m6A Regulator Information
General Information of the m6A Regulator (ID: REG00020)
| Regulator Name | RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
One-twenty two protein 1; RNA-binding protein 15; OTT; OTT1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | RBM15 | ||||
| Sequence |
MRTAGRDPVPRRSPRWRRAVPLCETSAGRRVTQLRGDDLRRPATMKGKERSPVKAKRSRG
GEDSTSRGERSKKLGGSGGSNGSSSGKTDSGGGSRRSLHLDKSSSRGGSREYDTGGGSSS SRLHSYSSPSTKNSSGGGESRSSSRGGGGESRSSGAASSAPGGGDGAEYKTLKISELGSQ LSDEAVEDGLFHEFKRFGDVSVKISHLSGSGSGDERVAFVNFRRPEDARAAKHARGRLVL YDRPLKIEAVYVSRRRSRSPLDKDTYPPSASVVGASVGGHRHPPGGGGGQRSLSPGGAAL GYRDYRLQQLALGRLPPPPPPPLPRDLERERDYPFYERVRPAYSLEPRVGAGAGAAPFRE VDEISPEDDQRANRTLFLGNLDITVTESDLRRAFDRFGVITEVDIKRPSRGQTSTYGFLK FENLDMSHRAKLAMSGKIIIRNPIKIGYGKATPTTRLWVGGLGPWVPLAALAREFDRFGT IRTIDYRKGDSWAYIQYESLDAAHAAWTHMRGFPLGGPDRRLRVDFADTEHRYQQQYLQP LPLTHYELVTDAFGHRAPDPLRGARDRTPPLLYRDRDRDLYPDSDWVPPPPPVRERSTRT AATSVPAYEPLDSLDRRRDGWSLDRDRGDRDLPSSRDQPRKRRLPEESGGRHLDRSPESD RPRKRHCAPSPDRSPELSSSRDRYNSDNDRSSRLLLERPSPIRDRRGSLEKSQGDKRDRK NSASAERDRKHRTTAPTEGKSPLKKEDRSDGSAPSTSTASSKLKSPSQKQDGGTAPVASA SPKLCLAWQGMLLLKNSNFPSNMHLLQGDLQVASSLLVEGSTGGKVAQLKITQRLRLDQP KLDEVTRRIKVAGPNGYAILLAVPGSSDSRSSSSSAASDTATSTQRPLRNLVSYLKQKQA AGVISLPVGGNKDKENTGVLHAFPPCEFSQQFLDSPAKALAKSEEDYLVMIIVRGFGFQI GVRYENKKRENLALTLL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | RRM Spen family | ||||
| Function |
RNA-binding protein that acts as a key regulator of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation of RNAs, thereby regulating different processes, such as hematopoietic cell homeostasis, alternative splicing of mRNAs and X chromosome inactivation mediated by Xist RNA. Associated component of the WMM complex, a complex that mediates N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation of RNAs, a modification that plays a role in the efficiency of mRNA splicing and RNA processing (By similarity). Plays a key role in m6A methylation, possibly by binding target RNAs and recruiting the WMM complex. Involved in random X inactivation mediated by Xist RNA: acts by binding Xist RNA and recruiting the WMM complex, which mediates m6A methylation, leading to target YTHDC1 reader on Xist RNA and promoting transcription repression activity of Xist. Required for the development of multiple tissues, such as the maintenance of the homeostasis of long-term hematopoietic stem cells and for megakaryocyte (MK) and B-cell differentiation (By similarity). Regulates megakaryocyte differentiation by regulating alternative splicing of genes important for megakaryocyte differentiation; probably regulates alternative splicing via m6A regulation. Required for placental vascular branching morphogenesis and embryonic development of the heart and spleen (By similarity). Acts as a regulator of thrombopoietin response in hematopoietic stem cells by regulating alternative splicing of MPL (By similarity). May also function as an mRNA export factor, stimulating export and expression of RTE-containing mRNAs which are present in many retrotransposons that require to be exported prior to splicing . High affinity binding of pre-mRNA to RBM15 may allow targeting of the mRNP to the export helicase DBP5 in a manner that is independent of splicing-mediated NXF1 deposition, resulting in export prior to splicing . May be implicated in HOX gene regulation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 64783 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Regulator Type | WRITER ERASER READER | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
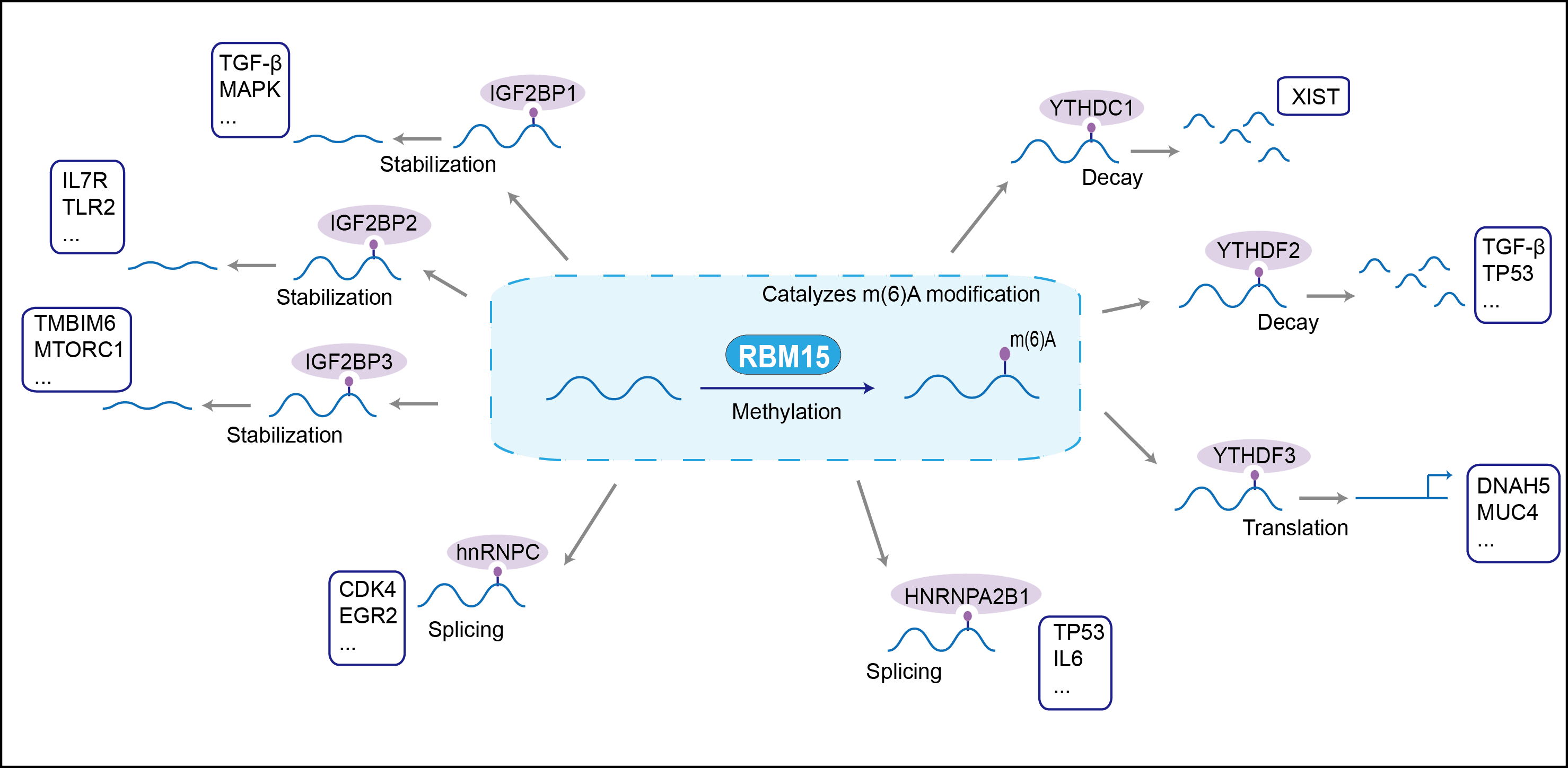
|
|||||
| Target Genes | Click to View Potential Target Genes of This Regulator | ||||
Full List of Target Gene(s) of This m6A Regulator and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
RBM15 can regulate the m6A methylation of following target genes, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulted from the regulation of certain target gene.
Browse Target Gene related Disease
Browse Target Gene related Drug
Bax inhibitor 1 (TMBIM6)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by RBM15 | ||
| Cell Line | Human BJ Fibroblast | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siRBM15 BJ fibroblast
Control: siControl BJ fibroblast
|
GSE154148 | |
| Regulation |
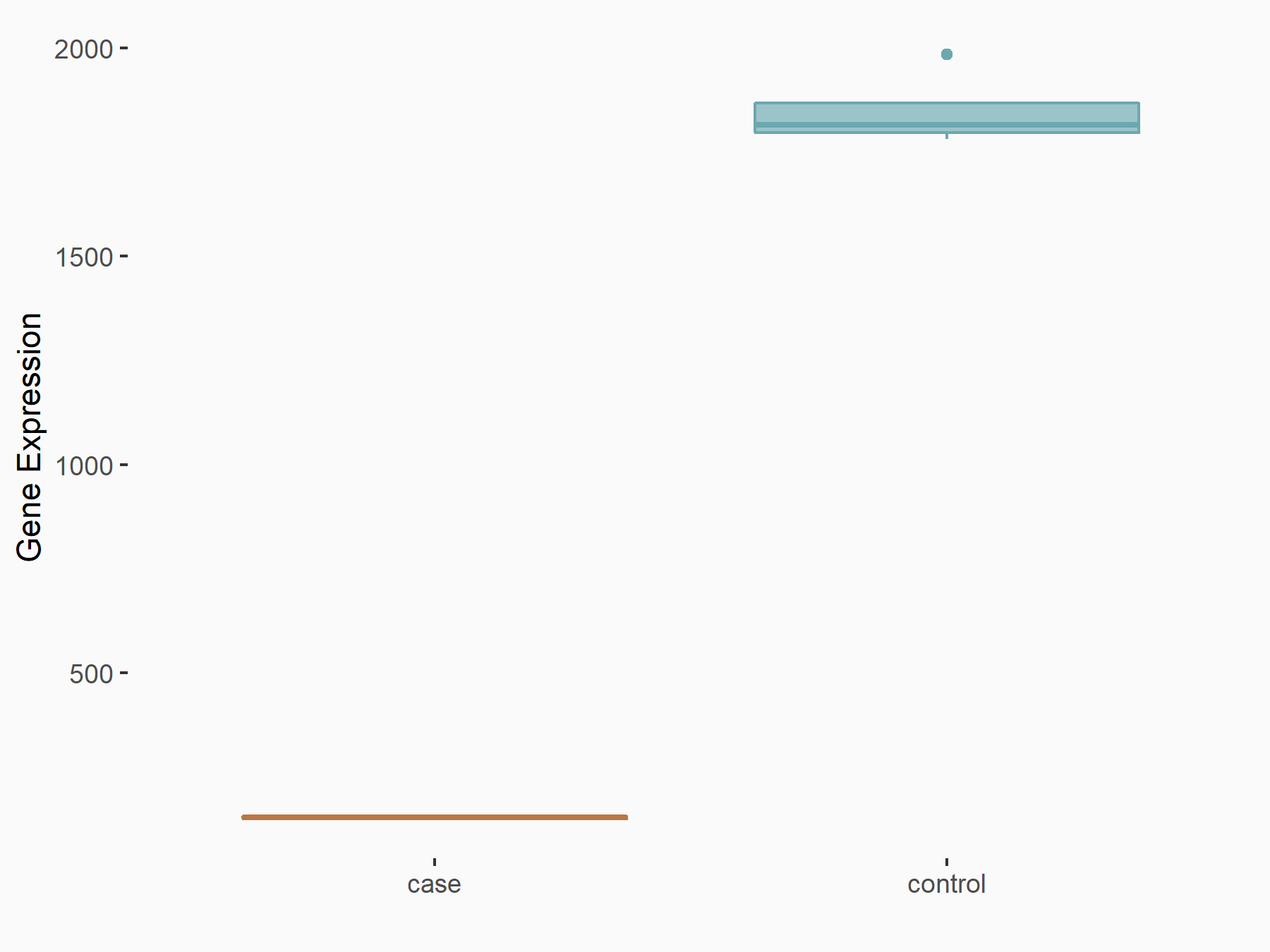  |
logFC: -3.57E+00 p-value: 2.49E-07 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
AMC-HN-8 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5966 |
| NHBEC (Normal human bronchial epithelial cell) | ||||
| Tu 177 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4913 | |
| Tu 212 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4915 | |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor growth studies, whether in vivo RBM15 knockdown/overexpression experiments or in vivo rescue experiments, each group included six mice. Each mouse was injected with 100 uL of lentivirus-transfected tumor cells. | |||
| Response Summary | RBM15-mediated m6A modification of Bax inhibitor 1 (TMBIM6) mRNA enhanced TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3-dependent. Laryngeal squamous cell cancer cells were transfected with shRBM15 lentivirus for 48h, and the qRT-PCR data indicated that the mRNA levels of CPNE5, TMBIM6, and ATAD3A decreased after RBM15 knockdown. | |||
Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88 (MYD88)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by RBM15 | ||
| Cell Line | Human BJ Fibroblast | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siRBM15 BJ fibroblast
Control: siControl BJ fibroblast
|
GSE154148 | |
| Regulation |
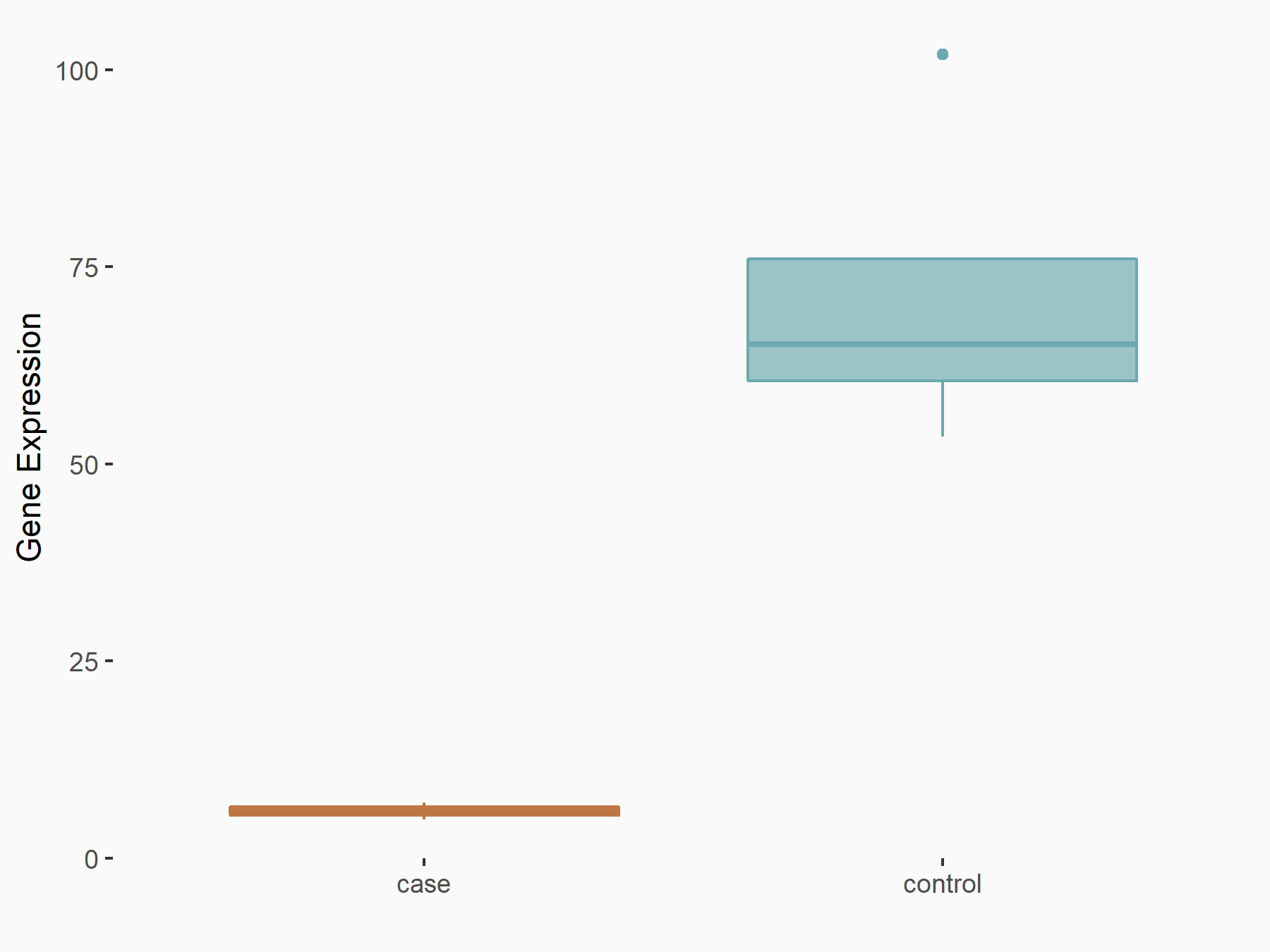 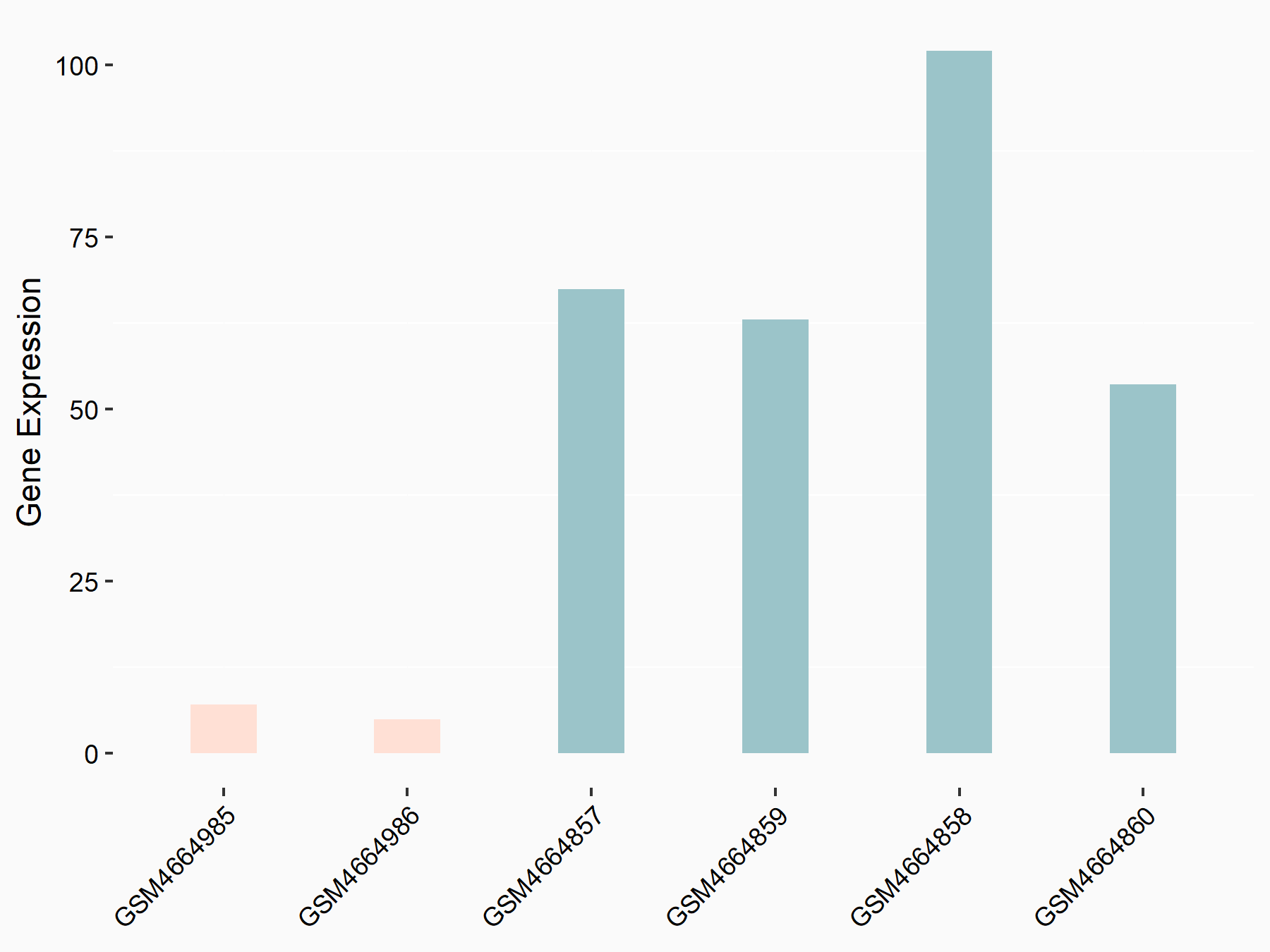 |
logFC: -3.36E+00 p-value: 3.10E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferative | |||
| Cell invasive | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response Summary | RBM15 silencing inhibited the CRC growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. RBM15 mediated m6A methylation modification of Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88 (MYD88) mRNA in colorectal cancer cells. | |||
Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 6 (UBA6)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by RBM15 | ||
| Cell Line | Human BJ Fibroblast | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siRBM15 BJ fibroblast
Control: siControl BJ fibroblast
|
GSE154148 | |
| Regulation |
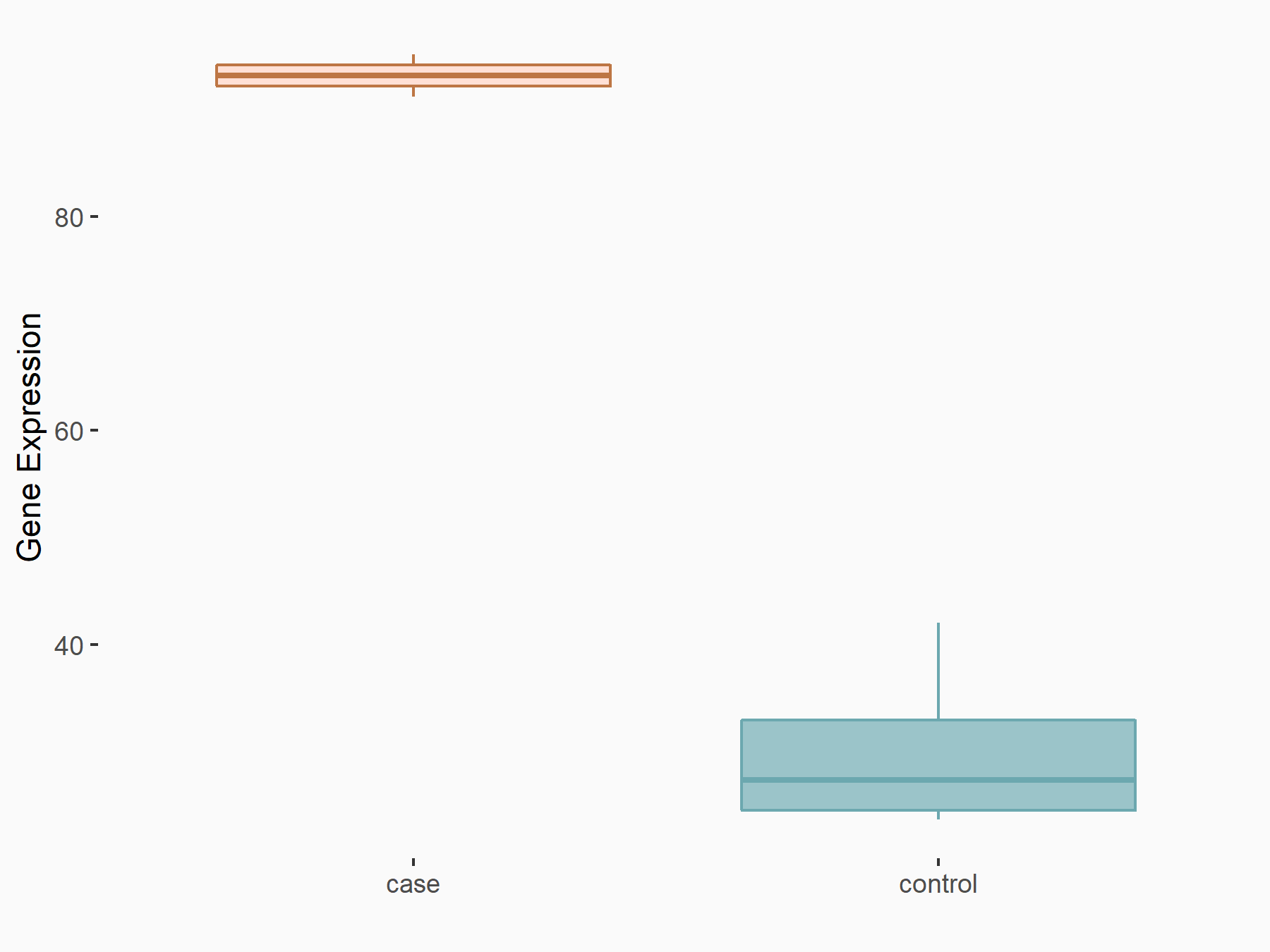 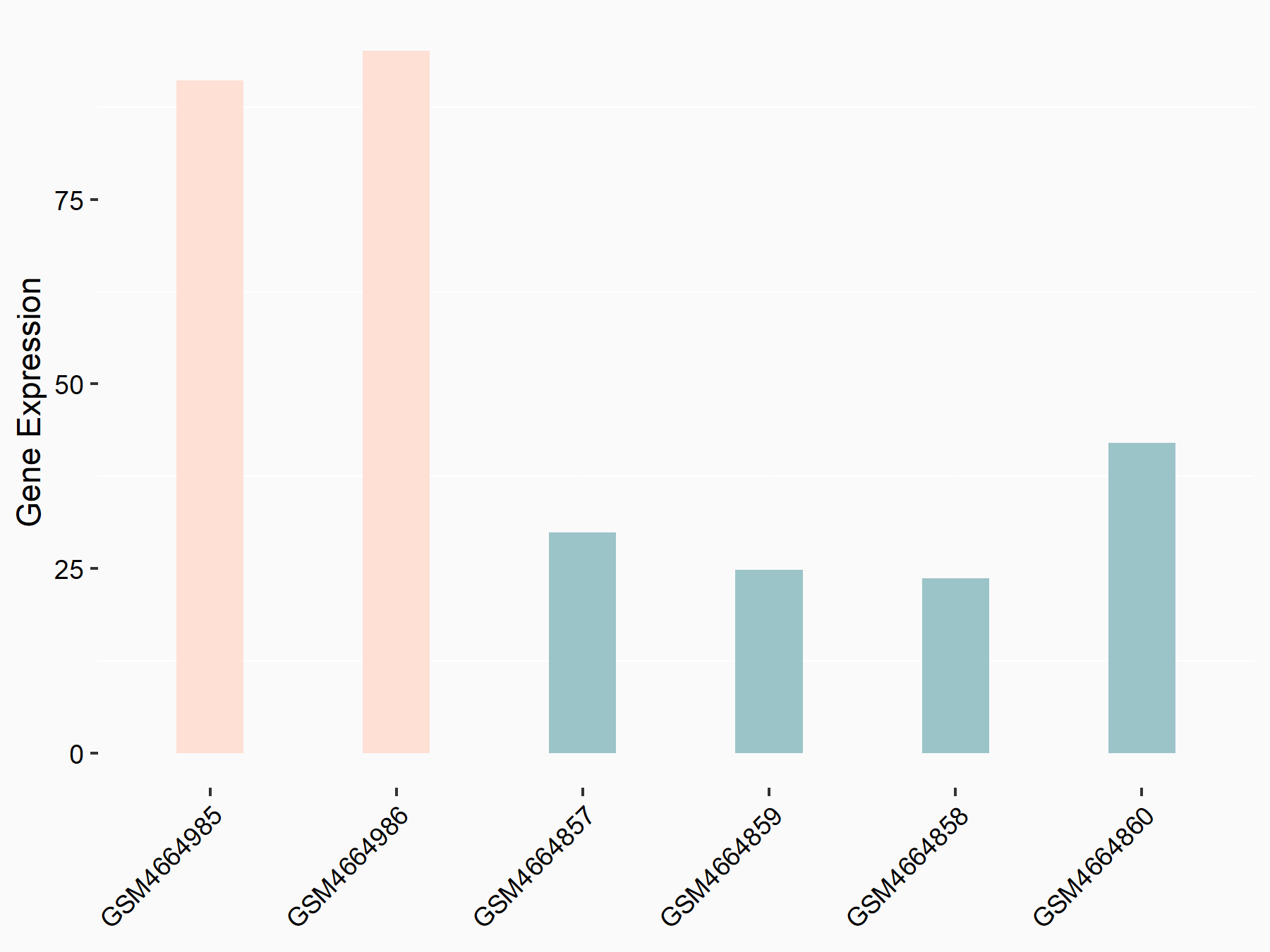 |
logFC: 1.63E+00 p-value: 2.87E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| Response Summary | IGF2BP1 was identified as the m6A reader protein of UBA6-AS1-RBM15-mediated m6A modification of Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 6 (UBA6) mRNA, which enhanced the stability of UBA6 mRNA. UBA6-AS1 suppressed the proliferation, migration and invasion of OC cells via UBA6. | |||
UBA6 divergent transcript (UBA6-DT/UBA6-AS1)
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by RBM15 | ||
| Cell Line | Human BJ Fibroblast | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siRBM15 BJ fibroblast
Control: siControl BJ fibroblast
|
GSE154148 | |
| Regulation |
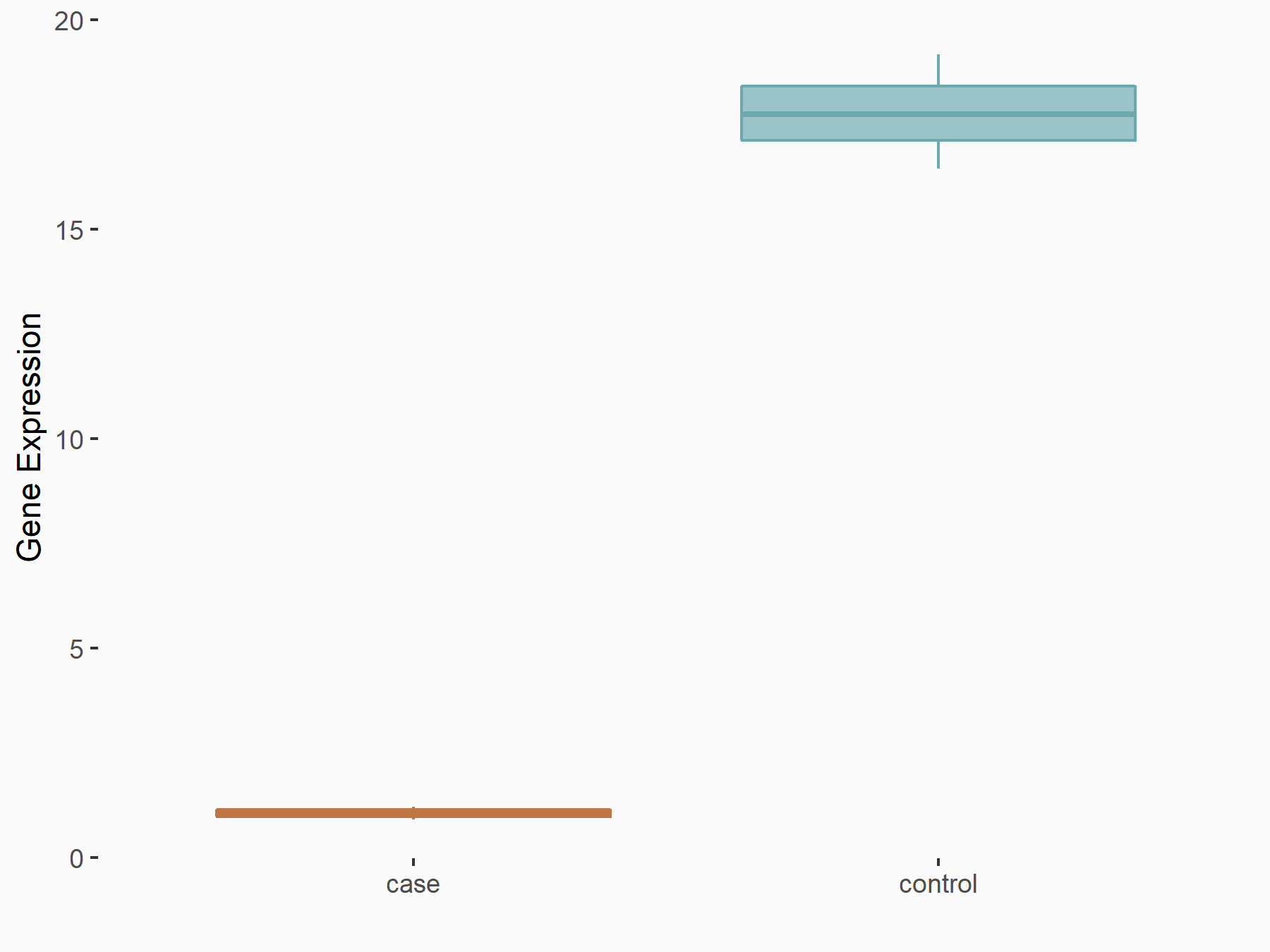 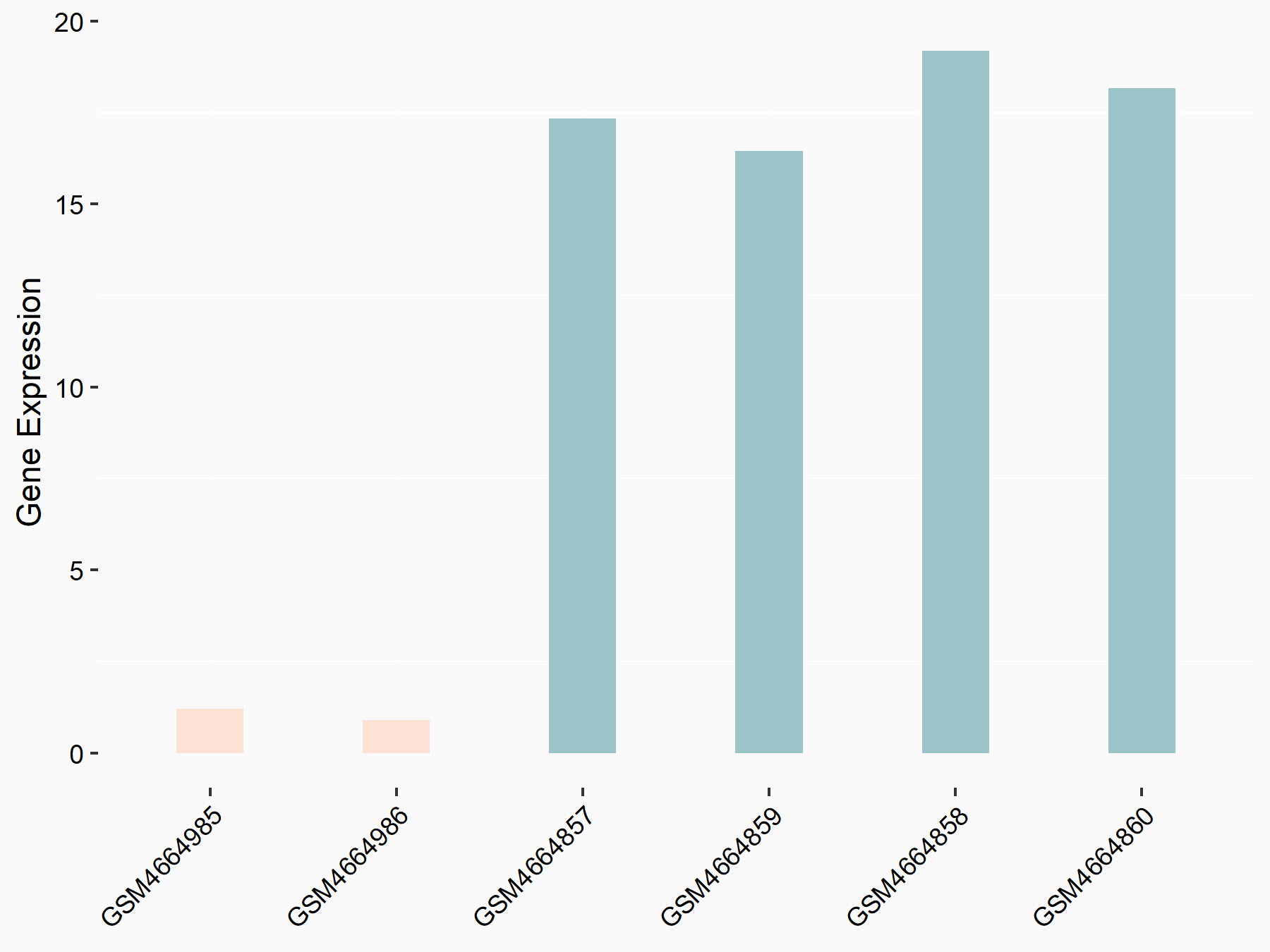 |
logFC: -3.20E+00 p-value: 2.22E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| Response Summary | IGF2BP1 was identified as the m6A reader protein of UBA6 divergent transcript (UBA6-DT/UBA6-AS1)-RBM15-mediated m6A modification of UBA6 mRNA, which enhanced the stability of UBA6 mRNA. UBA6-AS1 suppressed the proliferation, migration and invasion of OC cells via UBA6. | |||
Alpha-enolase (ENO1)
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
T24 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0554 |
| 5637 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0126 | |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1783 | |
| RT-4 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0036 | |
| J82 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0359 | |
| SV-HUC-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3798 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the subcutaneous implantation model, 5 × 106 cells (n = 6 per group) were subcutaneously injected into the flank regions of 4-5 weeks female BALB/c nude mice. Tumor volume was calculated as 0.5 × W2 × L (where W and L represent a tumor's width and length, respectively). After xenografts were generated, DMSOand SB431542 (10 mg/kg, #301836-41-9, SANTA CRUZ BIOTECHNOLOGY), or ENOblock (#1177827-73-4, 9 mg/kg, MCE) were administered daily. All animal experiments were approved by The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University Committee on Animal Care. | |||
ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1 (ABCB1)
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Paclitaxel | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
In-vitro Model |
IOSE-80
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5546 |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 5×106 NC-shRNA- or RBM15-shRNA-infected A2780-PTX cells in 100 μl medium were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of mice (n=5/group). Mice without any intervention were used as blank controls (n=5). Body weight, tumor initiation and tumor progression were monitored every other day for 29 days (day of tumor formation=day 1). | |||
ATPase family AAA domain-containing protein 3A (ATAD3A)
Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
AMC-HN-8 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5966 |
| NHBEC (Normal human bronchial epithelial cell) | ||||
| Tu 177 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4913 | |
| Tu 212 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4915 | |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor growth studies, whether in vivo RBM15 knockdown/overexpression experiments or in vivo rescue experiments, each group included six mice. Each mouse was injected with 100 uL of lentivirus-transfected tumor cells. | |||
| Response Summary | RBM15-mediated m6A modification of TMBIM6 mRNA enhanced TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3-dependent. Laryngeal squamous cell cancer cells were transfected with shRBM15 lentivirus for 48h, and the qRT-PCR data indicated that the mRNA levels of CPNE5, TMBIM6, and ATPase family AAA domain-containing protein 3A (ATAD3A) decreased after RBM15 knockdown. | |||
C-X-C motif chemokine 11 (CXCL11)
Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mRNA surveillance pathway | hsa03015 | ||
| RNA degradation | hsa03018 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HK-2 [Human kidney] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| Caki-2 | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0235 | |
| Caki-1 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0234 | |
| 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 5 × 106 786O cells were subcutaneously injected into the left flanks of the mice. | |||
| Response Summary | RBM15 enhanced the stability of C-X-C motif chemokine 11 (CXCL11) mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. These findings highlight the function of RBM15 in ccRCC and reveal a novel identified EP300/CBP-RBM15-CXCL11 signaling axis, which promotes ccRCC progression and provides new insight into ccRCC therapy. | |||
Copine-5 (CPNE5)
Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In-vitro Model |
AMC-HN-8 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5966 |
| NHBEC (Normal human bronchial epithelial cell) | ||||
| Tu 177 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4913 | |
| Tu 212 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4915 | |
| In-vivo Model | For tumor growth studies, whether in vivo RBM15 knockdown/overexpression experiments or in vivo rescue experiments, each group included six mice. Each mouse was injected with 100 uL of lentivirus-transfected tumor cells. | |||
| Response Summary | RBM15-mediated m6A modification of TMBIM6 mRNA enhanced TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3-dependent. Laryngeal squamous cell cancer cells were transfected with shRBM15 lentivirus for 48h, and the qRT-PCR data indicated that the mRNA levels of Copine-5 (CPNE5), TMBIM6, and ATAD3A decreased after RBM15 knockdown. | |||
Hexokinase-2 (HK2)
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)
Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease [ICD-11: DB9Z] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Rapamycin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and apoptosis | |||
| In-vivo Model | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) AB strain-derived Tg(lfabp:Dendra2-NTR)cq1 was used as WT, and rbm15cq96 mutant was generated by ENU treatment. | |||
| Response Summary | Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway is highly activated in rbm15-deficient hepatocytes. Rapamycin treatment partially restored normal hepatic gene expression as well as the nuclear location of the transcription factor Hnf4a. Taken together, these results reveal an unexpected role of Rbm15 in liver maturation. | |||
Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| In-vivo Model | (1) Lenti-NC and Lenti-vector were injected into caudal vein in group A; (2) Lenti-NC and Lenti-RBM15 OE were injected into caudal vein in group B; (3) Lenti-E6 shRNA and Lenti-vector were injected into caudal vein in group C; (4) Lenti-E6 shRNA and Lenti-RBM15 OE were injected into caudal vein in group D. The dosage of each lentivirus tail vein injection is 108 TU/animal. | |||
Yes tyrosine kinase (YES/YES1)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HCC-LM3 (HCC-LM3 were obtained from Guangzhou Cellcook Biotech Co., Ltd.) | |||
| MHCC97-H | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4972 | |
| B76.1/Huh7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U443 | |
| In-vivo Model | 5 × 106 Huh7 and HCC-LM3 cells resuspended in 100ul PBS were subcutaneously injected to the left flank of the mice (randomly selected, five mice per group for Huh7 cells in the first time and ten mice per group for HCC-LM3 cells in the second time. No blinding was performed). | |||
| Response Summary | RBM15-mediated m6A modification contributed to a post-transcriptional activation of Yes tyrosine kinase (YES/YES1) in an IGF2BP1-dependent manner. RBM15-mediated m6A modification facilitate the progression of HCC via the IGF2BP1-YES1-MAPK axis. | |||
Chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs)
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.1] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell survival | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell differentiation | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| Apoptosis | ||||
Claudin-4 (CLDN4)
Gestational diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: JA63]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gestational diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: JA63] | |||
In-vitro Model |
L-02 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 |
| In-vivo Model | GDM group and control group. GDM group was fed with high-fat diet (Research Diets D12451) for 1 week to mating and throughout pregnancy, while control group was fed with normal diet (Research Diet 1022). Then the two groups were mated with age-matched male mice. The presence of a vaginal plug was considered gestational day (GD) 0.5. Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and insulin tolerance test (ITT) were performed at GD0.5, GD11.5, and GD16.5. Six mice of each group were killed at GD18.5 to collect the liver tissue of the fetus. The remaining mice were left to delivery. All female offspring were selected for this study. Fetus weaning was done and then was separately fed with a standard diet for 12 weeks. OGTT and ITT were performed at 12 weeks. Then F1 generation was killed to collect serum and liver tissue. | |||
Decorin (DCN)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [13] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
CC
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_E520 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Ca Ski | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1100 | |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF5 (RNF5)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [14] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI)
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 (KRT17)
Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [15] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1)
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Semaphorin-3F (SEMA3F)
Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [16] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
In-vitro Model |
RWPE-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3791 |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | |
| PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 | |
| 22Rv1 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1045 | |
| LNCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0395 | |
| LNCaP C4-2B | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4784 | |
| VCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2235 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| In-vivo Model | All the animal studies and protocols followed the institutional guidelines of the First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University. | |||
Transcription factor E2F2 (E2F2)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 (TRIM72)
Preeclampsia [ICD-11: JA23]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Preeclampsia [ICD-11: JA23] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
Ubiquitin thioesterase OTUB2 (OTUB2)
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Ect1/E6E7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3679 |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MS751 | Human papillomavirus-related cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4996 | |
| C-33 A | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1094 | |
| ME-180 | Human papillomavirus-related cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1401 | |
| SiHa | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0032 | |
Unspecific Target Gene
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Response Summary | The prediction model was established based on the expression of m6A RNA methylation regulators FTO (fat mass and obesity-associated) and RBM15 (RNA binding motif protein 15). The two-methylase combination model was an independent prognostic factor of GC. | |||
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Response Summary | Pan-cancer analysis of RBM15 suggested it is served as a prognostic biomarker and immunotherapeutic target for PAAD. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [23] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
Myasthenia gravis [ICD-11: 8C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [24] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Myasthenia gravis [ICD-11: 8C60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
COVID-19 [ICD-11: RA01]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [25] | |||
| Responsed Disease | COVID-19 [ICD-11: RA01] | |||
| Cell Process | Programmed cell death | |||
| Inflammatory response | ||||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HuT 78 | T lymphocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0337 | |
| Response Summary | Knockdown of RBM15 remarkably suppressed the expression levels of multitarget genes related to programmed cell death and inflammatory response. These findings indicate that RBM15 can serve as a target for the treatment of COVID-19. | |||
ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1 (ABCB1)
Paclitaxel
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| In-vitro Model |
IOSE-80
|
N.A. | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5546 |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| In-vivo Model | A total of 5×106 NC-shRNA- or RBM15-shRNA-infected A2780-PTX cells in 100 μl medium were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of mice (n=5/group). Mice without any intervention were used as blank controls (n=5). Body weight, tumor initiation and tumor progression were monitored every other day for 29 days (day of tumor formation=day 1). | |||
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver disease | ICD-11: DB9Z | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation and apoptosis | |||
| In-vivo Model | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) AB strain-derived Tg(lfabp:Dendra2-NTR)cq1 was used as WT, and rbm15cq96 mutant was generated by ENU treatment. | |||
| Response Summary | Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway is highly activated in rbm15-deficient hepatocytes. Rapamycin treatment partially restored normal hepatic gene expression as well as the nuclear location of the transcription factor Hnf4a. Taken together, these results reveal an unexpected role of Rbm15 in liver maturation. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
DNA modification
m6A Target: Semaphorin-3F (SEMA3F)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02015 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Semaphorin-3F (SEMA3F) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
| Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| Drug | Docetaxel | |
Histone modification
m6A Target: C-X-C motif chemokine 11 (CXCL11)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03173 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney | |
| Drug | SETDB1-TTD-IN-1 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03174 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9Ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney | |
| Drug | SETDB1-TTD-IN-1 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03175 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney | |
| Drug | SETDB1-TTD-IN-1 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03176 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9Ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal cell carcinoma of kidney | |
| Drug | SETDB1-TTD-IN-1 | |
m6A Target: Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 (TRIM72)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03216 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Preeclampsia | |
| Drug | Actinomycin D | |
m6A Target: Chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05954 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Myeloid leukaemia | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Target: Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 (FAS)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05203 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | FTO intronic transcript 1 (FTO-IT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
m6A Target: Tumor protein p53-inducible nuclear protein 1 (TP53INP1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05204 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | FTO intronic transcript 1 (FTO-IT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
m6A Target: Sestrin-2 (SESN2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05205 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | FTO intronic transcript 1 (FTO-IT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
m6A Target: Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 6 (UBA6)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05339 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | UBA6 divergent transcript (UBA6-DT/UBA6-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
m6A Target: Hexokinase-2 (HK2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05347 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_CTNNB1 | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteosarcoma | |
m6A Target: Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05348 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_CTNNB1 | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteosarcoma | |
m6A Target: Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05349 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Circ_CTNNB1 | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteosarcoma | |
m6A Target: X inactive specific transcript (XIST)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05458 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | X inactive specific transcript (XIST) | |
| Regulated Target | Glypican-4 (GPC4) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06026 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | X inactive specific transcript (XIST) | |
| Regulated Target | Transcriptional regulator ATRX (ATRX) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: UBA6 divergent transcript (UBA6-DT/UBA6-AS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05591 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | UBA6 divergent transcript (UBA6-DT/UBA6-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 6 (UBA6) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
Xenobiotics Compound(s) Regulating the m6A Methylation Regulator
| Compound Name | Rapamycin | Approved |
|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Rapamune; Rapamycin (Sirolimus); AY-22989; Rapammune; sirolimusum; WY-090217; RAPA; Antibiotic AY 22989; AY 22989; UNII-W36ZG6FT64; CCRIS 9024; CHEBI:9168; SILA 9268A; W36ZG6FT64; HSDB 7284; C51H79NO13; NSC 226080; DE-109; NCGC00021305-05; DSSTox_CID_3582; DSSTox_RID_77091; DSSTox_GSID_23582; Cypher; Supralimus; Wy 090217; Perceiva; RAP; RPM; Rapamycin from Streptomyces hygroscopicus; SIIA 9268A; LCP-Siro; MS-R001; Rapamune (TN); Rapamycin (TN); Sirolimus (RAPAMUNE); Rapamycin C-7, analog 4; Sirolimus (USAN/INN); Sirolimus [USAN:BAN:INN]; Sirolimus, Rapamune,Rapamycin; Heptadecahydro-9,27-dihydroxy-3-[(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy; 23,27-Epoxy-3H-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclohentriacontine; 23,27-Epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine; 23,27-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29; 3H-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone; Sirolimus (MTOR inhibitor)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway is highly activated in rbm15-deficient hepatocytes. Rapamycin treatment partially restored normal hepatic gene expression as well as the nuclear location of the transcription factor Hnf4a. Taken together, these results reveal an unexpected role of Rbm15 inliver maturation.
|
[8] |
| Compound Name | Tretinoin | Investigative |
| Synonyms |
Retinoic acid; tretinoin; 302-79-4; all-trans-Retinoic acid; Vitamin A acid; trans-Retinoic acid; ATRA; Airol; Retin-A; Vesanoid; Aberel; Eudyna; Renova; All-trans Retinoic Acid; all-trans-Vitamin A acid; Dermairol; Aknoten; Aknefug; Cordes vas; Epi-aberel; TRETINON; Tretin M; Atralin; all-trans-Vitamin A1 acid; all-trans-Tretinoin; Retionic acid; All Trans Retinoic Acid; Vitamin A1 acid, all-trans-; Retin-A Micro; Retin A; beta-Retinoic acid; all-(E)-Retinoic acid; Vitamin A acid, all-trans-; Retinoate; (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid; Retinoic acid, all-trans-; Alltrans-retinoic acid; Retacnyl; Vesnaroid; NSC-122758; Ro 1-5488; Tretinoin, all-trans-; all trans-Retinoic acid; Stieva-A; Tretinoine; Solage; all-trans-beta-Retinoic acid; Effederm; .beta.-Retinoic acid; Tretinoin/All-Trans Retinoic Acid; Aberela [Norway]; Avitoin [Norway]; Effederm [France]; UNII-5688UTC01R; A-Acido (Argentina); 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; (all-E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; MLS000028588; b-Retinoic acid; RETINOIC ACID, ALL TRANS; Tretinoine [INN-French]; Tretinoinum [INN-Latin]; AT-RA; Tretinoina [INN-Spanish]; Tretinoino [INN-Spanish]; CHEMBL38; (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid; 2,4,6,8-Nonatetraenoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (all-E)-; MFCD00001551; NSC122758; Atragen; Retinova; SMR000058245; (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid; CHEBI:15367; 15-Apo-beta-caroten-15-oic acid; 5688UTC01R; Tretinoin (TN); beta-Ra; Acnavit [Denmark]; AGN 100335; REA; 9-cis-RA; Retin A (TN); NCGC00017280-10; Tretinoinum; Aberela; Acnavit; Avitoin; Betarretin; Tretinoina; Tretinoino; A-Vitaminsyre; all-trans-b-Retinoic acid; DSSTox_CID_1239; Cordes VAS [Germany]; A-Vitaminsyre [Denmark]; 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid (ECL); DSSTox_RID_76031; DSSTox_GSID_21239; trans-Retinoate; beta-Retinoate; tretinoine (French) (EINECS); cis-Retinoic acid; Acide retinoique (French) (DSL); Refissa; Nexret; Vitamin a acid, trans-; Retisol-A; Acid A Vit (Belgium, Netherlands); 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid; 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2E,4E,6E,8E-tetraenoic acid; (11Z)-retinoic acid; (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid; [3H]Retinoic acid; Renova (TN); CCRIS 3294; Avita (TN); HSDB 2169; SR-01000000239; EINECS 206-129-0; NSC 122758; BRN 2057223; Tretinoin (JAN/USP/INN); Kerlocal; Retinoic acid, cis-9,trans-13-; TNP00194; Oristar rna; BML2-E05; DTXSID7021239; 1cbr; [3H]tretinoin; [All-E]-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; Tretinoin [USAN:USP:INN:BAN]; CAS-302-79-4; Prestwick_424; all-(E)-Retinoate; Tretinoine (French); Retinoic acid, cis-; (5E)-Retinoic acid; [3H]Vitamin A acid; 1n4h; CPD000058245; Retinoic acid all trans; 6-s-trans-retinoic acid; Vitamin-A-sA currencyure; Opera_ID_1055; Prestwick2_000257; Prestwick3_000257; Spectrum5_001746; Spectrum5_001933; acide retinoique (French); Vesanoid (TN) (Roche); Tretinoin - Retinoic Acid; bmse000562; UPCMLD-DP097; R 2625; Renova (0.02% cream); SCHEMBL3145; (9Z,13Z)-Retinoic acid; 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-2,4,6,8-all-trans-tetraenoic acid; Altreno (0.05% lotion); BIDD:PXR0081; Lopac0_001061; Avita (0.025% gel); BSPBio_000074; BSPBio_001500; MLS001076515; MLS002207234; MLS002222211; MLS002548861; MLS006010222; BIDD:GT0483; SPECTRUM1502016; 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cRA); [3H]RA; BPBio1_000082; cid_444795; GTPL2644; .beta.-all-trans-Retinoic acid; all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA); SCHEMBL19091395; BDBM31883; HMS502N05; QCR-120; BCPP000036; BDBM323588; HMS1361K22; HMS1568D16; HMS1791K22; HMS1921D14; HMS1989K22; HMS2089D20; HMS2092N11; HMS2095D16; HMS2236N03; HMS3259E11; HMS3263E04; HMS3402K22; HMS3411B09; HMS3675B09; HMS3712D16; Pharmakon1600-01502016; Retinoic acid, all-trans- (8CI); 124510-04-9; 2,4,6,8-Nonatetraenoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-; 68070-35-9; ACT00012; BCP01405; US10188615, at-RA; Tox21_110812; Tox21_202330; Tox21_300305; Tox21_501061; All-trans Retinoic Acid (Tretinoin); CCG-39912; LMPR01090019; NSC759631; s1653; ZINC12358651; AKOS000280845; Tox21_110812_1; AC-6824; CS-1269; DB00755; GS-3578; LP01061; NC00481; NSC-759631; SDCCGSBI-0051031.P004; IDI1_000903; IDI1_033970; NCGC00017280-05; NCGC00017280-06; NCGC00017280-07; NCGC00017280-08; NCGC00017280-09; NCGC00017280-12; NCGC00017280-15; NCGC00017280-16; NCGC00017280-17; NCGC00017280-18; NCGC00017280-19; NCGC00017280-20; NCGC00017280-23; NCGC00017280-38; NCGC00021808-04; NCGC00021808-05; NCGC00021808-06; NCGC00021808-07; NCGC00021808-09; NCGC00021808-11; NCGC00021808-14; NCGC00021808-15; NCGC00254179-01; NCGC00259879-01; NCGC00261746-01; trans-Retinoic acid; ; ; Retinoid analogues; BP-20401; BR164493; HY-14649; Retinoic acid, >=98% (HPLC), powder; SBI-0051031.P003; EU-0101061; R0064; SW203749-4; 02T794; C00777; D00094; J10054; Q29417; AB00052318-15; AB00052318-16; AB00052318-17; AB00052318_18; AB00052318_19; A899883; L000833; Q-200610; SR-01000000239-3; SR-01000000239-4; SR-01000000239-6; SR-01000000239-7; BRD-K06926592-001-01-7; BRD-K71879491-001-15-0; BRD-K71879491-001-22-6; SR-01000000239-12; SR-01000000239-13; SR-01000000239-14; SR-01000000239-15; WLN: L6UTJ A1 B1U1Y1&U2U1Y1&U1VQ C1 C1; Tretinoin, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; WLN: L6UTJ A1 B1U1Y1 & U2U1Y1 & U1VQ C1 C1; Tretinoin, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 3,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; Tretinoin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; (2E,4E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; (4E,6E,8E)-9-(2,6,6-Trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; (all-E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoate; 2,4,6,8-Nonatetranoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-; 2,6,8-Nonatetranoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-; 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoate; 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2E,4E,6E,8E,-nonatetraenoic acid; all-trans-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid; 2,4, 6,8-Nonatetranoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6, 6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (2E, 4E, 6E, 8E)-; 2,4,6,8-Nonatetraenoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)--, (all trans)-; 2,4,6,8-Nonatetranoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (all trans)-; 2,6,8-Nonatetraenoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (all-E)-; 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid-, (all trans)-; 97950-17-9
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
To obtain and identify the differential proteome of apoptosis induced by realgar (tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide, As(4)S(4)) in retinoid acid (RA) resistant human acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cell line NB4-R1 cells.up-regulated RBM15 after exposed for 48 h.
|
[26] |
References