m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03076
|
[1] | |||
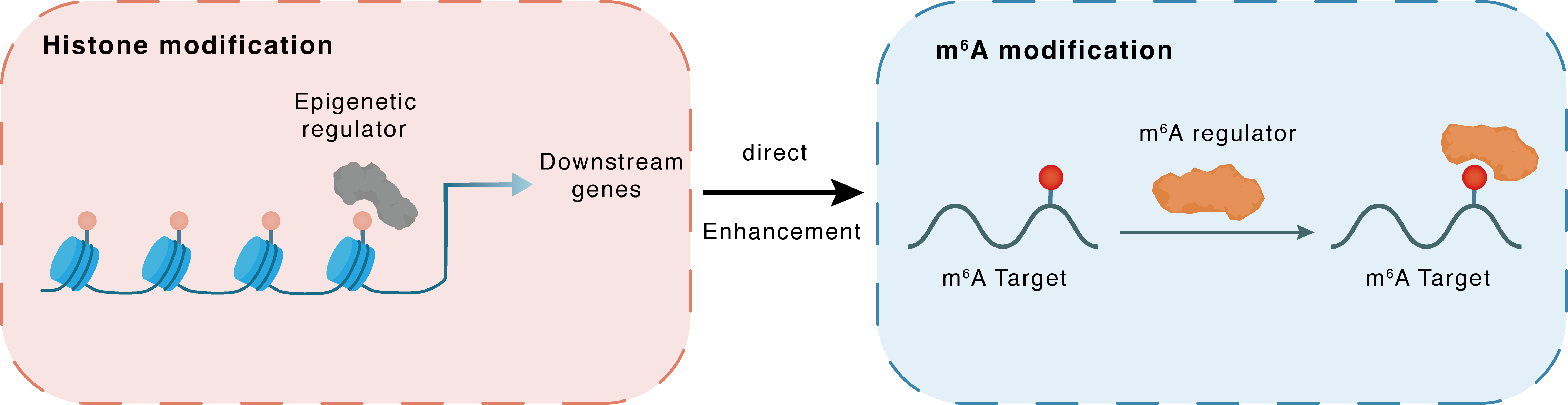 Histone modification
HNRNPA2B1
JMJD6
Downstream Gene
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
STING1
STING1
hnRNPA2B1
Histone modification
HNRNPA2B1
JMJD6
Downstream Gene
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
STING1
STING1
hnRNPA2B1
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1 (HNRNPA2B1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | Stimulator of interferon genes protein (STING1) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Bifunctional arginine demethylase and lysyl-hydroxylase JMJD6 (JMJD6) | ERASER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (HNRNPA2B1) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | Histone modification → m6A | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | histone modification directly impacts m6A modification through recruiting m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | the arginine demethylase JMJD6 promotes the demethylation of HNRNPA2B1 at Arg226 and activates its translocation to cytoplasm, which further magnifies the expression of CGAS, IFI16, and Stimulator of interferon genes protein (STING1) | ||||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | ||
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In-vivo Model | Hnrnpa2b1fl/fl and Hnrnpa2b1fl/flLyz2-Cre+ mice were infected with 1×108 plaque-forming units (PFU) of HSV-1 viruses intraperitoneally. Serum IFN-beta concentrations were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit. HSV-1 titers were determined by plaque assays using homogenates from brains of infected mice. | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| Stimulator of interferon genes protein (STING1) | 17 Compound(s) Regulating the Target | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| ADU-S100 | Phase 2 | [2] | ||
| Synonyms |
MIW815; IZJJFUQKKZFVLH-LTKSHMRXSA-N; 1638241-89-0; AKOS027321070; HY-12885
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Activator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| ADU- S100 | Phase 2 | [3] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| MK-1454 | Phase 2 | [4] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| IMSA101 | Phase 1/2 | [5] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| BMS-986301 | Phase 1 | [6] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| MK-2118 | Phase 1 | [7] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| XMT-2056 | Phase 1 | [8] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| TAK-500 | Phase 1 | [9] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SB 11285 | Phase 1 | [10] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| E7766 | Phase 1 | [11] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| GSK3745417 | Phase 1 | [12] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| A296 | Phase 1 | [13] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| TAK-676 | Phase 1 | [14] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SNX281 | Phase 1 | [15] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SYNB1891 | Phase 1 | [16] | ||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| C-178 | Investigative | [17] | ||
| Synonyms |
329198-87-0; STING inhibitor C-178; N-(dibenzo[b,d]furan-3-yl)-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide; N-dibenzofuran-3-yl-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide; Oprea1_355995; Oprea1_671722; 5-Nitro-furan-2-carboxylic acid dibenzofuran-3-ylamide; SCHEMBL21065360; BCP31292; ZINC4838645; s6667; AKOS000544527; MCULE-6315822200; BS-17017; C 178;C178;STING inhibitor C-178; HY-123963; CS-0087693; ST51004028; N-benzo[3,4-b]benzo[d]furan-3-yl(5-nitro(2-furyl))carboxamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
| C-176 | Investigative | [18] | ||
| Synonyms |
314054-00-7; N-(4-iodophenyl)-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide; C-176 STING inhibitor; STING inhibitor C-176; STING Inhibitor 1; Cambridge id 5344639; Oprea1_000586; Oprea1_014551; 5-Nitro-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-iodo-phenyl)-amide; CHEMBL3593839; SCHEMBL13219564; ZINC830011; BCP30174; EX-A2974; s6575; STK016322; AKOS000670518; MCULE-4963641555; BS-16912; HY-112906; AK00792625; CS-0067918; ST50232559; C176; C 176; AB00081654-01; N-(4-iodophenyl)(5-nitro(2-furyl))carboxamide; SR-01000406953; SR-01000406953-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Agonist | |||
| External Link | ||||
References