m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03353
|
[1], [2] | |||
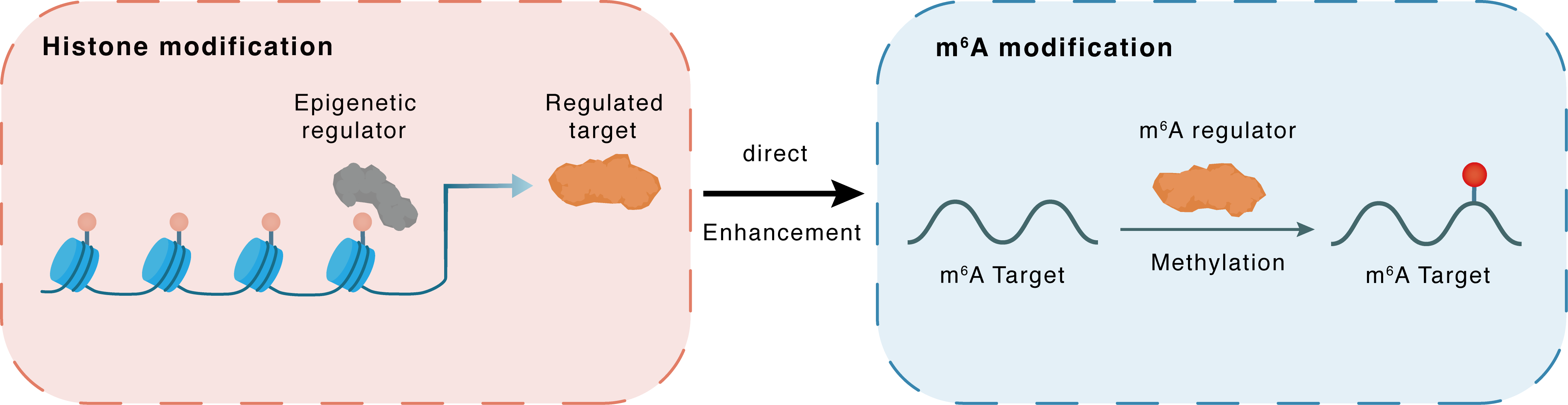 Histone modification
H3K27ac
p300
WTAP
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
DKK3
DKK3
WTAP
Methylation
Histone modification
H3K27ac
p300
WTAP
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
DKK3
DKK3
WTAP
Methylation
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Wilms tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | Dickkopf-related protein 3 (DKK3) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | View Details | |||
| Downstream Gene | WTAP | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | Histone modification → m6A | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | histone modification directly impacts m6A modification through modulating the level of m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | Histone acetyltransferase p300 promotes WTAP transcription through Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac). WTAP-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of NLRP3 mRNA in kidney injury of diabetic nephropathy.WTAP expression in HK-2 cells was examined with the introduction of C646, a histone acetyltransferase p300 inhibitor.the expression change pattern of Dickkopf-related protein 3 (DKK3) under DN circumstances is in line with those of METTL14 and WTAP. DKK3's m6A methylation sites were confirmed to be located in the 3'UTR region, which is how METTL14 and WTAP improved DKK3's mRNA stability. Finally, YTHDF1, a m6A reader, was demonstrated to recognize m6A-methylated DKK3 and promote DKK3 expression. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Diabetic nephropathy | ICD-11: GB61.Z | |||
| Responsed Drug | SETDB1-TTD-IN-1 | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HK-2 [Human kidney] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| In-vivo Model | Female mice (8 weeks old, 20-25 g) on a C57BL/6J background were fasted for 12 h but were allowed to drink water freely. They were then injected intraperitoneally with 50 mg/kg body weight of freshly dissolved STZ in sterile PBS for four consecutive days. Mice were given sterile PBS alone in the same way as an untreated control. The mice's blood glucose levels were assessed two weeks after their most recent treatment. Mice that exhibited glucose levels greater than 201 mg/dL were classified as successful hyperglycemic models and were utilized in subsequent studies. Five months after the final dose of STZ, the mice were euthanized, and the renal tissues were collected for pathological examination to confirm the successful establishment of the model of diabetes nephropathy induced by hyperglycemia. All animal experiments were performed according to the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the China Pharmaceutical University. Isoflurane was used to anesthetize mice. | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| Dickkopf-related protein 3 (DKK3) | 1 Compound(s) Regulating the Target | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| REIC gene therapy | Phase 1/2 | [3] | ||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | 2 Compound(s) Regulating the Target | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| CCS1477 | Phase 1/2 | [4] | ||
| Synonyms |
CCS-1477; CBP-IN-1; 2222941-37-7; (S)-1-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)-6-(5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1-((1r,4S)-4-methoxycyclohexyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperidin-2-one; SCHEMBL20094038; SCHEMBL21515367; SCHEMBL22134021; EX-A3687; NSC818619; NSC-818619; HY-111784; CS-0091862; (S)-1-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)-6-(5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1-(trans-4-methoxycyclohexyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperidin-2-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| FT-7051 | Phase 1 | [5] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| GB61: Chronic kidney disease | 15 Compound(s) Regulating the Disease | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| Finerenone | Approved | [6] | ||
| Synonyms |
UNII-DE2O63YV8R; BAY 94-8862; 1050477-31-0; BAY94-8862; DE2O63YV8R; Finerenone [USAN:INN]; Finerenone (JAN/USAN/INN); SCHEMBL8157011; GTPL8678; DTXSID10146928; J3.584.878I; D10633; 1,6-Naphthyridine-3-carboxamide, 4-(4-cyano-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-ethoxy-1,4-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-, (4S)-;1,6-Naphthyridine-3-carboxamide, 4-(4-cyano-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-ethoxy-1,4-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-, (4S)-; 1,6-Naphthyridine-3-carboxamide, 4-(4-cyano-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-ethoxy-1,4-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-, (4S)-; (4S)-4-(4-cyano-2-metho
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| Doxercalciferol | Approved | [7] | ||
| Synonyms |
Doxcercalciferol; Hectorol; Doxercalciferol [INN]; TSA 840; BCI-101; Doxercalciferol (INN); Hectorol (TN); (1R,3S,5Z)-5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(E,2R,5R)-5,6-dimethylhept-3-en-2-yl]-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-4-methylidenecyclohexane-1,3-diol; (5Z,7E,22E)-9,10-Secoergosta-5,7,10(19),22-tetraene-1alpha,3beta-diol; 1-Hydroxyergocalciferol; 1-alpha-Hydroxyvitamin D2; 1alpha-Hydroxyergocalciferol; 1alpha-OH-D2; 9,10-Secoergosta-5,7,10(19),22-tetraene-1,3-diol,(1-alpha,3-beta,5Z,7E,22E)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| Ferumoxytol | Approved | [8] | ||
| Synonyms |
MAGNETITE; Magnetic oxide; Ferrosoferric oxide; Magnetite (Fe3O4); Magnetic Black; Iron Black; Fenosoferric oxide; Black Iron BM; Meramec M 25; Black Gold F 89; RB-BL; 11557 Black; CCRIS 4376; H 3S; EPT 500; EINECS 215-169-8; KN 320; 1309-38-2; iron(ii; ferro ferric oxide; ferric ferrous oxide; Iron ores, magnetite; Ferumoxytol [USAN]; Eisen(II,III)-oxid; KBC 100 (mineral); Code 7228; CHEBI:50821; 1317-61-9 (Parent); LS-88610; 174794-75-3; 122303-97-3; 90577-09-6; 73904-98-0; 151820-32-5; 137263-94-6; 124364-57-4
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| Ferric citrate | Approved | [9] | ||
| Synonyms |
Nephoxil; Serene; Zerenex; JTT-751; KRX-0502; PBF-1681; Hyperphosphatemia therapy, Panion/Keryx
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| REACT | Phase 3 | [10] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| US-APR2020 | Phase 2/3 | [11] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| ALLN-346 | Phase 2 | [12] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| Runcaciguat | Phase 2 | [13] | ||
| Synonyms |
(3S)-3-(4-Chloro-3-(((2S,3R)-2-(4-chlorophenyl-4,4,4- trifluoro-3-methylbutanoyl)amino)phenyl)-3- cyclopropylpropanoic acid; (3S)-3-(4-chloro-3-{[(2S,3R)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-methylbutanoyl]amino}phenyl)-3-cyclopropylpropanoic acid; (3S)-3-[4-chloro-3-[[(2S,3R)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]phenyl]-3-cyclopropylpropanoic acid; 1402936-61-1; 5EZ01YDT5S; AC-37098; AKOS040742586; BAY 1101042; BAY1101042; BAY-1101042; BENZENEPROPANOIC ACID, 4-CHLORO-3-(((2S,3R)-2-(4-CHLOROPHENYL)-4,4,4-TRIFLUORO-3-METHYL-1-OXOBUTYL)AMINO)-.BETA.-CYCLOPROPYL-, (.BETA.S)-; Benzenepropanoic acid, 4-chloro-3-(((2S,3R)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-methyl-1-oxobutyl)amino)-beta-cyclopropyl-, (betaS)-; CHEMBL4650322; compound 45 [PMID: 33872507]; CS-0086784; GTPL12359; HY-109136; MS-29070; Runcaciguat; Runcaciguat [INN]; SCHEMBL20075857; UNII-5EZ01YDT5S; XZ7
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| GCS-100 | Phase 2 | [14] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| Neo-Kidney Augment | Phase 2 | [15] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| LY-2623091 | Phase 2 | [16] | ||
| Synonyms |
Chronic renal disease therapy, Eli Lilly
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| AZD1772//RDX5791 | Phase 2 | [17] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| LY3016859 | Phase 1/2 | [18] | ||
| Synonyms |
TGF-alpha.epiregulin mAb
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| ION532 | Phase 1 | [19] | ||
| Synonyms |
AZD2373
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| MEDI8367 | Phase 1 | [20] | ||
| External Link | ||||
References