m6A-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: M6ADRUG0100)
| Name |
Erlotinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Erlotinib; 183321-74-6; N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine; Erlotinib free base; 4-[(3-Ethynylphenyl)amino]-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazoline; OSI-774; UNII-J4T82NDH7E; 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-; N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine; 183321-74-6 (free base); NSC 718781; CHEMBL553; J4T82NDH7E; [6,7-BIS(2-METHOXY-ETHOXY)QUINAZOLINE-4-YL]-(3-ETHYNYLPHENYL)AMINE; CP358774; CHEBI:114785; MFCD02089651; NCGC00164574-01; [6,7-Bis-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazolin-4-yl]-(3-ethynyl-phenyl)-amine; DSSTox_CID_26454; DSSTox_RID_81628; DSSTox_GSID_46454; CP-358,774; Erlotinib(Tarceva); OSI-744; CAS-183321-74-6; NSC718781; RG-1415; Erlotinib [INN:BAN]; SR-05000001460; erlotinibum; Erotinib; R-1415; HSDB 8082; OSI 744; nchembio866-comp3; Erlotinib, Free Base; Kinome_3317; n-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine monohydrochloride; R 1415; SCHEMBL8413; BDBM5446; cid_176870; GTPL4920; DTXSID8046454; QCR-100; HMS2089F05; HMS3244M19; HMS3244M20; HMS3244N19; HMS3295A19; HMS3713C22; HMS3745M05; ZINC1546066; Tox21_112202; 3615AH; AC-399; NSC800097; s7786; STK623143; AKOS000282911; Tox21_112202_1; CCG-220420; CS-0620; DB00530; MCULE-7764565391; NSC-800097; Ro-508231; SB16916; NCGC00164574-03; NCGC00164574-05; NCGC00164574-06; NCGC00164574-14; NCGC00164574-25; AS-35132; BCB03_000783; BE164419; HY-50896; P443; SY028059; AM20090621; FT-0651539; R1415; CP-35877401; K00241; AB01273955-01; AB01273955-02; AB01273955-03; 321E746; Q418369; SR-05000001460-1; SR-05000001460-2; SR-05000001460-3; SR-05000001460-6; BRD-K70401845-003-04-7; n-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy) quinazolin-4-amine; 1429636-49-6
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status | Approved | [1] | |||
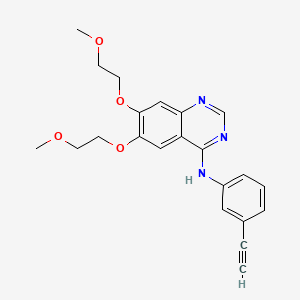
| Structure |
 |
||||
| Formula |
C22H23N3O4
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H23N3O4/c1-4-16-6-5-7-17(12-16)25-22-18-13-20(28-10-8-26-2)21(29-11-9-27-3)14-19(18)23-15-24-22/h1,5-7,12-15H,8-11H2,2-3H3,(H,23,24,25)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
AAKJLRGGTJKAMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Full List of m6A Targets Related to This Drug
LINC00902 (TUSC7)
| In total 1 item(s) under this target gene | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response by This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | In lung adenocarcinoma, The miR-146a/Notch signaling was sustained highly activated in a m6A dependent manner, and the m6A regulator of YTHDF2 suppressed LINC00902 (TUSC7), both of which contributed to the resistant features. Functionally, the sponge type of TUSC7 regulation of miR-146a inhibited Notch signaling functions, and affected the cancer progression and stem cells' renewal in Erlotinib resistant PC9 cells (PC9ER) and Erlotinib resistant HCC827 cells (HCC827ER) cells. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.0 | ||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Notch signaling pathway | hsa04330), EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | ||
| In-vitro Model | PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HCC827 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2063 | |
| In-vivo Model | Control vector, TUSC7 knockout, FLI-06 treated H1975 cells (1*107) cells were suspended in 100 uL of serum-free DMEM medium (Hyclone, USA), mixed with matrix gel (Corning, USA), and then were injected subcutaneously. The changes in the tumor size were recorded every 3 or 5 days. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Drug
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05633 | ||
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | |
| m6A Target | LINC00902 (TUSC7) | |
| Epigenetic Regulator | LINC00902 (TUSC7) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
References