m6A-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: M6ADRUG0103)
| Name |
Atorvastatin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
atorvastatin; 134523-00-5; Cardyl; Lipitor; Torvast; ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM; 110862-48-1; UNII-A0JWA85V8F; (3R,5R)-7-(2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; CI 981; Lipitor (TN); Tozalip; Xavator; A0JWA85V8F; CHEMBL1487; (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; (R-(R*,R*))-2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-1H-pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid; CHEBI:39548; (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; 134523-03-8; Atorvastatin [INN:BAN]; 1H-Pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-, (R-(R*,R*))-; 7-[2-(4-FLUORO-PHENYL)-5-ISOPROPYL-3-PHENYL-4-PHENYLCARBAMOYL-PYRROL-1-YL]- 3,5-DIHYDROXY-HEPTANOIC ACID; Atorvastatin calcium salt; atorvastatina; atorvastatine; atrovastin; Atofast; Atorcor; Atorlip; Lipilou; Lipinon; Atorin; Ator; Lipitor(TM); (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoic acid; (3R,5R)-7-[3-(anilinocarbonyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; Atorvastatin (INN); Sortis (TN); CCRIS 7159; MFCD00899261; C33H35FN2O5; HSDB 7039; NCGC00159458-03; atorvastatinum; rel-Atorvastatin; (betaR,deltaR)-2-(p-Fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid; Atorvastatin & Primycin; DSSTox_CID_9868; SCHEMBL3831; DSSTox_RID_78825; DSSTox_GSID_29868; BIDD:GT0336; Atorvastatin (Relative Stereo); GTPL2949; DTXSID8029868; BDBM22164; DTXSID60274003; HMS3715L05; HMS3886C20; Lipilou; Tozalip; Torvast; Cardyl; (3S,5S)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; ACT03225; HY-B0589; ZINC3920719; Tox21_302417; s5715; AKOS000281127; AC-9386; CCG-221172; DB01076; MCULE-2368532812; MRF-0000761; NCGC00159458-02; NCGC00159458-20; NCGC00255181-01; (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylcarbamoylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; 1H-Pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-, (betaR,deltaR)-; 7-[2-(4-FLUORO-PHENYL)-5-ISOPROPYL-3-PHENYL-4-PHENYLCARBAMOYL-PYRROL-1-YL]-3,5-DIHYDROXY-HEPTANOIC ACID; AS-35260; H942; CAS-134523-00-5; C06834; D07474; 523A005; A802259; A806791; A806793; Q668093; SR-01000872702; SR-01000872702-1; BRD-K69726342-001-02-6; UNII-36TN91XZ0V component XUKUURHRXDUEBC-KAYWLYCHSA-N; (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-FLUOROPHENYL)-3-PHENYL-4-(PHENYLCARBAMOYL)-5-PROPAN-2-YL-PYRROL-1-YL]-3,5-DIHYDROXY-HEPTANOIC ACID; (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylcarbamoyl-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoic acid; (3R,5R)-7-[3-(anilinocarbonyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-2-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; 1H-Pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-, (beta-R,delta-R)-;; sodium 7-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-2,3-dihydropyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoate
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status | Approved | [1] | |||
| Structure |
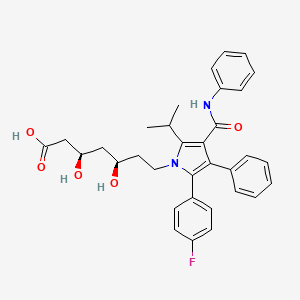 |
||||
| Formula |
C33H35FN2O5
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C33H35FN2O5/c1-21(2)31-30(33(41)35-25-11-7-4-8-12-25)29(22-9-5-3-6-10-22)32(23-13-15-24(34)16-14-23)36(31)18-17-26(37)19-27(38)20-28(39)40/h3-16,21,26-27,37-38H,17-20H2,1-2H3,(H,35,41)(H,39,40)/t26-,27-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XUKUURHRXDUEBC-KAYWLYCHSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Full List of m6A Targets Related to This Drug
Constitutive NOS (eNOS)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, downregulated those of KLF2 and Constitutive NOS (eNOS), and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1), downregulated those of KLF2 and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
Krueppel-like factor 2 (KLF2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, downregulated those of Krueppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO overexpression significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM1) and ICAM-1, downregulated those of KLF2 and eNOS, and strongly attenuated the atorvastatin-mediated induction of KLF2 and eNOS expression. FTO could serve as a novel molecular target to modulate endothelial function in vascular diseases. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Vascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | ||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| In-vitro Model | THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 |
| HUVEC-C | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2959 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
References