m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00351)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
NOTCH1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
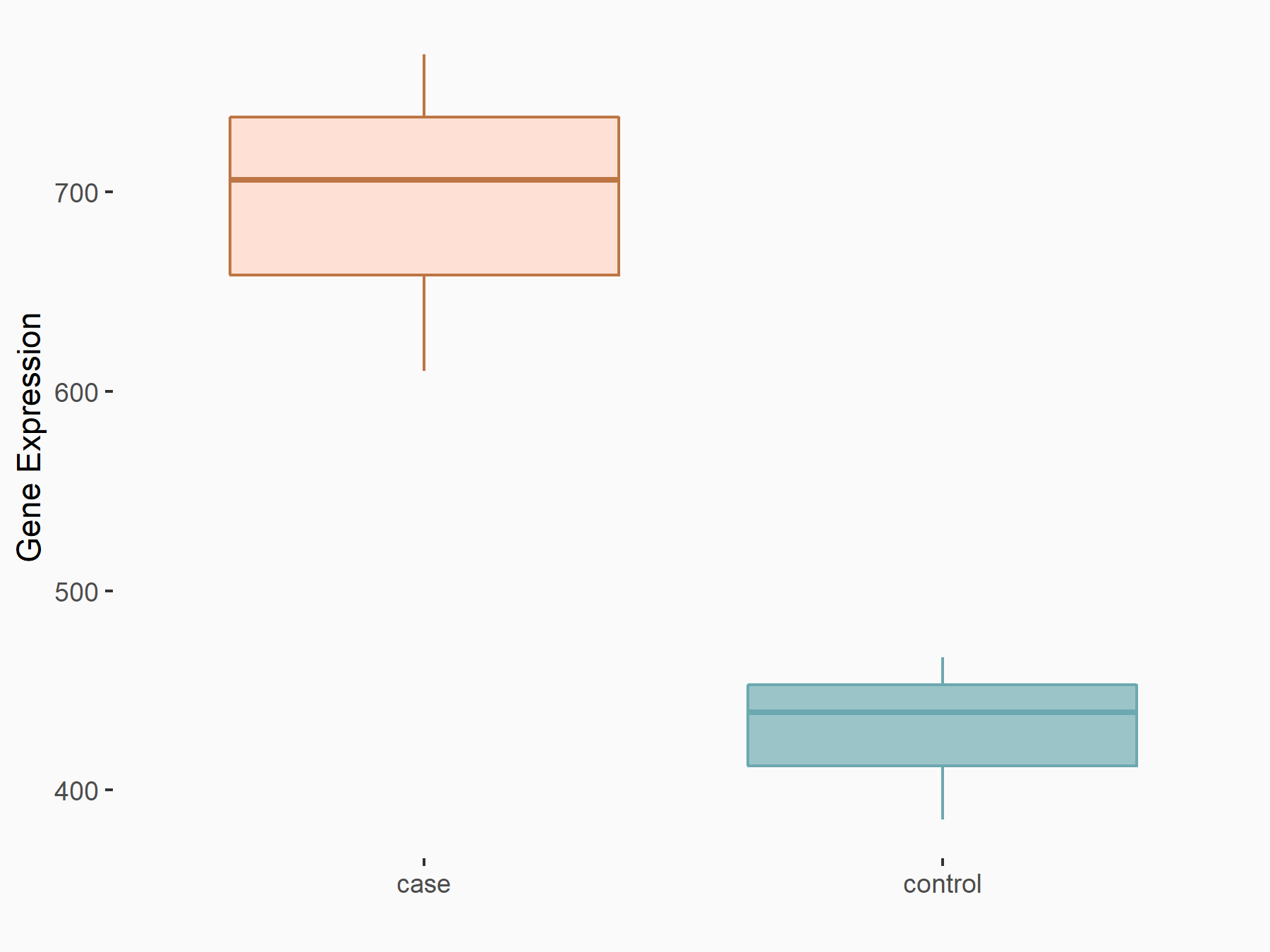  |
logFC: 6.94E-01 p-value: 5.11E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In bladder cancer, the changes in m6A methylation level mainly appeared at 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) of MALAT1 and Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) transcripts, and at 3' UTR of CSNK2A2 and ITGA6 transcripts, responding to the overexpression of FTO. SFPQ could influence the FTO-mediated m6A RNA demethylation, eventually affecting the gene expression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HT-1197 | Recurrent bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1291 |
| HT-1376 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1292 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/cnu/nu mice (4-5 weeks old) were used for the xenograft experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 6 for each group) and injected with 5 × 106 HT-1197 cells in control group or FTO plasmid group, respectively. | |||
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
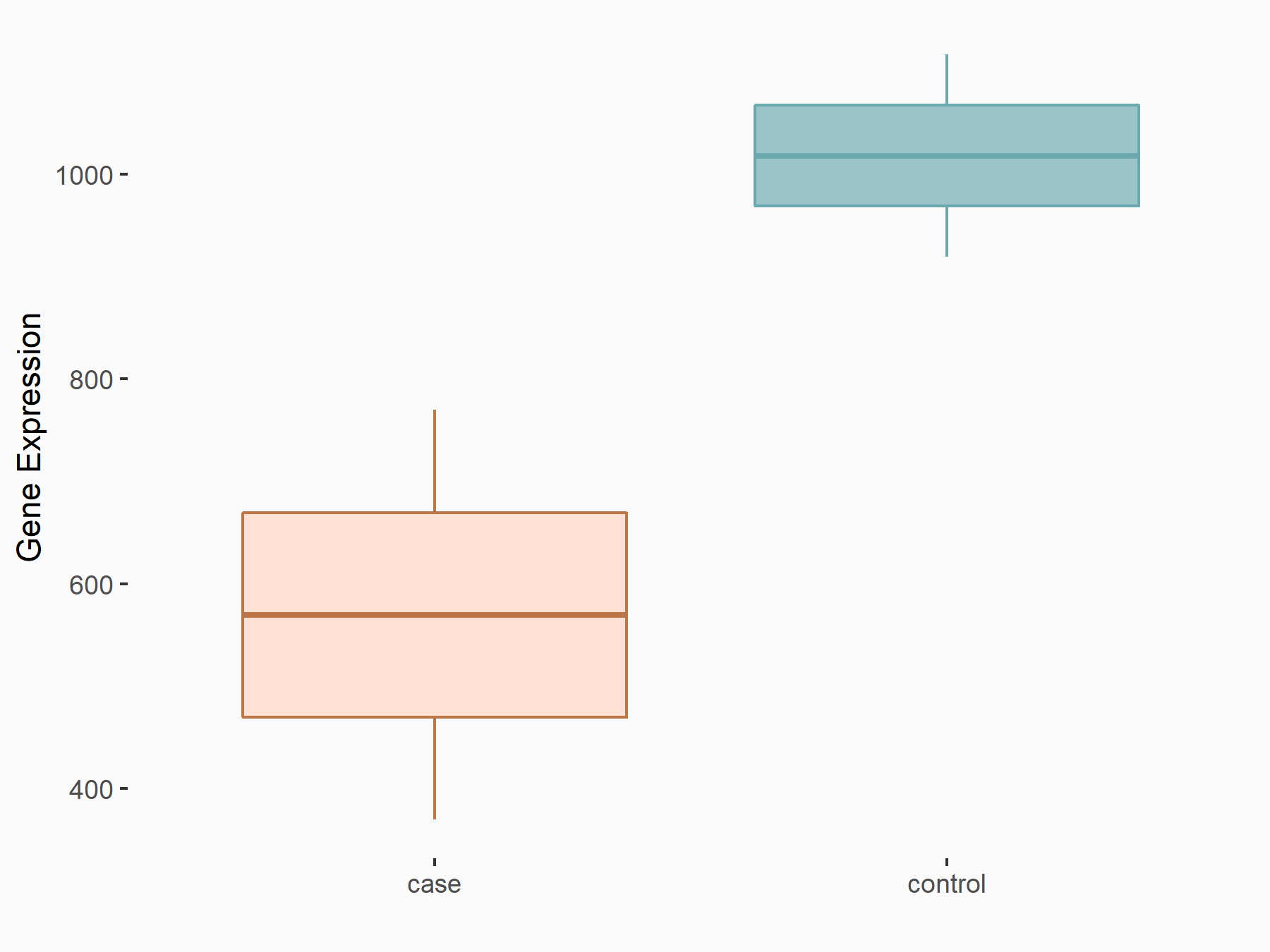  |
logFC: -8.37E-01 p-value: 6.43E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 and m6A modification participate in the RNA stability of Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) mRNA. Notch1 plays an essential role in bladder tumorigenesis and bladder TIC self-renewal. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Self-renewal | ||||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | Primary bladder cancer cells (Obtained from bladder cancer patients) | |||
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | LX2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 LX2 cells
Control: shLuc LX2 cells
|
GSE207909 | |
| Regulation |
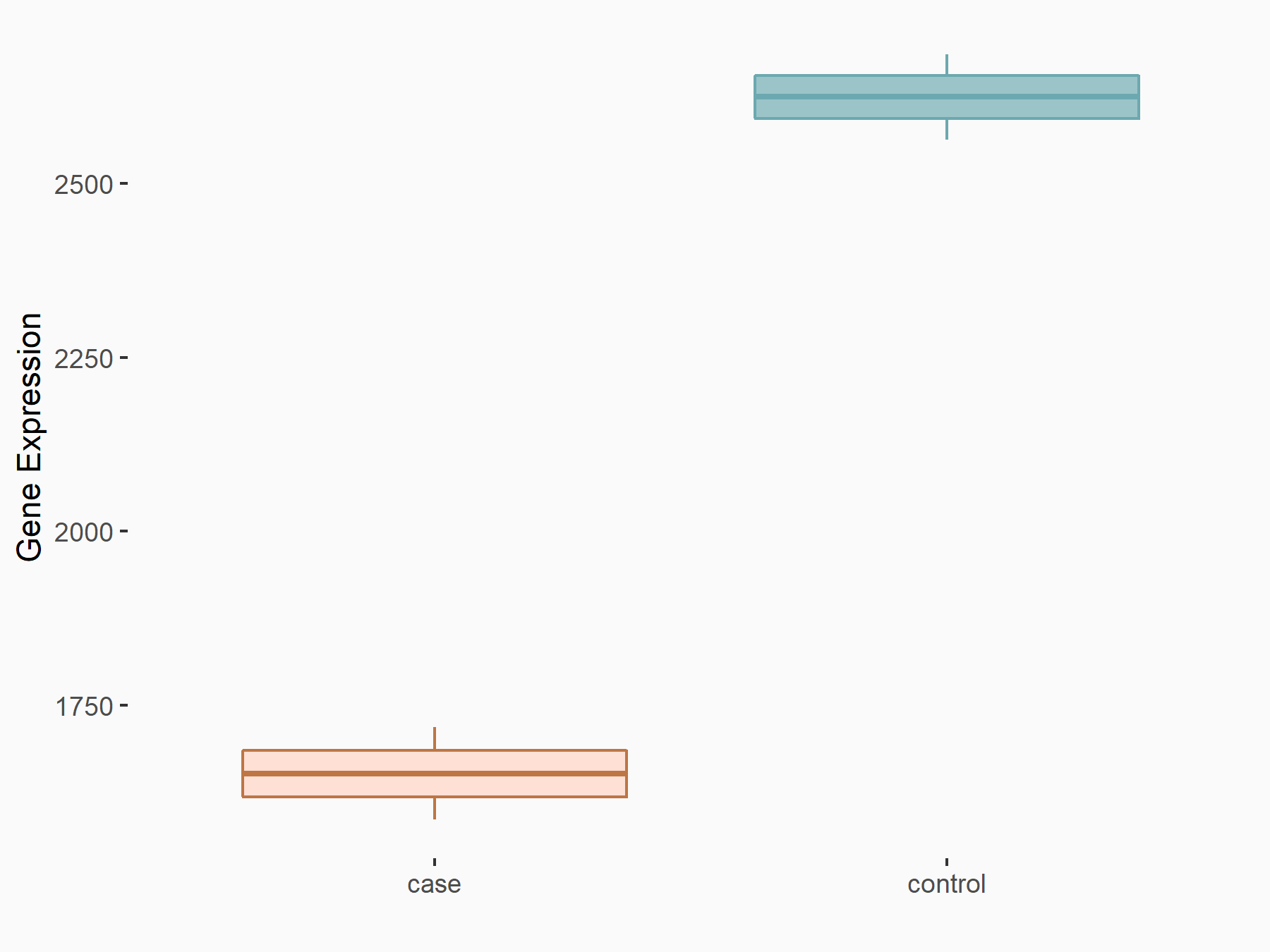  |
logFC: -6.68E-01 p-value: 1.32E-12 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3-catalyzed m6A modification promotes Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) expression and the activation of the Notch signaling pathway. Forced activation of Notch signaling pathway successfully rescues the growth, migration, and invasion capacities of METTL3-depleted ESCC cells. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B70.1 | ||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell migration | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In-vitro Model | TE-9 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1767 |
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| In-vivo Model | For induction of ESCC, 4-week-old mice were treated with drinking water containing 50 ug/mL 4NQO (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) for 16 weeks and then given normal drinking water for another 4-5 weeks. Cre was activated by the intraperitoneal injection of tamoxifen (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) at a dose of 9 mg per 40 g body weight every other day for a total of three injections. For tumor measurement, mice were sacrificed, and the esophagus was dissected immediately. The surface areas of tumors were measured as described previously. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF2 | ||
| Cell Line | Testis | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: YTHDF2 knockout mice testis
Control: Mice testis
|
GSE147574 | |
| Regulation |
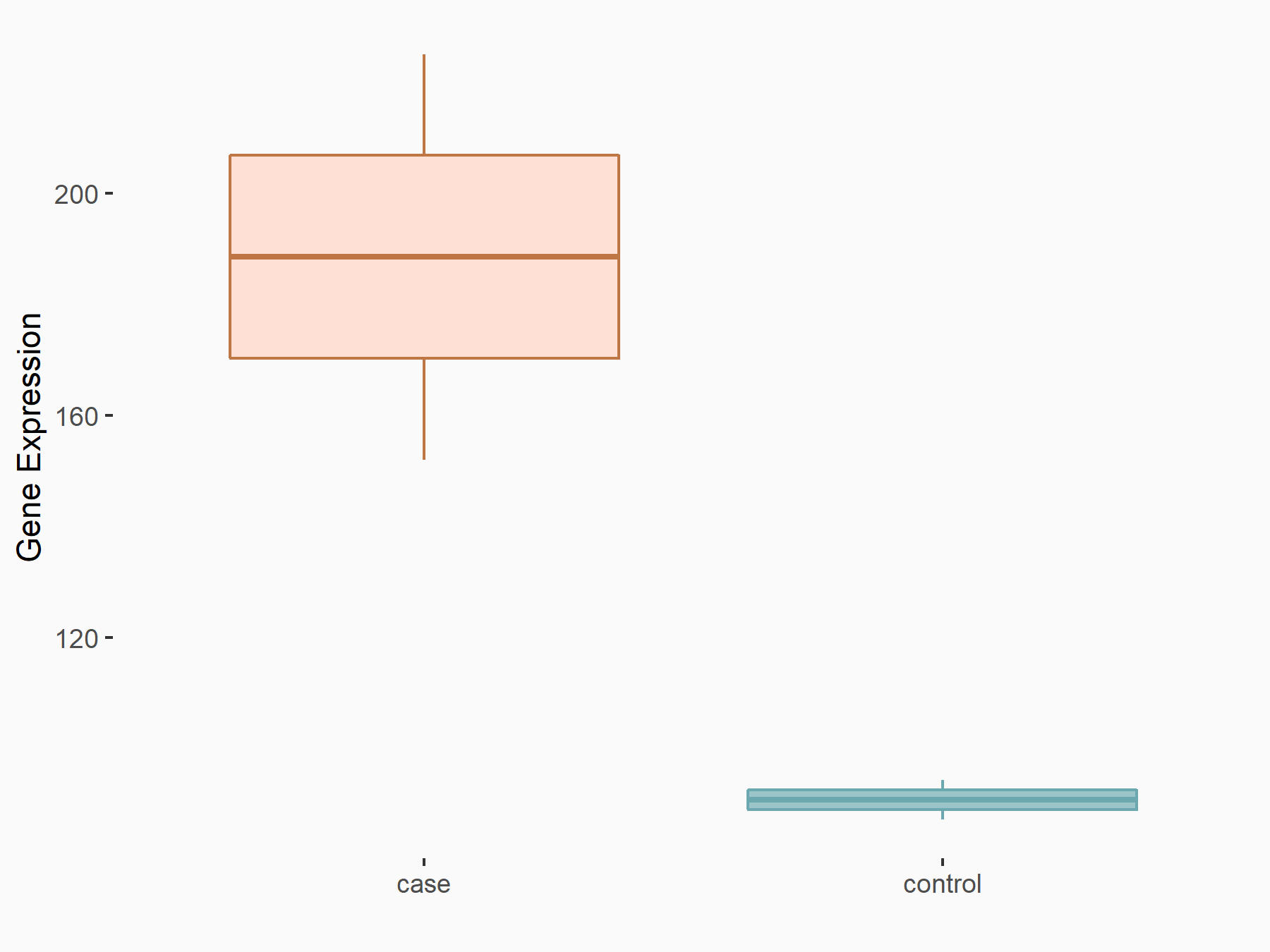  |
logFC: 1.06E+00 p-value: 8.73E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 inhibits Notch signaling by downregulating the Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1), HES1, and HES5 mRNA levels. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Extracellular stress | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3-catalyzed m6A modification promotes Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) expression and the activation of the Notch signaling pathway. Forced activation of Notch signaling pathway successfully rescues the growth, migration, and invasion capacities of METTL3-depleted ESCC cells. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell migration | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In-vitro Model | TE-9 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1767 |
| KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| In-vivo Model | For induction of ESCC, 4-week-old mice were treated with drinking water containing 50 ug/mL 4NQO (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) for 16 weeks and then given normal drinking water for another 4-5 weeks. Cre was activated by the intraperitoneal injection of tamoxifen (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) at a dose of 9 mg per 40 g body weight every other day for a total of three injections. For tumor measurement, mice were sacrificed, and the esophagus was dissected immediately. The surface areas of tumors were measured as described previously. | |||
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In bladder cancer, the changes in m6A methylation level mainly appeared at 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) of MALAT1 and Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) transcripts, and at 3' UTR of CSNK2A2 and ITGA6 transcripts, responding to the overexpression of FTO. SFPQ could influence the FTO-mediated m6A RNA demethylation, eventually affecting the gene expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HT-1197 | Recurrent bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1291 |
| HT-1376 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1292 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/cnu/nu mice (4-5 weeks old) were used for the xenograft experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 6 for each group) and injected with 5 × 106 HT-1197 cells in control group or FTO plasmid group, respectively. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 and m6A modification participate in the RNA stability of Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) mRNA. Notch1 plays an essential role in bladder tumorigenesis and bladder TIC self-renewal. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Self-renewal | ||||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | Primary bladder cancer cells (Obtained from bladder cancer patients) | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03373 | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00351)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003291 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136520661-136520662:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CACTGCAGCCTTGACCTCCCAGGCTAAAGCGATCCTTCTGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_139062 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE004508 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136504994-136504995:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGGACTGTGCGGAGCATGTACCCGAGAGGCTGGCGGCCGGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | lung | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_44141 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 103 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090422 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136494536-136494537:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGTGTAGTTTACAGAAAAAGACTTTAAAAGTGATCTACATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847564 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090423 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495016-136495017:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCCGTGTTTTGTAGGAGACTTGCCAGAGCCGGGCACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; H1A; H1B; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847565 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090424 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495052-136495053:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGGCCCCAGCTCGCGGGACCCGACCCCCCGTGGGCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847566 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090425 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495115-136495116:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCAGCACCTCAGCCTGCACAGTGTCCCCCAGGTTCCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847567 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090426 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495162-136495163:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTACCCTTTTCTGGGGAAAGACACTGCCTGGGCTGACCCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847568 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090427 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495218-136495219:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTCAAACATGAGATGTGTGGACTGTGGCACTTGCCTGGGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; CD4T; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847569 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090428 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495233-136495234:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTAGGCATCATGCATGTCAAACATGAGATGTGTGGACTGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; CD4T; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847570 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090429 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495598-136495599:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTTTCCCCGACGCCCACCCAACCCCAAGCCAGCCCGGCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.153267857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847571 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090430 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495750-136495751:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TCTGTGTTTATAAAATATAAACAAAGATTCATGATTTATAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESCs; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847572 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090431 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495821-136495822:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTTTTATCTATTCTGAGAAAACAAGCAAGTTCTGAGAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847573 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090432 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495842-136495843:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTATCTGGCCCCAGGTAGAAACTTTTATCTATTCTGAGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847574 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090433 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495891-136495892:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | TACTTTTATTTTACACAGAAACACTGCCTTTTTATTTATAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; HeLa; A549; hESC-HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847575 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090434 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136495971-136495972:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | ACCAGAGGAGCCTTTTTAAAACACATGTTTTTATACAAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; HeLa; A549; GM12878; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847576 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090435 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496052-136496053:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TAAACGGCGCGCCCCACGAGACCCCGGCTTCCTTTCCCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; MT4; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TIME; iSLK; MSC; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847577 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090436 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496232-136496233:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | AACACCCCCAGCCACCAGCTACAGGTGCCTGAGCACCCCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847578 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090437 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496254-136496255:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAGCTACTCCTCGCCTGTGGACAACACCCCCAGCCACCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847579 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090438 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496536-136496537:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCAGAACCTGCAGCCAGCAAACATCCAGCAGCAGCAAAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; A549; MT4; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847580 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090439 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496551-136496552:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTTACAGATGCAGCAGCAGAACCTGCAGCCAGCAAACATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; A549; MT4; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847581 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090440 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496568-136496569:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CAGGTGCAGCCACAAAACTTACAGATGCAGCAGCAGAACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847582 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090441 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496572-136496573:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCAGCAGGTGCAGCCACAAAACTTACAGATGCAGCAGCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; U2OS; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; A549; CD8T; MT4; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847583 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090442 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496594-136496595:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGCCTCACCTGGTGCAGACCCAGCAGGTGCAGCCACAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; A549; MT4; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847584 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090443 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496776-136496777:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCAGAGCGGCATGGTGCCGAACCAATACAACCCTCTGCGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; A549; HepG2; H1A; H1B; hESCs; GM12878; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847585 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090444 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136496936-136496937:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCGGCCGGCTGGCCTTTGAGACTGGCCCACCTCGTCTCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847586 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090445 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497136-136497137:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGGCATGCTCTCGCCCGTGGACTCCCTGGAGTCACCCCATG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847587 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090446 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497163-136497164:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGGCAAGGGCTGCCTGCTGGACAGCTCCGGCATGCTCTCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847588 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090447 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497214-136497215:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGGAAGCAAGGAGGCCAAGGACCTCAAGGCACGGAGGAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847589 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090448 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497442-136497443:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TATGGACCGCCTGCCGCGCGACATCGCACAGGAGCGCATGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847590 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090449 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497457-136497458:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGACATCACGGATCATATGGACCGCCTGCCGCGCGACATCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; A549; GM12878; MT4; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847591 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090450 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497475-136497476:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGACCACTTTGCCAACCGGGACATCACGGATCATATGGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; MT4; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847592 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090451 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497493-136497494:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GACCGCCAAGGTGCTGCTGGACCACTTTGCCAACCGGGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; MT4; peripheral-blood; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847593 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090452 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497512-136497513:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCGGGAGGGCAGCTACGAGACCGCCAAGGTGCTGCTGGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; MT4; peripheral-blood; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847594 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090453 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136497551-136497552:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCTCATCCCCCAGGAGGAGACACCCCTGTTTCTGGCCGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847595 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090454 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136498905-136498906:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCTAACAAAGATATGCAGAACAACAGGGTGAGCGCGAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847596 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090455 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136498962-136498963:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCACTGGGCCGCCGCCGTGAACAATGTGGATGCCGCAGTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847597 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090456 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136499155-136499156:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGTGGAGGGCATGCTGGAGGACCTCATCAACTCACACGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847598 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090457 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136499233-136499234:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GATCCGGAACCGAGCCACAGACCTGGATGCCCGCATGCATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847599 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090458 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136499245-136499246:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCAGATCCTGATCCGGAACCGAGCCACAGACCTGGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847600 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090459 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136500612-136500613:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGCAGATGCCAACATCCAGGACAACATGGGCCGCACCCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847601 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090460 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136500697-136500698:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGACAGACCGCACGGGCGAGACCGCCTTGCACCTGGCCGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847602 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090461 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136500715-136500716:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCGCCAGCCTGCACAACCAGACAGACCGCACGGGCGAGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847603 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090462 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136501855-136501856:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGACAGACCACCGGCAGTGGACTCAGCAGCACCTGGATGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847604 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090463 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136501873-136501874:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTGACCTGGACGACCAGACAGACCACCGGCAGTGGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847605 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090464 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136502014-136502015:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGGACGAGGACCTGGAGACCAAGAAGTTCCGGGTGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847606 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090465 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136502022-136502023:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAATGAGTGGGGGGACGAGGACCTGGAGACCAAGAAGTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847607 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090466 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136502286-136502287:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCGGGAGCCCCTCGGCGAGGACTCCGTGGGCCTCAAGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847608 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090467 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136502482-136502483:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCCCGTGCCCGCAGGTGAGACCGTGGAGCCGCCCCCGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000494783.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847609 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090468 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136504690-136504691:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCGGCGGCGGAGGGAGCTGGACCCCATGGACGTCCGCGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000494783.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847610 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090469 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136505011-136505012:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTGCGAGTGGGACGGGCTGGACTGTGCGGAGCATGTACCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; H1A; H1B; hESCs; CD8T; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; TIME; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847611 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090470 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136505077-136505078:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTACGACCAGTACTGCAAGGACCACTTCAGCGACGGGCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; H1B; hESCs; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847612 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090471 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136505429-136505430:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTTCAATGACCCCTGGAAGAACTGCACGCAGTCTCTGCAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847613 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090472 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136505609-136505610:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCTCTTGTGCCACATCCTGGACTACAGCTTCGGGGGTGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847614 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090473 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136505691-136505692:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACCCCTGCTACAACCAGGGGACCTGTGAGCCCACATCCGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847615 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090474 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136506768-136506769:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGACGCCCGTGGCACCCAGAACTGCGTGCAGCGCGTCAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847616 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090475 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136506879-136506880:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TAACAACGGCACCTGCGTGGACCAGGTGGGCGGCTACAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847617 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090476 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136507411-136507412:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGGCTACCACGGGGTGAACTGCTCTGAGGAGATCGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847618 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090477 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136507979-136507980:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAACGGGGCCACCTGCACGGACTACCTGGGCGGCTACTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847619 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090478 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136508033-136508034:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CACAGGCAGCTACTGTGAGGACCTGGTGGACGAGTGCTCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847620 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090479 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136508288-136508289:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCGAGTGCCCCAGCGGCTGGACCGGCCTTTACTGCGACGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847621 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090480 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136508327-136508328:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACGGCGGCAAATGCTGGCAGACCCACACCCAGTACCGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847622 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090481 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136509756-136509757:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAGCGGGATCCACTGTGAGAACAACACGCCTGACTGCACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847623 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090482 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136509807-136509808:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAACTGCACGGACTGCGTGGACAGCTACACGTGCACCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847624 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090483 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136509816-136509817:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAACGGGGCCAACTGCACGGACTGCGTGGACAGCTACACGT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847625 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090484 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136509867-136509868:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGCACTTTCTGTGAGGAGGACATCAACGAGTGTGCCAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847626 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090485 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136510676-136510677:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACAGTGGGCGCAACTGCGAGACCGACATCGACGACTGCCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000646957.1; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847627 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090486 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136510735-136510736:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCACGGCGCATCCTGCCAGAACACCCACGGCGGCTACCGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000646957.1; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847628 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090487 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136510799-136510800:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCTGCCCCGCAGGGCAGACCTGTGAGGTCGACATCAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000646957.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847629 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090488 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136511192-136511193:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGAGTGCAGGCAATCCGAGGACTATGAGAGCTTCTCCTGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000646957.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847630 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090489 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136513049-136513050:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TATTGACGACGTTGCCGGGTACAAGTGCAACTGCCTGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000646957.1; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847631 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090490 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136513082-136513083:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCGTCCAACCCATGTCTGAACCAGGGCACGTGTATTGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000646957.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847632 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090491 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136513115-136513116:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | AGGTCCCAACTGCCAGACCAACATCAACGAGTGTGCGTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; rmsk_2902491; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847633 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090492 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136513119-136513120:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTCCAGGTCCCAACTGCCAGACCAACATCAACGAGTGTGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1; rmsk_2902491 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847634 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090493 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136513435-136513436:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAACGGCGGCACCTGCAAAGACATGACCAGTGGCTACGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000645828.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847635 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090494 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136513483-136513484:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | GACCAACTGTGACATCAACAACAATGAGTGTGAATCCAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847636 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090495 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136513502-136513503:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTGACCCTGGGTGGAGTGGGACCAACTGTGACATCAACAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000645828.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847637 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090496 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136514521-136514522:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGTCCACGGGGCCTGCCGGGACAGCCTCAACGGGTATGCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847638 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090497 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136515333-136515334:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGACTCGGGCACCTGTCTGGACAAGATCGATGGCTACGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847639 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090498 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136515488-136515489:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCTTCTGCCTGAAGGGGACCACAGGTGGCCGGCCAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847640 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090499 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136515526-136515527:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCACGGGGGCACCTGCCAGGACCGCGACAACGCCTACCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847641 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090500 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136515581-136515582:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACACGGGCCACCACTGCGAGACCAACATCAACGAGTGCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847642 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090501 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136515688-136515689:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGGACGCACTGCGAGGTGGACATCGATGAGTGCGACCCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847643 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090502 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136516011-136516012:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGTGCCAAGTGCCTGGACGGACCCAACACTTACACCTGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847644 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090503 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136517306-136517307:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCACAATGGCCGCTGCCTGGACAAGATCAATGAGTTCCAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847645 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090504 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136517786-136517787:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAACGACGCCACCTGCCTGGACCAGATTGGGGAGTTCCAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847646 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090505 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136517816-136517817:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGTCAACGAGTGCGTCTCGAACCCGTGCCAGAACGACGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847647 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090506 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136518685-136518686:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGAGGACTGCAGCGAGAACATTGATGACTGTGCCAGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847648 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090507 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136518697-136518698:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAACGGCTGGACTGGTGAGGACTGCAGCGAGAACATTGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847649 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090508 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136518707-136518708:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCGTGTGTGTCAACGGCTGGACTGGTGAGGACTGCAGCGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847650 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090509 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136518733-136518734:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | CCACAACACCCACGGTGGCTACAACTGCGTGTGTGTCAACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847651 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090510 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136518751-136518752:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | CCAGAACGGCGGGACCTGCCACAACACCCACGGTGGCTACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847652 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090511 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136518758-136518759:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATGCCTGCCAGAACGGCGGGACCTGCCACAACACCCACGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847653 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090512 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136519445-136519446:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCCGCTGCCCGCCAGAGTGGACAGGCGCGTATACGGGTCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847654 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090513 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136519477-136519478:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTGTGTGGACGGCGTGAACACCTACAACTGCCGCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847655 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090514 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136519516-136519517:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TATCGACGATTGTCCAGGAAACAACTGCAAGAACGGGGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847656 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090515 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136519549-136519550:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCAGGCTTCACCGGCCAGAACTGTGAGGAAAATATCGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847657 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090516 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136522706-136522707:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGGGATGGCGAGTTCCCCAGACTGCGTGTGGTGTCGGGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000491649.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847658 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090517 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136523811-136523812:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTCTGCCTGACACCCCTGGACAATGCCTGCCTCACCAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000491649.1; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847659 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090518 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136523868-136523869:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGACCGCAGAGGCGTGGCAGACTATGCCTGCAGCTGTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000491649.1; ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847660 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090519 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136523886-136523887:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGGGACATGCCACGTGGTGGACCGCAGAGGCGTGGCAGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; TIME; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000491649.1; ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847661 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090520 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136523902-136523903:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCCCTGCAAGAACGCCGGGACATGCCACGTGGTGGACCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; TIME; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000277541.7; ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847662 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090521 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136523943-136523944:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGTGGGCCCGCGATGCCAGGACCCCAACCCGTGCCTCAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; TIME; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847663 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090522 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136544075-136544076:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GATGCTCCCAGCCCGGTGAGACCTGCCTGAATGGCGGGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; MT4; GSC-11; iSLK; TIME; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1; ENST00000277541.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847666 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090523 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136545871-136545872:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | CCGTCCGCCGCCGCCCCGGGACCGTACGCCGCGCGTGTGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Jurkat; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847667 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090524 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:136545892-136545893:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GCCGGGGAAGAGAGGGCGGGACCGTCCGCCGCCGCCCCGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Jurkat; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651671.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_847668 | ||
References