m6A-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: M6ADRUG0082)
| Name |
GLS-IN-968
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Compound 968; 5-[3-bromo-4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-2,2-dimethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[a]phenanthridin-4(1H)-one; CHEBI:60279; GLS-IN-968; 5-(3-bromo-4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[a]phenanthridin-4(1H)-one; 5-[3-bromo-4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-2,2-dimethyl-1,3,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[a]phenanthridin-4-one; 5-[3-Bromo-4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-2,3,5,6-tetrahydro-2,2-dimethylbenzo[a]phenanthridin-4(1H)-one; GAC Inhibitor 968; MLS006011732; SCHEMBL2635251; CHEMBL2133369; DTXSID90389215; GLS-968; HMS3865C03; BCP18024; EX-A2335; Glutaminase Inhibitor Compound 968; Glutaminase C-IN-1; Compound 968; QC-219; AKOS000518068; CS-4585; MCULE-7842076917; NCGC00263232-01; NCGC00263232-02; BS-16481; HY-12682; SMR003863855; EU-0084810; Y11333; AG-690/36107028; Q27127161; 5-[3-Bromo-4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-2,2-dimethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[a]phenanthridine-4(1H)-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status | Investigative | [1] | |||
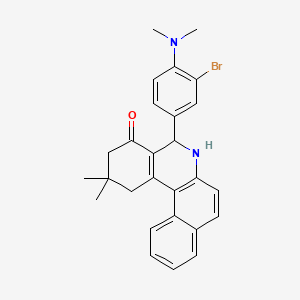
| Structure |
 |
||||
| Formula |
C27H27BrN2O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H27BrN2O/c1-27(2)14-19-24-18-8-6-5-7-16(18)9-11-21(24)29-26(25(19)23(31)15-27)17-10-12-22(30(3)4)20(28)13-17/h5-13,26,29H,14-15H2,1-4H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NVFRRJQWRZFDLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of m6A Targets Related to This Drug
Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4)
| In total 2 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Neutral amino acid transporter B(0) (SLC1A5)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic inactivation of FTO using multiple orthogonal approaches revealed that FTO inhibition selectively reduces the growth and survival of VHL-deficient cells in vitro and in vivo. Integrated analysis of transcriptome-wide m6A-seq and mRNA-seq analysis identified the glutamine transporter Neutral amino acid transporter B(0) (SLC1A5) as an FTO target that promotes metabolic reprogramming and survival of VHL-deficient ccRCC cells. GLS1 inhibitors that target mitochondrial glutaminase and the conversion of glutamine to glutamate are currently being evaluated in early-phase clinical trials in ccRCC. These findings identify FTO as a potential HIF-independent therapeutic target for the treatment of VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C90 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | hsa05230 | |||
| Metabolic pathways | hsa01100 | |||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | |||
| In-vitro Model | UMRC2-vec (CCRCC isogenic cell lines that are VHL-deficient) | |||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
| In total 2 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In colorectal cancer, Glutaminolysis inhibition upregulated ATF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner to activate pro-survival autophagy through transcriptional activation of the mTOR inhibitor DDIT4. Determined the relationship between FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO), YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2), and ATF4. ATF4 transcriptionally upregulated DDIT4 to suppress Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR), which induced pro-survival autophagy during glutaminolysis inhibition. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Pathway Response | mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| Cell growth and death | ||||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Drug
| In total 4 item(s) under this drug | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03335 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | |
| m6A Target | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03341 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | |
| m6A Target | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation (H3K18la) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03433 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| m6A Target | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (ATF4) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03439 | ||
| m6A Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| m6A Target | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
References