m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03216
|
[1] | |||
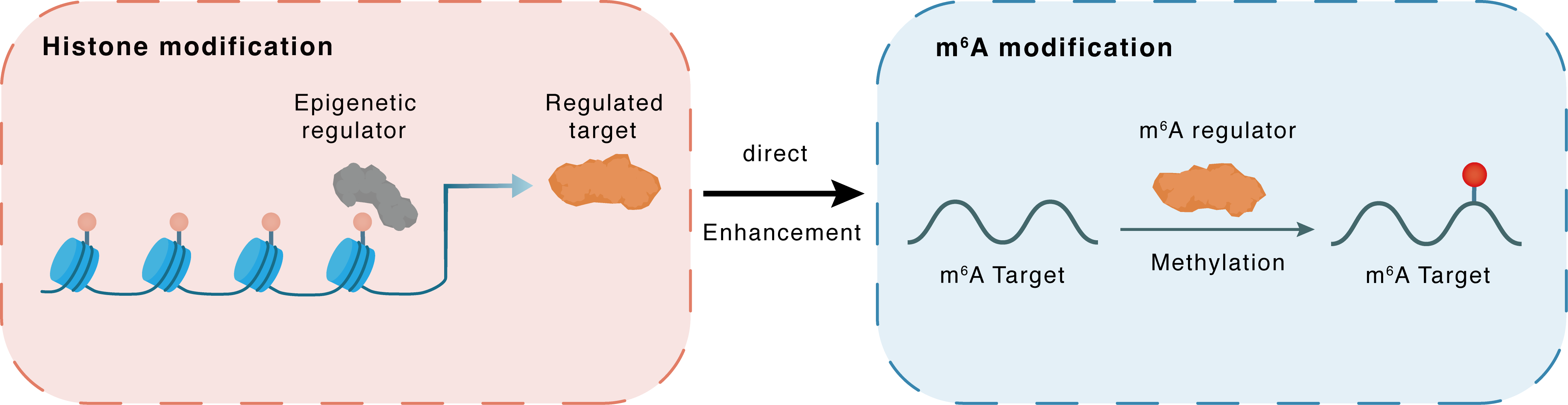 Histone modification
H3K4me3
MLL1
RBM15
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
TRIM72
TRIM72
RBM15
Methylation
Histone modification
H3K4me3
MLL1
RBM15
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
TRIM72
TRIM72
RBM15
Methylation
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 (TRIM72) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | View Details | |||
| Downstream Gene | RBM15 | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | Histone modification → m6A | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | histone modification directly impacts m6A modification through modulating the level of m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | KMT2A elevated RBM15 expression by increasing Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) on RBM15 promoter. RBM15 promoted the binding of Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 (TRIM72) to YTHDF2 by enhancing m6A modification on TRIM72 mRNA, thereby repressing TRIM72 expression. TRIM72 bound to ADAM9 and ubiquitinated it for degradation. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Preeclampsia | ICD-11: JA23 | |||
| Responsed Drug | Actinomycin D | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HTR-8/SVneo | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7162 | |