m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00308)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
TK1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by IGF2BP1 | ||
| Cell Line | MV3 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siIGF2BP1 MV3 cells
Control: siControl MV3 cells
|
GSE146803 | |
| Regulation |
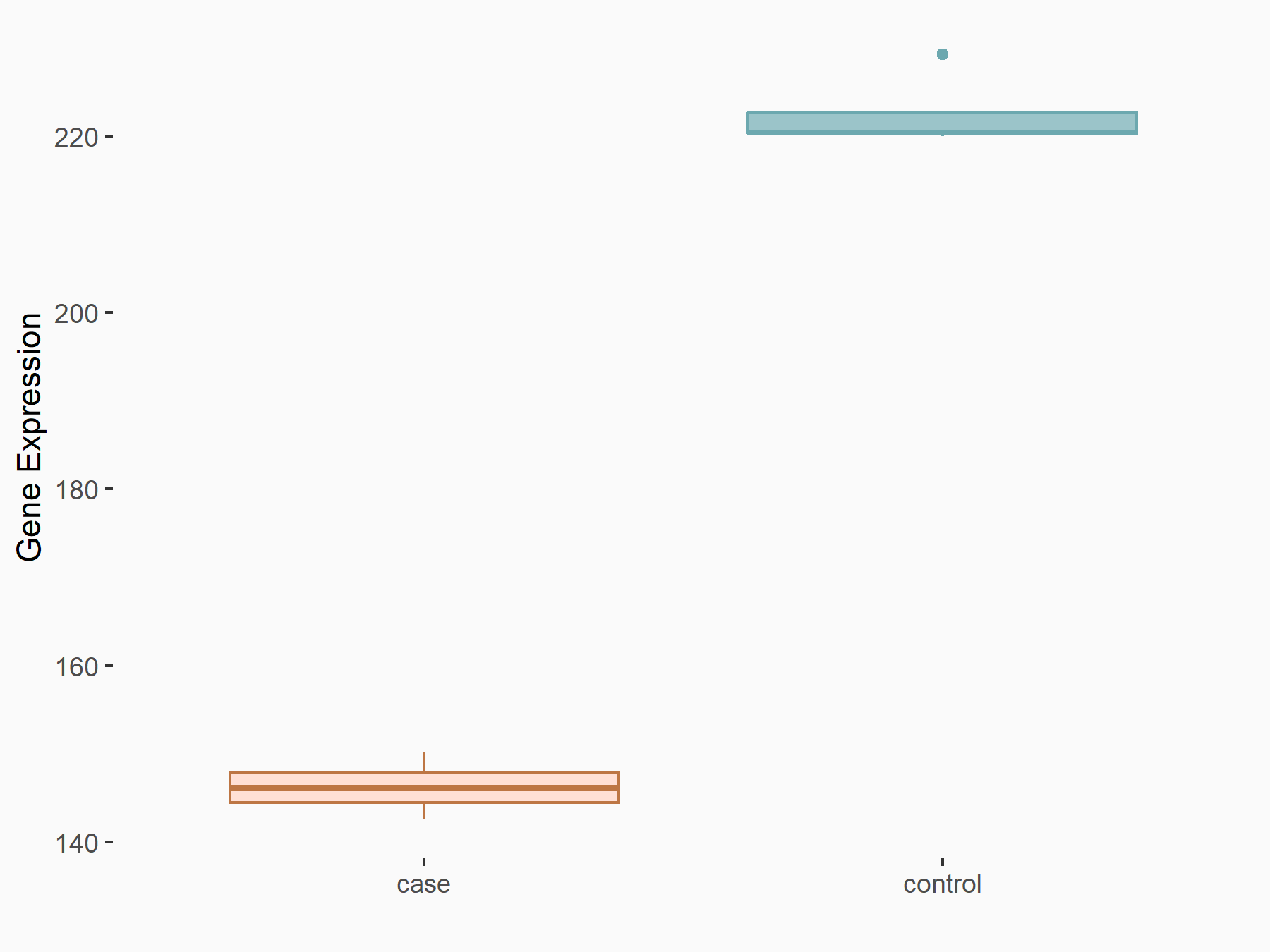 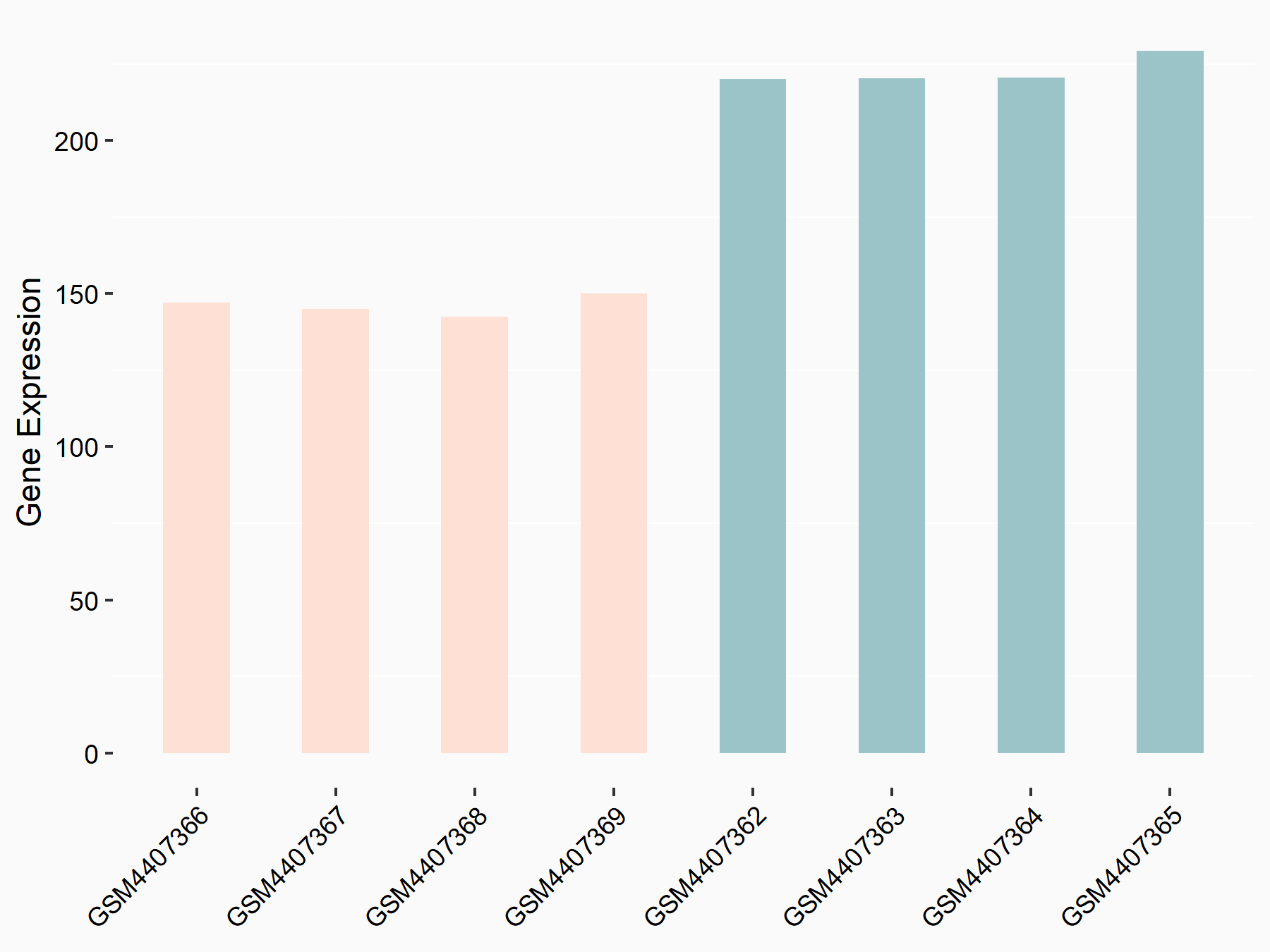 |
logFC: -6.03E-01 p-value: 6.27E-08 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In contrast to the mRNA-decay-promoting function of YTH domain-containing family protein 2, IGF2BPs promote the stability and storage of their target mRNAs (for example, MYC) in an m6A-dependent manner under normal and stress conditions and therefore affect gene expression output. Four representative high confidence targets, including MYC, FSCN1, Thymidine kinase, cytosolic (TK1), and MARCKSL1, exhibit strong binding with IGF2BPs around their m6A motifs in control cells. Knocking down of each individual IGF2BPs in Hela (cervical cancer) and HepG2 (liver cancer) cells significantly repressed MYC expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) [READER]
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In contrast to the mRNA-decay-promoting function of YTH domain-containing family protein 2, IGF2BPs promote the stability and storage of their target mRNAs (for example, MYC) in an m6A-dependent manner under normal and stress conditions and therefore affect gene expression output. Four representative high confidence targets, including MYC, FSCN1, Thymidine kinase, cytosolic (TK1), and MARCKSL1, exhibit strong binding with IGF2BPs around their m6A motifs in control cells. Knocking down of each individual IGF2BPs in Hela (cervical cancer) and HepG2 (liver cancer) cells significantly repressed MYC expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | In lung cancer, IGF2BP2 modified m6A to increase the expression of Thymidine kinase, cytosolic (TK1), thus promoting angiogenesis. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | ||
| In-vitro Model | NHBE (Normal bronchial epithelial cells) | |||
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | Suspension of H1299 cells (5.0 × 105) was subcutaneously injected into the right flanks of the mice. | |||
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In contrast to the mRNA-decay-promoting function of YTH domain-containing family protein 2, IGF2BPs promote the stability and storage of their target mRNAs (for example, MYC) in an m6A-dependent manner under normal and stress conditions and therefore affect gene expression output. Four representative high confidence targets, including MYC, FSCN1, Thymidine kinase, cytosolic (TK1), and MARCKSL1, exhibit strong binding with IGF2BPs around their m6A motifs in control cells. Knocking down of each individual IGF2BPs in Hela (cervical cancer) and HepG2 (liver cancer) cells significantly repressed MYC expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In contrast to the mRNA-decay-promoting function of YTH domain-containing family protein 2, IGF2BPs promote the stability and storage of their target mRNAs (for example, MYC) in an m6A-dependent manner under normal and stress conditions and therefore affect gene expression output. Four representative high confidence targets, including MYC, FSCN1, Thymidine kinase, cytosolic (TK1), and MARCKSL1, exhibit strong binding with IGF2BPs around their m6A motifs in control cells. Knocking down of each individual IGF2BPs in Hela (cervical cancer) and HepG2 (liver cancer) cells significantly repressed MYC expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | READER | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | In lung cancer, IGF2BP2 modified m6A to increase the expression of Thymidine kinase, cytosolic (TK1), thus promoting angiogenesis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | NHBE (Normal bronchial epithelial cells) | |||
| NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | Suspension of H1299 cells (5.0 × 105) was subcutaneously injected into the right flanks of the mice. | |||
Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | In contrast to the mRNA-decay-promoting function of YTH domain-containing family protein 2, IGF2BPs promote the stability and storage of their target mRNAs (for example, MYC) in an m6A-dependent manner under normal and stress conditions and therefore affect gene expression output. Four representative high confidence targets, including MYC, FSCN1, Thymidine kinase, cytosolic (TK1), and MARCKSL1, exhibit strong binding with IGF2BPs around their m6A motifs in control cells. Knocking down of each individual IGF2BPs in Hela (cervical cancer) and HepG2 (liver cancer) cells significantly repressed MYC expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77] | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | READER | ||
| Cell Process | RNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
DNA modification
m6A Regulator: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02193 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 13 (PTPN13) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03467 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1A (SETD1A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Regulator: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05011 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DARS1 antisense RNA 1 (DARS1-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Cervical cancer | |
m6A Regulator: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05367 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-320b | |
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00308)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008523 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78178149-78178150:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGCTGGGCACGGTGGCTCACACCTGTAATCCCAGCACTTTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1; rmsk_4772170; ENST00000590862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_61364 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008524 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181905-78181906:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGAAATTAGCCAGTCATAGCAGCGCACACCTGTGGTCCCTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4772178; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_61365 | ||
N1-methyladenosine (m1A)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M1ASITE000060 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174262-78174263:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTTTCCTTTTGGGCTCAAAGCCCTTCCTACCTCTGGTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m1A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m1A_site_487 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 32 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001288 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174186-78174187:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GATGGGTGGCACCAACCTTGCTGGGACTTGGATCCCAGGGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | m5C-RIP-seq; Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20105 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001289 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78175613-78175614:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CACGTGCCCTTTCCAGTTCCCTGACATCGTGGAGTTCTGCG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20106 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001290 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78178762-78178763:- | ||
| Sequence | AATCCCAGCTACTTGGGAGGCTGAGGCAGGAGAATCGCTTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; rmsk_4772171; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000590862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20107 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001291 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78178771-78178772:- | ||
| Sequence | CATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTTGGGAGGCTGAGGCAGGAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4772171; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590430.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20108 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001292 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78178774-78178775:- | ||
| Sequence | GCGCATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTTGGGAGGCTGAGGCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590430.5; rmsk_4772171 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20109 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001293 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78178777-78178778:- | ||
| Sequence | GTGGCGCATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTTGGGAGGCTGAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4772171; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20110 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001294 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78179820-78179821:- | ||
| Sequence | TGCCTCAGCCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGCGTGAGCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000590862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20111 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001295 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78179827-78179828:- | ||
| Sequence | ATCTGCCTGCCTCAGCCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20112 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001296 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78179828-78179829:- | ||
| Sequence | GATCTGCCTGCCTCAGCCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20113 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001297 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78179829-78179830:- | ||
| Sequence | TGATCTGCCTGCCTCAGCCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20114 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001298 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78180978-78180979:- | ||
| Sequence | GGGATTACAGGCGTGAGCCACCACGCCTGGTCTTGATCTTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20115 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001299 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78180980-78180981:- | ||
| Sequence | CTGGGATTACAGGCGTGAGCCACCACGCCTGGTCTTGATCT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20116 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001300 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78180981-78180982:- | ||
| Sequence | GCTGGGATTACAGGCGTGAGCCACCACGCCTGGTCTTGATC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20117 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001301 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78180987-78180988:- | ||
| Sequence | CAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGCGTGAGCCACCACGCCTGGTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20118 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001302 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78180991-78180992:- | ||
| Sequence | CTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGCGTGAGCCACCACGCCT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20119 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001303 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181466-78181467:- | ||
| Sequence | CGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCGGATTCAAGCGATTTT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20120 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001304 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181467-78181468:- | ||
| Sequence | TCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCGGATTCAAGCGATTT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590430.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20121 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001305 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181470-78181471:- | ||
| Sequence | ATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCGGATTCAAGCGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20122 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001306 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181472-78181473:- | ||
| Sequence | TGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCGGATTCAAGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20123 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001307 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181473-78181474:- | ||
| Sequence | GTGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCGGATTCAAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20124 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001308 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181476-78181477:- | ||
| Sequence | GGCGTGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCGGATTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20125 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001309 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181479-78181480:- | ||
| Sequence | AATGGCGTGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCGGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20126 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001310 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181481-78181482:- | ||
| Sequence | GCAATGGCGTGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACCCG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20127 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001311 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181483-78181484:- | ||
| Sequence | GTGCAATGGCGTGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCCACC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20128 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001312 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181486-78181487:- | ||
| Sequence | GGAGTGCAATGGCGTGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTCTGCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20129 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001313 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181494-78181495:- | ||
| Sequence | CCCAGGCTGGAGTGCAATGGCGTGATCTCGGCTCACTGCAA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20130 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001314 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181500-78181501:- | ||
| Sequence | CTGTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTGCAATGGCGTGATCTCGGCTCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20131 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001315 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181508-78181509:- | ||
| Sequence | GTCTTACTCTGTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTGCAATGGCGTGATC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20132 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001316 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181512-78181513:- | ||
| Sequence | CGGAGTCTTACTCTGTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTGCAATGGCGT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20133 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001317 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181513-78181514:- | ||
| Sequence | ACGGAGTCTTACTCTGTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTGCAATGGCG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20134 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001318 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78181514-78181515:- | ||
| Sequence | GACGGAGTCTTACTCTGTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTGCAATGGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20135 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001319 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78187064-78187065:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCGTGGTTTAAAGCGGTCGGCGCGGGAACCAGGGGCTTACT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_20136 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 28 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035559 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174105-78174106:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGCTGTAGCTTATGAAATTAACTAATTGAAAATTCACTGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385169 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035560 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174181-78174182:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GTGGCACCAACCTTGCTGGGACTTGGATCCCAGGGGCTTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385170 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035561 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174226-78174227:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGATGGTTTCCACAGGAACAACAGCATCTTTCACCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385171 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035562 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174232-78174233:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TACCTCTGGTGATGGTTTCCACAGGAACAACAGCATCTTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385172 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035563 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174289-78174290:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTGAGGATGGCCTGGATTCACGCCCTCTTGTTTCCTTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.021232143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385173 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035564 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174353-78174354:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACCTTTGAGCCTTGGCCCACACTGAGGCTTAGGCCTCTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.506922619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385174 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035565 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174355-78174356:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCACCTTTGAGCCTTGGCCCACACTGAGGCTTAGGCCTCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385175 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035566 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174446-78174447:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | GACAGAGCCCCACGCTGTTGACATCAGCCTGCTTCTTCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385176 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035567 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174465-78174466:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCCTCTCCTTGGGGTGAGGGACAGAGCCCCACGCTGTTGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; LCLs; H1299; MM6; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385177 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035568 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174490-78174491:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTGGTGGCCTGGGATCTGGCACACTCCCTCTCCTTGGGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385178 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035569 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174628-78174629:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CACACCTTGGCCTTCTGGGAACTCTCCTTTGTGTGGCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385179 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035570 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174647-78174648:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGGCGTGGAGGGTGACCACACCTTGGCCTTCTGGGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385180 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035571 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174708-78174709:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGCCACTGCCGCCTACTGGACGCTGCCCTGCATGCTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.616982143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385182 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035572 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174754-78174755:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCCCTGCCAACTGAGGGACCTGCGAGGGCCGCCCGCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385183 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035573 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174849-78174850:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CGGGCCGGACAACAAAGAGAACTGCCCAGTGCCAGGAAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385184 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035574 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174858-78174859:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCAGCCTGCCGGGCCGGACAACAAAGAGAACTGCCCAGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385185 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035575 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174861-78174862:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGGCCAGCCTGCCGGGCCGGACAACAAAGAGAACTGCCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385186 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035576 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78174927-78174928:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CGAGGTGATTGGGGGAGCAGACAAGTACCACTCCGTGTGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; A549; MM6; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385187 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035577 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78175149-78175150:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCCATTTGGGGCCATCCTGAACCTGGTGCCGCTGGCCGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; peripheral-blood; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385188 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035578 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78175542-78175543:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TTGTGGCTGCACTGGATGGGACCTTCCAGAGGAAGGTAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; peripheral-blood; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385189 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035579 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78175569-78175570:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCATGGCCAACGCCGGGAAGACCGTAATTGTGGCTGCACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; peripheral-blood; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385190 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035580 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78175610-78175611:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTGCCCTTTCCAGTTCCCTGACATCGTGGAGTTCTGCGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385191 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035581 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78182679-78182680:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTGGCTTTCTCTTCCCAGGAACACCATGGAGGCACTGCCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385192 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035582 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78185090-78185091:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | GGTGATCAAGTATGCCAAAGACACTCGCTACAGCAGCAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000301634.12 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385193 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035583 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78185120-78185121:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCGCTTCCAGATTGCTCAGTACAAGTGCCTGGTGATCAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000590430.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385194 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035584 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78186945-78186946:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGCCTGGCTCCCCCAGCAAGACCCGGGGGCAGATCCAGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000586613.1; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000590862.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385195 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035585 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78187009-78187010:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GAGAGTACTCGGGTTCGTGAACTTCCCGGAGGCGCAATGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000590430.5; ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000592126.1; ENST00000590862.5; ENST00000301634.12; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385196 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE035586 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:78187057-78187058:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TTAAAGCGGTCGGCGCGGGAACCAGGGGCTTACTGCGGGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000588734.5; ENST00000586613.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_385197 | ||
References