m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00425)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
RELA
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
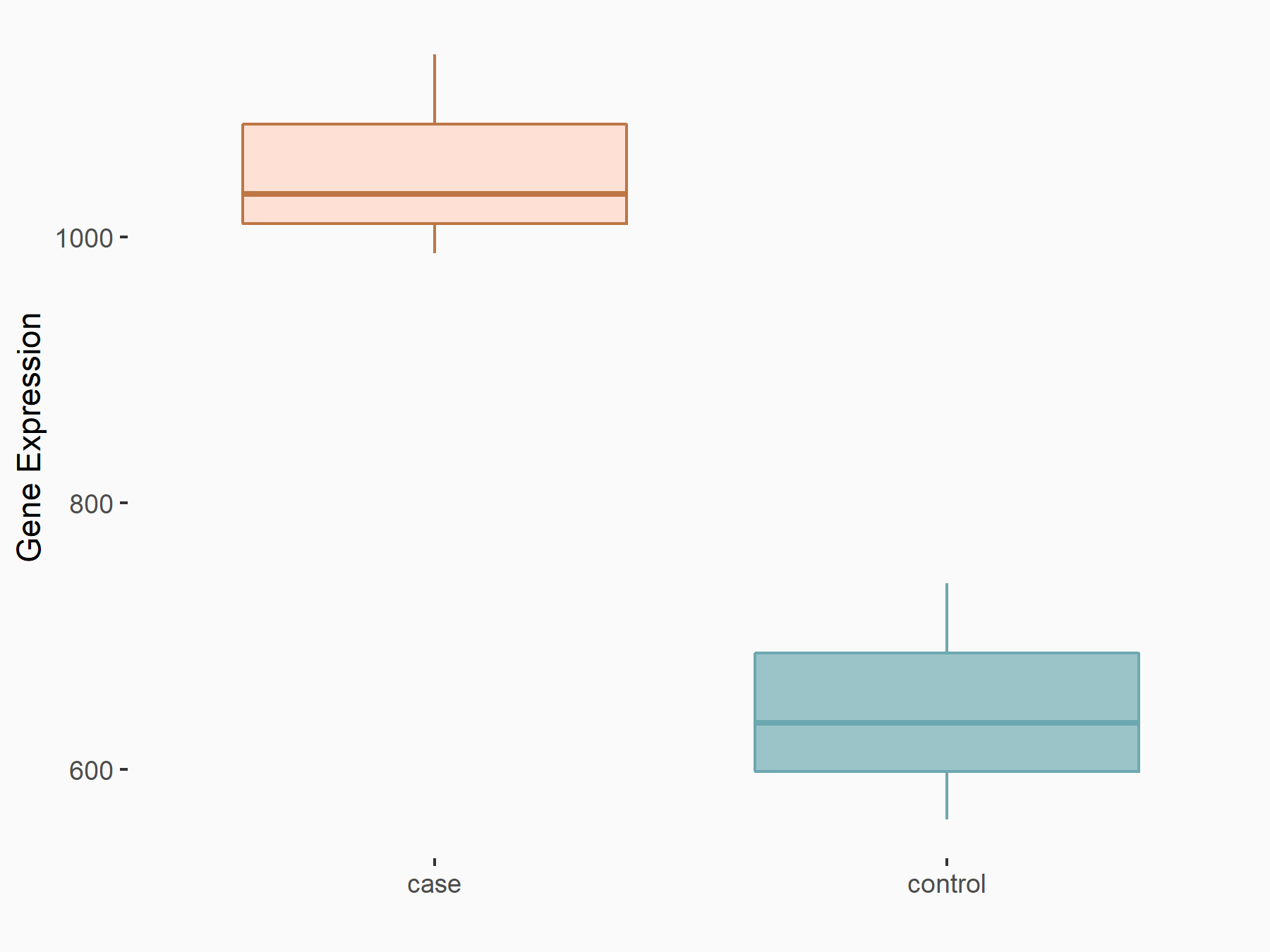  |
logFC: 7.00E-01 p-value: 8.41E-10 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Knocking down METTL14 could inhibit the development of atherosclerosis in high-fat diet-treated APOE mice. After transfection with si-METTL14, the bcl-2 expression level and the viability of ox-LDL-incubated cells increased, whereas the apoptosis rate and the expressions of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 decreased. However, the effect of METTL14 knockdown was reversed by Transcription factor p65 (RELA) overexpression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis | ICD-11: BD40.Z | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| EA.hy 926 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3901 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were randomly divided into control, Ad-sh-NC, and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups (10 mice per group). The mice in the control group were fed a normal diet, while the Ad-sh-NC and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups were fed a high-fat diet (20% fat and 0.25% cholesterol). Furthermore, 300 uL of constructed sh-NC or sh-METTL14 adenovirus was injected every 3 weeks into the caudal veins of mice from the Ad-sh-NC or Ad-sh-METTL14 groups, respectively. The constructed vectors were obtained from HanBio Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All mice were sacrificed after 24 weeks and the aortas were separated for further experiments. | |||
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | Caco-2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 Caco-2 cells
Control: shNTC Caco-2 cells
|
GSE167075 | |
| Regulation |
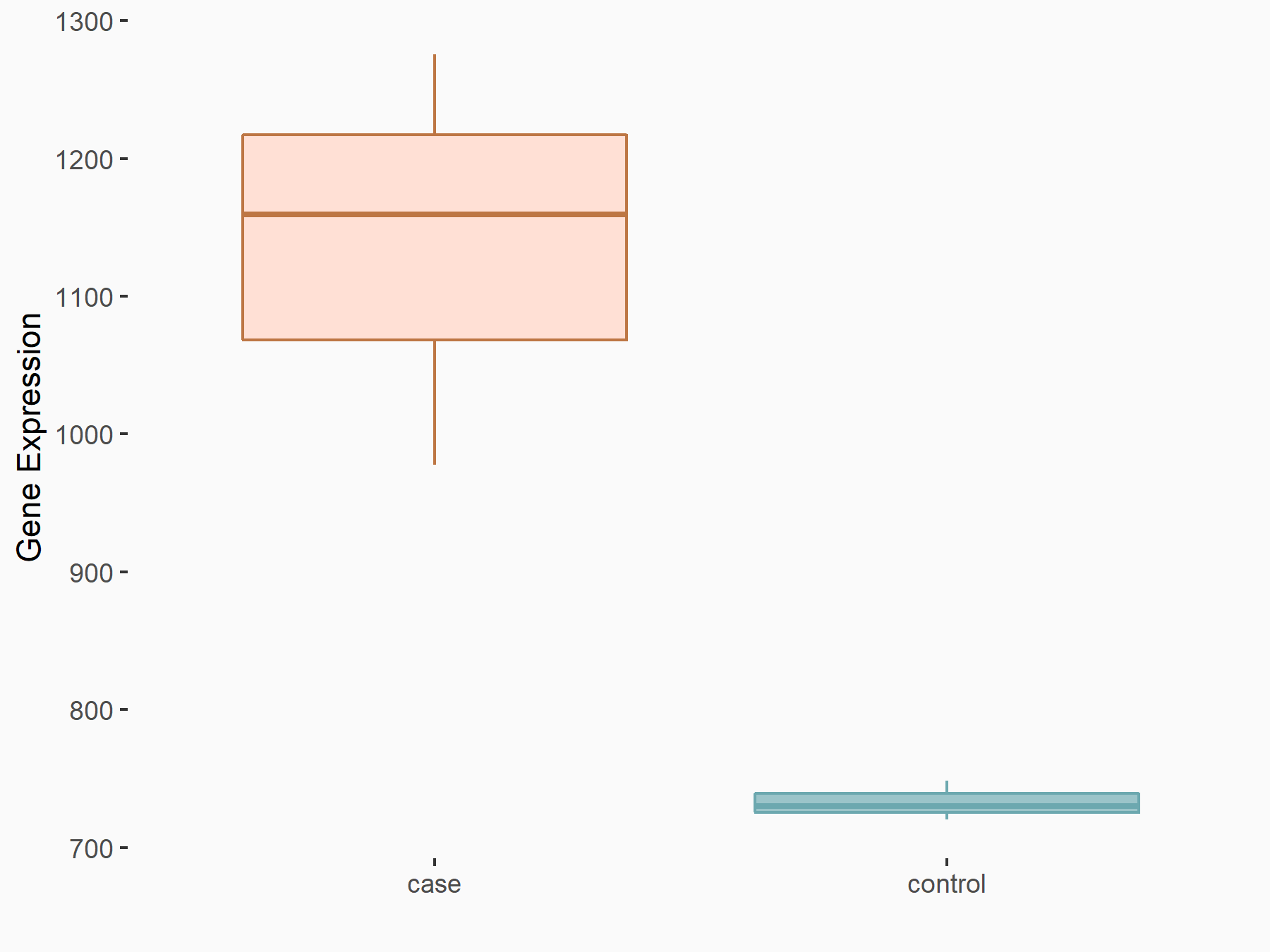  |
logFC: 6.33E-01 p-value: 3.93E-11 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | AF4/FMR2 family member 4 (AFF4), two key regulators of NF-Kappa-B pathway (IKBKB and Transcription factor p65 (RELA)) and MYC were further identified as direct targets of METTL3-mediated m6A modification.overexpression of METTL3 significantly promoted Bladder cancer cell growth and invasion. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 played a pivotal tumor-suppressor role in papillary thyroid cancer carcinogenesis through c-Rel and Transcription factor p65 (RELA) inactivation of the nuclear factor Kappa-B (NF-Kappa-B) pathway by cooperating with YTHDF2 and altered TAN infiltration to regulate tumor growth. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer | ICD-11: 2D10.1 | ||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| KTC-1 | Thyroid carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6300 | |
| B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 | |
| In-vivo Model | For xenograft models, 5 × 106 BCPAP or KTC-1 cells from each group were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of female BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks old, Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal, China, n = 5 per group) in a volume of 150 uL PBS. Tumor growth was measured with a digital caliper every 4 days and calculated using the following formula: (length × width2)/2. To study the effect of IL-8 on tumor growth in vivo, scramble or shMETTL3 BCPAP cells were implanted hypodermically into BALB/c nude mice (2 × 106 cells in 150 uL PBS, n = 10 per group). When palpable tumors formed on day 14, mice were treated with DMSO or the IL-8 inhibitor SB225002 (10 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection 3 times per week for 3 weeks. Six weeks post-injection, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumors were collected to analyze the frequency of TANs by flow cytometry. For the lung metastasis model, BCPAP and KTC-1 cells (2 × 106 cells in 100 uL PBS) with the corresponding vectors were injected into the tail veins of BALB/c nude mice. Eight weeks after injection, the mice were euthanized, and metastatic lung nodules were analyzed (n = 5 for each group). | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF2 | ||
| Cell Line | GSC11 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siYTHDF2 GSC11 cells
Control: siControl GSC11 cells
|
GSE142825 | |
| Regulation |
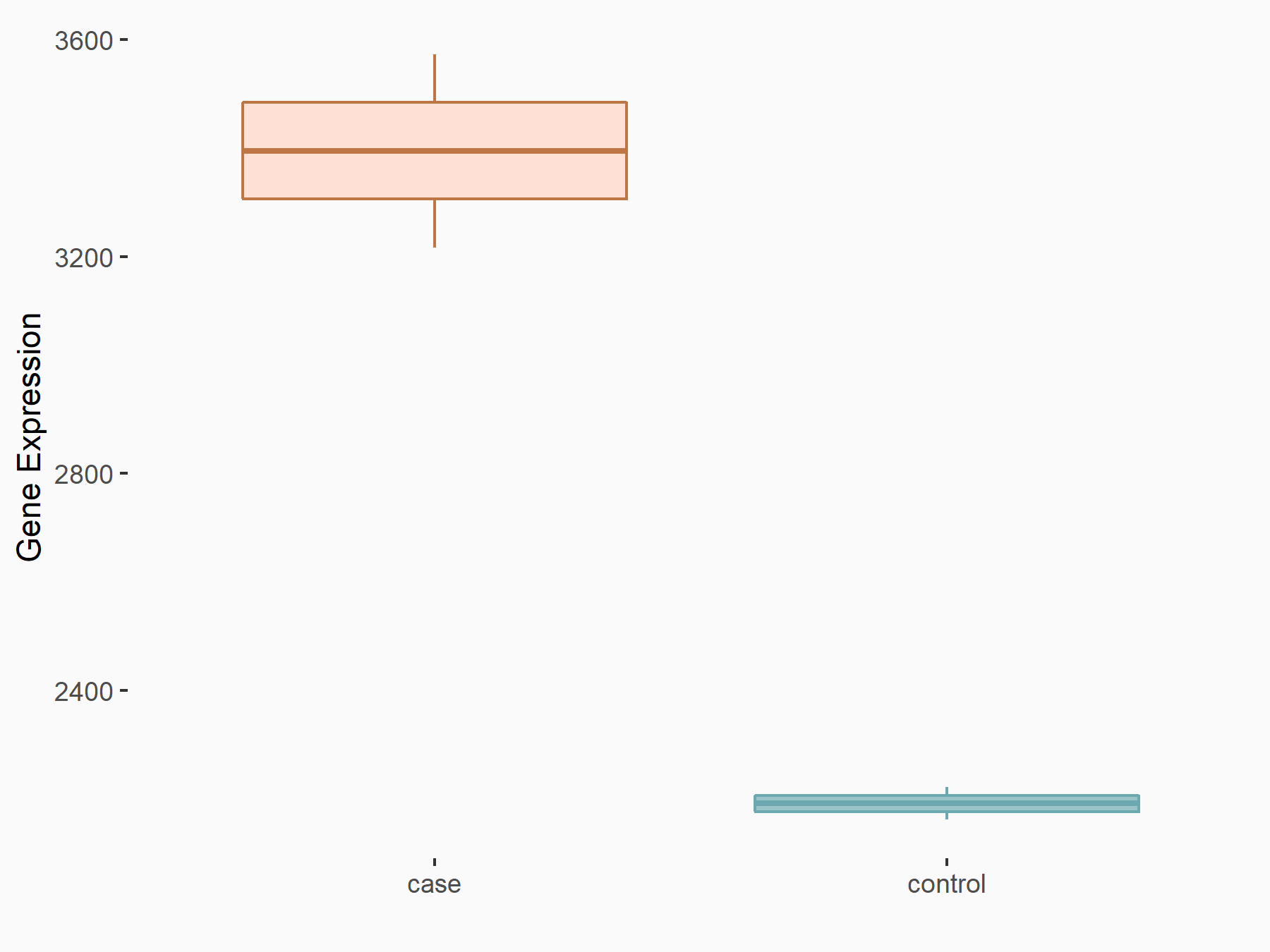  |
logFC: 6.31E-01 p-value: 1.53E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 played a pivotal tumor-suppressor role in papillary thyroid cancer carcinogenesis through c-Rel and Transcription factor p65 (RELA) inactivation of the nuclear factor Kappa-B (NF-Kappa-B) pathway by cooperating with YTHDF2 and altered TAN infiltration to regulate tumor growth. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer | ICD-11: 2D10.1 | ||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| KTC-1 | Thyroid carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6300 | |
| B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 | |
| In-vivo Model | For xenograft models, 5 × 106 BCPAP or KTC-1 cells from each group were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of female BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks old, Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal, China, n = 5 per group) in a volume of 150 uL PBS. Tumor growth was measured with a digital caliper every 4 days and calculated using the following formula: (length × width2)/2. To study the effect of IL-8 on tumor growth in vivo, scramble or shMETTL3 BCPAP cells were implanted hypodermically into BALB/c nude mice (2 × 106 cells in 150 uL PBS, n = 10 per group). When palpable tumors formed on day 14, mice were treated with DMSO or the IL-8 inhibitor SB225002 (10 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection 3 times per week for 3 weeks. Six weeks post-injection, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumors were collected to analyze the frequency of TANs by flow cytometry. For the lung metastasis model, BCPAP and KTC-1 cells (2 × 106 cells in 100 uL PBS) with the corresponding vectors were injected into the tail veins of BALB/c nude mice. Eight weeks after injection, the mice were euthanized, and metastatic lung nodules were analyzed (n = 5 for each group). | |||
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation modification is implicated in the pathogenesis of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. YTHDF3 or IGF2BP2 knockdown inhibited hypoxia/reoxygenation-activated p38, ERK1/2, AKT, and NF-Kappa-B pathways in BEAS-2B cells, and inhibited Transcription factor p65 (RELA), IL-1-beta and TNF-alpha secretion. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gangrene or necrosis of lung | ICD-11: CA43 | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| In-vivo Model | After being anesthetized with urethane (i.p.), SD rats were endotracheally intubated and ventilated using an animal ventilator under the conditions: respiratory rate of 70 breaths/min, tidal volume of 20 ml/kg, and inspiratory/expiratory ratio of 1:1. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation modification is implicated in the pathogenesis of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. YTHDF3 or IGF2BP2 knockdown inhibited hypoxia/reoxygenation-activated p38, ERK1/2, AKT, and NF-Kappa-B pathways in BEAS-2B cells, and inhibited Transcription factor p65 (RELA), IL-1-beta and TNF-alpha secretion. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gangrene or necrosis of lung | ICD-11: CA43 | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| In-vivo Model | After being anesthetized with urethane (i.p.), SD rats were endotracheally intubated and ventilated using an animal ventilator under the conditions: respiratory rate of 70 breaths/min, tidal volume of 20 ml/kg, and inspiratory/expiratory ratio of 1:1. | |||
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | AF4/FMR2 family member 4 (AFF4), two key regulators of NF-Kappa-B pathway (IKBKB and Transcription factor p65 (RELA)) and MYC were further identified as direct targets of METTL3-mediated m6A modification.overexpression of METTL3 significantly promoted Bladder cancer cell growth and invasion. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 played a pivotal tumor-suppressor role in papillary thyroid cancer carcinogenesis through c-Rel and Transcription factor p65 (RELA) inactivation of the nuclear factor Kappa-B (NF-Kappa-B) pathway by cooperating with YTHDF2 and altered TAN infiltration to regulate tumor growth. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| KTC-1 | Thyroid carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6300 | |
| B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 | |
| In-vivo Model | For xenograft models, 5 × 106 BCPAP or KTC-1 cells from each group were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of female BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks old, Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal, China, n = 5 per group) in a volume of 150 uL PBS. Tumor growth was measured with a digital caliper every 4 days and calculated using the following formula: (length × width2)/2. To study the effect of IL-8 on tumor growth in vivo, scramble or shMETTL3 BCPAP cells were implanted hypodermically into BALB/c nude mice (2 × 106 cells in 150 uL PBS, n = 10 per group). When palpable tumors formed on day 14, mice were treated with DMSO or the IL-8 inhibitor SB225002 (10 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection 3 times per week for 3 weeks. Six weeks post-injection, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumors were collected to analyze the frequency of TANs by flow cytometry. For the lung metastasis model, BCPAP and KTC-1 cells (2 × 106 cells in 100 uL PBS) with the corresponding vectors were injected into the tail veins of BALB/c nude mice. Eight weeks after injection, the mice were euthanized, and metastatic lung nodules were analyzed (n = 5 for each group). | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 played a pivotal tumor-suppressor role in papillary thyroid cancer carcinogenesis through c-Rel and Transcription factor p65 (RELA) inactivation of the nuclear factor Kappa-B (NF-Kappa-B) pathway by cooperating with YTHDF2 and altered TAN infiltration to regulate tumor growth. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||
| In-vitro Model | TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| KTC-1 | Thyroid carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6300 | |
| B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 | |
| In-vivo Model | For xenograft models, 5 × 106 BCPAP or KTC-1 cells from each group were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of female BALB/c nude mice (4-6 weeks old, Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal, China, n = 5 per group) in a volume of 150 uL PBS. Tumor growth was measured with a digital caliper every 4 days and calculated using the following formula: (length × width2)/2. To study the effect of IL-8 on tumor growth in vivo, scramble or shMETTL3 BCPAP cells were implanted hypodermically into BALB/c nude mice (2 × 106 cells in 150 uL PBS, n = 10 per group). When palpable tumors formed on day 14, mice were treated with DMSO or the IL-8 inhibitor SB225002 (10 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection 3 times per week for 3 weeks. Six weeks post-injection, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumors were collected to analyze the frequency of TANs by flow cytometry. For the lung metastasis model, BCPAP and KTC-1 cells (2 × 106 cells in 100 uL PBS) with the corresponding vectors were injected into the tail veins of BALB/c nude mice. Eight weeks after injection, the mice were euthanized, and metastatic lung nodules were analyzed (n = 5 for each group). | |||
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Knocking down METTL14 could inhibit the development of atherosclerosis in high-fat diet-treated APOE mice. After transfection with si-METTL14, the bcl-2 expression level and the viability of ox-LDL-incubated cells increased, whereas the apoptosis rate and the expressions of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 decreased. However, the effect of METTL14 knockdown was reversed by Transcription factor p65 (RELA) overexpression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 |
| EA.hy 926 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3901 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were randomly divided into control, Ad-sh-NC, and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups (10 mice per group). The mice in the control group were fed a normal diet, while the Ad-sh-NC and Ad-sh-METTL14 groups were fed a high-fat diet (20% fat and 0.25% cholesterol). Furthermore, 300 uL of constructed sh-NC or sh-METTL14 adenovirus was injected every 3 weeks into the caudal veins of mice from the Ad-sh-NC or Ad-sh-METTL14 groups, respectively. The constructed vectors were obtained from HanBio Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All mice were sacrificed after 24 weeks and the aortas were separated for further experiments. | |||
Gangrene or necrosis of lung [ICD-11: CA43]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation modification is implicated in the pathogenesis of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. YTHDF3 or IGF2BP2 knockdown inhibited hypoxia/reoxygenation-activated p38, ERK1/2, AKT, and NF-Kappa-B pathways in BEAS-2B cells, and inhibited Transcription factor p65 (RELA), IL-1-beta and TNF-alpha secretion. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gangrene or necrosis of lung [ICD-11: CA43] | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| In-vivo Model | After being anesthetized with urethane (i.p.), SD rats were endotracheally intubated and ventilated using an animal ventilator under the conditions: respiratory rate of 70 breaths/min, tidal volume of 20 ml/kg, and inspiratory/expiratory ratio of 1:1. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation modification is implicated in the pathogenesis of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. YTHDF3 or IGF2BP2 knockdown inhibited hypoxia/reoxygenation-activated p38, ERK1/2, AKT, and NF-Kappa-B pathways in BEAS-2B cells, and inhibited Transcription factor p65 (RELA), IL-1-beta and TNF-alpha secretion. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gangrene or necrosis of lung [ICD-11: CA43] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Biological regulation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| In-vivo Model | After being anesthetized with urethane (i.p.), SD rats were endotracheally intubated and ventilated using an animal ventilator under the conditions: respiratory rate of 70 breaths/min, tidal volume of 20 ml/kg, and inspiratory/expiratory ratio of 1:1. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Non-coding RNA
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05263 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-421-3p | |
| Regulated Target | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute ischemic stroke | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00425)
| In total 5 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE004949 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661107-65661108:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGGAGGTCACTGCTGCGGCAAGCTATGATTGCACCACTGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000406246.8; rmsk_3569895; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532879.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_22777 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE004950 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661126-65661127:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGGGAGGATCGCCTGAGCCCAGGAGGTCACTGCTGCGGCAA | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_3569895; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000529389.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_22778 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE004951 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661191-65661192:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTACAAAAAATAAGAAATTAGCTGGGTATGGTGGCATGCG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525658.5; rmsk_3569895; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000531238.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_22779 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE004952 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661194-65661195:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATGTCTACAAAAAATAAGAAATTAGCTGGGTATGGTGGCAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532879.5; rmsk_3569895; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_22780 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE004953 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661198-65661199:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCCCATGTCTACAAAAAATAAGAAATTAGCTGGGTATGGTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000615805.4; rmsk_3569895; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000529389.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_22781 | ||
N1-methyladenosine (m1A)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M1ASITE000021 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654139-65654140:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGAGCTGGGGAAACTCAAACTTTTCCCCTGTCCTGATG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m1A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m1A_site_203 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 3 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE005220 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654447-65654448:- | ||
| Sequence | GCTCCCCAATGGCCTCCTTTCAGGAGATGAAGACTTCTCCT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_7954 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE005221 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654471-65654472:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCCTGCTCCACTGGGGGCCCCGGGGCTCCCCAATGGCCTCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_7955 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE005222 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65662655-65662656:- | ||
| Sequence | AGGCGGGGAGGGGTCTGACTCAGTTTCCCCTCTGGGTGGAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000534283.1; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525658.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_7956 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 84 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007111 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653624-65653625:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCTTGCTCTTTCTACTCTGAACTAATAAATCTGTTGCCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148625 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007112 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653646-65653647:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGAACAATCAAAGCACTTGGACTCTTGCTCTTTCTACTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; HepG2; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148626 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007113 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653652-65653653:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TTTTACTGAACAATCAAAGCACTTGGACTCTTGCTCTTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148627 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007114 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653663-65653664:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGAGGCATAGTTTTTACTGAACAATCAAAGCACTTGGACTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME; TREX; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148628 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007115 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653668-65653669:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | AGTCAGGAGGCATAGTTTTTACTGAACAATCAAAGCACTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148629 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007117 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653771-65653772:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CAGAAGGGGTTTGGTCTGGGACTTCCTTGCTCTCCCTCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; A549; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148630 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007118 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653824-65653825:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTCAACCATGGCTGAAGGAAACCAGTGCAACAGCACTGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148631 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007119 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653872-65653873:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | GGGGCTGGCCTTCCTGCCCTACAGAGGTCTCTGCCGGCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148632 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007120 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653906-65653907:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TGGCATTGTCCCTGTGCCTAACACCAGCGTTTGAGGGGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148633 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007121 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65653973-65653974:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TCTTCCATCATGGATTCATTACAGCTTAATCAAAATAACGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148634 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007122 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654045-65654046:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | CTTCTGGTACTCTCCTAGAGACAGAAGCAGGCTGGAGGTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148635 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007123 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654057-65654058:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | CCCATCCTCCAGCTTCTGGTACTCTCCTAGAGACAGAAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.278136905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531484.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148636 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007124 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654095-65654096:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | AGCTCCCTTCTCTGTAGGGAACTCTGGGGTCCCCCATCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148637 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007125 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654138-65654139:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GGGGAGCTGGGGAAACTCAAACTTTTCCCCTGTCCTGATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000531484.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148638 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007126 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654144-65654145:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GAAAGGGGGGAGCTGGGGAAACTCAAACTTTTCCCCTGTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148639 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007128 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654173-65654174:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GTGCTTAAGCAGAAGCATTAACTTCTCTGGAAAGGGGGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148640 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007129 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654276-65654277:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GTGTGTTCCAACTGCCCCCAACTTTGTGGATGTCTTCCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148641 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007130 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654311-65654312:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCCCTCCAAAAGCACTTACGGATTCTGGTGGGGTGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.046785714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148642 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007131 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654315-65654316:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GATTGAAGCCCTCCAAAAGCACTTACGGATTCTGGTGGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148643 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007132 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654369-65654370:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GATCAGCTCCTAAGGGGGTGACGCCTGCCCTCCCCAGAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.833690476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; CD8T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148644 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007133 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654411-65654412:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTCCTCCATTGCGGACATGGACTTCTCAGCCCTGCTGAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148645 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007134 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654417-65654418:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGACTTCTCCTCCATTGCGGACATGGACTTCTCAGCCCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148646 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007135 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654435-65654436:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCTTTCAGGAGATGAAGACTTCTCCTCCATTGCGGACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148647 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007136 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654520-65654521:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | AGGCTATAACTCGCCTAGTGACAGGGGCCCAGAGGCCCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148648 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007137 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654573-65654574:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | GGGCATACCTGTGGCCCCCCACACAACTGAGCCCATGCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148649 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007139 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654597-65654598:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CGAGTTTCAGCAGCTGCTGAACCAGGGCATACCTGTGGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148650 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007140 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654624-65654625:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | CACAGACCTGGCATCCGTCGACAACTCCGAGTTTCAGCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531484.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148651 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007141 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654639-65654640:- | [16] | |
| Sequence | AGACCCAGCTGTGTTCACAGACCTGGCATCCGTCGACAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HEK293T; HeLa; A549; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148652 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007142 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654643-65654644:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GCACAGACCCAGCTGTGTTCACAGACCTGGCATCCGTCGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148653 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007143 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654657-65654658:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTTGCTTGGCAACAGCACAGACCCAGCTGTGTTCACAGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_3569880; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148654 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007144 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654687-65654688:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCTGCAGTTTGATGATGAAGACCTGGGGGCCTTGCTTGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; TIME; TREX; MSC; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; rmsk_3569880; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148655 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007145 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65654979-65654980:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | CACCCCAGCCCTATCCCTTTACGTCATCCCTGAGCACCATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.046785714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148656 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007146 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655167-65655168:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGAGGTGTGGCTAGAACTGGACCCTACAGGCTGGGTCAGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532999.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148657 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007147 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655172-65655173:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AAGGTGGAGGTGTGGCTAGAACTGGACCCTACAGGCTGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148658 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007148 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655197-65655198:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGCTTGAGTAGTCAGGGAGGACTCCAAGGTGGAGGTGTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148659 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007150 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655280-65655281:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | ACTTAGTTTTTCAGCTGTAAACTGAGGAGTCCAGCTTATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; H1B | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526283.6; rmsk_3569882; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531484.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148660 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007151 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655300-65655301:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGGGCTCATTGCCTCTCAGGACTTAGTTTTTCAGCTGTAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; H1B | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; rmsk_3569882; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148661 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007152 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655365-65655366:- | [17] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTGTGCGAGGCTCAAAAACTGACAAGCTCTGCACTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148662 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007153 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655418-65655419:- | [17] | |
| Sequence | CTCTCACTTGAATTGGGGGAACAAAAATCACCTCTAAATTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148663 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007154 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655513-65655514:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | ATGCACACTGAAGCCTGGGAACCACCGTGCCACTTAAATTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; rmsk_3569883; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148664 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007155 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655556-65655557:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TTTGAAAGGATGGCGCAGGAACCAGCGACTTCCTGGGATGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; rmsk_3569883; ENST00000532999.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148665 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007156 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655594-65655595:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | ACTCCTGGGCCCCATTACAGACCTACTGAATCAGAGGCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532999.5; rmsk_3569883; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148666 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007157 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655614-65655615:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GAGGAGCAGTGGAGATGAAGACTCCTGGGCCCCATTACAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; rmsk_3569883; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000526283.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148667 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007158 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655890-65655891:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AACGTAAAAGGACATATGAGACCTTCAAGAGCATCATGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000529389.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148668 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007159 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655899-65655900:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TTGAGGAGAAACGTAAAAGGACATATGAGACCTTCAAGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148669 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007161 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658387-65658388:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCGGACCCCTCCCTACGCAGACCCCAGCCTGCAGGCTCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000526257.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148670 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007162 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658403-65658404:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AAGTGGCCATTGTGTTCCGGACCCCTCCCTACGCAGACCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148671 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007163 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658425-65658426:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TCGCAAGCTGATGTGCACCGACAAGTGGCCATTGTGTTCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148672 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007164 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658473-65658474:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | ATTGAGGTGTATTTCACGGGACCAGGCTGGGAGGCCCGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148673 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007165 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658495-65658496:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | CACCGCATCTCCTGCAGAGGACATTGAGGTGTATTTCACGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; hESC-HEK293T; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148674 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007166 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658731-65658732:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TGAGATCTTCCTACTGTGTGACAAGGTGCAGAAAGGTATAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527909.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148675 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007167 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658776-65658777:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GATCTGCCGAGTGAACCGAAACTCTGGCAGCTGCCTCGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000406246.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148676 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007168 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658782-65658783:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GCTCAAGATCTGCCGAGTGAACCGAAACTCTGGCAGCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000531484.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148677 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007169 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65658812-65658813:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | CACTGCCTCAGGTGCCCCCAACACTGCCGAGCTCAAGATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000532999.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148678 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007170 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65659670-65659671:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | CCTTTCTCATCCCATCTTTGACAATCGTGAGTAGCGAGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000527749.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148679 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007172 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65659724-65659725:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | CTTCCAGGTGACAGTGCGGGACCCATCAGGCAGGCCCCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; MT4; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148680 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007173 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65659734-65659735:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | TGCGGCTCTGCTTCCAGGTGACAGTGCGGGACCCATCAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000526257.1; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000525693.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148681 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007174 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65659772-65659773:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | TATAGAAGAGCAGCGTGGGGACTACGACCTGAATGCTGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000527909.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148682 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007175 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660039-65660040:- | [18] | |
| Sequence | CATCTCCCTCACTGGCCAAGACACAGTAAAGCTGGAATCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000532879.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148683 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007176 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660112-65660113:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCCTTCCAAGGTGAGGGCAAACCTGCCTGCCACACCCGCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000534558.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148684 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007177 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660137-65660138:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCGCATCCAGACCAACAACAACCCCTTCCAAGGTGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526738.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148685 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007178 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660140-65660141:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | CAGTCAGCGCATCCAGACCAACAACAACCCCTTCCAAGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532879.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148686 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007179 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660144-65660145:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTATCAGTCAGCGCATCCAGACCAACAACAACCCCTTCCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000529330.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148687 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007180 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660176-65660177:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCAGTGTGTGAAGAAGCGGGACCTGGAGCAGGCTATCAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000527074.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148688 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007181 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660206-65660207:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGCGCTCAGTTTCCAGAACCTGGGAATCCAGTGTGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000529389.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148689 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007183 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660236-65660237:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCTCTGTGAGAGACAGTGGGACAGACGACTGGGGGCGCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000533546.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148690 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007184 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660244-65660245:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGGTCTGGGCTCTGTGAGAGACAGTGGGACAGACGACTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; MT4; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527874.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148691 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007185 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660369-65660370:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTCAGCTGAGTGAAGGGACAGGGTTCGTTGCAGCACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; LCLs; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000527749.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148692 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007186 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660510-65660511:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GAACATTCCAAGCCGACCAAACAAGTGCAAAGGCCTTGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000308639.13 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148693 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007187 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660528-65660529:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGAGAAGTAGGAAAAGAACATTCCAAGCCGACCAAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000531484.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148694 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007188 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660566-65660567:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GAAGGCCTCCCTCAGCTAAGACTTGAATGGTGAGAAGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000527909.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148695 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007189 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65660711-65660712:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | ATAAATACACAGATAAATAAACAAGGTGCTGTCAGAGTAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_3569893; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000526738.1; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000531238.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148696 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007190 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661701-65661702:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGAGGCTGAGCTCTGCCCGGACCGCTGCATCCACAGGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000529389.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148697 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007191 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661740-65661741:- | [19] | |
| Sequence | CCACGAGCTTGTAGGAAAGGACTGCCGGGATGGCTTCTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527909.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148698 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007192 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661782-65661783:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | CATCTCCCTGGTCACCAAGGACCCTCCTCACCGGCCTCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000615805.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148699 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007194 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661810-65661811:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | ATGGCTACACAGGACCAGGGACAGTGCGCATCTCCCTGGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532776.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148700 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007195 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661817-65661818:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | CAGATCAATGGCTACACAGGACCAGGGACAGTGCGCATCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000534305.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148701 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007196 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661824-65661825:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | CTTTGGACAGATCAATGGCTACACAGGACCAGGGACAGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000533546.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148702 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007197 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661838-65661839:- | [19] | |
| Sequence | TCTGGGCCTCTGTACTTTGGACAGATCAATGGCTACACAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000534305.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148703 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007198 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661895-65661896:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | TGCGGGGAAGGGACTGTGGAACCCCAGCCCTCTGTGTTTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa; MT4; A549; MM6; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148704 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007199 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661903-65661904:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | CCAGGGTGTGCGGGGAAGGGACTGTGGAACCCCAGCCCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa; MT4; A549; MM6; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000531238.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148705 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007200 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65661953-65661954:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GGAGCACAGATACCACCAAGACCCACCCCACCATCAAGGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HeLa; MT4; A549; MM6; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000534283.1; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000534558.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148706 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007201 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65662203-65662204:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GATCTCCCTCCCCTTTCAGAACTGTTCCCCCTCATCTTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000533187.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000534283.1; ENST00000527874.1; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000527749.5; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532776.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148707 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE007202 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65662840-65662841:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | ACCCCGGCCCCGCCCCCGGGACCCCGGCCATGGACGGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; U2OS; A549; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000534558.5; ENST00000532879.5; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000529389.5; ENST00000525301.5; ENST00000534305.1; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000533546.5; ENST00000532776.5; ENST00000527074.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000525858.5; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000531238.1; ENST00000525658.5; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000527909.5; ENST00000612991.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_148708 | ||
N7-methylguanosine (m7G)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: m7GSITE000010 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr11:65655734-65655735:- | [20] | |
| Sequence | CGACCCCCGGCCTCCACCTCGACGCATTGCTGTGCCTTCCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | BoRed-seq&m7G-RIP-seq; m7G-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615805.4; ENST00000532999.5; ENST00000531484.5; ENST00000406246.8; ENST00000525693.5; ENST00000612991.4; ENST00000526283.6; ENST00000308639.13; ENST00000526257.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m7G_site_170 | ||
References