m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00054)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
NFKB1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | LX2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 LX2 cells
Control: shLuc LX2 cells
|
GSE207909 | |
| Regulation |
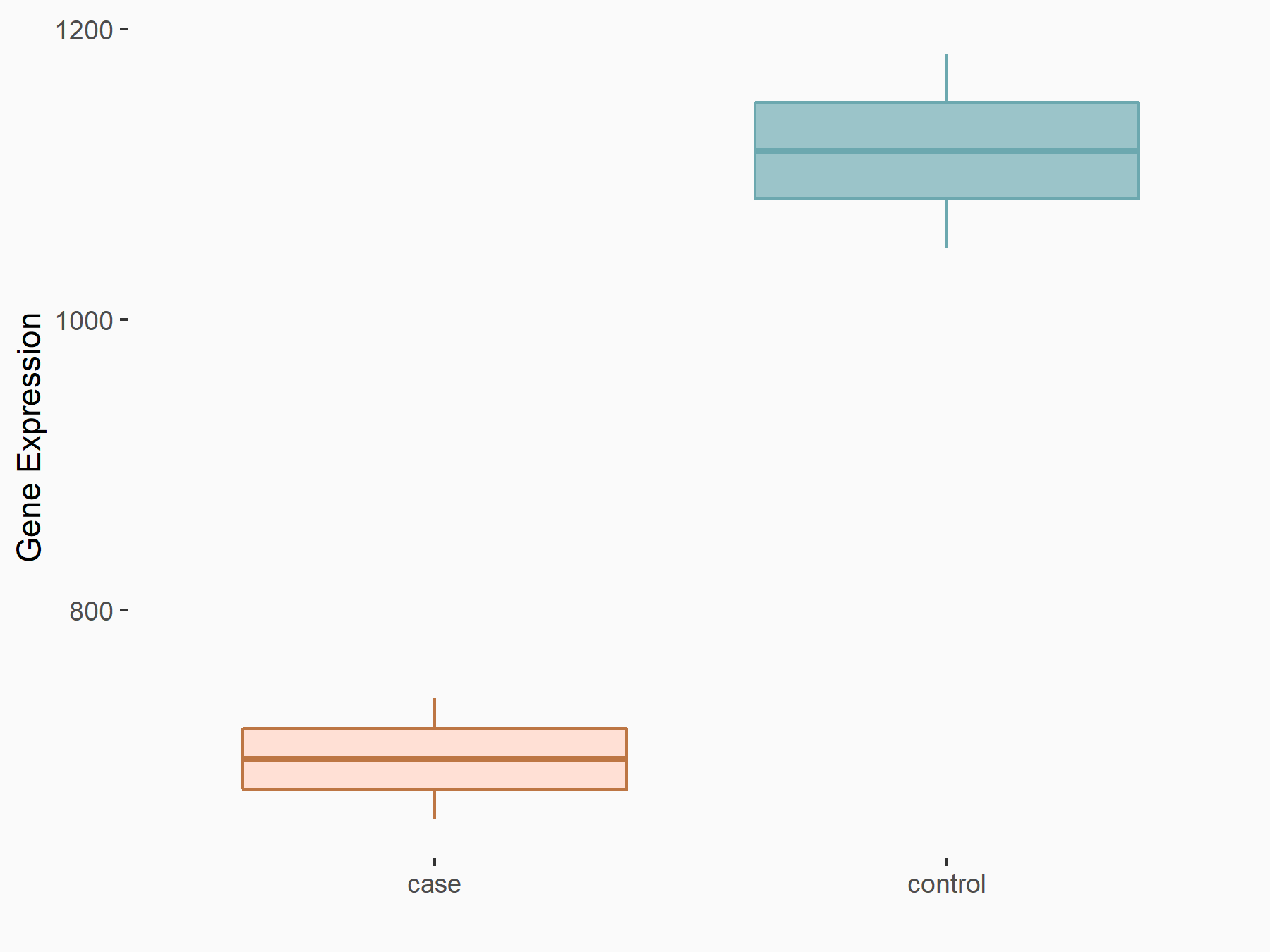  |
logFC: -6.78E-01 p-value: 1.44E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 4 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 accelerated UBXN1 mRNA degradation via METTL3-mediated m6A, which, in turn, promoted Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) activation. YTHDF2 promotes the malignant progression of gliomas and revealed important insight into the upstream regulatory mechanism of NF-Kappa-B activation via UBXN1 with a primary focus on m6A modification. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | |||
| N33 (The GBM patient-derived cell line) | ||||
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| H4 | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1239 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five-week-old female BALB/c nude mice (Charles Rivers, Beijing, China) were selected for the experiments. U87 cells (5 × 105) transfected with an empty vector, YTHDF2 overexpression, or METTL3 overexpression vectors were suspended in PBS and injected into the right frontal node of nude mice. The inoculation position was 2 mm lateral and 2 mm posterior to the anterior fontanel. Tumor size was estimated from luciferase volume measurements and MRI. The mice were sacrificed when they exhibited disturbed activity or convulsion. The brain was then harvested and embedded in paraffin. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | The contribution of METTL3-mediated m6A modif ication of Ddit4 mRNA to macrophage metabolic reprogramming in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity. In METTL3-deficient macrophages, there is a significant downregulation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) pathway activity in response to cellular stress and cytokine stimulation, which can be restored by knockdown of DDIT4. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| In-vivo Model | The 8-10 weeks old mice were fed either a high fat diet or HF-CDAA , ad lib for 6-12 weeks. Chow diet was used as control for HFD.The mouse liver was perfused with PBS through portal vein, and liver tissue was cut into small pieces by a scissor. The single cell was made using syringe plunger to mull the tissue, and passed through a 40 uM cell strainer. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | The contribution of Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1)-mediated m6A modification of Ddit4 mRNA to macrophage metabolic reprogramming in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity. In METTL3-deficient macrophages, there is a significant downregulation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) pathway activity in response to cellular stress and cytokine stimulation, which can be restored by knockdown of DDIT4. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity | ICD-11: 5B81 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| In-vivo Model | The 8-10 weeks old mice were fed either a high fat diet or HF-CDAA , ad lib for 6-12 weeks. Chow diet was used as control for HFD.The mouse liver was perfused with PBS through portal vein, and liver tissue was cut into small pieces by a scissor. The single cell was made using syringe plunger to mull the tissue, and passed through a 40 uM cell strainer. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) acts as transcription factor to transactivate METTL3/METTL14 genes upon LPS challenge, leading to global RNA m6A hypermethylation. m6A modification in TGF-beta1 upregulation, which helps to shed light on the molecular mechanism of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH) progression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis | ICD-11: DB92.1 | ||
| In-vitro Model | KCs (Mouse Kupffer cells (BeNa Culture Collection, Beijing, China; BNCC340733)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | At 8 weeks of age, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were challenged with LPS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; L2880, single intraperitoneal injection at 5 mg/kg, n = 3) or CCl4 (10%, Macklin, Shanghai, China; C805332, intraperitoneal injection at 5 mL/kg diluted with corn oil, twice per week for 4 weeks, n = 3). The corresponding control groups were treated with single intraperitoneal injection of saline (n = 3) or intraperitoneal injection of corn oil twice per week for 4 weeks (n = 3), respectively. Two hours after LPS injection and 4 weeks after CCl4 treatment, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were etherized and the primary KCs were isolated from liver according to a previously published method. | |||
Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by WTAP | ||
| Cell Line | mice hepatocyte | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: Wtap Hknockout mice hepatocyte
Control: Wtap flox/flox mice hepatocyte
|
GSE168850 | |
| Regulation |
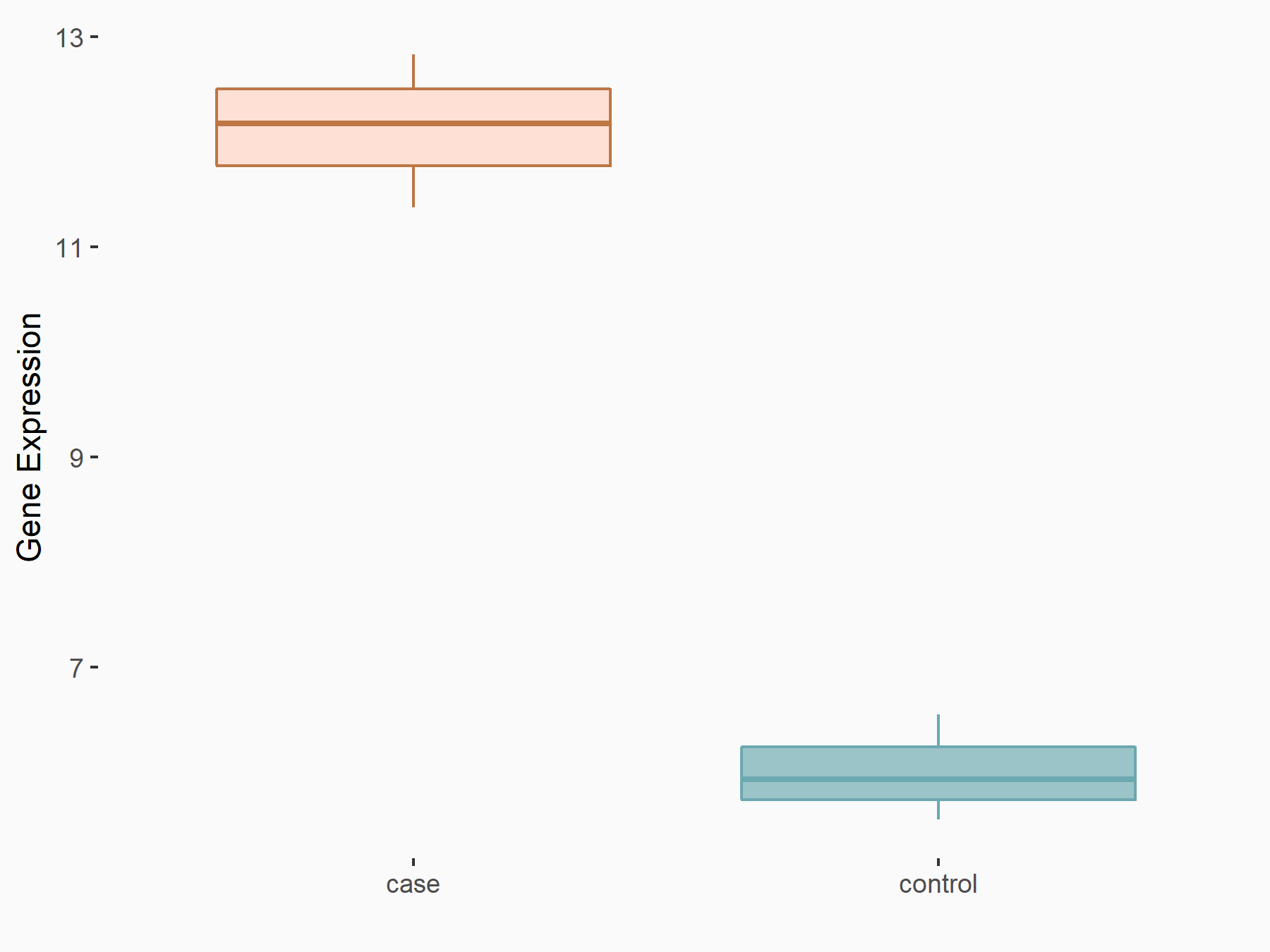  |
logFC: 9.05E-01 p-value: 1.07E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | WTAP could methylate 3'-UTR of CAV-1 and downregulate CAV-1 expression to activate Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) signaling pathway in EC, which promoted EC progression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometrial cancer | ICD-11: 2C76 | ||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | Ishikawa | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| HEC-1-A | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0293 | |
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 gene knockout significantly reduced the inflammatory response of macrophages and the development of atherosclerotic plaques, Mettl14 plays a vital role in macrophage inflammation in atherosclerosis via the Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1)/IL-6 signaling pathway. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis | ICD-11: BD40.Z | ||
| Pathway Response | IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | ||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14 heterozygous mice (Mettl14-/+) were established from C57/BL6 mice by Cyagen Biosciences, Inc. (Suzhou, Jiangsu, China), using CRISPR/Cas9-based targeting and homology-directed repair. C57/BL6 and APOE-/- mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). Mettl14-/+APOE-/- mice were generated by breeding Mettl14-/+ mice with APOE-/- mice. Eight- to 10-week-old male APOE-/- (WT) mice and Mettl14-/+APOE-/- (KO) mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (D12108C, Opensource diets) for 12 weeks. Then, the mice were euthanized for further analysis. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) acts as transcription factor to transactivate METTL3/METTL14 genes upon LPS challenge, leading to global RNA m6A hypermethylation. m6A modification in TGF-beta1 upregulation, which helps to shed light on the molecular mechanism of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH) progression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis | ICD-11: DB92.1 | ||
| In-vitro Model | KCs (Mouse Kupffer cells (BeNa Culture Collection, Beijing, China; BNCC340733)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | At 8 weeks of age, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were challenged with LPS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; L2880, single intraperitoneal injection at 5 mg/kg, n = 3) or CCl4 (10%, Macklin, Shanghai, China; C805332, intraperitoneal injection at 5 mL/kg diluted with corn oil, twice per week for 4 weeks, n = 3). The corresponding control groups were treated with single intraperitoneal injection of saline (n = 3) or intraperitoneal injection of corn oil twice per week for 4 weeks (n = 3), respectively. Two hours after LPS injection and 4 weeks after CCl4 treatment, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were etherized and the primary KCs were isolated from liver according to a previously published method. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 accelerated UBXN1 mRNA degradation via METTL3-mediated m6A, which, in turn, promoted Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) activation. YTHDF2 promotes the malignant progression of gliomas and revealed important insight into the upstream regulatory mechanism of NF-Kappa-B activation via UBXN1 with a primary focus on m6A modification. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | |||
| N33 (The GBM patient-derived cell line) | ||||
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| H4 | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1239 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five-week-old female BALB/c nude mice (Charles Rivers, Beijing, China) were selected for the experiments. U87 cells (5 × 105) transfected with an empty vector, YTHDF2 overexpression, or METTL3 overexpression vectors were suspended in PBS and injected into the right frontal node of nude mice. The inoculation position was 2 mm lateral and 2 mm posterior to the anterior fontanel. Tumor size was estimated from luciferase volume measurements and MRI. The mice were sacrificed when they exhibited disturbed activity or convulsion. The brain was then harvested and embedded in paraffin. | |||
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 accelerated UBXN1 mRNA degradation via METTL3-mediated m6A, which, in turn, promoted Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) activation. YTHDF2 promotes the malignant progression of gliomas and revealed important insight into the upstream regulatory mechanism of NF-Kappa-B activation via UBXN1 with a primary focus on m6A modification. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | |||
| N33 (The GBM patient-derived cell line) | ||||
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| H4 | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1239 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five-week-old female BALB/c nude mice (Charles Rivers, Beijing, China) were selected for the experiments. U87 cells (5 × 105) transfected with an empty vector, YTHDF2 overexpression, or METTL3 overexpression vectors were suspended in PBS and injected into the right frontal node of nude mice. The inoculation position was 2 mm lateral and 2 mm posterior to the anterior fontanel. Tumor size was estimated from luciferase volume measurements and MRI. The mice were sacrificed when they exhibited disturbed activity or convulsion. The brain was then harvested and embedded in paraffin. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 accelerated UBXN1 mRNA degradation via METTL3-mediated m6A, which, in turn, promoted Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) activation. YTHDF2 promotes the malignant progression of gliomas and revealed important insight into the upstream regulatory mechanism of NF-Kappa-B activation via UBXN1 with a primary focus on m6A modification. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | U87 (A primary glioblastoma cell line) | |||
| N33 (The GBM patient-derived cell line) | ||||
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| H4 | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1239 | |
| In-vivo Model | Five-week-old female BALB/c nude mice (Charles Rivers, Beijing, China) were selected for the experiments. U87 cells (5 × 105) transfected with an empty vector, YTHDF2 overexpression, or METTL3 overexpression vectors were suspended in PBS and injected into the right frontal node of nude mice. The inoculation position was 2 mm lateral and 2 mm posterior to the anterior fontanel. Tumor size was estimated from luciferase volume measurements and MRI. The mice were sacrificed when they exhibited disturbed activity or convulsion. The brain was then harvested and embedded in paraffin. | |||
Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | WTAP could methylate 3'-UTR of CAV-1 and downregulate CAV-1 expression to activate Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) signaling pathway in EC, which promoted EC progression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| Target Regulator | Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) | WRITER | ||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | Ishikawa | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| HEC-1-A | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0293 | |
Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | The contribution of METTL3-mediated m6A modif ication of Ddit4 mRNA to macrophage metabolic reprogramming in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity. In METTL3-deficient macrophages, there is a significant downregulation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) pathway activity in response to cellular stress and cytokine stimulation, which can be restored by knockdown of DDIT4. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| In-vivo Model | The 8-10 weeks old mice were fed either a high fat diet or HF-CDAA , ad lib for 6-12 weeks. Chow diet was used as control for HFD.The mouse liver was perfused with PBS through portal vein, and liver tissue was cut into small pieces by a scissor. The single cell was made using syringe plunger to mull the tissue, and passed through a 40 uM cell strainer. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | The contribution of Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1)-mediated m6A modification of Ddit4 mRNA to macrophage metabolic reprogramming in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity. In METTL3-deficient macrophages, there is a significant downregulation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) pathway activity in response to cellular stress and cytokine stimulation, which can be restored by knockdown of DDIT4. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| In-vivo Model | The 8-10 weeks old mice were fed either a high fat diet or HF-CDAA , ad lib for 6-12 weeks. Chow diet was used as control for HFD.The mouse liver was perfused with PBS through portal vein, and liver tissue was cut into small pieces by a scissor. The single cell was made using syringe plunger to mull the tissue, and passed through a 40 uM cell strainer. | |||
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [5] | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 gene knockout significantly reduced the inflammatory response of macrophages and the development of atherosclerotic plaques, Mettl14 plays a vital role in macrophage inflammation in atherosclerosis via the Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1)/IL-6 signaling pathway. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | ||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14 heterozygous mice (Mettl14-/+) were established from C57/BL6 mice by Cyagen Biosciences, Inc. (Suzhou, Jiangsu, China), using CRISPR/Cas9-based targeting and homology-directed repair. C57/BL6 and APOE-/- mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). Mettl14-/+APOE-/- mice were generated by breeding Mettl14-/+ mice with APOE-/- mice. Eight- to 10-week-old male APOE-/- (WT) mice and Mettl14-/+APOE-/- (KO) mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (D12108C, Opensource diets) for 12 weeks. Then, the mice were euthanized for further analysis. | |||
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) acts as transcription factor to transactivate METTL3/METTL14 genes upon LPS challenge, leading to global RNA m6A hypermethylation. m6A modification in TGF-beta1 upregulation, which helps to shed light on the molecular mechanism of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH) progression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [ICD-11: DB92.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | KCs (Mouse Kupffer cells (BeNa Culture Collection, Beijing, China; BNCC340733)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | At 8 weeks of age, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were challenged with LPS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; L2880, single intraperitoneal injection at 5 mg/kg, n = 3) or CCl4 (10%, Macklin, Shanghai, China; C805332, intraperitoneal injection at 5 mL/kg diluted with corn oil, twice per week for 4 weeks, n = 3). The corresponding control groups were treated with single intraperitoneal injection of saline (n = 3) or intraperitoneal injection of corn oil twice per week for 4 weeks (n = 3), respectively. Two hours after LPS injection and 4 weeks after CCl4 treatment, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were etherized and the primary KCs were isolated from liver according to a previously published method. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NF-Kappa-B/NFKB1) acts as transcription factor to transactivate METTL3/METTL14 genes upon LPS challenge, leading to global RNA m6A hypermethylation. m6A modification in TGF-beta1 upregulation, which helps to shed light on the molecular mechanism of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH) progression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [ICD-11: DB92.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | KCs (Mouse Kupffer cells (BeNa Culture Collection, Beijing, China; BNCC340733)) | |||
| In-vivo Model | At 8 weeks of age, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were challenged with LPS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; L2880, single intraperitoneal injection at 5 mg/kg, n = 3) or CCl4 (10%, Macklin, Shanghai, China; C805332, intraperitoneal injection at 5 mL/kg diluted with corn oil, twice per week for 4 weeks, n = 3). The corresponding control groups were treated with single intraperitoneal injection of saline (n = 3) or intraperitoneal injection of corn oil twice per week for 4 weeks (n = 3), respectively. Two hours after LPS injection and 4 weeks after CCl4 treatment, METTL14 cKO and WT mice were etherized and the primary KCs were isolated from liver according to a previously published method. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03321 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Probable JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2C (JMJD1C) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 monomethylation (H3K9me1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Brain cancer | |
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03541 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Brain cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00054)
| In total 8 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000499 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102512399-102512400:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCTCTGTCACACAGGCTGGAATGCAGTGGCGCAATCATGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000511926.5; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106022 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000500 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102512460-102512461:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGGTCCCAAGCTATCCTCCCACCTCAGCCACCCAAGTAGGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000511926.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106023 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000501 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102558719-102558720:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAGTGCAGTGGTGCGATCATAGCCCAATGCCACCTTGAACT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000502367.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106024 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000502 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102559817-102559818:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GTGTGGTGGCATGCACCTGTAGTCCTAGCTACCTAGGAGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000502367.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000507079.5; rmsk_1394736; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000510638.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106025 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000503 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102570474-102570475:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATGTTATTGATAGGGAATTTAGGTTGATTCCATGTCTTTGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000509165.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106026 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000504 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102570580-102570581:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTTTGATTGTGTACCCAACAGTGGGATTGCTGGGTCAAAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000510638.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106027 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000505 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102572555-102572556:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTTCCACAGTGGCTGAACTAATTTGCACTCCCACCAGCAGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106028 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE000506 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102572576-102572577:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTGCACTCCCACCAGCAGTATATAAGTGTACCCTCTTCTC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_106029 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 3 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003328 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102578982-102578983:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGCTTTTCTTCCGGATAGCACTGGCAGCTTCACAAGGCGCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_34268 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003329 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102597577-102597578:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGGCATGCCAATGCCCTTTTCGACTACGCGGTGACAGGAGA | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_34269 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003330 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102600943-102600944:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATTCTCAACTTGTGAGGGATCTACTAGAAGTCACATCTGGT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_34270 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 64 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066784 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102501345-102501346:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAAGTGAGAGAGTGAGCGAGACAGAAAGAGAGAGAAGTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; rmsk_1394649 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645711 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066785 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102501775-102501776:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGCCAGGAGGCCGAACGCGGACTCGCCACCCGGGTAAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000511926.5; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645712 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066786 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102501914-102501915:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGCGCTAACCGCTGGGCTAGACCGTGGGAGGAGGTTGACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000511926.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645713 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066787 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102525553-102525554:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCATATTTGGGAAGGCCTGAACAAGTAAGTGTCATAATCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000511926.5; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645714 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066788 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102533881-102533882:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CAAATATTAGAGCAACCTAAACAGGTAAGATTAAAGGGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000511926.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000651197.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645715 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066789 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102537904-102537905:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAAGGCCCATCCCATGGTGGACTACCTGGTGCCTCTAGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000502367.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645716 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066790 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102537930-102537931:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGCCTCTAGTGAAAAGAACAAGAAGTCTTACCCTCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000502367.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645717 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066791 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102557135-102557136:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGAGAAGAGAGAGTGAAGGAACTTGCACGCAGTGACTTCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000502367.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000509165.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645718 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066792 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102567031-102567032:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGGTTATTGTTCAGTTGGTCACAAATGGAAAAAATATCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000502367.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645719 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066793 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102567078-102567079:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCCCACAGCCTGGTGGGAAAACACTGTGAGGATGGGATCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000502367.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645720 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066794 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102567114-102567115:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATCTGCACTGTAACTGCTGGACCCAAGGACATGGTGGTCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645721 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066795 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102567122-102567123:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGTAACTGCTGGACCCAAGGACATGGTGGTCGGGTAAGTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000507079.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645722 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066796 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102576883-102576884:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTTCTCCAGCTTCGCAAACCTGGGTATACTTCATGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000509165.1; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645723 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066797 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102576903-102576904:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | ACCTGGGTATACTTCATGTGACAAAGAAAAAAGTATTTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645724 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066798 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102576924-102576925:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CAAAGAAAAAAGTATTTGAAACACTGGAAGCACGAATGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645725 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066799 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102576974-102576975:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATAAGGGGCTATAATCCTGGACTCTTGGTGCACCCTGACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645726 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066800 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102577024-102577025:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCAAGCAGAAGGTGGAGGGGACCGGCAGCTGGGAGGTAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000507079.5; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645727 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066801 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102577721-102577722:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTCCATCTTCTGATACCCAGACTCAAAACCTTCCCATCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645728 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066802 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102577728-102577729:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTCTGATACCCAGACTCAAAACCTTCCCATCCTCACTGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000513803.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645729 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066803 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102578921-102578922:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCCAAGCAGCTCTGCAGCAGACCAAGGAGATGGACCTCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000510638.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645730 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066804 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102578934-102578935:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCAGACCAAGGAGATGGACCTCAGCGTGGTGCGGCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645731 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066805 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102579007-102579008:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGCTTCACAAGGCGCCTGGAACCCGTGGTATCAGACGCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513803.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645732 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066806 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102580573-102580574:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTTGAAAATTGTAAGAATGGACAGGACAGCTGGATGTGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645733 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066807 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102580578-102580579:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAATTGTAAGAATGGACAGGACAGCTGGATGTGTGACTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000510638.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000651197.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645734 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066808 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102580624-102580625:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGAAATTTATCTTCTTTGTGACAAAGTTCAGAAAGGTAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645735 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066809 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102582868-102582869:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AATGTGATTGTTTGCAGATGACATCCAGATTCGATTTTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000508584.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645736 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066810 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102594950-102594951:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGATTACTTTCCATCCTGGAACTACTAAATCTAATGCTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645737 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066811 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102596139-102596140:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTGCATTTATCTTAGGAACCATGGACACTGAATCTAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645738 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066812 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102596146-102596147:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATTTATCTTAGGAACCATGGACACTGAATCTAAAAAGGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645739 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066813 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102596164-102596165:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGACACTGAATCTAAAAAGGACCCTGAAGGTTGTGACAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645740 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066814 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102596197-102596198:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGACAAAAGTGATGACAAAAACACTGTAAACCTCTTTGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645741 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066815 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102596206-102596207:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGATGACAAAAACACTGTAAACCTCTTTGGGAAAGTTATTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645742 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066816 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102596229-102596230:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCTTTGGGAAAGTTATTGAAACCACAGAGCAAGATCAGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645743 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066817 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102596304-102596305:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTCTAACGTATGCAACAGGAACAAAAGAAGAGAGTGCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000504044.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645744 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066818 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102600900-102600901:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGTTTTCATTCCAGTGTCTTACACTTAGCAATCATCCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645745 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066819 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102600955-102600956:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGAGGGATCTACTAGAAGTCACATCTGGTTTGATTTCTGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645746 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066820 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102600986-102600987:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GATTTCTGATGACATTATCAACATGAGAAATGATCTGTACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645747 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066821 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102606580-102606581:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGACCTGAGCCTTCTGGACCGCTTGGGTAACTCTGTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645748 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066822 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102606623-102606624:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CACCTAGCTGCCAAAGAAGGACATGATAAAGTTCTCAGTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645749 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066823 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102606655-102606656:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCTCAGTATCTTACTCAAGCACAAAAAGGCAGCACTACTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645750 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066824 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102610595-102610596:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGATCCCCTGGTGGAGAACTTTGAGCCTCTCTATGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645751 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066825 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102610666-102610667:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATGAAGGAGTTGTGCCTGGAACCACGCCTCTAGATATGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645752 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066826 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102612066-102612067:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTGACATATTAAATGGGAAACCATATGAGCCAGAGTTTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645753 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066827 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102612502-102612503:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACTAGAAATTCCTGATCCAGACAAAAACTGGGCTACTCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645754 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066828 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102612508-102612509:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AATTCCTGATCCAGACAAAAACTGGGCTACTCTGGCGCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645755 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066829 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102612545-102612546:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | CAGAAATTAGGTCTGGGGATACTTAATAATGCCTTCCGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645756 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066830 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102612585-102612586:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGAGTCCTGCTCCTTCCAAAACACTTATGGACAACTATGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645757 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066831 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102612595-102612596:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCCTTCCAAAACACTTATGGACAACTATGAGGTAACACCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645758 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066832 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102613476-102613477:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGCCCTGAGACAAATGGGCTACACCGAAGCAATTGAAGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645759 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066833 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102613523-102613524:+ | [14] | |
| Sequence | CAGCCTCCAGCCCAGTGAAGACCACCTCTCAGGCCCACTCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645760 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066834 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102613565-102613566:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTCTCTCGCCTGCCTCCACAAGGCAGCAAATAGGTAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645761 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066835 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616445-102616446:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | CCCCTCAGACGAGCTCCGAGACAGTGACAGTGTCTGCGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645762 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066836 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616463-102616464:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | AGACAGTGACAGTGTCTGCGACAGCGGCGTGGAGACATCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645763 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066837 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616477-102616478:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCGACAGCGGCGTGGAGACATCCTTCCGCAAACTCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645764 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066838 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616491-102616492:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | GTGGAGACATCCTTCCGCAAACTCAGCTTTACCGAGTCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645765 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066839 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616534-102616535:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | CCAGTGGTGCCTCACTGCTAACTCTCAACAAAATGCCCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645766 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066840 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616541-102616542:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTCACTGCTAACTCTCAACAAAATGCCCCATGATTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; CD8T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645767 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066841 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616572-102616573:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | CATGATTATGGGCAGGAAGGACCTCTAGAAGGCAAAATTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; CD8T; Huh7; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645768 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066842 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616601-102616602:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGGCAAAATTTAGCCTGCTGACAATTTCCCACACCGTGTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645769 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066843 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616611-102616612:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TAGCCTGCTGACAATTTCCCACACCGTGTAAACCAAAGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645770 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066844 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616622-102616623:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CAATTTCCCACACCGTGTAAACCAAAGCCCTAAAATTCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; MT4; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000651197.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645771 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066845 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616653-102616654:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AAAATTCCACTGCGTTGTCCACAAGACAGAAGCTGAAGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652619.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645772 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066846 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616658-102616659:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | TCCACTGCGTTGTCCACAAGACAGAAGCTGAAGTGCATCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; MT4; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000600343.5; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645773 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE066847 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr4:102616729-102616730:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | CATTCTCGATTTAACTCGAGACCTTTTCAACTTGGCTTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652619.1; ENST00000651197.1; ENST00000394820.8; ENST00000226574.9; ENST00000652569.1; ENST00000505458.5; ENST00000600343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_645774 | ||
References