m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00223)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
CXCR4
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF2 | ||
| Cell Line | Testis | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: YTHDF2 knockout mice testis
Control: Mice testis
|
GSE147574 | |
| Regulation |
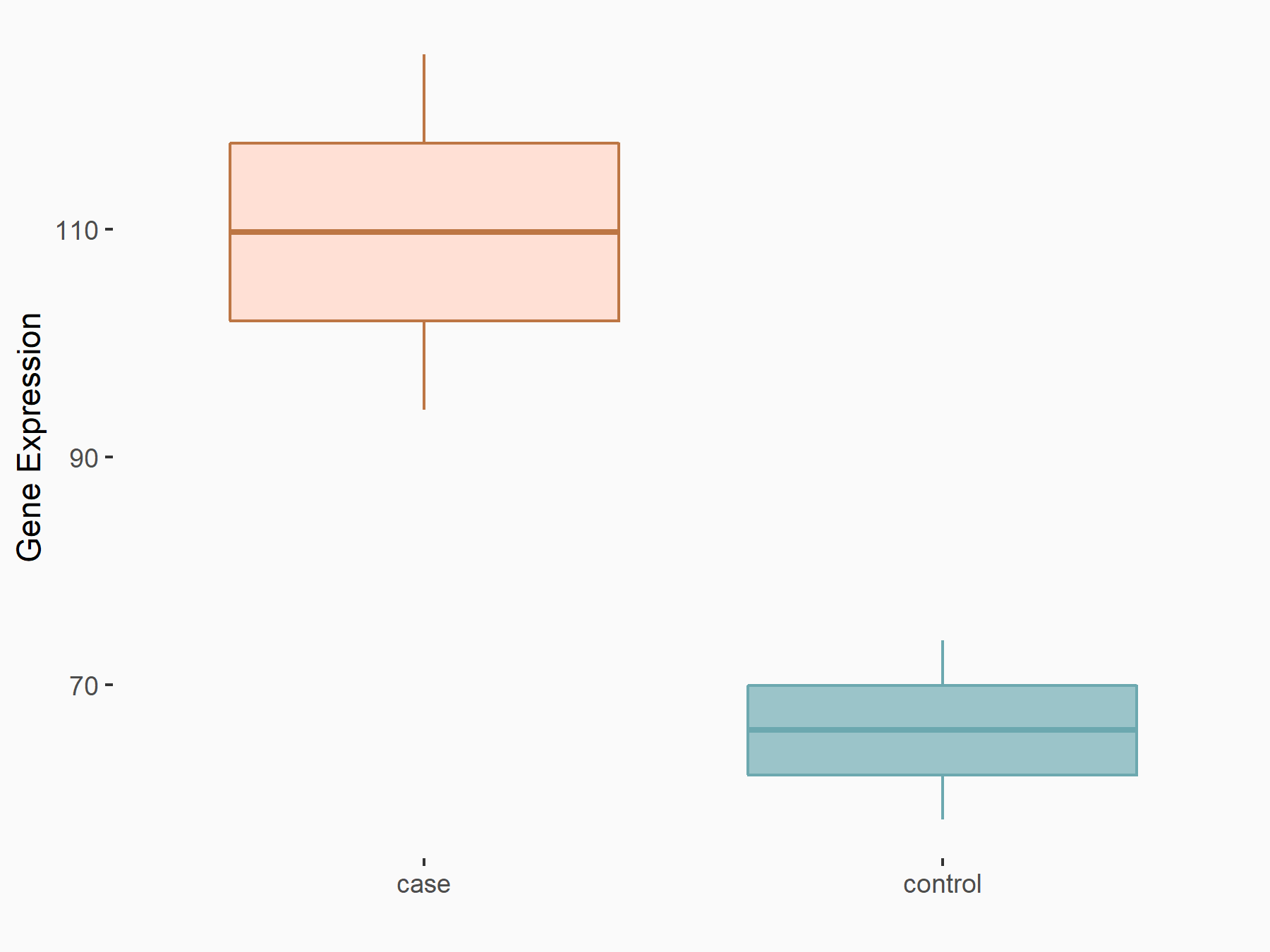  |
logFC: 7.39E-01 p-value: 4.60E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between CXCR4 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | Hela | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 2.20E+00 | GSE49339 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
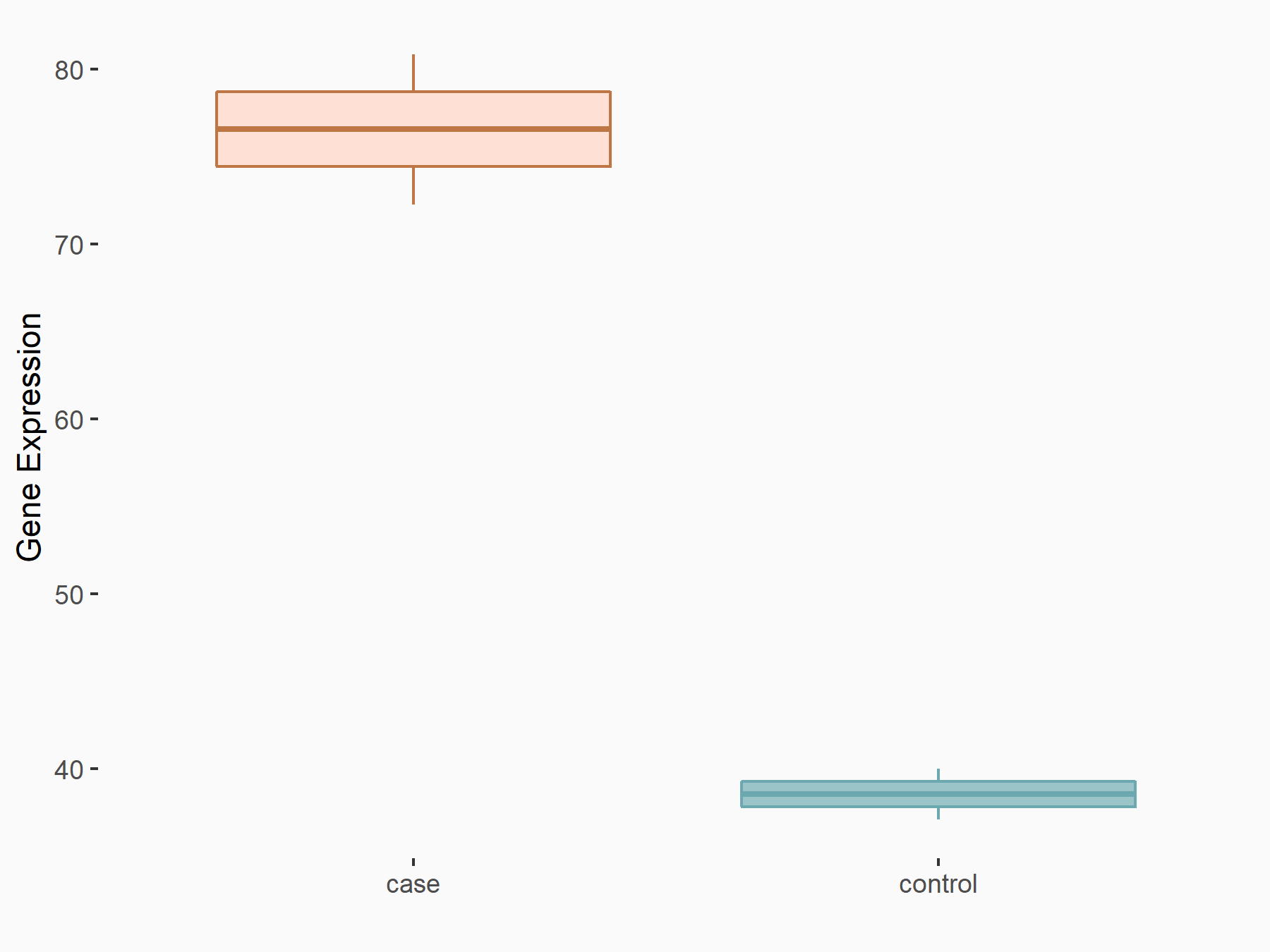  |
logFC: 9.72E-01 p-value: 3.86E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
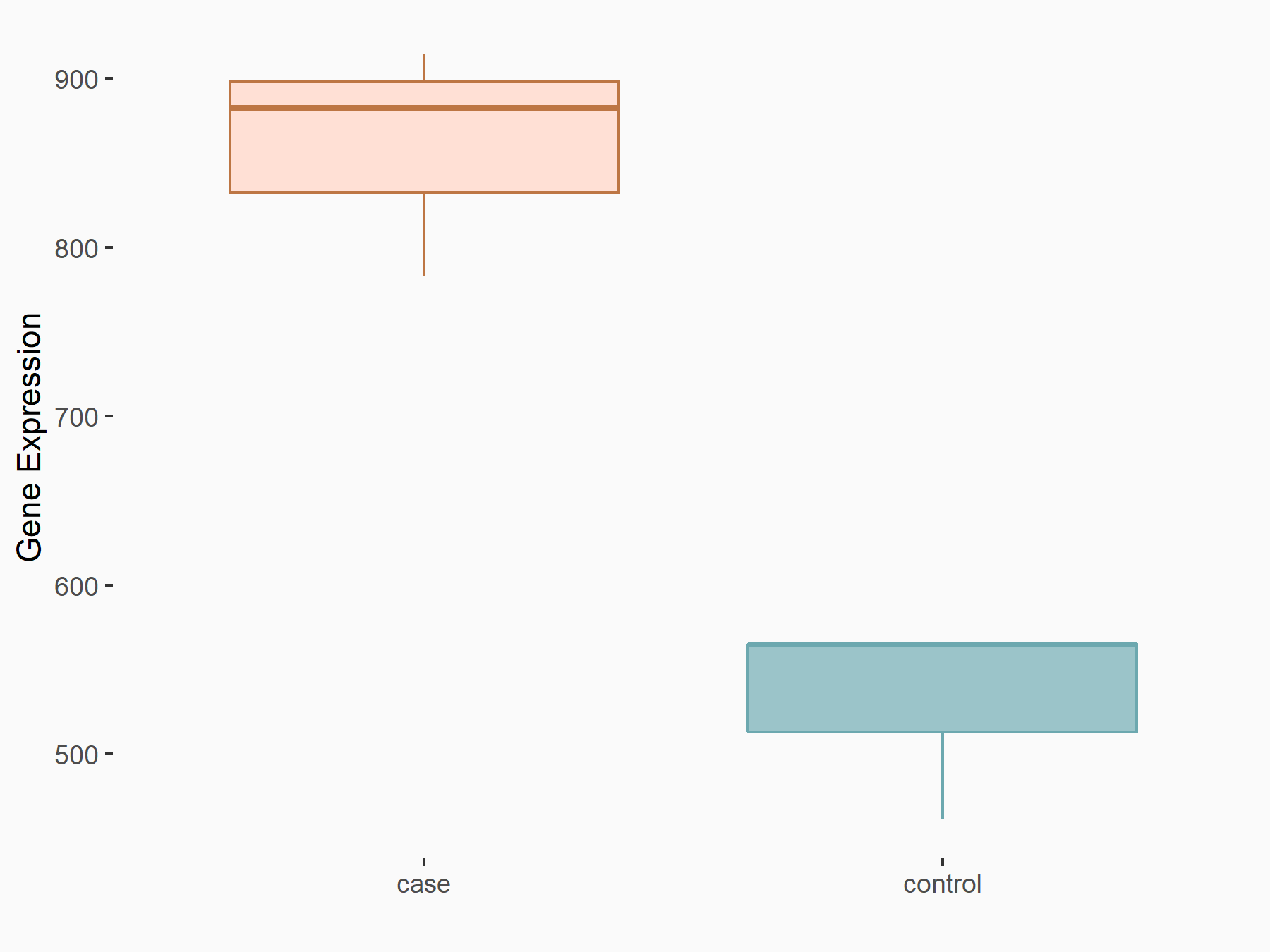  |
logFC: 7.03E-01 p-value: 9.23E-10 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | LNC942-METTL14-C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)/CYP1B1 signaling axis, which provides new targets and crosstalk m6A epigenetic modification mechanism for breast cancer prevention and treatment. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | LNC942-METTL14-C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)/CYP1B1 signaling axis, which provides new targets and crosstalk m6A epigenetic modification mechanism for breast cancer prevention and treatment. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody
[Investigative]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), and SOX10, leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
DNA modification
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02204 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02228 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02252 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05173 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa_circ_0125169 (Circ_METTL14(11)S) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05352 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 942 (LINC00942) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00223)
| In total 30 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047624 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114352-136114353:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTAATAAAAGTACATGTTAAACTTACTTAGTGTTATGTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494530 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047625 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114473-136114474:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATTTTGCTGTAGAAGATGGCACTTATAACCAAAGCCCAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494531 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047626 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114603-136114604:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | ACTGTAGAAAAGGGAACTGAACATTCCAGAGCGTGTAGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; kidney; hESC-HEK293T; HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494532 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047627 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114608-136114609:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GTAGGACTGTAGAAAAGGGAACTGAACATTCCAGAGCGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494533 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047628 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114623-136114624:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCTGTATGTCTCGTGGTAGGACTGTAGAAAAGGGAACTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494534 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047629 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114665-136114666:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TTGATGTGTGTCTAGGCAGGACCTGTGGCCAAGTTCTTAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494535 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047630 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114794-136114795:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | ACATTTTTCAGATATAAAAGACTGACCAATATTGTACAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; HeLa; GM12878; CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494536 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047631 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114831-136114832:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTTTTATACGATAAATAACTTTTTTTTAAGTTACACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494537 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047632 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114853-136114854:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGCTAACACAGATGTAAAAGACTTTTTTTTATACGATAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; Huh7; Jurkat; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494538 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047633 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114868-136114869:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCAAGTTTTCACTCCAGCTAACACAGATGTAAAAGACTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494539 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047634 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114919-136114920:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCAAAGGAAAGCGAGGTGGACATTCATCTGTTTCCACTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; hNPCs; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; Jurkat; TIME; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494540 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047635 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136114996-136114997:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCTTGGAGCCAAATTTAAAACCTCTGCCCAGCACGCACTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; HepG2; hNPCs; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494541 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047636 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115034-136115035:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTCTTCCACTGTTGTCTGAACCCCATCCTCTATGCTTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; HepG2; hNPCs; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494542 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047637 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115094-136115095:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCAAGGGTGTGAGTTTGAGAACACTGTGCACAAGTGGATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; Huh7; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494543 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047638 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115160-136115161:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGCCTGTTGGCTGCCTTACTACATTGGGATCAGCATCGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494544 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047639 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115209-136115210:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGAAGCGCAAGGCCCTCAAGACCACAGTCATCCTCATCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494545 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047640 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115246-136115247:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATTATCATCTCCAAGCTGTCACACTCCAAGGGCCACCAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494546 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047641 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115349-136115350:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGACCGCTTCTACCCCAATGACTTGTGGGTGGTTGTGTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494547 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047642 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115529-136115530:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGCCTTCATCAGTCTGGACCGCTACCTGGCCATCGTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; H1A; H1B; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494548 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047643 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115610-136115611:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCAAACTGGTACTTTGGGAACTTCCTATGCAAGGCAGTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494549 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047644 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115625-136115626:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCAGTTGATGCCGTGGCAAACTGGTACTTTGGGAACTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494550 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047645 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115706-136115707:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAACTGAGAAGCATGACGGACAAGTACAGGCTGCACCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; H1B; H1A; hNPCs; hESCs; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494551 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047646 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115723-136115724:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTCATGGGTTACCAGAAGAAACTGAGAAGCATGACGGACAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000466288.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494552 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047647 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115849-136115850:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GACTATGACTCCATGAAGGAACCCTGTTTCCGTGAAGAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; hNPCs; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494553 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047648 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115868-136115869:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGAGGAAATGGGCTCAGGGGACTATGACTCCATGAAGGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; hNPCs; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000409817.1; ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494554 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047649 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136115892-136115893:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GATATACACTTCAGATAACTACACCGAGGAAATGGGCTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3; ENST00000409817.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494555 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047650 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136117687-136117688:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGCGCTGCCTCGGGACTCAGACCACCGGTCTCTTCCTTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; GM12878; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494556 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047651 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136117693-136117694:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCGTGCGCGCTGCCTCGGGACTCAGACCACCGGTCTCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; GM12878; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466288.1; ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494557 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047652 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136118072-136118073:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTAGCCACCGCATCTGGAGAACCAGCGGTTACCATGGAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; GM12878; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494558 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE047653 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr2:136118153-136118154:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGTCCGGCCGCGGCCAGAAACTTCAGTTTGTTGGCTGCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; GM12878; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000241393.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_494559 | ||
References