAGTAGGAGCG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000535524.1; rmsk_3929244; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000542540.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000539380.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_32919 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE005928 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121286793-121286794:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | GCCCTCCTGAAGCACTCAGAAGCTGGATGATTGTGAGCAAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000446440.6; rmsk_3929282; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000652382.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_32920 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 7 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000119 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274460-121274461:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCCAGGATGAGCTGGGGGGCAGGGGCAGCAGCAGCAGCGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000446440.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_11137 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000120 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274477-121274478:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCAACCGGGCCGCCCCCCAGGATGAGCTGGGGGGCAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000392473.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_11138 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000121 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274478-121274479:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGCAACCGGGCCGCCCCCCAGGATGAGCTGGGGGGCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_11139 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000122 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274479-121274480:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CAGCAGCAACCGGGCCGCCCCCCAGGATGAGCTGGGGGGCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000543477.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_11140 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000123 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274480-121274481:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCAGCAGCAACCGGGCCGCCCCCCAGGATGAGCTGGGGGGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_11141 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000124 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274481-121274482:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGCAGCAACCGGGCCGCCCCCCAGGATGAGCTGGGGGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000543477.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_11142 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000125 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274482-121274483:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCCAGCAGCAACCGGGCCGCCCCCCAGGATGAGCTGGGGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_11143 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 81 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015606 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121237787-121237788:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGTATTTATCACTAAAAAGTACATGAACTTAAGAGACAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213582 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015607 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121237811-121237812:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCAGGTGTATAAAGTTAAATACTGTGTATTTATCACTAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213583 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015608 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121237903-121237904:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGGGACTGCAGATTTTTCTACTCTGTGATCGATTCAATGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213584 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015609 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121237918-121237919:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGGAGGCCGAGTTTCTGGGGACTGCAGATTTTTCTACTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213585 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015610 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238098-121238099:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTCCTCAGAGCCTTTCTGGAACAAGGAGAATGCCTGTGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213586 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015611 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238152-121238153:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCTGCGGAGGCCTCTCCCTACTGGTCTGGCCTTTCCTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213587 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015612 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238180-121238181:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCTTATTGAGCCCCTTGTTGACACTTGGGGCTGCGGAGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213588 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015613 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238270-121238271:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCACAAACCCTCCATCCACTTCCCATTTCCTCTGCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.475107143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213589 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015615 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238281-121238282:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGGCCTCGAAGGAAGCACAAACCCTCCATCCACTTCCCATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1A; H1B; Huh7; Jurkat; GSC-11; iSLK; TREX; MSC; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213590 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015616 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238285-121238286:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTGGCCTCGAAGGAAGCACAAACCCTCCATCCACTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213591 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015617 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238306-121238307:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTAAGCAACCTGTGGCCTGCACTTGTGGCCTCGAAGGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213592 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015618 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238337-121238338:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATTGCTAGCTCATCTGTGGGACCAATTTGGTGTAAGCAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1A; GSC-11; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213593 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015619 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238462-121238463:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CACAGAGCATTTGAGCTGCCACTCTTGGAGCACATTGATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.475107143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213594 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015620 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238483-121238484:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATAAGCCAAGATGGCTGTAAACACAGAGCATTTGAGCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213595 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015621 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238583-121238584:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGTGGGGTGGGGGAGACCCACATTGATGACTTTTTTTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213596 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015622 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121238691-121238692:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGTTTACACAGCTGCATCAGACAATGCCATTTCTCCCCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213597 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015623 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239066-121239067:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCATAGATCCTAAGCTCTTGACTGTAGTTTAGCCAGACTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213598 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015624 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239148-121239149:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTGGTGTGAGGACTTCTCAGACAAAGGCAAGGCCTCGTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213599 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015626 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239157-121239158:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGATCAGCTGTGGTGTGAGGACTTCTCAGACAAAGGCAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000652382.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213600 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015627 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239202-121239203:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGAAAGACGGCACCGGGAAACTCTGCTTCCCCATTGTTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213601 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015628 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239279-121239280:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGAGGAAAGCTGGAAGGACTCTGCCTTGGGAGATTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213602 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015629 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239449-121239450:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACTCGTTGGGGTATGAGGAAACCAGGGCTTGGCACAGGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1B; H1A; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213603 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015630 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239469-121239470:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGACTGTTGAAACCCACAGCACTCGTTGGGGTATGAGGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213604 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015631 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239478-121239479:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTTTAGAGAAGACTGTTGAAACCCACAGCACTCGTTGGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1B; H1A; A549; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213605 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015632 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239487-121239488:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGGCACCCTTTTAGAGAAGACTGTTGAAACCCACAGCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1B; H1A; A549; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213606 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015633 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239520-121239521:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCTGAGCTTCCCTAGACTCCACACAATAACCTTGGGGCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213607 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015634 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239525-121239526:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAGGATCTGAGCTTCCCTAGACTCCACACAATAACCTTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1B; A549; HEK293A-TOA; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213608 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015635 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239560-121239561:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGCTTTCACTGGACCAACACACAAATGATCATCCTGAGGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.084928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213609 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015637 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239568-121239569:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTGGGAAATGCTTTCACTGGACCAACACACAAATGATCATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; HEK293A-TOA; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213610 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015638 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239666-121239667:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATAACCTGTATATTCTAAAGACTGCTAAGGTTTTGTTTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213611 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015639 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239683-121239684:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGCTTAGCTAGTTCATAACCTGTATATTCTAAAGACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.147452381 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | AML | ||
| Seq Type List | miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213612 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015640 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239728-121239729:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GATCAGTTAGAGCCGATGAAACCTATGCCCGCCTGTATATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213613 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015641 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239792-121239793:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TAGAGCACAGTAGTTCAGAAACTATTTAGAGCTTCCAGGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213614 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015642 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239816-121239817:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAAGTCTCTAACTAGAGTGAACTCTAGAGCACAGTAGTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213615 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015643 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239902-121239903:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | CTCTTTGTCAAATTACGAAAACTTCAGGGTGAAATCCTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213616 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015644 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121239992-121239993:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGAAACATTTCTCCTGAAAGACTGAACGTGTTTCTTCATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213617 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015645 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240008-121240009:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCAGCTGTGGTGGGGAAACATTTCTCCTGAAAGACTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213618 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015646 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240092-121240093:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTAGAATTGTAGTCAGGAAAACAGAAAGGGCTTGAAATTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213619 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015648 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240228-121240229:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCTAGTGCAAACCGGAAACCATGGCACCTTCCAGAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213620 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015649 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240235-121240236:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGATGTGGCTCCTAGTGCAAACCGGAAACCATGGCACCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213621 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015650 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240313-121240314:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGAAAGGCGAGCAGAAAACTCCGGCGGTCTGAGGCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213622 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015651 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240338-121240339:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTGACTGTGTGTGGGGTTTGACAACTGTGGAAAGGCGAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213623 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015652 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240355-121240356:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CACGTCAGATATACCAAGTGACTGTGTGTGGGGTTTGACAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | AML | ||
| Seq Type List | miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213624 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015653 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240377-121240378:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTTCATTGTGATTTTCAGAACCACGTCAGATATACCAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213625 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015654 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240416-121240417:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGGACAATTGCTTTTTAAAACGTTTTTATGCCAAAAATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.179660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213626 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015655 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240432-121240433:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AAACCCACGTGCATTTTGGGACAATTGCTTTTTAAAACGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213627 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015656 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240450-121240451:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTGAGGAGTTGCAGACCCAAACCCACGTGCATTTTGGGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213628 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015657 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240456-121240457:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCGGGTGTGAGGAGTTGCAGACCCAAACCCACGTGCATTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213629 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015659 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240480-121240481:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGTGGCCGCTGGCTGGCTGGACAGGCGGGTGTGAGGAGTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; brain; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213630 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015660 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240516-121240517:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAAAAAAAAAAAAGGACTTGACTCCATGACGTCGACCGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213631 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015661 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240521-121240522:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGACAAAAAAAAAAAAAGGACTTGACTCCATGACGTCGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213632 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015662 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240538-121240539:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTTTGTTGTTTTAAAGGGGACAAAAAAAAAAAAAGGACTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213633 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015663 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240609-121240610:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TAGCAGCATGTCCTACGGAAACCCAGCACGTGTGTAGAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; MM6; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000545538.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213634 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015664 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121240851-121240852:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAGGAAGCAAGGCAGCGAAGACAACCTCCAGGGCACCGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213635 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015665 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121245199-121245200:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACGTAAACGCTCCTTTGGGAACCCATTCGAGGGCAGCCGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213636 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015666 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121245227-121245228:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTCTTCAGATCCTGGTGAAGACCATGATACGTAAACGCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213637 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015667 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121248629-121248630:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAGGTCGAGAACTCAGTCAAACACATTCCCAGCTTGGCAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213638 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015668 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121248639-121248640:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GACTGAAGAGGAGGTCGAGAACTCAGTCAAACACATTCCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213639 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015670 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121248678-121248679:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTTGCCGTCGGAGGATGAGAACTGCACGCTGGTCGAAGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213640 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015671 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121249820-121249821:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CACCCGTATGCTGGACAAGAACCCCGAGTCGAGGATCGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000446440.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213641 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015672 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121249826-121249827:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTGATCACCCGTATGCTGGACAAGAACCCCGAGTCGAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213642 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015673 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121249847-121249848:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CATAGCTGAGGACTTGAAGGACCTGATCACCCGTATGCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213643 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015674 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121249856-121249857:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAGGCCCGACATAGCTGAGGACTTGAAGGACCTGATCACCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213644 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015675 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121249868-121249869:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCTCTCCATCCCCAGGCCCGACATAGCTGAGGACTTGAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; kidney; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213645 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015676 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121249963-121249964:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCAGGCCCTGGAATTTCCAGACCAGTGAGTATCTCCCGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000652382.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213646 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015677 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121252686-121252687:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATGTTTGGGCCATGGGTGTGACACTATACTGCTTTGTCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213647 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015678 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121253295-121253296:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CACCCGAGTCGCTCTCTGAGACCCGCAAGATCTTCTCTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000412367.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213648 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015679 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121253342-121253343:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGTGACGCGCTCCTCTCCAACACCGTGGGCACGCCCGCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213649 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015681 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121253405-121253406:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGTCGGAGAAGATGGGCACATCAAGATCGCTGACTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213650 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015682 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121253437-121253438:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATCATCCACCGTGACATCAAACCTTCCAACCTCCTGGTCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000412367.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213651 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015683 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121253444-121253445:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCAGAAGATCATCCACCGTGACATCAAACCTTCCAACCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213652 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015684 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121255596-121255597:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTCAAACCACTCTCTGAAGACCAGGCCCGTTTCTACTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213653 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015685 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121255610-121255611:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATGGAAGTGCCCACCCTCAAACCACTCTCTGAAGACCAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213654 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015686 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121255796-121255797:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTCTTCCCTACAGTGTTCGAACTGGTCAACCAAGGGTGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213655 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015687 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121260323-121260324:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCCCAATGAGGACCATCTGTACATGGGTAAGGAAGCCCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000446440.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213656 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015688 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121260332-121260333:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGATGACCCCAATGAGGACCATCTGTACATGGGTAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545538.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000392474.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213657 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015689 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121269552-121269553:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGTCGTCAAGTTGGCCTACAATGAAAATGACAATACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000542540.5; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000539380.1; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000337174.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213658 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015690 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121269843-121269844:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTTGGCCAGGCTGGTCTCAAACTCCTTAACTCAAGTGATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000542540.5; ENST00000539380.1; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000324774.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213659 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015692 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274179-121274180:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCAGCCGGTGGCAGCCTGGACATGAACGGACGCTGCATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; H1B; H1A; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000539380.1; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000542540.5; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000347034.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213660 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015693 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274314-121274315:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGACCTCGGCTTGGCGCGGGACCGGCCCCTGGAGGCCGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1B; MM6; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; TIME; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000538733.5; ENST00000542540.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000539380.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213661 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE015694 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:121274332-121274333:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGAGCCGGGCTGTGCTGTGGACCTCGGCTTGGCGCGGGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; iSLK; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000539380.1; ENST00000652382.1; ENST00000347034.6; ENST00000542540.5; ENST00000402834.8; ENST00000535524.1; ENST00000544485.1; ENST00000392473.2; ENST00000324774.9; ENST00000446440.6; ENST00000392474.6; ENST00000404169.8; ENST00000337174.7; ENST00000543477.1; ENST00000412367.6; ENST00000538733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_213662 | ||
References