m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00475)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
PPARA
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
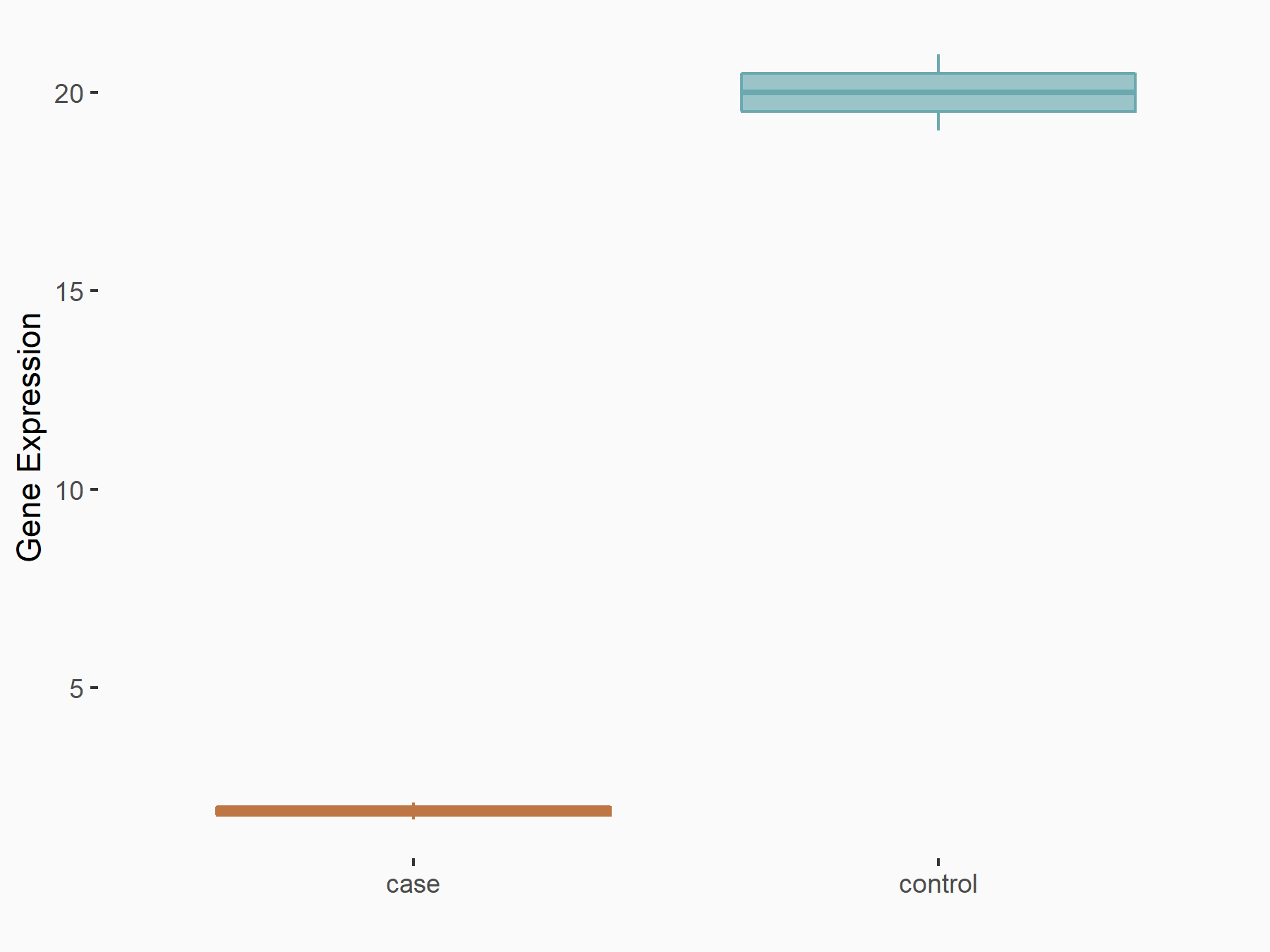  |
logFC: -3.42E+00 p-value: 1.41E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between PPARA and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 8.50E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Hepatic deletion of Bmal1 increases m6A mRNA methylation, particularly of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha/PPARA). Inhibition of m6A methylation via knockdown of m6A methyltransferase METTL3 decreases PPaR-Alpha m6A abundance and increases PPaRalpha mRNA lifetime and expression, reducing lipid accumulation in cells in vitro. YTHDF2 binds to PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Transcriptional regulation of circadian rhythms is essential for lipid metabolic homeostasis, disruptions of which can lead to metabolic diseases. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Metabolic disorders | ICD-11: 5D2Z | ||
| Pathway Response | PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | |||
| Cell Process | Llipid metabolism | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Hepa 1-6 | Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse | Mus musculus | CVCL_0327 | |
| In-vivo Model | Liver-specific Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory. C57BI/6J or Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout male mice were maintained under a 12 hr light/12 hr dark (LD) cycle (ZT0 = 6 AM) and fed ad libitum with normal rodent chow (2018 Global 18% Protein diet, Envigo) and water. At 10-14 weeks of age, 10 male mice per group were sacrificed via CO2 asphyxiation at Zeitgeber Time (ZT) 0,2,6,10,12,14,18,22. In order to induce high levels of ROS in the liver, WT male mice were fasted 12 h and followed by intraperitoneal injection with 300 mg/kg APAP dissolved in PBS and re-fed. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF2 | ||
| Cell Line | GSC11 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siYTHDF2 GSC11 cells
Control: siControl GSC11 cells
|
GSE142825 | |
| Regulation |
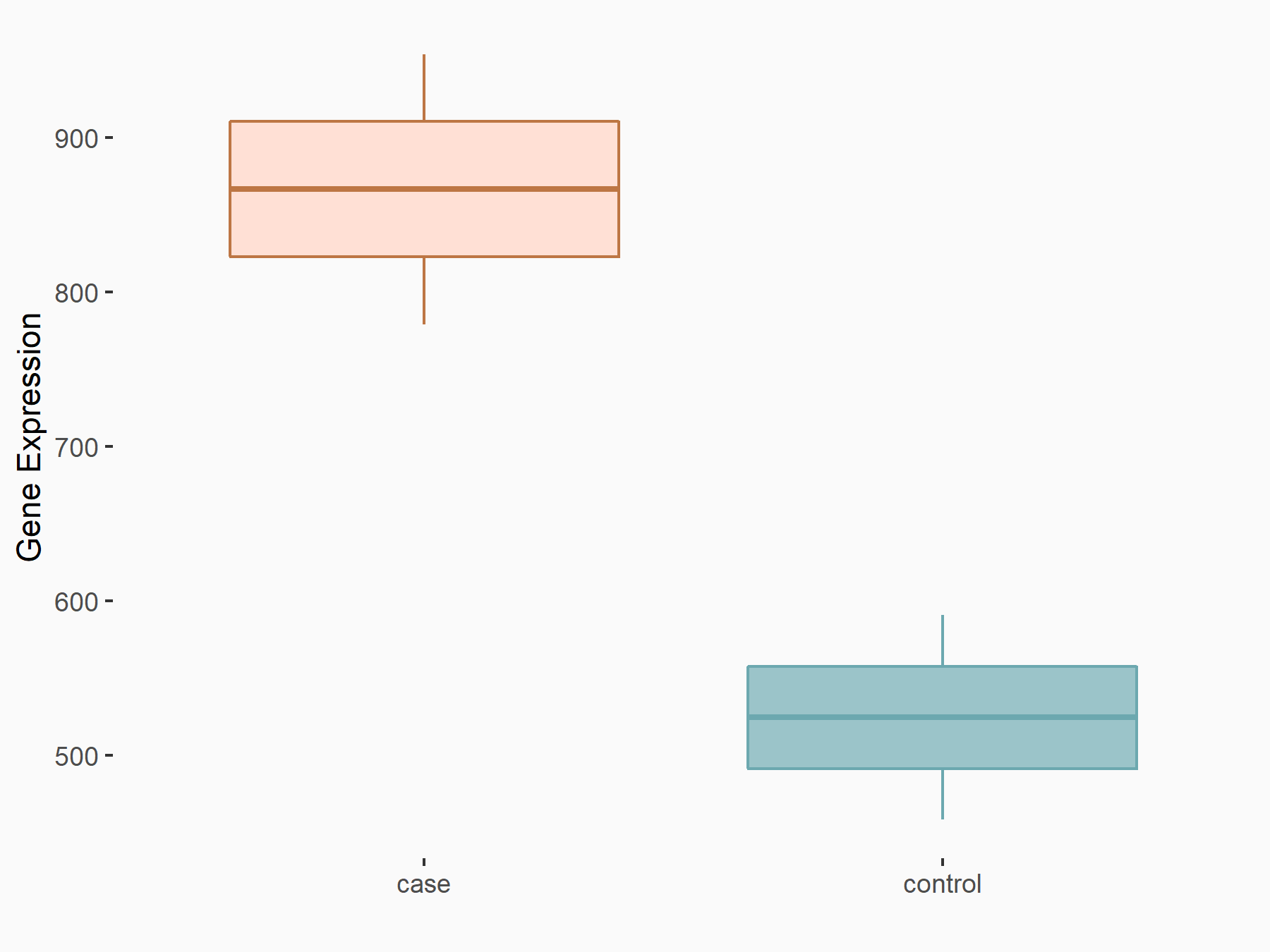  |
logFC: 7.24E-01 p-value: 8.81E-04 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between PPARA and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | Hela | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.45E+00 | GSE49339 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Hepatic deletion of Bmal1 increases m6A mRNA methylation, particularly of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha/PPARA). Inhibition of m6A methylation via knockdown of m6A methyltransferase METTL3 decreases PPaR-Alpha m6A abundance and increases PPaRalpha mRNA lifetime and expression, reducing lipid accumulation in cells in vitro. YTHDF2 binds to PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Transcriptional regulation of circadian rhythms is essential for lipid metabolic homeostasis, disruptions of which can lead to metabolic diseases. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Metabolic disorders | ICD-11: 5D2Z | ||
| Pathway Response | PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | |||
| Cell Process | Llipid metabolism | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Hepa 1-6 | Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse | Mus musculus | CVCL_0327 | |
| In-vivo Model | Liver-specific Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory. C57BI/6J or Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout male mice were maintained under a 12 hr light/12 hr dark (LD) cycle (ZT0 = 6 AM) and fed ad libitum with normal rodent chow (2018 Global 18% Protein diet, Envigo) and water. At 10-14 weeks of age, 10 male mice per group were sacrificed via CO2 asphyxiation at Zeitgeber Time (ZT) 0,2,6,10,12,14,18,22. In order to induce high levels of ROS in the liver, WT male mice were fasted 12 h and followed by intraperitoneal injection with 300 mg/kg APAP dissolved in PBS and re-fed. | |||
Metabolic disorders [ICD-11: 5D2Z]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Hepatic deletion of Bmal1 increases m6A mRNA methylation, particularly of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha/PPARA). Inhibition of m6A methylation via knockdown of m6A methyltransferase METTL3 decreases PPaR-Alpha m6A abundance and increases PPaRalpha mRNA lifetime and expression, reducing lipid accumulation in cells in vitro. YTHDF2 binds to PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Transcriptional regulation of circadian rhythms is essential for lipid metabolic homeostasis, disruptions of which can lead to metabolic diseases. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Metabolic disorders [ICD-11: 5D2Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | |||
| Cell Process | Llipid metabolism | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Hepa 1-6 | Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse | Mus musculus | CVCL_0327 | |
| In-vivo Model | Liver-specific Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory. C57BI/6J or Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout male mice were maintained under a 12 hr light/12 hr dark (LD) cycle (ZT0 = 6 AM) and fed ad libitum with normal rodent chow (2018 Global 18% Protein diet, Envigo) and water. At 10-14 weeks of age, 10 male mice per group were sacrificed via CO2 asphyxiation at Zeitgeber Time (ZT) 0,2,6,10,12,14,18,22. In order to induce high levels of ROS in the liver, WT male mice were fasted 12 h and followed by intraperitoneal injection with 300 mg/kg APAP dissolved in PBS and re-fed. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Hepatic deletion of Bmal1 increases m6A mRNA methylation, particularly of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha/PPARA). Inhibition of m6A methylation via knockdown of m6A methyltransferase METTL3 decreases PPaR-Alpha m6A abundance and increases PPaRalpha mRNA lifetime and expression, reducing lipid accumulation in cells in vitro. YTHDF2 binds to PPaRalpha to mediate its mRNA stability to regulate lipid metabolism. Transcriptional regulation of circadian rhythms is essential for lipid metabolic homeostasis, disruptions of which can lead to metabolic diseases. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Metabolic disorders [ICD-11: 5D2Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | |||
| Cell Process | Llipid metabolism | |||
| In-vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 |
| Hepa 1-6 | Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse | Mus musculus | CVCL_0327 | |
| In-vivo Model | Liver-specific Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory. C57BI/6J or Bmal1f/f-AlbCre-knockout male mice were maintained under a 12 hr light/12 hr dark (LD) cycle (ZT0 = 6 AM) and fed ad libitum with normal rodent chow (2018 Global 18% Protein diet, Envigo) and water. At 10-14 weeks of age, 10 male mice per group were sacrificed via CO2 asphyxiation at Zeitgeber Time (ZT) 0,2,6,10,12,14,18,22. In order to induce high levels of ROS in the liver, WT male mice were fasted 12 h and followed by intraperitoneal injection with 300 mg/kg APAP dissolved in PBS and re-fed. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
DNA modification
m6A Regulator: Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02019 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02020 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02021 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02022 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02023 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A (DNMT3A) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02024 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) | |
| Regulated Target | FTO alpha-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury | |
| Drug | 5-azacytidine | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00475)
| In total 20 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011448 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46160494-46160495:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TTTAGTAGAGATGGGGTTTCACCACGTTGGCCAGGCTGGTC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000440343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94018 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011449 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46160783-46160784:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTAGATTTTGTGTTTTTTGTAGAGATGGGGTTTAGCCATGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94019 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011450 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46170522-46170523:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGTGTGAGCCACTGCACC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94020 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011451 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46174657-46174658:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | GAGACCCTGTCTCTACAAAAATTTAAAAAATTATCCAGGCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000420804.5; rmsk_5309698; ENST00000481567.5; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000484619.1; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94021 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011452 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46196851-46196852:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCCTCAACCTCCTGAGTAGCTGGGATTACAGGTGCCTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000481567.5; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000484619.1; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94022 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011453 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46220709-46220710:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTGGCACTCTGGGGAGGCCAAGGTGGGCAGATTGCTTGAGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309821; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94023 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011454 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46228363-46228364:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GACCAACATGGTGAAACCCCATCTCTACTAAAAATACAGAA | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309834; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94024 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011455 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46228414-46228415:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CGTGGTTGGTGGGTGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCAGGAGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; rmsk_5309834 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94025 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011456 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46228415-46228416:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTGGTTGGTGGGTGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCAGGAGGCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309834 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94026 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011457 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46228428-46228429:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCAGGAGGCTGAGGCAGGAGAAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309834; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94027 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011458 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46228849-46228850:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CGTGGTGGCTCACGCCTGTAATCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; rmsk_5309836; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94028 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011459 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46228854-46228855:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGGCTCACGCCTGTAATCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGCTGAGGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309836 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94029 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011460 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46228995-46228996:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGGCGCCTGTAGTCCCAGCTACTGGGGAGGCTGAGGCAGGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; rmsk_5309836 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94030 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011461 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46229027-46229028:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GAGGCAGGAGAATGGCATGAACCCGGGAGGCGGAGCTTGCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309836; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94031 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011462 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46230146-46230147:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTTGGGAGGCTGAGGTGGGCAGATTACCTGAGGTCAGGAGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309838; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94032 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011463 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46230181-46230182:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGTGCGACACCAGCCTGACCAACATGGTGTAACCCCGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309838; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94033 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011464 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46230194-46230195:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CAGCCTGACCAACATGGTGTAACCCCGTCTCTACTAAAAAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309838; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94034 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011465 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46230241-46230242:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTAGCTGGGCGTGGTGGCGCATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACT | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309838; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94035 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011466 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46230249-46230250:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCGTGGTGGCGCATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCAGAAGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309838; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94036 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE011467 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46230250-46230251:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CGTGGTGGCGCATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCAGAAGGCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309838 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_94037 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 132 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058986 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46150938-46150939:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCGCTGGGGGCCTGCCCGGAACCCGAGTCCGCGGCTGTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; Jurkat; CD4T; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000460086.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571605 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058987 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46150994-46150995:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGCGGAGGTCGGGTCTGGGGACCGCAGCGACTCTGGGTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; Jurkat; CD4T; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000460086.1; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000415785.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571606 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058988 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46151052-46151053:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGGGCCCACGGGCGGGGACATCGGGACTTGCCCTTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; CD4T; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000460086.1; ENST00000420804.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571607 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058989 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46151060-46151061:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCACGGGCGGGGACATCGGGACTTGCCCTTTCCTCGGCGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000460086.1; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000415785.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571608 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058990 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46151122-46151123:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTCAGAAGGTGCTTTCCGAGACCTCCAGGGATCTCCGAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000460086.1; ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000420804.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571609 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058992 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46151149-46151150:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGGATCTCCGAGGCGAGGAAACCCGGGCCCCGGACAGACCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000460086.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000440343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571610 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058993 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46151162-46151163:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CGAGGAAACCCGGGCCCCGGACAGACCGACCCTGGGTGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000460086.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000440343.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571611 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058994 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46198390-46198391:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCATCTGGTCGCGATGGTGGACACGGAAAGCCCACTCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000484619.1; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000481567.5; ENST00000440343.5; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000415785.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571612 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058995 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46198480-46198481:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTCCTGCAAGAAATGGGAAACATCCAAGAGATTTCGCAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000415785.5; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571613 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058996 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46215259-46215260:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTCTCCCAGTGGAGCATTGAACATCGAATGTAGAATCTGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571614 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058997 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46215283-46215284:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGAATGTAGAATCTGCGGGGACAAGGCCTCAGGCTATCATT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000420804.5; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571615 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058998 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46218302-46218303:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCGACTCAAGCTGGTGTATGACAAGTGCGACCGCAGCTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000493286.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571616 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058999 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46218338-46218339:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGCAAGATCCAGAAAAAGAACAGAAACAAATGCCAGTATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; BGC823 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571617 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059000 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46218344-46218345:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GATCCAGAAAAAGAACAGAAACAAATGCCAGTATTGTCGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; BGC823 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571618 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059001 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46219851-46219852:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCAAGATCTGAGAAAGCAAAACTGAAAGCAGAAATTCTTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000493286.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571619 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059003 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46219878-46219879:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCAGAAATTCTTACCTGTGAACATGACATAGAAGATTCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571620 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059004 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46219900-46219901:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATGACATAGAAGATTCTGAAACTGCAGATCTCAAATCTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571621 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059005 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46219952-46219953:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTACGAGGCCTACTTGAAGAACTTCAACATGAACAAGGTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571622 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059006 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46219964-46219965:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTTGAAGAACTTCAACATGAACAAGGTCAAAGCCCGGGTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571623 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059007 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46220056-46220057:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTTCTCTTGGCAACATGGAACCAGTGTCGTAGAGGACGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESCs; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571624 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059008 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46220082-46220083:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTCGTAGAGGACGATTAAGGACACATGTGTTGAATGTTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESCs; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000493286.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571625 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059009 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46220135-46220136:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATCCCACAGTTAAGCAAAGGACAGCGAAGATGGAAACAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESCs; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000493286.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571626 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059010 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46220150-46220151:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAAGGACAGCGAAGATGGAAACAGTTCATTCTGAGACTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESCs; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571627 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059011 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46220165-46220166:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGAAACAGTTCATTCTGAGACTCTGAGCTGTAGCTTAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESCs; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000493286.1; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571628 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059012 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46231815-46231816:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTGTCATACATGATATGGAGACACTGTGTATGGCTGAGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571629 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059014 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46231873-46231874:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTGGCCAATGGCATCCAGAACAAGGAGGCGGAGGTCCGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; GM12878; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571630 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059015 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46231926-46231927:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCAGTGCACGTCAGTGGAGACCGTCACGGAGCTCACGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; H1A; H1B; GM12878; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571631 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059016 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46231975-46231976:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCCATCCCAGGCTTCGCAAACTTGGACCTGAACGATCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; H1A; H1B; A549; GM12878; CD8T; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571632 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059017 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46231981-46231982:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGGCTTCGCAAACTTGGACCTGAACGATCAAGTGACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; H1A; H1B; A549; GM12878; CD8T; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571633 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059018 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46231987-46231988:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTTCGCAAACTTGGACCTGAACGATCAAGTGACATTGCTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.925321429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571634 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059019 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46231998-46231999:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGGACCTGAACGATCAAGTGACATTGCTAAAATACGGAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571635 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059020 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46232056-46232057:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CATGCTGTCTTCTGTGATGAACAAAGACGGGATGCTGGTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hESCs; A549; GM12878; CD8T; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571636 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059021 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46232126-46232127:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTCCTAAAAAGCCTAAGGAAACCGTTCTGTGATATCATGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; GM12878; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571637 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059022 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46232147-46232148:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCGTTCTGTGATATCATGGAACCCAAGTTTGATTTTGCCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571638 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059023 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46232186-46232187:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATGAAGTTCAATGCACTGGAACTGGATGACAGTGATATCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571639 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059025 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235157-46235158:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGCCTTCTAAACGTAGGACACATTGAAAAAATGCAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571640 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059026 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235199-46235200:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTATTGTACATGTGCTCAGACTCCACCTGCAGAGCAACCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; GM12878; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; TIME; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571641 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059027 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235247-46235248:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GATATCTTTCTCTTCCCAAAACTTCTTCAAAAAATGGCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; H1B; A549; GM12878; Jurkat; CD4T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571642 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059028 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235267-46235268:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACTTCTTCAAAAAATGGCAGACCTCCGGCAGCTGGTGACGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; H1B; A549; GM12878; Jurkat; CD4T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000402126.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571643 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059029 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235369-46235370:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACTGCAGGAGATCTACAGGGACATGTACTGAGTTCCTTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; H1B; H1A; fibroblasts; A549; GM12878; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000402126.1; ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571644 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059030 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235497-46235498:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACTTTAACCTTAGAGCTTGGACAGTCTGAGCTGTAGGTAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; fibroblasts; GM12878; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571645 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059031 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235569-46235570:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGTACTTCTAAGAGCATAGAACTCAAATGCTGGGGGTAGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; fibroblasts; GM12878; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571646 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059032 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235603-46235604:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTAGGTGGCTAATCTCAGGACTGGGAAGATTACGGCGAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; fibroblasts; GM12878; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571647 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059033 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235787-46235788:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCTTTATAATTCTGAAAACTAATCAGCACTTTTTAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; GM12878; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571648 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059034 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235883-46235884:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCAAAATATTTATTTCAAAGACTTCACTTCTGTTTCCTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; Huh7; iSLK; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571649 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059036 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235915-46235916:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTCCTGAATCTAAAGAAAGACAACATGCTGCTTTTTAATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; GM12878; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571650 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059037 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46235958-46235959:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGATGGAGAATTTTAAAGAACTGTTTGGGCCAGGCACAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; GM12878; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571651 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059038 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236047-46236048:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CACAAGGTCAGCAGATCGAGACCATCCTGGCCAACATGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309850 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571652 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059039 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236070-46236071:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATCCTGGCCAACATGGTGAAACCCTGTCTCTACTAAAAATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9; rmsk_5309850 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571653 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059040 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236167-46236168:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGGCAGGAGAATTGCTTGAACCAGGGAGTTGGAGGTTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309850; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571654 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059041 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236198-46236199:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGAGGTTGCAGTGAGCTAAGACTGCACCACTGCACTCCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309850 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571655 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059042 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236235-46236236:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CAGCCTGGTGACAGAACGAGACTCTGTCTTAAAAACAAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309850 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571656 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059043 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236249-46236250:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AACGAGACTCTGTCTTAAAAACAAACAAACAAAAAAAAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309850; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571657 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059044 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236257-46236258:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCTGTCTTAAAAACAAACAAACAAAAAAAAAATCTGTTAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; rmsk_5309850; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571658 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059045 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236386-46236387:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCGTAGAAGAGCCCAGAAAACAGAGTCTCAAGACCCCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571659 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059047 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236399-46236400:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCAGAAAACAGAGTCTCAAGACCCCCGCTCTGGACTGTCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571660 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059048 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236449-46236450:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCCGTGGTAAGCGGGACGAGACAAGCTCCCGAAGCCCGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571661 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059049 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236507-46236508:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCGTCCAGTCAACCTGAACCCACCCAGTCCAGCTGTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571662 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059050 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46236552-46236553:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAATGGTGGTGTTCTTAGGGACAGACTGACACCTTACTTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571663 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059051 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46237229-46237230:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGGAAGGACACAGTGTGAGACTTCCACTAGAAAAAAGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571664 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059052 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46237264-46237265:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGTGAAAGTTAGGGTTAGGACATCCTTTTTTAAAAATTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571665 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059053 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46237518-46237519:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGGTGGGAGGATTGCTTGAACCCAGGAGGTCGAGGCTGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5309851; ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571666 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059054 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46237698-46237699:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCCCAAGTGTCTTAGGAACCAAAAGCAAATAAAAGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571667 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059055 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46237999-46238000:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTGTTTACATTTTCATAAAACCTGTTTAAAATAGCTCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571668 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059056 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238079-46238080:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTCGATGTTAGCTCCCGGGACACTCAGCAGCGATGGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571669 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059058 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238128-46238129:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTCCTTAAGGCCCAGCAAGACTTCCAGGGACATCTCTGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571670 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059059 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238138-46238139:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCCAGCAAGACTTCCAGGGACATCTCTGGTGAAGCCAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571671 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059060 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238164-46238165:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGGTGAAGCCAGAATGGAGACACCCGTGACCTCAGGCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571672 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059061 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238257-46238258:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTATTTCTTTAAATAACAAAACCACTAATTGCCACTCAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571673 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059062 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238364-46238365:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATGCCCCAGTTCAAATGGGAACTATTAACAGAGTGCATTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571674 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059063 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238406-46238407:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCTTGCTGGGTTTCAACAGACATCAGCCAAAAGAACAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571675 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059064 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238421-46238422:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AACAGACATCAGCCAAAAGAACAAAAGAGATGTCAGGACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; Huh7; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571676 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059065 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238438-46238439:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGAACAAAAGAGATGTCAGGACAGATTCCAGGAGTGTCGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; kidney; HepG2; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571677 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059066 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238542-46238543:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTCAACAAGTCATTGTTTAAACACGGTTTTTCATTTTCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571678 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059067 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238598-46238599:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGTGCCAAAGTCCTCAGAGACCTAACAGCCTTGGTCTACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571679 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059069 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238649-46238650:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGGTGAAGGCACGGCGAGGGACTCCTCCCAGACGTGCCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GM12878; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571680 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059070 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238806-46238807:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTTGGATTCCGTCCCCACCACACTTCCAGAGACCGGAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571681 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059071 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238818-46238819:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCCCACCACACTTCCAGAGACCGGAGAACTGTGCAGGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571682 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059072 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238826-46238827:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACACTTCCAGAGACCGGAGAACTGTGCAGGGCCTAAGGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571683 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059073 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238865-46238866:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGTTTGGATGAATTGTCAAAACAAGATGCTTCCAGTTACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571684 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059074 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46238899-46238900:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTACAGCGGCAGGAGCGGGACTGGGAGCACGGGCTGACGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571685 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059075 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239009-46239010:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GAGTATAAAGCATCTTCCTAACGGGTGTGTTTGCTATACGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.142029762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571686 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059076 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239030-46239031:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGGGTGTGTTTGCTATACGAACATAATGGACGTGAAGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; A549; iSLK; MSC; TREX; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571687 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059077 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239039-46239040:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TTGCTATACGAACATAATGGACGTGAAGTGGGGCAGAAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.616982143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571688 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059078 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239057-46239058:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGACGTGAAGTGGGGCAGAAACCCAGAACTCAGCATTCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; A549; iSLK; MSC; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571689 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059080 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239064-46239065:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGTGGGGCAGAAACCCAGAACTCAGCATTCAAGGATGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; A549; iSLK; MSC; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571690 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059081 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239145-46239146:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTTCGCATTTAGAGAGCAGACAAGGCACCCTTCTGCTGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571691 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059082 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239197-46239198:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTTACACTGGGCCATTTTAGACCCCCAGGGAAACAGCCTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571692 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059083 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239209-46239210:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CATTTTAGACCCCCAGGGAAACAGCCTTCCTGGAGCGTTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571693 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059084 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239245-46239246:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTGTCTGGAGGTTCCAGGGACAGGGCAGCCTCCCAGAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; GM12878; Huh7; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571694 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059085 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239320-46239321:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TATACCGTGAGAAGTCAACAACTTAGCCACCACTTCCCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571695 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059086 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239346-46239347:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCACCACTTCCCCGCAATGGACCATGTAACAAATACCTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; U2OS; GM12878; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571696 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059087 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239443-46239444:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTAGGGCAGGTGGGATGGAGACTCCTTGAGTGCACACACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hESCs; GM12878; MM6; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571697 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059088 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239514-46239515:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCGTATGACGTCTGGAAGGAACTTCGGTTGTGTAAAGGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1B; hESCs; GM12878; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571698 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059089 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239577-46239578:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCTACCCCAATTTGGTGAAACTGACATTGGGCACGTCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1B; H1A; hESCs; GM12878; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571699 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059091 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239640-46239641:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTCCCGGCCTGCAGTGACAAACCCCCCTCCCCGCACCGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1B; H1A; hESCs; GM12878; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571700 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059092 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239724-46239725:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCCACTTCCTCAGAGAGACCCTACCAGATGCGGATGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; GM12878; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571701 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059093 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239746-46239747:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTACCAGATGCGGATGGAAACAGATGCACCAAAGCAAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; GM12878; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571702 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059094 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239775-46239776:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCAAAGCAAGCCCTGATGAAACCGCGACTTCCTAAGGTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571703 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059095 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239806-46239807:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTAAGGTCTGTCTCCTCTGAACTTGCACCTGGGCCTCTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; U2OS; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571704 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059096 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239856-46239857:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCAAGCACTTCCCACCTCAAACTCCCATTTTCAAACCACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; U2OS; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571705 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059097 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239870-46239871:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCAAACTCCCATTTTCAAACCACTGTATCTCTGCGCACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571706 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059098 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239949-46239950:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTGGTCCTGATCCAGTGGCCACACCTGTCTTTGAAATGTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571707 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059099 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46239976-46239977:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTTTGAAATGTCTCACTGAACTCCAGTTTTAAAATAGATT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571708 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059100 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240036-46240037:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCCAATGCACCCAGCTAAGACTGGCTTGACCGACAGCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571709 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059102 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240162-46240163:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATGCAGATGCCACCAGGAGAACATGCCCACAGCTCACCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571710 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059103 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240284-46240285:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCTCCATTTTAAAATGAAAACACCAGCCTCCAGATGTAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571711 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059104 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240385-46240386:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGCCTCCCTGTTGTTTCTAGACTCTTGCACCTGGTGAGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571712 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059105 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240459-46240460:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCAGCTCCCATCTCCTGGACTGCCAGCCTCACCCTCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571713 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059106 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240529-46240530:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | CCCGAGGGATTACTTTTTAGACCTTCTTTCACATTCAGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; GM12878; iSLK; MSC; TREX; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571714 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059107 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240610-46240611:+ | ||
| Sequence | CATAGAAGTCACCCATGAAGACTGATGCCACCACCTGAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571715 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059108 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240659-46240660:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGTTAAAAATGTCCACGGGAACCTCTCGTCCACAGGAGGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571716 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059109 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240911-46240912:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CAAGCCCATCTTCAGACGTCACAGTCTGGAAGTGAAATGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571717 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059110 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240937-46240938:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGAAGTGAAATGTCCACAAACATCTGTGGCAGAAAAGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571718 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059111 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46240964-46240965:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGCAGAAAAGGCTATACGGACCACCCAGTTGTGCTGCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571719 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059113 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46241277-46241278:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AACGGTTATTGACCCCATAGACTAGGGTAAGAATAAAGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571720 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059114 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46241676-46241677:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTCAGAATTTCAGTTTGAGACATGAGAGGTATAATCAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571721 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059115 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46241954-46241955:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGAAAAAATAATTGATTTTTACATCAGAGATAGCAAACTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571722 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059116 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46242093-46242094:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTCTTGCCCCTCTTCTGCCCACACATCCAGCATCCAAAATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571723 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059117 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46242148-46242149:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATTGATAAAGTGCCGTGCAAACTGGTGCACAAACAGGCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571724 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059118 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46242160-46242161:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCGTGCAAACTGGTGCACAAACAGGCCCCCAGTCCACGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571725 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059119 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46242237-46242238:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGGCATGCCGCAGCCCTGGGACACAGTCGGGCACCTTCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571726 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059120 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46242484-46242485:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTTAAATATCACTTTTTTCTACATTGTGTGGTAAAAAGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571727 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059121 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46242562-46242563:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTGAAAAATATCCTAATACAAATATTTTACTAACTTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571728 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059122 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243156-46243157:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | GTTTCCAATAACTTGGCAAAACTTCTTGGTGCATATTGGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571729 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059124 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243272-46243273:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGGCAGATCCCAGAGCAAGGACTGGGCCCAGACTCTCCACA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571730 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059125 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243283-46243284:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGAGCAAGGACTGGGCCCAGACTCTCCACATGTGCTCTACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571731 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059126 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243290-46243291:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGACTGGGCCCAGACTCTCCACATGTGCTCTACTAGTGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney; liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571732 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059127 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243383-46243384:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGTGCAGTTCCAAAGTAGGAACTGCCACACAGGCCCCAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571733 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059128 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243456-46243457:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGGAGCGGGCATCCAGGACCTCCGGAATCAAGGATGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000262735.9; ENST00000407236.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571734 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059129 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243513-46243514:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAATTTTTCTAGTCACATGAACTGATTGGTTCCAGGCAATT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571735 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE059130 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:46243688-46243689:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACTGTAAGACTGATGAATGTACAGAGTTAATTTCAGGGTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000407236.5; ENST00000262735.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_571736 | ||
References