m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00690)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
DAPK3
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Protein virilizer homolog (VIRMA) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by VIRMA | ||
| Cell Line | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siVIRMA HUVECs
Control: siControl HUVECs
|
GSE167067 | |
| Regulation |
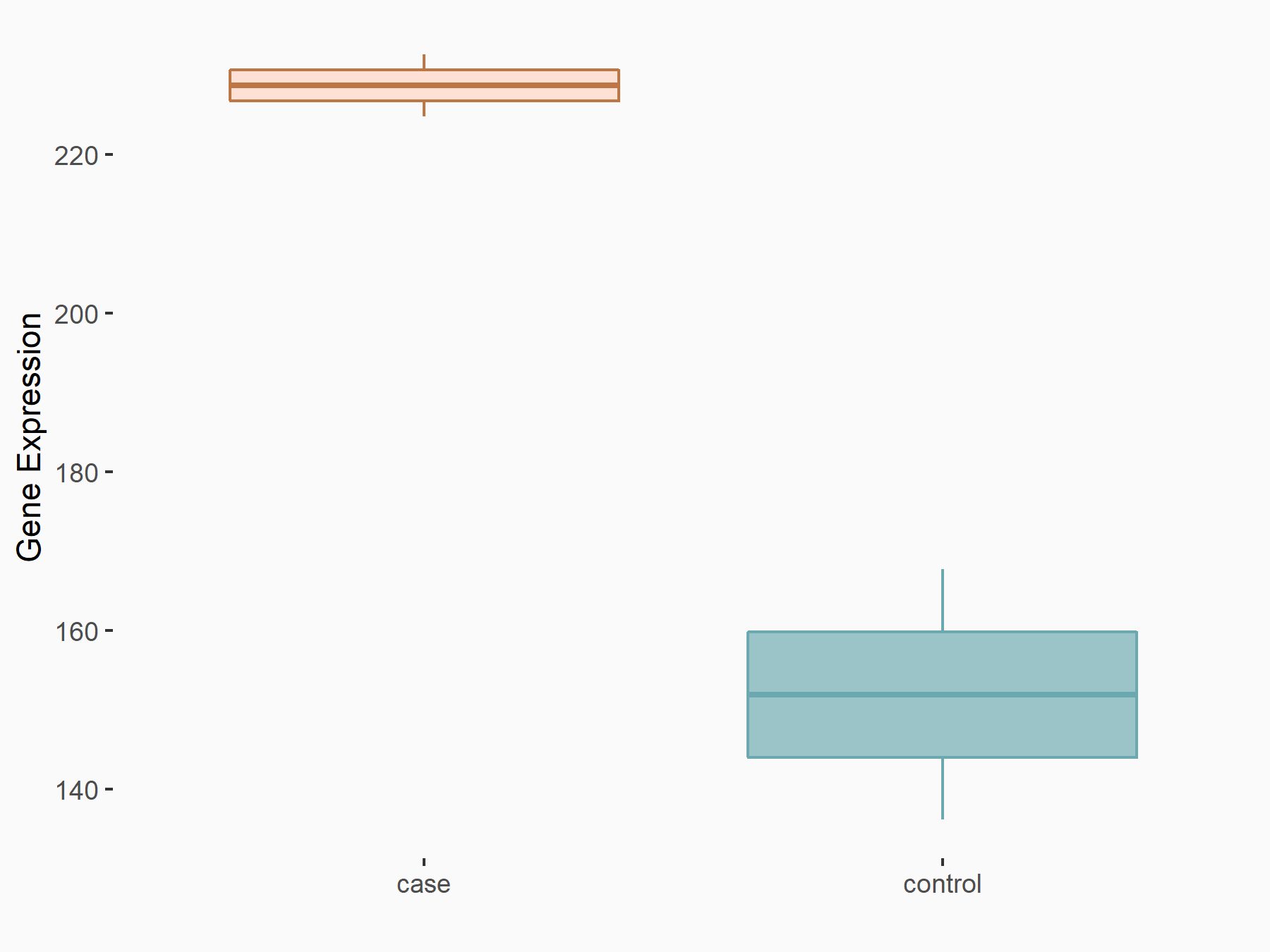  |
logFC: 5.95E-01 p-value: 2.81E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | High expression of KIAA1429 was testified in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and predicted worse prognosis in patients. KIAA1429-guided m6A modifications promoted NSCLC progression via m6A-dependent degradation of Death-associated protein kinase 3 (DAPK3) mRNA. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| In-vitro Model | PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | High expression of KIAA1429 was testified in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and predicted worse prognosis in patients. KIAA1429-guided m6A modifications promoted NSCLC progression via m6A-dependent degradation of Death-associated protein kinase 3 (DAPK3) mRNA. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | Protein virilizer homolog (VIRMA) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| NCI-H520 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1566 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00690)
| In total 7 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008748 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3962137-3962138:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | TGGGCCGGGTGCGATGGCTCACGCCTGTAATCTCAGCACTT | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4918501; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_64672 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008749 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3962693-3962694:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | ACCTCTGCCTCCCGGGTTCAAGTGATTCCCATGCCTCAGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_64673 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008750 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3962750-3962751:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTTGCCCAGGCTGGATGAAGTGCCAAGGCCCCGTCTCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_64674 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008751 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3963377-3963378:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTCCTGTCCCTCTGGCTGCTAGGGAGCCCAGCCTCCTCTCG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_64675 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008752 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3965980-3965981:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGCCTGGGCAATACGGCAAGACCCTGTCTCTACAAAAA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000545797.7; rmsk_4918511; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_64676 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008753 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3966016-3966017:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGTGGGAGGATCTCTTGAGGCCAGGAGTTCCAAAGCAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000601824.1; rmsk_4918511; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_64677 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE008754 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3966287-3966288:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTGGGACAGCTGGGTCTGTTAGCAGGAGACAGCGTGGAGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_64678 | ||
N1-methyladenosine (m1A)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M1ASITE000065 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959236-3959237:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGGGACCAGCGGCCTCAAGCGCCGCTTCAGCCGCCTGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m1A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m1A_site_518 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 39 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038326 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3958543-3958544:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGGGTGCCCTGCTGCGGACTCCTCCGCGAGCCCCATCG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; GM12878; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411418 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038327 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3958649-3958650:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGGGTGGGATGGACGGCGGACAGGCAGTCCCCACGCTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411419 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038328 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3958729-3958730:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTTGCGGGTAGTTGCACGGACAATTCGGCGGGGTGCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411420 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038329 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3958805-3958806:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTGGCACCGTGAGGGTTGGGACCCACCGAGGCGCAGAGGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000595279.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411421 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038330 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3958846-3958847:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCATCGTCGGTGACCCTGGGACCCTCCAGGCAGCGTGGCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411422 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038331 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959072-3959073:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGGGTGGGCCAGGCCCCAGGACAGCCGGAGCTCGGCCTGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000595279.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411423 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038332 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959158-3959159:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGAGATGCGCTTCGTGCAGGACCTCGTGCGCGCCCTGGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411424 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038333 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959212-3959213:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCGCTTCAGCCGCCTGGAGAACCGCTACGAGGCGCTGGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411425 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038334 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959249-3959250:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCAAGGGCGCGCTGCTGGGGACCAGCGGCCTCAAGCGCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000595279.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411426 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038335 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959303-3959304:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TACGGCAGGAGCTGCTCAAGACCGAGGCGCTCAAGCGGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411427 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038336 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959335-3959336:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGCGACAGCCTGGGCCAGGACCTGCGGAGGCTACGGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411428 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038337 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959350-3959351:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGGTACCGCGAGGAGAGCGACAGCCTGGGCCAGGACCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411429 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038338 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959551-3959552:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GACCACGCGTCTGAAGGAGTACACCATCAAGTCGCACTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411430 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038339 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959570-3959571:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCGAGCGGCGGCGCCTGAAGACCACGCGTCTGAAGGAGTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GM12878; A549; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; TREX; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411431 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038340 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959605-3959606:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCGGAACGTGCGTGGTGAGGACAGCGGCCGCAAGCCCGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GM12878; A549; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; TREX; MSC; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411432 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038341 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959664-3959665:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCTGGGTGGCATCGCGGGGACCCCGCTCAGGCTTCCCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; MM6; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; iSLK; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000594894.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411433 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038342 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959718-3959719:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCTGCCGGATGAGCCCCTGAACCTCAGTTCACACTGGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000594894.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411434 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038343 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3960073-3960074:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACCATTGCCCAGAGCCTGGAACATTCCTGGATTAAGGTAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; HeLa; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000594894.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411435 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038344 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3961041-3961042:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CACCAGCGAGCTGGCCAAGGACTTCATTCGCCGGCTGCTCG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000594894.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411436 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038345 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3961062-3961063:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CGACGAGGAGTACTTCAGCAACACCAGCGAGCTGGCCAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000594894.1; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411437 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038346 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3961092-3961093:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CACCAACATCTCAGCCGTGAACTACGACTTCGACGAGGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000594894.1; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411438 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038347 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3961107-3961108:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CAAGCAGGAGACGCTCACCAACATCTCAGCCGTGAACTACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000594894.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411439 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038348 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3961129-3961130:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CATCCCCGTTCCTGGGCGAGACCAAGCAGGAGACGCTCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000594894.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411440 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038349 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3961191-3961192:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGTGGTGGGAGCCCAGGACCCCACTGAGCCCCCACGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411441 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038350 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3961836-3961837:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAAGTGCCAGAGGTGGTTAGACACCCCCGTTTTCCACTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411442 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038351 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3963876-3963877:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCGCTGGGCCTGGAGGCGGACATGTGGTGAGTGTACCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411443 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038352 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3963903-3963904:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCAGCCCCAGAGATTGTGAACTATGAGCCGCTGGGCCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411444 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038353 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3964269-3964270:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCGGGGAACGAGTTCAAGAACATCTTCGGCACCCCGGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411445 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038354 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3964299-3964300:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CATCGACTTCGGCATCGCGCACAAGATCGAGGCGGGGAACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411446 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038355 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3964350-3964351:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGAAAACATCATGCTGCTGGACAAGAACGTGCCCAACCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000596311.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411447 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038356 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3964365-3964366:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCCACCCCAGCCGGAAAACATCATGCTGCTGGACAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000601824.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411448 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038357 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3964645-3964646:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTGCACTCTAAGCGCATCGCACACTTTGACCTGAAGGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000596311.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411449 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038358 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3964799-3964800:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCACGACATCTTCGAGAACAAGACGGACGTGGTCCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411450 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038359 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3964856-3964857:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGAGATCGAGCGGGAGGTGAACATCCTGCGGGAGATCCGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000593844.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411451 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038360 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3969703-3969704:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAGGCAGGAGGACGTGGAGGACCATTATGAGATGGGGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000596311.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411452 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038361 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3969744-3969745:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGAAGCTGCTGGAAGGCGGACCGGCCGCCATGTCCACGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7; ENST00000593844.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411453 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038362 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3969813-3969814:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCAGGGTTGCCATTAGGGGACTCCTGAGGTCCTATCTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411454 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038363 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3969904-3969905:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGGCTTGTGTTTGCTGGACAGGTCTGTCCATTAATCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000593844.1; ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411455 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE038364 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3970601-3970602:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGAGGTTAATCTTGCGAGGACAGTGGAGGTCAGCGGGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000601824.1; ENST00000596311.5; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_411456 | ||
Pseudouridine (Pseudo)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: PSESITE000118 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:3959501-3959502:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | CCAACAACAGCTACGCCGACTTCGAGCGCTTCTCCAAGGTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000595279.1; ENST00000301264.7; ENST00000545797.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Pseudo_site_2409 | ||
References