m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05322
|
[1] | |||
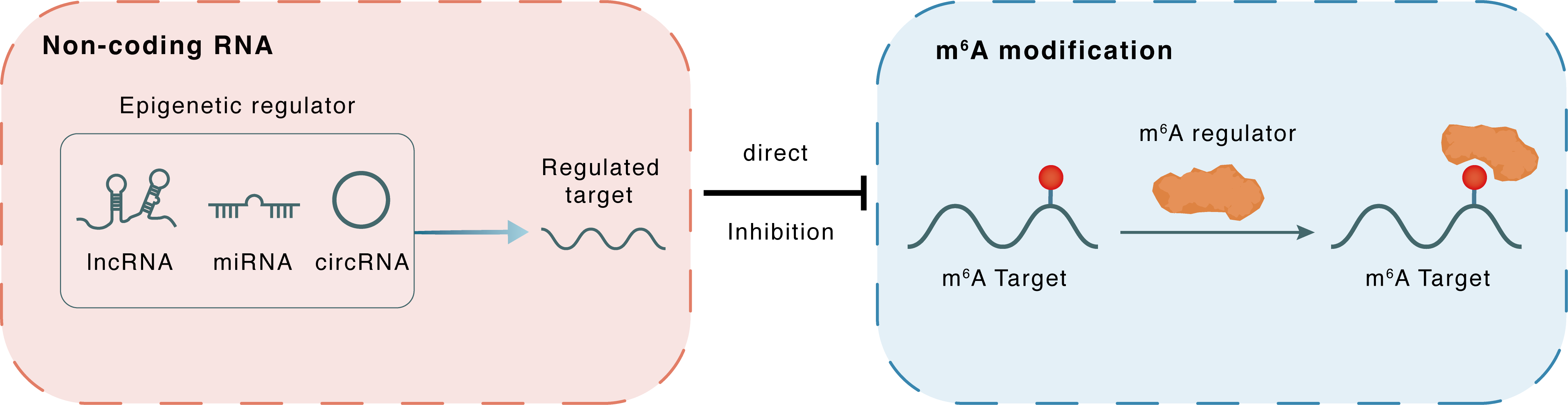 Non-coding RNA
miR-16-5p
YTHDF1
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
PKM
PKM
YTHDF1
Non-coding RNA
miR-16-5p
YTHDF1
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
PKM
PKM
YTHDF1
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-16-5p | microRNA | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | ncRNA → m6A | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | ncRNAs directly impacts m6A modification through modulating the expression level of m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | tumor hypoxia can transcriptionally induce HIF1alpha and post-transcriptionally inhibit the expression of hsa-miR-16-5p to promote YTHDF1 expression, which could sequentially enhance tumor glycolysis by upregulating Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM) and eventually increase the tumorigenesis and metastasis potential of breast cancer cells. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | |||
| Pathway Response | HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | ||||
| In-vivo Model | To investigate the effect of YTHDF1 on breast cancer progression in mice, the reared mice were randomly divided into two groups (n = 5). Each mouse was injected subcutaneously with 5 × 106 units of tumor cells to construct the tumor model. In the shCtrl group, shCtrl-transfected 4T1 (ATCC, #CRL-2539) cells were injected subcutaneously into mice to construct YTHDF1-normal 4T1 tumors. To investigate the effect of miR-16-5p on breast cancer progression by regulating the expression of YTHDF1, three experimental groups (n = 5) were designed for the in vivo experiment, which were the agomiR-nc+antgomiR-nc, agomiR-16-5p + antgomiR-nc, and agomiR-16-5p + antgomiR-16-5p groups | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| Pyruvate kinase PKM (PKM2/PKM) | 2 Compound(s) Regulating the Target | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| CAP-232 | Phase 2a | [2] | ||
| Synonyms |
TT-232; UNII-49D4Q4254Z; TT 232; 49D4Q4254Z; 147159-51-1; Phe-cys-tyr-trp-lys-cys-thr-NH2 (2-6)-disulfide; TLN 232; CAP 232; Phenylalanyl-cysteinyl-tyrosyl-tryptophyl-lysyl-cysteinyl-threoninamide (2-6)-disulfide; AC1OCF7X; CHEMBL539934; TLN-232; L-Threoninamide, D-phenylalanyl-L-cysteinyl-L-tyrosyl-D-tryptophyl-L-lysyl-L-cysteinyl-, cyclic (2-6)-disulfide; TT2-32; ZINC169289417; AKOS024458270; DB12088; NCGC00249606-01
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| TP-1454 | Phase 1 | [3] | ||
| MOA | Activator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| 2C60: Breast cancer | 2 Compound(s) Regulating the Disease | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| Entrectinib | Approved | [4] | ||
| Synonyms |
1108743-60-7; RXDX-101; UNII-L5ORF0AN1I; Entrectinib (RXDX-101); L5ORF0AN1I; Benzamide, N-[5-[(3,5-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1H-indazol-3-yl]-4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-[(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)amino]-; Benzamide, N-(5-((3,5-difluorophenyl)methyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)-4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-((tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)amino)-; Entrectinib [USAN:INN]; YMX; Kinome_2659; Entrectinib(rxdx-101); Entrectinib (USAN/INN); SCHEMBL3512601; GTPL8290; CHEMBL1983268; KS-00000TSK
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| Everolimus | Approved | [5] | ||
| External Link | ||||
References