m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03094
|
[1] | |||
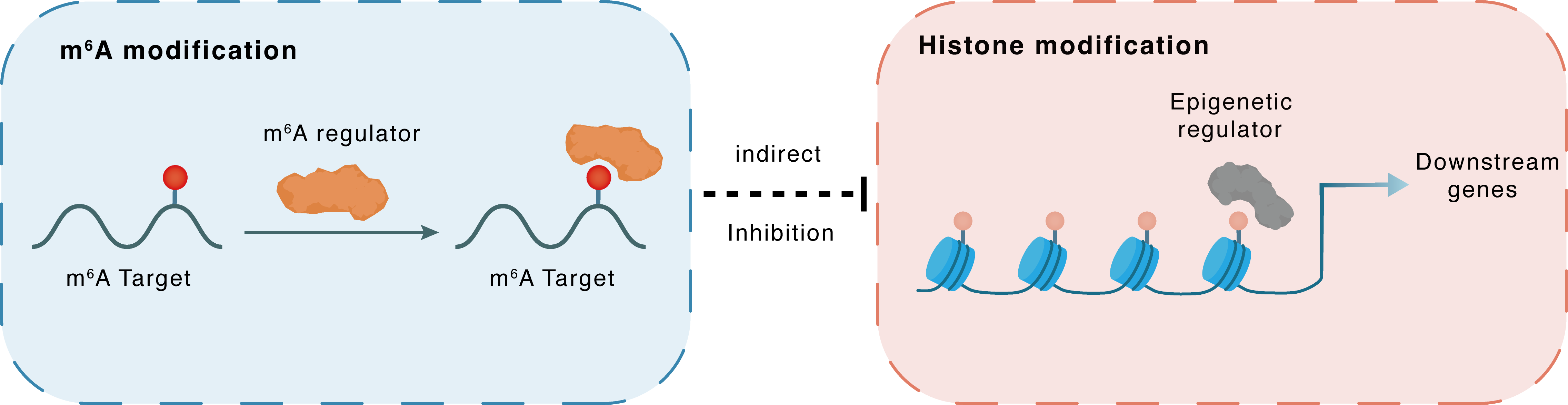 m6A modification
LINE1
LINE1
YTHDC1
m6A modification
LINE1
LINE1
YTHDC1
 : m6A sites
Indirect
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K9me3
SETDB1
Downstream Gene : m6A sites
Indirect
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K9me3
SETDB1
Downstream Gene
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing protein 1 (YTHDC1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | LINE-1 retrotransposable element ORF1 protein (LINE1) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETDB1 (SETDB1) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → Histone modification | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification indirectly regulates histone modification through downstream signaling pathways | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | YTHDC1 binds to the transcripts of retrotransposons (such as intracisternal A particles, ERVK and LINE-1 retrotransposable element ORF1 protein (LINE1)) in mouse ES cells and its depletion results in the reactivation of these silenced retrotransposons, accompanied by a global decrease in SETDB1-mediated Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3). | ||||