m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00683)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
Nfkbia
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
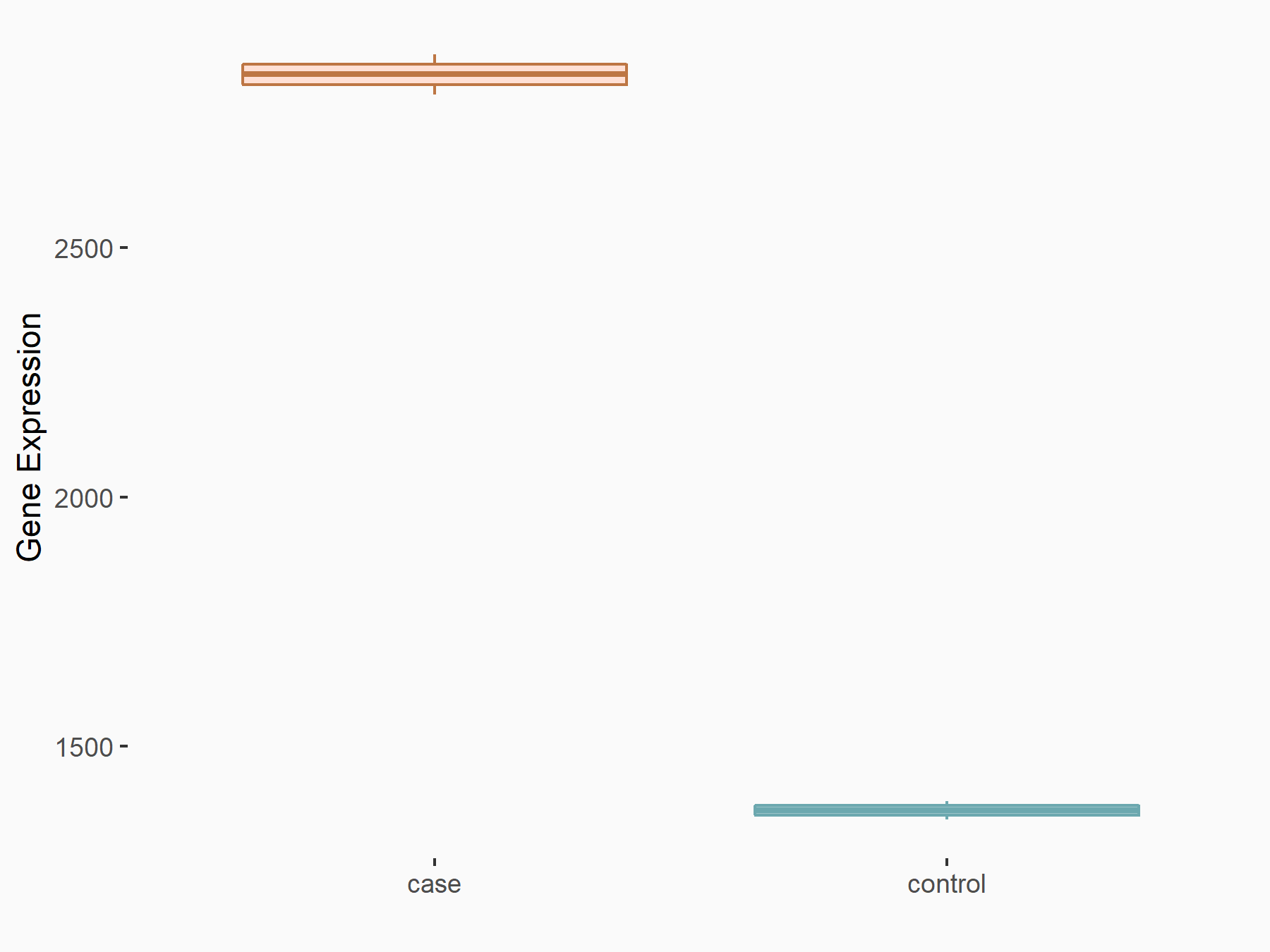 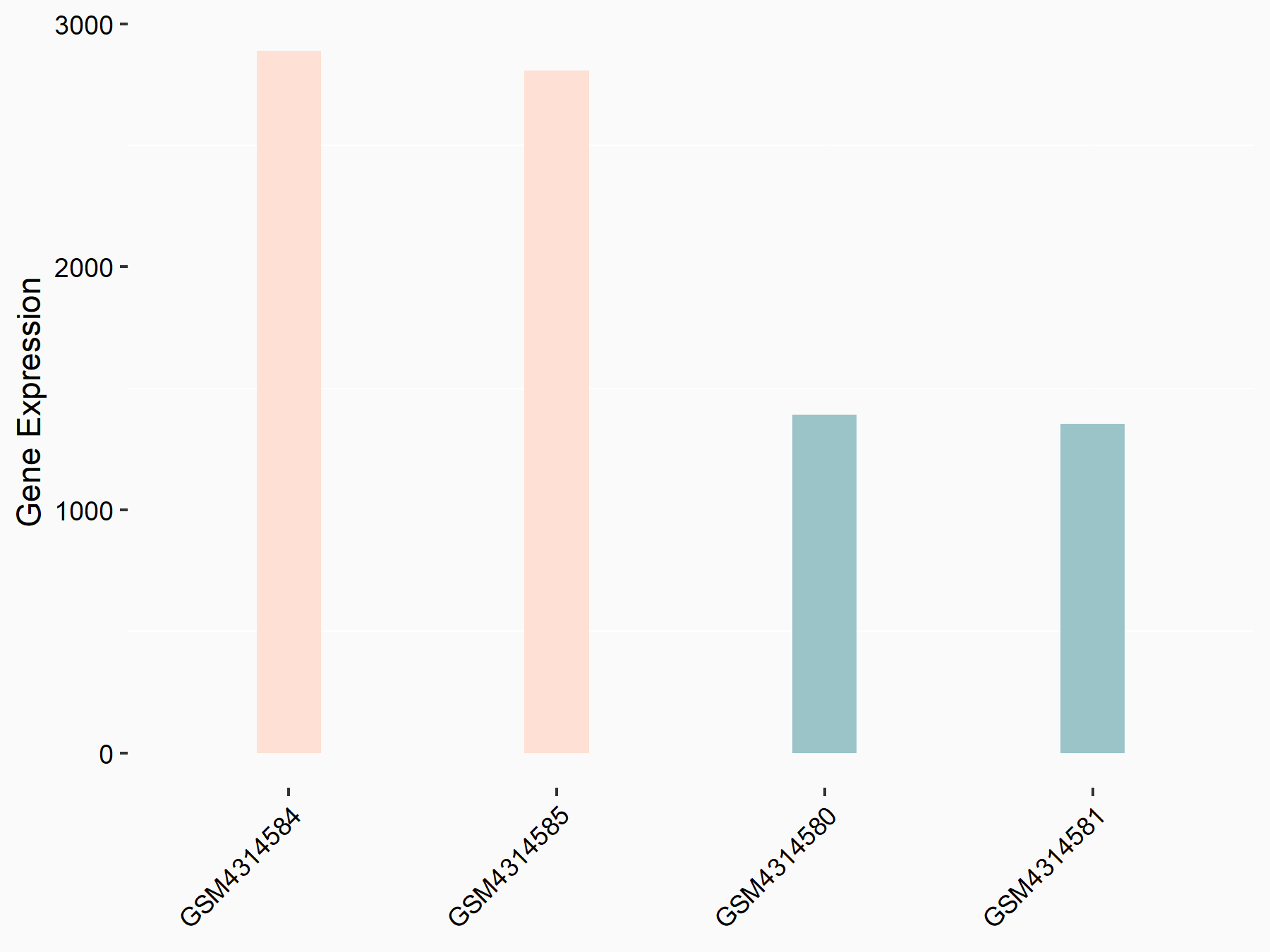 |
logFC: 1.05E+00 p-value: 4.32E-28 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Colonic mucosal barrier dysfunction is one of the major causes of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mettl14 restricted colonic epithelial cell death by regulating the stability of NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (Nfkbia) mRNA and modulating the NF-Kappa-B pathway,suggesting that m6A modification could be a potential therapeutic target for IBD. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Inflammatory bowel disease | ICD-11: DD7Z | ||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14f/f mice were generated as previously described with CRISPR-Cas9 technology by insertion of two loxp sites into Mettl14 genome loci. Mettl14f/f mice without Villin-Cre were used as WT controls (Mettl14 WT) for Mettl14 KO mice. Mettl14f/f mice were crossed with Lgr5-eGFP-IRES-creERT2 (Lgr5-Cre) mice to generate Mettl14 depletion in Lgr5+ stem cells. | |||
Inflammatory bowel disease [ICD-11: DD7Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Colonic mucosal barrier dysfunction is one of the major causes of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mettl14 restricted colonic epithelial cell death by regulating the stability of NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (Nfkbia) mRNA and modulating the NF-Kappa-B pathway,suggesting that m6A modification could be a potential therapeutic target for IBD. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Inflammatory bowel disease [ICD-11: DD7Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14f/f mice were generated as previously described with CRISPR-Cas9 technology by insertion of two loxp sites into Mettl14 genome loci. Mettl14f/f mice without Villin-Cre were used as WT controls (Mettl14 WT) for Mettl14 KO mice. Mettl14f/f mice were crossed with Lgr5-eGFP-IRES-creERT2 (Lgr5-Cre) mice to generate Mettl14 depletion in Lgr5+ stem cells. | |||
References