m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05607
|
[1] | |||
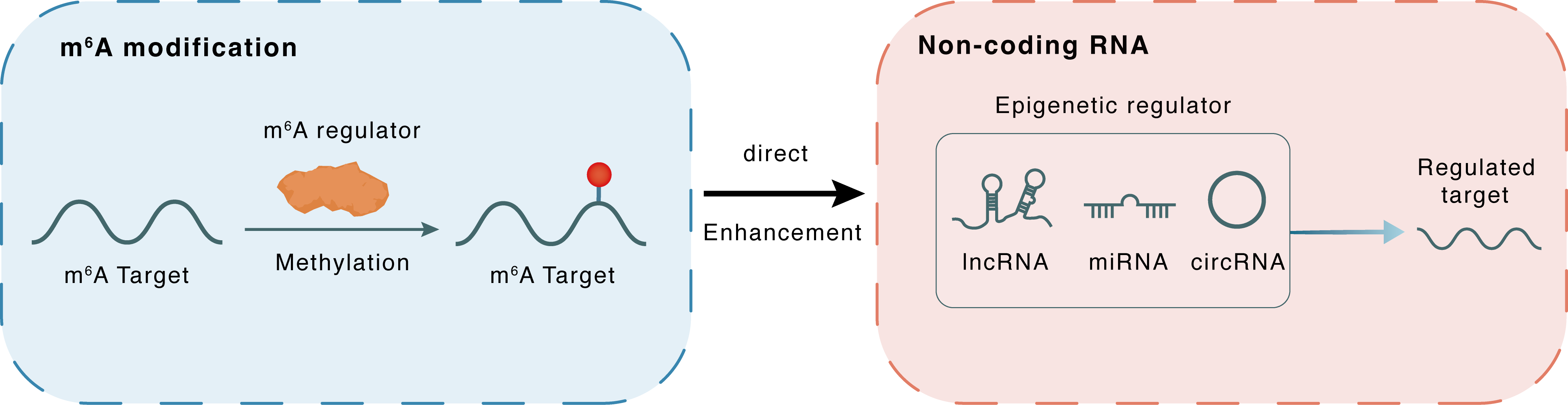 m6A modification
hsa-miR-34a
hsa-miR-34a
METTL3
Methylation
m6A modification
hsa-miR-34a
hsa-miR-34a
METTL3
Methylation
 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Non-coding RNA
miR-34a
SIRT1
lncRNA miRNA circRNA : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Non-coding RNA
miR-34a
SIRT1
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-34a | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-34a | microRNA | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → ncRNA | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A regulators directly modulate the functionality of ncRNAs through specific targeting ncRNA | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | METTL3/m6A-mediated hsa-miR-34a maturation in AAA formation and provide a novel therapeutic target and diagnostic biomarker for AAA treatment. miR-34a overexpression significantly decreased NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) expression. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Abdominal aortic aneurysm | ICD-11: BD50.4 | |||
In-vitro Model |
VSMC (Human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells) | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Male C57BL/6J mice were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (40 mg/kg). The abdominal aorta between the renal arteries and the bifurcation of the iliac arteries was disassociated from the surrounding structures. Video microscopy was used to assay the diameter of the aorta in triplicate. After the measurements were taken, a small piece of gauze dipped in 0.5 mol/L CaCl2 was spread perivascularly onto the aortic passage for 15 min. Control mice received substitute treatment with NaCl (0.9%)-soaked gauze for 15 min. Then, the aorta was rinsed with 0.9% sterile saline, and the incision was sutured. After 3 or 6 weeks, all the animals were sacrificed, and the aortas were harvested for further analysis. | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) | 22 Compound(s) Regulating the Target | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| Resveratrol | Phase 3 | [2] | ||
| Synonyms |
Resvida; KUC104385N; R 5010; SRT 501; Cis-resveratrol; PREVENTION 8 (RESVERATROL); RM-1812; SRT-501; Trans-resveratrol; CU-01000001503-3; KSC-10-164; Resveratrol-3-sulfate; Trans-3,4',5-trihydroxystilbene; Trans-3,4′,5-Trihydroxystilbene; Trans-1,2-(3,4',5-Trihydroxydiphenyl)ethylene; (E)-5-(2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl)-1,3-benzenediol
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | EC50 = 23600 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| GSK2245840 | Phase 2 | [3] | ||
| Synonyms |
Gepirone hydrochloride; Gepirone HCl; UNII-80C9L8EP6V; Gepirone hydrochloride [USAN]; 80C9L8EP6V; 83928-66-9; CHEMBL1204187; Gepirone hydrochloride (USAN); BMY 138951; AC1Q3ELB; AC1L1IK3; SCHEMBL318838; DTXSID30232812; AOB5299; 83928-76-1 (Parent); ORG-33062; SB19633; BMY-13805-1; BMY 13805-1; 3,3-Dimethyl-1-(4-(4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl)butyl)glutarimide monohydrochloride; D04314; 4,4-dimethyl-1-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-ylpiperazin-1-yl)butyl]piperidine-2,6-dione hydrochloride; 2,6-Piperidinedione,
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SEN-196 | Phase 2 | [4] | ||
| Synonyms |
EX-527; SEN-0014196; SIRT1 inhibitors (Huntingtons disease), Elixir/Siena; Sirtuin-1 inhibitors (oral, Huntington's disease), Elixir/Siena
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 85 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| MB-12066 | Phase 2 | [5] | ||
| Synonyms |
B-lapachone (obesity), Mazence; Beta-lapachone (obesity), Mazence
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SRT2379 | Phase 1 | [6] | ||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SRT3025 | Phase 1 | [7] | ||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| PMID25435179-Compound-WO2012106509Salermide | Patented | [2] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| CAMBINOL | Patented | [8] | ||
| Synonyms |
14513-15-6; SIRT1/2 Inhibitor IV, Cambinol; NSC112546; NSC-112546; NSC-1125476; 5-[(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)methyl]-2-mercapto-6-phenyl-4(3H)-Pyrimidinone; 5-(2-Hydroxynaphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-6-phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrimidin-4-one; 5-(2-Hydroxy-naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-6-phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrimidin-4-one; Tetrahydro-5-[(2-hydroxy-1-naphthalenyl)methyl]-6-phenyl-2-thioxo-4(1H)-Pyrimidinone; AC1MMYEF; NCIStruc2_001159; NCIStruc1_001428; SCHEMBL2538372; CHEMBL491960; CTK8G3107; BDBM29040
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 8850 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| PMID25435179-Compound-WO2012106509CAY10602 | Patented | [2] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| PMID25435179-Compound-WO2012106509Tenovin-6 | Patented | [2] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| GSK184072 | Discontinued in Phase 2 | [9] | ||
| Synonyms |
Flutimide; 162666-34-4; AC1O5YLM; AKOS027326745; (5Z)-1-hydroxy-3-isobutyl-5-(2-methylpropylidene)pyrazine-2,6-dione; 2,6-(1H,3H)-Pyrazinedione, 1-hydroxy-5-(2-methylpropyl)-3-(2-methylpropylidene)-, (Z)-; 2,6-(1H,3H)-Pyrazinedione, 1-hydroxy-5-(2-methylpropyl)-3-(2-methylpropylidene)-, (3Z)-; (5Z)-1-hydroxy-3-(2-methylpropyl)-5-(2-methylpropylidene)pyrazine-2,6-dione
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Activator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| Meta-sirtinol | Investigative | [10] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 59000 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| 2H-chromeno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4(3H)-dione | Investigative | [11] | ||
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL611665; chromeno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione; AC1LQMEG; 5-Deaza-10-oxaflavin; SCHEMBL11333239; BFMCRAXOACCPEL-UHFFFAOYSA-; ZINC1280587; STK236511; BDBM50309832; AKOS000428551; MCULE-3496773034; ST50987740; 3-hydrochromeno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione; 2H,3H,4H-chromeno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione; 2H-[1]Benzopyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4(3H)-dione; InChI=1/C11H6N2O3/c14-9-7-5-6-3-1-2-4-8(6)16-10(7)13-11(15)12-9/h1-5H,(H,12,14,15)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 5300 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| (R)-sirtinol | Investigative | [10] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 55000 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SRT1720 | Investigative | [12] | ||
| Synonyms |
925434-55-5; N-(2-(3-(piperazin-1-ylmethyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazol-6-yl)phenyl)quinoxaline-2-carboxamide; SRT 1720; SRT-1720; CHEMBL257991; N-[2-[3-(1-PIPERAZINYLMETHYL)IMIDAZO[2,1-B]THIAZOL-6-YL]PHENYL]-2-QUINOXALINECARBOXAMIDE; N-(2-{3-[(Piperazin-1-yl)methyl]imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazol-6-yl}phenyl)quinoxaline-2-carboxamide; Tafluprost enone; N-[2-[3-(piperazin-1-ylmethyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazol-6-yl]phenyl]quinoxaline-2-carboxamide; IASPBORHOMBZMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Activator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| YK-3237 | Investigative | [13] | ||
| Synonyms |
Angiogenesis inhibitors (cancer); Angiogenesis inhibitors (cancer), Georgetown University
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| splitomicin | Investigative | [11] | ||
| Synonyms |
1,2-Dihydro-3H-naphtho[2,1-b]pyran-3-one; 1,2-dihydro-3h-benzo[f]chromen-3-one; 1H-benzo[f]chromen-3(2H)-one; CHEMBL86537; CHEBI:75272; 1,2-dihydrobenzo[f]chromen-3-one; 1H,2H,3H-naphtho[2,1-b]pyran-3-one; Splitomycin; Bio2_000878; Tocris-1542; AC1L1JZ6; AC1Q6ML4; KBioGR_000456; BSPBio_001116; KBioSS_000456; GTPL8101; SCHEMBL2544804; ZINC27374; KBio3_000852; KBio2_003024; BDBM29590; KBio3_000851; KBio2_005592; KBio2_000456; MolPort-003-959-546; ISFPDBUKMJDAJH-UHFFFAOYSA-N; HMS1362H17; HMS1990H17; Bio2_000398
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 96200 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-1-carboxamide | Investigative | [14] | ||
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL112265; 352549-39-4; CBMicro_001045; Cambridge id 5870454; AC1N6ME3; Oprea1_743470; SCHEMBL251128; CTK1B0687; DTXSID20401358; MolPort-000-735-346; HMS1632P07; SMSF0008851; STL525366; BDBM50178767; carboxamido-1,2,3-tetrahydrocarbazole; AKOS004917884; CB02357; BIM-0000968.P001; SR-01000154363; SR-01000154363-1; 1H-Carbazole-1-carboxamide, 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 1470 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| (S)-sirtinol | Investigative | [10] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 67000 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| Para-sirtinol | Investigative | [10] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 13000 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| Ro31-8220 | Investigative | [15] | ||
| Synonyms |
Bisindolylmaleimide IX; ro 31-8220; 125314-64-9; Ro 31 8220; Ro 318220; UNII-W9A0B5E78O; Ro-318220; Ro-31-8220; CHEMBL6291; W9A0B5E78O; CHEBI:38912; 3-{3-[4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2,5-dioxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-1H-indol-1-yl}propyl carbamimidothioate; 3-{3-[4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2,5-dioxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-1H-indol-1-yl}propyl imidothiocarbamate; CHEMBL1591531; Carbamimidothioic acid, 3-(3-(2,5-dihydro-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2,5-dioxo-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)-1H-indol-1-yl)propyl; bisindolymaleimide IX
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 3500 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| RO-316233 | Investigative | [15] | ||
| Synonyms |
119139-23-0; bisindolylmaleimide iv; 3,4-di(1H-indol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione; Arcyriarubin A; 3,4-Bis(3-indolyl)maleimide; 3,4-Di-1H-indol-3-yl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione; UNII-MBK3OO5K8T; BIM IV; 3,4-bis(1H-indol-3-yl)pyrrole-2,5-dione; MBK3OO5K8T; CHEMBL266487; 3,4-bis(1H-indol-3-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione; DQYBRTASHMYDJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N; 2,3-bis(1H-Indol-3-yl)maleimide; 1H-Pyrrole-2,5-dione, 3,4-di-1H-indol-3-yl-; Ro-31-6233; AK-15401; 3,4-bis(3-indolyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione; Bisindoylmaleimide; Bisindolyl deriv. 3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| BD50: Aortic aneurysm or dissection | 3 Compound(s) Regulating the Disease | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| CRD-007 | Phase 2 | [16] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| WAY-644 | Investigative | [17] | ||
| Synonyms |
MMP-12 inhibitor (aortic abdominal aneurysm), Pfizer; MMP-12 inhibitor (aortic abdominal aneurysm), Wyeth
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| VDA-1124 | Investigative | [18] | ||
| Synonyms |
Granzyme B inhibitors (abdominal aortic aneurysms), viDA Therapeutics
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
References