m6A Regulator Information
General Information of the m6A Regulator (ID: REG00017)
| Regulator Name | Methyltransferase-like 16 (METTL16) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Methyltransferase 10 domain-containing protein; RNA N6-adenosine-methyltransferase METTL16; N6-adenosine-methyltransferase METTL16; U6 small nuclear RNA (adenine-(43)-N(6))-methyltransferase; METT10D
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | METTL16 | ||||
| Sequence |
MALSKSMHARNRYKDKPPDFAYLASKYPDFKQHVQINLNGRVSLNFKDPEAVRALTCTLL
REDFGLSIDIPLERLIPTVPLRLNYIHWVEDLIGHQDSDKSTLRRGIDIGTGASCIYPLL GATLNGWYFLATEVDDMCFNYAKKNVEQNNLSDLIKVVKVPQKTLLMDALKEESEIIYDF CMCNPPFFANQLEAKGVNSRNPRRPPPSSVNTGGITEIMAEGGELEFVKRIIHDSLQLKK RLRWYSCMLGKKCSLAPLKEELRIQGVPKVTYTEFCQGRTMRWALAWSFYDDVTVPSPPS KRRKLEKPRKPITFVVLASVMKELSLKASPLRSETAEGIVVVTTWIEKILTDLKVQHKRV PCGKEEVSLFLTAIENSWIHLRRKKRERVRQLREVPRAPEDVIQALEEKKPTPKESGNSQ ELARGPQERTPCGPALREGEAAAVEGPCPSQESLSQEENPEPTEDERSEEKGGVEVLESC QGSSNGAQDQEASEQFGSPVAERGKRLPGVAGQYLFKCLINVKKEVDDALVEMHWVEGQN RDLMNQLCTYIRNQIFRLVAVN Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | methyltransferase superfamily; METTL16/RlmF family | ||||
| Function |
RNA N6-methyltransferase that methylates adenosine residues at the N(6) position of a subset of RNAs and is involved in S-adenosyl-L-methionine homeostasis by regulating expression of MAT2A transcripts . Able to N6-methylate a subset of mRNAs and U6 small nuclear RNAs (U6 snRNAs). In contrast to the METTL3-METTL14 heterodimer, only able to methylate a limited number of RNAs: requires both a 5'UACAGAGAA-3' nonamer sequence and a specific RNA structure. Plays a key role in S-adenosyl-L-methionine homeostasis by mediating N6-methylation of MAT2A mRNAs, altering splicing of MAT2A transcripts: in presence of S-adenosyl-L-methionine, binds the 3'-UTR region of MAT2A mRNA and specifically N6-methylates the first hairpin of MAT2A mRNA, preventing recognition of their 3'-splice site by U2AF1/U2AF35, thereby inhibiting splicing and protein production of S-adenosylmethionine synthase. In S-adenosyl-L-methionine-limiting conditions, binds the 3'-UTR region of MAT2A mRNA but stalls due to the lack of a methyl donor, preventing N6-methylation and promoting expression of MAT2A. In addition to mRNAs, also able to mediate N6-methylation of U6 small nuclear RNA (U6 snRNA): specifically N6-methylates adenine in position 43 of U6 snRNAs . Also able to bind various lncRNAs, such as 7SK snRNA (7SK RNA) or 7SL RNA. Specifically binds the 3'-end of the MALAT1 long non-coding RNA.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 79066 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Regulator Type | WRITER ERASER READER | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
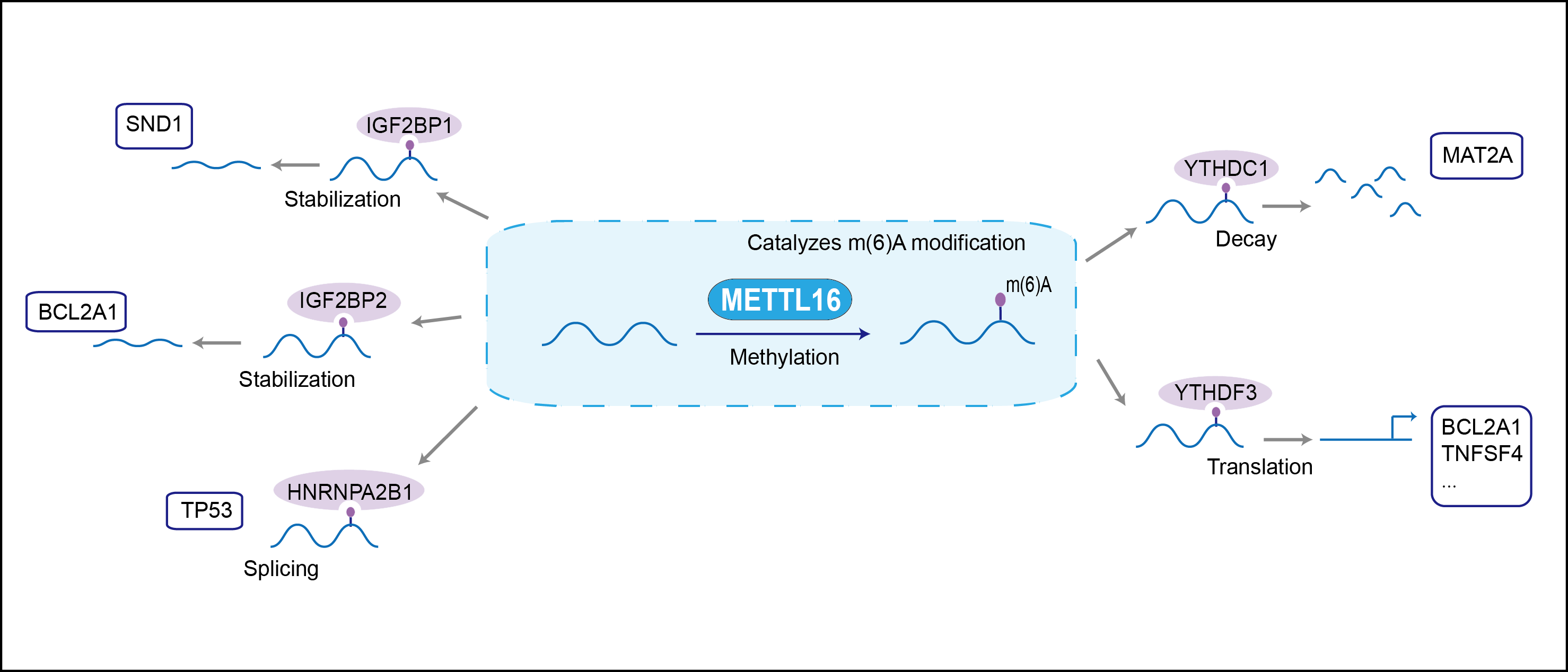
|
|||||
| Target Genes | Click to View Potential Target Genes of This Regulator | ||||
Full List of Target Gene(s) of This m6A Regulator and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
METTL16 can regulate the m6A methylation of following target genes, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulted from the regulation of certain target gene.
Browse Target Gene related Disease
Browse Target Gene related Drug
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Response Summary | Deletion of METTL16 or ALKBH5 predicted poor OS and DFS of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. And this study found significant associations between the genetic alterations and clinicopathological features as well as Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53/p53) alteration. | |||
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (CDKN1A)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| In-vivo Model | Six-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were obtained from Peking University Animal Center (Beijing, China). These mice were randomized into experimental (N = 8 per group) and control groups (N = 8 per group). PC cells were resuspended in PBS (approximately 2 × 106 cells/100 μL) and subcutaneously inoculated into the left armpit of each nude mouse. The tumor length and width of the mice were monitored weekly. All mice were sacrificed 5 weeks postinjection, and tumors were excised and weighed. | |||
Extracellular sulfatase Sulf-2 (Sulf2)
Injury of blood vessels of thorax [ICD-11: NB30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of pulmonary blood vessels [ICD-11: NB30.4] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) were isolated from lung tissues) | |||
| In-vivo Model | The rats were randomly divided into a fresh air group and a COPD group and each group contained 10 rats. The COPD group was placed into a breathable cage and exposed to PM2.5 (1.46 mg/m3) from the motor vehicle exhaust for two 2-h exposure periods (from 9:00 a.m. to 11:00 a.m. and from 15:00 p.m. to 17:00 p.m.), 5 days per week, for 7 months. After each period of exposure, the animals were exposed to fresh air for 30 min to take a rest. Gasoline-powered motorcycle used as of source of the Particulate matter (PM) pollution was located next door to the rat exposure room, and the PM was directed towards the exposure room through a metal tube. Fresh air was sent to through an air pump. After exposed for 7 months, rats were performed lung function test using a Forced Pulmonary Maneuver System (Buxco Research Systems, Wilmington, NC, USA). | |||
| Response Summary | METTL16 regulates Extracellular sulfatase Sulf-2 (Sulf2) expression via m6A modification and thereby contribute to PM2.5-induced pulmonary microvascular injury. | |||
G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Cell cycle | hsa04110 | ||
| Cell Process | G1/S blocking | |||
In-vitro Model |
SNU-719 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5086 |
| SGC-7901 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | |
| MKN28 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1416 | |
| MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| HGC-27 | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1279 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | |
| In-vivo Model | Xenograft mouse model was used to verify the tumorigenic effect of METTL16 in vivo. BALB/c nude mice (4 weeks old) were injected with METTL16 gene knock-down stable MGC803 GC cells (3 × 106 cells/mice, subcutaneous injection) or shNC control cells (3 × 106, subcutaneous injection), and the dose was 100 uL, with PBS as solvent. The tumour size was measured every 3-5 days. At the end of feeding (6 weeks after subcutaneous injection), the mice were killed and the tumours were extracted for histological analysis. | |||
| Response Summary | METTL16-mediated m6A methylation promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells through enhancing G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1) expression. | |||
Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274/PD-L1)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
NCM460 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0460 |
| RKO | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0504 | |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| COLO 320 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1989 | |
| DLD-1 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0248 | |
| HCe-8693 | Cecum adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6909 | |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| HT29 | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| FHC | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3688 | |
| In-vivo Model | Male BALB/c nude mice that aged 4 to 6-week-old were bought from Vital River Laboratory (China). SW480 cells transfected with control or METTL16 overexpression vectors (5 x 106 cells/site) were suspended in 50 μl saline and inoculated into the fact pat on back. Tumor size was measured and calculated every three days. After feeding for 30 days, the tumors were collected and made into paraffine-embedded samples. | |||
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)
Papillary Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: XH1ND9]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: XH1ND9] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Simvastatin | Approved | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 |
| TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 | |
| K1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2537 | |
| In-vivo Model | These mice were provided with unrestricted access to both water and food, following a 12-h light and 12-h dark cycle. Subcutaneous injections of stably transfected K1 cells (2 × 106 cells per mouse) were administered in the armpits of the mice. Once the tumors became palpable, their volume was measured every three days and calculated using the formula: length × width2 × 0.5. The tumor weight was detected after the mice were sacrificed. | |||
Branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferase, cytosolic (BCAT1)
Leukemogenesis [ICD-11: 2A82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukemogenesis [ICD-11: 2A82] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
Branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferase, mitochondrial (BCAT2)
Leukemogenesis [ICD-11: 2A82]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukemogenesis [ICD-11: 2A82] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| HL-60 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0002 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2119 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0589 | |
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E type 2 (EIF4E2)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H226 | Pleural epithelioid mesothelioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1544 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| MEF | Fibrosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C1M8 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | |
| In-vivo Model | For xenograft tumor growth assay, 5×106 NSCLC cells were subcutaneously injected into the left armpit of BALB/c nude mice (n=6 per group). | |||
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2 (SETD2)
Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
AGS | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 |
| MKN28 | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1416 | |
| GES-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_EQ22 | |
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1)
Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [10] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
lnc-CSMD1-7
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [11] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
In-vitro Model |
SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 |
| SNU-449 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0454 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
Microtubule cross-linking factor 2 (SOGA1)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0547 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HeLa | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
NUTM2B antisense RNA 1 (NUTM2B-AS1)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [14] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase GPX4 (GPX4)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [15] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
MCF-10A | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| In-vivo Model | The width and length of tumors were recorded every 5 days and calculated as width [2] × length/2. After growth for 30 days, the mice were sacrificed and tumors were collected for further experiments. | |||
PR domain zinc finger protein 15 (PRDM15)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [16] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
CC-LP-1 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0205 |
| HuCC-T1 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0324 | |
| In-vivo Model | For subcutaneous inoculation, 1 × 106 control or METTL16-depleted CCA cells suspended in 100 μL PBS mixed with matrix gel (BD, 356,234) at 1:1 ratio was injected into the mice's flanks.For intrahepatic inoculation, 1 × 106 control or METTL16-depleted CCLP1 cells suspended in 10 μL PBS mixed with matrix gel (BD, 356,234) at a 1:1 ratio was implanted into the livers of NOD-SCID mice. | |||
Protein MROH8 (MROH8)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
In-vitro Model |
AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 |
| Capan-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0237 | |
| Capan-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic fibrosis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| THLE-3 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3804 | |
Segment polarity protein dishevelled homolog DVL-2 (DVL2)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | ||
In-vitro Model |
PANC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| SW1990 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| BxPC-3 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| AsPC-1 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | |
| HPDE6c7 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0P38 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| In-vivo Model | The hepatic metastasis model was used to detect the function of METTL16 in vivo. BALB/c nude mice aged 4 weeks were divided into four groups randomly (n = 3). Subsequently, a longitudinal abdominal median incision was created after the mice were anesthetized. A total of 2.0 x 106 cells were injected into the spleen. Approximately 2.5 months later, liver tissues were harvested, imaged, and subjected to H&E staining. | |||
transcript inducer of AURKA lysosomal degradation (TIALD)
Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.02] | |||
| Responsed Drug | MLN8237 | Phase 3 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
SNU-449 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0454 |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| Hep-G2/C3A | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1098 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| In-vivo Model | In the therapeutic study, TIALD stable knockdown or control cells were further infected by lentiviruses (Ubi-MCS-firefly_Luciferase-SV40-neomycin, Genechem, China) and selected by G418 (500 μg/mL). 45 B-NDG mice were divided into 3 groups, including the control group (n = 15), TIALD knockdown group (n = 15) and Alisertib treatment group (n = 15). The modified control cells described above were injected into the mice of control group via tail vein, while the modified TIALD knockdown cells were injected into the mice of TIALD knockdown group and Alisertib treatment group. | |||
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 33B (VPS33B)
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [20] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||
In-vitro Model |
HOS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0312 |
| MG-63 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 | |
| SaOS-2 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0548 | |
| 143B | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 | |
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| hFOB 1.19 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3708 | |
| OS-RC-2 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1626 | |
| In-vivo Model | Nude mice (6 weeks, female) were injected with shNC, shMETTL16, shMETTL16 + shNC, and shMETTL16 + shVPS33B HOS cells to induce subcutaneous tumor formation randomly (n = 6 per group). | |||
Unspecific Target Gene
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [21] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
In-vitro Model |
LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
Male fertility disorders [ICD-11: VV5Y]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [22] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Male fertility disorders [ICD-11: VV5Y] | |||
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)
Simvastatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary Thyroid Cancer | ICD-11: XH1ND9 | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 |
| TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 | |
| K1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2537 | |
| In-vivo Model | These mice were provided with unrestricted access to both water and food, following a 12-h light and 12-h dark cycle. Subcutaneous injections of stably transfected K1 cells (2 × 106 cells per mouse) were administered in the armpits of the mice. Once the tumors became palpable, their volume was measured every three days and calculated using the formula: length × width2 × 0.5. The tumor weight was detected after the mice were sacrificed. | |||
transcript inducer of AURKA lysosomal degradation (TIALD)
MLN8237
[Phase 3]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response of This Target Gene | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12.02 | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | SNU-449 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0454 |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | |
| Hep-G2/C3A | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1098 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | |
| In-vivo Model | In the therapeutic study, TIALD stable knockdown or control cells were further infected by lentiviruses (Ubi-MCS-firefly_Luciferase-SV40-neomycin, Genechem, China) and selected by G418 (500 μg/mL). 45 B-NDG mice were divided into 3 groups, including the control group (n = 15), TIALD knockdown group (n = 15) and Alisertib treatment group (n = 15). The modified control cells described above were injected into the mice of control group via tail vein, while the modified TIALD knockdown cells were injected into the mice of TIALD knockdown group and Alisertib treatment group. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
RNA modification
m6A Target: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-Alpha/HIF1A)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00523 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 (ADARB1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 142 (MIR142) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | A-to-I → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00527 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 576 (MIR576) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6Am → m6A | |
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00534 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Interferon-inducible protein 4 (ADAR1) | |
| Regulated Target | MicroRNA 26a-1 (MIR26A1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → A-to-I | |
DNA modification
m6A Target: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02050 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase 16, RNA N6-adenosine (METTL16) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Papillary Thyroid Cancer | |
| Drug | Simvastatin | |
Histone modification
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2 (SETD2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03046 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2 (SETD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 36 trimethylation (H3K36me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Gastric cancer | |
m6A Target: PR domain zinc finger protein 15 (PRDM15)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03069 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | |
m6A Target: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03180 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Ageing-related disease | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06002 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 (SUV39H1) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Ageing-related disease | |
m6A Target: NUTM2B antisense RNA 1 (NUTM2B-AS1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03252 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → Histone modification | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Target: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05374 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05794 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: Transcript inducer of AURKA lysosomal degradation (TIALD)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05726 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Transcript inducer of AURKA lysosomal degradation (TIALD) | |
| Regulated Target | Aurora kinase A (AURKA) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
| Drug | alisertib | |
m6A Target: Lnc-CSMD1-7
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05747 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Lnc-CSMD1-7 | |
| Regulated Target | RNA binding fox-1 homolog 2 (RBFOX2) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Liver cancer | |
m6A Target: RNA, U6 small nuclear 1 (RNU6-1)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05782 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA, U6 small nuclear 1 (RNU6-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05783 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA, U6 small nuclear 1 (RNU6-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05790 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA, U6 small nuclear 1 (RNU6-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: RNA, 18S ribosomal 1 (RNA18S1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05791 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA, 18S ribosomal 1 (RNA18S1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: RNA28S1
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05792 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA28S1 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
m6A Target: RNA5S1
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05793 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | RNA5S1 | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
Xenobiotics Compound(s) Regulating the m6A Methylation Regulator
| Compound Name | Butyrate | Investigative |
|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
butyrate; butanoate; N-Butyrate; n-butanoate; Butanoic acid, ion(1-); propylformate; 461-55-2; butanate; 1-butanoate; propanecarboxylate; 1-butyrate; 1-propanecarboxylate; CHEMBL62381; NCGC00167555-01; ethyl,acetate; Sodium; butyrate; C11H23NOS; DTXSID8040432; CHEBI:17968; CH3-[CH2]2-COO(-); BDBM50079401; c0035; M135; AB01566831_01; Q55582441
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
In cell model induced by sodium butyrate and cell density, while METTL3, METTL16 and WTAP were decreased during the differentiation of cells.
|
[23] |
References