m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00411)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
SREBF1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | 253J cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: siFTO 253J cells
Control: 253J cells
|
GSE150239 | |
| Regulation |
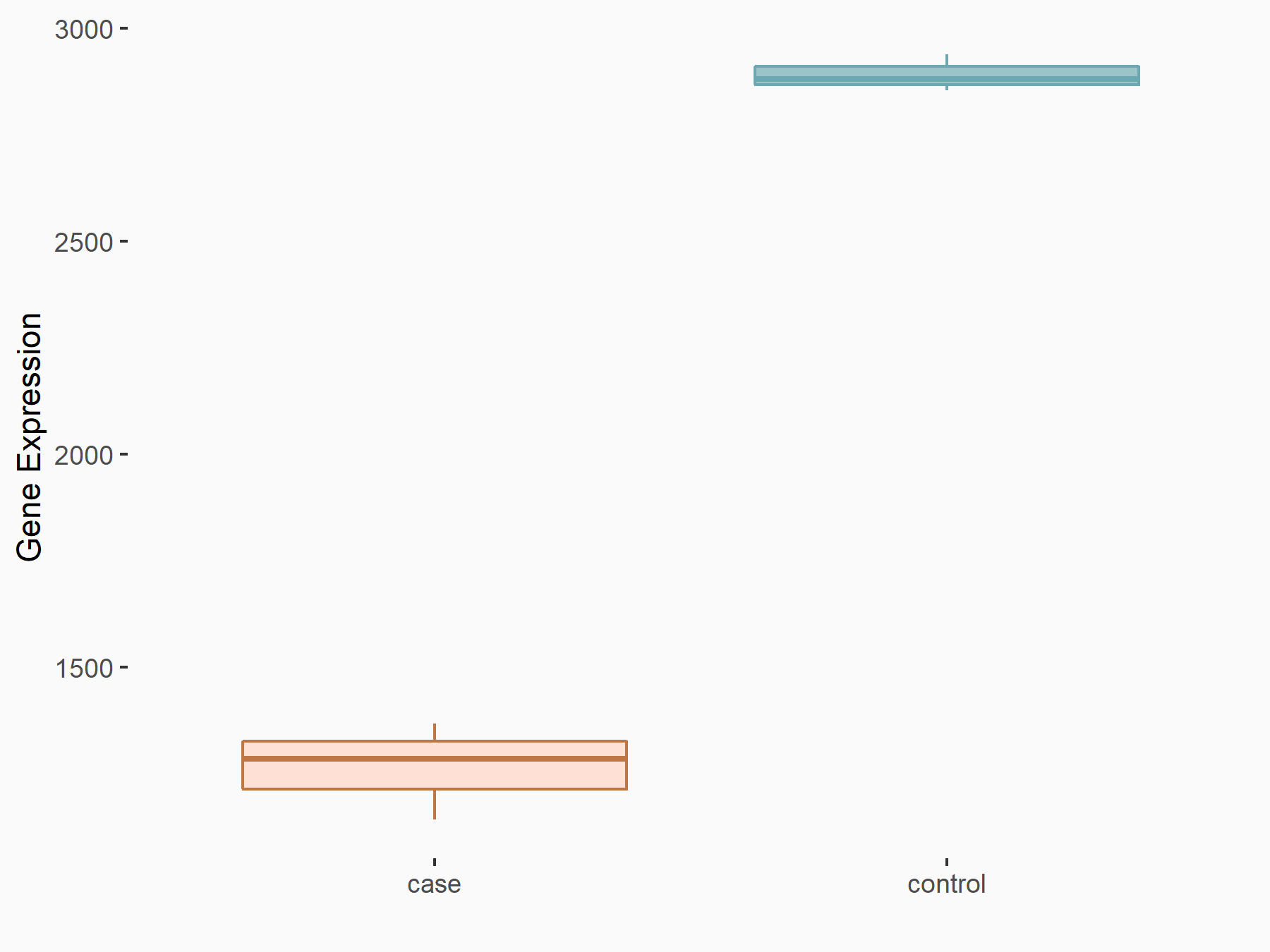  |
logFC: -1.19E+00 p-value: 4.36E-38 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO increased the lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by increasing nuclear translocation of Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1) and SREBP1c maturation, thus improving the transcriptional activity of LD-associated protein CIDEC.The studies provide new mechanistic insight into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) mediated by FTO. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | ICD-11: DB92 | ||
| Cell Process | Lipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | After being fed with high-fat diet for 4 weeks, mice were given twice vena caudalis injection of control siRNA or Cidec siRNA (50 ug/mouse) mixed with liposome. Liposomes were prepared as described elsewhere. | |||
YTH domain-containing protein 2 (YTHDC2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, Ythdc2 could bind to mRNA of lipogenic genes, including Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1), fatty acid synthase, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1, to decrease their mRNA stability and inhibit gene expression. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | ICD-11: DB92 | ||
| Pathway Response | RNA degradation | hsa03018 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| In-vivo Model | All mice were housed at 21℃ ± 1℃ with a humidity of 55% ± 10% and a 12-hour light/dark cycle. The high-fat diets (HFDs), containing 60% kcal from fat, 20% kcal from carbohydrate, and 20% kcal from protein. | |||
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO increased the lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by increasing nuclear translocation of Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1) and SREBP1c maturation, thus improving the transcriptional activity of LD-associated protein CIDEC.The studies provide new mechanistic insight into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) mediated by FTO. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Lipogenesis | |||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| In-vivo Model | After being fed with high-fat diet for 4 weeks, mice were given twice vena caudalis injection of control siRNA or Cidec siRNA (50 ug/mouse) mixed with liposome. Liposomes were prepared as described elsewhere. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, Ythdc2 could bind to mRNA of lipogenic genes, including Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1), fatty acid synthase, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1, to decrease their mRNA stability and inhibit gene expression. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing protein 2 (YTHDC2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | RNA degradation | hsa03018 | ||
| Cell Process | RNA stability | |||
| In-vivo Model | All mice were housed at 21℃ ± 1℃ with a humidity of 55% ± 10% and a 12-hour light/dark cycle. The high-fat diets (HFDs), containing 60% kcal from fat, 20% kcal from carbohydrate, and 20% kcal from protein. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00411)
| In total 15 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007762 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17815422-17815423:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CGGCACTTCCCAGTGGCCCTAGGTGTGGCCCCAGCCCACCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55438 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007763 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17821336-17821337:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACATTGAGAAACAGGCCCCAAGTGGAGCCAGGGAAGGCTGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000583732.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55439 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007764 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17828911-17828912:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTGAGCCAGTTTGTTTTTAGAGACGGGGTCTTGCTCTGTCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55440 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007765 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17830286-17830287:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTATAATCTTATTGACTTTAGAGGCTGAGGTTGGAGGATT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; rmsk_4650087 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55441 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007766 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832663-17832664:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGCGTGAGCCACTGTGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55442 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007767 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832675-17832676:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCGCCTCGGCCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGCGTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55443 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007768 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832676-17832677:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGCCCGCCTCGGCCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGCGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55444 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007769 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832698-17832699:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTCGATCTCCTGACCTCATGATCTGCCCGCCTCGGCCTCCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55445 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007770 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832730-17832731:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGACGGGGTTTCACCGTGTTAGCCAGGATGGTCTCGATCTC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55446 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007771 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832752-17832753:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TAATTTTTTGTATTTTTAGTAGAGACGGGGTTTCACCGTGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55447 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007772 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832808-17832809:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCCTCAGCCTCCCGAGTAGCTTGGGACTATAGGTGCGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55448 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007773 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17832820-17832821:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCACACCATTCTCCTGCCTCAGCCTCCCGAGTAGCTTGGGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55449 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007774 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17834262-17834263:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TCCTGTCTCTACAAAAATAAAAAATTAGCTGGGTGTGGGTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; rmsk_4650101; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55450 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007775 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17834264-17834265:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | AATCCTGTCTCTACAAAAATAAAAAATTAGCTGGGTGTGGG | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4650101; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55451 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007776 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17834293-17834294:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTTTGAGACCAGCCTGGGCAACATGACAAAATCCTGTCTCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; rmsk_4650101 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_55452 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 8 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001000 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813481-17813482:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCCTCCACTCTCCTGGCCCCCAGGTGTTCCTACATGAGGCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000613934.1; ENST00000395757.5; MIMAT0027455; ENST00000478616.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18182 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001001 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813482-17813483:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGCCTCCACTCTCCTGGCCCCCAGGTGTTCCTACATGAGGC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000613934.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000395756.5; MIMAT0027455; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000486311.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18183 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001002 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813483-17813484:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCTCCACTCTCCTGGCCCCCAGGTGTTCCTACATGAGG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000613934.1; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000486311.5; MIMAT0027455; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000478616.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18184 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001003 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813484-17813485:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGAGCCTCCACTCTCCTGGCCCCCAGGTGTTCCTACATGAG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000486311.5; MIMAT0027455; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000613934.1; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18185 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001004 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813485-17813486:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTGAGCCTCCACTCTCCTGGCCCCCAGGTGTTCCTACATGA | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000485080.6; MIMAT0027455; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000613934.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18186 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001005 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17814752-17814753:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | TTCAGGGGACCCTCCCTCTTCTGCAGGCGTAGACCCGGTGG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18187 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001006 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816018-17816019:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTCCCCTACAGCGCTTCTTCCTGAGCAGTGCCCGCCAGGCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000584760.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18188 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001007 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820824-17820825:- | ||
| Sequence | CTGCAGTCTTGGGCCCGACCCTGGGCTCAGCCCCAGCCTAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | muscle | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000423161.3; rmsk_4650064 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_18189 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 87 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030750 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811046-17811047:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGGTGGTGGCTGCGTGGACAAGTGGCGTCGCGGTAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; peripheral-blood; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350969 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030751 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811075-17811076:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGGCGGACGGACTGGCAGGGACTGGCCCGGGCCGGTGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; MM6; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350970 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030752 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811085-17811086:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACGGACGGACAGGCGGACGGACTGGCAGGGACTGGCCCGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350971 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030753 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811097-17811098:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGAGCTGAGGACACGGACGGACAGGCGGACGGACTGGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350972 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030754 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811107-17811108:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AAGCGTGGACAGAGCTGAGGACACGGACGGACAGGCGGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350973 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030755 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811119-17811120:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCAGGCCTATCGAAGCGTGGACAGAGCTGAGGACACGGACG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350974 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030761 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811302-17811303:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCAATATACTAATAAGAACACTAGTCGTCTTAACATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350980 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030763 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811350-17811351:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAAATAAACATCTTTTAGAAACAGCTCGATACACACAATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350982 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030764 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811363-17811364:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TTTACTCTTAAGGAAAATAAACATCTTTTAGAAACAGCTCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293; liver; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350983 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030767 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811443-17811444:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGGGCTGCAGATTTTCCAAAACAATCGTTGTATCTTTATTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350986 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030768 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17811656-17811657:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TCCCGGCCCCTGGTCATCTCACAGCAAAGAAGCCTCCTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350987 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030769 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812135-17812136:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TGCTACTTTGCCTTTTGCAAACTTTATTTTCATAGATTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350988 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030770 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812201-17812202:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | GTCGTGGGAGAGAGACGTGTACATAGTGTAGGTCAGCGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350989 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030771 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812259-17812260:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGCCAACTTGGCTTTCCCGGACTGCAAGCAGGGCTCTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350990 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030772 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812300-17812301:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGTACAGGGAAGAGAGGGGTACATTTCCCTGTGCTGACGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000485080.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350991 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030773 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812438-17812439:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCGCGATCTTGACCCTAAGACCGGCGGCCATGATGGTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; A549; MM6; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350992 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030774 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812519-17812520:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGAAGGCAGTGCAAGAGACTCTGGCCTCCACAGTTCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1B; A549; MM6; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350993 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030775 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812620-17812621:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCACTGTCACTTCCAGCTAGACCCCGTGTCCCCGGCCTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; MM6; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350994 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030776 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812641-17812642:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCATGCGCCTGGGCGGTGGGACCACTGTCACTTCCAGCTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350995 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030777 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17812982-17812983:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACTAGGGTGGGGAGAGGGGAACCCGCCAGGCCCCCGCCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; GSC-11; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000486311.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350996 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030778 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813002-17813003:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GACTTTGTGTGTGGGCTGAGACTAGGGTGGGGAGAGGGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350997 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030779 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813021-17813022:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTGCGTGACTCAGTCTGTGGACTTTGTGTGTGGGCTGAGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350998 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030780 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813131-17813132:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGTCTCAAAAAAAAAAAAAGACCAAGCATCTTCTTGATGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000485080.6; rmsk_4650055; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_350999 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030781 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813208-17813209:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGGGAGGCTCAGTTGGGAGGACAGCTTGAGCCCAGGAGTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4650055; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000395756.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351000 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030782 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813266-17813267:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTGTGTGTGTGTCAGACGGGACAGACAGGCCTGGCGCAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000478616.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351001 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030783 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813424-17813425:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGGGGGCCAGCCCCACACGGACACACCAGCTCCTCGACCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; MM6; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000578469.1; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351002 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030784 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17813620-17813621:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCTGCGTGGCTTCCAACGGGACCTGAGCAGCCTGAGGCGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000485080.6; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351003 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030785 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17814284-17814285:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCCAGTGGGTACCTGCAGGACAGCCTGGCTACCACACCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000478616.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000486311.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351004 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030786 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17814406-17814407:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCTGGTCCCAACAGGAGACCCCTGCCCAGGGCAGCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395756.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351005 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030787 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17814448-17814449:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CACTCAGCCAGGGCTTGTGGACTGGTCTGACTGGCACTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395756.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351006 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030788 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17814491-17814492:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCACCTTTTTTCCTCAGGGAACTCGAGCCAGGGAAGTGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351007 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030789 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17814740-17814741:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCCCTCTTCTGCAGGCGTAGACCCGGTGGCCAAGTGGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351008 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030790 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17814905-17814906:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CGGGTACCTGCAGCTGCTGAACAGCTGTTCTGATGCTGCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351009 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030791 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17815223-17815224:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCCTGGGTCAGCTGATGGGGACAAGTAAGTGTCGTTGTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; kidney; liver; hESC-HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000581707.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351010 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030792 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17815268-17815269:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | TCTCTTAGAGCGAGCACTGAACTGTGTGACCCAGCCCAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000490796.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351011 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030793 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17815291-17815292:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | GTGACTCAGCTATTCCGGGAACATCTCTTAGAGCGAGCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000581707.1; ENST00000447641.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351012 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030794 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17815864-17815865:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTGTACAGCTTGGCCGGGAACCCAGGTGCTCTCTTACCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000584760.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000447641.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351013 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030795 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17815915-17815916:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCGTTTCTTCGTGGATGGGGACTGGTCCGTGCTCAGTACCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000584760.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351014 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030796 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816208-17816209:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | CACGGGCCTTGCATTTTCTGACAGTGAGTGGGTTGGGGGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000584760.1; ENST00000447641.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351015 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030797 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816238-17816239:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGGCTGCATTGAGAGTGAAGACCAGTCTCCCACGGGCCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000584760.1; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351016 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030798 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816318-17816319:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGCGCTGAGTGCCCTGAACCTGGCAGAGTGTGCAGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000584760.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000490796.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351017 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030799 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816366-17816367:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | TGCTTGCCTTCCAGGGAAGCACACAGGCGGGCACCTCACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000447641.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000490796.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351018 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030800 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816464-17816465:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | CCATAAGCTGCACCAGCTGCACACCATGGGTAGGACTGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351019 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030801 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816539-17816540:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCAGGGGGCCTGCAGCAGGACTGTGCTCTGCGAGTGGATG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000471445.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351020 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030802 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816614-17816615:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCTTGTAGCCTCCTCTGGAACCTCATCCGTCACCTGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351021 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030803 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816638-17816639:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCCCACCTCCCACCTGGACCTGGCTTGTAGCCTCCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000469356.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351022 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030804 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816713-17816714:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AAACCCTCATCCACAGGGAGACTTTGCCCAGGCTGCCCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351023 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030805 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17816967-17816968:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCGCAAGCAGGCTGACCTGGACCTGGCCCGGGTAAGGGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351024 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030806 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817191-17817192:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTGAGCCCCCAGGCTTGTGAACTTGGGGCTCTGGATTTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000395756.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351025 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030807 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817220-17817221:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCTGGGCATCTTTGGGAGGGACACTCGGGGTGAGCCCCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351026 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030808 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817249-17817250:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCACCGAGAGCAGAGGTGGGACCGGCCAGCCTGGGCATCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395756.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351027 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030809 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817410-17817411:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCACAGCCGGGGCATGCTGGACCGCTCCCGCCTGGCCCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; CD4T; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000469356.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351028 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030810 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817590-17817591:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCCTACCTCCCATTTCATAGACAGAATAACTGAGGCCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000583080.1; ENST00000487401.1; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351029 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030811 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817621-17817622:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CTCATGACAGGGCCGGGAAGACCCTAACAGATCCTACCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000583080.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000487401.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000471445.5; ENST00000395756.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351030 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030812 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817702-17817703:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGACAGCCCAGTCTTTGAGGACAGCAAGGTTGGGCCCTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; A549; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000583080.1; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000487401.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000471445.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351031 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030813 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817831-17817832:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGTGAAGACTGAGGTGGAGGACACACTGACCCCACCCCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; A549; CD4T; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000583080.1; ENST00000487401.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351032 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030814 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817844-17817845:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCTCATGGAGGGCGTGAAGACTGAGGTGGAGGACACACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; CD4T; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000487401.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000583080.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351033 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030815 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17817873-17817874:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGCCTGTGGCAGTGGAGGGAACACAGACGTGCTCATGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; A549; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000487401.1; ENST00000580540.1; ENST00000583080.1; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351034 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030816 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17818267-17818268:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AAGTCTGCGCACTGCTGTCCACAAAAGCAGTGAGTCCTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000470247.1; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000487401.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351035 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030817 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17818320-17818321:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | GACTACATTCGCTTTCTGCAACACAGCAACCAGAAACTCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395756.5; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000470247.1; ENST00000487401.1; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351036 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030818 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17818336-17818337:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | CTTGCGCAAGGCCATCGACTACATTCGCTTTCTGCAACACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000470247.1; ENST00000487401.1; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351037 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030819 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17818503-17818504:- | [15] | |
| Sequence | GAACGGTTCAGGTAGAAGGAACAAGTGCAAAGGTCCTGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000469356.3; ENST00000470247.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351038 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030820 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17818590-17818591:- | [16] | |
| Sequence | GCACAGCAGCAGCTAGCCAGACCCTGCTGTCTGCATCTTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000470247.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000469356.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351039 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030821 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819058-17819059:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | CTACCGCTCCTCCATCAATGACAAAATCATTGAGCTCAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000470247.1; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351040 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030822 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819203-17819204:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GTGGCGGAACCATCTTGGCAACAGTCCCACTGGTCGTAGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000470247.1; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000577897.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351041 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030823 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819215-17819216:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGACCCTGGTGAGTGGCGGAACCATCTTGGCAACAGTCCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000470247.1; ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351042 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030824 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819333-17819334:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCTCTGGCACCACTGTGCAGACAGGGCCTTTGCCGGTGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000395751.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351043 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030825 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819396-17819397:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCTTCTGACAGCCATGAAGACAGACGGAGCCACTGTGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351044 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030826 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819408-17819409:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGGCAGACTCGCTGCTTCTGACAGCCATGAAGACAGACGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000583732.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351045 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030827 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819422-17819423:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCACTTCATCAAGGCAGACTCGCTGCTTCTGACAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351046 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030828 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819643-17819644:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | GGTCCCGCCCGTCTCCTTGCACACCCAGGTCCAGAGTGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351047 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030829 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819709-17819710:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCAGGAAGCCCTCCCGGGAACACCCAGCAGCCGCTGCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000583732.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351048 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030830 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819792-17819793:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AAGGCCAGTCGGTGATAGAGACCTGAAGAGCAGGTTGAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000395757.5; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351049 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030831 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17819850-17819851:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCATCAGAGCCCAGGCAGGGACTGTCCATAGGAAGCCACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000395757.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351050 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030832 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820062-17820063:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGATGTGTGGCGGGAGGGGACACCCGGGGTGGGGCTTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000577897.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351051 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030833 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820212-17820213:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGCCACTGAGCATCCTGCAGACCCCCACCCCACAGCCCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MT4; A549; Huh7; HEK293T; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000583732.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351052 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030834 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820380-17820381:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCTTGTCTCCACCTCCTGCCACATTGAGCTCCTCTCTTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000577897.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351053 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030835 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820433-17820434:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GAGTGGGGCAGGGGGCACAGACCCTGCCAGCCCCGATACCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HepG2; MT4; H1299; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; TREX; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000476994.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351054 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030836 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820487-17820488:- | [17] | |
| Sequence | TATCAACAACCAAGACAGTGACTTCCCTGGCCTATTTGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000423161.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351055 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030837 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820493-17820494:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCTTATCAACAACCAAGACAGTGACTTCCCTGGCCTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; MT4; H1299; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; TREX; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000577897.1; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000423161.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351056 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030838 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820520-17820521:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCTCTTCTCCTTTTCACAGACATGCTTCAGCTTATCAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; MT4; H1299; Jurkat; GSC-11; TREX; HEC-1-A; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351057 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030839 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820683-17820684:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AAATGGCTGTATGTCCGGGAACACCAGCTCCTGTGGGTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000583732.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351058 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030840 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17820721-17820722:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGCAGGCATTGCTTTAGACAGCACAGGTGCTCGCAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000476994.1; ENST00000423161.3; ENST00000583732.1; ENST00000395751.8; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351059 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030841 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17836734-17836735:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | GGACGCGGCGCTGCTGACCGACATCGAAGGTGCGTCAGGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351060 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030842 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17836932-17836933:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCCTCTGAGGCCAGGGCAGGACACGAACGCGCGGAGCGGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1B; H1A; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; MSC; TREX; iSLK; TIME; HEC-1-A; GSCs; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000355815.8; ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351061 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030843 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17836973-17836974:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GGGAACCCAGTTTCCGAGGAACTTTTCGCCGGCGCCGGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HepG2; H1B; H1A; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; TREX; iSLK; TIME; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9; ENST00000355815.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351062 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE030844 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr17:17836989-17836990:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCAGAGCTGCGGCCGGGGGAACCCAGTTTCCGAGGAACTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HepG2; H1B; H1A; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; TREX; iSLK; TIME; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000261646.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_351063 | ||
References