m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00403)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
SOX10
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Cerebral cortex | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3 (f/f, Emx1-cre) cerebral cortex
Control: Wild type cerebral cortex
|
GSE154992 | |
| Regulation |
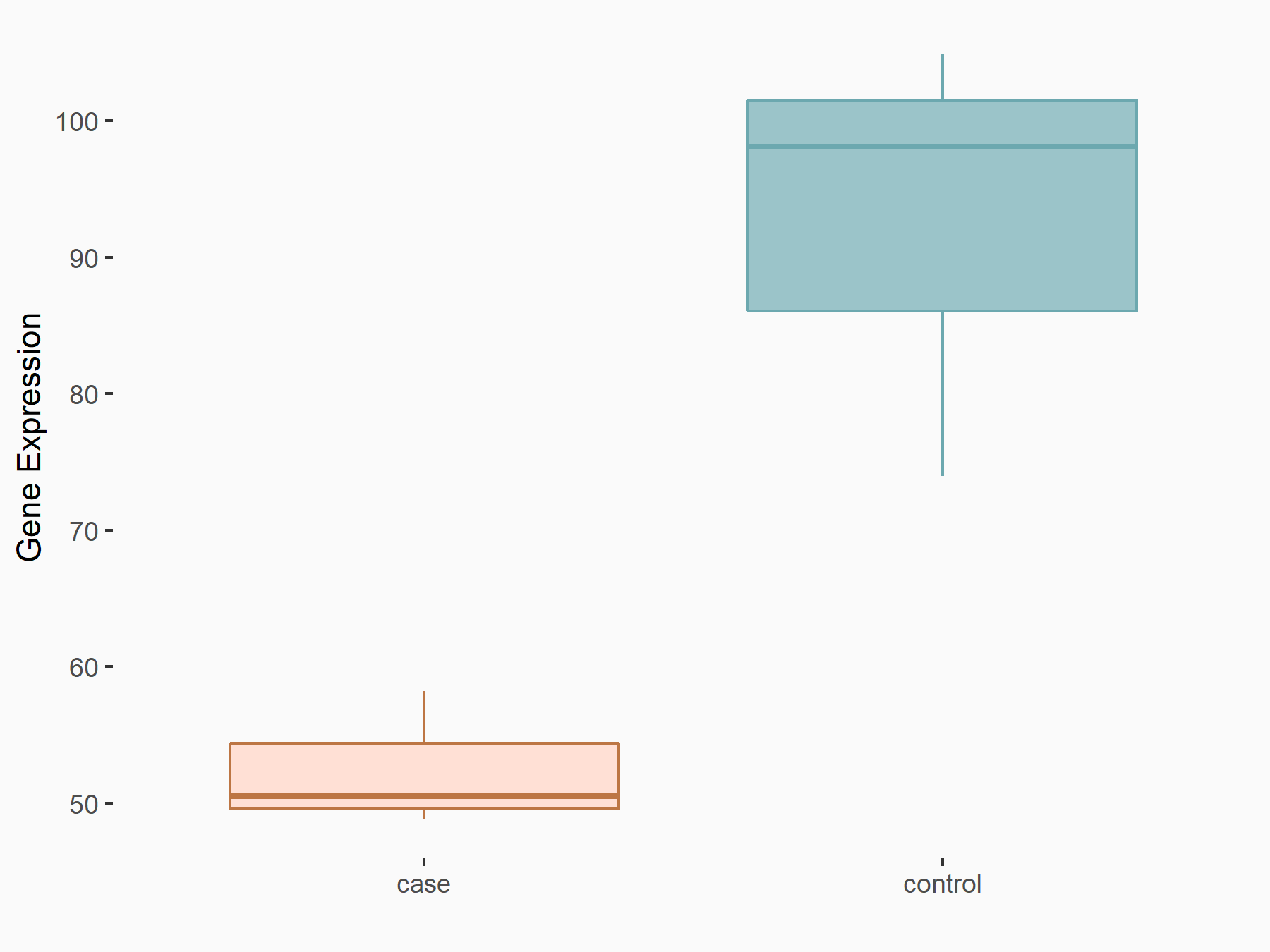 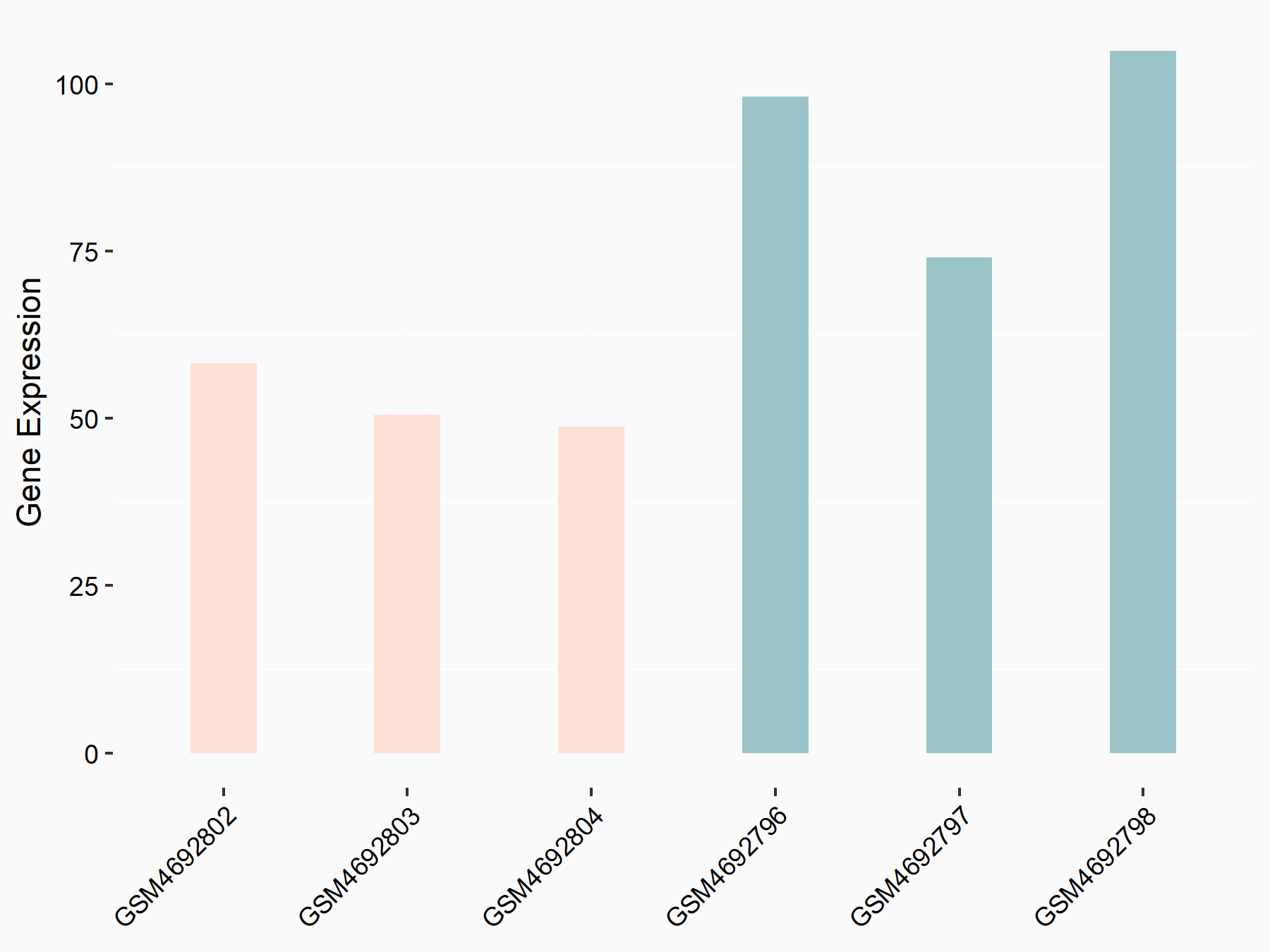 |
logFC: -8.13E-01 p-value: 2.61E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
PMID31239444-anti-PD1 antibody
[Investigative]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | These findings demonstrate a crucial role of FTO as an m6A demethylase in promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 resistance, and suggest that the combination of FTO inhibition with anti-PD-1 blockade reduces the resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Knockdown of FTO increases m6A methylation in the critical protumorigenic melanoma cell-intrinsic genes including PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and Transcription factor SOX-10 (SOX10), leading to increased RNA decay through the m6A reader YTHDF2. | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Pathway Response | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | hsa05235 | ||
| Cell Process | mRNA decay | |||
| In-vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0159 |
| CHL-1 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1122 | |
| 624-mel | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8054 | |
| NHEM (Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes) | ||||
| SK-MEL-30 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0039 | |
| WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0040 | |
| WM35 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | |
| WM3670 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6799 | |
| WM793 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_8787 | |
| In-vivo Model | When the tumors reached a volume of 80-100 mm3, mice were treated with anti-PD-1 or isotype control antibody (200 ug/mouse) by i.p. injection, every other day for three times. For IFNγ blockade treatment, C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti-IFNγ antibody or isotype control IgG (250 ug/mouse) every other day after tumor cell inoculation. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00403)
| In total 16 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058127 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37972428-37972429:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | TTCTGCAGCCCCCCAAATCCACATGTAACTCATTACTGTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000446929.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565693 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058128 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37972735-37972736:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | CTCCAGGAAAGGAATCAGAGACAATTCACAGAGCCTCCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000360880.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565694 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058129 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37973195-37973196:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GAATGACCCTCTATCCCAGGACCTGAGAAGGGCCTGCTCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1A; H1B | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000360880.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565695 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058130 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37973280-37973281:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCAGGAGAACAGGCTGGACAGAGGAGAAGGAGGTTGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1B; H1A; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000360880.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565696 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058131 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37973289-37973290:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGCAAAGCCCCAGGAGAACAGGCTGGACAGAGGAGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1B; H1A; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000396884.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565697 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058132 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37973817-37973818:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | AAGCCCAGGTGAAGACAGAGACCGCGGGGCCCCAGGGGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1A; H1B; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000446929.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565698 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058133 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37973823-37973824:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | ATGCCAAAGCCCAGGTGAAGACAGAGACCGCGGGGCCCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1A; H1B; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000446929.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565699 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058134 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37973908-37973909:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCCCTGGCCGTGGCCAGTGGACACTCCGCCTGGATCTCCAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1A; H1B; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000651746.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565700 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058135 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37974002-37974003:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTTTGATGTGGCTGAGTTGGACCAGTACCTGCCGCCCAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1A; H1B; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000396884.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565701 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058136 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37974024-37974025:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | AGGTAATGTCCAACATGGAGACCTTTGATGTGGCTGAGTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1A; H1B; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000651746.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565702 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058137 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37974065-37974066:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | CATCGACTTCGGCAACGTGGACATTGGTGAGATCAGCCACG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain; H1A; H1B; hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000360880.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565703 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058138 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37974131-37974132:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCTGCAGTCGGGCAAGGCAGACCCGAAGCGGGACGGGCGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000651746.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565704 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058139 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37974156-37974157:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCCTCCAACCACCCCGAAGACAGAGCTGCAGTCGGGCAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000360880.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565705 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058140 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37977883-37977884:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTCCCCCATGTCAGATGGGAACCCCGAGCACCCCTCAGGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hNPCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000651746.1; ENST00000446929.5; ENST00000360880.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565706 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058141 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37983843-37983844:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCGTTGGACTCTTTGCGAGGACCCCGGCGGCTGGCCCGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1B | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000470555.1; ENST00000652356.1; ENST00000427770.1; ENST00000396884.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565707 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE058142 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr22:37983856-37983857:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | TCCATCCAGGTGGGCGTTGGACTCTTTGCGAGGACCCCGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1B | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000652356.1; ENST00000360880.6; ENST00000396884.7; ENST00000470555.1; ENST00000427770.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_565708 | ||
References