m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05553
|
[1] | |||
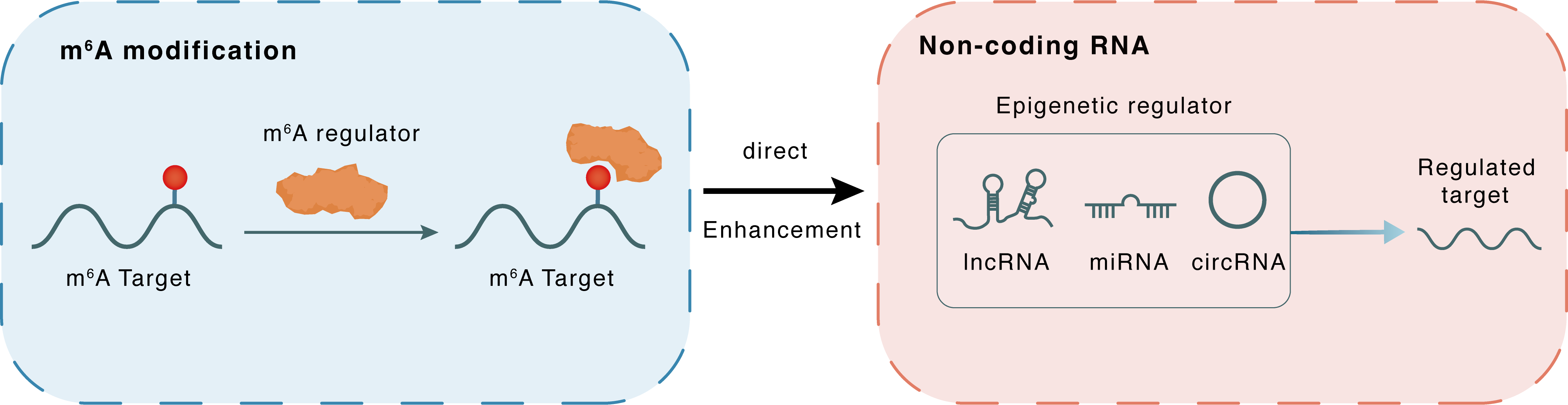 m6A modification
S-mu-GLT
S-mu-GLT
YTHDC1
m6A modification
S-mu-GLT
S-mu-GLT
YTHDC1
 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Non-coding RNA
SugLT
Regulated Target
lncRNA miRNA circRNA : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Non-coding RNA
SugLT
Regulated Target
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing protein 1 (YTHDC1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | S-mu-GLT (SugLT) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | S-mu-GLT (SugLT) | LncRNA | View Details | ||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → ncRNA | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A regulators directly modulate the functionality of ncRNAs through specific targeting ncRNA | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | Direct suppression of m6A modification of S-mu-GLT (SugLT) or of m6A reader YTHDC1 reduces CSR. METTL3 enzyme-catalyzed N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification drives recognition and 3' end processing of S-mu-GLT by the RNA exosome, promoting class switch recombination and suppressing chromosomal translocations. Tamoxifen affects the role of METTL3 in B cell development. | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Tamoxifen* | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell cycle | |||||
In-vitro Model |
CH12F3 | Mouse lymphoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_E067 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In-vivo Model | 6- to 12-week-old mice were used for experiments. | ||||