m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05334
|
[1] | |||
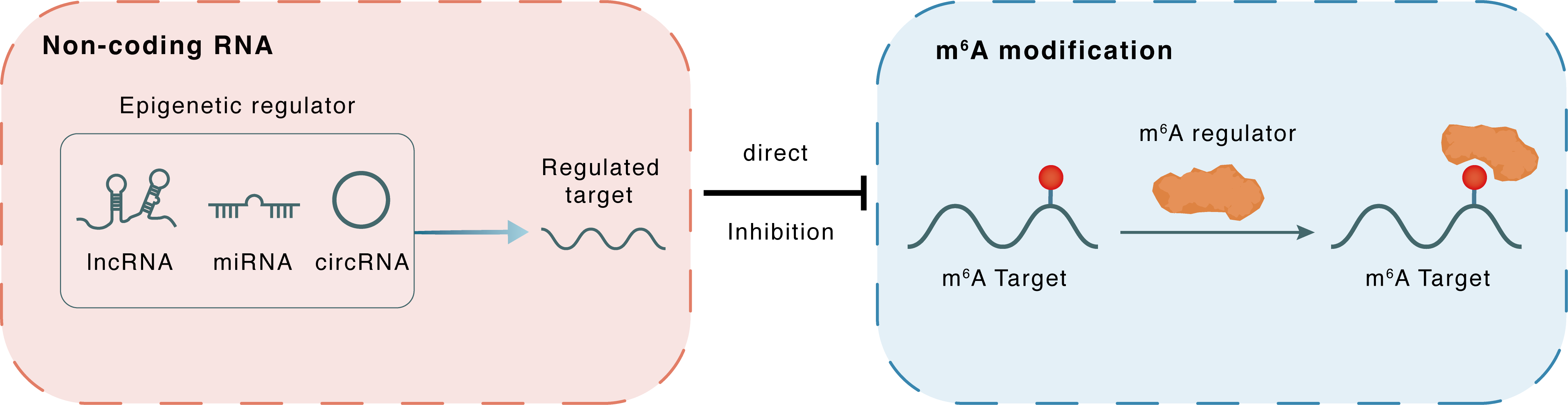 Non-coding RNA
miR-4294
IGF2BP3
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
KCNMB2-AS1
KCNMB2-AS1
IGF2BP3
Non-coding RNA
miR-4294
IGF2BP3
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
KCNMB2-AS1
KCNMB2-AS1
IGF2BP3
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | KCNMB2 antisense RNA 1 (KCNMB2-AS1) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-4294 | microRNA | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | ncRNA → m6A | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | ncRNAs directly impacts m6A modification through modulating the expression level of m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | KCNMB2 antisense RNA 1 (KCNMB2-AS1) was predominantly located in the cytoplasm and served as a competing endogenous RNA to abundantly sponge miR-130b-5p and hsa-miR-4294, resulting in the upregulation of IGF2BP3, a well-documented oncogene in CC. Moreover, IGF2BP3 was able to bind KCNMB2-AS1 by three N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification sites on KCNMB2-AS1, in which IGF2BP3 acted as an m6A "reader" and stabilized KCNMB2-AS1. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer | ICD-11: 2C77 | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In-vivo Model | A total of 1 × 107 control or KCNMB2-AS1-depleted SiHa cells were resuspended in 0.1 ml phosphate-buffered saline and inoculated into the armpit of 5-week-old male BALB/c nude mice. | ||||