m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00524)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
Stat1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | Raw 264.7 cell line | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 knockout Raw 264.7 cells
Control: Wild type Raw 264.7 cells
|
GSE162248 | |
| Regulation |
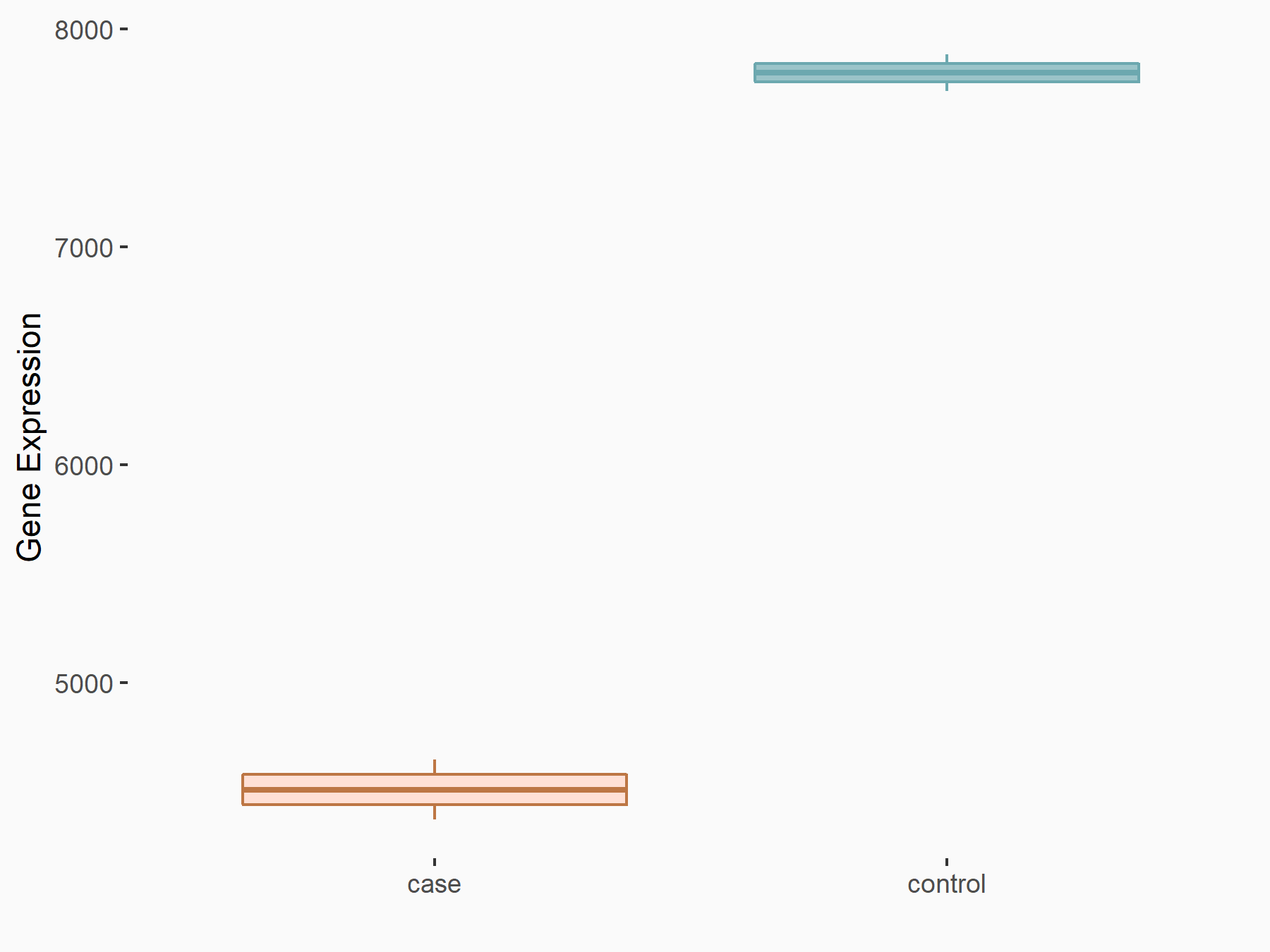 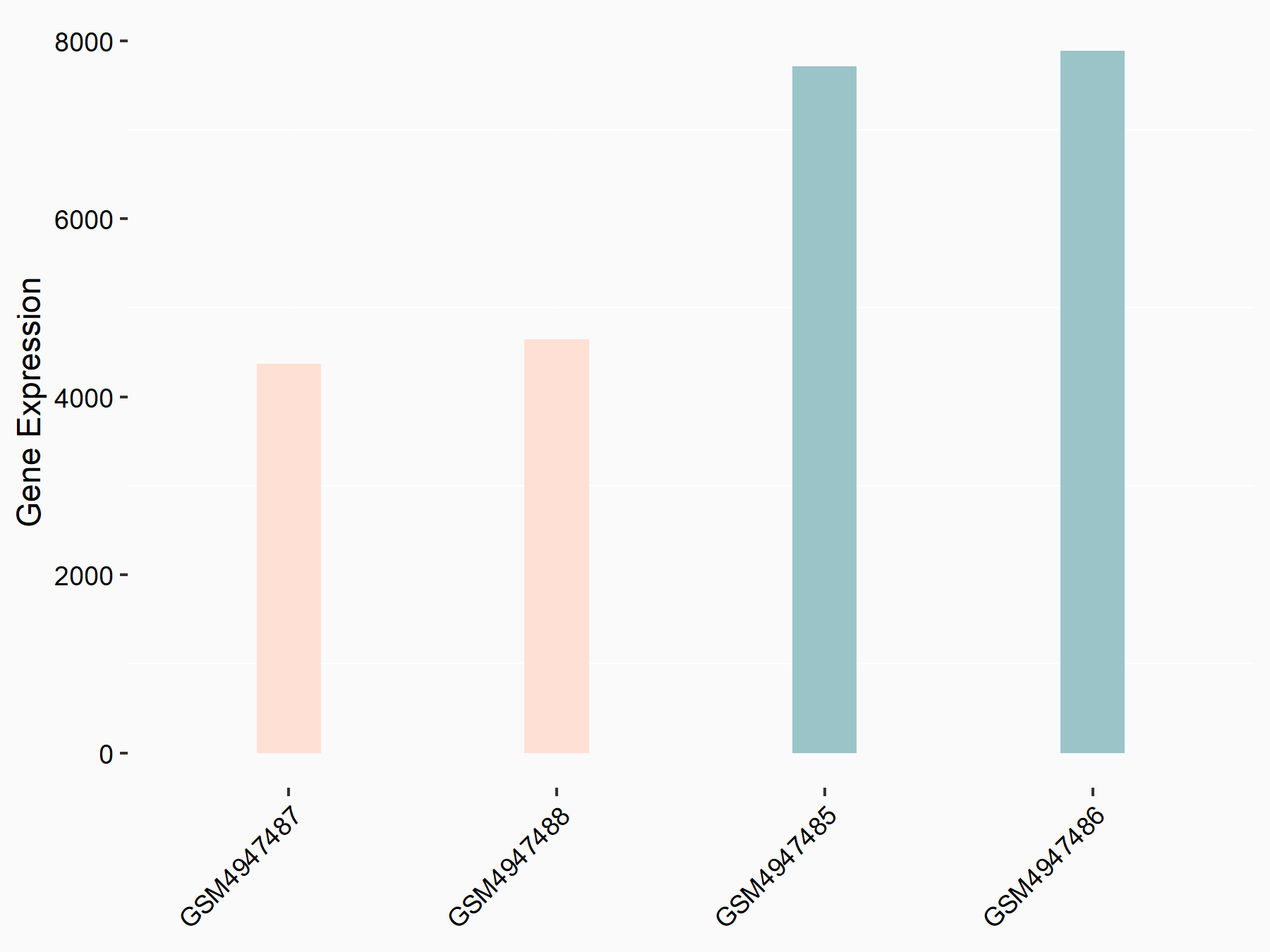 |
logFC: -7.90E-01 p-value: 1.53E-25 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between Stat1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 2.34E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl3 promotes oxLDL-triggered inflammation through interacting with Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) protein and mRNA in RAW264.7 macrophages. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
| In-vitro Model | RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
| In-vitro Model | CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | Embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mESCs
Control: Wild type mESCs
|
GSE156481 | |
| Regulation |
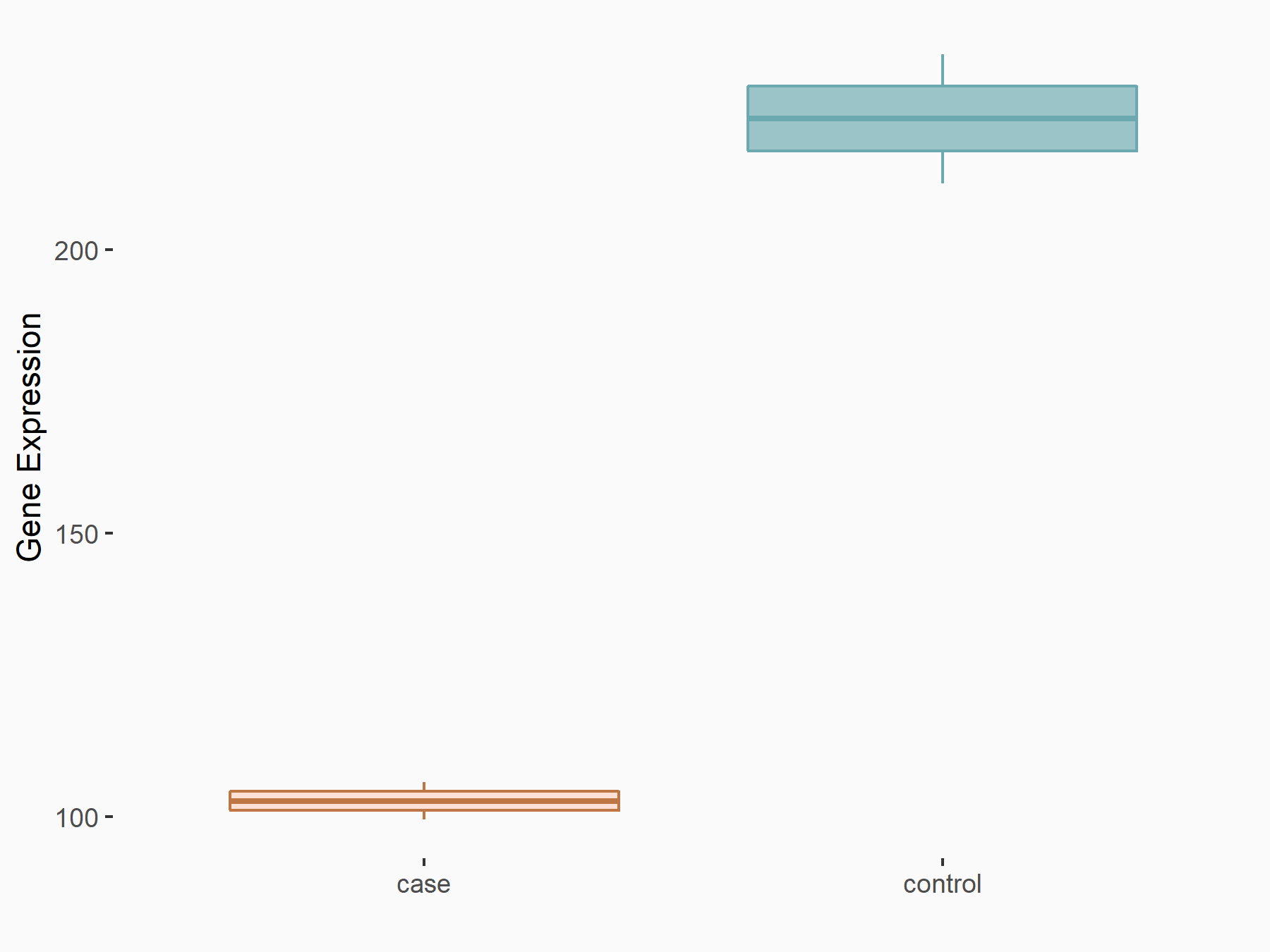 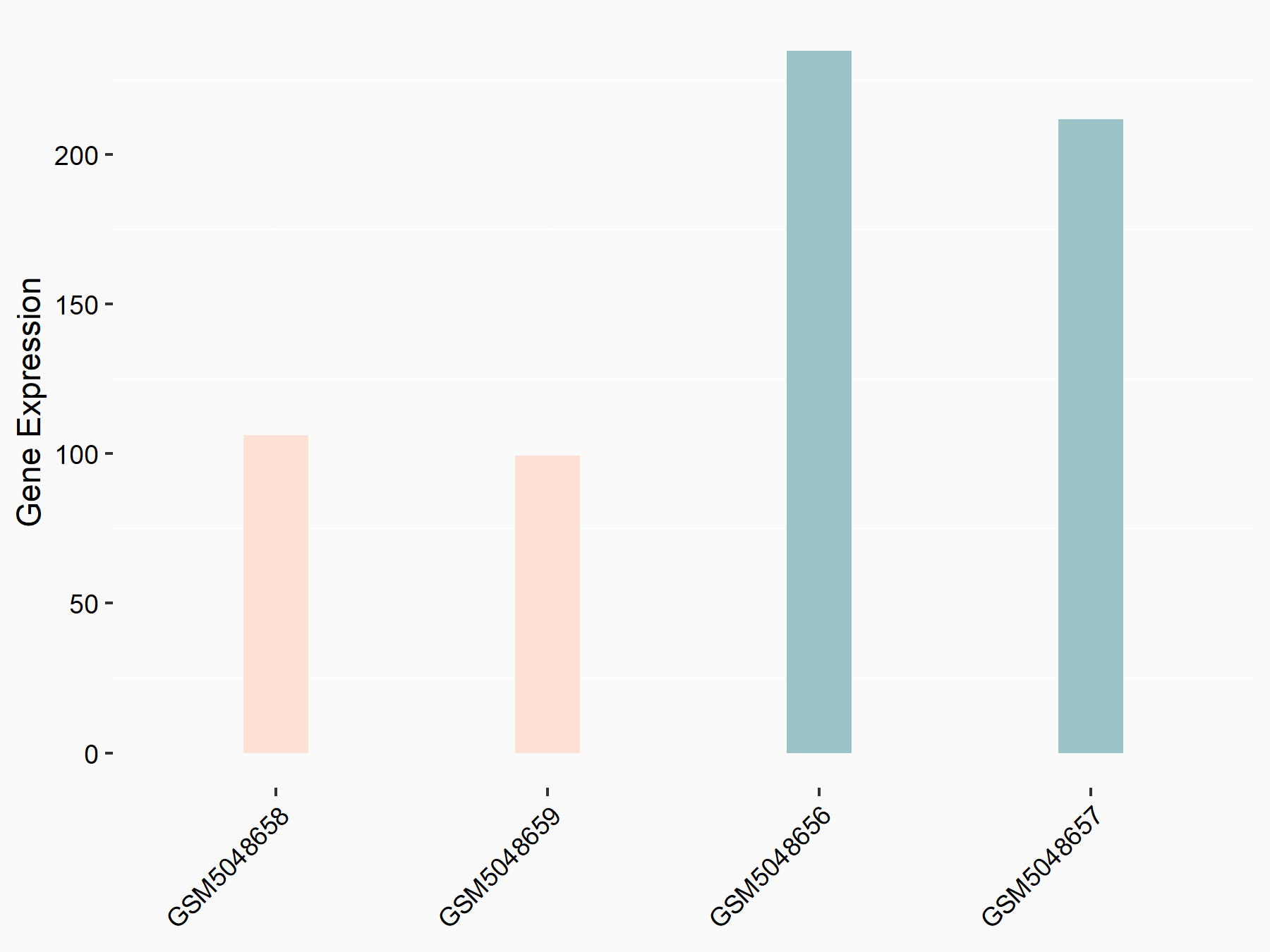 |
logFC: -1.12E+00 p-value: 2.46E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
| In-vitro Model | CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | RBM4 interacts with YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2) to degrade m6A modified Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) mRNA, thereby regulating glycolysis and M1 macrophage polarization. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | ||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
| In-vitro Model | RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
| In-vitro Model | CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
| In-vitro Model | CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
| In-vitro Model | CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Mettl3- or Mettl14-deficient tumors increased cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and elevated secretion of IFN-gamma, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 in tumor microenvironment in vivo. Mechanistically, Mettl3 or Mettl14 loss promoted IFN-gamma-Stat1-Irf1 signaling through stabilizing the Transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84 (Stat1) and Irf1 mRNA via Ythdf2. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | Immunity | |||
| In-vitro Model | CT26 | Mouse colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 |
| B16-GM-CSF (B16-GM-CSF cell line was a kind gift from Drs. Glenn Dranoff and Michael Dougan (Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center)) | ||||
| B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 | |
| In-vivo Model | 2 × 106 CT26 cells with knockout of Mettl3, Mettl14, Mettl3/Stat1, Mettl3/Irf1, Mettl14/Stat1, or Mettl14/Irf1 and control were suspended in 200 uL of PBS/Matrigel (Corning) (1:1) and then subcutaneously inoculated into flank of each mouse. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03281 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03290 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 5C (KDM5C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03346 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03569 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03614 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
References