m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00529)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
IL-6
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siMETTL14 MDA-MB-231 cells
Control: MDA-MB-231 cells
|
GSE81164 | |
| Regulation |
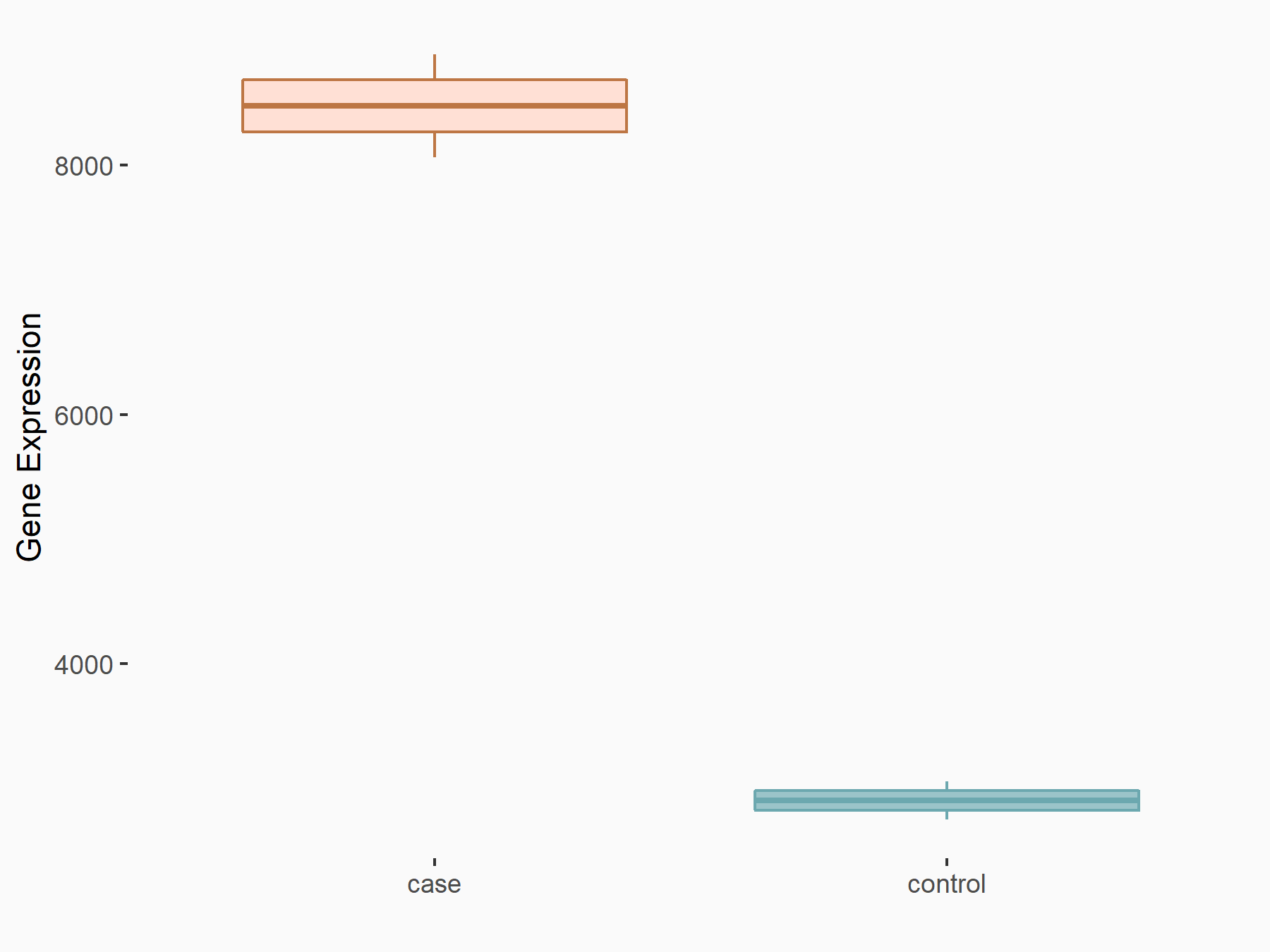 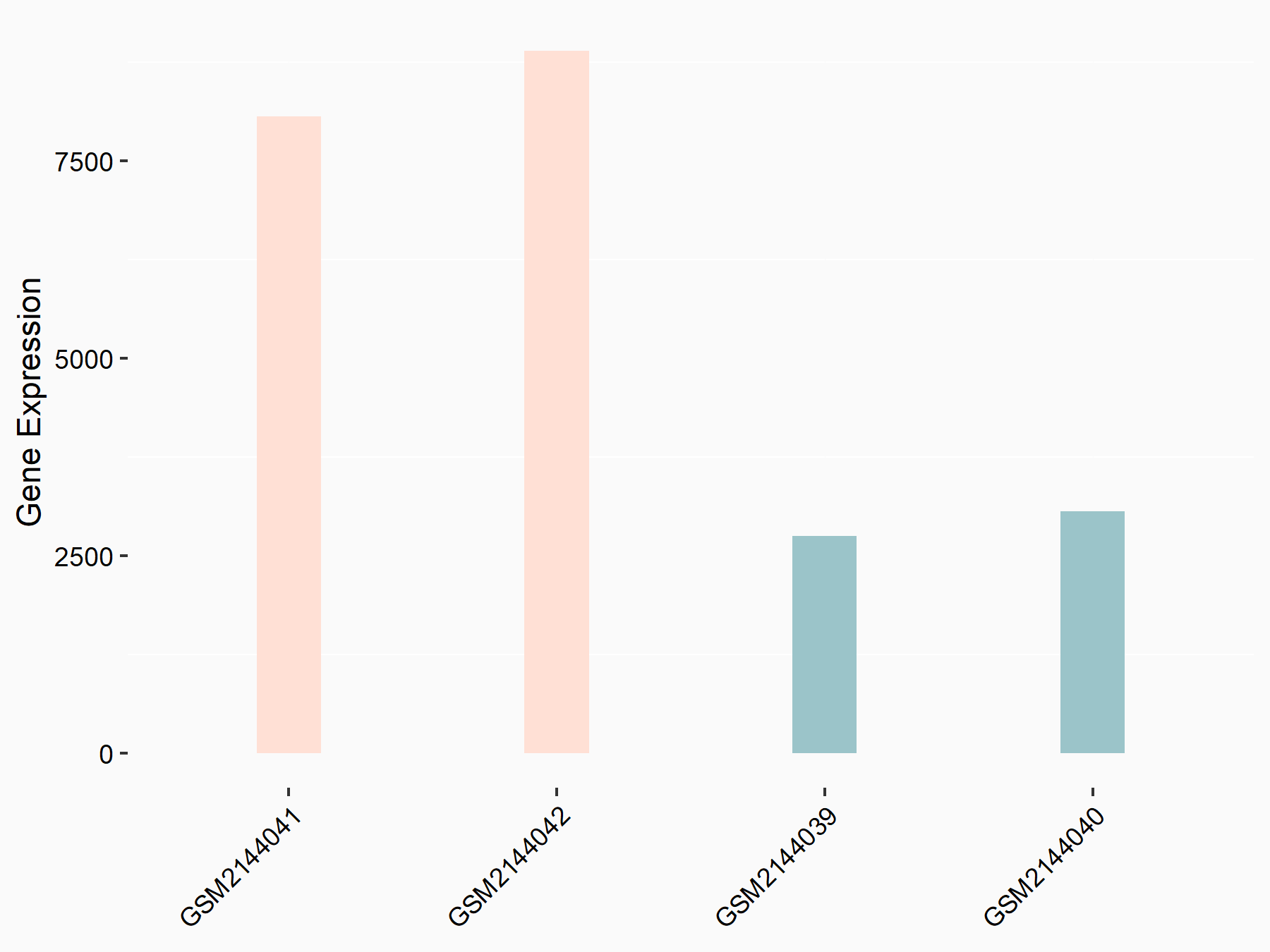 |
logFC: 1.55E+00 p-value: 4.20E-30 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 gene knockout significantly reduced the inflammatory response of macrophages and the development of atherosclerotic plaques, Mettl14 plays a vital role in macrophage inflammation in atherosclerosis via the NF-Kappa-B/Interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling pathway. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis | ICD-11: BD40.Z | ||
| Pathway Response | IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | ||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14 heterozygous mice (Mettl14-/+) were established from C57/BL6 mice by Cyagen Biosciences, Inc. (Suzhou, Jiangsu, China), using CRISPR/Cas9-based targeting and homology-directed repair. C57/BL6 and APOE-/- mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). Mettl14-/+APOE-/- mice were generated by breeding Mettl14-/+ mice with APOE-/- mice. Eight- to 10-week-old male APOE-/- (WT) mice and Mettl14-/+APOE-/- (KO) mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (D12108C, Opensource diets) for 12 weeks. Then, the mice were euthanized for further analysis. | |||
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | ARPE-19 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 ARPE-19 cells
Control: shControl ARPE-19 cells
|
GSE202017 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.10E+00 p-value: 7.68E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 knockdown suppressed Interleukin-6 (IL-6), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, and MMP-9 levels in human RA-FLSs and rat AIA-FLSs. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis | ICD-11: FA20 | ||
| Cell Process | Inflammatory response | |||
| In-vitro Model | FLS (Rat fibroblast synovial cell line) | |||
| In-vivo Model | To establish the adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) model, the rats were given complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA; Chondrex, Inc.) on the left paw of 0.1 ml per 100 g of body weight. Additionally, the rats were injected with normal saline to create the negative control (NC) group. | |||
YTH domain-containing protein 2 (YTHDC2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | This modification recruits the m6A reader YTHDC2 and found that YTHDC2 is necessary for the escape of the IL-6 transcript. m6A modification is essential to confer SOX resistance to the Interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA. These results shed light on how the host cell has evolved to use RNA modifications to circumvent viral manipulation of RNA fate during KSHV infection Kaposi's sarcoma. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kaposi's sarcoma | ICD-11: 2B57 | ||
| In-vitro Model | iSLK.219 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B6YV |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | |
Kaposi's sarcoma [ICD-11: 2B57]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | This modification recruits the m6A reader YTHDC2 and found that YTHDC2 is necessary for the escape of the IL-6 transcript. m6A modification is essential to confer SOX resistance to the Interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA. These results shed light on how the host cell has evolved to use RNA modifications to circumvent viral manipulation of RNA fate during KSHV infection Kaposi's sarcoma. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kaposi's sarcoma [ICD-11: 2B57] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing protein 2 (YTHDC2) | READER | ||
| In-vitro Model | iSLK.219 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B6YV |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | |
Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Mettl14 gene knockout significantly reduced the inflammatory response of macrophages and the development of atherosclerotic plaques, Mettl14 plays a vital role in macrophage inflammation in atherosclerosis via the NF-Kappa-B/Interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling pathway. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BD40.Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | ||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| In-vivo Model | Mettl14 heterozygous mice (Mettl14-/+) were established from C57/BL6 mice by Cyagen Biosciences, Inc. (Suzhou, Jiangsu, China), using CRISPR/Cas9-based targeting and homology-directed repair. C57/BL6 and APOE-/- mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). Mettl14-/+APOE-/- mice were generated by breeding Mettl14-/+ mice with APOE-/- mice. Eight- to 10-week-old male APOE-/- (WT) mice and Mettl14-/+APOE-/- (KO) mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (D12108C, Opensource diets) for 12 weeks. Then, the mice were euthanized for further analysis. | |||
Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 knockdown suppressed Interleukin-6 (IL-6), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, and MMP-9 levels in human RA-FLSs and rat AIA-FLSs. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Inflammatory response | |||
| In-vitro Model | FLS (Rat fibroblast synovial cell line) | |||
| In-vivo Model | To establish the adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) model, the rats were given complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA; Chondrex, Inc.) on the left paw of 0.1 ml per 100 g of body weight. Additionally, the rats were injected with normal saline to create the negative control (NC) group. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03017 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03018 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03019 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Inflammatory response | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00529)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE004095 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22727770-22727771:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGATTTGAGGCCAACGGGGCCGACTAGACTGACTTCTGTAT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000426291.5; ENST00000258743.10; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000485300.1; ENST00000406575.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_39115 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE004096 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22730184-22730185:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCAGTAGCTGGCTATTCAGACAGCAGGGAGTAGACTTGCTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | lung | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485300.1; ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000258743.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_39116 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 13 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078886 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22725977-22725978:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGCTGTCTGGGTCTCTGGAGACTGGAGGGACAACCTAGTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_2181165; ENST00000404625.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_749992 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078887 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22725986-22725987:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGTCTCTGGAGACTGGAGGGACAACCTAGTCTAGAGCCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_2181165; ENST00000404625.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_749993 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078888 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22726016-22726017:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTAGAGCCCATTTGCATGAGACCAAGGATCCTCCTGCAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_2181165; ENST00000404625.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_749995 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078889 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22726038-22726039:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAAGGATCCTCCTGCAAGAGACACCATCCTGAGGGAAGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_2181165; ENST00000404625.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_749996 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078890 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22726067-22726068:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGAGGGAAGAGGGCTTCTGAACCAGCTTGACCCAATAAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_2181165; ENST00000404625.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_749997 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078891 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22726180-22726181:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTTTTGATTTCAAATCAAGACTTACAGGGAGAGGGAGCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000404625.5; rmsk_2181165 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_749999 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078893 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22727179-22727180:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAACCCCCAATAAATATAGGACTGGAGATGTCTGAGGCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000426291.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_750002 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078894 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22727266-22727267:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTCCAGGAGCCCAGCTATGAACTCCTTCTCCACAAGTAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; iSLK; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000406575.1; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000485300.1; ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000258743.10; ENST00000426291.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_750003 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078895 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22727309-22727310:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGGAAATCCTTAGCCCTGGAACTGCCAGCGGCGGTCGAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; iSLK; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000406575.1; ENST00000485300.1; ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000426291.5; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000258743.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_750004 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078896 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22727555-22727556:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GATGTAGCCGCCCCACACAGACAGCCACTCACCTCTTCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485300.1; ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000258743.10; ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000426291.5; ENST00000406575.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_750005 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078897 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22727588-22727589:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTTCAGAACGAATTGACAAACAAATTCGGTACATCCTCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000258743.10; ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000426291.5; ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000485300.1; ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000406575.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_750006 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078898 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22729580-22729581:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | ATACCTAGAGTACCTCCAGAACAGATTTGAGAGTAGTGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000426291.5; ENST00000464710.1; ENST00000258743.10; ENST00000406575.1; ENST00000404625.5; ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000485300.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_750007 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE078899 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr7:22729602-22729603:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGATTTGAGAGTAGTGAGGAACAAGCCAGAGCTGTGCAGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407492.5; ENST00000401630.7; ENST00000485300.1; ENST00000401651.5; ENST00000406575.1; ENST00000258743.10; ENST00000464710.1; ENST00000426291.5; ENST00000404625.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_750008 | ||
References