m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00185)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
ATF4
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
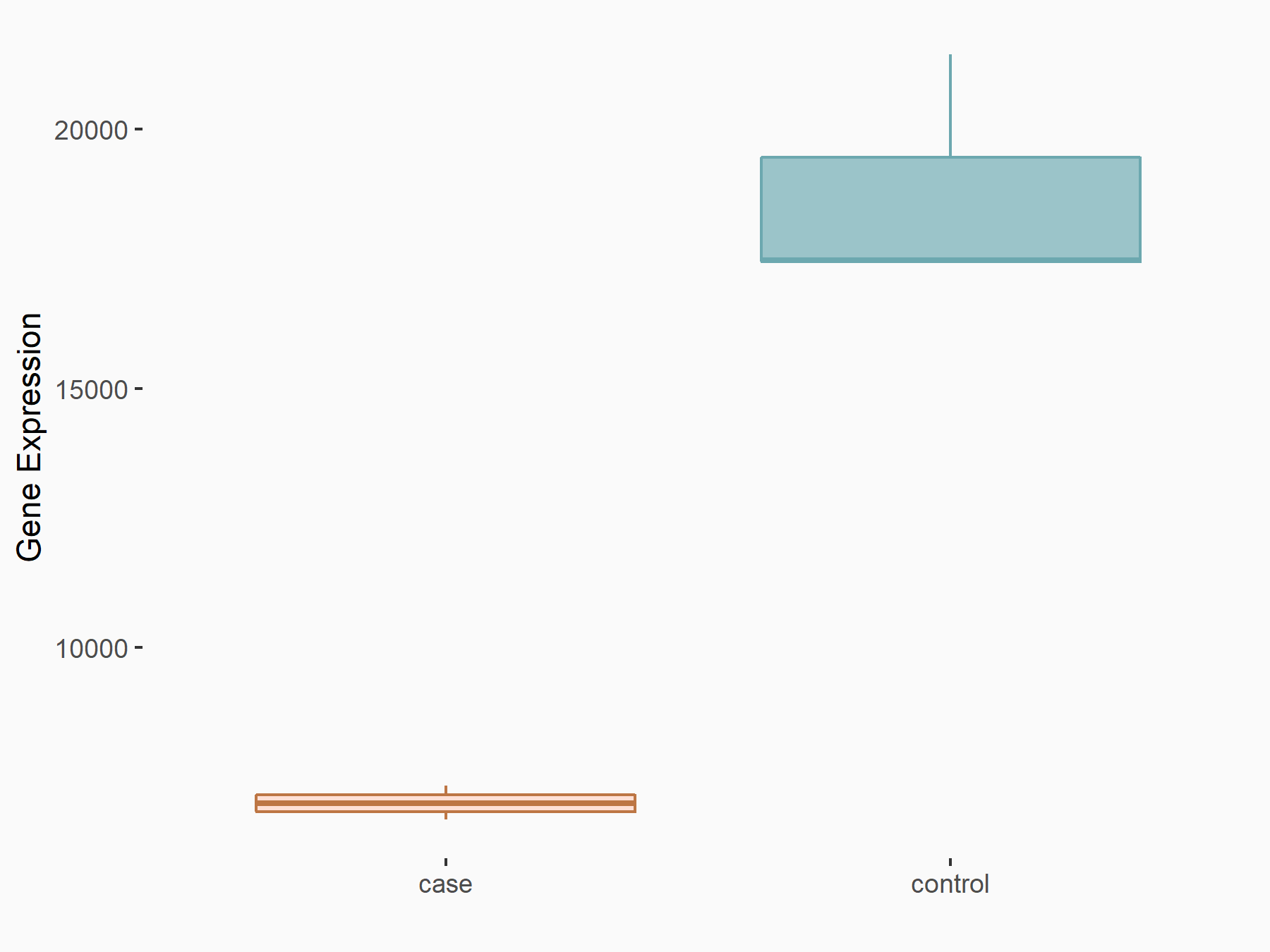 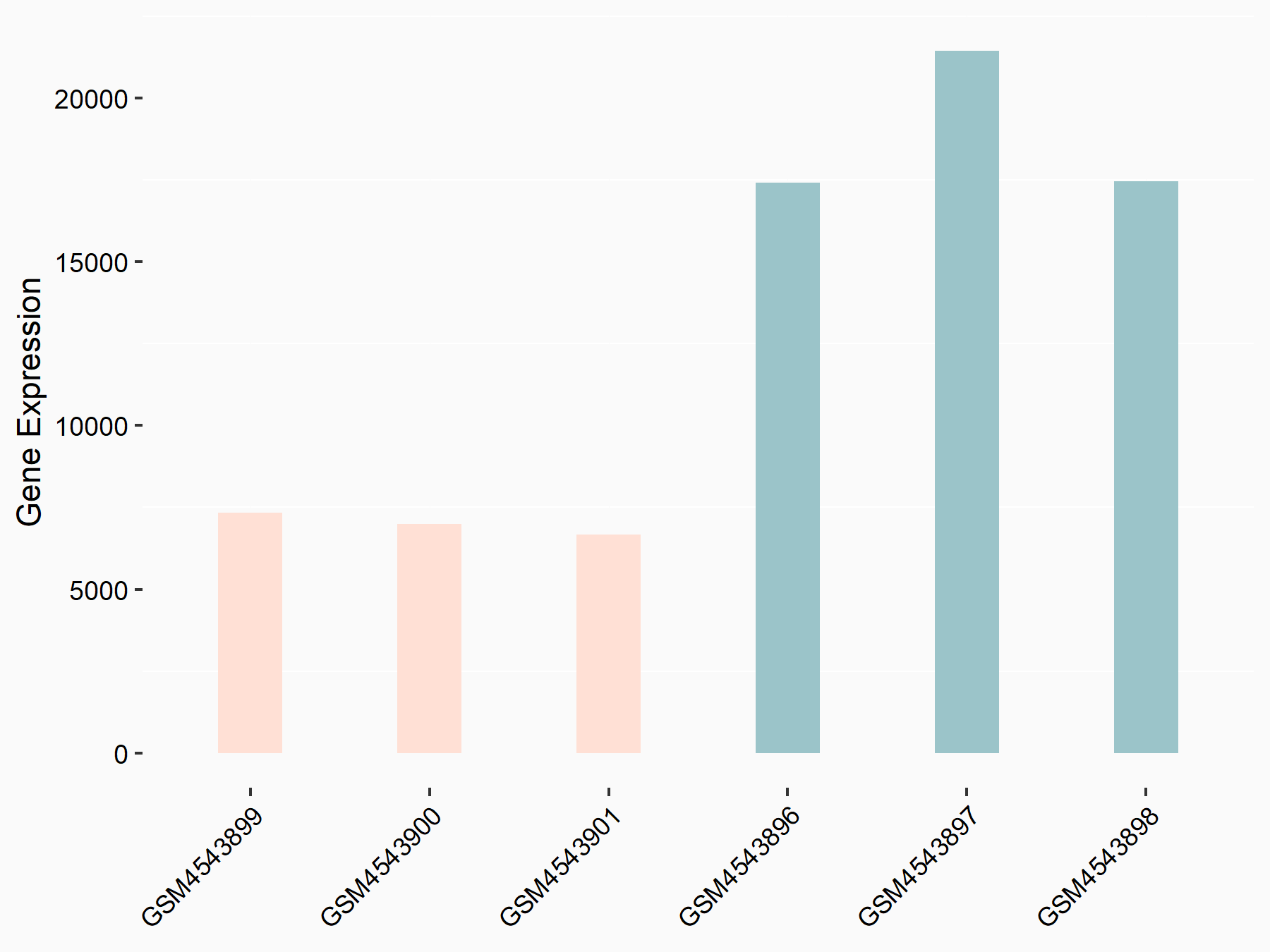 |
logFC: -1.42E+00 p-value: 2.68E-47 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 4 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Chloroquine | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | CB-839 | Phase 2 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by WTAP | ||
| Cell Line | mice hepatocyte | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: Wtap Hknockout mice hepatocyte
Control: Wtap flox/flox mice hepatocyte
|
GSE168850 | |
| Regulation |
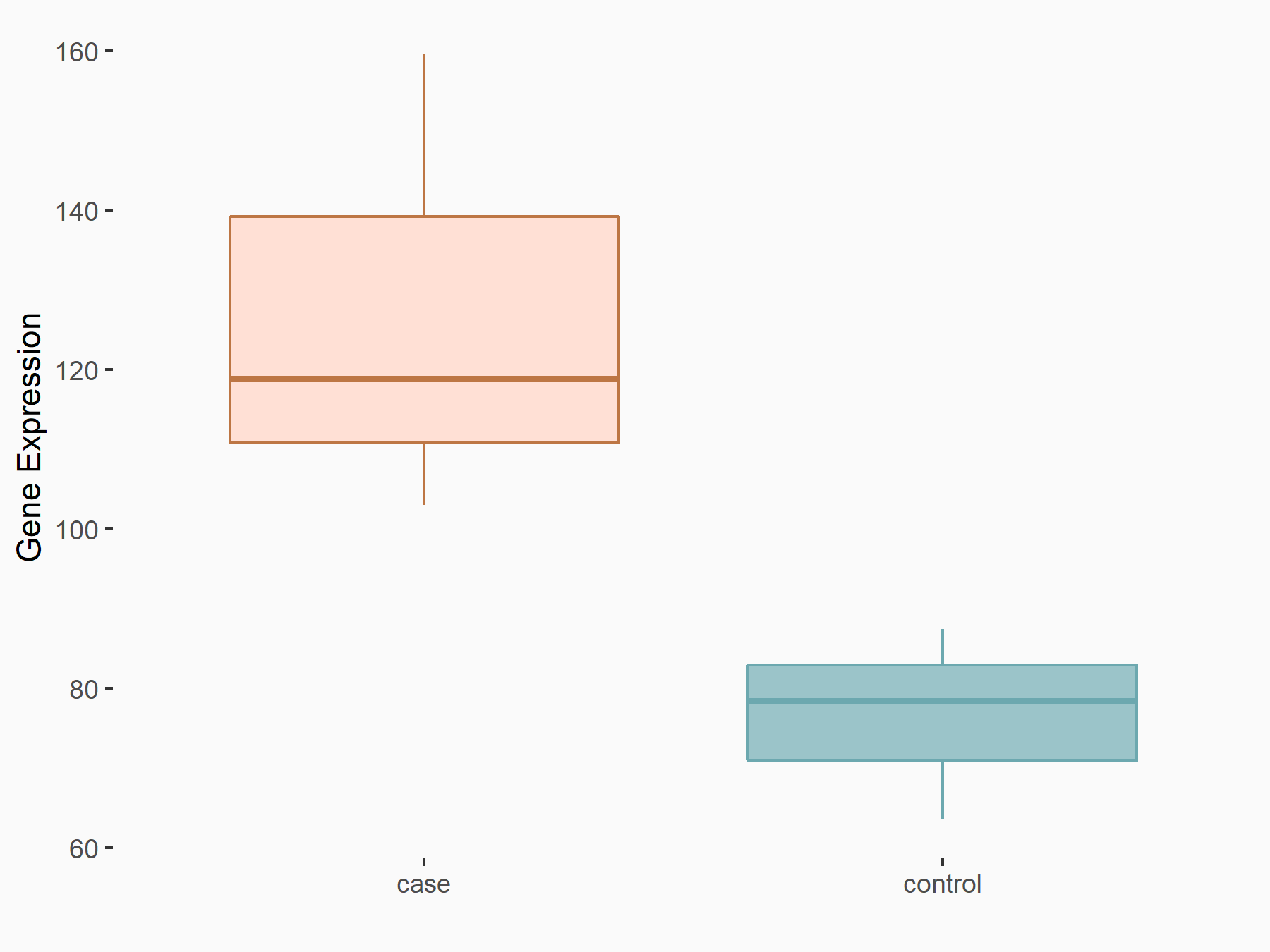 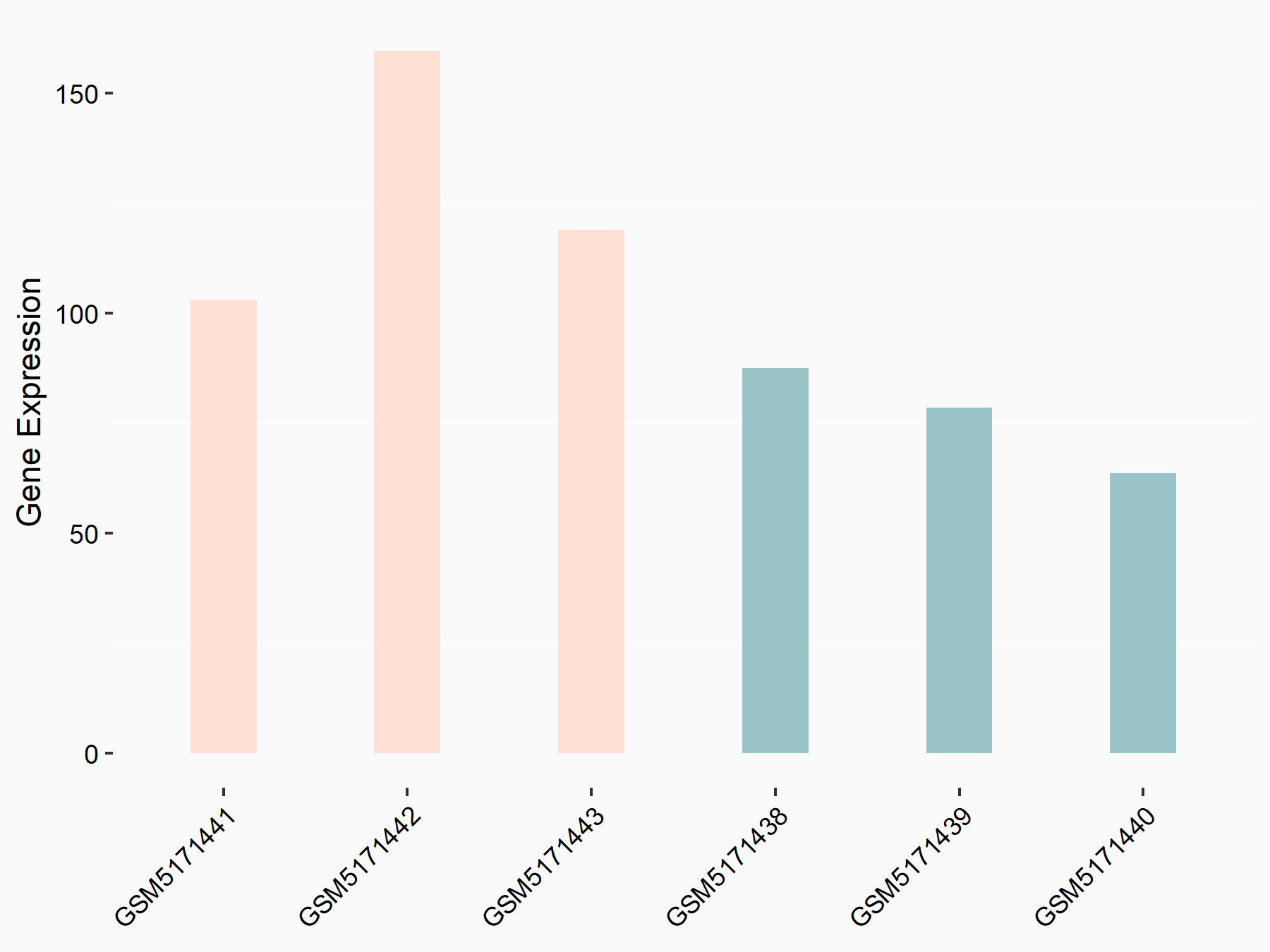 |
logFC: 7.14E-01 p-value: 2.43E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Myocardial infarction (MI) is one of the leading causes of death. WTAP promoted myocardial I/R injury through promoting ER stress and cell apoptosis by regulating m6A modification of Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) mRNA. H/R effects on ER stress and apoptosis were all blocked by silencing of WTAP, promoted by WTAP overexpression, and ameliorated by administration of ER stress inhibitor, 4-PBA. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction | ICD-11: BA41 | ||
| Cell Process | Endoplasmic reticulum stress | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | AC16 [Human hybrid cardiomyocyte] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4U18 |
| In-vivo Model | Left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) was ligated for 20 minutes, followed by 48 h reperfusion. Controls underwent same procedures except LAD ligation. WTAP shRNA vector or its negative control (shNC) was injected into the left ventricular anterior wall 24 h before I/R. A pressure volume catheter was used for cardiac function assay. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| In total 4 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Chloroquine | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Drug | CB-839 | Phase 2 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 4 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Drug | Chloroquine | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Drug | CB-839 | Phase 2 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Myocardial infarction (MI) is one of the leading causes of death. WTAP promoted myocardial I/R injury through promoting ER stress and cell apoptosis by regulating m6A modification of Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) mRNA. H/R effects on ER stress and apoptosis were all blocked by silencing of WTAP, promoted by WTAP overexpression, and ameliorated by administration of ER stress inhibitor, 4-PBA. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41] | |||
| Target Regulator | Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Endoplasmic reticulum stress | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | AC16 [Human hybrid cardiomyocyte] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4U18 |
| In-vivo Model | Left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) was ligated for 20 minutes, followed by 48 h reperfusion. Controls underwent same procedures except LAD ligation. WTAP shRNA vector or its negative control (shNC) was injected into the left ventricular anterior wall 24 h before I/R. A pressure volume catheter was used for cardiac function assay. | |||
Asparagine inhibitor
[Approved]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Chloroquine
[Approved]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Meclofenamate sodium
[Approved]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Rapamycin
[Approved]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
CB-839
[Phase 2]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress mTOR, which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
GLS-IN-968
[Investigative]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 6 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03334 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Rapamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03335 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | GLS-IN-968 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03336 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | CB-839 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03337 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03338 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Chloroquine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03339 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | |
m6A Regulator: Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO)
| In total 6 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03432 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Rapamycin | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03433 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | GLS-IN-968 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03434 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | CB-839 | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03435 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Meclofenamate sodium | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03436 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Chloroquine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03437 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Drug | Asparagine inhibitor | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00185)
| In total 3 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000300 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521399-39521400:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTGCTGTAACCGACAAAGACACCTTCGAATTAAGCACATTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293 | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_4856 | ||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000301 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521400-39521401:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGCTGTAACCGACAAAGACACCTTCGAATTAAGCACATTCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293 | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_4857 | ||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000302 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521403-39521404:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGTAACCGACAAAGACACCTTCGAATTAAGCACATTCCTCG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_4858 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 4 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002926 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521497-39521498:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GTTGGTGGGGGACTTGATGTCCCCCTTCGACCAGTCGGGTT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30981 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002927 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521498-39521499:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TTGGTGGGGGACTTGATGTCCCCCTTCGACCAGTCGGGTTT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30982 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002928 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521500-39521501:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGTGGGGGACTTGATGTCCCCCTTCGACCAGTCGGGTTTGG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30983 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE002929 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522053-39522054:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TTCCCCTTTCCCCAGGGGTCCTGTCCTCCACTCCAGATCAT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_30984 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 41 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058147 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39519700-39519701:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGGCCTTTGGGGGTAGGTGGACAGGCCCGGCGCGCCCTCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567292 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058148 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39519784-39519785:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATGAATGGGGCCTCTGGAAAACTCAGGCTTGGAACAGGTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567293 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058149 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39519797-39519798:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGGAAAACTCAGGCTTGGAACAGGTAACCCCCCGGTTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567294 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058150 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39520220-39520221:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCGGCCTTCACAATAAAAACTCTTCGCCGGAAAACGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567295 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058151 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39520323-39520324:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCGGCGAAGGAAAGAACGGACTCTGATCATAGAAGCCTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567296 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058152 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39520383-39520384:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTTTCGTGAGGCCATAAGAACAAACTCCTTTTCTCGTCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567297 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058153 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39520568-39520569:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGGCCACGGCAGCCATTTCTACTTTGCCCGCCCACAGATGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.500660714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567298 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058154 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39520948-39520949:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGCGTAGTCGGGTGCCCGGACTGCTTCCCCAGGAGCCCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567299 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058155 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39520979-39520980:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGCCCTACAGCCCTCGGACCCCGAGCCCCGCAAGGGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567300 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058156 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521039-39521040:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCCCACGAAACGTGGCAGGAACCAAGATGGCGGCGGCAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567301 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058157 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521387-39521388:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCAGCAGCGTTGCTGTAACCGACAAAGACACCTTCGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.147452381 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567302 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058158 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521391-39521392:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGCAGCGTTGCTGTAACCGACAAAGACACCTTCGAATTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567303 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058159 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521443-39521444:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GATTCCAGCAAAGCACCGCAACATGACCGAAATGAGCTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567304 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058160 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521488-39521489:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAGCGAGGTGTTGGTGGGGGACTTGATGTCCCCCTTCGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567305 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058161 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521572-39521573:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTACCTGGAGGTGGCCAAGCACTTCAAACCTCATGGGTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567306 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058162 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521579-39521580:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAGGTGGCCAAGCACTTCAAACCTCATGGGTTCTCCAGCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HepG2; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567307 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058163 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521599-39521600:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | ACCTCATGGGTTCTCCAGCGACAAGGCTAAGGCGGGCTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567308 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058164 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521659-39521660:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGGGTTGGTCAGTCCCTCCAACAACAGCAAGGGTGAGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567309 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058165 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521789-39521790:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAGAGGATGCCTTCTCCGGGACAGATTGGATGTTGGAGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HepG2; A549; H1299; MM6; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567310 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058166 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521829-39521830:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AATGGATTTGAAGGAGTTCGACTTGGATGCCCTGTTGGGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.287565476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567311 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058167 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521864-39521865:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGGGTATAGATGACCTGGAAACCATGCCAGATGACCTTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HepG2; A549; H1299; MM6; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567312 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058168 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521898-39521899:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTTCTGACCACGTTGGATGACACTTGTGATCTCTTTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567313 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058169 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521933-39521934:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTGCCCCCCTAGTCCAGGAGACTAATAAGCAGCCCCCCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HepG2; A549; H1299; MM6; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567314 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058170 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521954-39521955:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTAATAAGCAGCCCCCCCAGACGGTGAACCCAATTGGCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.871321429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567315 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058171 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521961-39521962:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCCCCCCCAGACGGTGAACCCAATTGGCCATCTCCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; A549; H1299; MM6; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567316 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058172 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521990-39521991:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCCATCTCCCAGAAAGTTTAACAAAACCCGACCAGGTTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567317 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058173 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521995-39521996:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTCCCAGAAAGTTTAACAAAACCCGACCAGGTTGCCCCCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; A549; H1299; MM6; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567318 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058174 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522000-39522001:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGAAAGTTTAACAAAACCCGACCAGGTTGCCCCCTTCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.844928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567319 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058175 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522025-39522026:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTTGCCCCCTTCACCTTCTTACAACCTCTTCCCCTTTCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567320 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058176 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522062-39522063:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCCCAGGGGTCCTGTCCTCCACTCCAGATCATTCCTTTAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.475107143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567321 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058177 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522132-39522133:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGAAGGAGATAGGAAGCCAGACTACACTGCTTACGTTGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; H1299; endometrial; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567322 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058178 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522135-39522136:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGATAGGAAGCCAGACTACACTGCTTACGTTGCCATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567323 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058179 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522144-39522145:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCCAGACTACACTGCTTACGTTGCCATGATCCCTCAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.046785714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567324 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058180 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522180-39522181:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCAGTGCATAAAGGAGGAAGACACCCCTTCAGATAATGATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; hESC-HEK293T; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567325 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058181 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522257-39522258:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTCCTCAGCACAGCCCCTCTACCAGGGGCTCTCCAAATAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.05802381 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567326 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058182 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522322-39522323:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGGTCTGCCCGTCCCAAACCTTACGATCCTCCTGGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; fibroblasts; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567327 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058183 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522327-39522328:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTCTGCCCGTCCCAAACCTTACGATCCTCCTGGAGAGAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.046785714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567328 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058184 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522376-39522377:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCAAAAGTAAAGGGTGAGAAACTGGATAAGAAGCTGAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567329 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058185 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522408-39522409:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCTGAAAAAAATGGAGCAAAACAAGACAGCAGCCACTAGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567330 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058186 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522413-39522414:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AAAAAATGGAGCAAAACAAGACAGCAGCCACTAGGTACCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2; ENST00000396680.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567331 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058187 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39522634-39522635:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGCGTCAATGTGCTTGTACATAGAGTGCTGTAGCTGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_567332 | ||
N7-methylguanosine (m7G)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: m7GSITE000095 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521352-39521353:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGCTTCTGATTCTCATTCAGGCTTCTCACGGCATTCAGCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | BoRed-seq&m7G-RIP-seq; m7G-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m7G_site_621 | ||
Pseudouridine (Pseudo)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: PSESITE000183 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:39521355-39521356:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTTCTGATTCTCATTCAGGCTTCTCACGGCATTCAGCAGCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404241.6; ENST00000396680.2; ENST00000337304.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Pseudo_site_3446 | ||
References