m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00349)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
GRIN1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | UMRC2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: FTO knockdown UMRC2 cells
Control: Wild type UMRC2 cells
|
GSE139123 | |
| Regulation |
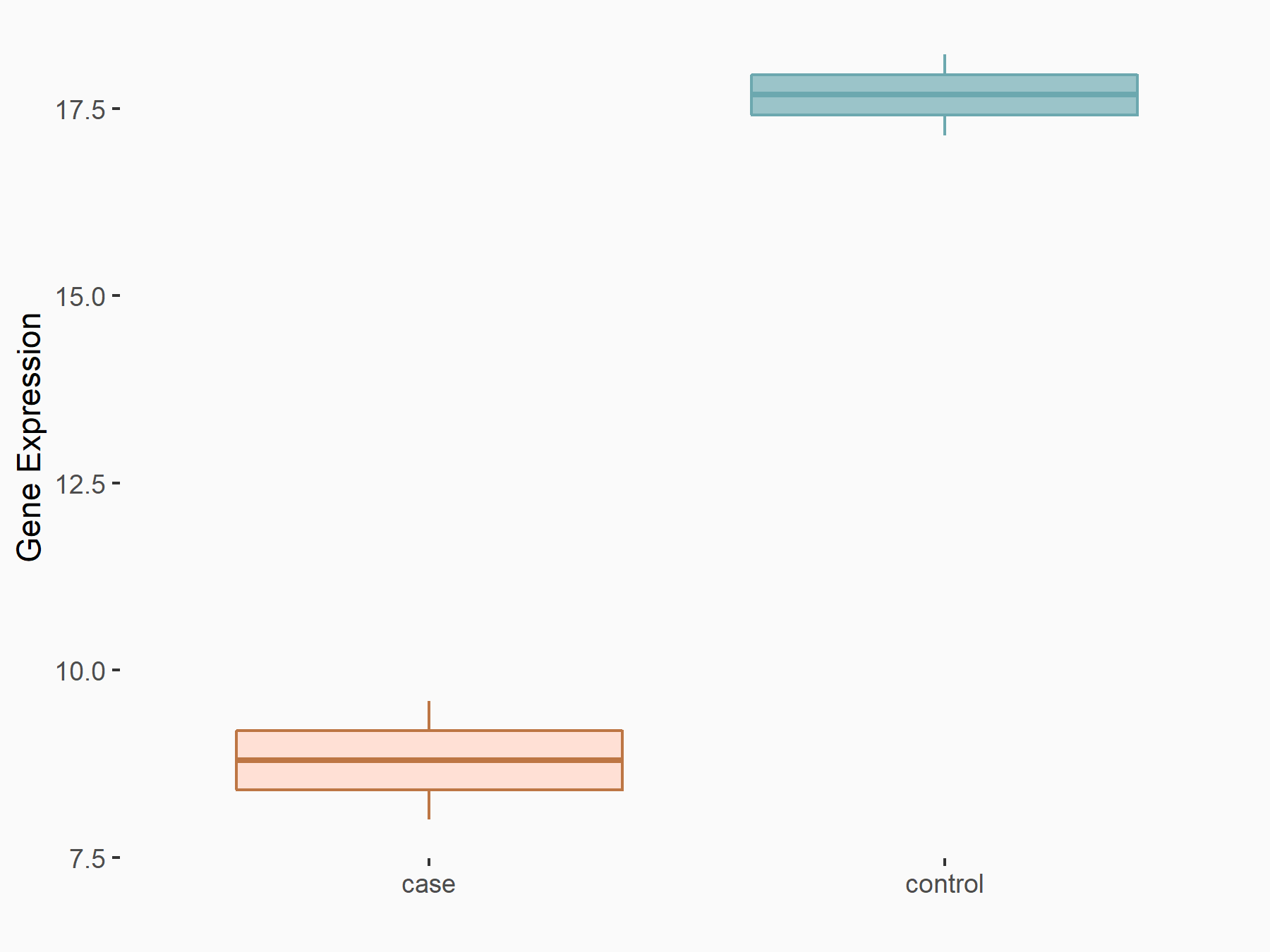 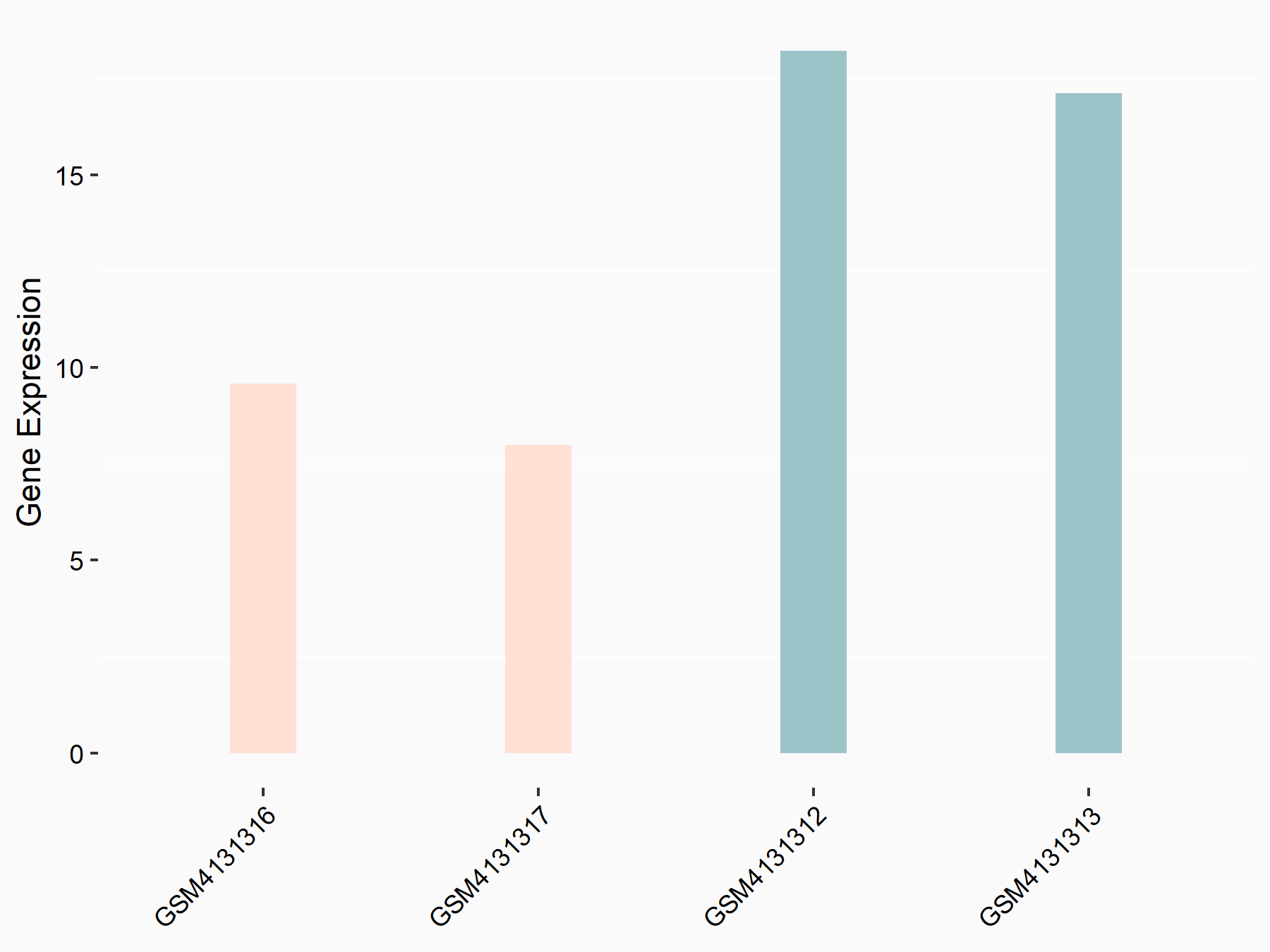 |
logFC: -9.35E-01 p-value: 3.38E-05 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Decreased m6A in dopaminergic cells by overexpressing a nucleic acid demethylase, FTO, or by m6A inhibitor. m6A reduction could induce the expression of Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 (NMDAR1/GRIN1), and elevate oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx, resulting in dopaminergic neuron apoptosis. m6A modification plays a vital role in the death of dopaminergic neuron, which provides a novel view of mRNA methylation to understand the epigenetic regulation of Parkinson's disease. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | ||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| PC-12 | Lung papillary adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S979 | |
| SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In-vivo Model | Two weeks after the stereotaxic surgery, all the animals were intraperitoneally injected with apomorphine at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg to induce the contralateral rotations. Ten minutes after the injection, a video was used to record the rotations of each rat for 20 min. Only those 6-OHDA induced rats showing robust contralateral turning (>7 turns/min) that were injected with 6-OHDA were used in subsequent experiments. | |||
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Decreased m6A in dopaminergic cells by overexpressing a nucleic acid demethylase, FTO, or by m6A inhibitor. m6A reduction could induce the expression of Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 (NMDAR1/GRIN1), and elevate oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx, resulting in dopaminergic neuron apoptosis. m6A modification plays a vital role in the death of dopaminergic neuron, which provides a novel view of mRNA methylation to understand the epigenetic regulation of Parkinson's disease. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| PC-12 | Lung papillary adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_S979 | |
| SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In-vivo Model | Two weeks after the stereotaxic surgery, all the animals were intraperitoneally injected with apomorphine at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg to induce the contralateral rotations. Ten minutes after the injection, a video was used to record the rotations of each rat for 20 min. Only those 6-OHDA induced rats showing robust contralateral turning (>7 turns/min) that were injected with 6-OHDA were used in subsequent experiments. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00349)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003293 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137146917-137146918:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GACCAGAGGGTCCTGGGAGTACTGTCGTGGGGGGTCTGCTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371561.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_139104 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE003294 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137166582-137166583:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CTTGGCATCAAGCAAGCCAAATCCCGAGATGAAGCCACCAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000473811.1; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371553.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_139105 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 33 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090580 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137139634-137139635:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CGAGGCCGTGAACCAGGCCAACAAGCGGCACGGCTCCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371560.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849022 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090581 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137139727-137139728:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGCTCTGTCGGTGTGCGAGGACCTCATCTCCAGCCAGGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371546.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849023 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090582 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137156967-137156968:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CGAGCTCCTCGAGAAGGAGAACATCACCGACCCGCCGCGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371559.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849024 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090583 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137161353-137161354:+ | ||
| Sequence | TGCTCATCAAGCTGGCACGGACCATGAACTTCACCTACGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371561.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849025 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090584 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137162193-137162194:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | GATTCCCCGGAGCACGCTGGACTCGTTCATGCAGCCGTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371553.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849026 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090585 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137162280-137162281:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGTGATGCTGTACCTGCTGGACCGCTTCAGGTGAGCGCGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371559.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849027 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090586 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137162426-137162427:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTTCGGCCGGTTCAAGGTGAACAGCGAGGAGGAGGAGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371553.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849028 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090587 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137162698-137162699:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCGGCCTTCCTGGTGCTGGACCGGCCGGAGGAGCGCATCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371559.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849029 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090588 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137163290-137163291:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGGCATAGGCATGCGCAAAGACAGCCCCTGGAAGCAGAACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000460273.1; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371555.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849030 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090589 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137163659-137163660:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCGACCCTTACTTTTGAGAACATGGCCGGTGCGTTCTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000460273.1; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371546.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849031 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090590 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137163896-137163897:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGTTAACGTGTGGCGGAAGAACCTGCAGGTAGGGCAGGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000460273.1; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000471122.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849032 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090591 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164009-137164010:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTCTGGCTCTGGTGGGCAGGACTGGAGCTAGGAGCCATGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000460273.1; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371561.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849033 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090592 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164220-137164221:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGCAATCAGGCAGGGTAAGACAGGGGCCCGCCTGTGTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371559.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849034 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090593 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164303-137164304:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCCCTTGACACCCTTCGGAGACCCCCCCCTTTCCTGCTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371560.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849035 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090594 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164436-137164437:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCCACGGCCCACCTGGGACAGGGTGGGCAGTGGGCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; HepG2; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371559.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849036 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090595 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164656-137164657:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCCCCACAGGTCCCCTGGGGACCTGGCCGCTGCCAGCACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000350902.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849037 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090596 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164703-137164704:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACAGGCCACCTGGCCATCAGACCTGAGGCCAGAGTCCCGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371553.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849038 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090597 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164828-137164829:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGTCAGTGGCCTCCACGCAGACAGCTGGTGTGGCCTGAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000350902.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849039 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090598 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164872-137164873:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACTCCTCCAGTCCTCAGAGGACTCCTCCTCCTCGGGACGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371559.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849040 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090599 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164932-137164933:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGAGCCAGGGAGCCAGGCGGACCTCCCAGGAAGAGCCAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371560.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849041 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090600 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137164999-137165000:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGAGCAAGGTCAGGCCCGAGACCCCGGGCAGGAGAAGAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000371546.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849042 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090601 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137165291-137165292:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGGCGTAGGTCCTCCAAAGACACGGTAAGGGGGAGAGCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000473811.1; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371559.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849043 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090602 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137165380-137165381:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCATCACCCCGCCCCGGACCCTGGGCTCCTGTGGCCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000471122.5; ENST00000350902.9; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000473811.1; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371546.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849044 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090603 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137167441-137167442:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGACGCGGCGCTTTGCAAAACCAAAAAGACACAGTGCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000473811.1; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371555.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849045 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090604 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137167450-137167451:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGCTTTGCAAAACCAAAAAGACACAGTGCTGCCGCGACGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000473811.1; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371555.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849046 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090605 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137167528-137167529:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCGTCATAGGGAGAGCTGAGACTCCCCGCCCGCCCTCCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000473811.1; ENST00000371550.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849047 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090606 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137167884-137167885:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGTTAGCCCGGCCAAGGACACTGATGGGTCCTGCTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371550.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849048 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090607 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137167940-137167941:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCCCACCCGCCCCAGAGACTGCCCACCCTGGGCCTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000462584.1; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371546.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849049 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090608 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137168008-137168009:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGGCGGGCAGCCCCTGCTGGACCAAGGTGCGGACCGGAGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1B; GSC-11 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000462584.1; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371560.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849050 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090609 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137168020-137168021:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCTGGACCAAGGTGCGGACCGGAGCGGCTGAGGACGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | H1B; GSC-11 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000462584.1; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371546.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849051 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090610 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137168419-137168420:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCGGGCCGCCTCCTCCAGACTCGAGAGGGCTGAGCCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; H1B; H1A; GSC-11 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000462584.1; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371555.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849052 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090611 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137168505-137168506:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCCCGGACGCTGGCTCGGGACTGTCTTCAACCCTGCCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; H1A; H1B; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000462584.1; ENST00000371546.8; ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371561.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849053 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE090612 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr9:137168606-137168607:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCCCGCCACCTTGTACAGAACCAGCACTCCCAGGGCCCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000371559.8; ENST00000462584.1; ENST00000371550.8; ENST00000371560.4; ENST00000371561.8; ENST00000371555.8; ENST00000371553.7; ENST00000371546.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_849054 | ||
References