m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT02006
|
[1] | |||
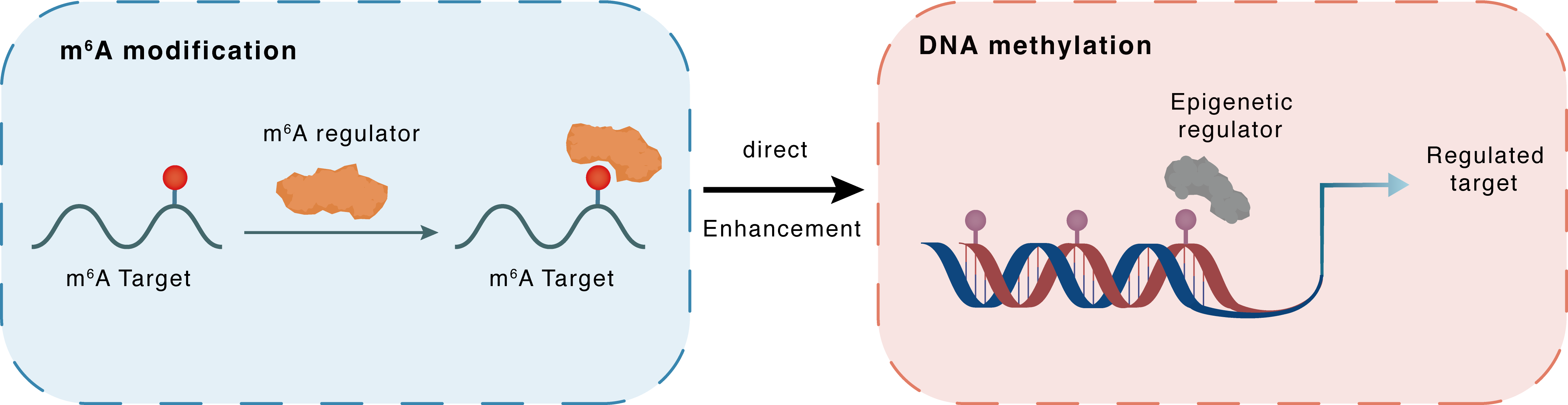 m6A modification
HERV-H
HERV-H
YTHDC2
m6A modification
HERV-H
HERV-H
YTHDC2
 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
DNA methylation
TET1
LTR7 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
DNA methylation
TET1
LTR7
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing protein 2 (YTHDC2) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | ANKRD13C divergent transcript (ANKRD13C-DT) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | DNA methylation (DNAMeth) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET1 (TET1) | ERASER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Long Terminal Repeat 7 (LTR7) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → DNA methylation | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification directly impacts DNA methylation through recruiting DNA methyltransferases or demethylases. | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) reader, YTHDC2, occupies genomic loci of the primate-specific TE, Long Terminal Repeat 7 (LTR7)/ANKRD13C divergent transcript (ANKRD13C-DT), specifically through its interaction with m6A-modified HERV-H RNAs. Unexpectedly, YTHDC2 recruits the DNA 5-methylcytosine (5mC)-demethylase, TET1, to remove 5mC from LTR7/HERV-H and prevent epigenetic silencing. Functionally, the YTHDC2/LTR7 axis inhibits neural differentiation of hESCs. | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell differentiation | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |