m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00396)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
SMAD3
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF2 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: shYthdf2 embryonic stem cells
Control: shLuc embryonic stem cells
|
GSE156437 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 5.96E-01 p-value: 6.99E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between SMAD3 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | Hela | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.21E+00 | GSE49339 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 inhibits the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating the FAM83D-TGFbeta1-Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) pathway, which will play an important role in lung cancer metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | ||
| Pathway Response | mRNA surveillance pathway | hsa03015 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | mouse embryonic stem cells | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL3-/- ESCs
Control: Wild type ESCs
|
GSE145309 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: 1.25E+00 p-value: 1.46E-105 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3-induced circ1662 promoted colorectal cancer cell invasion and migration by accelerating YAP1 nuclear transport. Circ1662 enhanced CRC invasion and migration depending on YAP1 and Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3). This result implies that circ1662 is a new prognostic and therapeutic marker for CRC metastasis. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c nude mice (4 weeks old) were acquired from Vital River Laboratory (Beijing, China). HCT116 cells with stable circ1662 expression (2 × 106 in 100 L of PBS) were injected via the tail vein. After 45 days, the mice were sacrificed. The lung metastatic carcinoma specimens were processed into paraffin-embedded sections for subsequent H&E staining and IHC. | |||
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by ALKBH5 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shALKBH5 MOLM-13 cells
Control: shNS MOLM-13 cells
|
GSE144968 | |
| Regulation |
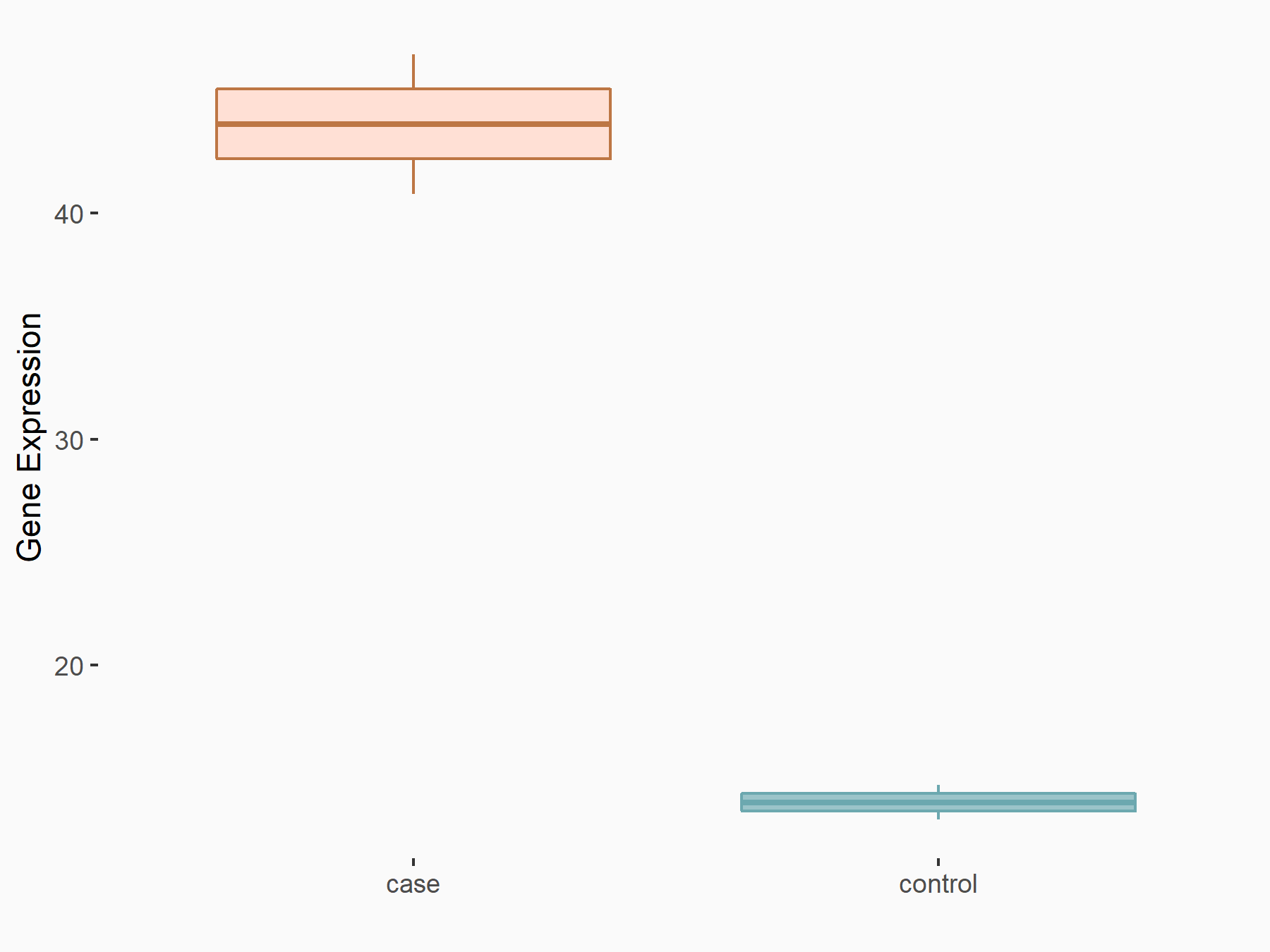 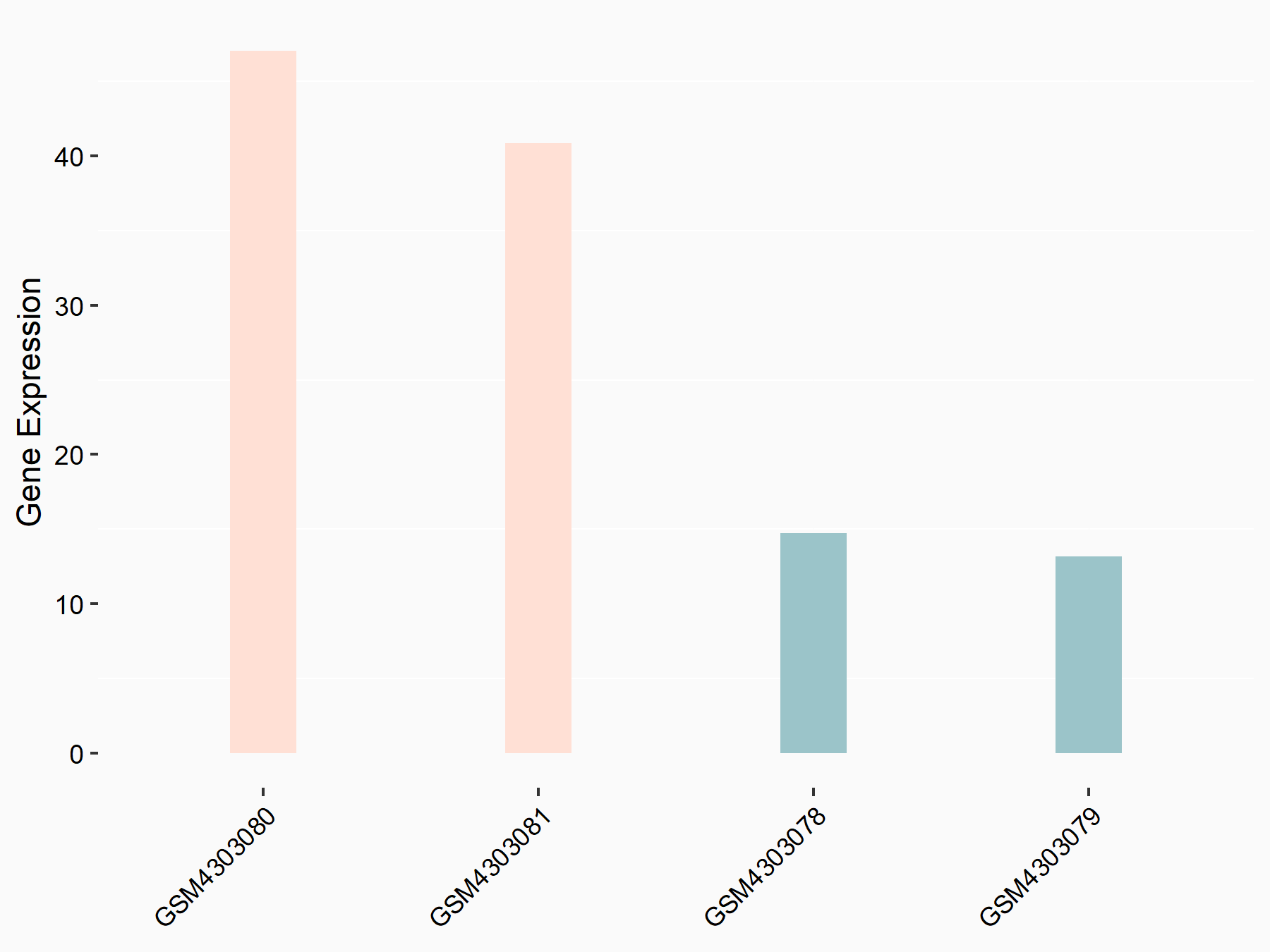 |
logFC: 1.59E+00 p-value: 2.50E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 weakens YTHDF1/3-mediated TGF-Beta-R2 and Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) mRNA stabilization, and abolishes YTHDF2-mediated SMAD6 mRNA degradation, supporting the notion that ALKBH5 inhibits TGF-Beta-induced EMT and invasion of NSCLC cells via YTHD1/2/3-mediated mechanism. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C25.Y | ||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were divided into control group and ALKBH5-overexpressing group (9 mice per group). ALKBH5-overexpressing and control A549 cells (3 × 106 cells/mouse) in 200 uL PBS were intravenously (i.v.) injected into the lateral tail vein of mice. At every 5th day post-inoculation, TGF-Beta-1 (4 ug/kg body weight) was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected to promote tumor cell metastasis. Eight weeks later, the mice were euthanized, and then their lungs and livers were taken out and fixed in Bouin's solution (Sigma Aldrich, HT101128) or 4% Paraformaldehyde (Beyotime, p0099, Shanghai, China) for macroscopically metastatic nodule analysis. | |||
ETS-related transcription factor Elf-3 (ELF3) [WRITER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | Elf3 plays an important role in the process of phenotypic alterations of podocyte induced by the activation of TGF-beta signals. Elf3 protein levels in patients with DN (R2 = 0.7259) were useful as an early non-invasive marker for podocyte injuries in DN. The epithelium-specific transcription factor, Elf3 was induced by AGE stimulation and, subsequently, upregulated RII expression in cultured podocytes. Induction of Elf3 and activation of RII-Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) signaling, leading to a decrease in WT1 expression, were observed in podocytes in diabetic human kidneys. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease | ICD-11: GB61.Z | ||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Murine podocytes | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_5737 |
| In-vivo Model | In the present study, we assessed Smad3 +/- mice for a comparatively long period to examine the effects of Smad3 expression and phosphorylation and to evaluate the involvement of Smad3 in DN. Heterozygous Smad3- knockout mice were kindly provided by Dr. Yasue, University of Tokushima. We attempted to generate Smad3-null mice using pairs of Smad3 mice, but progeny was rarely obtained, and pups were fragile and could not survive for a long period (5 weeks at the most). Therefore, BKS/Cg-m Lepr db (db/db) x Smad3 +/- mice were developed using pairs of Lepr db +/- x Smad3 +/-. Smad3 +/-;db/+ mice were generated by crossing Smad3 +/- and db/+ mice. Moreover, Smad3 +/-;db/db were generated by crossing Smad3 +/-;db/+ and db/+ mice as previously described. Blood glucose concentrations were measured from the tail vein (glucose assay kit; Abbott). The diabetic phenotype was confirmed 4 weeks after birth by blood glucose >300 mg/dl. | |||
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3-induced circ1662 promoted colorectal cancer cell invasion and migration by accelerating YAP1 nuclear transport. Circ1662 enhanced CRC invasion and migration depending on YAP1 and Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3). This result implies that circ1662 is a new prognostic and therapeutic marker for CRC metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell invasion | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 | |
| SW480 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| In-vivo Model | BALB/c nude mice (4 weeks old) were acquired from Vital River Laboratory (Beijing, China). HCT116 cells with stable circ1662 expression (2 × 106 in 100 L of PBS) were injected via the tail vein. After 45 days, the mice were sacrificed. The lung metastatic carcinoma specimens were processed into paraffin-embedded sections for subsequent H&E staining and IHC. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [3] | |||
| Response Summary | ALKBH5 weakens YTHDF1/3-mediated TGF-Beta-R2 and Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) mRNA stabilization, and abolishes YTHDF2-mediated SMAD6 mRNA degradation, supporting the notion that ALKBH5 inhibits TGF-Beta-induced EMT and invasion of NSCLC cells via YTHD1/2/3-mediated mechanism. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Target Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| In-vitro Model | HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 |
| NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1483 | |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| In-vivo Model | The mice were divided into control group and ALKBH5-overexpressing group (9 mice per group). ALKBH5-overexpressing and control A549 cells (3 × 106 cells/mouse) in 200 uL PBS were intravenously (i.v.) injected into the lateral tail vein of mice. At every 5th day post-inoculation, TGF-Beta-1 (4 ug/kg body weight) was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected to promote tumor cell metastasis. Eight weeks later, the mice were euthanized, and then their lungs and livers were taken out and fixed in Bouin's solution (Sigma Aldrich, HT101128) or 4% Paraformaldehyde (Beyotime, p0099, Shanghai, China) for macroscopically metastatic nodule analysis. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | YTHDF2 inhibits the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating the FAM83D-TGFbeta1-Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) pathway, which will play an important role in lung cancer metastasis. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | mRNA surveillance pathway | hsa03015 | ||
| Cell Process | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [4] | |||
| Response Summary | Elf3 plays an important role in the process of phenotypic alterations of podocyte induced by the activation of TGF-beta signals. Elf3 protein levels in patients with DN (R2 = 0.7259) were useful as an early non-invasive marker for podocyte injuries in DN. The epithelium-specific transcription factor, Elf3 was induced by AGE stimulation and, subsequently, upregulated RII expression in cultured podocytes. Induction of Elf3 and activation of RII-Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) signaling, leading to a decrease in WT1 expression, were observed in podocytes in diabetic human kidneys. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61.Z] | |||
| Target Regulator | ETS-related transcription factor Elf-3 (ELF3) | WRITER | ||
| Pathway Response | TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | ||
| In-vitro Model | Murine podocytes | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_5737 |
| In-vivo Model | In the present study, we assessed Smad3 +/- mice for a comparatively long period to examine the effects of Smad3 expression and phosphorylation and to evaluate the involvement of Smad3 in DN. Heterozygous Smad3- knockout mice were kindly provided by Dr. Yasue, University of Tokushima. We attempted to generate Smad3-null mice using pairs of Smad3 mice, but progeny was rarely obtained, and pups were fragile and could not survive for a long period (5 weeks at the most). Therefore, BKS/Cg-m Lepr db (db/db) x Smad3 +/- mice were developed using pairs of Lepr db +/- x Smad3 +/-. Smad3 +/-;db/+ mice were generated by crossing Smad3 +/- and db/+ mice. Moreover, Smad3 +/-;db/db were generated by crossing Smad3 +/-;db/+ and db/+ mice as previously described. Blood glucose concentrations were measured from the tail vein (glucose assay kit; Abbott). The diabetic phenotype was confirmed 4 weeks after birth by blood glucose >300 mg/dl. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
DNA modification
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02140 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Lung cancer | |
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06017 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT06018 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → DNA modification | |
Histone modification
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 2 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03556 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT03601 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 (SMYD2) | |
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | Histone modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Colorectal cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00396)
| In total 4 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007032 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67123240-67123241:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CGCAGTGGCTCACACCTGTAATCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4368260; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_44758 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007033 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67124153-67124154:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CAGGCCACCACGTCTGGCTAATTTTTGTATTTTTCTGTTGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_44759 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007034 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67186158-67186159:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGCCCAAGCGCACACAGCTAGTAAGTGGCCAAGCCGGGAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_44760 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE007035 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191144-67191145:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACTGATTGGGAGGTGCGTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_44761 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 18 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000457 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066086-67066087:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CGGCCGAGCTCCCCTCTGCGCCCCCGGCGTCCCGTCGAGCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14181 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000458 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066087-67066088:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGAGCTCCCCTCTGCGCCCCCGGCGTCCCGTCGAGCCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14182 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000459 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066088-67066089:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCCGAGCTCCCCTCTGCGCCCCCGGCGTCCCGTCGAGCCCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14183 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000460 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066089-67066090:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCGAGCTCCCCTCTGCGCCCCCGGCGTCCCGTCGAGCCCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14184 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000461 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066090-67066091:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CGAGCTCCCCTCTGCGCCCCCGGCGTCCCGTCGAGCCCAGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14185 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000462 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066093-67066094:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCCCTCTGCGCCCCCGGCGTCCCGTCGAGCCCAGCCCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14186 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000463 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066115-67066116:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TCCCGTCGAGCCCAGCCCCGCCGGGGGCGCTCCTCGCCGCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14187 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000464 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066116-67066117:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CCCGTCGAGCCCAGCCCCGCCGGGGGCGCTCCTCGCCGCCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14188 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000465 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066122-67066123:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCCAGCCCCGCCGGGGGCGCTCCTCGCCGCCCGCGCGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14189 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000466 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67178626-67178627:+ | ||
| Sequence | TGGGCAGTGGTGGCCAGCAGCACTGATACATTGCTTGACCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000537194.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14190 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000467 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191127-67191128:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGAGGGAGTTTTGTCTGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATAC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14191 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000468 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191128-67191129:+ | ||
| Sequence | GAGGGAGTTTTGTCTGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14192 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000469 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191129-67191130:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGGGAGTTTTGTCTGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14193 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000470 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191131-67191132:+ | ||
| Sequence | GGAGTTTTGTCTGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACTGAT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14194 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000471 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191132-67191133:+ | ||
| Sequence | GAGTTTTGTCTGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACTGATT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14195 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000472 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191133-67191134:+ | ||
| Sequence | AGTTTTGTCTGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACTGATTG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14196 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000473 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191134-67191135:+ | ||
| Sequence | GTTTTGTCTGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACTGATTGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14197 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE000474 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194142-67194143:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTTGGCTAGAGTTGGGAGTTCCCCCAAAATAAACGTGTCCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_14198 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 131 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023922 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67063886-67063887:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTGCAGTCTCAAGATCGGAGACTGAGGCTTCAACAAAGTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4368145; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284297 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023923 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67063937-67063938:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTCCAGCTCTGCCACTTGGAACCCTGAGTAAGTAATGTAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; U2OS; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_4368145; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284298 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023924 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67065604-67065605:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGCACGCGGATTTGCATGAAACACAGACTGGGAGCGGGCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; hESCs; fibroblasts; Jurkat; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; iSLK; TIME; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284304 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023925 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67065610-67065611:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGGATTTGCATGAAACACAGACTGGGAGCGGGCGGGAGCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; hESCs; fibroblasts; Jurkat; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; iSLK; TIME; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284305 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023926 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67065780-67065781:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAAGTTTGGCCGGGGGTTGGACTTTCCTTCCCGGAGGCGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; HEK293T; GM12878; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284306 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023927 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67065807-67065808:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTCCCGGAGGCGGCACCCAAACAGCTACCCCGTGCGGAAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; HEK293T; GM12878; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284307 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023928 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67065826-67065827:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AACAGCTACCCCGTGCGGAAACCCAAACTTCTGCTGCCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284308 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023929 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67065832-67065833:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TACCCCGTGCGGAAACCCAAACTTCTGCTGCCACTTGGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284309 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023930 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67066276-67066277:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTCAAGAGCCTGGTCAAGAAACTCAAGAAGACGGGGCAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; A549; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; TIME; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284310 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023931 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098594-67098595:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCTTGGCAGCACAGAGGCAAACCACAGAGTACATTTGAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; A549; CD4T; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000559092.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284311 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023932 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098681-67098682:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CAGTGAGCTAATTAAAGAAAACAAGCTTCGGGAGTTGGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560175.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284312 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023933 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098705-67098706:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCTTCGGGAGTTGGGAGAGAACTGTCCACAGGACACTTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559092.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284313 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023934 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098717-67098718:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGAGAACTGTCCACAGGACACTTGGGGAGGCTTGCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000559092.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284314 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023935 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098885-67098886:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATACATGGATGGGAGGGTGGACTCCGTTCCTGAGGGGGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000560175.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284315 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023936 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098941-67098942:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGGCAGCCCATGGAGATGGGACAGTGTTCTGAAATGCTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559092.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284316 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023937 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098971-67098972:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAAATGCTTCACAAATGTGGACTTTTGCCCCAAACTGTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000559092.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284317 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023938 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098984-67098985:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AATGTGGACTTTTGCCCCAAACTGTGGACAGAGCGTATGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284318 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023939 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67098991-67098992:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACTTTTGCCCCAAACTGTGGACAGAGCGTATGTCCTGAGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284319 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023940 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67125933-67125934:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGACATTCCCACAGGATGGGACAACTGCATGGAAACCCACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559092.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284320 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023941 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67125947-67125948:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GATGGGACAACTGCATGGAAACCCACACTCGGGCCTGTGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559092.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284321 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023942 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67138489-67138490:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | GTACTGAGCGGTTCCCTGGGACAGTTGAACCCAGGGGAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD4T; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000558739.1; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000560175.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284322 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023943 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67138497-67138498:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | CGGTTCCCTGGGACAGTTGAACCCAGGGGAACTGAATTCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD4T; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000558739.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000540846.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284323 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023944 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67138507-67138508:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | GGACAGTTGAACCCAGGGGAACTGAATTCATCTGTGTAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD4T; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000558739.1; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000540846.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284324 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023945 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67164974-67164975:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCGCCTGTGGCGATGGCCAGACCTGCACAGCCACCACGAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; CD4T; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559092.1; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000558739.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284325 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023946 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67165081-67165082:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACCACTACCAGAGAGTAGAGACACCAGGTATGCTGCCTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; A549; Huh7; CD4T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000558739.1; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284326 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023947 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67165339-67165340:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CAGCCATTCCATCCCCGAAAACACTAACTTCCCCGCAGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; LCLs; A549; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558739.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284327 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023948 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166140-67166141:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTCAGAGTGTTAAGGAGGAGACCCACTGTCCAACCTTCTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284328 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023949 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166619-67166620:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGAGGTGGACAGGGGCGAGGACAACAGAACCAAGAGCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284329 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023950 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166627-67166628:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACAGGGGCGAGGACAACAGAACCAAGAGCTGGAACCTCTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284330 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023951 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166640-67166641:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CAACAGAACCAAGAGCTGGAACCTCTACTCCAAGACCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558428.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284331 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023952 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166654-67166655:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGAACCTCTACTCCAAGACCTGGAGCTCCTACAGCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284332 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023953 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166755-67166756:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | CTGTGAAGGCCTTTTAACAGACCACCTTCCTTCTGATTCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | LCLs; A549; H1299; Huh7; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000540846.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284333 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023954 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166780-67166781:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTTCCTTCTGATTCCCAGAGACCCCACCCCCTGGCTACCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; MT4; A549; H1299; Huh7; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000559460.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284334 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023955 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166816-67166817:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACCTGAGTGAAGATGGAGAAACCAGTGACCACCAGATGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; MT4; A549; H1299; Huh7; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000559937.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284335 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023956 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67166835-67166836:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AACCAGTGACCACCAGATGAACCACAGCATGGACGCAGGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; MT4; A549; H1299; Huh7; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000559460.5; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284336 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023957 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67170562-67170563:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCACCTCGCAGGTTCTCCAAACCTATCCCCGAATCCGATGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; MT4; A549; H1299; Huh7; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000560175.5; ENST00000558827.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284337 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023958 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67170633-67170634:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCCTTGTGCACACAACTGGAACCCCCTCTAGCTGCAGCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; H1299; Huh7; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000559937.1; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000540846.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284338 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023959 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67174365-67174366:+ | [14] | |
| Sequence | ACCCAGCTCAAGATGGAAAGACAGCCAGAGATGCGCTCGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000439724.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284339 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023960 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67174467-67174468:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | GGGGAGGCAAGCCCTGAAGGACAGTGGCTACAAGCGGGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000540846.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284340 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023961 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67181303-67181304:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CATCTCCTACTACGAGCTGAACCAGCGCGTCGGGGAGACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000537194.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284341 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023962 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67181320-67181321:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGAACCAGCGCGTCGGGGAGACATTCCACGCCTCGCAGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; hESC-HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000558428.5; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558894.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284342 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023963 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67181445-67181446:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCAGTGGAGCTGACACGGAGACACATCGGTATGGGGTGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000558827.1; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000439724.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284343 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023964 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67184783-67184784:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | CTTCGCAGAGTGCCTCAGTGACAGCGCTATTTTTGTCCAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284344 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023965 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67187385-67187386:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | ATGCAACCTGAAGATCTTCAACAACCAGGAGTTCGCTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558894.5; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000439724.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284345 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023966 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190415-67190416:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTCCCTATTTCTTACAGGAGACAGACTGTGACCAGTACCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; HepG2; A549; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284346 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023967 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190538-67190539:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGTTCCAGTGTGTCTTAGAGACATCAAGTATGGTAGGGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284347 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023968 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190605-67190606:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGGTGGAGAAAATTGGAACTCTACTCAACCCATTGTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000537194.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284348 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023969 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190654-67190655:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | GAAGAAATCTTTCTCCCTCAACTGAAGGGGTGCACCCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000439724.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284349 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023970 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190685-67190686:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCACCCACCTGTTTTCTGAAACACACGAGCAAACCCAGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284350 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023971 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190697-67190698:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTCTGAAACACACGAGCAAACCCAGAGGTGGATGTTATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000560424.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284351 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023972 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190718-67190719:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGAGGTGGATGTTATGAACAGCTGTGTCTGCCAAACAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000439724.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284352 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023973 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190735-67190736:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGAACAGCTGTGTCTGCCAAACACATTTACCCTTTGGCCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000540846.6; ENST00000537194.6; ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284353 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023974 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190806-67190807:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGTGGCTTAAGTGAGCAGAACAGGTAGTATTACACCACCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560424.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000439724.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284354 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023975 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190842-67190843:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CACCGGCCCCCTCCCCCCAGACTCTTTTTTTGAGTGACAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284355 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023976 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190858-67190859:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | CCAGACTCTTTTTTTGAGTGACAGCTTTCTGGGATGTCACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284356 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023977 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190884-67190885:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | TTCTGGGATGTCACAGTCCAACCAGAAACACCCCTCTGTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.153267857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284357 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023978 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190891-67190892:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATGTCACAGTCCAACCAGAAACACCCCTCTGTCTAGGACTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; H1A; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000439724.7; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284358 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023979 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190908-67190909:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAAACACCCCTCTGTCTAGGACTGCAGTGTGGAGTTCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; H1A; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284359 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023980 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67190972-67190973:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAGCCCGCAGGGCCATGCAGACCTCATGCCCAGCTCTCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284360 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023981 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191001-67191002:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | CCAGCTCTCTGACGCTTGTGACAGTGCCTCTTCCAGTGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284361 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023982 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191020-67191021:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GACAGTGCCTCTTCCAGTGAACATTCCCAGCCCAGCCCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284362 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023983 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191067-67191068:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCGCCCCACCACTCCAGCAGACCTTGCCCCTTGTGAGCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284363 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023984 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191092-67191093:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCTTGTGAGCTGGATAGACTTGGGATGGGGAGGGAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284364 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023985 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191142-67191143:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGTCTCCCTCCCCTCTCAGAACATACTGATTGGGAGGTGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284365 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023986 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191174-67191175:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGAGGTGCGTGTTCAGCAGAACCTGCACACAGGACAGCGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284366 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023987 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191187-67191188:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CAGCAGAACCTGCACACAGGACAGCGGGAAAAATCGATGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284367 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023988 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191224-67191225:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGAGCGCCACCTCTTTAAAAACTCACTTACGTTTGTCCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284368 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023989 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191312-67191313:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | AATGTATAGTGTCTATTATCACATTAATCTCAAAGAGATTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284369 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023990 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191404-67191405:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | ATTTGGTCTCAGGCAGCACCACACTGGGTGCGTCTCCAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000558763.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284370 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023991 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191578-67191579:+ | [19] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGCACATTGACTGGGAAACCTGAGTGAGACCCAGCAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284371 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023992 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191589-67191590:+ | [19] | |
| Sequence | GACTGGGAAACCTGAGTGAGACCCAGCAACTGCTTCTCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284372 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023993 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191712-67191713:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCAAATTCACCAGAAGGGAAACATCTCAGGCCAACATAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; iSLK; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284373 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023994 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191880-67191881:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | TATAGCAGTTGTATTGTGTAACAAGTACTGCTCCCAGCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284374 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023995 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191914-67191915:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CAGCAGCAATTAGGGAGAAAACTAGTCTAAATTATTTCAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284375 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023996 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191982-67191983:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | TTTTCCCAGCCTTTTGCAGAACACAGTAGACAGAACTGCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284376 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023997 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191991-67191992:+ | [20] | |
| Sequence | CCTTTTGCAGAACACAGTAGACAGAACTGCCACCTTCAATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284377 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023998 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67191996-67191997:+ | [20] | |
| Sequence | TGCAGAACACAGTAGACAGAACTGCCACCTTCAATTGGTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284378 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE023999 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192278-67192279:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCATGAGGTTTCCAGGTAGGACAGCTGCTCCCCAAGCCTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1B; H1A; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; MM6; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284379 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024000 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192304-67192305:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCTCCCCAAGCCTCCTGAGGACACAGGAAGAGACGGAAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284380 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024001 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192333-67192334:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | GAGACGGAAGGAGCACCTTGACAGACTTGTGTGAGTCTTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284381 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024002 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192337-67192338:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGGAAGGAGCACCTTGACAGACTTGTGTGAGTCTTCTCGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284382 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024003 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192374-67192375:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGAAGGAGGGTTGACTCAGAACCCAGAGACAATACAAAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284383 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024004 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192382-67192383:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGTTGACTCAGAACCCAGAGACAATACAAAACCCCTCACTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284384 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024005 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192392-67192393:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAACCCAGAGACAATACAAAACCCCTCACTTCCTCTGAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284385 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024006 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192492-67192493:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTACACAGGAAGCCCCCTGAACCTCCTGTACATGTGTTCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; fibroblasts; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284386 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024007 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192532-67192533:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGTTCCCAGCCAGCTCTGAGACCCAGGAACCAAATATTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HeLa; U2OS; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284387 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024008 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192540-67192541:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCCAGCTCTGAGACCCAGGAACCAAATATTCCATTTTGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; HeLa; U2OS; Huh7; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284388 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024009 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192689-67192690:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGCCCTCTGGGTGCTTGGGAACTAGCTTCAGGCACAGCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284389 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024010 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192796-67192797:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TATACTTTGGCAGGTTATGAACTTTGAATGTGATGAAATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; fibroblasts; A549; CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284390 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024011 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192816-67192817:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | ACTTTGAATGTGATGAAATGACACGTTTGGCTGCATTTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284391 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024012 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67192849-67192850:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CATTTGGATGGTGTCTTAGAACCCTCATTGCTCAGACCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; fibroblasts; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284392 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024013 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193066-67193067:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | CATTCCCACCTTAGAGTGCTACATAGGTGCTTTGGGCGTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284393 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024014 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193090-67193091:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | AGGTGCTTTGGGCGTATGTAACATTAGTGTCCTTCCTTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9; ENST00000560402.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284394 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024015 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193172-67193173:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | AATGGCATTTGTATATTAAAACACTTTTTTAAAGGACAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000560402.1; ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284395 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024016 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193187-67193188:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | TTAAAACACTTTTTTAAAGGACAGTTGAAAAGGGCAAGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284396 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024017 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193275-67193276:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | AAGTGGCGTTCACCTAGTCAACACGACCGCGTGTGTTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284397 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024018 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193318-67193319:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | GCCCTGGGCTCCCCGCCATGACATCTTCACCTTGCAGCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284398 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024019 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193346-67193347:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | ACCTTGCAGCTTGTGCTGAGACTGACCCAAGTGCAGCTAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284399 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024020 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193373-67193374:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | CAAGTGCAGCTAGCACTGGGACACAGATCCTTGTCTTCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284400 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024021 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193465-67193466:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | CGCTTCTTCCCAATTTAGTAACTTAGATGCTTCCAGCACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284401 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024022 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193482-67193483:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | GTAACTTAGATGCTTCCAGCACATACGTAGGTAGCTACCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284402 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024023 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193517-67193518:+ | [16] | |
| Sequence | TACCCCAGCCGGTTTGGATTACAGGCCTGTGCTGGAACATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | brain | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284403 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024024 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193533-67193534:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | GATTACAGGCCTGTGCTGGAACATCATCTCAGTTGGCCACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284404 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024025 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67193571-67193572:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | ACCTTCCTGGCAGGCTGTAGACCTGACATTTTGAGACAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284405 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024026 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194047-67194048:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATCTGCAGGCTGCTTGTAGGACTGTTCACCAAGGGGGATAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; H1A; fibroblasts; CD8T; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284406 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024027 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194101-67194102:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTGCACCCGTTTAGCCCTGGACCCTGTTTCTTACTGTGTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; H1A; H1B; fibroblasts; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284407 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024028 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194175-67194176:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CGTGTCCCCATTTTACCAGAACCAAACCTCAACACAGCGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; HepG2; LCLs; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284408 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024029 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194180-67194181:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | CCCCATTTTACCAGAACCAAACCTCAACACAGCGAAGCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; iSLK; TIME; TREX; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284409 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024030 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194201-67194202:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | CCTCAACACAGCGAAGCTGTACTGTCTTTGTGTGGCAAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.278136905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284410 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024031 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194339-67194340:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGAAAAACGTACGCAAGAGGACATGGATCCAAAATGATGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; hESCs; fibroblasts; A549; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284411 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024032 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194406-67194407:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTGGGGAGATGATGGGCTAAACAGGCAACTTTTCAAAAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; hESCs; fibroblasts; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284412 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024033 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194424-67194425:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAACAGGCAACTTTTCAAAAACACAGCTATCATAGAAAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; fibroblasts; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284413 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024034 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194446-67194447:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACAGCTATCATAGAAAAGAAACTTGCCTCATGTAAACTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; fibroblasts; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284414 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024035 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194461-67194462:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAGAAACTTGCCTCATGTAAACTGGATTGAGAAATTCTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; fibroblasts; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284415 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024036 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194524-67194525:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | TTAATGCAGAAGTAATGTATACTCTAGTATTCTGGTGTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284416 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024037 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194570-67194571:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTATGTAATAATTTCTTAAAACCATTCAGACAGATAACTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284417 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024038 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194579-67194580:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AATTTCTTAAAACCATTCAGACAGATAACTATTTAATTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284418 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024039 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194634-67194635:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAAGGTCTCTCCTCCCAAGGACAGTGGCTGGAAGAGTTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; HepG2; HEK293A-TOA; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284419 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024040 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194715-67194716:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTTGGCTCAGCATCCAGAAACACCAAACCAGGCTGGCTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MM6; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284420 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024041 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194722-67194723:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCATCCAGAAACACCAAACCAGGCTGGCTAAACAAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284421 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024042 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194736-67194737:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CACCAAACCAGGCTGGCTAAACAAGTGGCCGCGTGTAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284422 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024043 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194756-67194757:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACAAGTGGCCGCGTGTAAAAACAGACAGCTCTGAGTCAAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284423 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024044 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194760-67194761:+ | [17] | |
| Sequence | GTGGCCGCGTGTAAAAACAGACAGCTCTGAGTCAAATCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; CD8T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284424 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024045 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194804-67194805:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTTCCACAAGGGTCCTCTGAACCAAGCCCCACTCCCTTGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284425 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024046 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194900-67194901:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | CCTTCACTGCTGCTGTTGCAACTCGGCTGTTCTGGACTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284426 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024047 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194915-67194916:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTGCAACTCGGCTGTTCTGGACTCTGATGTGTGTGGAGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284427 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024048 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194947-67194948:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GTGGAGGGATGGGGAATAGAACATTGACTGTGTTGATTACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284428 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024049 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194953-67194954:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | GGATGGGGAATAGAACATTGACTGTGTTGATTACCTTCACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T; A549; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284429 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024050 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194965-67194966:+ | [21] | |
| Sequence | GAACATTGACTGTGTTGATTACCTTCACTATTCGGCCAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.052208333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284430 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024051 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67194999-67195000:+ | [18] | |
| Sequence | GCCAGCCTGACCTTTTAATAACTTTGTAAAAAGCATGTATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284431 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE024052 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr15:67195154-67195155:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TGTAAGTGCCCTTCTAATAAACTTTTCATGGAAAAGCTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000327367.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_284432 | ||
References