m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT02115
|
[1] | |||
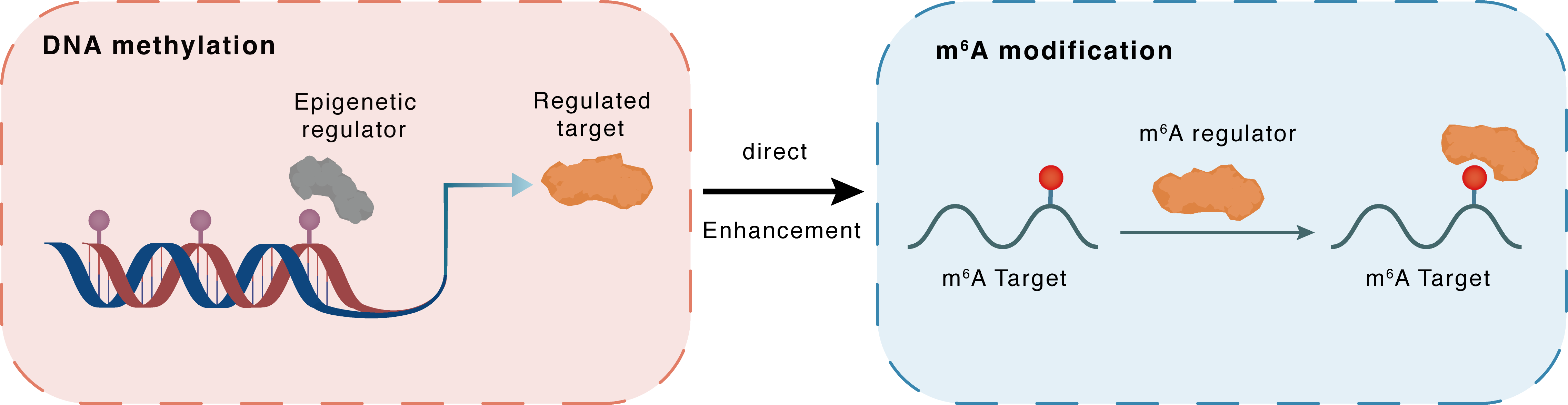 DNA methylation
TET2
PCK2
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
PCK2
PCK2
IGF2BP1
DNA methylation
TET2
PCK2
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
PCK2
PCK2
IGF2BP1
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP], mitochondrial (PCK2) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | DNA methylation (DNAMeth) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET2 (TET2) | ERASER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP], mitochondrial (PCK2) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | DNA methylation → m6A | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | DNA methylation regulates m6A modification through both regulatory proteins targeting the same gene. | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | The suppression of 5mC demethylation or m6A hypermethylation significantly alleviates the upregulation of Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP], mitochondrial (PCK2) and proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-challenged KCs. Further reciprocal tests indicate TET2-mediated 5mC demethylation is upstream of m6A hypermethylation. Specifically, CpG islands in the promoters of PCK2 and RNA methyltransferase (METTL3 and METTL14) genes are demethylated, while the 3'UTR of PCK2 mRNA is m6A hypermethylated, in LPS-stimulated KCs. These modifications contribute to the transactivation of the PCK2 gene as well as increased PCK2 mRNA stability and protein production via a m6A-mediated mechanism with IGF2BP1 as the reader protein. These results indicate that DNA 5mC and RNA m6A collaborate to upregulate PCK2 expression, respectively, at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels during KC activation. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatic inflammation | ICD-11: DB97 | |||