m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00727)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
GJA1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF3 | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse embryonic fibroblasts | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shYthdf3 embryonic fibroblasts
Control: shLuc embryonic fibroblasts
|
GSE156437 | |
| Regulation |
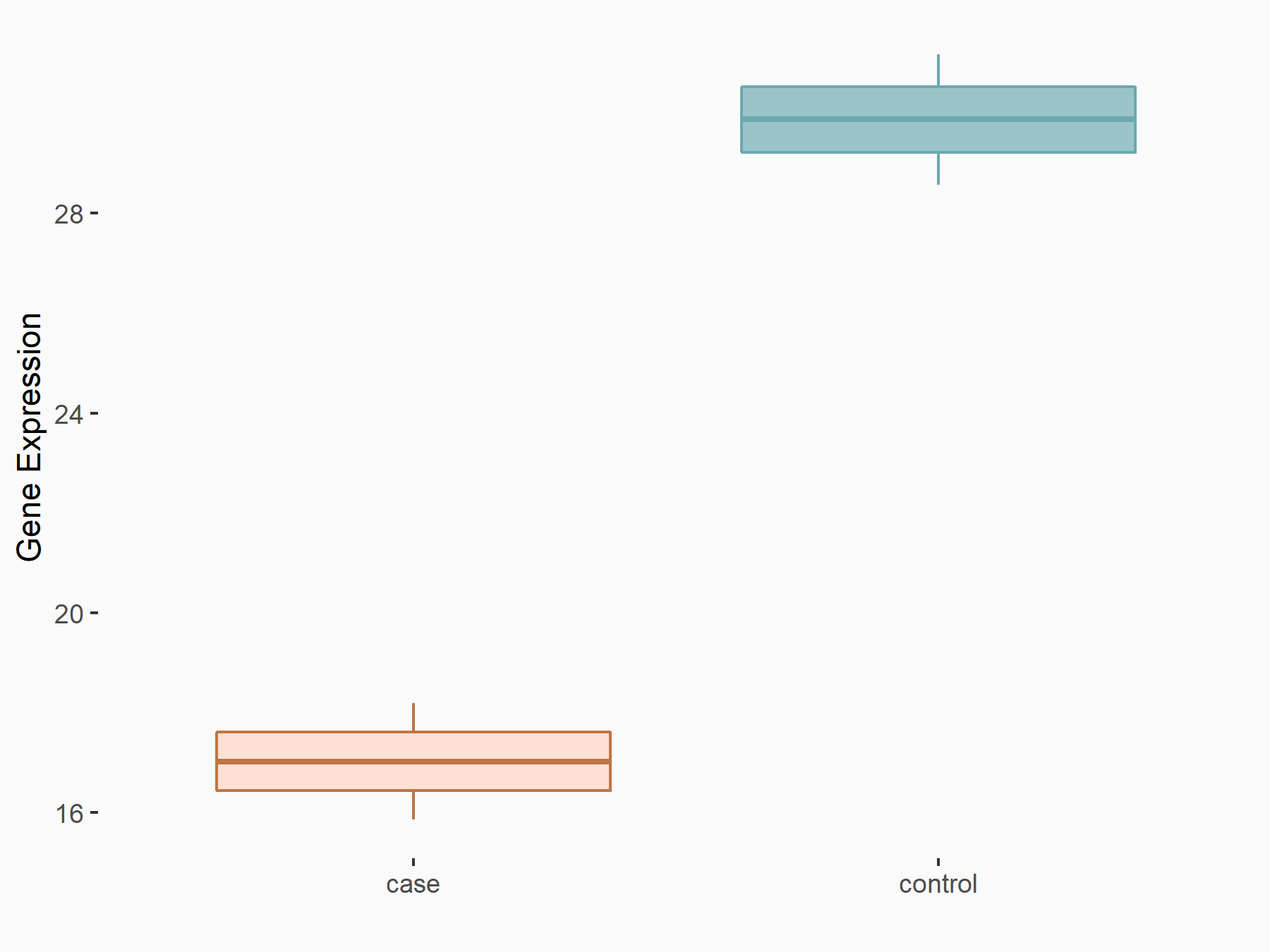 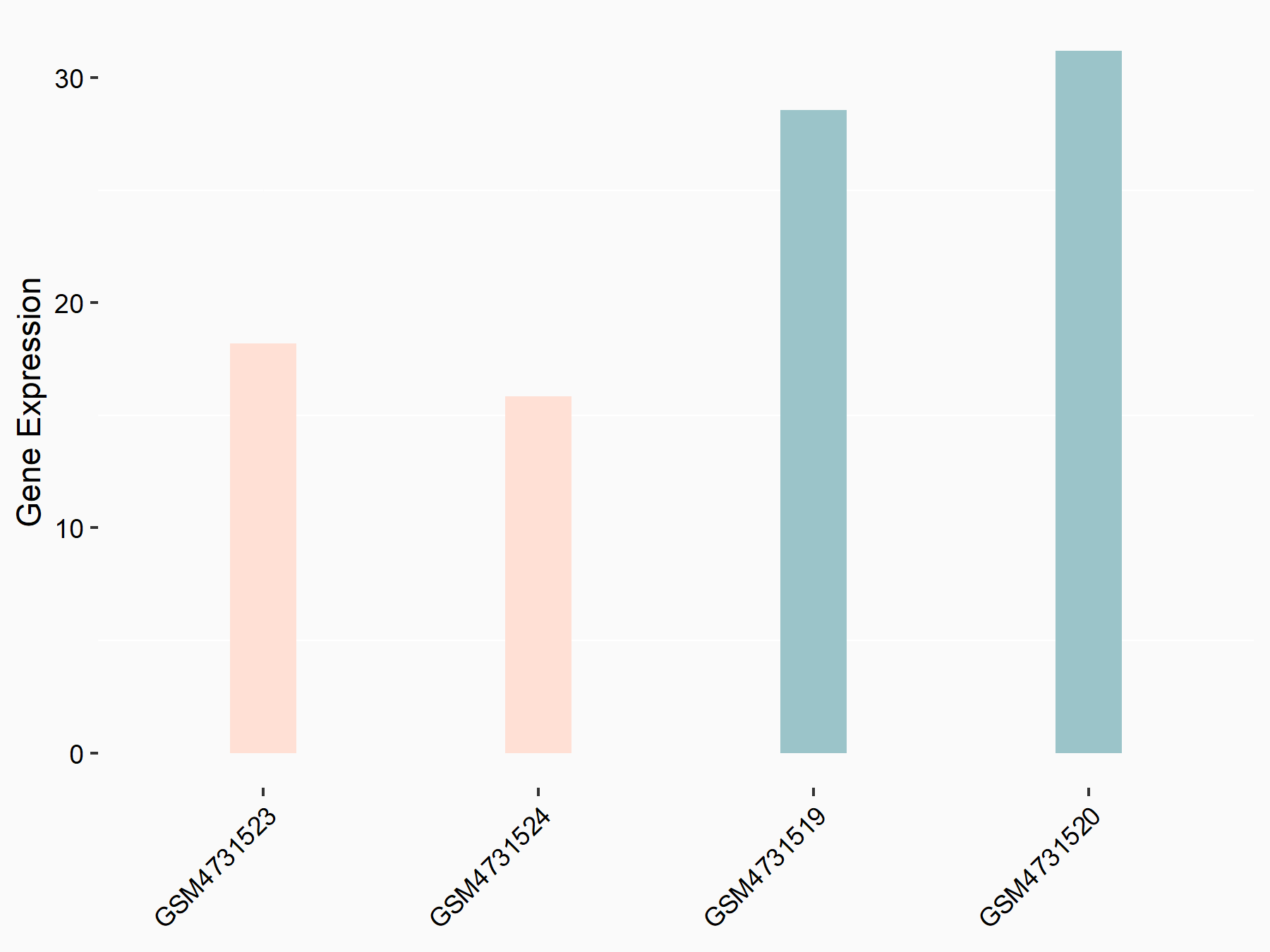 |
logFC: -7.79E-01 p-value: 7.79E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Mechanistically, YTHDF3 enhances the translation of m6A-enriched transcripts for ST6GALNAC5, Gap junction alpha-1 protein (GJA1), and EGFR, all associated with breast cancer brain metastasis. This work uncovers an essential role of YTHDF3 in controlling the interaction between cancer cells and brain microenvironment, thereby inducing brain metastatic competence. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell metastasis | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231Br (After brain metastases of MDA-MB-361 breast adenocarcinoma cells) | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MDA-IBC-3 | Breast inflammatory carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_HC47 | |
| JIMT-1Br3 (After brain metastases of JIMT-1 breast cancer cells) | ||||
| JIMT-1 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2077 | |
| HEK293-FT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6911 | |
| HCC1954Br (After brain metastases of HCC1954 breast cancer cells) | ||||
| HCC1954 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1259 | |
| bEnd.3 | Cerebrovascular endothelioma cells from mice | Mus musculus | CVCL_0170 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| 4T1Br (After brain metastases of 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells) | ||||
| 4T1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0125 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the in vivo brain and bone extravasation and seeding assays, cancer cells labeled with CMFDA C2925 (Thermo fisher scientific) or GFP were injected intracardially into the nude mice. Cell number and injection procedure were described in "Animal Experiments". For the in vivo lung extravasation and seeding assays, cancer cells labeled with GFP (2.5 × 105 cells/mouse) were injected into the tail vein of nude mice. At 24 or 48 hrs later, the mice were sacrificed. | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Mechanistically, YTHDF3 enhances the translation of m6A-enriched transcripts for ST6GALNAC5, Gap junction alpha-1 protein (GJA1), and EGFR, all associated with breast cancer brain metastasis. This work uncovers an essential role of YTHDF3 in controlling the interaction between cancer cells and brain microenvironment, thereby inducing brain metastatic competence. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 (YTHDF3) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell metastasis | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231Br (After brain metastases of MDA-MB-361 breast adenocarcinoma cells) | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MDA-IBC-3 | Breast inflammatory carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_HC47 | |
| JIMT-1Br3 (After brain metastases of JIMT-1 breast cancer cells) | ||||
| JIMT-1 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2077 | |
| HEK293-FT | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6911 | |
| HCC1954Br (After brain metastases of HCC1954 breast cancer cells) | ||||
| HCC1954 | Breast ductal carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1259 | |
| bEnd.3 | Cerebrovascular endothelioma cells from mice | Mus musculus | CVCL_0170 | |
| BEAS-2B | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| 4T1Br (After brain metastases of 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells) | ||||
| 4T1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0125 | |
| In-vivo Model | For the in vivo brain and bone extravasation and seeding assays, cancer cells labeled with CMFDA C2925 (Thermo fisher scientific) or GFP were injected intracardially into the nude mice. Cell number and injection procedure were described in "Animal Experiments". For the in vivo lung extravasation and seeding assays, cancer cells labeled with GFP (2.5 × 105 cells/mouse) were injected into the tail vein of nude mice. At 24 or 48 hrs later, the mice were sacrificed. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00727)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: AC4SITE000112 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448083-121448084:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | ACCAGGTGTTAATTTTGATCCGGTGGAGGTGGTACTCAACA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1 | ||
| Seq Type List | ac4C-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: ac4C_site_1617 | ||
2'-O-Methylation (2'-O-Me)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000413 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121443632-121443633:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | AATAAAGACTATACTTTCAGGGATCATTTCTATAGTTTGTT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293 | ||
| Seq Type List | RiboMeth-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1; rmsk_2058536 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_5969 | ||
Other RNA modification (m2,2,7Gpp(pN))
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: RNASITE000001 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121443615-121443616:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTTTATAGAATGTAAATAAAGACTATACTTTCAGGGAT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | nucleoplasmic | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: otherMod_site_1067 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 65 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076896 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121435614-121435615:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGTTGAGTCAGTGGCTTGAAACTTTTAAAAGCTCTGTGCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; A549; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732519 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076897 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121435709-121435710:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGGCGTGAGGAAAGTACCAAACAGCAGCGGAGTTTTAAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732520 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076898 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121435727-121435728:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AAACAGCAGCGGAGTTTTAAACTTTAAATAGACAGGTCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732521 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076899 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121435738-121435739:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGTTTTAAACTTTAAATAGACAGGTCTGAGTGCCTGAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732522 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076900 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121435756-121435757:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGACAGGTCTGAGTGCCTGAACTTGCCTTTTCATTTTACTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732523 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076901 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121437386-121437387:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTCTTTTTTCCTCTTAAACTTGCTGAATCCCACTATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; Huh7; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732524 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076902 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121446845-121446846:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTCAGGTGGTGCCCAGGCAACATGGGTGACTGGAGCGCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732525 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076903 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121446873-121446874:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GACTGGAGCGCCTTAGGCAAACTCCTTGACAAGGTTCAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; H1A; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732526 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076904 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121446881-121446882:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGCCTTAGGCAAACTCCTTGACAAGGTTCAAGCCTACTCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732527 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076905 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121446961-121446962:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCCGAATCCTGCTGCTGGGGACAGCGGTTGAGTCAGCCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; kidney; H1A; H1B; A549; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732528 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076906 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447010-121447011:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCAGTCTGCCTTTCGTTGTAACACTCAGCAACCTGGTTGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; HEK293; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732529 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076907 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447046-121447047:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTGTGAAAATGTCTGCTATGACAAGTCTTTCCCAATCTCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732530 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076908 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447111-121447112:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCATATTTGTGTCTGTACCCACACTCTTGTACCTGGCTCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732531 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076909 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447161-121447162:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTGATGCGAAAGGAAGAGAAACTGAACAAGAAAGAGGAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732532 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076910 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447166-121447167:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCGAAAGGAAGAGAAACTGAACAAGAAAGAGGAAGAACTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732533 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076911 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447182-121447183:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGAACAAGAAAGAGGAAGAACTCAAGGTTGCCCAAACTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732534 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076912 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447198-121447199:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGAACTCAAGGTTGCCCAAACTGATGGTGTCAATGTGGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; Brain; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732535 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076913 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447217-121447218:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AACTGATGGTGTCAATGTGGACATGCACTTGAAGCAGATTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; brain; A549; hESC-HEK293T; Brain; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732536 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076914 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447223-121447224:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGTCAATGTGGACATGCACTTGAAGCAGATTGAGATAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732537 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076915 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447306-121447307:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCGAGGGGGGTTGCTGCGAACCTACATCATCAGTATCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732538 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076916 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447310-121447311:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGGGGGGTTGCTGCGAACCTACATCATCAGTATCCTCTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732539 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076917 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447370-121447371:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTTCTTGCTGATCCAGTGGTACATCTATGGATTCAGCTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732540 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076918 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447436-121447437:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCCTGCCCACATCAGGTGGACTGTTTCCTCTCTCGCCCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732541 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076919 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447465-121447466:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTCTCGCCCCACGGAGAAAACCATCTTCATCATCTTCATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732542 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076920 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447527-121447528:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGGCCTTGAATATCATTGAACTCTTCTATGTTTTCTTCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732543 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076921 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447594-121447595:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGAGCGACCCTTACCATGCGACCAGTGGTGCGCTGAGCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.844928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732544 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076922 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447622-121447623:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCGCTGAGCCCTGCCAAAGACTGTGGGTCTCAAAAATATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732545 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076923 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447727-121447728:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGTTACTGGCGACAGAAACAATTCTTCTTGCCGCAATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; U2OS; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732546 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076924 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447772-121447773:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAAGCAAGCAAGTGAGCAAAACTGGGCTAATTACAGTGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732547 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076925 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447794-121447795:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGGCTAATTACAGTGCAGAACAAAATCGAATGGGGCAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; Brain; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732548 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076926 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447884-121447885:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GATAACCAGAATTCTAAAAAACTAGCTGCTGGACATGAATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HepG2; Brain; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732549 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076927 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447896-121447897:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTAAAAAACTAGCTGCTGGACATGAATTACAGCCACTAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; brain; A549; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; Brain; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732550 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076928 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447925-121447926:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACAGCCACTAGCCATTGTGGACCAGCGACCTTCAAGCAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HepG2; Brain; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732551 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076929 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121447968-121447969:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGTCGTGCCAGCAGCAGACCTCGGCCTGATGACCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HepG2; Brain; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732552 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076930 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448127-121448128:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTATTCATGAGGCTTAGAAAACACAAAGACATTAGAATACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732553 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076931 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448135-121448136:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGGCTTAGAAAACACAAAGACATTAGAATACCTAGGTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732554 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076932 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448238-121448239:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TAAAGTAGTGGATTCAAAGAACTTAGATTATAAATAAGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732555 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076933 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448272-121448273:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TAAGAGTTCCATTAGGTGATACATAGATAAGGGCTTTTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732556 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076934 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448301-121448302:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGGCTTTTTCTCCCCGCAAACACCCCTAAGAATGGTTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; fibroblasts; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732557 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076935 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448377-121448378:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | TATTTTTGTTTTACCAAGAAACTGAAATAATTCTGGCCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732558 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076936 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448414-121448415:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAGGAATAAATACTTCCTGAACATCTTAGGTCTTTTCAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732559 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076937 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448473-121448474:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTCCTTAAGTCCCTGCTAAAACATTCCATTGTTAAAATTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732560 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076938 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448589-121448590:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGTATCAGTTTAAAATTCAGACAAGGCCCACAGAATAAGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732561 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076939 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448656-121448657:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTCTTTTTCCATCCACTTGCACAATATCATTACCATCACTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732562 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076940 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448702-121448703:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCATTCCTCAGCTACTACTCACATTCATTTAATGGTTTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000647564.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732563 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076941 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448807-121448808:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAAGCCATGCTTAATATTTAACAATCACTTATATGTGTGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732564 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076942 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448859-121448860:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTGTTTGTCATGTATTGGTACAAGCAGATACAGTATAAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732565 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076943 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448907-121448908:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CACAGATTTGAAAATAATGCACATATGGTGTTCAAATTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732566 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076944 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121448971-121448972:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGGCCAATATGGTGTTTACATTATATAATTCCTGCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732567 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076945 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449121-121449122:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GATATAGCAGTAATGCTATTACTGAAATGAATTTCCTTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732568 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076946 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449183-121449184:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTGAATGATAGAATTTTAGTACTGTAAACAGGCTTTAGTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.278136905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732569 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076947 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449190-121449191:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATAGAATTTTAGTACTGTAAACAGGCTTTAGTCATTAATGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hNPCs; hESCs; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732570 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076948 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449216-121449217:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTAGTCATTAATGTGAGAGACTTAGAAAAAATGCTTAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732571 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076949 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449240-121449241:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | AGAAAAAATGCTTAGAGTGGACTATTAAATGTGCCTAAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hNPCs; hESCs; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732572 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076950 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449302-121449303:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTTGGGTTTTCCTACTTAATACACAGTAATTCAGAACTTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732573 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076951 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449317-121449318:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TTAATACACAGTAATTCAGAACTTGTATTCTATTATGAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hNPCs; hESCs | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732574 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076952 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449427-121449428:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTGAAAGAGGATTCAGTAGTACACATACAACTAATTTATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732575 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076953 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449450-121449451:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CATACAACTAATTTATTTGAACTATATGTTGAAGACATCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732576 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076954 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449464-121449465:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATTTGAACTATATGTTGAAGACATCTACCAGTTTCTCCAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732577 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076955 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449498-121449499:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTCCAAATGCCTTTTTTAAAACTCATCACAGAAGATTGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hNPCs; fibroblasts; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; DART-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732578 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076956 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449569-121449570:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CATGCATGTCAGCTACATAAACAGTTTTGTACAATGAAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; fibroblasts; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732579 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076957 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449604-121449605:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAAAATTACTAATTTGTTTGACATTCCATGTTAAACTACGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732580 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076958 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449618-121449619:+ | ||
| Sequence | TGTTTGACATTCCATGTTAAACTACGGTCATGTTCAGCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000282561.4; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649132.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732581 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076959 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449655-121449656:+ | ||
| Sequence | CTTCATTGCATGTAATGTAGACCTAGTCCATCAGATCATGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732582 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE076960 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121449722-121449723:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AAAGTTTTAATTTAGTATAAACATAGCTTCTATATTCCGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_732583 | ||
Pseudouridine (Pseudo)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: PSESITE000241 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121443623-121443624:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TAGAATGTAAATAAAGACTATACTTTCAGGGATCATTTCTA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000649003.1; rmsk_2058536; ENST00000650427.1; ENST00000282561.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Pseudo_site_4332 | ||
| mod ID: PSESITE000242 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr6:121443627-121443628:+ | [14] | |
| Sequence | ATGTAAATAAAGACTATACTTTCAGGGATCATTTCTATAGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649003.1; ENST00000649132.1; ENST00000282561.4; rmsk_2058536; ENST00000647564.1; ENST00000650427.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Pseudo_site_4333 | ||
References